Starlink on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation operated by
 Starlink was publicly announced in January 2015 with the opening of the SpaceX satellite development facility in
Starlink was publicly announced in January 2015 with the opening of the SpaceX satellite development facility in  In March 2018, the FCC granted SpaceX approval for the initial 4,425 satellites, with some conditions. SpaceX would need to obtain a separate approval from the
In March 2018, the FCC granted SpaceX approval for the initial 4,425 satellites, with some conditions. SpaceX would need to obtain a separate approval from the
 In February 2021, SpaceX opened up pre-orders to the public. SpaceX completed raising an additional $3.5 billion in equity financing over the previous six months, to support the capital-intensive phase of the operational fielding of Starlink, plus the development of the Starship launch system. In April 2021, SpaceX clarified that they have already tested two generations of Starlink technology, with the second one having been less expensive than the first. The third generation, with laser inter-satellite links, is expected to begin launching "in the next few months nd will bemuch less expensive than earlier versions".
, SpaceX has over 3000 Starlink satellites in orbit, and announced having over one million active subscribers. They continue to launch up to 53 more satellites per Falcon 9 flight.
On 6 November 2020, Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada announced regulatory approval for the Starlink low Earth orbit satellite constellation.
The FCC initially awarded SpaceX with $885.5 million worth of federal subsidies to support rural broadband customers through the company's Starlink satellite Internet network. SpaceX won subsidies to bring service to customers in 35 U.S. states. The $885.5 million aid package was revoked in August 2022, with the FCC stating that Starlink "failed to demonstrate" its ability to deliver the promised service. SpaceX later appealed the decision saying they met or surpassed all RDOF deployment requirements that existed during bidding and that the FCC created "new standards that no bidder could meet today".
In March 2021, SpaceX put an application into FCC for mobile variations of their terminal for vehicles, vessels and aircraft.
In May 2021, SpaceX announced agreements with
In February 2021, SpaceX opened up pre-orders to the public. SpaceX completed raising an additional $3.5 billion in equity financing over the previous six months, to support the capital-intensive phase of the operational fielding of Starlink, plus the development of the Starship launch system. In April 2021, SpaceX clarified that they have already tested two generations of Starlink technology, with the second one having been less expensive than the first. The third generation, with laser inter-satellite links, is expected to begin launching "in the next few months nd will bemuch less expensive than earlier versions".
, SpaceX has over 3000 Starlink satellites in orbit, and announced having over one million active subscribers. They continue to launch up to 53 more satellites per Falcon 9 flight.
On 6 November 2020, Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada announced regulatory approval for the Starlink low Earth orbit satellite constellation.
The FCC initially awarded SpaceX with $885.5 million worth of federal subsidies to support rural broadband customers through the company's Starlink satellite Internet network. SpaceX won subsidies to bring service to customers in 35 U.S. states. The $885.5 million aid package was revoked in August 2022, with the FCC stating that Starlink "failed to demonstrate" its ability to deliver the promised service. SpaceX later appealed the decision saying they met or surpassed all RDOF deployment requirements that existed during bidding and that the FCC created "new standards that no bidder could meet today".
In March 2021, SpaceX put an application into FCC for mobile variations of their terminal for vehicles, vessels and aircraft.
In May 2021, SpaceX announced agreements with

 On 26 February 2022, Elon Musk announced that the Starlink satellites had become active over
On 26 February 2022, Elon Musk announced that the Starlink satellites had become active over
 In order to offer satellite services in any nation-state,
In order to offer satellite services in any nation-state,
 The system does not directly connect from its satellites to handsets (like the constellations from
The system does not directly connect from its satellites to handsets (like the constellations from
