Through-hole Technology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 Through-hole technology almost completely replaced earlier electronics assembly techniques such as point-to-point construction. From the second generation of computers in the 1950s until surface-mount technology (SMT) became popular in the mid 1980s, every component on a typical PCB was a through-hole component. PCBs initially had tracks printed on one side only, later both sides, then multi-layer boards were in use. Through holes became plated-through holes (PTH) in order for the components to make contact with the required conductive layers. Plated-through holes are no longer required with SMT boards for making the component connections, but are still used for making interconnections between the layers and in this role are more usually called vias.
Through-hole technology almost completely replaced earlier electronics assembly techniques such as point-to-point construction. From the second generation of computers in the 1950s until surface-mount technology (SMT) became popular in the mid 1980s, every component on a typical PCB was a through-hole component. PCBs initially had tracks printed on one side only, later both sides, then multi-layer boards were in use. Through holes became plated-through holes (PTH) in order for the components to make contact with the required conductive layers. Plated-through holes are no longer required with SMT boards for making the component connections, but are still used for making interconnections between the layers and in this role are more usually called vias.
 Components with wire leads are generally used on through-hole boards. Axial leads protrude from each end of a typically cylindrical or elongated box-shaped component, on the geometrical axis of symmetry. Axial-leaded components resemble wire jumpers in shape, and can be used to span short distances on a board, or even otherwise unsupported through an open space in point-to-point wiring. Axial components do not protrude much above the surface of a board, producing a low-profile or flat configuration when placed "lying down" or parallel to the board.
Radial leads project more or less in parallel from the same surface or aspect of a component package, rather than from opposite ends of the package. Originally, radial leads were defined as more-or-less following a
Components with wire leads are generally used on through-hole boards. Axial leads protrude from each end of a typically cylindrical or elongated box-shaped component, on the geometrical axis of symmetry. Axial-leaded components resemble wire jumpers in shape, and can be used to span short distances on a board, or even otherwise unsupported through an open space in point-to-point wiring. Axial components do not protrude much above the surface of a board, producing a low-profile or flat configuration when placed "lying down" or parallel to the board.
Radial leads project more or less in parallel from the same surface or aspect of a component package, rather than from opposite ends of the package. Originally, radial leads were defined as more-or-less following a
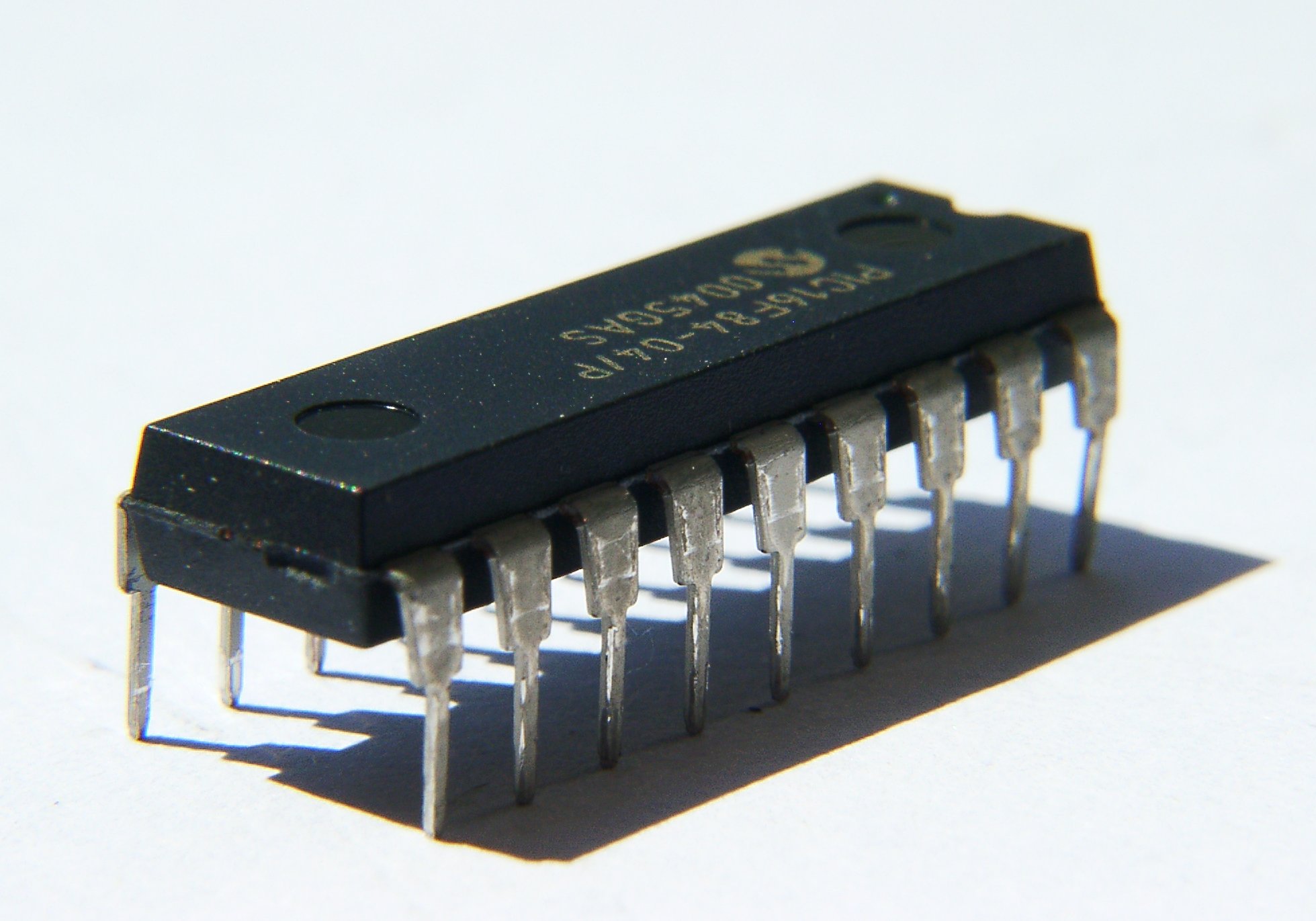 For electronic components with two or more leads, for example, diodes, transistors, ICs, or resistor packs, a range of standard-sized semiconductor packages are used, either directly onto the PCB or via a socket.
