Sughana on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Srughna, also spelt Shrughna in
Srughna, also spelt Shrughna in
Gazatteer of Haryana: Yamunanagar.
Haryana tourism
in Tribune India
Ancient Geography of India
by Alexander Cunningham (1871) Locations in Hindu mythology Archaeological sites in Haryana
 Srughna, also spelt Shrughna in
Srughna, also spelt Shrughna in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
, or Sughna, Sughana or Sugh in the spoken form, was an ancient city or kingdom of India frequently referred to in early and medieval texts. It was visited by Chinese traveller, Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
(Hiuen Tsang) in the 7th century and was reported to be in ruins even then although the foundations still remained. Xuanzang described the kingdom as extending from the mountains to the north, to the Ganges river
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
to the East, and with the Yamuna river
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Ba ...
flowing through it. He described the capital city on the west bank of the Yamuna as possessing a large Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
vihara and a grand stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation.
In Buddhism, circum ...
dating to the time of the Mauryan
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
emperor, Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
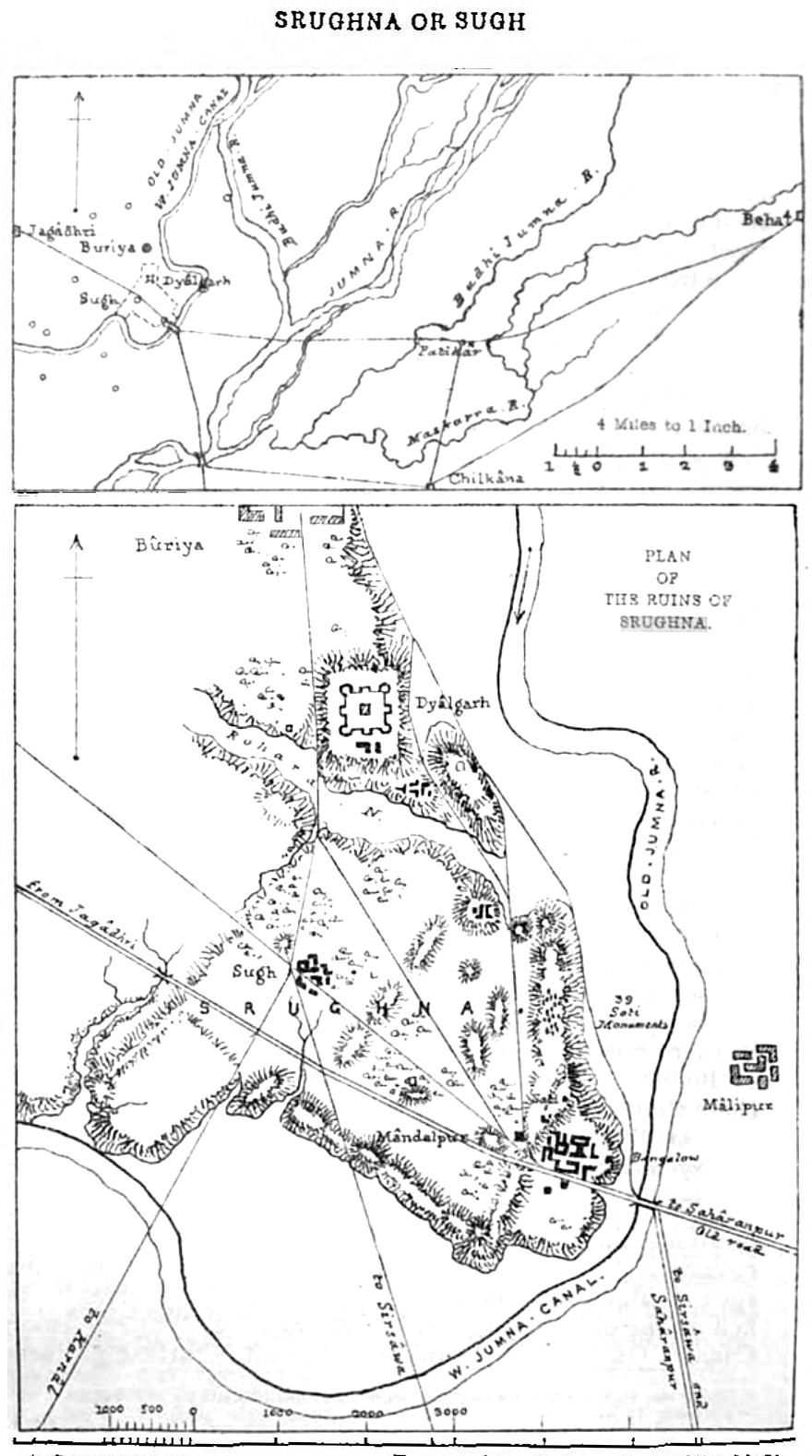
. Srughna is identified with the Sugh Ancient Mound
Sugh Ancient Mound, also known as the Ancient Site of Sugh, is located in the village of Amadalpur Dayalgarh, in the Yamunanagar district of Haryana, India. Suryamandir-Tirth in Amadalpur is nearby. Buddhist stupa here is identified with th ...
