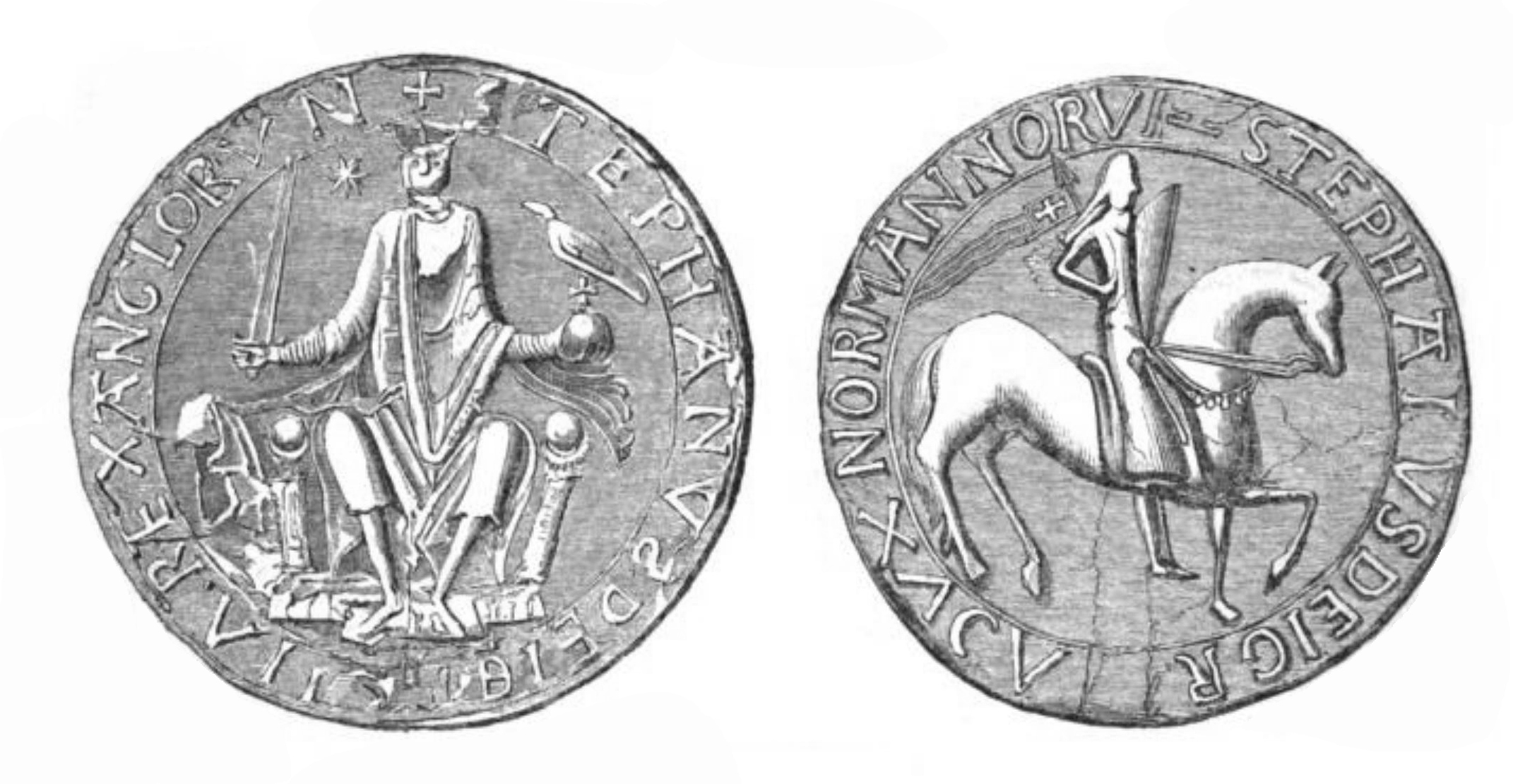
Stephen Of Blois on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was
 Stephen was born in
Stephen was born in
 Stephen's early life was heavily influenced by his relationship with his uncle
Stephen's early life was heavily influenced by his relationship with his uncle
 In 1120, the English political landscape changed dramatically. Three hundred passengers embarked on the '' White Ship'' to travel from Barfleur in Normandy to England, including the heir to the throne, William Adelin, and many other senior nobles. Stephen had intended to sail on the same ship but changed his mind at the last moment and got off to await another vessel, either out of concern for overcrowding on board the ship, or because he was suffering from
In 1120, the English political landscape changed dramatically. Three hundred passengers embarked on the '' White Ship'' to travel from Barfleur in Normandy to England, including the heir to the throne, William Adelin, and many other senior nobles. Stephen had intended to sail on the same ship but changed his mind at the last moment and got off to await another vessel, either out of concern for overcrowding on board the ship, or because he was suffering from
 Stephen was a well established figure in Anglo-Norman society by 1135. He was extremely wealthy, well-mannered and liked by his peers; he was also considered a man capable of firm action.King (2010), p. 301. Chroniclers recorded that despite his wealth and power he was a modest and easy-going leader, happy to sit with his men and servants, casually laughing and eating with them. He was very pious, both in terms of his observance of religious rituals and his personal generosity to the church. Stephen also had a personal Augustinian confessor appointed to him by the Archbishop of Canterbury, who implemented a penitential regime for him, and Stephen encouraged the new order of
Stephen was a well established figure in Anglo-Norman society by 1135. He was extremely wealthy, well-mannered and liked by his peers; he was also considered a man capable of firm action.King (2010), p. 301. Chroniclers recorded that despite his wealth and power he was a modest and easy-going leader, happy to sit with his men and servants, casually laughing and eating with them. He was very pious, both in terms of his observance of religious rituals and his personal generosity to the church. Stephen also had a personal Augustinian confessor appointed to him by the Archbishop of Canterbury, who implemented a penitential regime for him, and Stephen encouraged the new order of  When news began to spread of Henry I's death, many of the potential claimants to the throne were not well placed to respond. Geoffrey and Matilda were in Anjou, rather awkwardly supporting the rebels in their campaign against the royal army, which included a number of Matilda's supporters such as Robert of Gloucester. Many of these barons had taken an oath to stay in Normandy until the late King was properly buried, which prevented them from returning to England. Stephen's elder brother Theobald was further south still, in Blois.Barlow, pp. 163–164. Stephen, however, was in Boulogne, and when news reached him of Henry's death he left for England, accompanied by his military household. Robert of Gloucester had garrisoned the ports of Dover and Canterbury and some accounts suggest that they refused Stephen access when he first arrived. Nonetheless, Stephen probably reached his own estate on the edge of London by 8 December and over the next week he began to seize power in England.
The crowds in London traditionally claimed a right to elect the King, and they proclaimed Stephen the new monarch, believing that he would grant the city new rights and privileges in return. Henry of Blois delivered the support of the church to Stephen: Stephen was able to advance to
When news began to spread of Henry I's death, many of the potential claimants to the throne were not well placed to respond. Geoffrey and Matilda were in Anjou, rather awkwardly supporting the rebels in their campaign against the royal army, which included a number of Matilda's supporters such as Robert of Gloucester. Many of these barons had taken an oath to stay in Normandy until the late King was properly buried, which prevented them from returning to England. Stephen's elder brother Theobald was further south still, in Blois.Barlow, pp. 163–164. Stephen, however, was in Boulogne, and when news reached him of Henry's death he left for England, accompanied by his military household. Robert of Gloucester had garrisoned the ports of Dover and Canterbury and some accounts suggest that they refused Stephen access when he first arrived. Nonetheless, Stephen probably reached his own estate on the edge of London by 8 December and over the next week he began to seize power in England.
The crowds in London traditionally claimed a right to elect the King, and they proclaimed Stephen the new monarch, believing that he would grant the city new rights and privileges in return. Henry of Blois delivered the support of the church to Stephen: Stephen was able to advance to
 Stephen's new Anglo-Norman kingdom had been shaped by the
Stephen's new Anglo-Norman kingdom had been shaped by the
 Stephen was attacked on several fronts during 1138. First, Robert, Earl of Gloucester, rebelled against the King, starting the descent into civil war in England. An illegitimate son of Henry I and the half-brother of the Empress Matilda, Robert was one of the most powerful Anglo-Norman barons, controlling estates in Normandy. He was known for his qualities as a statesman, his military experience, and leadership ability.Barlow, p. 169. Robert had tried to convince Theobald to take the throne in 1135; he did not attend Stephen's first court in 1136 and it took several summonses to convince him to attend court at
Stephen was attacked on several fronts during 1138. First, Robert, Earl of Gloucester, rebelled against the King, starting the descent into civil war in England. An illegitimate son of Henry I and the half-brother of the Empress Matilda, Robert was one of the most powerful Anglo-Norman barons, controlling estates in Normandy. He was known for his qualities as a statesman, his military experience, and leadership ability.Barlow, p. 169. Robert had tried to convince Theobald to take the throne in 1135; he did not attend Stephen's first court in 1136 and it took several summonses to convince him to attend court at  Stephen's personal qualities as a military leader focused on his skill in personal combat, his capabilities in siege warfare and a remarkable ability to move military forces quickly over relatively long distances. In response to the revolts and invasions, he rapidly undertook several military campaigns, focusing primarily on England rather than Normandy. His wife Matilda was sent to Kent with ships and resources from Boulogne, with the task of retaking the key port of
Stephen's personal qualities as a military leader focused on his skill in personal combat, his capabilities in siege warfare and a remarkable ability to move military forces quickly over relatively long distances. In response to the revolts and invasions, he rapidly undertook several military campaigns, focusing primarily on England rather than Normandy. His wife Matilda was sent to Kent with ships and resources from Boulogne, with the task of retaking the key port of
 Stephen prepared for the Angevin invasion by creating a number of additional
Stephen prepared for the Angevin invasion by creating a number of additional
 The Angevin invasion finally arrived in 1139. Baldwin de Redvers crossed over from Normandy to Wareham in August in an initial attempt to capture a port to receive the Empress Matilda's invading army, but Stephen's forces forced him to retreat into the south-west.Davis, p. 39. The following month, however, the Empress was invited by the Dowager Queen Adeliza to land at
The Angevin invasion finally arrived in 1139. Baldwin de Redvers crossed over from Normandy to Wareham in August in an initial attempt to capture a port to receive the Empress Matilda's invading army, but Stephen's forces forced him to retreat into the south-west.Davis, p. 39. The following month, however, the Empress was invited by the Dowager Queen Adeliza to land at  At the start of 1140, Nigel, Bishop of Ely, whose castles Stephen had confiscated the previous year, rebelled against Stephen as well. Nigel hoped to seize
At the start of 1140, Nigel, Bishop of Ely, whose castles Stephen had confiscated the previous year, rebelled against Stephen as well. Nigel hoped to seize
 While Stephen and his army besieged Lincoln Castle at the start of 1141, Robert of Gloucester and Ranulf of Chester advanced on the King's position with a somewhat larger force.Davis, p. 52. When the news reached Stephen, he held a council to decide whether to give battle or to withdraw and gather additional soldiers: Stephen decided to fight, resulting in the Battle of Lincoln on 2 February 1141. The King commanded the centre of his army, with Alan of Brittany on his right and William of Aumale on his left.Bradbury, p. 105. Robert and Ranulf's forces had superiority in cavalry and Stephen dismounted many of his own knights to form a solid infantry block; he joined them himself, fighting on foot in the battle. Stephen was not a gifted public speaker, and delegated the pre-battle speech to
While Stephen and his army besieged Lincoln Castle at the start of 1141, Robert of Gloucester and Ranulf of Chester advanced on the King's position with a somewhat larger force.Davis, p. 52. When the news reached Stephen, he held a council to decide whether to give battle or to withdraw and gather additional soldiers: Stephen decided to fight, resulting in the Battle of Lincoln on 2 February 1141. The King commanded the centre of his army, with Alan of Brittany on his right and William of Aumale on his left.Bradbury, p. 105. Robert and Ranulf's forces had superiority in cavalry and Stephen dismounted many of his own knights to form a solid infantry block; he joined them himself, fighting on foot in the battle. Stephen was not a gifted public speaker, and delegated the pre-battle speech to  Stephen's wife Matilda played a critical part in keeping the King's cause alive during his captivity. Queen Matilda gathered Stephen's remaining lieutenants around her and the royal family in the south-east, advancing into London when the population rejected the Empress.Crouch (2002), p. 261. Stephen's long-standing commander William of Ypres remained with the Queen in London; William Martel, the royal steward, commanded operations from
Stephen's wife Matilda played a critical part in keeping the King's cause alive during his captivity. Queen Matilda gathered Stephen's remaining lieutenants around her and the royal family in the south-east, advancing into London when the population rejected the Empress.Crouch (2002), p. 261. Stephen's long-standing commander William of Ypres remained with the Queen in London; William Martel, the royal steward, commanded operations from
 The war between the two sides in England reached a stalemate in the mid-1140s, while Geoffrey of Anjou consolidated his hold on power in Normandy. 1143 started precariously for Stephen when he was besieged by Robert of Gloucester at
The war between the two sides in England reached a stalemate in the mid-1140s, while Geoffrey of Anjou consolidated his hold on power in Normandy. 1143 started precariously for Stephen when he was besieged by Robert of Gloucester at
 England had suffered extensively from the war by 1147, leading later Victorian historians to call the period of conflict "
England had suffered extensively from the war by 1147, leading later Victorian historians to call the period of conflict "
 Stephen's relationship with the church deteriorated badly towards the end of his reign.Davis, p. 98. The reforming movement within the church, which advocated greater autonomy from royal authority for the clergy, had continued to grow, while new voices such as the Cistercians had gained additional prestige within the monastic orders, eclipsing older orders such as the Cluniacs. Stephen's dispute with the church had its origins in 1140, when Archbishop Thurstan of York died. An argument then broke out between a group of reformers based in York and backed by
Stephen's relationship with the church deteriorated badly towards the end of his reign.Davis, p. 98. The reforming movement within the church, which advocated greater autonomy from royal authority for the clergy, had continued to grow, while new voices such as the Cistercians had gained additional prestige within the monastic orders, eclipsing older orders such as the Cluniacs. Stephen's dispute with the church had its origins in 1140, when Archbishop Thurstan of York died. An argument then broke out between a group of reformers based in York and backed by
 Henry FitzEmpress returned to England again at the start of 1153 with a small army, supported in the north and east of England by Ranulf of Chester and Hugh Bigod. Stephen's castle at
Henry FitzEmpress returned to England again at the start of 1153 with a small army, supported in the north and east of England by Ranulf of Chester and Hugh Bigod. Stephen's castle at
King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Baili ...
from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne
Count of Boulogne was a historical title in the Kingdom of France. The city of Boulogne-sur-Mer became the centre of the county of Boulogne during the ninth century. Little is known of the early counts, but the first holder of the title is recor ...
''jure uxoris
''Jure uxoris'' (a Latin phrase meaning "by right of (his) wife"), citing . describes a title of nobility used by a man because his wife holds the office or title '' suo jure'' ("in her own right"). Similarly, the husband of an heiress could beco ...
'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy
In the Middle Ages, the duke of Normandy was the ruler of the Duchy of Normandy in north-western France. The duchy arose out of a grant of land to the Viking leader Rollo by the French king Charles III in 911. In 924 and again in 933, Normand ...
from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin, the only legi ...
, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda ( 7 February 110210 September 1167), also known as the Empress Maude, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter of King Henry I of England, she moved to Germany as ...
, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England
The Angevins (; "from Anjou") were a royal house of French origin that ruled England in the 12th and early 13th centuries; its monarchs were Henry II, Richard I and John. In the 10 years from 1144, two successive counts of Anjou in France, G ...
.
