Sultanate of Rum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
fa, سلجوقیان روم () , status = , government_type =
Triarchy (1249–1254)
Persian (official, court, literature, spoken) , title_leader = Sultan , leader1 = Suleiman ibn Qutalmish (first) , year_leader1 = 1077–1086 , leader3 = Mesud II (last) , year_leader3 = 1303–1308 , common_name = Rum , today =
 The Sultanate of Rum), Sultanate of Iconium, Anatolian Seljuk State ( tr, Anadolu Selçuklu Devleti) or Seljuks of Turkey ( tr, Türkiye Selçukluları, link=no) was a culturally Turco-Persian
The Sultanate of Rum), Sultanate of Iconium, Anatolian Seljuk State ( tr, Anadolu Selçuklu Devleti) or Seljuks of Turkey ( tr, Türkiye Selçukluları, link=no) was a culturally Turco-Persian



 In their construction of
In their construction of  The largest caravanserai is the Sultan Han (built in 1229) on the road between the cities of Konya and Aksaray, in the township of Sultanhanı, covering . There are two caravanserais that carry the name "Sultan Han", the other one being between Kayseri and Sivas. Furthermore, apart from Sultanhanı, five other towns across Turkey owe their names to caravanserais built there. These are Alacahan in Kangal, Durağan, Hekimhan and Kadınhanı, as well as the township of Akhan within the
The largest caravanserai is the Sultan Han (built in 1229) on the road between the cities of Konya and Aksaray, in the township of Sultanhanı, covering . There are two caravanserais that carry the name "Sultan Han", the other one being between Kayseri and Sivas. Furthermore, apart from Sultanhanı, five other towns across Turkey owe their names to caravanserais built there. These are Alacahan in Kangal, Durağan, Hekimhan and Kadınhanı, as well as the township of Akhan within the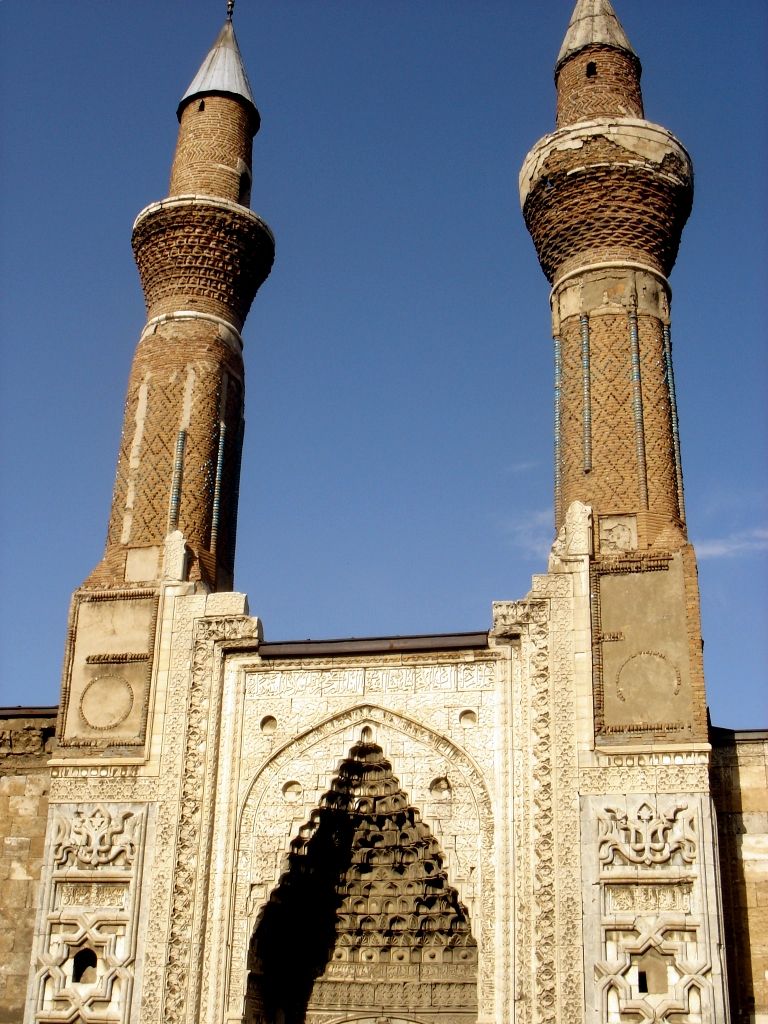  The Seljuk palaces, as well as their armies, were staffed with ghulams (plural ''ghilmân'', ar, غِلْمَان), enslaved youths taken from non-Muslim communities, mainly Greeks from former Byzantine territories. The practice of keeping ghulams may have offered a model for the later devşirme during the time of the Ottoman Empire., page 306
The Seljuk palaces, as well as their armies, were staffed with ghulams (plural ''ghilmân'', ar, غِلْمَان), enslaved youths taken from non-Muslim communities, mainly Greeks from former Byzantine territories. The practice of keeping ghulams may have offered a model for the later devşirme during the time of the Ottoman Empire., page 306
 As regards the names of the sultans, there are variants in form and spelling depending on the preferences displayed by one source or the other, either for fidelity in transliterating the Persian variant of the Arabic script which the sultans used, or for a rendering corresponding to the modern
As regards the names of the sultans, there are variants in form and spelling depending on the preferences displayed by one source or the other, either for fidelity in transliterating the Persian variant of the Arabic script which the sultans used, or for a rendering corresponding to the modern
fa, سلجوقیان روم () , status = , government_type =