FCC documents website, PDF, 19 August 2022. Starlink v2.0 is both larger and heavier than Starlink v1 satellites: * Lasers for inter-satellite communication * Mass: ∼ * Length: ∼ (Starship form factor)
TBD, <7m (Falcon 9 form factor) * Further improvements to reduce its brightness, including the use of a
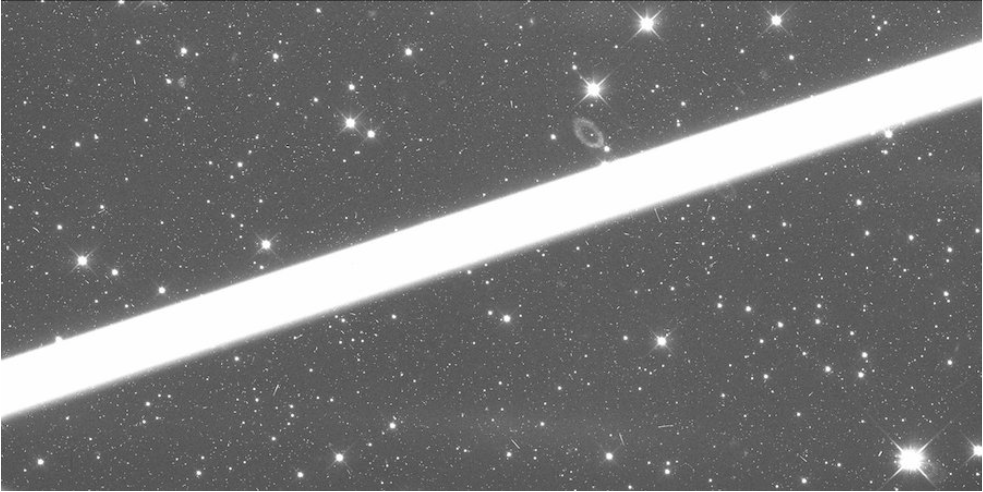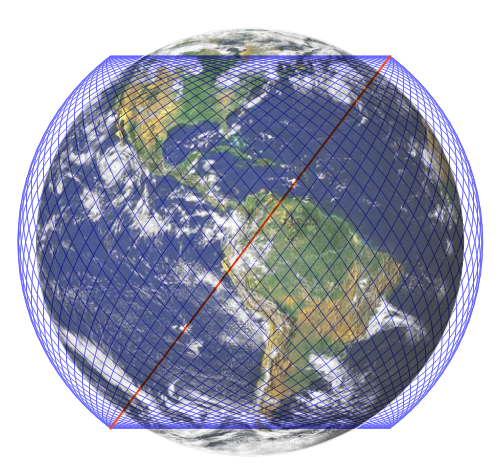


 The planned large number of satellites has been met with criticism from the astronomical community because of concerns over
The planned large number of satellites has been met with criticism from the astronomical community because of concerns over
Official Starlink Availability Map
Starlink Satellite and Groundstation Locations, Data Links, path projection, environmental Information etc. (starlink.sx)
Starlink Coverage Area, Satellite and Groundstation Locations for Starlink, OneWeb and GPS constellations (satellitemap.space)
Complete Starlink Satellite Catalog allowing tracking location details from user location.
Starlink Satellite Locations and Information on individual coverage area, connections, etc.
See A Satellite Tonight
shows when Starlink satellites can be seen.
Shows real-time Starlink satellites position
Starlink Professional Installers Directory
List of Starlink dish firmware updates
''A User Friendly Real-Time SpaceX Satellite Locator''
{{Portal bar, Spaceflight Articles containing video clips Communications satellite constellations Communications satellites in low Earth orbit Communications satellites of the United States Communications satellite operators High throughput satellites Internet service providers Internet service providers of the United States Satellite Internet access SpaceX satellites Spacecraft launched in 2019 Spacecraft launched in 2020 Spacecraft launched in 2021 Spacecraft launched in 2022 Space hazards
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal o ...
, providing satellite Internet access
Satellite Internet access is Internet access provided through communication satellites. Modern consumer grade satellite Internet service is typically provided to individual users through geostationary satellites that can offer relatively high d ...
coverage to 45 countries. It also aims for global mobile phone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link whi ...
service after 2023. SpaceX started launching Starlink satellites in 2019. As of December 2022, Starlink consists of over 3,300 mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
(LEO), which communicate with designated ground transceivers. In total, nearly 12,000 satellites are planned to be deployed, with a possible later extension to 42,000. SpaceX announced reaching more than one million subscribers in December 2022.
The SpaceX satellite development facility in Redmond, Washington
Redmond is a city in King County, Washington, United States, located east of Seattle. The population was 73,256 at the 2020 census, up from 54,144 in 2010.
Redmond is best known as the home of Microsoft and Nintendo of America.
With an ann ...
houses the Starlink research, development, manufacturing, and orbit control teams. The cost of the decade-long project to design, build, and deploy the constellation was estimated by SpaceX in May 2018 to be at least US$10 billion.
SpaceX expects more than $30 billion in revenue by 2025 from its satellite constellation, while revenues from its launch business were expected to reach $5 billion in the same year.
Astronomers have raised concerns about the effect the constellation can have on ground-based astronomy and how the satellites will add to an already congested orbital environment. SpaceX has attempted to mitigate astronomy concerns by implementing several upgrades to Starlink satellites aimed at reducing their brightness during operation. The satellites are equipped with krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is of ...
-fueled Hall thrusters which allow them to de-orbit at the end of their life. Additionally, the satellites are designed to autonomously avoid collisions based on uplinked tracking data.
History
Background
Constellations oflow Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
satellites were first conceptualized in the mid-1980s as part of the Strategic Defense Initiative
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons ( intercontinental ballist ...
, where weapons were to be staged in orbit to intercept ballistic missiles on short notice. The potential for low-latency communication was also recognized and development offshoots in the 1990s led to numerous commercial megaconstellations using around 100 satellites such as Celestron, Teledesic, Iridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density o ...