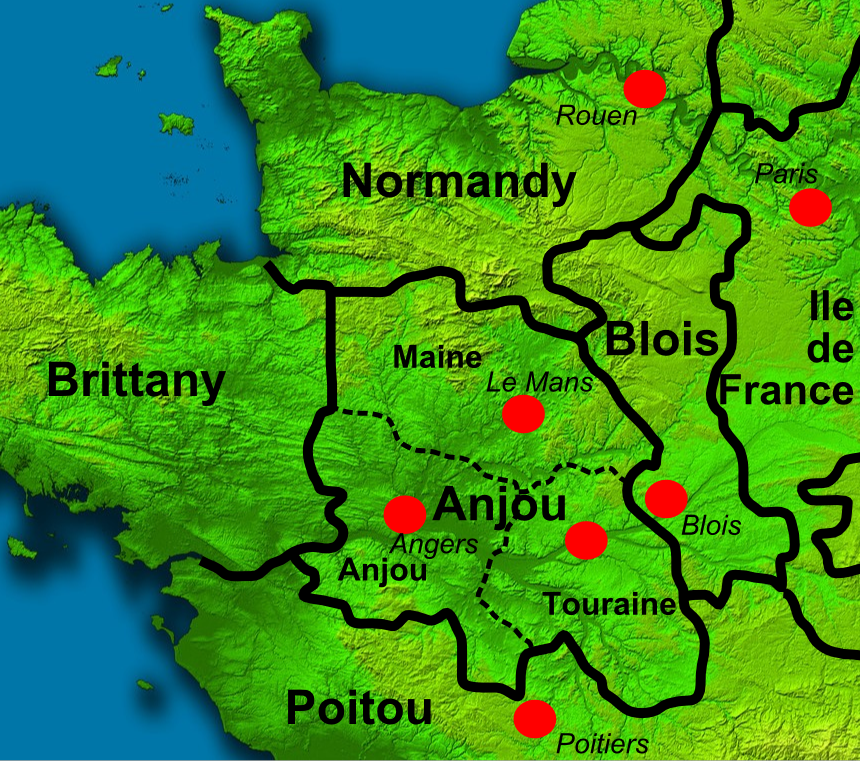
Stephen was born in the County of Blois in central France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
as the fourth son of Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois, and Adela
Adela may refer to:
* ''Adela'', a 1933 Romanian novel by Garabet Ibrăileanu
* ''Adela'' (1985 film), a 1985 Romanian film directed by Mircea Veroiu
* ''Adela'' (2000 film), a 2000 Argentine thriller film directed and written by Eduardo Mign ...
, daughter of William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
. His father died while Stephen was still young, and he was brought up by his mother. Placed into the court of his uncle Henry I of England
Henry I (c. 1068 – 1 December 1135), also known as Henry Beauclerc, was King of England from 1100 to his death in 1135. He was the fourth son of William the Conqueror and was educated in Latin and the liberal arts. On William's death in ...
, Stephen rose in prominence and was granted extensive lands. He married Matilda of Boulogne, inheriting additional estates in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
and Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the C ...
that made the couple one of the wealthiest in England. Stephen narrowly escaped drowning with Henry I's son, William Adelin, in the sinking of the '' White Ship'' in 1120; William's death left the succession of the English throne open to challenge. When Henry died in 1135, Stephen quickly crossed the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
and with the help of his brother Henry, Bishop of Winchester
Henry of Blois ( c. 1096 8 August 1171), often known as Henry of Winchester, was Abbot of Glastonbury Abbey from 1126, and Bishop of Winchester from 1129 to his death. He was a younger son of Stephen Henry, Count of Blois by Adela of Normandy, da ...
and Abbot of Glastonbury __NOTOC__
The Abbot of Glastonbury was the head (or abbot) of Anglo-Saxon and eventually Benedictine house of Glastonbury Abbey at Glastonbury in Somerset, England.
The following is a list of abbots of Glastonbury:
Abbots
See also
* Abbot's K ...
, took the throne, arguing that the preservation of order across the kingdom took priority over his earlier oaths to support the claim of Henry I's daughter, the Empress Matilda.
The early years of Stephen's reign were largely successful, despite a series of attacks on his possessions in England and Normandy by David I of Scotland
David I or Dauíd mac Maíl Choluim (Modern: ''Daibhidh I mac haoilChaluim''; – 24 May 1153) was a 12th-century ruler who was Prince of the Cumbrians from 1113 to 1124 and later King of Scotland from 1124 to 1153. The youngest son of Malco ...
, Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
rebels, and the Empress Matilda's husband Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou
Geoffrey V (24 August 1113 – 7 September 1151), called the Handsome, the Fair (french: link=no, le Bel) or Plantagenet, was the count of Anjou, Touraine and Maine by inheritance from 1129, and also Duke of Normandy by conquest from 1144. ...
. In 1138, the Empress's half-brother Robert of Gloucester rebelled against Stephen, threatening civil war. Together with his close advisor, Waleran de Beaumont, Stephen took firm steps to defend his rule, including arresting a powerful family of bishops. When the Empress and Robert invaded in 1139, Stephen was unable to crush the revolt rapidly, and it took hold in the south-west of England. Captured at the battle of Lincoln in 1141, he was abandoned by many of his followers and lost control of Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
. He was freed only after his wife and William of Ypres
William of Ypres ( nl, Willem van Yper; 1090 – 24 January 116524 January 1164 O.S., 1165 N.S.) was a Flemish nobleman and one of the first mercenary captains of the Middle Ages. Following two unsuccessful bids for the County of Flanders, ...
, one of his military commanders, captured Robert at the Rout of Winchester, but the war dragged on for many years with neither side able to win an advantage.
Stephen became increasingly concerned with ensuring that his son Eustace would inherit his throne. The King tried to convince the Church to agree to crown Eustace to reinforce his claim; Pope Eugene III refused, and Stephen found himself in a sequence of increasingly bitter arguments with his senior clergy. In 1153, the Empress's son Henry invaded England and built an alliance of powerful regional barons to support his claim for the throne. The two armies met at Wallingford, but neither side's barons were keen to fight another pitched battle. Stephen began to examine a negotiated peace, a process hastened by the sudden death of Eustace. Later in the year Stephen and Henry agreed to the Treaty of Winchester
The Treaty of Wallingford, also known as the Treaty of Winchester or the Treaty of Westminster, was an agreement reached in England in the summer of 1153. It effectively ended a civil war known as ''the Anarchy'' (1135–54), caused by a dispute ...
, in which Stephen recognised Henry as his heir in exchange for peace, passing over William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
, Stephen's second son. Stephen died the following year. Modern historians have extensively debated the extent to which his personality, external events, or the weaknesses in the Norman state contributed to this prolonged period of civil war.
Early life (1097–1135)
Childhood
 Stephen was born in
Stephen was born in Blois
Blois ( ; ) is a commune and the capital city of Loir-et-Cher department, in Centre-Val de Loire, France, on the banks of the lower Loire river between Orléans and Tours.
With 45,898 inhabitants by 2019, Blois is the most populated city of the ...
, France, in either 1092 or 1096.Davis, p. 1; King (2010), p. 5. His father was Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois and Chartres, an important French nobleman, and an active crusader, who played only a brief part in Stephen's early life. During the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ...
Stephen-Henry had acquired a reputation for cowardice, and he returned to the Levant again in 1101 to rebuild his reputation; there he was killed at the battle of Ramlah.Davis, p. 4. Stephen's mother, Adela
Adela may refer to:
* ''Adela'', a 1933 Romanian novel by Garabet Ibrăileanu
* ''Adela'' (1985 film), a 1985 Romanian film directed by Mircea Veroiu
* ''Adela'' (2000 film), a 2000 Argentine thriller film directed and written by Eduardo Mign ...
, was the daughter of William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
and Matilda of Flanders
Matilda of Flanders (french: link=no, Mathilde; nl, Machteld) ( 1031 – 2 November 1083) was Queen of England and Duchess of Normandy by marriage to William the Conqueror, and regent of Normandy during his absences from the duchy. She was t ...
, famous amongst her contemporaries for her piety, wealth and political talent. She had a strong matriarchal influence on Stephen during his early years.King (2010), p. 5.
France in the 12th century was a loose collection of counties and smaller polities, under the minimal control of the King of France. The King's power was linked to his control of the rich province of Île-de-France
The Île-de-France (, ; literally "Isle of France") is the most populous of the eighteen regions of France. Centred on the capital Paris, it is located in the north-central part of the country and often called the ''Région parisienne'' (; en, Pa ...
, just to the east of Stephen's home county of Blois. In the west lay the three counties of Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
, Anjou Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
*County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
**Duke ...
and Touraine
Touraine (; ) is one of the traditional provinces of France. Its capital was Tours. During the political reorganization of French territory in 1790, Touraine was divided between the departments of Indre-et-Loire, :Loir-et-Cher, Indre and Vien ...
, and to the north of Blois was the Duchy of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans.
From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman c ...
, from which William the Conqueror had conquered England in 1066. William's children were still fighting over the collective Anglo-Norman inheritance. The rulers across this region spoke a similar language, albeit with regional dialects, followed the same religion, and were closely interrelated; they were also highly competitive and frequently in conflict with one another for valuable territory and the castles that controlled them.
Stephen had at least four brothers and one sister, along with two probable half-sisters. His eldest brother was William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
, who under normal circumstances would have ruled Blois and Chartres. William was probably intellectually disabled
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation,Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signifi ...
, and Adela instead had the counties pass to her second son, later also Count Theobald II of Champagne. Stephen's remaining older brother, Odo, died young, probably in his early teens. His younger brother, Henry of Blois
Henry of Blois ( c. 1096 8 August 1171), often known as Henry of Winchester, was Abbot of Glastonbury Abbey from 1126, and Bishop of Winchester from 1129 to his death. He was a younger son of Stephen Henry, Count of Blois by Adela of Normandy, ...
, was probably born four years after him. The brothers formed a close-knit family group, and Adela encouraged Stephen to take up the role of a feudal knight, whilst steering Henry towards a career in the church, possibly so that their personal career interests would not overlap. Unusually, Stephen was raised in his mother's household rather than being sent to a close relative; he was taught Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
and riding, and was educated in recent history and Biblical stories by his tutor, William the Norman.
Relationship with Henry I
 Stephen's early life was heavily influenced by his relationship with his uncle
Stephen's early life was heavily influenced by his relationship with his uncle Henry I Henry I may refer to:
876–1366
* Henry I the Fowler, King of Germany (876–936)
* Henry I, Duke of Bavaria (died 955)
* Henry I of Austria, Margrave of Austria (died 1018)
* Henry I of France (1008–1060)
* Henry I the Long, Margrave of the N ...
. Henry seized power in England following the death of his elder brother William Rufus. In 1106 he invaded and captured the Duchy of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans.
From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman c ...
, controlled by his eldest brother, Robert Curthose, defeating Robert's army at the battle of Tinchebray. Henry then found himself in conflict with Louis VI of France
Louis VI (late 1081 – 1 August 1137), called the Fat (french: link=no, le Gros) or the Fighter (french: link=no, le Batailleur), was King of the Franks from 1108 to 1137.
Chronicles called him "King of Saint-Denis". Louis was the first member ...
, who took the opportunity to declare Robert's son William Clito the Duke of Normandy.Huscroft, p. 70. Henry responded by forming a network of alliances with the western counties of France against Louis, resulting in a regional conflict that would last throughout Stephen's early life. Adela and Theobald allied themselves with Henry, and Stephen's mother decided to place him in Henry's court.King (2010), p. 13. Henry fought his next military campaign in Normandy, from 1111 onwards, where rebels led by Robert of Bellême were opposing his rule. Stephen was probably with Henry during the military campaign of 1112, when he was knighted by the King. He was present at court during the King's visit to the Abbey of Saint-Evroul The Abbey of Saint-Evroul or Saint-Evroul-sur-Ouche (''Saint-Evroult-sur-Ouche, Saint-Evroul-en-Ouche, Saint-Evroult-en-Ouche, Abbaye de Saint-Evroult, Sanctus Ebrulphus Uticensis '') is a former Benedictine abbey in Normandy, located in the present ...
in 1113. Stephen probably first visited England in either 1113 or 1115, almost certainly as part of Henry's court.
Henry became a powerful patron of Stephen, and probably chose to support him because Stephen was part of his extended family and a regional ally, yet not sufficiently wealthy or powerful in his own right to represent a threat to either the King or his heir, William Adelin.Davis, p. 10. As a third surviving son, even of an influential regional family, Stephen still needed the support of a powerful patron to progress in life. With Henry's support, he rapidly began to accumulate lands and possessions. Following the battle of Tinchebray in 1106, Henry confiscated the County of Mortain
The County of Mortain was a medieval county in France centered on the town of Mortain. A choice landholding, usually either kept within the family of the duke of Normandy (or the king of France) or granted to a noble in return for service and favo ...
from his cousin William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
, and the Honour of Eye, a large lordship previously owned by Robert Malet
Robert Malet (c. 1050 – by 1130) was a Norman- English baron and a close advisor of Henry I.
Early life
Malet was the son of William Malet, and inherited his father's great honour of Eye in 1071. This made him one of the dozen or so gr ...
.Davis, p. 7; King (2010), p. 13. In 1113, Stephen was granted both the title and the honour, although without the lands previously held by William in England. The gift of the Honour of Lancaster also followed after it was confiscated by Henry from Roger the Poitevin.Davis, p. 8. Stephen was also given lands in Alençon
Alençon (, , ; nrf, Alençoun) is a commune in Normandy, France, capital of the Orne department. It is situated west of Paris. Alençon belongs to the intercommunality of Alençon (with 52,000 people).
History
The name of Alençon is fi ...
in southern Normandy by Henry, but the local Normans rebelled, seeking assistance from Fulk IV, Count of Anjou Fulk is an old European personal name, probably deriving from the Germanic '' folk'' ("people" or "chieftain"). It is cognate with the French Foulques, the German Volk, the Italian Fulco and the Swedish Folke, along with other variants such as F ...
. Stephen and his older brother Theobald were comprehensively beaten in the subsequent campaign, which culminated in the Battle of Alençon, and the territories were not recovered.
Finally, the King arranged for Stephen to marry Matilda
Matilda or Mathilda may refer to:
Animals
* Matilda (chicken) (1990–2006), World's Oldest Living Chicken record holder
* Matilda (horse) (1824–1846), British Thoroughbred racehorse
* Matilda, a dog of the professional wrestling tag-team The ...
in 1125, the daughter and only heiress of Eustace III, Count of Boulogne
Count of Boulogne was a historical title in the Kingdom of France. The city of Boulogne-sur-Mer became the centre of the county of Boulogne during the ninth century. Little is known of the early counts, but the first holder of the title is recor ...
, who owned both the important continental port of Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the C ...
and vast estates in the north-west and south-east of England. In 1127, William Clito, a potential claimant to the English throne, seemed likely to become the Count of Flanders
The count of Flanders was the ruler or sub-ruler of the county of Flanders, beginning in the 9th century. Later, the title would be held for a time, by the rulers of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain. During the French Revolution, in 1790, the ...
; Stephen was sent by the King on a mission to prevent this, and in the aftermath of his successful election, William Clito attacked Stephen's lands in neighbouring Boulogne in retaliation. Eventually a truce was declared, and William Clito died the following year.
''White Ship'' and succession
 In 1120, the English political landscape changed dramatically. Three hundred passengers embarked on the '' White Ship'' to travel from Barfleur in Normandy to England, including the heir to the throne, William Adelin, and many other senior nobles. Stephen had intended to sail on the same ship but changed his mind at the last moment and got off to await another vessel, either out of concern for overcrowding on board the ship, or because he was suffering from
In 1120, the English political landscape changed dramatically. Three hundred passengers embarked on the '' White Ship'' to travel from Barfleur in Normandy to England, including the heir to the throne, William Adelin, and many other senior nobles. Stephen had intended to sail on the same ship but changed his mind at the last moment and got off to await another vessel, either out of concern for overcrowding on board the ship, or because he was suffering from diarrhoea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
.Bradbury, p. 2. The ship foundered ''en route'', and all but two of the passengers died, including William Adelin.Bradbury, p. 3.
