Swartkrans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Swartkrans is a fossil-bearing cave designated as a South African National Heritage Site, located about from
 Some of the earliest evidence of controlled use of fire by humans can be found at Swartkrans, up to 1.5 million years ago.
In addition, some of the earliest evidence of modified bone tools has also been found at Swartkrans and Sterkfontein, with the oldest at Swartkrans dating to about 1.8 million years ago. These tools may have been made by ''
Some of the earliest evidence of controlled use of fire by humans can be found at Swartkrans, up to 1.5 million years ago.
In addition, some of the earliest evidence of modified bone tools has also been found at Swartkrans and Sterkfontein, with the oldest at Swartkrans dating to about 1.8 million years ago. These tools may have been made by ''
University of Chicago Press page
for ''The Hunters or the Hunted?'' {{Authority control Archaeological sites in South Africa World Heritage Sites in South Africa Pleistocene paleontological sites of Africa Paleoanthropological sites Geography of Gauteng South African heritage sites Archaeological sites of Southern Africa
Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu language, Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a Megacity#List of megacities, megacity, and is List of urban areas by p ...
. It is located in the Cradle of Humankind
The Cradle of Humankind is a paleoanthropological site and is located about northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa, in the Gauteng province. Declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1999, the site is home to the largest concentration of h ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
and is notable for being extremely rich in archaeological material, particularly hominin
The Hominini form a taxonomic tribe of the subfamily Homininae ("hominines"). Hominini includes the extant genera ''Homo'' (humans) and '' Pan'' (chimpanzees and bonobos) and in standard usage excludes the genus ''Gorilla'' (gorillas).
The ...
remains. Fossils discovered in the limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
of Swartkrans include ''Homo ergaster
''Homo ergaster'' is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether ''H. ergaster'' constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into '' H. erectus'' is an ongoing and unresol ...
'' (a variety of ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor ...
''), ''Paranthropus
''Paranthropus'' is a genus of extinct hominin which contains two widely accepted species: '' P. robustus'' and '' P. boisei''. However, the validity of ''Paranthropus'' is contested, and it is sometimes considered to be synonymous with ''Austr ...
'' and ''Homo habilis
''Homo habilis'' ("handy man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.31 million years ago to 1.65 million years ago (mya). Upon species description in 1964, ''H. habilis'' was highly ...
''. The oldest deposits present at the site are believed to be between 1.9 and 2.1 million years old.
Noted paleontologist Robert Broom
Robert Broom FRS FRSE (30 November 1866 6 April 1951) was a British- South African doctor and palaeontologist. He qualified as a medical practitioner in 1895 and received his DSc in 1905 from the University of Glasgow.
From 1903 to 1910, he ...
was a frequent digger. He was followed by C. K. 'Bob' Brain, whose excavations at the site inspired his book '' The Hunters or the Hunted?'' in which he demonstrated that instead of being bloodthirsty killer apes, the hominin fossils found at the site were themselves victims of predation by big cat
The term "big cat" is typically used to refer to any of the five living members of the genus ''Panthera'', namely the tiger, lion, jaguar, leopard, and snow leopard.
Despite enormous differences in size, various cat species are quite similar ...
s. Originally, it was believed that ''Dinofelis
''Dinofelis'' is a genus of extinct sabre-toothed cats belonging to the tribe Metailurini or possibly Smilodontini. They were widespread in Europe, Asia, Africa and North America at least 5 million to about 1.2 million years ago (Early Pliocene ...
'' was responsible for such killings, though recent evidence suggests that hominids were likely the victims of '' Megantereon'' or leopards
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus ''Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
based on carbon isotope ratios taken from each predator.
History of investigations
Swartkrans is located on the Blaauwbank River in the Cradle of Humankind, which has a long record of some of the oldest hominin remain discoveries in the world. It is located fromSterkfontein
Sterkfontein (Afrikaans for ''Strong Spring'') is a set of limestone caves of special interest to paleo-anthropologists located in Gauteng province, about northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa in the Muldersdrift area close to the town of ...
, a site that has yielded similar discoveries of the same era. The private farmland the cave was originally on was purchased by the University of the Witwatersrand
The University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg (), is a multi-campus South African public research university situated in the northern areas of central Johannesburg. It is more commonly known as Wits University or Wits ( or ). The university ...
in 1968.