located in the village of Amadalpur Dayalgarh, in the Yamunanagar district of Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ...
state of India. To this day, the ancient Chaneti Buddhist Stupa
Chaneti Buddhist Stupa is a 3rd century BC monument protected by the Government of India. The stupa is located in the Yamunanagar district of Haryana, three kilometers east of Jagadhri, and about three kilometers northwest of the archaeological ...
, probably dating to the Mauryan period, stands in the area, about northwest of Sugh.
Identification
Xuanzang saw several stupas, which commemorated the visit of the Buddha or enshrined the relics of Buddhist monks Sariputra andMaudgalyayana
Maudgalyāyana ( pi, Moggallāna), also known as Mahāmaudgalyāyana or by his birth name Kolita, was one of the Buddha's closest disciples. Described as a contemporary of disciples such as Subhuti, Śāriputra ('), and Mahākāśyapa ( pi, M ...
.Yamunanagar HistoryGazatteer of Haryana: Yamunanagar.
Alexander Cunningham
Major General Sir Alexander Cunningham (23 January 1814 – 28 November 1893) was a British Army engineer with the Bengal Engineer Group who later took an interest in the history and archaeology of India. In 1861, he was appointed to the newl ...
identified the lost city with the village of Sugh (or Sugha) situated from Yamunanagar
Yamunanagar (), is a city and a municipal corporation in Yamunanagar district in the Indian state of Haryana. This town is known for the cluster of plywood units and paper industries. It provides timber to larger industries. The older tow ...
in the state of Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ...
. The city probably lost its importance after the 7th century and the name survived in a localized form. Panjab University
Panjab University (PU) is a collegiate public state university located in Chandigarh, Punjab. Funded through both State and Union governments, it is considered a state university. It traces its origins to the University of the Punjab in Laho ...
's 1965 excavation found artifacts dating from 600 BCE to 300 CE, including grey ware and red ware
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to Orange (colour), orange and opposite Violet (color), violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the ...
pottery, coins, seals, animal remains, male and female terracotta figurines, animal terracotta figurines and miscellaneous terracotta objects such as flesh rubbers, crucibles
A crucible is a ceramic or metal container in which metals or other substances may be melted or subjected to very high temperatures. While crucibles were historically usually made from clay, they can be made from any material that withstands t ...
, rattle, gamesmen, stamp, seal impression, discs, frames and wheels, balls, goldsmiths heating cup, an ear ornament grooved on the exterior and a broken figurine of a headless child with writing board in lap with sunga (187 BCE to 78 BCE) period alphabets. Collection of these figurines belong to Sunga, Mauryan
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
, Kushana
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
, Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by sev ...
and medieval period.
Srughna is regularly mentioned in Panini's Ashtadhyayi, Patanjali
Patanjali ( sa, पतञ्जलि, Patañjali), also called Gonardiya or Gonikaputra, was a Hindu author, mystic and philosopher. Very little is known about him, and while no one knows exactly when he lived; from analysis of his works it i ...
's Mahabhashya
''Mahabhashya'' ( sa, महाभाष्य, IAST: '','' , "great commentary"), attributed to Patañjali, is a commentary on selected rules of Sanskrit grammar from Pāṇini's treatise, the ''Aṣṭādhyāyī'', as well as Kātyāyana's '' ...
, the Divyavadana
The ''Divyāvadāna'' or Divine narratives is a Sanskrit anthology of Buddhist avadana tales, many originating in Mūlasarvāstivādin vinaya texts. It may be dated to 2nd century CE. The stories themselves are therefore quite ancient and may be ...