Hereditary monarchy
A hereditary monarchy is a form of government and succession of power in which the throne passes from one member of a ruling family to another member of the same family. A series of rulers from the same family would constitute a dynasty.
It is hi ...
Triarchy (1249–1254)
Diarchy
Diarchy (from Greek , ''di-'', "double", and , ''-arkhía'', "ruled"),Occasionally misspelled ''dyarchy'', as in the ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' article on the colonial British institution duarchy, or duumvirate (from Latin ', "the office o ...
(1257–1262)
, year_start = 1077
, year_end = 1308
, p1 = Byzantine Empire under the Doukas dynastyByzantine Empire
, p2 = Seljuk Empire
, p3 = Danishmends
, p4 = Mengujekids
, p5 = Saltukids
, p6 = Artuqids
, s1 = Anatolian beyliks
, s2 = Ilkhanate,
, event_pre = Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and ...
, date_pre = 1071
, event_start = Division from the Seljuk Empire
, event1 = Battle of Köse Dağ
, date_event1 = 1243
, event_end = Karamanid conquest
, image_flag = Double-headed eagle of the Sultanate of Rum.svg
, flag_size = 100px
, flag_type = Double-headed eagle used by the Rum Seljuks
, flag_border = no
, image_coat = Lion and Sun of the Sultanate of Rum.svg
, coa_size = 100px
, symbol_type_article = Lion and Sun
, symbol_type = Lion and Sun adopted by Kaykhusraw II
, image_map = Sultanate of Rûm.svg
, image_map_size = 285px
, image_map_caption = Expansion of the Sultanate c. 1100–1240
, capital =
, religion = Sunni Islam (official), Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also call ...
(subjects)
, common_languages = Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
(numismatics)Byzantine Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman c ...
(chancery)Old Anatolian Turkish
Old Anatolian Turkish (OAT, tr, Eski Anadolu Türkçesi, ''EAT'') is the stage in the history of the Turkish language spoken in Anatolia from the 11th to 15th centuries. It developed into Early Ottoman Turkish. It was written in the Arabic sc ...
(spoken)Persian (official, court, literature, spoken) , title_leader = Sultan , leader1 = Suleiman ibn Qutalmish (first) , year_leader1 = 1077–1086 , leader3 = Mesud II (last) , year_leader3 = 1303–1308 , common_name = Rum , today =
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
 The Sultanate of Rum), Sultanate of Iconium, Anatolian Seljuk State ( tr, Anadolu Selçuklu Devleti) or Seljuks of Turkey ( tr, Türkiye Selçukluları, link=no) was a culturally Turco-Persian
The Sultanate of Rum), Sultanate of Iconium, Anatolian Seljuk State ( tr, Anadolu Selçuklu Devleti) or Seljuks of Turkey ( tr, Türkiye Selçukluları, link=no) was a culturally Turco-Persian Sunni Muslim
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
state, established over conquered Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
territories and peoples (Rûm
Rūm ( ar, روم , collective; singulative: Rūmī ; plural: Arwām ; fa, روم Rum or Rumiyān, singular Rumi; tr, Rûm or , singular ), also romanized as ''Roum'', is a derivative of the Aramaic (''rhπmÈ'') and Parthian language, Par ...
