Södermanland Runic Inscription 86 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sö 86 is the
Sö 86 is the
-
Photograph of Åby inscription
- Arild Hauge webpage on mask stones {{DEFAULTSORT:Sodermanland Runic Inscription 086 Runestones in Södermanland Thor
 Sö 86 is the
Sö 86 is the Rundata
The Scandinavian Runic-text Data Base ( sv, Samnordisk runtextdatabas) is a project involving the creation and maintenance of a database of runic inscriptions. The project's goal is to comprehensively catalog runestones in a machine-readable way ...
catalog number for a Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Germ ...
memorial runic inscription
A runic inscription is an inscription made in one of the various runic alphabets. They generally contained practical information or memorials instead of magic or mythic stories. The body of runic inscriptions falls into the three categories of El ...
located in Åby, which is about one kilometer north of Ålberga, Södermanland County
Södermanland County ( sv, Södermanlands län) is a county or ''län'' on the southeast coast of Sweden. In the local Sörmlandic dialects it is virtually universally shortened and pronounced as Sörmlands län, or simply Sörmland, which is th ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, and in the historic province of Södermanland
Södermanland ( or ), locally Sörmland, sometimes referred to under its Latin form ''Sudermannia'' or ''Sudermania'', is a historical province or ''landskap'' on the south eastern coast of Sweden. It borders Östergötland, Närke, Västmanl ...
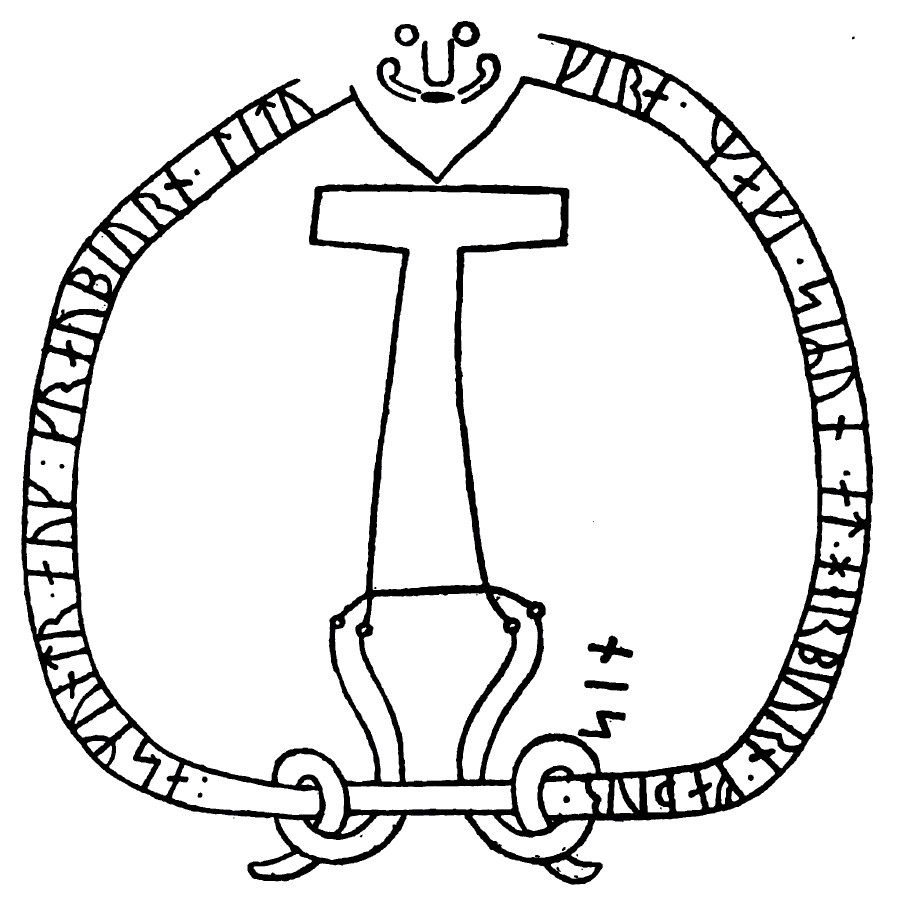
. The inscription features a depiction of the hammer of the Norse pagan god Thor named Mjöllnir and a facial mask.