, the Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
, the Mahamayuri
Mahamayuri ( sa, महामायूरी ("great peacock"), ''Kǒngquè Míngwáng'', vi, Khổng Tước Minh Vương, ja, 孔雀明王, ''Kujaku Myōō'', ko, 공작명왕 ''Gongjak Myeongwang''), or Mahāmāyūrī Vidyārājñī is a b ...
, the ''Brihatsamhita'' of Varahamihira, etc. Tūrghna, another location mentioned in ancient literary texts, is considered synonymous with Srughna.
The village of Sugh, with the nearby Sugh Ancient Mound
Sugh Ancient Mound, also known as the Ancient Site of Sugh, is located in the village of Amadalpur Dayalgarh, in the Yamunanagar district of Haryana, India. Suryamandir-Tirth in Amadalpur is nearby. Buddhist stupa here is identified with th ...
, is now a well known archaeological site which has yielded a trove of coins. It was excavated by Cunningham in the 19th century. Suraj Bhan
Suraj Bhan (1 October 1928 – 6 August 2006) was a former Governor, Member of Parliament and an Indian politician from Bharatiya Janata Party.
Personal life
Suraj Bhan Banswal was born on 1 October 1928 at Mehlanwali, Yamuna Nagar dis ...
partially excavated the site in 1964–65.
The original site of the Topra Kalan
Topra, combined name for the larger Topra Kalan and adjacent smaller Topra Khurd, is a Mauryan Empire-era village in Yamunanagar district of Haryana state in India.
It lies 14 km west of Yamunanagar, 14 km from Radaur and 90 k ...
pillar of Ashoka is located about to the west. Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
's Rock edicts of Khalsi is also from the region, about to the northeast.
Dhanabhuti, king of "Sugana"
It has been proposed that KingDhanabhuti
Dhanabhūti (Brahmi: 𑀥𑀦𑀪𑀽𑀢𑀺) or Vatsiputra Dhanabhūti was a 2nd or 1st-century BCE Buddhist king in Central India, and the most prominent donor for the Bharhut stupa. He appears in two or three major dedicatory inscriptions at ...
, the main sponsor of the Buddhist stupa at Bharhut
Bharhut is a village located in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for its famous relics from a Buddhist stupa. What makes Bharhut panels unique is that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters mentioni ...
, came from Srughna or Sughana, and that Dhanabhuti was one of its important kings, who, besides building magnificent stupas in his capital city, also made some of the most important donations for the building of the torana
''Torana'' ( sa, तोरण; '' awr-uh-nuh') is a free-standing ornamental or arched gateway for ceremonial purposes in Hindu, Buddhist and Jain architecture of the Indian subcontinent. Toranas can also be widely seen in Southeast Asia and ...
s and railings at Bharhut
Bharhut is a village located in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for its famous relics from a Buddhist stupa. What makes Bharhut panels unique is that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters mentioni ...
."A local Buddhist kingdom in Punjab with Srughna, modern Sugh, near Jagadhri in the district of Ambala, as its capital city, and covering an area of about 1000 miles in circuit. Raja Dhanabhuti, the pre-eminent king of this royal family ruled from 240 B.C. to 210 B.C. This pious Buddhist king apart from building magnificent stupas in his capital city, also made munificent donations to the world famous Stupa of Bharhut" in
See also
*Sugh Ancient Mound
Sugh Ancient Mound, also known as the Ancient Site of Sugh, is located in the village of Amadalpur Dayalgarh, in the Yamunanagar district of Haryana, India. Suryamandir-Tirth in Amadalpur is nearby. Buddhist stupa here is identified with th ...
* Buddhist pilgrimage sites in Haryana
* Buddhist pilgrimage sites
The most important places in Buddhism are located in the Indo-Gangetic Plain of northern India and southern Nepal, in the area between New Delhi and Rajgir. This is the area where Gautama Buddha lived and taught, and the main sites connected to ...
* Buddhist pilgrimage sites in India
In religion and spirituality, a pilgrimage is a long journey or search of great moral significance. Sometimes, it is a journey to a sacred place or to a shrine of importance to a person's beliefs and faith. Members of every major religion par ...
Notes
References
* * * {{cite journal, last1=Bharadwaj, first1=O. P., title=Gautama Buddha in Kurukṣetra, journal=Annals of the Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute, date=1980, volume=61, issue=1/4, pages=189–204, jstor=41691865External links
Haryana tourism
in Tribune India
Ancient Geography of India
by Alexander Cunningham (1871) Locations in Hindu mythology Archaeological sites in Haryana