) of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
by the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
following their entry into Anatolia after the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and ...
(1071). The name ''Rûm
Rūm ( ar, روم , collective; singulative: Rūmī ; plural: Arwām ; fa, روم Rum or Rumiyān, singular Rumi; tr, Rûm or , singular ), also romanized as ''Roum'', is a derivative of the Aramaic (''rhπmÈ'') and Parthian language, Par ...
'' was a synonym for the medieval Roman (Byzantine) Empire and its peoples, as it remains in modern Turkish. The name is derived from the Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
(''rhπmÈ'') and Parthian (''frwm'') names for ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–50 ...
, itself ultimately a loan from Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
.
The Sultanate of Rum seceded from the Great Seljuk Empire under Suleiman ibn Qutalmish in 1077, just six years after the Byzantine provinces of central Anatolia were conquered at the Battle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and ...
(1071). It had its capital first at Nicaea and then at Iconium
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
. It reached the height of its power during the late 12th and early 13th century, when it succeeded in taking key Byzantine ports on the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on th ...
and Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
coasts. In the east, the sultanate reached Lake Van
Lake Van ( tr, Van Gölü; hy, Վանա լիճ, translit=Vana lič̣; ku, Gola Wanê) is the largest lake in Turkey. It lies in the far east of Turkey, in the provinces of Van and Bitlis in the Armenian highlands. It is a saline soda lake, ...
. Trade through Anatolia from Iran and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
was developed by a system of caravanserai
A caravanserai (or caravansary; ) was a roadside inn where travelers ( caravaners) could rest and recover from the day's journey. Caravanserais supported the flow of commerce, information and people across the network of trade routes coverin ...
. Especially strong trade ties with the Genoese
Genoese may refer to:
* a person from Genoa
* Genoese dialect, a dialect of the Ligurian language
* Republic of Genoa (–1805), a former state in Liguria
See also
* Genovese, a surname
* Genovesi, a surname
*
*
*
*
* Genova (disambiguati ...
formed during this period. The increased wealth allowed the sultanate to absorb other Turkish states that had been established following the conquest of Byzantine Anatolia: Danishmendids, House of Mengüjek
The House of Mengüjek (Turkish language, Modern Turkish: ''Mengüçoğulları'', ''Mengücek Beyliği'' or ''Mengüçlü Beyliği''; the reigning dynasty is known as Mengujekids or Menkujakids) was an Anatolian beylik of the first period, fou ...
, Saltukids, Artuqids.
The Seljuk sultans bore the brunt of the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were ...
and eventually succumbed to the Mongol invasion at the 1243 Battle of Köse Dağ. For the remainder of the 13th century, the Seljuks acted as vassals of the Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm, ...
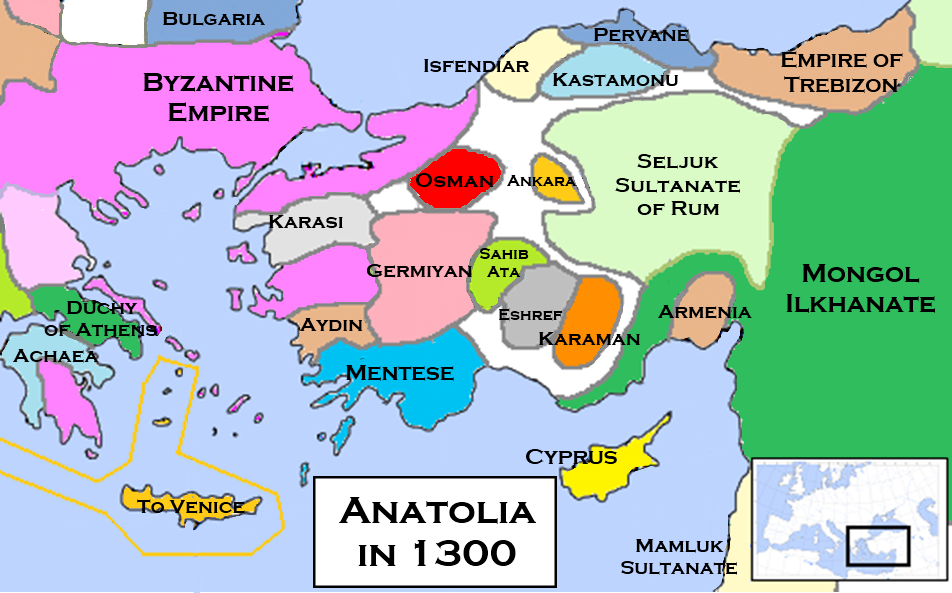
.John Joseph Saunders, ''The History of the Mongol Conquests'', (University of Pennsylvania Press, 1971), 79. Their power disintegrated during the second half of the 13th century. The last of the Seljuk vassal sultans of the Ilkhanate, Mesud II, was murdered in 1308. The dissolution of the Seljuk state left behind many small Anatolian beyliks
Anatolian beyliks ( tr, Anadolu beylikleri, Ottoman Turkish: ''Tavâif-i mülûk'', ''Beylik'' ) were small principalities (or petty kingdoms) in Anatolia governed by beys, the first of which were founded at the end of the 11th century. A sec ...
