Symbion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Symbion'' is a
''Symbion'' is a
 ''Symbion'' is a
''Symbion'' is a genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
of commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit fro ...
aquatic animals, less than 0.5 mm wide, found living attached to the mouthparts of cold-water lobsters. They have sac-like bodies, and three distinctly different forms in different parts of their two-stage life-cycle. They appear so different from other animals that they were assigned their own, new phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
Cycliophora shortly after they were discovered in 1995. This was the first new phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
of multicelled organism to be discovered since the Loricifera in 1983.
Taxonomy
''Symbion'' was discovered in 1995 byReinhardt Kristensen
Reinhardt Møbjerg Kristensen (born 1948) is a Danish invertebrate biologist, noted for the discovery of three new phyla of microscopic animals: the Loricifera in 1983, the Cycliophora in 1995, and the Micrognathozoa in 2000. He is also conside ...
and Peter Funch
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a s ...
on the mouthparts of the Norway lobster
''Nephrops norvegicus'', known variously as the Norway lobster, Dublin Bay prawn, ' (compare langostino) or ''scampi'', is a slim, orange-pink lobster which grows up to long, and is "the most important commercial crustacean in Europe". It is n ...
(''Nephrops norvegicus''). Other, related, species have since been discovered on:
* the American lobster
The American lobster (''Homarus americanus'') is a species of lobster found on the Atlantic coast of North America, chiefly from Labrador to New Jersey. It is also known as Atlantic lobster, Canadian lobster, true lobster, northern lobster, Can ...
(''Homarus americanus'', host to '' Symbion americanus'')
* the European lobster
''Homarus gammarus'', known as the European lobster or common lobster, is a species of clawed lobster from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea and parts of the Black Sea. It is closely related to the American lobster, ''H. americ ...
(''Homarus gammarus'', host to an as yet unnamed species of ''Symbion'')
The genus is so named because of its commensal relationship
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit fr ...
with the lobster (a form of symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or para ...
) – it feeds on the leftovers from the lobster's own meals.
The genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''Symbion'' are peculiar microscopic animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
s, with no obvious close relatives, and which was therefore given its own phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature ...
, called Cycliophora. The phylogenetic position of ''Symbion'' remains unclear: originally the phyla Ectoprocta
Bryozoa (also known as the Polyzoa, Ectoprocta or commonly as moss animals) are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about long, they have a special feeding structure called a l ...
and Entoprocta
Entoprocta (), or Kamptozoa , is a phylum of mostly sessile aquatic animals, ranging from long. Mature individuals are goblet-shaped, on relatively long stalks. They have a "crown" of solid tentacles whose cilia generate water currents that ...
were considered possible relatives of ''Symbion'', based on structural similarities. However, genetic studies suggest that ''Symbion'' may be more closely related to Gnathifera.
Description
''Symbion pandora'' has abilateral
Bilateral may refer to any concept including two sides, in particular:
*Bilateria, bilateral animals
*Bilateralism, the political and cultural relations between two states
*Bilateral, occurring on both sides of an organism ( Anatomical terms of l ...
, sac-like body with no coelom
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in most animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, ...