For electronic components with two or more leads, for example, diodes, transistors, ICs, or resistor packs, a range of standard-sized semiconductor packages are used, either directly onto the PCB or via a socket.
 While through-hole mounting provides strong mechanical bonds when compared to SMT techniques, the additional drilling required makes the boards more expensive to produce. They also limit the available routing area for signal traces on layers immediately below the top layer on multilayer boards since the holes must pass through all layers to the opposite side. To that end, through-hole mounting techniques are now usually reserved for bulkier or heavier components such as
While through-hole mounting provides strong mechanical bonds when compared to SMT techniques, the additional drilling required makes the boards more expensive to produce. They also limit the available routing area for signal traces on layers immediately below the top layer on multilayer boards since the holes must pass through all layers to the opposite side. To that end, through-hole mounting techniques are now usually reserved for bulkier or heavier components such as
electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
, through-hole technology (also spelled "thru-hole") is a manufacturing scheme in which lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
s on the components are inserted through holes drilled in printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
s (PCB) and soldered to pads on the opposite side, either by manual assembly (hand placement) or by the use of automated insertion mount machines.
History
 Through-hole technology almost completely replaced earlier electronics assembly techniques such as point-to-point construction. From the second generation of computers in the 1950s until surface-mount technology (SMT) became popular in the mid 1980s, every component on a typical PCB was a through-hole component. PCBs initially had tracks printed on one side only, later both sides, then multi-layer boards were in use. Through holes became plated-through holes (PTH) in order for the components to make contact with the required conductive layers. Plated-through holes are no longer required with SMT boards for making the component connections, but are still used for making interconnections between the layers and in this role are more usually called vias.
Through-hole technology almost completely replaced earlier electronics assembly techniques such as point-to-point construction. From the second generation of computers in the 1950s until surface-mount technology (SMT) became popular in the mid 1980s, every component on a typical PCB was a through-hole component. PCBs initially had tracks printed on one side only, later both sides, then multi-layer boards were in use. Through holes became plated-through holes (PTH) in order for the components to make contact with the required conductive layers. Plated-through holes are no longer required with SMT boards for making the component connections, but are still used for making interconnections between the layers and in this role are more usually called vias.