(Turkish principalities), among them that of the Ottoman dynasty, which eventually conquered the rest and reunited Anatolia to become the Ottoman Empire.
History
Establishment
In the 1070s, after thebattle of Manzikert
The Battle of Manzikert or Malazgirt was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071 near Manzikert, theme of Iberia (modern Malazgirt in Muş Province, Turkey). The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and ...
, the Seljuk commander Suleiman ibn Qutulmish, a distant cousin of Alp Arslan and a former contender for the throne of the Seljuk Empire
The Great Seljuk Empire, or the Seljuk Empire was a high medieval, culturally Turko-Persian, Sunni Muslim empire, founded and ruled by the Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. It spanned a total area of from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to ...
, came to power in western Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
. In 1075, he captured the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
cities of Nicaea (present-day İznik
İznik is a town and an administrative district in the Province of Bursa, Turkey. It was historically known as Nicaea ( el, Νίκαια, ''Níkaia''), from which its modern name also derives. The town lies in a fertile basin at the eastern end ...
) and Nicomedia (present-day İzmit
İzmit () is a district and the central district of Kocaeli province, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental ...
). Two years later, he declared himself sultan of an independent Seljuk state and established his capital at İznik.
Suleiman was killed in Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
in 1086 by Tutush I, the Seljuk ruler of Syria, and Suleiman's son Kilij Arslan I was imprisoned. When Malik Shah died in 1092, Kilij Arslan was released and immediately established himself in his father's territories.
Crusades
Kilij Arslan, although victorious in the People's Crusade of 1096, was defeated by soldiers of theFirst Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ...
and driven back into south-central Anatolia, where he set up his state with capital in Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
. He defeated three Crusade contingents in the 1101 Crusade. In 1107, he ventured east and captured Mosul
Mosul ( ar, الموصل, al-Mawṣil, ku, مووسڵ, translit=Mûsil, Turkish: ''Musul'', syr, ܡܘܨܠ, Māwṣil) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. The city is considered the second large ...
but died the same year fighting Malik Shah's son, Mehmed Tapar. He was the first Muslim commander against the crusades.
Meanwhile, another Rum Seljuk, Malik Shah Malik-Shah ( fa, ملكشاه, link=no), also transliterated as ''Malek-Shah'', ''Malikshah'' or ''Melikshah'', may refer to:
* Malik-Shah I (1055–1092), sultan of Great Seljuq
* Malik-Shah II (), grandson of Malik Shah I, sultan of Great Seljuq ...
(not to be confused with the Seljuk sultan of the same name), captured Konya. In 1116 Kilij Arslan's son, Mesud I, took the city with the help of the Danishmends.