With Adelin dead, the inheritance to the English throne was thrown into doubt. Rules of succession in western Europe at the time were uncertain; in some parts of France, male primogeniture
Primogeniture ( ) is the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent's entire or main estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relativ ...
, in which the eldest son would inherit a title, was becoming more popular.Barlow, p. 162. It was also traditional for the King of France to crown his successor whilst he himself was still alive, making the intended line of succession relatively clear, but this was not the case in England. In other parts of Europe, including Normandy and England, the tradition was for lands to be divided up, with the eldest son taking patrimonial lands—usually considered to be the most valuable—and younger sons being given smaller, or more recently acquired, partitions or estates. The problem was further complicated by the sequence of unstable Anglo-Norman successions over the previous sixty years—William the Conqueror had gained England by force, William Rufus and Robert Curthose had fought a war between them to establish their inheritance, and Henry had only acquired control of Normandy by force. There had been no peaceful, uncontested successions.
With William Adelin dead, Henry had only one other legitimate child, the future Empress Matilda
Empress Matilda ( 7 February 110210 September 1167), also known as the Empress Maude, was one of the claimants to the English throne during the civil war known as the Anarchy. The daughter of King Henry I of England, she moved to Germany as ...
, but as a woman she was at a substantial political disadvantage. Despite the King taking a second wife, Adeliza of Louvain
Adeliza of Louvain, sometimes known in England as Adelicia of Louvain, also called Adela and Aleidis; (c. 1103 – March/April 1151) was Queen of England from 1121 to 1135, as the second wife of King Henry I. She was the daughter of Godfrey I, ...
, it became increasingly unlikely that he would have another legitimate son, and he instead looked to Matilda as his intended heir. Matilda claimed the title of Holy Roman Empress through her marriage to Emperor Henry V, but her husband died in 1125, and she was remarried in 1128 to Geoffrey Plantagenet, Count of Anjou
Geoffrey V (24 August 1113 – 7 September 1151), called the Handsome, the Fair (french: link=no, le Bel) or Plantagenet, was the count of Anjou, Touraine and Maine by inheritance from 1129, and also Duke of Normandy by conquest from 1144. ...
, whose lands bordered the Duchy of Normandy. Geoffrey was unpopular with the Anglo-Norman elite: as an Angevin ruler, he was a traditional enemy of the Normans.Barlow, p. 161. At the same time, tensions continued to grow as a result of Henry's domestic policies, in particular the high level of revenue he was raising to pay for his various wars. Conflict was curtailed, however, by the power of the King's personality and reputation.
Henry attempted to build up a base of political support for Matilda in both England and Normandy, demanding that his court take oath
Traditionally an oath (from Anglo-Saxon ', also called plight) is either a statement of fact or a promise taken by a sacrality as a sign of verity. A common legal substitute for those who conscientiously object to making sacred oaths is to g ...
s first in 1127, and then again in 1128 and 1131, to recognise Matilda as his immediate successor and recognise her descendants as the rightful rulers after her. Stephen was amongst those who took this oath in 1127. Nonetheless, relations between Henry, Matilda, and Geoffrey became increasingly strained towards the end of the King's life. Matilda and Geoffrey suspected that they lacked genuine support in England, and proposed to Henry in 1135 that the King should hand over the royal castles in Normandy to Matilda whilst he was still alive and insist on the Norman nobility swearing immediate allegiance to her, thereby giving the couple a much more powerful position after Henry's death. Henry angrily declined to do so, probably out of a concern that Geoffrey would try to seize power in Normandy somewhat earlier than intended. A fresh rebellion broke out in southern Normandy, and Geoffrey and Matilda intervened militarily on behalf of the rebels. In the middle of this confrontation, Henry unexpectedly fell ill and died near Lyons-la-Forêt
Lyons-la-Forêt () is a commune of the Eure department, Normandy, in northwest France. Lyons-la-Forêt has distinctive historical geography, and architecture, and contemporary culture, as a consequence of the Forest of Lyons, and its bocage, and ...
.
Succession (1135)
 Stephen was a well established figure in Anglo-Norman society by 1135. He was extremely wealthy, well-mannered and liked by his peers; he was also considered a man capable of firm action.King (2010), p. 301. Chroniclers recorded that despite his wealth and power he was a modest and easy-going leader, happy to sit with his men and servants, casually laughing and eating with them. He was very pious, both in terms of his observance of religious rituals and his personal generosity to the church. Stephen also had a personal Augustinian confessor appointed to him by the Archbishop of Canterbury, who implemented a penitential regime for him, and Stephen encouraged the new order of
Stephen was a well established figure in Anglo-Norman society by 1135. He was extremely wealthy, well-mannered and liked by his peers; he was also considered a man capable of firm action.King (2010), p. 301. Chroniclers recorded that despite his wealth and power he was a modest and easy-going leader, happy to sit with his men and servants, casually laughing and eating with them. He was very pious, both in terms of his observance of religious rituals and his personal generosity to the church. Stephen also had a personal Augustinian confessor appointed to him by the Archbishop of Canterbury, who implemented a penitential regime for him, and Stephen encouraged the new order of Cistercians
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint ...
to form abbeys on his estates, winning him additional allies within the church.
Rumours about his father's cowardice during the First Crusade, however, continued to circulate, and a desire to avoid the same reputation may have influenced some of Stephen's rasher military actions. His wife, Matilda, played a major role in running their vast English estates, which contributed to the couple being the second-richest lay household in the country after the King and Queen. The landless Flemish nobleman William of Ypres
William of Ypres ( nl, Willem van Yper; 1090 – 24 January 116524 January 1164 O.S., 1165 N.S.) was a Flemish nobleman and one of the first mercenary captains of the Middle Ages. Following two unsuccessful bids for the County of Flanders, ...
had joined Stephen's household in 1133.
Stephen's younger brother, Henry of Blois
Henry of Blois ( c. 1096 8 August 1171), often known as Henry of Winchester, was Abbot of Glastonbury Abbey from 1126, and Bishop of Winchester from 1129 to his death. He was a younger son of Stephen Henry, Count of Blois by Adela of Normandy, ...
, had also risen to power under Henry I. Henry of Blois had become a Cluniac
The Cluniac Reforms (also called the Benedictine Reform) were a series of changes within medieval monasticism of the Western Church focused on restoring the traditional monastic life, encouraging art, and caring for the poor. The movement began ...
monk and followed Stephen to England, where the King made him Abbot of Glastonbury __NOTOC__
The Abbot of Glastonbury was the head (or abbot) of Anglo-Saxon and eventually Benedictine house of Glastonbury Abbey at Glastonbury in Somerset, England.
The following is a list of abbots of Glastonbury:
Abbots
See also
* Abbot's K ...
, the richest abbey in England.King (2010), p. 29. The King then appointed him Bishop of Winchester
The Bishop of Winchester is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Winchester in the Church of England. The bishop's seat (''cathedra'') is at Winchester Cathedral in Hampshire. The Bishop of Winchester has always held ''ex officio'' (except ...
, one of the richest bishoprics, allowing him to retain Glastonbury as well. The combined revenues of the two positions made Henry of Winchester the second-richest man in England after the King. Henry of Winchester was keen to reverse what he perceived as encroachment by the Norman kings on the rights of the church. The Norman kings had traditionally exercised a great deal of power and autonomy over the church within their territories. From the 1040s onwards, however, successive popes had put forward a reforming message that emphasised the importance of the church being "governed more coherently and more hierarchically from the centre" and established "its own sphere of authority and jurisdiction, separate from and independent of that of the lay ruler", in the words of historian Richard Huscroft.
 When news began to spread of Henry I's death, many of the potential claimants to the throne were not well placed to respond. Geoffrey and Matilda were in Anjou, rather awkwardly supporting the rebels in their campaign against the royal army, which included a number of Matilda's supporters such as Robert of Gloucester. Many of these barons had taken an oath to stay in Normandy until the late King was properly buried, which prevented them from returning to England. Stephen's elder brother Theobald was further south still, in Blois.Barlow, pp. 163–164. Stephen, however, was in Boulogne, and when news reached him of Henry's death he left for England, accompanied by his military household. Robert of Gloucester had garrisoned the ports of Dover and Canterbury and some accounts suggest that they refused Stephen access when he first arrived. Nonetheless, Stephen probably reached his own estate on the edge of London by 8 December and over the next week he began to seize power in England.
The crowds in London traditionally claimed a right to elect the King, and they proclaimed Stephen the new monarch, believing that he would grant the city new rights and privileges in return. Henry of Blois delivered the support of the church to Stephen: Stephen was able to advance to
When news began to spread of Henry I's death, many of the potential claimants to the throne were not well placed to respond. Geoffrey and Matilda were in Anjou, rather awkwardly supporting the rebels in their campaign against the royal army, which included a number of Matilda's supporters such as Robert of Gloucester. Many of these barons had taken an oath to stay in Normandy until the late King was properly buried, which prevented them from returning to England. Stephen's elder brother Theobald was further south still, in Blois.Barlow, pp. 163–164. Stephen, however, was in Boulogne, and when news reached him of Henry's death he left for England, accompanied by his military household. Robert of Gloucester had garrisoned the ports of Dover and Canterbury and some accounts suggest that they refused Stephen access when he first arrived. Nonetheless, Stephen probably reached his own estate on the edge of London by 8 December and over the next week he began to seize power in England.
The crowds in London traditionally claimed a right to elect the King, and they proclaimed Stephen the new monarch, believing that he would grant the city new rights and privileges in return. Henry of Blois delivered the support of the church to Stephen: Stephen was able to advance to Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
, where Roger, Bishop of Salisbury
Roger of Salisbury (died 1139), was a Normans, Norman medieval bishop of Salisbury and the seventh Lord Chancellor and Lord Keeper of Norman England, England.
Life
Roger was originally priest of a small chapel near Caen in Duchy of Normandy, Norm ...
and Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
, instructed the royal treasury to be handed over to Stephen. On 15 December, Henry delivered an agreement under which Stephen would grant extensive freedoms and liberties to the church, in exchange for the Archbishop of Canterbury and the Papal Legate supporting his succession to the throne. There was the slight problem of the religious oath that Stephen had taken to support the Empress Matilda, but Henry convincingly argued that the late King had been wrong to insist that his court take the oath.Crouch (2002), p. 247.
Furthermore, the late King had only insisted on that oath to protect the stability of the kingdom, and in light of the chaos that might now ensue, Stephen would be justified in ignoring it. Henry was also able to persuade Hugh Bigod, the late King's royal steward, to swear that the King had changed his mind about the succession on his deathbed, nominating Stephen instead. Stephen's coronation was held a week later at Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
on 22 December.
Meanwhile, the Norman nobility gathered at Le Neubourg to discuss declaring Theobald king, probably following the news that Stephen was gathering support in England. The Normans argued that the count, as the more senior grandson of William the Conqueror, had the most valid claim over the kingdom and the duchy, and was certainly preferable to Matilda.
Theobald met with the Norman barons and Robert of Gloucester at Lisieux
Lisieux () is a commune in the Calvados department in the Normandy region in northwestern France. It is the capital of the Pays d'Auge area, which is characterised by valleys and hedged farmland.
Name
The name of the town derives from the ...
on 21 December. Their discussions were interrupted by the sudden news from England that Stephen's coronation was to occur the next day. Theobald then agreed to the Normans' proposal that he be made king, only to find that his former support immediately ebbed away: the barons were not prepared to support the division of England and Normandy by opposing Stephen, who subsequently financially compensated Theobald, who in return remained in Blois and supported his brother's succession.
Early reign (1136–1139)
Initial years (1136–1137)
 Stephen's new Anglo-Norman kingdom had been shaped by the
Stephen's new Anglo-Norman kingdom had been shaped by the Norman conquest of England
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqu ...
in 1066, followed by the Norman expansion into south Wales over the coming years. Both the kingdom and duchy were dominated by a small number of major barons who owned lands on both sides of the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
, with the lesser barons beneath them usually having more localised holdings. The extent to which lands and positions should be passed down through hereditary right or by the gift of the King was still uncertain, and tensions concerning this issue had grown during the reign of Henry I. Certainly lands in Normandy, passed by hereditary right, were usually considered more important to major barons than those in England, where their possession was less certain. Henry had increased the authority and capabilities of the central royal administration, often bringing in "new men
New men is a term referring to various groups of the socially upwardly mobile in England during the House of Lancaster, House of York and Tudor periods. The term may refer to the new aristocracy, or the enriched gentry. It is used by some hi ...
" to fulfil key positions rather than using the established nobility. In the process he had been able to maximise revenues and contain expenditures, resulting in a healthy surplus and a famously large treasury, but also increasing political tensions.
Stephen had to intervene in the north of England immediately after his coronation. David I of Scotland
David I or Dauíd mac Maíl Choluim (Modern: ''Daibhidh I mac haoilChaluim''; – 24 May 1153) was a 12th-century ruler who was Prince of the Cumbrians from 1113 to 1124 and later King of Scotland from 1124 to 1153. The youngest son of Malco ...
invaded the north on the news of Henry's death, taking Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers Eden, Caldew and Petteril. It is the administrative centre of the City ...
, Newcastle and other key strongholds. Northern England was a disputed territory at this time, with the Scottish kings laying a traditional claim to Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic counties of England, historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th c ...
, and David also claiming Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
by virtue of his marriage to the daughter of Waltheof, Earl of Northumbria
Waltheof, Earl of Northumbria ( enm, Wallef, on, Valþjóf) (died 31 May 1076) was the last of the Anglo-Saxon earls and the only English aristocrat to be executed during the reign of William I.
Early life
Waltheof was the second son of Siw ...
.Carpenter, p. 165. Stephen rapidly marched north with an army and met David at Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
* Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in N ...
.King (2010), p. 53. An agreement was made under which David would return most of the territory he had taken, with the exception of Carlisle. In return, Stephen confirmed the English possessions of David's son Henry, including the Earldom of Huntingdon.
Returning south, Stephen held his first royal court at Easter 1136. A wide range of nobles gathered at Westminster for the event, including many of the Anglo-Norman barons and most of the higher officials of the church. Stephen issued a new royal charter, confirming the promises he had made to the church, promising to reverse Henry I's policies on the royal forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the ...
s and to reform any abuses of the royal legal system. He portrayed himself as the natural successor to Henry's policies, and reconfirmed the existing seven earldoms in the kingdom on their existing holders. The Easter court was a lavish event, and a large amount of money was spent on the event itself, clothes and gifts. Stephen gave out grants of land and favours to those present and endowed numerous church foundations with land and privileges. His accession to the throne still needed to be ratified by the Pope, however, and Henry of Blois appears to have been responsible for ensuring that testimonials of support were sent both from Stephen's brother Theobald and from the French king Louis VI, to whom Stephen represented a useful balance to Angevin power in the north of France. Pope Innocent II
Pope Innocent II ( la, Innocentius II; died 24 September 1143), born Gregorio Papareschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 14 February 1130 to his death in 1143. His election as pope was controversial and the fi ...
confirmed Stephen as king by letter later that year, and Stephen's advisers circulated copies widely around England to demonstrate his legitimacy.
Troubles continued across Stephen's kingdom. After the Welsh victory at the battle of Llwchwr
The Battle of Llwchwr (or Battle of Gower) was a battle fought between Welsh and Norman forces between Loughor and Swansea on New Year's Day 1136.
Background
In 1135–1136 an opportunity arose for the Welsh to recover lands lost to the Marc ...
in January 1136 and the successful ambush of Richard Fitz Gilbert de Clare
Richard fitz Gilbert de Clare (died 15 April 1136) 3rd feudal baron of Clare in Suffolk, was an Anglo-Norman nobleman. A marcher lord in Wales, he was also the founder of Tonbridge Priory in Kent.