The cave was discovered in 1948, and initial excavations were carried out by paleontologist Robert Broom
Robert Broom FRS FRSE (30 November 1866 6 April 1951) was a British- South African doctor and palaeontologist. He qualified as a medical practitioner in 1895 and received his DSc in 1905 from the University of Glasgow.
From 1903 to 1910, he ...
. His team uncovered several remains of ''Paranthropus robustus
''Paranthropus robustus'' is a species of robust australopithecine from the Early and possibly Middle Pleistocene of the Cradle of Humankind, South Africa, about 2.27 to 0.87 (or, more conservatively, 2 to 1) million years ago. It has been iden ...
'' and early ''Homo
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely rela ...
'' species. It was the first site at which both ''Paranthropus
''Paranthropus'' is a genus of extinct hominin which contains two widely accepted species: '' P. robustus'' and '' P. boisei''. However, the validity of ''Paranthropus'' is contested, and it is sometimes considered to be synonymous with ''Austr ...
'' and ''Homo'' had been found together, indicating that they were contemporary.
Excavation then halted until the mid-1960s and continued until the 1980s, when C. K. Brain brought a team to Swartkrans. Thousands of artifacts and faunal remains were uncovered, 415 of which are considered to be hominin. Brain expanded upon the site's stratigraphy, which was more complex than previously thought.
Discoveries
 Some of the earliest evidence of controlled use of fire by humans can be found at Swartkrans, up to 1.5 million years ago.
In addition, some of the earliest evidence of modified bone tools has also been found at Swartkrans and Sterkfontein, with the oldest at Swartkrans dating to about 1.8 million years ago. These tools may have been made by ''
Some of the earliest evidence of controlled use of fire by humans can be found at Swartkrans, up to 1.5 million years ago.
In addition, some of the earliest evidence of modified bone tools has also been found at Swartkrans and Sterkfontein, with the oldest at Swartkrans dating to about 1.8 million years ago. These tools may have been made by ''Australopithecus robustus
''Paranthropus robustus'' is a species of robust australopithecine from the Early and possibly Middle Pleistocene of the Cradle of Humankind, South Africa, about 2.27 to 0.87 (or, more conservatively, 2 to 1) million years ago. It has been iden ...
'' or an early species of ''Homo'', which both inhabited the cave around the same time.
These early tools were first speculated to have been used to dig up tubers
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure used as storage organs for nutrients in some plants. They are used for the plant's perennation (survival of the winter or dry months), to provide energy and nutrients for regrowth during the next growing s ...
, but they may instead have been used to harvest termites, which were present during Swartkrans's occupation; many of these tools may have been multipurpose. Re-evaluation of wear on stone and bone tools uncovered by Brain in earlier excavations and experiments by researchers have led to the conclusion that termites, a high source of nutrients, were a supplementary food source for early hominids. Bone tools would have allowed for easier extraction of the insects than stones would have.
In 2016, the discovery of the earliest known evidence of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
in hominins was announced. An osteosarcoma
An osteosarcoma (OS) or osteogenic sarcoma (OGS) (or simply bone cancer) is a cancerous tumor in a bone. Specifically, it is an aggressive malignant neoplasm that arises from primitive transformed cells of mesenchymal origin (and thus a sarcoma ...
was found on a partial left fifth metatarsal from an unclassified hominin.
