Sustainable Development Goal 13 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sustainable Development Goal 13 (SDG 13 or Global Goal 13) is about
A/RES/71/313
SDG 13 has five targets which are to be achieved by 2030. They cover a wide range of issues surrounding climate action. The first three targets are "output targets": Strengthen resilience and
 In 2018, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the United Nations body for assessing the science related to climate change, published a special report "Global Warming of 1.5 °C''".'' It outlined the impacts of a 1.5 °C global temperature rise above pre-industrial levels and related global
In 2018, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the United Nations body for assessing the science related to climate change, published a special report "Global Warming of 1.5 °C''".'' It outlined the impacts of a 1.5 °C global temperature rise above pre-industrial levels and related global



Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
" (SDG 13) ''SDG-Tracker.org, website'' To explain the concept of "Education for Sustainable Development and
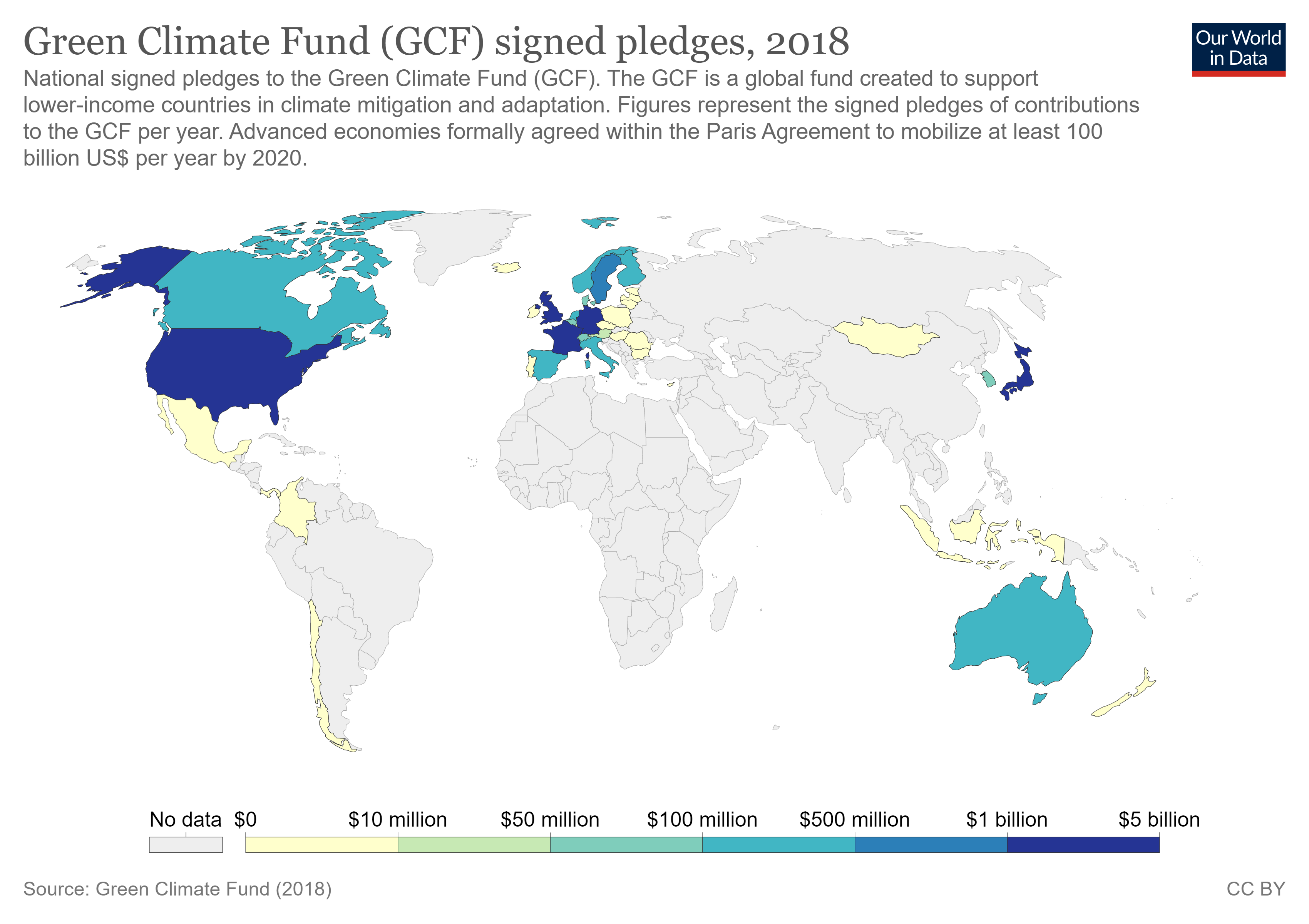 The full text of Target 13.a is: "Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the
The full text of Target 13.a is: "Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the
Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals Report of the Secretary-General
High-level political forum on sustainable development, convened under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (E/2020/57), 28 April 2020 Updates and progress can also be found on the SDG website that is managed by the United Nations and at
 The Sustainable Development Goal 13 is related tightly with the other SDGs. For the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals the implementation the Paris Agreement is essential.