Upon Mesud's death in 1156, the sultanate controlled nearly all of central Anatolia. Mesud's son, Kilij Arslan II, captured the remaining territories around Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', Σεβάστεια, Σεβαστή, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak river, is ...
and Malatya
Malatya ( hy, Մալաթիա, translit=Malat'ya; Syro-Aramaic ܡܠܝܛܝܢܐ Malīṭīná; ku, Meletî; Ancient Greek: Μελιτηνή) is a large city in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey and the capital of Malatya Province. The city ...
from the last of the Danishmends. At the Battle of Myriokephalon in 1176, Kilij Arslan II also defeated a Byzantine army led by Manuel I Komnenos. Despite a temporary occupation of Konya in 1190 by the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
's forces of the Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189–1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity ( Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
, the sultanate was quick to recover and consolidate its power.''Anatolia in the period of the Seljuks and the "beyliks"'', Osman Turan, ''The Cambridge History of Islam'', Vol. 1A, ed. P.M. Holt, Ann K.S. Lambton and Bernard Lewis, (Cambridge University Press, 1995), 244-245. During the last years of Kilij Arslan II's reign, the sultanate experienced a civil war with Kaykhusraw I fighting to retain control and losing to his brother Suleiman II in 1196.
Suleiman II rallied his vassal emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
s and marched against Georgia, with an army of 150,000-400,000 and encamped in the Basiani valley. Tamar of Georgia
Tamar the Great ( ka, თამარ მეფე, tr, Literal translation, lit. "King Tamar") ( 1160 – 18 January 1213) queen regnant, reigned as the List of monarchs of Georgia#Kings of unified Georgia (1008–1490), Queen of Kingdom of ...
quickly marshaled an army throughout her possessions and put it under command of her consort, David Soslan. Georgian troops under David Soslan made a sudden advance into Basiani and assailed the enemy's camp in 1203 or 1204. In a pitched battle, the Seljukid forces managed to roll back several attacks of the Georgians but were eventually overwhelmed and defeated. Loss of the sultan's banner to the Georgians resulted in a panic within the Seljuk ranks. Süleymanshah himself was wounded and withdrew to Erzurum. Both the Rum Seljuk and Georgian armies suffered heavy casualties, but coordinated flanking attacks won the battle for the Georgians.Alexander Mikaberidze, ''Historical Dictionary of Georgia'', (Rowman & Littlefield, 2015), 184.
Suleiman II died in 1204 Claude Cahen, ''The Formation of Turkey: The Seljukid Sultanate of Rum: Eleventh to Fourteenth'', transl. & ed. P.M. Holt, (Pearson Education Limited, 2001), 42. and was succeeded by his son Kilij Arslan III, whose reign was unpopular. Kaykhusraw I seized Konya in 1205 reestablishing his reign. Under his rule and those of his two successors, Kaykaus I and Kayqubad I, Seljuk power in Anatolia reached its apogee. Kaykhusraw's most important achievement was the capture of the harbour of Attalia (Antalya) on the Mediterranean coast in 1207. His son Kaykaus captured Sinop and made the Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through t ...
his vassal in 1214. He also subjugated Cilician Armenia but in 1218 was forced to surrender the city of Aleppo, acquired from al-Kamil. Kayqubad continued to acquire lands along the Mediterranean coast from 1221 to 1225.
In the 1220s, he sent an expeditionary force across the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
to Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
. In the east he defeated the Mengujekids and began to put pressure on the Artuqids.
Mongol conquest
Kaykhusraw II (1237–1246) began his reign by capturing the region around Diyarbakır, but in 1239 he had to face an uprising led by a popular preacher namedBaba Ishak
Baba Ishak, also spelled Baba Ishāq, Babaî, or Bābā’ī, a charismatic preacher, led an uprising of the Turkoman of Anatolia against the Seljuq Sultanate of Rûm well known as Babai Revolt ''c.'' 1239 until he was hanged in 1241. Balcıoğlu ...
. After three years, when he had finally quelled the revolt, the Crimean foothold was lost and the state and the sultanate's army had weakened. It is in these conditions that he had to face a far more dangerous threat, that of the expanding Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
. The forces of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe ...
took Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a List of cities in Turkey, city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses t ...
in 1242 and in 1243, the sultan was crushed by Baiju in the Battle of Köse Dağ (a mountain between the cities of Sivas
Sivas (Latin and Greek: ''Sebastia'', ''Sebastea'', Σεβάστεια, Σεβαστή, ) is a city in central Turkey and the seat of Sivas Province.
The city, which lies at an elevation of in the broad valley of the Kızılırmak river, is ...
and Erzincan), and the Seljuk Turks were forced to swear allegiance to the Mongols and became their vassals. The sultan himself had fled to Antalya after the 1243 battle, where he died in 1246, his death starting a period of tripartite, and then dual, rule that lasted until 1260.