Life
Richard was the eldest son of Gilbert Fit ...
in April, south Wales rose in rebellion, starting in east Glamorgan
, HQ = Cardiff
, Government = Glamorgan County Council (1889–1974)
, Origin=
, Code = GLA
, CodeName = Chapman code
, Replace =
* West Glamorgan
* Mid Glamorgan
* South Glamorgan
, Mot ...
and rapidly spreading across the rest of south Wales during 1137. Owain Gwynedd
Owain ap Gruffudd ( 23 or 28 November 1170) was King of Gwynedd, North Wales, from 1137 until his death in 1170, succeeding his father Gruffudd ap Cynan. He was called Owain the Great ( cy, Owain Fawr) and the first to be ...
and Gruffydd ap Rhys
Gruffydd ap Rhys (c. 1090 – 1137) was Prince of Deheubarth, in Wales. His sister was the Princess Nest ferch Rhys. He was the father of Rhys ap Gruffydd, known as 'The Lord Rhys', who was one of the most successful rulers of Deheubarth du ...
successfully captured considerable territories, including Carmarthen Castle
Carmarthen Castle ( Welsh: ''Castell Caerfyrddin'') is a ruined castle in Carmarthen, West Wales, UK. First built by Walter, Sheriff of Gloucester in the early 1100s, the castle was captured and destroyed on several occasions before being rebu ...
. Stephen responded by sending Richard's brother Baldwin and the Marcher Lord Robert Fitz Harold of Ewyas into Wales to pacify the region. Neither mission was particularly successful, and by the end of 1137 the King appears to have abandoned attempts to put down the rebellion. Historian David Crouch
Sir David Lance Crouch (23 June 1919 – 18 February 1998) was a British Conservative politician.
Crouch was educated at University College School, London and became a marketing consultant. He contested Leeds West in 1959, and served as Memb ...
suggests that Stephen effectively "bowed out of Wales" around this time to concentrate on his other problems. Meanwhile, he had put down two revolts in the south-west led by Baldwin de Redvers and Robert of Bampton; Baldwin was released after his capture and travelled to Normandy, where he became an increasingly vocal critic of the King.
The security of Normandy was also a concern. Geoffrey of Anjou invaded in early 1136 and, after a temporary truce, invaded later the same year, raiding and burning estates rather than trying to hold the territory.Barlow, p. 168. Events in England meant that Stephen was unable to travel to Normandy himself, so Waleran de Beaumont, appointed by Stephen as the lieutenant of Normandy, and Theobald led the efforts to defend the duchy. Stephen himself only returned to the duchy in 1137, where he met with Louis VI and Theobald to agree to an informal regional alliance, probably brokered by Henry, to counter the growing Angevin power in the region. As part of this deal, Louis recognised Stephen's son Eustace as Duke of Normandy in exchange for Eustace giving fealty to the French King. Stephen was less successful, however, in regaining the Argentan province along the Normandy and Anjou border, which Geoffrey had taken at the end of 1135. Stephen formed an army to retake it, but the frictions between his Flemish mercenary forces led by William of Ypres and the local Norman barons resulted in a battle between the two halves of his army. The Norman forces then deserted Stephen, forcing the King to give up his campaign. He agreed to another truce with Geoffrey, promising to pay him 2,000 marks a year in exchange for peace along the Norman borders.
In the years following his succession, Stephen's relationship with the church became gradually more complex. The royal charter of 1136 had promised to review the ownership of all the lands that had been taken by the crown from the church since 1087, but these estates were now typically owned by nobles. Henry of Blois's claims, in his role as Abbot of Glastonbury, to extensive lands in Devon resulted in considerable local unrest. In 1136, Archbishop of Canterbury William de Corbeil died. Stephen responded by seizing his personal wealth, which caused some discontent amongst the senior clergy. Henry wanted to succeed to the post, but Stephen instead supported Theobald of Bec
Theobald of Bec ( c. 1090 – 18 April 1161) was a Norman archbishop of Canterbury from 1139 to 1161. His exact birth date is unknown. Some time in the late 11th or early 12th century Theobald became a monk at the Abbey of Bec, risi ...
, who was eventually appointed. The papacy named Henry papal legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the pope's legate.
A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title '' legatus'') is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic ...
, possibly as consolation for not receiving Canterbury.
Stephen's first few years as king can be interpreted in different ways. He stabilised the northern border with Scotland, contained Geoffrey's attacks on Normandy, was at peace with Louis VI, enjoyed good relations with the church and had the broad support of his barons. There were significant underlying problems, nonetheless. The north of England was now controlled by David and Prince Henry, Stephen had abandoned Wales, the fighting in Normandy had considerably destabilised the duchy, and an increasing number of barons felt that Stephen had given them neither the lands nor the titles they felt they deserved or were owed. Stephen was also rapidly running out of money: Henry's considerable treasury had been emptied by 1138 due to the costs of running Stephen's more lavish court and the need to raise and maintain his mercenary armies fighting in England and Normandy.Carpenter, p. 169.
Defending the kingdom (1138–1139)
 Stephen was attacked on several fronts during 1138. First, Robert, Earl of Gloucester, rebelled against the King, starting the descent into civil war in England. An illegitimate son of Henry I and the half-brother of the Empress Matilda, Robert was one of the most powerful Anglo-Norman barons, controlling estates in Normandy. He was known for his qualities as a statesman, his military experience, and leadership ability.Barlow, p. 169. Robert had tried to convince Theobald to take the throne in 1135; he did not attend Stephen's first court in 1136 and it took several summonses to convince him to attend court at
Stephen was attacked on several fronts during 1138. First, Robert, Earl of Gloucester, rebelled against the King, starting the descent into civil war in England. An illegitimate son of Henry I and the half-brother of the Empress Matilda, Robert was one of the most powerful Anglo-Norman barons, controlling estates in Normandy. He was known for his qualities as a statesman, his military experience, and leadership ability.Barlow, p. 169. Robert had tried to convince Theobald to take the throne in 1135; he did not attend Stephen's first court in 1136 and it took several summonses to convince him to attend court at Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
later that year. In 1138, Robert renounced his fealty to Stephen and declared his support for Matilda, triggering a major regional rebellion in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
and across the south-west of England, although Robert himself remained in Normandy. In France, Geoffrey of Anjou took advantage of the situation by re-invading Normandy. David of Scotland also invaded the north of England once again, announcing that he was supporting the claim of his niece the Empress Matilda to the throne, pushing south into Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a Historic counties of England, historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other Eng ...
.
Anglo-Norman warfare during the reign of Stephen was characterised by attritional military campaigns, in which commanders tried to seize key enemy castles in order to allow them to take control of their adversaries' territory and ultimately win a slow, strategic victory.Bradbury, p. 71. The armies of the period centred on bodies of mounted, armoured knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of knighthood by a head of state (including the Pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the Christian denomination, church or the country, especially in a military capacity. Knighthood ...
s, supported by infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
and crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an Elasticity (physics), elastic launching device consisting of a Bow and arrow, bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar ...
men. These forces were either feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
levies, drawn up by local nobles for a limited period of service during a campaign, or, increasingly, mercenaries, who were expensive but more flexible and often more skilled. These armies, however, were ill-suited to besieging castles, whether the older motte-and-bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy t ...
designs or the newer, stone-built keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
s. Existing siege engines were significantly less powerful than the later trebuchet
A trebuchet (french: trébuchet) is a type of catapult that uses a long arm to throw a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weight ...
designs, giving defenders a substantial advantage over attackers. As a result, slow sieges to starve defenders out, or mining operations
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic viab ...
to undermine walls, tended to be preferred by commanders over direct assaults. Occasionally pitched battles were fought between armies but these were considered highly risky endeavours and were usually avoided by prudent commanders. The cost of warfare had risen considerably in the first part of the 12th century, and adequate supplies of ready cash were increasingly proving important in the success of campaigns.
 Stephen's personal qualities as a military leader focused on his skill in personal combat, his capabilities in siege warfare and a remarkable ability to move military forces quickly over relatively long distances. In response to the revolts and invasions, he rapidly undertook several military campaigns, focusing primarily on England rather than Normandy. His wife Matilda was sent to Kent with ships and resources from Boulogne, with the task of retaking the key port of
Stephen's personal qualities as a military leader focused on his skill in personal combat, his capabilities in siege warfare and a remarkable ability to move military forces quickly over relatively long distances. In response to the revolts and invasions, he rapidly undertook several military campaigns, focusing primarily on England rather than Normandy. His wife Matilda was sent to Kent with ships and resources from Boulogne, with the task of retaking the key port of Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maids ...
, under Robert's control. A small number of Stephen's household knights were sent north to help the fight against the Scots, where David's forces were defeated later that year at the battle of the Standard
The Battle of the Standard, sometimes called the Battle of Northallerton, took place on 22 August 1138 on Cowton Moor near Northallerton in Yorkshire, England. English forces under William of Aumale repelled a Scottish army led by King Dav ...
in August by the forces of Thurstan, the Archbishop of York
The archbishop of York is a senior bishop in the Church of England, second only to the archbishop of Canterbury. The archbishop is the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of York and the metropolitan bishop of the province of York, which covers ...
.Carpenter, p. 166. Despite this victory, however, David still occupied most of the north. Stephen himself went west in an attempt to regain control of Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of ...
, first striking north into the Welsh Marches
The Welsh Marches ( cy, Y Mers) is an imprecisely defined area along the border between England and Wales in the United Kingdom. The precise meaning of the term has varied at different periods.
The English term Welsh March (in Medieval Latin ...
, taking Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester, England, Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. ...
and Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , also ) is a market town, civil parish, and the county town of Shropshire, England, on the River Severn, north-west of London; at the 2021 census, it had a population of 76,782. The town's name can be pronounced as either 'Sh ...
, before heading south to Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
. The town of Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, city, Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Glouces ...
itself proved too strong for him, and Stephen contented himself with raiding and pillaging the surrounding area. The rebels appear to have expected Robert to intervene with support that year, but he remained in Normandy throughout, trying to persuade the Empress Matilda to invade England herself. Dover finally surrendered to the queen's forces later in the year.Crouch (2002), p. 256.
Stephen's military campaign in England had progressed well, and historian David Crouch describes it as "a military achievement of the first rank". The King took the opportunity of his military advantage to forge a peace agreement with Scotland. Stephen's wife Matilda was sent to negotiate another agreement between Stephen and David, called the treaty of Durham; Northumbria and Cumbria would effectively be granted to David and his son Henry, in exchange for their fealty and future peace along the border. Unfortunately, the powerful Ranulf I, Earl of Chester, considered himself to hold the traditional rights to Carlisle and Cumberland and was extremely displeased to see them being given to the Scots. Nonetheless, Stephen could now focus his attention on the anticipated invasion of England by Robert and Matilda's forces.
Road to civil war (1139)
 Stephen prepared for the Angevin invasion by creating a number of additional
Stephen prepared for the Angevin invasion by creating a number of additional earldoms
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant "chieftain", particul ...
. Only a handful of earldoms had existed under Henry I and these had been largely symbolic in nature. Stephen created many more, filling them with men he considered to be loyal, capable military commanders, and in the more vulnerable parts of the country assigning them new lands and additional executive powers. He appears to have had several objectives in mind, including both ensuring the loyalty of his key supporters by granting them these honours, and improving his defences in key parts of the kingdom. Stephen was heavily influenced by his principal advisor, Waleran de Beaumont, the twin brother of Robert of Leicester. The Beaumont twins and their younger brother and cousins received the majority of these new earldoms. From 1138 onwards, Stephen gave them the earldoms of Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Engla ...
, Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest settlement in the East Midlands.
The city l ...
, Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester, England, Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. ...
, Warwick
Warwick ( ) is a market town, civil parish and the county town of Warwickshire in the Warwick District in England, adjacent to the River Avon, Warwickshire, River Avon. It is south of Coventry, and south-east of Birmingham. It is adjoined wit ...
and Pembroke, which – especially when combined with the possessions of Stephen's new ally, Prince Henry, in Cumberland and Northumbria – created a wide block of territory to act as a buffer zone
A buffer zone is a neutral zonal area that lies between two or more bodies of land, usually pertaining to countries. Depending on the type of buffer zone, it may serve to separate regions or conjoin them.
Common types of buffer zones are demili ...
between the troubled south-west, Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
, and the rest of the kingdom. With their new lands, the power of the Beamounts grew to the point where David Crouch suggests that it became "dangerous to be anything other than a friend of Waleran" at Stephen's court.
Stephen took steps to remove a group of bishops he regarded as a threat to his rule. The royal administration under Henry I had been headed by Roger, the Bishop of Salisbury
The Bishop of Salisbury is the ordinary of the Church of England's Diocese of Salisbury in the Province of Canterbury. The diocese covers much of the counties of Wiltshire and Dorset. The see is in the City of Salisbury where the bishop's seat ...
, supported by Roger's nephews, Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
and Nigel, the Bishops of Lincoln and Ely respectively, and Roger's son, Lord Chancellor
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
Roger le Poer. These bishops were powerful landowners as well as ecclesiastical rulers, and they had begun to build new castles and increase the size of their military forces, leading Stephen to suspect that they were about to defect to the Empress Matilda. Roger and his family were also enemies of Waleran, who disliked their control of the royal administration. In June 1139, Stephen held his court in Oxford, where a fight between Alan of Brittany and Roger's men broke out, an incident probably deliberately created by Stephen.Davis, p. 32. Stephen responded by demanding that Roger and the other bishops surrender all of their castles in England. This threat was backed up by the arrest of the bishops, with the exception of Nigel who had taken refuge in Devizes Castle; the bishop only surrendered after Stephen besieged the castle and threatened to execute Roger le Poer. The remaining castles were then surrendered to the King.
Stephen's brother, Henry of Blois, was alarmed by this, both as a matter of principle, since Stephen had previously agreed in 1135 to respect the freedoms of the church, and more pragmatically because he himself had recently built six castles and had no desire to be treated in the same way.Barlow, p. 173. As the papal legate, he summoned the King to appear before an ecclesiastical council to answer for the arrests and seizure of property. Henry asserted the Church's right to investigate and judge all charges against members of the clergy. Stephen sent Aubrey de Vere II
Aubrey de Vere (''c.'' 1085 – May 1141) — also known as "Alberic sde Ver" and "Albericus ''regis camerarius''" (the king's chamberlain)— was the second of that name in England after the Norman Conquest, being the eldest surviving son of A ...
as his spokesman to the council, who argued that Roger of Salisbury had been arrested not as a bishop, but rather in his role as a baron who had been preparing to change his support to the Empress Matilda. The King was supported by Hugh of Amiens, Archbishop of Rouen
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Rouen (Latin: ''Archidioecesis Rothomagensis''; French: ''Archidiocèse de Rouen'') is an archdiocese of the Latin Rite of the Roman Catholic Church in France. As one of the fifteen Archbishops of France, the Arch ...
, who challenged the bishops to show how canon law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is t ...
entitled them to build or hold castles. Aubrey threatened that Stephen would complain to the pope that he was being harassed by the English church, and the council let the matter rest following an unsuccessful appeal to Rome. The incident successfully removed any military threat from the bishops, but it may have damaged Stephen's relationship with the senior clergy, and in particular with his brother Henry.
Civil war (1139–1154)
Initial phase of the war (1139–1140)
 The Angevin invasion finally arrived in 1139. Baldwin de Redvers crossed over from Normandy to Wareham in August in an initial attempt to capture a port to receive the Empress Matilda's invading army, but Stephen's forces forced him to retreat into the south-west.Davis, p. 39. The following month, however, the Empress was invited by the Dowager Queen Adeliza to land at
The Angevin invasion finally arrived in 1139. Baldwin de Redvers crossed over from Normandy to Wareham in August in an initial attempt to capture a port to receive the Empress Matilda's invading army, but Stephen's forces forced him to retreat into the south-west.Davis, p. 39. The following month, however, the Empress was invited by the Dowager Queen Adeliza to land at Arundel
Arundel ( ) is a market town and civil parish in the Arun District of the South Downs, West Sussex, England.