It was stated in 2015 that a high-ambition climate agreement is most crucial to achieving the SDGs relating to poverty ( SDG 1), inequality ( SDG 10), climate change (SDG 13) and global partnerships for sustainable development ( SDG 17). The report also states that tackling climate change will only be possible if the SDGs are met. Further, economic development and climate change are inextricably linked, particularly around poverty,
The Sustainable Development Goal 13 is related tightly with the other SDGs. For the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals the implementation the Paris Agreement is essential.
It was stated in 2015 that a high-ambition climate agreement is most crucial to achieving the SDGs relating to poverty ( SDG 1), inequality ( SDG 10), climate change (SDG 13) and global partnerships for sustainable development ( SDG 17). The report also states that tackling climate change will only be possible if the SDGs are met. Further, economic development and climate change are inextricably linked, particularly around poverty,
Tracking SDG 7: The Energy Progress Report 2019
Washington DC (o
Tracking SDG 7 website
The leading sources of the
Climate Action and Climate Justice in the US
This online tool enables users to see related indicators nationally and by state, as well as relevant information for over three thousand tax-exempt organizations in the US working on issues related to UN SDG 13. The nonprofit data in the tool is updated every 15 days while the indicators are updated annually.
UN Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform – SDG 13
“Global Goals” Campaign - SDG 13
SDG-Track.org - SDG 13
UN SDG 13 in the US
{{Sustainable Development Goals Sustainable development Sustainable Development Goals Climate change mitigation Climate change adaptation Climate change policy
climate action
Climate change mitigation is action to limit climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases or removing those gases from the atmosphere. The recent rise in global average temperature is mostly caused by emissions from fossil fuels bur ...
and is one of 17 Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
established by the United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Cur ...
in 2015. The official mission statement of this goal is to "Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts".United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable DevelopmentA/RES/71/313
SDG 13 has five targets which are to be achieved by 2030. They cover a wide range of issues surrounding climate action. The first three targets are "output targets": Strengthen resilience and
adaptive capacity Adaptive capacity relates to the capacity of systems, institutions, humans and other organisms to adjust to potential damage, to take advantage of opportunities, or to respond to consequences. In the context of ecosystems, adaptive capacity is deter ...
to climate-related disaster
A disaster is a serious problem occurring over a short or long period of time that causes widespread human, material, economic or environmental loss which exceeds the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources ...
s; integrate climate change measures into policies and planning; build knowledge and capacity to meet climate change. The remaining two targets are "means of achieving" targets: To implement the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in the ...
, and to promote mechanisms to raise capacity for planning and management. Along with each target, there are “indicators” that provide a method to review the overall progress of each target, along with SDG 13 as a whole. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is the primary international, intergovernmental forum for negotiating the global response to climate change.
The average worldwide temperature in 2021 was approximately 1.1°C higher than pre-industrial levels (from 1850 to 1900). The years from 2015 to 2021 were the seven warmest on record; the top three being 2016, 2019 and 2020. Currently climate change is affecting the global community in every nation across the world. The impact of climate change not only impacts national economies, but also lives and livelihoods, especially those in vulnerable conditions. By 2018, climate change continued exacerbating the frequency of natural disasters, such as massive wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identi ...
s, drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
s, hurricanes
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depe ...
, and flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrolog ...
s. Over the period 2000–2018, the greenhouse emissions of developed countries in transitions have declined by 6.5%. However, the emissions of the developing countries are up by 43% in the period between 2000 and 2013. In 2019, at least 120 of 153 developing countries had undertaken activities to formulate and implement national adaptation plans.
SDG 13 and SDG 7 on clean energy are closely related and complementary. The leading sources of the greenhouse gas savings that countries need to focus on in order to fulfill their commitments under the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and ...
are switching fuels to renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
and enhancing end-use energy efficiency
Energy efficiency may refer to:
* Energy efficiency (physics), the ratio between the useful output and input of an energy conversion process
** Electrical efficiency, useful power output per electrical power consumed
** Mechanical efficiency, a ...
.