. There are three basic life stages:
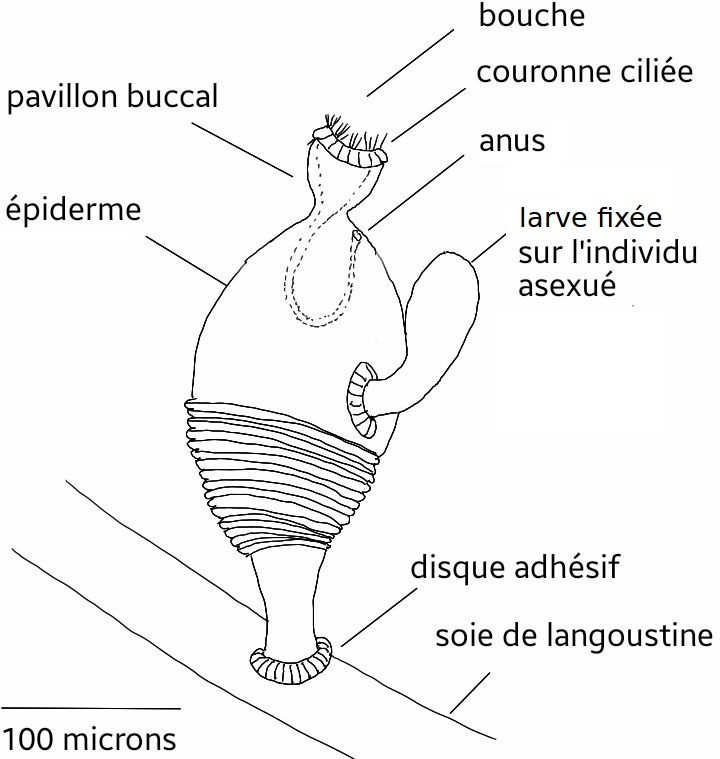
* Asexual Feeding Stage – At this stage, ''S. pandora'' is neither male nor female. It has a length of 347 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Uni ...
and a width of 113 μm. On the posterior end of the sac-like body is a stalk with an adhesive disc, which attaches itself to the host. On the anterior end is a ciliated funnel (mouth) and an anus.
* Sexual Stage
** Male – ''S. pandora'' has a length of 84 μm and a width of 42 μm during this stage. It has no mouth or anus, which signifies the absence of a digestive system
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller compone ...
. It also has two reproductive organs.
** Female – ''S. pandora'' is the same size as the male in this stage. It does, however, have a digestive system which collapses and reconstitutes itself as a larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
.
Reproduction
''Symbion'' reproduces both asexually and sexually, and has a complex reproduction cycle, a strategy evolved to produce as many offspring as possible that can survive and find a new host when the lobster they live on sheds its shell. The asexual individuals are the largest ones. The sexual individuals do not eat. During the autumn they make copies of themselves, where a new individual grows inside the parent body, one offspring at the time. The new offspring attach themselves to an available spot on the lobster, begin to feed and eventually start making new copies of themselves. In early winter, the asexual animals start producing males. When a male is born, it crawls away from its parent and glues itself to another asexual individual. Once attached, the male produces two dwarf males inside its body, which turns into a hollow pouch. Each of the two dwarf males are about one hundred times smaller than the asexual individual to which they are attached. Their bodies start out with about 200 cells, but this number has been reduced to just 47 by the time they reach maturity. Thirty-four of the cells form its nervous system, and three more become sensory cells used to help them feel their surroundings. Eight cells becomes mucus glands, which produce mucus that helps them move across the surface. The final two cells form the testes, which make the sperm that fertilize the female’s egg. Most of the cells of the dwarf males also lose their nucleus and shrink to almost half their size, which is an adaptation that allows two mature individuals to fit inside the body of the parent male. Two males increases their chances to fertilize a female. By late winter, when the large feeding individuals in the colony have males attached to their bodies, they start making females. Each female has a single egg inside her. When she is about the be born, one of the two dwarf males fertilizes her when she comes out. The fertilized female finds herself a place on the host's whiskers where she attaches herself. Inside her the developing embryo extracts all the nutrients it needs to grow from its mother, and by the time it is ready to be born, all that remains of the mother is an empty husk. This new offspring is a strong swimmer unlike all the other forms in the colony, and those who succeed in finding a new host will attach themselves to its mouthparts, where it will grow a stomach and mouthparts, morphing into a large, feeding and asexual type, starting the cycle all over again. The larval stage may be unscientifically referred to as sea worms. Piper, Ross (2007), ''Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals'',Greenwood Press
Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc. (GPG), also known as ABC-Clio/Greenwood (stylized ABC-CLIO/Greenwood), is an educational and academic publisher (middle school through university level) which is today part of ABC-Clio. Established in 1967 as Gr ...
.
References
{{Taxonbar, from1=Q502012, from2=Q2783567, from3=Q14427009, from4=Q14426976, from5=Q276292 Platyzoa genera Parasites of crustaceans