The much-conserved town has a medieval castle and Roman Catholic cathedral. Arundel has a museum and comes second behind much larg ...
instead, and on 30 September Robert of Gloucester and the Empress arrived in England with 140 knights. The Empress stayed at Arundel Castle
Arundel Castle is a restored and remodelled medieval castle in Arundel, West Sussex, England. It was established during the reign of Edward the Confessor and completed by Roger de Montgomery. The castle was damaged in the English Civil War a ...
, whilst Robert marched north-west to Wallingford and Bristol, hoping to raise support for the rebellion and to link up with Miles of Gloucester
Miles FitzWalter of Gloucester, 1st Earl of Hereford (died 24 December 1143) (''alias'' Miles of GloucesterSanders, I.J. English Baronies: A Study of their Origin and Descent 1086-1327, Oxford, 1960, p.7) was a great magnate based in the west of ...
, a capable military leader who took the opportunity to renounce his fealty to the King. Stephen promptly moved south, besieging Arundel and trapping Matilda inside the castle.Bradbury, p. 78.
Stephen then agreed to a truce proposed by his brother, Henry; the full details of the truce are not known, but the results were that Stephen first released Matilda from the siege and then allowed her and her household of knights to be escorted to the south-west, where they were reunited with Robert of Gloucester. The reasoning behind Stephen's decision to release his rival remains unclear. Contemporary chroniclers suggested that Henry argued that it would be in Stephen's own best interests to release the Empress and concentrate instead on attacking Robert, and Stephen may have seen Robert, not the Empress, as his main opponent at this point in the conflict. He also faced a military dilemma at Arundel—the castle was considered almost impregnable, and he may have been worried that he was tying down his army in the south whilst Robert roamed freely in the west. Another theory is that Stephen released Matilda out of a sense of chivalry
Chivalry, or the chivalric code, is an informal and varying code of conduct developed in Europe between 1170 and 1220. It was associated with the medieval Christian institution of knighthood; knights' and gentlemen's behaviours were governed b ...
; he was certainly known for having a generous, courteous personality and women were not normally expected to be targeted in Anglo-Norman warfare.
Having released the Empress, Stephen focused on pacifying the south-west of England. Although there had been few new defections to the Empress, his enemies now controlled a compact block of territory stretching out from Gloucester and Bristol south-west into Devon and Cornwall, west into the Welsh Marches and east as far as Oxford and Wallingford, threatening London. Stephen started by attacking Wallingford Castle
Wallingford Castle was a major medieval castle situated in Wallingford in the English county of Oxfordshire (historically Berkshire), adjacent to the River Thames. Established in the 11th century as a motte-and-bailey design within an Anglo-Sa ...
, held by the Empress's childhood friend Brien FitzCount, only to find it too well defended. He then left behind some forces to blockade the castle and continued west into Wiltshire to attack Trowbridge Castle
Trowbridge Castle was a castle in Trowbridge, Wiltshire.Firs ...
, taking the castles of South Cerney and Malmesbury
Malmesbury () is a town and civil parish in north Wiltshire, England, which lies approximately west of Swindon, northeast of Bristol, and north of Chippenham. The older part of the town is on a hilltop which is almost surrounded by the upp ...
en route. Meanwhile, Miles of Gloucester marched east, attacking Stephen's rearguard forces at Wallingford and threatening an advance on London. Stephen was forced to give up his western campaign, returning east to stabilise the situation and protect his capital.Davis, p. 43.
East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
and established his base of operations in the Isle of Ely, then surrounded by protective fenland. Stephen responded quickly, taking an army into the fens and using boats lashed together to form a causeway that allowed him to make a surprise attack on the isle.Bradbury, p. 88. Nigel escaped to Gloucester, but his men and castle were captured, and order was temporarily restored in the east. Robert of Gloucester's men retook some of the territory that Stephen had taken in his 1139 campaign. In an effort to negotiate a truce, Henry of Blois held a peace conference at Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, to which Stephen sent his wife. The conference collapsed over the insistence by Henry and the clergy that they should set the terms of any peace deal, which Stephen found unacceptable.
Ranulf of Chester remained upset over Stephen's gift of the north of England to Prince Henry.Davis, p. 50. Ranulf devised a plan for dealing with the problem by ambushing Henry whilst the prince was travelling back from Stephen's court to Scotland after Christmas. Stephen responded to rumours of this plan by escorting Henry himself north, but this gesture proved the final straw for Ranulf. Ranulf had previously claimed that he had the rights to Lincoln Castle
Lincoln Castle is a major medieval castle constructed in Lincoln, England, during the late 11th century by William the Conqueror on the site of a pre-existing Roman fortress. The castle is unusual in that it has two mottes. It is one of only ...
, held by Stephen, and under the guise of a social visit, Ranulf seized the fortification in a surprise attack. Stephen marched north to Lincoln and agreed to a truce with Ranulf, probably to keep him from joining the Empress's faction, under which Ranulf would be allowed to keep the castle.Davis, p. 51. Stephen returned to London but received news that Ranulf, his brother and their family were relaxing in Lincoln Castle with a minimal guard force, a ripe target for a surprise attack of his own. Abandoning the deal he had just made, Stephen gathered his army again and sped north, but not quite fast enough—Ranulf escaped Lincoln and declared his support for the Empress. Stephen was forced to place the castle under siege.
Second phase of the war (1141–1142)
 While Stephen and his army besieged Lincoln Castle at the start of 1141, Robert of Gloucester and Ranulf of Chester advanced on the King's position with a somewhat larger force.Davis, p. 52. When the news reached Stephen, he held a council to decide whether to give battle or to withdraw and gather additional soldiers: Stephen decided to fight, resulting in the Battle of Lincoln on 2 February 1141. The King commanded the centre of his army, with Alan of Brittany on his right and William of Aumale on his left.Bradbury, p. 105. Robert and Ranulf's forces had superiority in cavalry and Stephen dismounted many of his own knights to form a solid infantry block; he joined them himself, fighting on foot in the battle. Stephen was not a gifted public speaker, and delegated the pre-battle speech to
While Stephen and his army besieged Lincoln Castle at the start of 1141, Robert of Gloucester and Ranulf of Chester advanced on the King's position with a somewhat larger force.Davis, p. 52. When the news reached Stephen, he held a council to decide whether to give battle or to withdraw and gather additional soldiers: Stephen decided to fight, resulting in the Battle of Lincoln on 2 February 1141. The King commanded the centre of his army, with Alan of Brittany on his right and William of Aumale on his left.Bradbury, p. 105. Robert and Ranulf's forces had superiority in cavalry and Stephen dismounted many of his own knights to form a solid infantry block; he joined them himself, fighting on foot in the battle. Stephen was not a gifted public speaker, and delegated the pre-battle speech to Baldwin of Clare
Baldwin of Clare ( fl. 1141) was the youngest son of Gilbert Fitz Richard (de Clare), of the elder branch of the line of Gilbert, count of Eu, grandson of Richard the Fearless.
His mother was Adeliza, daughter of the count of Claremont, though ...
, who delivered a rousing declaration. After an initial success in which William's forces destroyed the Angevins' Welsh infantry, the battle went badly for Stephen.Bradbury, p. 108. Robert and Ranulf's cavalry encircled Stephen's centre, and the King found himself surrounded by the enemy army. Many of his supporters, including Waleran de Beaumont and William of Ypres, fled from the field at this point but Stephen fought on, defending himself first with his sword and then, when that broke, with a borrowed battle axe.Bradbury, pp. 108–109. Finally, he was overwhelmed by Robert's men and taken away from the field in custody.
Robert took Stephen back to Gloucester, where the King met with the Empress Matilda, and was then moved to Bristol Castle, traditionally used for holding high-status prisoners.King (2010), p. 154. He was initially left confined in relatively good conditions, but his security was later tightened and he was kept in chains. The Empress now began to take the necessary steps to have herself crowned queen in his place, which would require the agreement of the church and her coronation at Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
. Stephen's brother Henry summoned a council at Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
before Easter in his capacity as papal legate to consider the clergy's view. He had made a private deal with the Empress Matilda that he would deliver the support of the church, if she agreed to give him control over church business in England.King (2010), p. 156. Henry handed over the royal treasury, rather depleted except for Stephen's crown, to the Empress, and excommunicated
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to end or at least regulate the communion of a member of a congregation with other members of the religious institution who are in normal communion with each other. The purpose ...
many of Stephen's supporters who refused to switch sides. Archbishop Theobald of Canterbury was unwilling to declare Matilda queen so rapidly, however, and a delegation of clergy and nobles, headed by Theobald, travelled to see Stephen in Bristol and consult about their moral dilemma: should they abandon their oaths of fealty to the King? Stephen agreed that, given the situation, he was prepared to release his subjects from their oath of fealty to him, and the clergy gathered again in Winchester after Easter to declare the Empress "Lady of England and Normandy" as a precursor to her coronation. When Matilda advanced to London in an effort to stage her coronation in June, though, she faced an uprising by the local citizens in support of Stephen that forced her to flee to Oxford, uncrowned.
Once news of Stephen's capture reached him, Geoffrey of Anjou invaded Normandy again and, in the absence of Waleran of Beaumont, who was still fighting in England, Geoffrey took all the duchy south of the river Seine
)
, mouth_location = Le Havre/ Honfleur
, mouth_coordinates =
, mouth_elevation =
, progression =
, river_system = Seine basin
, basin_size =
, tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle
, tributa ...
and east of the river Risle
The Risle (; less common: ''Rille'') is a long river in Normandy, left tributary of the Seine.
The river begins in the Orne department west of L'Aigle, crosses the western part of the department of Eure flowing from south to north and out i ...
. No help was forthcoming from Stephen's brother Theobald this time either, who appears to have been preoccupied with his own problems with France—the new French king, Louis VII
Louis VII (1120 – 18 September 1180), called the Younger, or the Young (french: link=no, le Jeune), was King of the Franks from 1137 to 1180. He was the son and successor of King Louis VI (hence the epithet "the Young") and married Duchess ...
, had rejected his father's regional alliance, improving relations with Anjou and taking a more bellicose line with Theobald, which would result in war the following year. Geoffrey's success in Normandy and Stephen's weakness in England began to influence the loyalty of many Anglo-Norman barons, who feared losing their lands in England to Robert and the Empress, and their possessions in Normandy to Geoffrey. Many started to leave Stephen's faction. His friend and advisor Waleran was one of those who decided to defect in mid-1141, crossing into Normandy to secure his ancestral possessions by allying himself with the Angevins, and bringing Worcestershire into the Empress's camp. Waleran's twin brother, Robert of Leicester, effectively withdrew from fighting in the conflict at the same time. Other supporters of the Empress were restored in their former strongholds, such as Bishop Nigel of Ely, or received new earldoms in the west of England. The royal control over the minting of coins broke down, leading to coins being struck by local barons and bishops across the country.
Sherborne
Sherborne is a market town and civil parish in north west Dorset, in South West England. It is sited on the River Yeo, on the edge of the Blackmore Vale, east of Yeovil. The parish includes the hamlets of Nether Coombe and Lower Clatcombe. ...
in Dorset, and Faramus of Boulogne ran the royal household. The Queen appears to have generated genuine sympathy and support from Stephen's more loyal followers. Henry's alliance with the Empress proved short-lived, as they soon fell out over political patronage and ecclesiastical policy; the bishop met the Queen at Guildford
Guildford ()
is a town in west Surrey, around southwest of central London. As of the 2011 census, the town has a population of about 77,000 and is the seat of the wider Borough of Guildford, which had around inhabitants in . The name "Guildf ...
and transferred his support to her.Barlow, p. 176.
The King's eventual release resulted from the Angevin defeat at the rout of Winchester. Robert of Gloucester and the Empress besieged Henry in the city of Winchester in July. Queen Matilda and William of Ypres then encircled the Angevin forces with their own army, reinforced with fresh troops from London. In the subsequent battle the Empress's forces were defeated and Robert of Gloucester himself was taken prisoner.Barlow, p. 177. Further negotiations attempted to deliver a general peace agreement but the Queen was unwilling to offer any compromise to the Empress, and Robert refused to accept any offer to encourage him to change sides to Stephen. Instead, in November the two sides simply exchanged Robert and the King, with Stephen releasing Robert on 1 November 1141.Crouch (2002), p. 187 Stephen began re-establishing his authority. Henry held another church council, which this time reaffirmed Stephen's legitimacy to rule, and a fresh coronation of Stephen and Matilda occurred at Christmas 1141.
At the beginning of 1142 Stephen fell ill, and by Easter rumours had begun to circulate that he had died. Possibly this illness was the result of his imprisonment the previous year, but he finally recovered and travelled north to raise new forces and to successfully convince Ranulf of Chester to change sides once again.Barlow, p. 178. Stephen then spent the summer attacking some of the new Angevin castles built the previous year, including Cirencester
Cirencester (, ; see below for more variations) is a market town in Gloucestershire, England, west of London. Cirencester lies on the River Churn, a tributary of the River Thames, and is the largest town in the Cotswolds. It is the home of ...
, Bampton and Wareham.Bradbury, p. 136. In September, he spotted an opportunity to seize the Empress Matilda herself in Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
. Oxford was a secure town, protected by walls and the river Isis
"The Isis" () is an alternative name for the River Thames, used from its source in the Cotswolds until it is joined by the Thame at Dorchester in Oxfordshire. It derives from the ancient name for the Thames, ''Tamesis'', which in the Middle ...
, but Stephen led a sudden attack across the river, leading the charge and swimming part of the way.Bradbury, p. 137. Once on the other side, the King and his men stormed into the town, trapping the Empress in the castle. Oxford Castle
Oxford Castle is a large, partly ruined medieval castle on the western side of central Oxford in Oxfordshire, England. Most of the original moated, wooden motte and bailey castle was replaced in stone in the late 12th or early 13th century and ...
, however, was a powerful fortress and, rather than storming it, Stephen had to settle down for a long siege, albeit secure in the knowledge that Matilda was now surrounded. Just before Christmas, the Empress left the castle unobserved, crossed the icy river on foot and made her escape to Wallingford. The garrison surrendered shortly afterwards, but Stephen had lost an opportunity to capture his principal opponent.
Stalemate (1143–1146)
 The war between the two sides in England reached a stalemate in the mid-1140s, while Geoffrey of Anjou consolidated his hold on power in Normandy. 1143 started precariously for Stephen when he was besieged by Robert of Gloucester at
The war between the two sides in England reached a stalemate in the mid-1140s, while Geoffrey of Anjou consolidated his hold on power in Normandy. 1143 started precariously for Stephen when he was besieged by Robert of Gloucester at Wilton Castle
Wilton Castle is a 12th-century Norman castle located in south-eastern Herefordshire, England on the River Wye adjacent to the town of Ross-on-Wye. The castle is named after the manor associated with it.
This castle in Herefordshire, sti ...
, an assembly point for royal forces in Herefordshire
Herefordshire () is a county in the West Midlands of England, governed by Herefordshire Council. It is bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh counties of Monmouths ...
.Bradbury, p. 139. Stephen attempted to break out and escape, resulting in the battle of Wilton
The Battle of Wilton was a battle of the civil war in England known as The Anarchy. It was fought on 1 July 1143The date is from Gervase of Canterbury (Davis, p.72n; Crouch, p.207), but Gervase only began writing his chronicle around 1188 (Dav ...
. Once again, the Angevin cavalry proved too strong, and for a moment it appeared that Stephen might be captured for a second time. On this occasion, however, William Martel
William Martel (fl. 1130–1153) was a steward of the royal households of King Henry I and King Stephen of England. He was castellan of Sherborne Castle until 1143.