Background
SDG 13 intends to take urgent action in order to combat climate change and its impacts. The contributing countries to this SDG are making plans to prioritize food security and production, terrestrial and wetland ecosystems, freshwater resources, human health, and key economic sectors and services. The year 2019 was the second warmest on record with an average temperature of 1.71 degrees F above the 20th-century average. Carbon dioxide () levels and other greenhouse gases also rose to new records in 2019. It was at the end of the warmest decade, from 2010 to 2019. The UN discussions and negotiations identified the links between the post-2015 SDG process and theFinancing for Development The Monterrey Consensus was the outcome of the 2002 Monterrey Conference, the United Nations International Conference on Financing for Development. in Monterrey, Mexico. It was adopted by Heads of State and Government on 22 March 2002. Over fifty He ...
process that concluded in Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; am, አዲስ አበባ, , new flower ; also known as , lit. "natural spring" in Oromo), is the capital and largest city of Ethiopia. It is also served as major administrative center of the Oromia Region. In the 2007 census, t ...
in July 2015 and the COP 21 Climate Change conference in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
in December 2015.
The Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and ...
, adopted in 2015, aims to strengthen the global response to the threat of climate change by keeping a global temperature rise this century well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. The Agreement aims to strengthen the ability of countries to deal with the impacts of climate change, through appropriate financial flows, a new technology framework and an enhanced capacity building framework. It also provides a path for the more developed countries to help out the undeveloped countries by adapting to the changes with trying to help fight against climate change. The main goal of the Agreement is to eventually become a net-zero emissions world; however, the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
is crucial for the Paris Agreement to be of any effect.
 In 2018, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the United Nations body for assessing the science related to climate change, published a special report "Global Warming of 1.5 °C''".'' It outlined the impacts of a 1.5 °C global temperature rise above pre-industrial levels and related global
In 2018, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the United Nations body for assessing the science related to climate change, published a special report "Global Warming of 1.5 °C''".'' It outlined the impacts of a 1.5 °C global temperature rise above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and larg ...
pathways, and highlighted the possibility of avoiding a number of such impacts by limiting global warming to 1.5 °C compared to 2 °C, or more. The report mentioned that this would require global net human-caused emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) to fall by about 45% from 2010 levels by 2030, reaching "net zero" around 2050, through “rapid and far-reaching” transitions in land, energy, industry, buildings, transport, and cities.
In 2022, the report the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) published, some of the topics covered were the different emission trends, longterm pathways for mitigation, national policies, international cooperation, and how to accelerate the transition to more sustainable development.
Targets, indicators and progress
SDG 13 has five targets. The targets include to strengthening resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related disasters (Target 13.1), integrate climate change measures into policies and planning (Target 13.2), build knowledge and capacity to meet climate change (Target 13.3), implement theUN Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in the ...
(Target 13.a), and promote mechanisms to raise capacity for planning and management (Target 13.b).
Each target includes one or more indicators that help to measure and monitor the progress. Some of the indicators are number of deaths, missing people and directly affected people attributed to disasters per 100,000 population (13.1.1) or total greenhouse emissions generated by year (13.2.2.)
Target 13.1: Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related disasters
The full text of Target 13.1 is: "Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries". This target has 3 indicators. * Indicator 13.1.1: "Number of deaths, missing people and directly affected people attributed to disasters per 100,000 population" * Indicator 13.1.2: "Number of countries that adopt and implement national disaster risk reduction strategies in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030" * Indicator 13.1.3: "Proportion of local governments that adopt and implement local disaster risk reduction strategies in line with national disaster risk reduction strategies" For Indicator 13.1.1 theUnited Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
considers three concepts that are relevant for its understanding: a) Death, which is related to people who died during the disaster, or directly after, as a result of the hazardous event; b) Missing, people whose whereabouts are unknown since the hazardous event; and c) Directly affected refers to the people who have suffered injuries, illness, or other health effects; who were evacuated, displaced, relocated, or have suffered direct damage to their livelihoods, economic, physical, social, cultural, and environmental assets.
Indicator 13.1.2 serves as a bridge between the Sustainable Development Goals and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction
The Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (2015–2030) is an international document that was adopted by the United Nations (UN) member states between 14 and 18 March 2015 at the World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction held in Sendai, Ja ...
.