Description
This inscription has runic text in theyounger futhark
The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet and a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, with only 16 characters, in use from about the 9th century, after a "transitional period" during the 7th and 8th centuries.
The r ...
within a band that circles an image of Thor's hammer which is supported by two serpents. The inscription is carved on an outcropping of granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies unde ...
and the image is approximately 1.8 meters in height. Above the hammer is a facial mask of a man with a moustache and beard. The face represented by the mask is typically interpreted as being that of Thor due to its proximity to the hammer, although there are some who have suggested that the image represents the face of Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
above a cross
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a sa ...
. A mask was a motif common on inscriptions and is found on several other surviving runestones in Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swed ...
including DR 62 in Sjelle, DR 66 in Århus, DR 81 in Skern, DR 258 in Bösarp, the now-lost DR 286 in Hunnestad, DR 314 in Lund, DR 335 in Västra Strö, Vg 106 in Lassegården, Sö 112 in Kolunda, Sö 167 in Landshammar, Sö 367 in Släbro, Nä 34 in Nasta, U 508 in Gillberga, U 670 in Rölunda, U 678 in Skokloster, U 824 in Holms, U 1034 in Tensta, and U 1150 in Björklinge, and on the Sjellebro Stone. The Sö 86 inscription is numbered among several in Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swed ...
that have a dedication to Thor. The image of Thor's hammer was used on several other memorial runestone
A runestone is typically a raised stone with a runic inscription, but the term can also be applied to inscriptions on boulders and on bedrock. The tradition began in the 4th century and lasted into the 12th century, but most of the runestones da ...
s in Sweden and Denmark, perhaps as a parallel to or a pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judais ...
reaction to the use of the cross
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a sa ...
by Christians. Other surviving runestones depicting Thor's hammer include runestones U 1161 in Altuna, Sö 111 in Stenkvista, Vg 113 in Lärkegapet, Öl 1 in Karlevi, DR 26 in Laeborg, DR 48 in Hanning, DR 120 in Spentrup, and DR 331 in Gårdstånga.
The runic text indicates that Ásmundr and Freybjôrn raised the stone as a memorial their father Herbjôrn. Of the personal names mentioned in the text, Freybjôrn contains the Norse god Freyr
Freyr (Old Norse: 'Lord'), sometimes anglicized as Frey, is a widely attested god in Norse mythology, associated with kingship, fertility, peace, and weather. Freyr, sometimes referred to as Yngvi-Freyr, was especially associated with Sweden an ...
as a theophoric name
A theophoric name (from Greek: , ''theophoros'', literally "bearing or carrying a god") embeds the word equivalent of 'god' or God's name in a person's name, reflecting something about the character of the person so named in relation to that deit ...
element and means "Freyr Bear." The name Ásmundr means "Devine Hand" and has a first element that refers to the Æsir
The Æsir (Old Norse: ) are the gods of the principal pantheon in Norse religion. They include Odin, Frigg, Höðr, Thor, and Baldr. The second Norse pantheon is the Vanir. In Norse mythology, the two pantheons wage war against each other, ...
, the name of the principal group of Norse gods. The names in the text also reflect a common practice of that time in Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swed ...
of repeating an element in a parent's name in the names of the children. p. 750. Here the ''bjôrn'' from the father's name, Herbjôrn, is repeated in the name one of the sons, Freybjôrn, to show the family relationship.
Inscription
Transliteration of the runes into Latin characters
:: asmuhtr : auk : fraybiurn * litu kera : meki * siʀun * at * herbiurn * faþur : sin :Project Samnordisk Runtextdatabas Svensk-
Rundata
The Scandinavian Runic-text Data Base ( sv, Samnordisk runtextdatabas) is a project involving the creation and maintenance of a database of runic inscriptions. The project's goal is to comprehensively catalog runestones in a machine-readable way ...
entry for Sö 86.
Transcription into Old Norse
:''Ásmundr ok Freybjôrn létu gera merki sírún/sírýn at Herbjôrn, fôður sinn.''Translation in English
:Ásmundr and Freybjôrn had the rune-decorated landmark made in memory of Herbjôrn, their father.References
External links
Photograph of Åby inscription
- Arild Hauge webpage on mask stones {{DEFAULTSORT:Sodermanland Runic Inscription 086 Runestones in Södermanland Thor