The Seljuk realm was divided among Kaykhusraw's three sons. The eldest, Kaykaus II (1246–1260), assumed the rule in the area west of the river Kızılırmak. His younger brothers, Kilij Arslan IV (1248–1265) and Kayqubad II (1249–1257), were set to rule the regions east of the river under Mongol administration. In October 1256, Bayju defeated Kaykaus II near Aksaray and all of Anatolia became officially subject to Möngke Khan. In 1260 Kaykaus II fled from Konya to Crimea where he died in 1279. Kilij Arslan IV was executed in 1265, and Kaykhusraw III
Kaykhusraw III ( 1ca, كَیخُسرو سوم) or Ghiyāth ad-Dīn Kaykhusraw bin Qilij Arslān ( fa, غياث الدين كيخسرو بن قلج ارسلان; – 1284) was between two and six years old when in 1265 he was named Seljuq Su ...
(1265–1284) became the nominal ruler of all of Anatolia, with the tangible power exercised either by the Mongols or the sultan's influential regents.
Disintegration
The Seljuk state had started to split into small emirates ( beyliks) that increasingly distanced themselves from both Mongol and Seljuk control. In 1277, responding to a call from Anatolia, the Mamluk Sultan Baibars raided Anatolia and defeated the Mongols at the Battle of Elbistan, temporarily replacing them as the administrator of the Seljuk realm. But since the native forces who had called him to Anatolia did not manifest themselves for the defense of the land, he had to return to his home base inEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
, and the Mongol administration was re-assumed, officially and severely. Also, the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia
The Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia (Middle Armenian: , '), also known as Cilician Armenia ( hy, Կիլիկեան Հայաստան, '), Lesser Armenia, Little Armenia or New Armenia, and formerly known as the Armenian Principality of Cilicia ( hy, ...
captured the Mediterranean coast from Selinos to Seleucia, as well as the cities of Marash and Behisni, from the Seljuk in the 1240s.
Near the end of his reign, Kaykhusraw III could claim direct sovereignty only over lands around Konya. Some of the beyliks (including the early Ottoman state) and Seljuk governors of Anatolia continued to recognize, albeit nominally, the supremacy of the sultan in Konya, delivering the khutbah in the name of the sultans in Konya in recognition of their sovereignty, and the sultans continued to call themselves Fahreddin, ''the Pride of Islam''. When Kaykhusraw III was executed in 1284, the Seljuk dynasty suffered another blow from internal struggles which lasted until 1303 when the son of Kaykaus II, Mesud II, established himself as sultan in Kayseri. He was murdered in 1308 and his son Mesud III soon afterwards. A distant relative to the Seljuk dynasty momentarily installed himself as emir of Konya, but he was defeated and his lands conquered by the Karamanids
The Karamanids ( tr, Karamanoğulları or ), also known as the Emirate of Karaman and Beylik of Karaman ( tr, Karamanoğulları Beyliği), was one of the Anatolian beyliks, centered in South-Central Anatolia around the present-day Karaman Pr ...
in 1328. The sultanate's monetary sphere of influence lasted slightly longer and coins of Seljuk mint, generally considered to be of reliable value, continued to be used throughout the 14th century, once again, including by the Ottomans.




Culture and society
The Seljuk dynasty of Rum, as successors to the Great Seljuks, based its political, religious and cultural heritage on the Perso-Islamic tradition andGreco-Roman
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were dir ...
tradition, even to the point of naming their sons with Persian names. As an expression of Turko-Persian culture, Rum Seljuks patronized Persian art, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
, and literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to inclu ...
. Unlike the Seljuk Empire, the Seljuk sultans of Rum had Persian names such as Kay-Khusraw, Kay-Qubadh and Kay-Ka'us. The bureaucrats and religious elite of their realm was of Persian stock. In the 13th-century, the majority of the Muslim inhabitants in major Anatolian urban hubs reportedly spoke Persian as their main language. It was in this century that the proneness of imitating Iran in terms of administration, religion and culture reached its zenith, resulting in the creation of a "second Iran" in Anatolia.