Indicator 13.1.3 needs to be aligned with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030, disaster risk reduction and should mainstream and integrate disaster risk reduction within and across all sectors.
By 2018, climate change continued exacerbating the frequency of natural disasters, such as massive wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identi ...
s, drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
s, hurricanes
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depe ...
, and flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrolog ...
s, affecting more than 39 million of people. In April 2020, the number of countries and territories that adopted national disaster risk reduction strategies increased to 118 compared to 48 from the first year of the Sendai Framework.
Approximately 60,000 people globally die from the natural disasters each year. Totally, the deaths from natural disasters represent around 0.1% of global deaths. However, in case of high-impact events, the number can change and range from 0.01% to 0.4% of total deaths.
There was a significant decline in global deaths from natural disasters since second half of the 20th century. At the beginning of 20th century, the annual average was around 400,000–500,000 deaths. In the early 2000s, there has been a significant decline to 100,000 and less. That is at least five times lower than in the early 1900s. Considering this data in terms of death rates a population growth (measured per 100,000 people) – there was at least 10-fold decline over the past century.
Improvement in living standards is crucial to avoid more deaths or injuries from the natural disasters. Access to resilient infrastructure, local development and effective response systems are especially problematic in low-income countries, which are facing higher risks during natural disasters.
Target 13.2: Integrate climate change measures into policy and planning
The full text of Target 13.2 is: "Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning". This target has two indicators: * Indicator 13.2.1: "Number of countries with nationally determined contributions, long-term strategies, national adaptation plans, strategies as reported in adaptation communications and national communications". * Indicator 13.2.2: "Totalgreenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and lar ...
per year"
In order to avoid catastrophic impacts, carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions need to decline by about 45%by 2030 and reach net zero in 2050. To be able to meet the 1.5 °C or even 2 °C, which is the maximum target made by the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and ...
, greenhouse gas emissions must start to fall by 7.6% per year starting on 2020. However, the world is way off track in meeting this target at the current level of nationally determined contributions. Over the period 2000–2018, green house emissions of developed countries and economies in transitions have declined by 6.5%. The emissions of the developing countries are up by 43% in the period between 2000 and 2013.
As of 2015 170 countries are a part of at least one multilateral environmental agreement. With each year having an increase in the amount of countries signing onto environmental agreements.
Target 13.3: Build knowledge and capacity to meet climate change
The full text of Target 13.3 is: "Improve education, awareness-raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and early warning". This target has two indicators: * Indicator 13.3.1: "The extent to which (i)global citizenship education Global citizenship education (GCED) is a form of civic learning that involves students' active participation in projects that address global issues of a social, political, economic, or environmental nature. The two main elements of GCE are ' global ...
and (ii) education for sustainable development
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The desi ...
are mainstreamed in (a) national education policies; (b) curricula; (c) teacher education; and (d) student assessment"
* Indicator 13.3.2: "Number of countries that have communicated the strengthening of institutional, systemic and individual capacity-building to implement adaptation, mitigation and technology transfer, and development actions"
The indicator 13.3.1 measures the extent to which countries mainstream Global Citizenship Education (GCED) and Education for Sustainable Development
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The desi ...
(ESD) in their education systems and educational policies.
The indicator 13.3.2 identifies countries who have and have not adopted and implemented disaster risk management strategies in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction. The goal by 2030 is to strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.Ritchie, Roser, Mispy, Ortiz-Ospina (2018)Measuring progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals
" (SDG 13) ''SDG-Tracker.org, website'' To explain the concept of "Education for Sustainable Development and
Global Citizenship
Global citizenship is the idea that one's identity transcends geography or political borders and that responsibilities or rights are derived from membership in a broader class: "humanity". This does not mean that such a person denounces or waives ...
seeks to equip learners with the knowledge of how their choices impact others and their immediate environment.
There are currently no data available for this indicator as of September 2020.
Target 13.a: Implement the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change
 The full text of Target 13.a is: "Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the
The full text of Target 13.a is: "Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in th ...
to a goal of mobilizing jointly $100 billion annually by 2020 from all sources to address the needs of developing countries in the context of meaningful mitigation actions and transparency on implementation and fully operationalize the Green Climate Fund through its capitalization as soon as possible."
This target only has one indicator: Indicator 13.a is the "Amounts provided and mobilized in United States dollars per year in relation to the continued existing collective mobilization goal of the $100 billion commitment through to 2025".
Previously, the indicator was worded as "Mobilized amount of United States dollars per year between 2020 and 2025 accountable towards the $100 billion commitment".