William Martel was of Norman descent. His grandfather and his uncle were sheri ...
, Stephen's steward, made a fierce rear guard effort, allowing Stephen to escape from the battlefield. Stephen valued William's loyalty sufficiently to agree to exchange Sherborne Castle for his safe release—this was one of the few instances where Stephen was prepared to give up a castle to ransom one of his men.
In late 1143, Stephen faced a new threat in the east, when Geoffrey de Mandeville, Earl of Essex
Geoffrey de Mandeville II, 1st Earl of Essex (died September 1144) was a prominent figure during the reign of King Stephen of England. His biographer, the 19th-century historian J. H. Round, called him "the most perfect and typical presentment of ...
, rose up in rebellion against him in East Anglia. The King had disliked the Earl for several years, and provoked the conflict by summoning Geoffrey to court, where the King arrested him. He threatened to execute Geoffrey unless the Earl handed over his various castles, including the Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
, Saffron Walden
Saffron Walden is a market town in the Uttlesford district of Essex, England, north of Bishop's Stortford, south of Cambridge and north of London. It retains a rural appearance and some buildings of the medieval period. The population was 15, ...
and Pleshey, all important fortifications because they were in, or close to, London.Bradbury, p. 143. Geoffrey gave in, but once free he headed north-east into the Fens to the Isle of Ely, from where he began a military campaign against Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
, with the intention of progressing south towards London. With all of his other problems and with Hugh Bigod, 1st Earl of Norfolk, in open revolt in Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
, Stephen lacked the resources to track Geoffrey down in the Fens and made do with building a screen of castles between Ely and London, including Burwell Castle.
For a period, the situation continued to worsen. Ranulf of Chester revolted once again in the summer of 1144, splitting up Stephen's Honour of Lancaster between himself and Prince Henry.Barlow, p. 179. In the west, Robert of Gloucester and his followers continued to raid the surrounding royalist territories, and Wallingford Castle remained a secure Angevin stronghold, too close to London for comfort. Meanwhile, Geoffrey of Anjou finished securing his hold on southern Normandy and in January 1144 he advanced into Rouen
Rouen (, ; or ) is a city on the River Seine in northern France. It is the prefecture of the region of Normandy and the department of Seine-Maritime. Formerly one of the largest and most prosperous cities of medieval Europe, the population ...
, the capital of the duchy, concluding his campaign. Louis VII recognised him as Duke of Normandy shortly after. By this point in the war, Stephen was depending increasingly on his immediate royal household, such as William of Ypres and others, and lacked the support of the major barons who might have been able to provide him with significant additional forces; after the events of 1141, Stephen made little use of his network of earls.
After 1143 the war ground on, but progressing slightly better for Stephen. Miles of Gloucester, one of the most talented Angevin commanders, had died whilst hunting over the previous Christmas, relieving some of the pressure in the west. Geoffrey de Mandeville's rebellion continued until September 1144, when he died during an attack on Burwell.Bradbury, p. 146. The war in the west progressed better in 1145, with the King recapturing Faringdon Castle in Oxfordshire. In the north, Stephen came to a fresh agreement with Ranulf of Chester, but then in 1146 repeated the ruse he had played on Geoffrey de Mandeville in 1143, first inviting Ranulf to court, before arresting him and threatening to execute him unless he handed over a number of castles, including Lincoln and Coventry
Coventry ( or ) is a city in the West Midlands, England. It is on the River Sherbourne. Coventry has been a large settlement for centuries, although it was not founded and given its city status until the Middle Ages. The city is governed b ...
. As with Geoffrey, the moment Ranulf was released he immediately rebelled, but the situation was a stalemate: Stephen had few forces in the north with which to prosecute a fresh campaign, whilst Ranulf lacked the castles to support an attack on Stephen. By this point, however, Stephen's practice of inviting barons to court and arresting them had brought him into some disrepute and increasing distrust.
Final phases of the war (1147–1152)
 England had suffered extensively from the war by 1147, leading later Victorian historians to call the period of conflict "
England had suffered extensively from the war by 1147, leading later Victorian historians to call the period of conflict "the Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin, the only legi ...
". The contemporary ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of A ...
'' recorded how "there was nothing but disturbance and wickedness and robbery". Certainly in many parts of the country, such as Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire ...
, Berkshire, the Thames Valley and East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
, the fighting and raiding had caused serious devastation.Barlow, p. 181. Numerous " adulterine", or unauthorised, castles had been built as bases for local lords—the chronicler Robert of Torigny
Robert of Torigni (also known as Roburtus de Monte) (c. 1110–1186) was a Norman monk, prior, abbot and twelfth century chronicler.
Religious life
Robert was born at Torigni-sur-Vire, Normandy c. 1110 most probably to an aristocratic family but ...
complained that as many as 1,115 such castles had been built during the conflict, although this was probably an exaggeration as elsewhere he suggested an alternative figure of 126. The previously centralised royal coinage system was fragmented, with Stephen, the Empress and local lords all minting their own coins. The royal forest law had collapsed in large parts of the country. Some parts of the country, though, were barely touched by the conflict—for example, Stephen's lands in the south-east and the Angevin heartlands around Gloucester and Bristol were largely unaffected, and David I ruled his territories in the north of England effectively. Stephen's overall income from his estates, however, declined seriously during the conflict, particularly after 1141, and royal control over the minting of new coins remained limited outside of the south-east and East Anglia. With Stephen often based in the south-east, increasingly Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
, rather than the older site of Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
, was used as the centre of royal government.
The character of the conflict in England gradually began to shift; as historian Frank Barlow suggests, by the late 1140s "the civil war was over", barring the occasional outbreak of fighting.Barlow, p. 180. In 1147 Robert of Gloucester died peacefully, and the next year the Empress Matilda left south-west England for Normandy, both of which contributed to reducing the tempo of the war. The Second Crusade
The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Cru ...
was announced, and many Angevin supporters, including Waleran of Beaumont, joined it, leaving the region for several years. Many of the barons were making individual peace agreements with each other to secure their lands and war gains. Geoffrey and Matilda's son, the future King Henry II of England
Henry II (5 March 1133 – 6 July 1189), also known as Henry Curtmantle (french: link=no, Court-manteau), Henry FitzEmpress, or Henry Plantagenet, was King of England from 1154 until his death in 1189, and as such, was the first Angevin kin ...
, mounted a small mercenary invasion of England in 1147 but the expedition failed, not least because Henry lacked the funds to pay his men. Surprisingly, Stephen himself ended up paying their costs, allowing Henry to return home safely; his reasons for doing so are unclear. One potential explanation is his general courtesy to a member of his extended family; another is that he was starting to consider how to end the war peacefully, and saw this as a way of building a relationship with Henry.
The young Henry FitzEmpress returned to England again in 1149, this time planning to form a northern alliance with Ranulf of Chester. The Angevin plan involved Ranulf agreeing to give up his claim to Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers Eden, Caldew and Petteril. It is the administrative centre of the City ...
, held by the Scots, in return for being given the rights to the whole of the Honour of Lancaster; Ranulf would give homage to both David and Henry FitzEmpress, with Henry having seniority. Following this peace agreement, Henry and Ranulf agreed to attack York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
, probably with help from the Scots. Stephen marched rapidly north to York and the planned attack disintegrated, leaving Henry to return to Normandy, where he was declared duke by his father.Davis, p. 107; King (2010), p. 255.
Although still young, Henry was increasingly gaining a reputation as an energetic and capable leader. His prestige and power increased further when he unexpectedly married the attractive Eleanor, Duchess of Aquitaine
Eleanor ( – 1 April 1204; french: Aliénor d'Aquitaine, ) was Queen of France from 1137 to 1152 as the wife of King Louis VII, Queen of England from 1154 to 1189 as the wife of King Henry II, and Duchess of Aquitaine in her own right from ...
, the recently divorced wife of Louis VII, in 1152. The marriage made Henry the future ruler of a huge swathe of territory across France.
In the final years of the war, Stephen began to focus on the issue of his family and the succession. He wanted to confirm his eldest son, Eustace, as his successor, although chroniclers recorded that Eustace was infamous for levying heavy taxes and extorting money from those on his lands. Stephen's second son, William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
, was married to the extremely wealthy heiress Isabel de Warenne
Isabel de Warenne, Countess of Arundel (c. 1228 – 23 November 1282) was an English peer. She was widowed before she was 20 years old, with a large estate, upon which she founded a Cistercian order convent, England's only convent to be Cister ...
. In 1148, Stephen built the Cluniac
The Cluniac Reforms (also called the Benedictine Reform) were a series of changes within medieval monasticism of the Western Church focused on restoring the traditional monastic life, encouraging art, and caring for the poor. The movement began ...
Faversham Abbey
Faversham Abbey was a Cluniac style monastery immediately to the north-east of the town of Faversham, in north Kent, England.
History
It was founded by King Stephen and his wife Matilda of Boulogne in 1148. A party of monks from Bermondsey ...
as a resting place for his family. Both Stephen's wife, Queen Matilda, and his older brother Theobald died in 1152.
Argument with the church (1145–1152)
 Stephen's relationship with the church deteriorated badly towards the end of his reign.Davis, p. 98. The reforming movement within the church, which advocated greater autonomy from royal authority for the clergy, had continued to grow, while new voices such as the Cistercians had gained additional prestige within the monastic orders, eclipsing older orders such as the Cluniacs. Stephen's dispute with the church had its origins in 1140, when Archbishop Thurstan of York died. An argument then broke out between a group of reformers based in York and backed by
Stephen's relationship with the church deteriorated badly towards the end of his reign.Davis, p. 98. The reforming movement within the church, which advocated greater autonomy from royal authority for the clergy, had continued to grow, while new voices such as the Cistercians had gained additional prestige within the monastic orders, eclipsing older orders such as the Cluniacs. Stephen's dispute with the church had its origins in 1140, when Archbishop Thurstan of York died. An argument then broke out between a group of reformers based in York and backed by Bernard of Clairvaux
Bernard of Clairvaux, O. Cist. ( la, Bernardus Claraevallensis; 109020 August 1153), venerated as Saint Bernard, was an abbot, mystic, co-founder of the Knights Templars, and a major leader in the reformation of the Benedictine Order through t ...
, the head of the Cistercian order, who preferred William of Rievaulx as the new archbishop, and Stephen and his brother Henry, who preferred various Blois family relatives. The row between Henry and Bernard grew increasingly personal, and Henry used his authority as legate to appoint his nephew William of York to the post in 1144 only to find that, when Pope Innocent II
Pope Innocent II ( la, Innocentius II; died 24 September 1143), born Gregorio Papareschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 14 February 1130 to his death in 1143. His election as pope was controversial and the fi ...
died in 1145, Bernard was able to get the appointment rejected by Rome. Bernard then convinced Pope Eugene III to overturn Henry's decision altogether in 1147, deposing William, and appointing Henry Murdac as archbishop instead.
Stephen was furious over what he saw as potentially precedent-setting papal interference in his royal authority, and initially refused to allow Murdac into England.Davis, pp. 101, 104. When Theobald, the Archbishop of Canterbury, went to consult with the Pope on the matter against Stephen's wishes, the King refused to allow him back into England either, and seized his estates. Stephen also cut his links to the Cistercian order, and turned instead to the Cluniacs, of which Henry was a member.
Nonetheless, the pressure on Stephen to get Eustace confirmed as his legitimate heir continued to grow. The King gave Eustace the County of Boulogne in 1147, but it remained unclear whether Eustace would inherit England.Davis, p. 105. Stephen's preferred option was to have Eustace crowned while he himself was still alive, as was the custom in France, but this was not the normal practice in England, and Celestine II, during his brief tenure as pope between 1143 and 1144, had banned any change to this practice. Since the only person who could crown Eustace was Archbishop Theobald, who refused to do so without agreement from the current pope, Eugene III, the matter reached an impasse. At the end of 1148, Stephen and Theobald came to a temporary compromise that allowed Theobald to return to England. Theobald was appointed a papal legate in 1151, adding to his authority. Stephen then made a fresh attempt to have Eustace crowned at Easter 1152, gathering his nobles to swear fealty to Eustace, and then insisting that Theobald and his bishops anoint him king.King (2010), p. 264. When Theobald refused yet again, Stephen and Eustace imprisoned both him and the bishops and refused to release them unless they agreed to crown Eustace. Theobald escaped again into temporary exile in Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
, pursued to the coast by Stephen's knights, marking a low point in Stephen's relationship with the church.
Treaties and peace (1153–1154)
Malmesbury
Malmesbury () is a town and civil parish in north Wiltshire, England, which lies approximately west of Swindon, northeast of Bristol, and north of Chippenham. The older part of the town is on a hilltop which is almost surrounded by the upp ...
was besieged by Henry's forces, and the King responded by marching west with an army to relieve it.Bradbury, p. 180. He unsuccessfully attempted to force Henry's smaller army to fight a decisive battle along the river Avon. In the face of the increasingly wintry weather, Stephen agreed to a temporary truce and returned to London, leaving Henry to travel north through the Midlands
The Midlands (also referred to as Central England) are a part of England that broadly correspond to the Kingdom of Mercia of the Early Middle Ages, bordered by Wales, Northern England and Southern England. The Midlands were important in the In ...
where the powerful Robert de Beaumont, Earl of Leicester, announced his support for the Angevin cause. Despite only modest military successes, Henry and his allies now controlled the south-west, the Midlands and much of the north of England.
Over the summer, Stephen intensified the long-running siege of Wallingford Castle
Wallingford Castle was a major medieval castle situated in Wallingford in the English county of Oxfordshire (historically Berkshire), adjacent to the River Thames. Established in the 11th century as a motte-and-bailey design within an Anglo-Sa ...
in a final attempt to take this major Angevin stronghold. The fall of Wallingford appeared imminent and Henry marched south in an attempt to relieve the siege, arriving with a small army and placing Stephen's besieging forces under siege themselves.Bradbury, p. 183. Upon news of this, Stephen gathered up a large force and marched from Oxford, and the two sides confronted each other across the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
at Wallingford in July. By this point in the war, the barons on both sides seem to have been eager to avoid an open battle.Bradbury, p. 183; King (2010), p. 277; Crouch (2002), p. 276. As a result, instead of a battle ensuing, members of the church brokered a truce, to the annoyance of both Stephen and Henry.
In the aftermath of Wallingford, Stephen and Henry spoke together privately about a potential end to the war; Stephen's son Eustace, however, was furious about the peaceful outcome at Wallingford. He left his father and returned home to Cambridge to gather more funds for a fresh campaign, where he fell ill and died the next month. Eustace's death removed an obvious claimant to the throne and was politically convenient for those seeking a permanent peace in England. It is possible, however, that Stephen had already begun to consider passing over Eustace's claim; historian Edmund King observes that Eustace's claim to the throne was not mentioned in the discussions at Wallingford, for example, and this may have added to his anger.
Fighting continued after Wallingford, but in a rather half-hearted fashion. Stephen lost the towns of Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
and Stamford to Henry while the King was diverted fighting Hugh Bigod in the east of England, but Nottingham Castle survived an Angevin attempt to capture it. Meanwhile, Stephen's brother Henry of Blois and Archbishop Theobald of Canterbury were for once unified in an effort to broker a permanent peace between the two sides, putting pressure on Stephen to accept a deal. The armies of Stephen and Henry FitzEmpress met again at Winchester, where the two leaders would ratify the terms of a permanent peace in November. Stephen announced the Treaty of Winchester
The Treaty of Wallingford, also known as the Treaty of Winchester or the Treaty of Westminster, was an agreement reached in England in the summer of 1153. It effectively ended a civil war known as ''the Anarchy'' (1135–54), caused by a dispute ...
in Winchester Cathedral: he recognised Henry FitzEmpress as his adopted son and successor, in return for Henry doing homage
Homage (Old English) or Hommage (French) may refer to:
History
*Homage (feudal) /ˈhɒmɪdʒ/, the medieval oath of allegiance
*Commendation ceremony, medieval homage ceremony Arts
*Homage (arts) /oʊˈmɑʒ/, an allusion or imitation by one arti ...
to him; Stephen promised to listen to Henry's advice, but retained all his royal powers; Stephen's remaining son, William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
, would do homage to Henry and renounce his claim to the throne, in exchange for promises of the security of his lands; key royal castles would be held on Henry's behalf by guarantors, whilst Stephen would have access to Henry's castles; and the numerous foreign mercenaries would be demobilised and sent home. Stephen and Henry sealed the treaty with a kiss of peace
The kiss of peace is an ancient traditional Christian greeting, sometimes also called the "holy kiss", "brother kiss" (among men), or "sister kiss" (among women). Such greetings signify a wish and blessing that peace be with the recipient, and bes ...
in the cathedral.