Despite their Turkic origins, the Seljuks used Persian for administrative purposes, even their histories, which replaced Arabic, were in Persian. Their usage of Turkish was hardly promoted at all. Even Sultan Kilij Arslan II, as a child, spoke to courtiers in Persian. Khanbaghi states the Anatolian Seljuks were even more Persianized than the Seljuks that ruled the Iranian plateau. The '' Rahat al-sudur'', the history of the Great Seljuk Empire and its breakup, written in Persian by Muhammad bin Ali Rawandi, was dedicated to Sultan Kaykhusraw I. Even the '' Tārikh-i Āl-i Saldjūq'', an anonymous history of the Sultanate of Rum, was written in Persian.
One of its most famous Persian writers, Rumi, took his name from the name of the state. Moreover, Byzantine influence in the Sultanate was also significant, since Byzantine Greek aristocracy remained part of the Seljuk nobility, and the native Byzantine (Rûm) peasants remained numerous in the region. Cultural Turkification in Anatolia first started during the 14th-century, particularly during the gradual rise of the Ottomans.
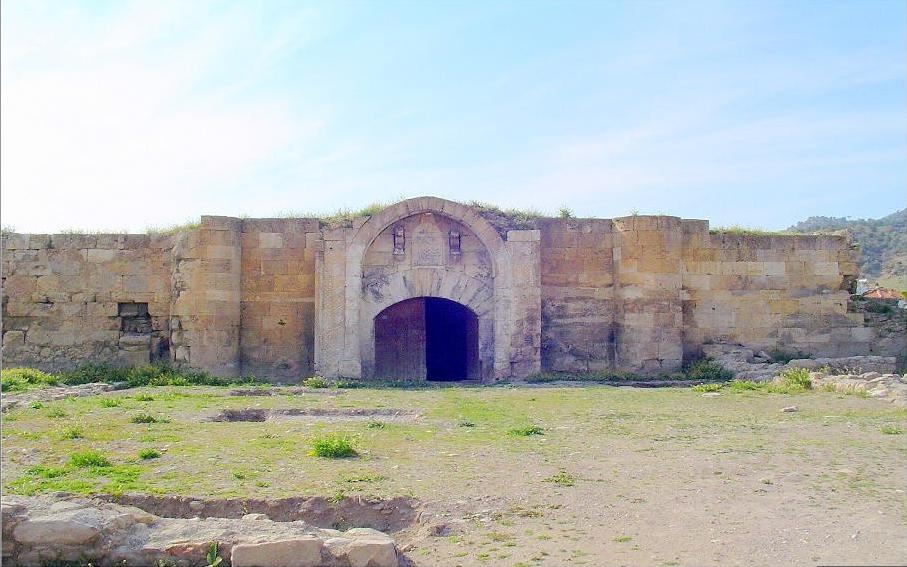
 In their construction of
In their construction of caravanserai
A caravanserai (or caravansary; ) was a roadside inn where travelers ( caravaners) could rest and recover from the day's journey. Caravanserais supported the flow of commerce, information and people across the network of trade routes coverin ...
s, madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , pl. , ) is the Arabic word for any type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary instruction or higher learning. The word is variously transliterated '' ...
s and mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a Place of worship, place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers (sujud) ...
s, the Rum Seljuks translated the Iranian Seljuk architecture of bricks and plaster into the use of stone. Among these, the ''caravanserais'' (or ''hans''), used as stops, trading posts and defense for caravans, and of which about a hundred structures were built during the Anatolian Seljuk period, are particularly remarkable. Along with Persian influences, which had an indisputable effect, Seljuk architecture was inspired by local Byzantine (Rûm
Rūm ( ar, روم , collective; singulative: Rūmī ; plural: Arwām ; fa, روم Rum or Rumiyān, singular Rumi; tr, Rûm or , singular ), also romanized as ''Roum'', is a derivative of the Aramaic (''rhπmÈ'') and Parthian language, Par ...
) architects, for example the Gök Medrese (Sivas), and by Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
. As such, Anatolian architecture represents some of the most distinctive and impressive constructions in the entire history of Islamic architecture. Later, this Anatolian architecture would be inherited by the Sultanate of India.