This indicator measures the current pledged commitments from countries to the Green Climate Fund
The Green Climate Fund (GCF) is a fund established within the framework of the UNFCCC as an operating entity of the Financial Mechanism to assist developing countries in adaptation and mitigation practices to counter climate change. The GCF is b ...
(GCF), the amounts provided and mobilized in United States dollars (USD) per year in relation to the continued existing collective mobilization goal of the US$100 billion commitment to 2025. As of 2018, $51.93 billion had been contributed showing an increase from the $45.51 billion that was provided in 2017.
Regarding funding, by December 2019, 81 countries submitted 83 proposals totaling $203.8 million requesting support from the GCF.
There was an increase of $681 billion from 2015 to 2016 with regard to global climate finance. Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
received high levels of new private investment. This represents the largest segment of the global total. These financial flows are relatively small in relation to the scale of annual investment needed for a low-carbon
A low-carbon economy (LCE) or decarbonised economy is an economy based on energy sources that produce low levels of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. GHG emissions due to human activity are the dominant cause of observed climate change since the m ...
, climate-resilient transition.
In April 2018, 175 countries ratified the Paris Agreement and 168 parties had communicated their first nationally determined contributions to the UN framework convention on Climate Change Secretariat. As of March 2020, 189 countries had ratified the Paris Agreement and 186 of them – including the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been ...
– have communicated their Nationally Determined Contributions
A nationally determined contribution (NDC) or intended nationally determined contribution (INDC) is a non-binding national plan highlighting climate change mitigation, including climate-related targets for greenhouse gas emission reductions. Thes ...
(NDC) to the Secretariat of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in th ...
.
Target 13.b: Promote mechanisms to raise capacity for planning and management
The full text of Target 13.b is: "Promote mechanisms for raising capacity for effective climate change-related planning and management in least developed countries and small island developing States, including focusing on women, youth and local and marginalized communities acknowledging that the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is the primary international, intergovernmental forum for negotiating the global response to climate change." This target has one indicator: Indicator 13.b.1 is the "Number of least developed countries andsmall island developing states
Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are a group of developing countries that are small island countries which tend to share similar sustainable development challenges. These include small but growing populations, limited resources, remoteness ...
with nationally determined contributions, long-term strategies, national adaptation plans, strategies as reported in adaptation communications and national communications".
A previous version of this indicator was: "Indicator 13.b.1: Number of least developed countries and small island developing states that are receiving specialized support, and amount of support, including finance, technology and capacity building, for mechanisms for raising capacities for effective climate change-related planning and management, including focusing on women, youth and local and marginalized communities." This indicator's previous focus on women, youth and local and marginalized communities is not included anymore in the latest version of the indicator.
In 2019, at least 120 of 153 developing countries had undertaken activities to formulate and implement national adaptation plans. This is an increase of 29 countries, compared with 2018. The plans will help countries achieve the global goal on adaptation under the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and ...
.
Custodian agencies
Custodian agencies are in charge of reporting on the following indicators: * Indicators 13.1.1, 13.1.2 and 13.1.3: UN International Strategy for Disaster Reduction ( UNISDR). * Indicator 13.2.1:United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in th ...
(UNFCCC), UN Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization-Institute for Statistics (UNESCO-UIS).
* Indicators 13.3.1, 13.a.1 and 13.b.1: United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
Monitoring
High-level progress reports for all the SDGs are published in the form of reports by theUnited Nations Secretary General
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or SG) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
The role of the secretary-g ...
. The most recent one is from April 2020.United Nations Economic and Social Council (2020Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals Report of the Secretary-General
High-level political forum on sustainable development, convened under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (E/2020/57), 28 April 2020 Updates and progress can also be found on the SDG website that is managed by the United Nations and at
Our World in Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, climate change, war, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Change Data Lab, a regi ...
. In a progress update reported by the United Nations, it is made clear that SDG 13 has made little progress towards reducing global greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and lar ...
.
Challenges
Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic
As countries move toward rebuilding their economies after COVID-19, recovery plans can shape the 21st century economy in ways that are clean, green, healthy, safe and more resilient. As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a drastic reduction in human activity. This has resulted in a 6% drop in greenhouse gas emissions from what was initially projected for 2020, however these improvements are only temporary. Once the global economy begins to recover from the pandemic, emissions are expected to rise once again to high levels. The year 2020 has seen a decreased motion of climate crises as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. A drop of 6% in emissions was noted in 2020 and potentially up to 8%, the largest year-on-year reduction on record. This has resulted toUNEP
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on th ...
supporting all investors and policy makers to financing and fiscal stimulus packages and to prioritize green and descent jobs.