Death
Stephen's decision to recognise Henry as his heir was, at the time, not necessarily a final solution to the civil war.Bradbury, p. 211; Holt, p. 306. Despite the issuing of new currency and administrative reforms, Stephen might potentially have lived for many more years, whilst Henry's position on the continent was far from secure. Although Stephen's son William was unprepared to challenge Henry for the throne in 1153, the situation could well have shifted in subsequent years—there were widespread rumours during 1154 that William planned to assassinate Henry, for example.Crouch (2002), p. 277. Historian Graham White describes the treaty of Winchester as a "precarious peace", in line with the judgement of most modern historians that the situation in late 1153 was still uncertain and unpredictable. Certainly many problems remained to be resolved, including re-establishing royal authority over the provinces and resolving the complex issue of which barons should control the contested lands and estates after the long civil war. Stephen burst into activity in early 1154, travelling around the kingdom extensively. He began issuing royalwrit
In common law, a writ (Anglo-Saxon ''gewrit'', Latin ''breve'') is a formal written order issued by a body with administrative or judicial jurisdiction; in modern usage, this body is generally a court. Warrants, prerogative writs, subpoenas, a ...
s for the south-west of England once again and travelled to York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
where he held a major court in an attempt to impress upon the northern barons that royal authority was being reasserted. After a busy summer in 1154, however, Stephen travelled to Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maids ...
to meet Thierry, Count of Flanders
Theoderic ( nl, Diederik, french: Thierry, german: Dietrich; – 17 January 1168), commonly known as Thierry of Alsace, was the fifteenth count of Flanders from 1128 to 1168. With a record of four campaigns in the Levant and Africa (including pa ...
; some historians believe that the King was already ill and preparing to settle his family affairs.King (2010), p. 300. Stephen fell ill with a stomach disease and died on 25 October at the local priory, being buried at Faversham Abbey
Faversham Abbey was a Cluniac style monastery immediately to the north-east of the town of Faversham, in north Kent, England.
History
It was founded by King Stephen and his wife Matilda of Boulogne in 1148. A party of monks from Bermondsey ...
with his wife Matilda and son Eustace.
Legacy
Aftermath
After Stephen's death, Henry II succeeded to the throne of England. Henry vigorously re-established royal authority in the aftermath of the civil war, dismantling castles and increasing revenues, although several of these trends had begun under Stephen.White (1998), p. 137; Amt, p. 44. The destruction of castles under Henry was not as dramatic as once thought, and although he restored royal revenues, the economy of England remained broadly unchanged under both rulers. Stephen's son William was confirmed as the Earl of Surrey by Henry, and prospered under the new regime, with the occasional point of tension with Henry. Stephen's daughter Marie I, Countess of Boulogne, also survived her father; she had been placed in a convent by Stephen, but after his death she left and married. Stephen's middle son, Baldwin, and second daughter, Matilda, had died before 1147 and were buried atHoly Trinity Priory, Aldgate
The Holy Trinity Priory, also known as Christchurch Aldgate, was a priory of Austin canons ( Black Canons) founded around 1108 by the English queen Matilda of Scotland near Aldgate in London.Gervase, Abbot of Westminster, Ralph and Americ, by his mistress Damette; Gervase became abbot in 1138, but after his father's death he was removed by Henry in 1157 and died shortly afterwards.
 Much of the modern history of Stephen's reign is based on accounts of
Much of the modern history of Stephen's reign is based on accounts of
Review of King Stephen, (review no. 1038)
', David Crouch, ''Reviews in History''. Retrieved 12 May 2011; Stubbs (1874), cited
Review of King Stephen, (review no. 1038)
', David Crouch, ''Reviews in History''. Retrieved 12 May 2011. Stubbs' analysis, focusing on the disorder of the period, influenced his student John Round to coin the term "the Anarchy" to describe the period, a label that, whilst sometimes critiqued, continues to be used today. The late-Victorian scholar
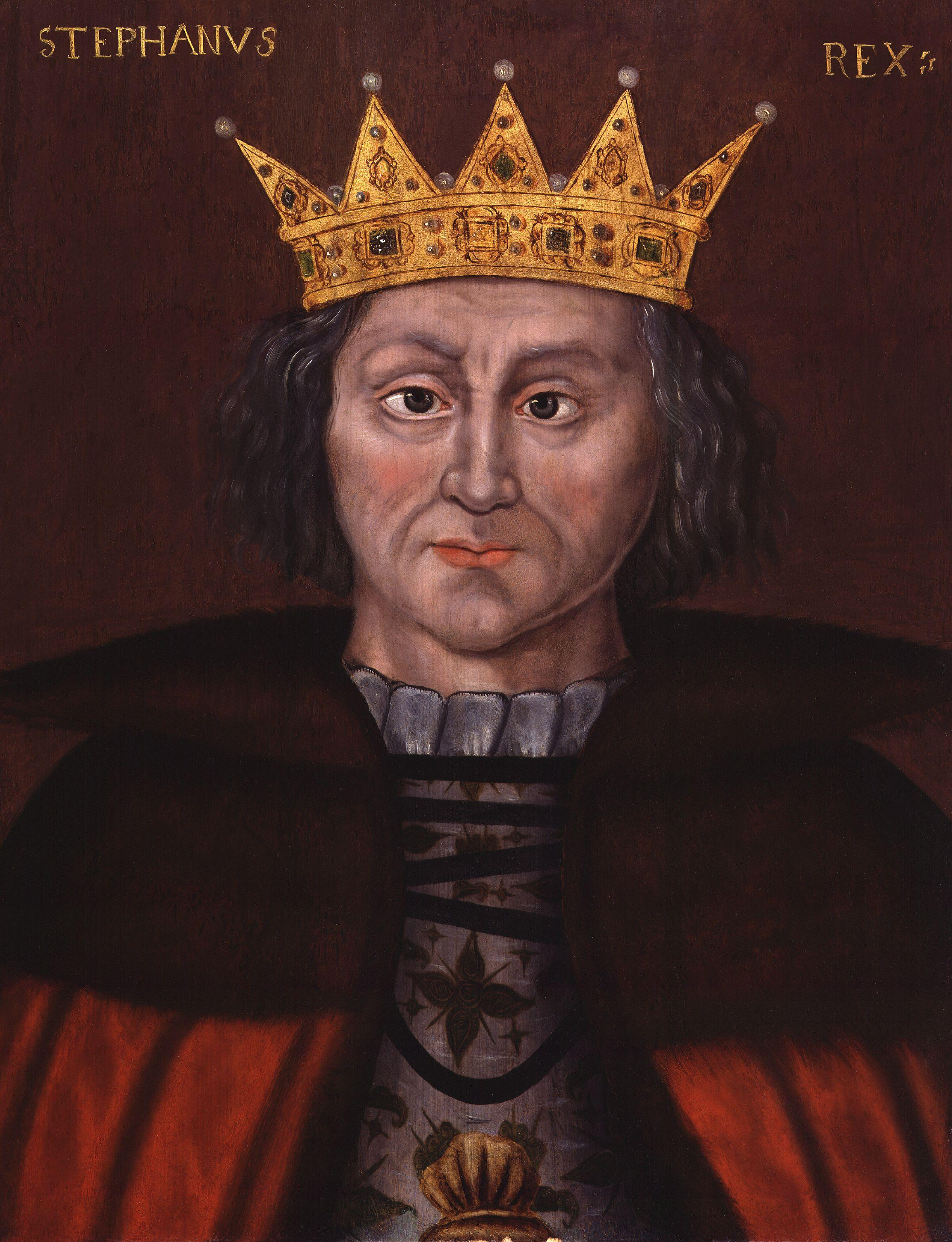 Stephen and his reign have been occasionally used in historical fiction. Stephen and his supporters appear in
Stephen and his reign have been occasionally used in historical fiction. Stephen and his supporters appear in
Blood on Their Hands, and Sex on Their Minds
', Mike Hale, ''The New York Times'', published 22 July 2010. Retrieved 15 May 2011.
The Accession of Henry II in England: Royal Government Restored, 1149–1159.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Barlow, Frank. (1999)
The Feudal Kingdom of England, 1042–1216.
' (5th edition) Harlow, UK: Pearson Education. . * Bennett, Matthew. (2000) "The Impact of 'Foreign' Troops in the Civil Wars of Stephen's Reign," in Dunn, Diana E. S. (ed) (2000)
War and society in medieval and early modern Britain.
' Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. . * Blackburn, Mark. (1998) "Coinage and Currency," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Bradbury, Jim. (2009)
Stephen and Matilda: the Civil War of 1139–53.
' Stroud, UK: The History Press. . * Carpenter, David. (2004)
Struggle for Mastery: The Penguin History of Britain 1066–1284.
' London: Penguin. . * Chibnall, Marjorie. (2008) "Introduction," in Dalton, Paul and Graeme J. White. (eds) (2008)
King Stephen's reign (1135–1154).
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Coulson, Charles. (1994) "The Castles of the Anarchy," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Coss, Peter. (2002) "From Feudalism to Bastard Feudalism," in Fryde, Natalie, Pierre Monnet and Oto Oexle. (eds) (2002) ''Die Gegenwart des Feudalismus.'' Göttingen, Germany: Vandenhoeck and Ruprecht. . * Crouch, David. (1998) "The March and the Welsh Kings," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Crouch, David (2000) ''The Reign of King Stephen, 1135–1154'' Harlow: Longman. * Crouch, David. (2002)
The Normans: The History of a Dynasty.
' London: Hambledon Continuum. . * Crouch, David. (2008a)
The Beaumont Twins: The Roots and Branches of Power in the Twelfth Century.
' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . * Crouch, David. (2008b) "King Stephen and northern France," in Dalton, Paul and Graeme J. White. (eds) (2008)
King Stephen's reign (1135–1154).
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Davis, R. H. C. (1977)
King Stephen.
' (1st edition) London: Longman. . * Duby, Georges. (1993)
France in the Middle Ages 987–1460: From Hugh Capet to Joan of Arc.
' Oxford: Blackwell. . * Dyer, Christopher. (2009)
Making a Living in the Middle Ages: The People of Britain, 850 – 1520
'' London: Yale University Press. . * Fryde, Natalie, Pierre Monnet and Oto Oexle. (eds) (2002) ''Die Gegenwart des Feudalismus.'' Göttingen, Germany: Vandenhoeck and Ruprecht. . * Garnett, George and John Hudsdon. (eds) (1994)
Law and Government in Medieval England and Normandy: Essays in Honour of Sir James Holt.
' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . * Gillingham, John. (1994) "1066 and the Introduction of Chivalry into England," in Garnett, George and John Hudsdon. (eds) (1994)
Law and Government in Medieval England and Normandy: Essays in Honour of Sir James Holt.
' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . * Green, J. A. (1992) "Financing Stephen's War," ''Anglo-Norman Studies'' 14, pp. 91–114. * Helmerichs, Robert. (2001) "'Ad tutandos partriae fines': The Defense of Normandy, 1135," in Abels, Richard Philip and Bernard S. Bachrach. (eds) (2001)
The Normans and Their Adversaries at War.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Holt, J. C. (1998) "1153: The Treaty of Westminster," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Huscroft, Richard. (2005)
Ruling England, 1042–1217.
' Harlow, UK: Pearson. . * Kadish, Alon. (1989)
Historians, Economists, and Economic History.
' London: Routledge. . * King, Edmund. (2006) "The ''Gesta Stephani''," in Bates, David, Julia C. Crick and Sarah Hamilton. (eds) (2006)
Writing Medieval Biography, 750–1250: Essays in Honour of Professor Frank Barlow.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * King, Edmund. (2010)
King Stephen.
' New Haven, US: Yale University Press. . * Koziol, Geoffrey. (1992)
Begging Pardon and Favor: Ritual and Political Order in Early Medieval France.
' New York: Cornell University. . * Mason, Emma. (1996)
Westminster Abbey and its people, c.1050-c.1216.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Pettifer, Adrian. (1995)
English Castles: A Guide by Counties.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Ramet, Carlos. (1999)
Ken Follett: The Transformation of a Writer.
' Bowling Green, US: Bowling Green State University Popular Press. . * Rielly, Edward J. (2000) "Ellis Peters: Brother Cadfael," in Browne, Ray Broadus and Lawrence A. Kreiser. (eds) (2000)
The Detective as Historian: History and Art in Historical Crime.
' Bowling Green, US: Bowling Green State University Press. . * Round, John H. (1888) "Danegeld and the Finance of Domesday," in Dove, P. E. (ed) (1888) ''Domesday Studies.'' London: Longmans, Green, and Co. . * * Stringer, Keith J. (1993)
The Reign of Stephen: Kingship, Warfare and Government in Twelfth-Century England.
' London: Routledge. . * Stubbs, William. (1874) ''The Constitutional History of England, I.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Thompson, Kathleen. (2002)
Power and Border Lordship in Medieval France: The County of the Perche, 1000–1226.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Turner, Richard Charles.
Ken Follett: A Critical Companion.
' Westport, US: Greenwood Press. . *
God's War: a New History of the Crusades.
' London: Penguin. . * Weir, Alison. (1995) ''Britain's Royal Families: The Complete Genealogy, Revised Edition''. London: Random House. . * White, Graeme. (1990) "The End of Stephen's Reign," ''History'', 75(243), pp. 3–22. . . * White, Graeme. (1998) "Continuity in Government," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * White, Graeme. (2000) "Earls and Earldoms during King Stephen's Reign," in Dunn, Diana E. S. (ed) (2000)
War and Society in Medieval and Early Modern Britain.
' Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. . * White, Graeme. (2008) "Royal Income and Regional Trends," in Dalton, Paul and Graeme J. White. (eds) (2008)
King Stephen's reign (1135–1154).
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Yoshitake, Kenji. (1988) "The Arrest of the Bishops in 1139 and its Consequences," ''Journal of Medieval History'', 14(2), pp. 97–114.
"King Stephen and the Bishops"
''Anglo-Norman Studies'', 24, pp. 129–145. * Watkins, Carl. (2019) ''Stephen: The Reign of Anarchy''. Penguin. * Weiler, Bjorn. (2001) "Kingship, usurpation and propaganda in twelfth century Europe: the case of Stephen", ''Anglo-Norman Studies'', 23, pp. 299–326. {{DEFAULTSORT:Stephen, King Of England 1090s births 1154 deaths 12th-century English monarchs 12th-century Dukes of Normandy House of Blois Jure uxoris officeholders People of The Anarchy Christians of the Second Crusade Anglo-Normans English people of French descent 11th-century French people 12th-century French people English Roman Catholics French Roman Catholics Deaths from digestive disease Monarchs taken prisoner in wartime Burials at Faversham Abbey Norman warriors
Historiography
 Much of the modern history of Stephen's reign is based on accounts of
Much of the modern history of Stephen's reign is based on accounts of chronicle
A chronicle ( la, chronica, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and ...
rs who lived in, or close to, the middle of the 12th century, forming a relatively rich account of the period. All of the main chronicler accounts carry significant regional biases in how they portray the disparate events. Several of the key chronicles were written in the south-west of England, including the ''Gesta Stephani
__NOTOC__
''Deeds of King Stephen'' or ''Acts of Stephen'' or ''Gesta Regis Stephani'' is a mid-12th-century English history by an anonymous author about King Stephen of England and his struggles with his cousin, Empress Matilda, also known as the ...