Leads
Axial and radial leads
 Components with wire leads are generally used on through-hole boards. Axial leads protrude from each end of a typically cylindrical or elongated box-shaped component, on the geometrical axis of symmetry. Axial-leaded components resemble wire jumpers in shape, and can be used to span short distances on a board, or even otherwise unsupported through an open space in point-to-point wiring. Axial components do not protrude much above the surface of a board, producing a low-profile or flat configuration when placed "lying down" or parallel to the board.
Radial leads project more or less in parallel from the same surface or aspect of a component package, rather than from opposite ends of the package. Originally, radial leads were defined as more-or-less following a
Components with wire leads are generally used on through-hole boards. Axial leads protrude from each end of a typically cylindrical or elongated box-shaped component, on the geometrical axis of symmetry. Axial-leaded components resemble wire jumpers in shape, and can be used to span short distances on a board, or even otherwise unsupported through an open space in point-to-point wiring. Axial components do not protrude much above the surface of a board, producing a low-profile or flat configuration when placed "lying down" or parallel to the board.
Radial leads project more or less in parallel from the same surface or aspect of a component package, rather than from opposite ends of the package. Originally, radial leads were defined as more-or-less following a radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is th ...
of a cylindrical component (such as a ceramic disk capacitor). Over time, this definition was generalized in contrast to axial leads, and took on its current form. When placed on a board, radial components "stand up" perpendicular, occupying a smaller footprint on sometimes-scarce "board real estate", making them useful in many high-density designs. The parallel leads projecting from a single mounting surface gives radial components an overall "plugin nature", facilitating their use in high-speed automated component insertion ("board-stuffing") machines.
When needed, an axial component can be effectively converted into a radial component, by bending one of its leads into a "U" shape so that it ends up close to and parallel with the other lead. Extra insulation with heat-shrink tubing may be used to prevent shorting out on nearby components. Conversely, a radial component can be pressed into service as an axial component by separating its leads as far as possible, and extending them into an overall length-spanning shape. These improvisations are often seen in breadboard or prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype ...
construction, but are deprecated for mass production designs. This is because of difficulties in use with automated component placement machinery, and poorer reliability because of reduced vibration and mechanical shock resistance in the completed assembly.
Multiple lead devices
 For electronic components with two or more leads, for example, diodes, transistors, ICs, or resistor packs, a range of standard-sized semiconductor packages are used, either directly onto the PCB or via a socket.
For electronic components with two or more leads, for example, diodes, transistors, ICs, or resistor packs, a range of standard-sized semiconductor packages are used, either directly onto the PCB or via a socket.
Characteristics
 While through-hole mounting provides strong mechanical bonds when compared to SMT techniques, the additional drilling required makes the boards more expensive to produce. They also limit the available routing area for signal traces on layers immediately below the top layer on multilayer boards since the holes must pass through all layers to the opposite side. To that end, through-hole mounting techniques are now usually reserved for bulkier or heavier components such as
While through-hole mounting provides strong mechanical bonds when compared to SMT techniques, the additional drilling required makes the boards more expensive to produce. They also limit the available routing area for signal traces on layers immediately below the top layer on multilayer boards since the holes must pass through all layers to the opposite side. To that end, through-hole mounting techniques are now usually reserved for bulkier or heavier components such as electrolytic capacitor
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
s or semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
s in larger packages such as the TO-220 that require the additional mounting strength, or for components such as plug connectors or electromechanical relays that require great strength in support.
Design engineers often prefer the larger through-hole rather than surface mount parts when prototyping, because they can be easily used with breadboard sockets. However, high-speed or high-frequency designs may require SMT technology to minimize stray inductance and capacitance in wire leads, which would impair circuit function. Ultra-compact designs may also dictate SMT construction, even in the prototype phase of design.
Through-hole components are ideal for prototyping circuits with breadboards using microprocessors such as Arduino
Arduino () is an Italian open-source hardware and open-source software, software company, project, and user community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollers and microcontroller kits for building digital devices. Its hardwar ...
or PICAXE
PICAXE is a microcontroller system based on a range of Microchip Technology, Microchip PIC microcontroller, PIC microcontrollers. PICAXE devices are Microchip PIC devices with pre-programmed firmware that enables bootloading of code directly from a ...
. These components are large enough to be easy to use and solder by hand.
See also
* Point-to-point construction * Board-to-board connector * Surface-mount technology * Via (electronics)References
Further reading
* * * *External links
* {{Wikibooks-inline, Practical Electronics, PCB Layout#Holes, Hole sizes for through-hole parts Chip carriers Printed circuit board manufacturing