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused worldwide disruptions for both production and human activity with some positive consequences for the environment in terms of GHG emissions. China especially has seen a sharp drop in coal-fired power station utilization, likely because of the 5% drop in energy demand nationwide and globally. Many parts of the world have experienced a reduction in air pollution and atmospheric Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)emissions. Air quality along with climate variability like latitude, temperature, and humidity have been speculated to affect rates of COVID-19 outbreaks; should this be the case it only stands to substantiate the importance of close monitoring, effective and collaborative international communication, and early warning systems as well as adherence to SDGs for their focus on preparedness, adaptation and resilience for natural disasters and pandemics.
Despite the slight benefits to emissions reduction which the COVID-19 pandemic has caused, SDG 13 still faces several threats to its progress. The GHG emissions saw a decline from 36.7 billion metric tons to 34.81 billion metric tons emitted from 2019 to 2020, however these emissions have already seen a sharp increase back to 36.4 billion metric tons emitted in 2021. Also, energy-related CO2 emissions for 2021 increased by 6%, hitting their highest level ever and erasing the pandemic-related decrease witnessed in 2020. This is due to the rush for governments globally to stimulate local economies by putting money towards fossil fuel production and in turn economic stimulation. Funding for economic policies will likely divert the emergency funds usually afforded to climate funding like The Green Climate Fund and other sustainable policies, unless an emphasis is put on green deals in the redirection of monetary funds.
A rebound in transport pollution has occurred since restrictions of government lockdown policies have been lifted. Transport pollution accounts for roughly 21% of global carbon emissions due to it being still 95% dependent on oil. This is because countries like the United States are reducing efficiency standards and restricting environmental standard enforcement. The outcome of the UN Climate Change Conference UK '20, or, COP26, was postponed to October 31, 2021, where action was agreed upon to accelerate the rate in which GHG emissions are limited. This included strictly steering away from coal usage and oil, along with attempting to reach zero emissions from transport by 2040, among many other items of action discussed in COP26.
In order to slow the rate of climate change and to shift to a more sustainable economy, the UN Secretary General
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or SG) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
The role of the secretary-ge ...
has proposed six climate-positive actions for governments to take as they go about rebuilding their economies and societies post pandemic.
# Green transition: Investments must accelerate the decarbonization of all aspects of our economy.
# Green job
Green jobs (green-collar jobs, sustainability jobs, eco jobs or environmental jobs) are, according to the United Nations Environment Program, "work in agricultural, manufacturing, research and development (R&D), administrative, and serv ...
s and sustainable and inclusive growth
# Green economy
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politi ...
: making societies and people more resilient through a transition that is fair to all and leaves no one behind.
# Invest in sustainable solutions: fossil fuel subsidies must end and polluters must pay for their pollution.
# Confront all climate risks
# Cooperation – no country can succeed alone.
The most effective way to address this climate crisis is that long-term systematic shifts must be made in order to produce a more climate-conscious, sustainable society.
Links with other SDGs
 The Sustainable Development Goal 13 is related tightly with the other SDGs. For the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals the implementation the Paris Agreement is essential.
It was stated in 2015 that a high-ambition climate agreement is most crucial to achieving the SDGs relating to poverty ( SDG 1), inequality ( SDG 10), climate change (SDG 13) and global partnerships for sustainable development ( SDG 17). The report also states that tackling climate change will only be possible if the SDGs are met. Further, economic development and climate change are inextricably linked, particularly around poverty,
The Sustainable Development Goal 13 is related tightly with the other SDGs. For the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals the implementation the Paris Agreement is essential.
It was stated in 2015 that a high-ambition climate agreement is most crucial to achieving the SDGs relating to poverty ( SDG 1), inequality ( SDG 10), climate change (SDG 13) and global partnerships for sustainable development ( SDG 17). The report also states that tackling climate change will only be possible if the SDGs are met. Further, economic development and climate change are inextricably linked, particularly around poverty, gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
, and energy. The UN encourages the public sector
The public sector, also called the state sector, is the part of the economy composed of both public services and public enterprises. Public sectors include the public goods and governmental services such as the military, law enforcement, infra ...
to take initiative in this effort to minimize negative impacts on the environment.