'', or "Acts of Stephen", and William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury ( la, Willelmus Malmesbiriensis; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as " ...
's ''Historia Novella'', or "New History".Davis, p. 146. In Normandy, Orderic Vitalis
Orderic Vitalis ( la, Ordericus Vitalis; 16 February 1075 – ) was an English chronicler and Benedictine monk who wrote one of the great contemporary chronicles of 11th- and 12th-century Normandy and Anglo-Norman England. Modern historia ...
wrote his ''Ecclesiastical History'', covering Stephen's reign until 1141, and Robert of Torigni wrote a later history of the rest of the period. Henry of Huntingdon, who lived in the east of England, produced the ''Historia Anglorum'' that provides a regional account of the reign. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of A ...
'' was past its prime by the time of Stephen but is remembered for its striking account of conditions during "the Anarchy". Most of the chronicles carry some bias for or against Stephen, Robert of Gloucester or other key figures in the conflict. Those writing for the church after the events of Stephen's later reign, such as John of Salisbury
John of Salisbury (late 1110s – 25 October 1180), who described himself as Johannes Parvus ("John the Little"), was an English author, philosopher, educationalist, diplomat and bishop of Chartres.
Early life and education
Born at Salisbury, E ...
for example, paint the King as a tyrant due to his argument with the Archbishop of Canterbury; by contrast, clerics in Durham regarded Stephen as a saviour, due to his contribution to the defeat of the Scots at the battle of the Standard
The Battle of the Standard, sometimes called the Battle of Northallerton, took place on 22 August 1138 on Cowton Moor near Northallerton in Yorkshire, England. English forces under William of Aumale repelled a Scottish army led by King Dav ...
. Later chronicles written during the reign of Henry II were generally more negative: Walter Map
Walter Map ( la, Gualterius Mappus; 1130 – 1210) was a medieval writer. He wrote '' De nugis curialium'', which takes the form of a series of anecdotes of people and places, offering insights on the history of his time.
Map was a court ...
, for example, described Stephen as "a fine knight, but in other respects almost a fool". A number of charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the re ...
s were issued during Stephen's reign, often giving details of current events or daily routine, and these have become widely used as sources by modern historians.
Historians in the "Whiggish
Whig history (or Whig historiography) is an approach to historiography that presents history as a journey from an oppressive and benighted past to a "glorious present". The present described is generally one with modern forms of liberal democrac ...
" tradition that emerged during the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwa ...
traced a progressive and universalist course of political and economic development in England over the medieval period.Dyer, p. 4; Coss, p. 81. William Stubbs focused on these constitutional aspects of Stephen's reign in his 1874 volume the ''Constitutional History of England'', beginning an enduring interest in Stephen and his reign.Review of King Stephen, (review no. 1038)
', David Crouch, ''Reviews in History''. Retrieved 12 May 2011; Stubbs (1874), cited
Review of King Stephen, (review no. 1038)
', David Crouch, ''Reviews in History''. Retrieved 12 May 2011. Stubbs' analysis, focusing on the disorder of the period, influenced his student John Round to coin the term "the Anarchy" to describe the period, a label that, whilst sometimes critiqued, continues to be used today. The late-Victorian scholar
Frederic William Maitland
Frederic William Maitland (28 May 1850 – ) was an English historian and lawyer who is regarded as the modern father of English legal history.
Early life and education, 1850–72
Frederic William Maitland was born at 53 Guilford Street, L ...
also introduced the possibility that Stephen's reign marked a turning point in English legal history—the so-called "tenurial crisis".
Stephen remains a popular subject for historical study: David Crouch suggests that after King John he is "arguably the most written-about medieval king of England". Modern historians vary in their assessments of Stephen as a king. Historian R. H. C. Davis's influential biography paints a picture of a weak king: a capable military leader in the field, full of activity and pleasant, but "beneath the surface ... mistrustful and sly", with poor strategic judgement that ultimately undermined his reign. Stephen's lack of sound policy judgement and his mishandling of international affairs, leading to the loss of Normandy and his consequent inability to win the civil war in England, is also highlighted by another of his biographers, David Crouch. Historian and biographer Edmund King, whilst painting a slightly more positive picture than Davis, also concludes that Stephen, while a stoic, pious and genial leader, was also rarely, if ever, his own man, usually relying upon stronger characters such as his brother or wife. Historian Keith Stringer provides a more positive portrayal of Stephen, arguing that his ultimate failure as king was the result of external pressures on the Norman state, rather than the result of personal failings.
Popular representations
 Stephen and his reign have been occasionally used in historical fiction. Stephen and his supporters appear in
Stephen and his reign have been occasionally used in historical fiction. Stephen and his supporters appear in Ellis Peters
Edith Mary Pargeter (28 September 1913 – 14 October 1995), also known by her '' nom de plume'' Ellis Peters, was an English author of works in many categories, especially history and historical fiction, and was also honoured for her trans ...
' historical detective series '' The Cadfael Chronicles'', set between 1137 and 1145.Rielly, p. 62. Peters' depiction of Stephen's reign is an essentially local narrative, focused on the town of Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , also ) is a market town, civil parish, and the county town of Shropshire, England, on the River Severn, north-west of London; at the 2021 census, it had a population of 76,782. The town's name can be pronounced as either 'Sh ...
and its environs. Peters paints Stephen as a tolerant man and a reasonable ruler, despite his execution of the Shrewsbury defenders after the taking of the city in 1138. In contrast, he is depicted unsympathetically in both Ken Follett
Kenneth Martin Follett, (born 5 June 1949) is a British author of thrillers and historical novels who has sold more than 160 million copies of his works.
Many of his books have achieved high ranking on best seller lists. For example, in the ...
's historical novel ''The Pillars of the Earth
''The Pillars of the Earth'' is a historical novel by British author Ken Follett published in 1989 about the building of a cathedral in the fictional town of Kingsbridge, England. Set in the 12th century, the novel covers the time between the ...
'' and the TV mini-series
A miniseries or mini-series is a television series that tells a story in a predetermined, limited number of episodes. " Limited series" is another more recent US term which is sometimes used interchangeably. , the popularity of miniseries format ...
adapted from it.Turner, p. 122; Ramet, p. 108; Blood on Their Hands, and Sex on Their Minds
', Mike Hale, ''The New York Times'', published 22 July 2010. Retrieved 15 May 2011.
Issue
Stephen of Blois married Matilda of Boulogne in 1125. They had five children:Weir, pp. 50–54. * Baldwin (died in or before 1135) * Matilda (died before 1141), married in infancy toWaleran de Beaumont, Count of Meulan Waleran, Galeran, or Walram is a Germanic first name, common in the Middle Ages, that may refer to:
People
*Waleran I of Limburg (died 1082)
* Waleran the Hunter (fl. 1086)
* Walram (bishop of Naumburg) (r. 1091–1111)
*Waleran of Le Puiset (died ...
* Eustace IV, Count of Boulogne
Eustace IV (c. 1129/1131 17 August 1153) ruled the County of Boulogne from 1146 until his death. He was the eldest son of King Stephen of England and Countess Matilda I of Boulogne. When his father seized the English throne on Henry I's death i ...
(c. 1130 – 1153), ruled Boulogne 1146–1153
* William I, Count of Boulogne (c. 1135 – 1159), ruled Boulogne 1153–1159
* Marie I, Countess of Boulogne (c. 1136 – 1182), ruled Boulogne 1159–1182
King Stephen's illegitimate children by his mistress Damette included:
* Gervase, Abbot of Westminster
* Ralph
* Amalric
Genealogical chart
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Amt, Emilie. (1993)The Accession of Henry II in England: Royal Government Restored, 1149–1159.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Barlow, Frank. (1999)
The Feudal Kingdom of England, 1042–1216.
' (5th edition) Harlow, UK: Pearson Education. . * Bennett, Matthew. (2000) "The Impact of 'Foreign' Troops in the Civil Wars of Stephen's Reign," in Dunn, Diana E. S. (ed) (2000)
War and society in medieval and early modern Britain.
' Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. . * Blackburn, Mark. (1998) "Coinage and Currency," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Bradbury, Jim. (2009)
Stephen and Matilda: the Civil War of 1139–53.
' Stroud, UK: The History Press. . * Carpenter, David. (2004)
Struggle for Mastery: The Penguin History of Britain 1066–1284.
' London: Penguin. . * Chibnall, Marjorie. (2008) "Introduction," in Dalton, Paul and Graeme J. White. (eds) (2008)
King Stephen's reign (1135–1154).
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Coulson, Charles. (1994) "The Castles of the Anarchy," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Coss, Peter. (2002) "From Feudalism to Bastard Feudalism," in Fryde, Natalie, Pierre Monnet and Oto Oexle. (eds) (2002) ''Die Gegenwart des Feudalismus.'' Göttingen, Germany: Vandenhoeck and Ruprecht. . * Crouch, David. (1998) "The March and the Welsh Kings," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Crouch, David (2000) ''The Reign of King Stephen, 1135–1154'' Harlow: Longman. * Crouch, David. (2002)
The Normans: The History of a Dynasty.
' London: Hambledon Continuum. . * Crouch, David. (2008a)
The Beaumont Twins: The Roots and Branches of Power in the Twelfth Century.
' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . * Crouch, David. (2008b) "King Stephen and northern France," in Dalton, Paul and Graeme J. White. (eds) (2008)
King Stephen's reign (1135–1154).
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Davis, R. H. C. (1977)
King Stephen.
' (1st edition) London: Longman. . * Duby, Georges. (1993)
France in the Middle Ages 987–1460: From Hugh Capet to Joan of Arc.
' Oxford: Blackwell. . * Dyer, Christopher. (2009)
Making a Living in the Middle Ages: The People of Britain, 850 – 1520
'' London: Yale University Press. . * Fryde, Natalie, Pierre Monnet and Oto Oexle. (eds) (2002) ''Die Gegenwart des Feudalismus.'' Göttingen, Germany: Vandenhoeck and Ruprecht. . * Garnett, George and John Hudsdon. (eds) (1994)
Law and Government in Medieval England and Normandy: Essays in Honour of Sir James Holt.
' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . * Gillingham, John. (1994) "1066 and the Introduction of Chivalry into England," in Garnett, George and John Hudsdon. (eds) (1994)
Law and Government in Medieval England and Normandy: Essays in Honour of Sir James Holt.
' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . * Green, J. A. (1992) "Financing Stephen's War," ''Anglo-Norman Studies'' 14, pp. 91–114. * Helmerichs, Robert. (2001) "'Ad tutandos partriae fines': The Defense of Normandy, 1135," in Abels, Richard Philip and Bernard S. Bachrach. (eds) (2001)
The Normans and Their Adversaries at War.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Holt, J. C. (1998) "1153: The Treaty of Westminster," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Huscroft, Richard. (2005)
Ruling England, 1042–1217.
' Harlow, UK: Pearson. . * Kadish, Alon. (1989)
Historians, Economists, and Economic History.
' London: Routledge. . * King, Edmund. (2006) "The ''Gesta Stephani''," in Bates, David, Julia C. Crick and Sarah Hamilton. (eds) (2006)
Writing Medieval Biography, 750–1250: Essays in Honour of Professor Frank Barlow.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * King, Edmund. (2010)
King Stephen.
' New Haven, US: Yale University Press. . * Koziol, Geoffrey. (1992)
Begging Pardon and Favor: Ritual and Political Order in Early Medieval France.
' New York: Cornell University. . * Mason, Emma. (1996)
Westminster Abbey and its people, c.1050-c.1216.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Pettifer, Adrian. (1995)
English Castles: A Guide by Counties.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Ramet, Carlos. (1999)
Ken Follett: The Transformation of a Writer.
' Bowling Green, US: Bowling Green State University Popular Press. . * Rielly, Edward J. (2000) "Ellis Peters: Brother Cadfael," in Browne, Ray Broadus and Lawrence A. Kreiser. (eds) (2000)
The Detective as Historian: History and Art in Historical Crime.
' Bowling Green, US: Bowling Green State University Press. . * Round, John H. (1888) "Danegeld and the Finance of Domesday," in Dove, P. E. (ed) (1888) ''Domesday Studies.'' London: Longmans, Green, and Co. . * * Stringer, Keith J. (1993)
The Reign of Stephen: Kingship, Warfare and Government in Twelfth-Century England.
' London: Routledge. . * Stubbs, William. (1874) ''The Constitutional History of England, I.'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * Thompson, Kathleen. (2002)
Power and Border Lordship in Medieval France: The County of the Perche, 1000–1226.
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Turner, Richard Charles.
Ken Follett: A Critical Companion.
' Westport, US: Greenwood Press. . *
Tyerman, Christopher
Christopher Tyerman (born 22 May 1953) is an academic historian focusing on the Crusades. In 2015, he was appointed Professor of History of the Crusades at the University of Oxford.
Life and career
He graduated from New College, Oxford, with a f ...
. (2007) God's War: a New History of the Crusades.
' London: Penguin. . * Weir, Alison. (1995) ''Britain's Royal Families: The Complete Genealogy, Revised Edition''. London: Random House. . * White, Graeme. (1990) "The End of Stephen's Reign," ''History'', 75(243), pp. 3–22. . . * White, Graeme. (1998) "Continuity in Government," in King, Edmund. (ed) (1998)
The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign.
' Oxford: Clarendon Press. . * White, Graeme. (2000) "Earls and Earldoms during King Stephen's Reign," in Dunn, Diana E. S. (ed) (2000)
War and Society in Medieval and Early Modern Britain.
' Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. . * White, Graeme. (2008) "Royal Income and Regional Trends," in Dalton, Paul and Graeme J. White. (eds) (2008)
King Stephen's reign (1135–1154).
' Woodbridge, UK: Boydell Press. . * Yoshitake, Kenji. (1988) "The Arrest of the Bishops in 1139 and its Consequences," ''Journal of Medieval History'', 14(2), pp. 97–114.
Further reading
* Davies, R. H. C. (1964) "What happened in Stephen's reign 1135–54?", ''History'', 49(165), pp. 1–12. . . * King, Edmund. (1974) "King Stephen and the Anglo-Norman Aristocracy", ''History'', 59(196), pp. 180–194. . . * King, Edmund. (1984) "The Anarchy of King Stephen's Reign", ''Transactions of the Royal Historical Society'', 5th series, 34, pp. 133–153. . . * King, Edmund. (2000) "Stephen of Blois, count of Mortain and Boulogne", ''English Historical Review'', 115(461), pp. 271–296. . * Le Patourel, John (1973) "What did not happen in Stephen's reign?", ''History'', 58(192), pp. 1–17. . . * Marritt, Stephen. (2002"King Stephen and the Bishops"
''Anglo-Norman Studies'', 24, pp. 129–145. * Watkins, Carl. (2019) ''Stephen: The Reign of Anarchy''. Penguin. * Weiler, Bjorn. (2001) "Kingship, usurpation and propaganda in twelfth century Europe: the case of Stephen", ''Anglo-Norman Studies'', 23, pp. 299–326. {{DEFAULTSORT:Stephen, King Of England 1090s births 1154 deaths 12th-century English monarchs 12th-century Dukes of Normandy House of Blois Jure uxoris officeholders People of The Anarchy Christians of the Second Crusade Anglo-Normans English people of French descent 11th-century French people 12th-century French people English Roman Catholics French Roman Catholics Deaths from digestive disease Monarchs taken prisoner in wartime Burials at Faversham Abbey Norman warriors