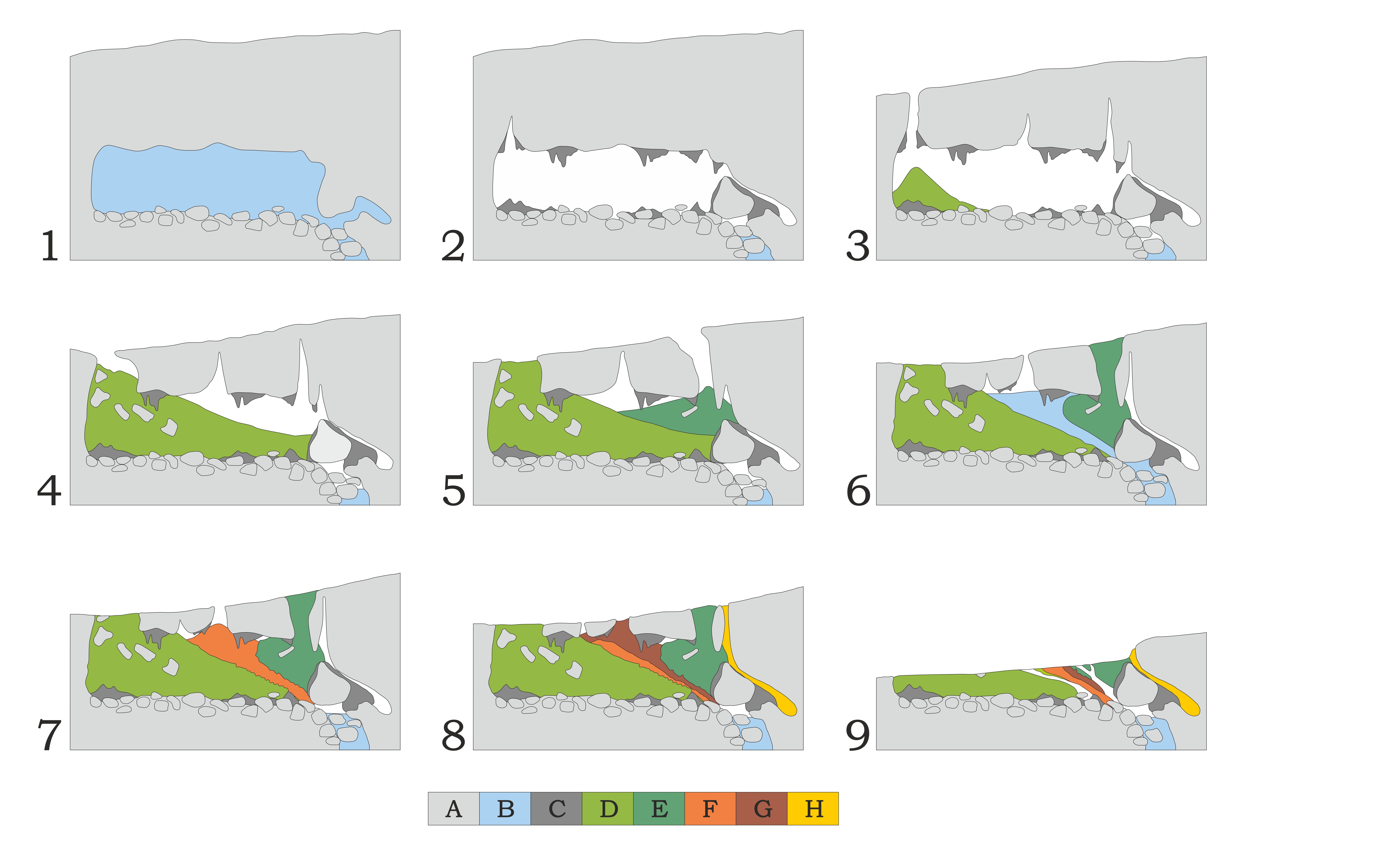
Geology
Swartkrans is alimestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
cave and has been divided geologically into five members
Member may refer to:
* Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon
* Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set
* In object-oriented programming, a member of a class
** Field (computer science), entries in ...
. Member 1 consists of two large masses, named the Hanging Remnant and Lower Bank. ''Homo ergaster
''Homo ergaster'' is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Africa in the Early Pleistocene. Whether ''H. ergaster'' constitutes a species of its own or should be subsumed into '' H. erectus'' is an ongoing and unresol ...
'' and ''Paranthropus robustus
''Paranthropus robustus'' is a species of robust australopithecine from the Early and possibly Middle Pleistocene of the Cradle of Humankind, South Africa, about 2.27 to 0.87 (or, more conservatively, 2 to 1) million years ago. It has been iden ...
'' remains have been found in Member 1, and Member 2 has yielded the same genera.

References
External links
*University of Chicago Press page
for ''The Hunters or the Hunted?'' {{Authority control Archaeological sites in South Africa World Heritage Sites in South Africa Pleistocene paleontological sites of Africa Paleoanthropological sites Geography of Gauteng South African heritage sites Archaeological sites of Southern Africa