SDG 13 (Climate Action) is vital in enabling other Sustainable Development Goals to succeed. Not only SDG 13 but all other SDGs need to be collaboratively conducted in harmony to achieve the mutual goal of developing a sustainable society. In comparison with the other 17 sustainable development goals, SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 4 (Quality Education) are considered to be the two most impactful. Additionally, two other SDGs that will significantly influence the course of success in the other 15 SDGs are SDG 16 (Peace Justice and Strong Institution) and SDG 17 (Partnership for Goals). These two SDGs will guide how other SDGs implement their actions and management.
Additionally, the decrease in gas emissions resulting from the actions of SDG 13 will benefit many other SDGs. Those SDGs include good health & well-being ( SDG 3), clean water & sanitation ( SDG 6), responsible consumption & production ( SDG 12), life below water ( SDG 14), and life on land ( SDG 15).
SDG 13 is closely tied to other SDGs in a sense that the climate crisis is a globally experienced phenomenon. The climate on earth closely dictates the state of how humanity can function. For example SDG 2
Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG 2 or Global Goal 2) aims to achieve "zero hunger". It is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording is: "End hunger, achieve food security and im ...
, which has a target to end hunger. Agriculture across the globe is niche, and majority of agricultural products are not generalist and requires particular environmental conditions in order to be successful. With global climate changing so rapidly, this coincides with a steady decline in available area to produce a sufficient amount of agricultural products. For example, sea-level rise, a direct impact of climate change, can lead to saline intrusion of groundwater aquifers, increasing the salinity of water supplies used for agriculture. This is currently happening in the Mekong delta, a region that produces the most rice for Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it ...
, a country with a 19.3% share of the global rice trade. However, increased saline levels in agricultural water supplies have significantly lowered their production, which has already created national concern and, if left unresolved, could lead to a global shortage of rice. Saline intrusion also affects SDG 6, "Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all." As saline intrusion can penetrate coastal groundwater aquifers, communities with limited freshwater sources like those on islands are likely to face increased saline contamination events leading to freshwater shortages as sea levels continue to rise. SDG 13 and SDG 7 on clean energy are also closely related and complementary.IEA, IRENA, UNSD, WB, WHO (2019)Tracking SDG 7: The Energy Progress Report 2019
Washington DC (o
Tracking SDG 7 website
The leading sources of the
greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane ...
savings that countries need to focus on in order to realize their commitments under the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and ...
are switching fuels to renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
and enhancing end-use energy efficiency
Energy efficiency may refer to:
* Energy efficiency (physics), the ratio between the useful output and input of an energy conversion process
** Electrical efficiency, useful power output per electrical power consumed
** Mechanical efficiency, a ...
.
Another SDG which is linked closely with SDG 13 is SDG 12, which is about responsible production and consumption. Currently, production and consumption are increasing exponentially, which is not sustainable long-term. Many increased levels of greenhouse gas emissions began during the industrial revolution due to the increased usage of heavy machinery and the burning of fossil fuels. Due to industrialization
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econom ...
, there have been significant increases in both production and consumption, to the detriment of our environment. These two sustainable development goals are linked because as one decreases, so does the other. SDG 13 is closely tied to various other SDGs in that the climate crisis is a globally experienced phenomenon. The climate on earth closely dictates the state of how humanity can function.
Organizations
United Nations organizations
* TheUnited Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in th ...
(UNFCC) secretariat supports the response to climate change of its 197 parties in advancing the implementation of the UNFCC, the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement, providing technical expertise, assisting them on the analysis on the information they do report on the frame of the implementation of the Kyoto mechanism and maintains the registry of the National Determined Contributions (NDCs). The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was created as a pioneer step to address climate change by the United Nations. With currently 197 parties (countries) which ratifying the convention, it calls for member states to even in moments of scientific uncertainty, act in the interest of human safety.
* UNFCCC Non Parties Participants are organized in three different categories to attend and participate of the UNFCCC process' conferences and meetings: 1. United Nations System and its Specialized Agencies, intergovernmental organizations (IGOs), and non-governmental organizations (NGOs). By 2018, the admitted observers included over 2,200 NGOs and 130 IGOs.
* The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): provides governments on their different constituencies with scientific information, regarding climate change, its impact, future risk adaptation and mitigation processes, so they can develop their climate policies. The IPPC issues reports that are key for international climate negotiations.
* The Conferences of the Parties (COP): the main international body to measure the actions taken by parties (countries) and the progress made regarding the effective implementation of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), that is held every year, unless the parties decide otherwise.
* World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Internat ...