 The largest caravanserai is the Sultan Han (built in 1229) on the road between the cities of Konya and Aksaray, in the township of Sultanhanı, covering . There are two caravanserais that carry the name "Sultan Han", the other one being between Kayseri and Sivas. Furthermore, apart from Sultanhanı, five other towns across Turkey owe their names to caravanserais built there. These are Alacahan in Kangal, Durağan, Hekimhan and Kadınhanı, as well as the township of Akhan within the
The largest caravanserai is the Sultan Han (built in 1229) on the road between the cities of Konya and Aksaray, in the township of Sultanhanı, covering . There are two caravanserais that carry the name "Sultan Han", the other one being between Kayseri and Sivas. Furthermore, apart from Sultanhanı, five other towns across Turkey owe their names to caravanserais built there. These are Alacahan in Kangal, Durağan, Hekimhan and Kadınhanı, as well as the township of Akhan within the Denizli
Denizli is an industrial city in the southwestern part of Turkey and the eastern end of the alluvial valley formed by the river Büyük Menderes, where the plain reaches an elevation of about . Denizli is located in the country's Aegean Region.
...
metropolitan area. The caravanserai of Hekimhan is unique in having, underneath the usual inscription in Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
with information relating to the edifice, two further inscriptions in Armenian and Syriac, since it was constructed by the sultan Kayqubad I's doctor (''hekim'') who is thought to have been a former Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
who converted to Islam. There are other particular cases like the settlement in Kalehisar (contiguous to an ancient Hittite site) near Alaca Alaca () may refer to the following places in Turkey:
* Alaca, Çorum, a large district in Çorum Province
** Alaca Dam
* Alaca, Borçka, a village in Artvin Province
* Alaca, Beşiri, a village in Batman Province
* Alaca, Elâzığ, a village in E ...
, founded by the Seljuk commander Hüsameddin Temurlu, who had taken refuge in the region after the defeat in the Battle of Köse Dağ and had founded a township comprising a castle, a madrasa, a habitation zone and a caravanserai, which were later abandoned apparently around the 16th century. All but the caravanserai, which remains undiscovered, was explored in the 1960s by the art historian Oktay Aslanapa, and the finds as well as a number of documents attest to the existence of a vivid settlement in the site, such as a 1463 Ottoman firman which instructs the headmaster of the madrasa to lodge not in the school but in the caravanserai.
 The Seljuk palaces, as well as their armies, were staffed with ghulams (plural ''ghilmân'', ar, غِلْمَان), enslaved youths taken from non-Muslim communities, mainly Greeks from former Byzantine territories. The practice of keeping ghulams may have offered a model for the later devşirme during the time of the Ottoman Empire., page 306
The Seljuk palaces, as well as their armies, were staffed with ghulams (plural ''ghilmân'', ar, غِلْمَان), enslaved youths taken from non-Muslim communities, mainly Greeks from former Byzantine territories. The practice of keeping ghulams may have offered a model for the later devşirme during the time of the Ottoman Empire., page 306
Dynasty
 As regards the names of the sultans, there are variants in form and spelling depending on the preferences displayed by one source or the other, either for fidelity in transliterating the Persian variant of the Arabic script which the sultans used, or for a rendering corresponding to the modern
As regards the names of the sultans, there are variants in form and spelling depending on the preferences displayed by one source or the other, either for fidelity in transliterating the Persian variant of the Arabic script which the sultans used, or for a rendering corresponding to the modern Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
phonology and orthography. Some sultans had two names that they chose to use alternatively in reference to their legacy. While the two palaces built by Alaeddin Keykubad I carry the names Kubadabad Palace and Keykubadiye Palace, he named his mosque in Konya as Alâeddin Mosque and the port city of Alanya he had captured as " Alaiye". Similarly, the medrese built by Kaykhusraw I in Kayseri, within the complex ('' külliye'') dedicated to his sister Gevher Nesibe
Gevher Nesibe was an early 13th century princess of the Sultanate of Rum, the daughter of Kilij Arslan II and sister of Kaykhusraw I.
Legends
According to legend, Gevher Nesibe fell in love with a cavalry officer defending the palace of the Selju ...
, was named Gıyasiye Medrese, and the one built by Kaykaus I in Sivas as Izzediye Medrese.
See also
* Timeline of the Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm * Babai Revolt * Byzantine–Seljuk Wars * List of battles involving the Seljuk Empire * Rûm Province, Ottoman EmpireNotes
Footnotes
References
Sources
* * * * * * *82 * * * * *External links
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Rum, Sultanate of States and territories established in 1077 1308 disestablishments in Asia History of Konya Province 1077 establishments in Asia Turkic rump states Former sultanates