(WMO)
* UN-Habitat
The United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat) is the United Nations programme for human settlements and sustainable urban development. It was established in 1977 as an outcome of the first United Nations Conference on Human Settlem ...
: promotes social and environmentally sustainable towns, cities and communities as part of its mandates by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA).
* United Nations Environment Program
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on th ...
(UNEP): global authority that sets the environmental agenda, enabling nations and people to improve their quality of life without compromising future generations.
* Green Climate Fund
The Green Climate Fund (GCF) is a fund established within the framework of the UNFCCC as an operating entity of the Financial Mechanism to assist developing countries in adaptation and mitigation practices to counter climate change. The GCF is b ...
(GCF), established in 2010 by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC): the GCF is the largest dedicated fund dedicated to help developing countries reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and enhance their ability to respond to climate change.
* NDC Partnerships, hosted by the World Resource Institute and the United Nations Climate Change: this partnership with over 100 members that include developed and developing countries worldwide, non state actors and major institutions to fast track climate and development actions supporting countries to implement their Nationally Determined Contributions
A nationally determined contribution (NDC) or intended nationally determined contribution (INDC) is a non-binding national plan highlighting climate change mitigation, including climate-related targets for greenhouse gas emission reductions. Thes ...
(NDCs), which are part of their commitments to the Paris Agreement.
* YOUNGO: recognized on 2009 by the UNFCCC as the official youth constituency, was fully recognized at COP 17 at Durban, South Africa on 2011 after operating on a provisional status. YOUNGO is a network or youth lead, organization, groups, delegations and individuals working on climate affairs, ensuring youth perspectives and future generations are taken in consideration at the UNFCCC negotiations and multilateral decision-making processes.
NGOs and others
The following NGOs and other organizations are focused on SDG 13 at the global level: * Climate Action Network (CAN), is a worldwide network that coordinates the development of NGO strategies to address international, regional and national climate issues. *Fridays for Future
School Strike for Climate ( sv, Skolstrejk för klimatet), also known variously as Fridays for Future (FFF), Youth for Climate, Climate Strike or Youth Strike for Climate, is an international movement of school students who skip Friday ...
(FFF) is a global strike movement that encourages other people to take action for the planet through a global school strike for climate. The movement started in August 2018, after Greta Thunberg
Greta Tintin Eleonora Ernman Thunberg (; born 3 January 2003) is a Swedish environmental activist who is known for challenging world leaders to take immediate action for climate change mitigation.
Thunberg's activism began when she persuaded ...
's strikes demanding action to face the climate crisis, in front of the Swedish Parliament.
* World Resources Institute
The World Resources Institute (WRI) is a global research non-profit organization established in 1982 with funding from the MacArthur Foundation under the leadership of James Gustave Speth. WRI's activities are focused on seven areas: food, fore ...
(WRI) is a research organization focusing on seven critical intersections between development and environment: cities and ocean, food, forest, water, climate and energy.
* Asia Pacific Adaptation Network (APAN): The Asia Pacific Adaptation Network (APAN) is a regional program that supports governments and other organizations working on adaptation, with a focus on knowledge management and capacity building.
* Arab Forum for Environment and Development (AFED): Arab Forum for Environment and Development's mission is "to advance prudent environmental policies and action in the Arab countries based on science and awareness." They advocate for sustainable development, and influence planners, decision makers, businessmen, civil society, and media.
* Caribbean Community Climate Change Center (CCCCC): The CCCCC attempts to coordinate the Caribbean region's response to climate change. The Center provides a number of materials and tools to assist people in taking the proper action in their areas. In the Caribbean region, they also work on a number of programs to address problems brought on by climate change.
US Based Organizations
In the US there are over three thousand tax-exempt organizations working on issues related to UN SDG 13, according to data filed with the Internal Revenue Service –IRS and aggregated by X4Impact. X4Impact, with the support of the Rockefeller Foundation, Ford Foundation, Hewlett Foundation, and Giving Tech Labs, created a free online interactive tooClimate Action and Climate Justice in the US
This online tool enables users to see related indicators nationally and by state, as well as relevant information for over three thousand tax-exempt organizations in the US working on issues related to UN SDG 13. The nonprofit data in the tool is updated every 15 days while the indicators are updated annually.
References
External links
UN Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform – SDG 13
“Global Goals” Campaign - SDG 13
SDG-Track.org - SDG 13
UN SDG 13 in the US
{{Sustainable Development Goals Sustainable development Sustainable Development Goals Climate change mitigation Climate change adaptation Climate change policy