, and Globalstar. However all entities entered bankruptcy by the dot-com bubble
The dot-com bubble (dot-com boom, tech bubble, or the Internet bubble) was a stock market bubble in the late 1990s, a period of massive growth in the use and adoption of the Internet.
Between 1995 and its peak in March 2000, the Nasdaq Comp ...
burst, due in part to excessive launch costs at the time.
In June 2004, the newly formed company SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal o ...
acquired a stake in Surrey Satellite Technology (SSTL) as part of a "shared strategic vision". SSTL was at that time working to extend the Internet into space. However, SpaceX's stake was eventually sold back to EADS Astrium in 2008 after the company became more focused on navigation and Earth observation.
In early 2014, Elon Musk
Elon Reeve Musk ( ; born June 28, 1971) is a business magnate and investor. He is the founder, CEO and chief engineer of SpaceX; angel investor, CEO and product architect of Tesla, Inc.; owner and CEO of Twitter, Inc.; founder of The B ...
and Greg Wyler
Gregory Thane Wyler (born 12 November 1969) is an American tech entrepreneur, engineer, and inventor. He was the founder and executive chairman of OneWeb and the founder of O3b Networks.
Business ventures
Wyler spent four years developing tel ...
were reportedly working together planning a constellation of around 700 satellites called WorldVu, which would be over 10 times the size of the then largest Iridium satellite constellation. However, these discussions broke down by June 2014, and SpaceX instead filed an ITU application via the Norway telecom regulator under the name STEAM. SpaceX confirmed the connection in the 2016 application to license Starlink with the Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdicti ...
(FCC). SpaceX trademarked the name ''Starlink'' in the United States for their satellite broadband network; the name was inspired by the book '' The Fault in Our Stars''. While Starlink is deployed worldwide, it has encountered trademark conflicts in some countries such as Mexico.
Development phase (2015–2020)
 Starlink was publicly announced in January 2015 with the opening of the SpaceX satellite development facility in
Starlink was publicly announced in January 2015 with the opening of the SpaceX satellite development facility in Redmond, Washington
Redmond is a city in King County, Washington, United States, located east of Seattle. The population was 73,256 at the 2020 census, up from 54,144 in 2010.
Redmond is best known as the home of Microsoft and Nintendo of America.
With an ann ...
. During the opening, Elon Musk
Elon Reeve Musk ( ; born June 28, 1971) is a business magnate and investor. He is the founder, CEO and chief engineer of SpaceX; angel investor, CEO and product architect of Tesla, Inc.; owner and CEO of Twitter, Inc.; founder of The B ...
stated there is still significant unmet demand worldwide for low-cost broadband capabilities. and that Starlink would target bandwidth to carry up to 50% of all backhaul communications traffic, and up to 10% of local Internet traffic, in high-density cities.
Starting with 60 engineers, the company operated in of leased space, and by January 2017 had taken on a second facility, both in Redmond. In August 2018, SpaceX consolidated all their Seattle-area operations with a move to a larger three-building facility at Redmond Ridge Corporate Center to support satellite manufacturing in addition to R&D. In July 2016, SpaceX acquired an additional creative space in Irvine, California
Irvine () is a master-planned city in South Orange County, California, United States, in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. The Irvine Company started developing the area in the 1960s and the city was formally incorporated on December 28, 197 ...
(Orange County). The Irvine office would include signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, ...
, RFIC RFIC is an abbreviation of radio-frequency integrated circuit. Applications for RFICs include radar and communications, although the term RFIC might be applied to any electrical integrated circuit operating in a frequency range suitable for wireless ...
, and ASIC
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficie ...
development for the satellite program.
By October 2016, the satellite division was focusing on a significant business challenge of achieving a sufficiently low-cost design for the user equipment. SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell said then that the project remained in the "design phase as the company seeks to tackle issues related to user-terminal cost".
In November 2016, SpaceX filed an application with the FCC for a "non-geostationary orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitu ...
( NGSO) satellite system in the Fixed-Satellite Service using the Ku- and Ka- frequency bands".
In March 2017, SpaceX filed plans with the FCC to field a second orbital shell of more than 7,500 " V-band satellites in non-geosynchronous orbits to provide communications services" in an electromagnetic spectrum that has not previously been heavily employed for commercial communications services. Called the "Very-Low Earth Orbit ( VLEO) constellation", it was to have comprised 7,518 satellites that were to orbit at just altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
, while the smaller, originally planned group of 4,425 satellites would operate in the Ka- and Ku-bands and orbit at altitude. In the event, by 2022 SpaceX had withdrawn plans to field the 7518-satellite V-band system superseding in with a more comprehensive Gen2 Starlink satellite design.
In September 2017, the FCC ruled that half of the constellation must be in orbit within six years to comply with licensing terms, while the full system should be in orbit within nine years from the date of the license.
SpaceX filed documents in late 2017 with the FCC to clarify their space debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, or space garbage) are defunct human-made objects in space—principally in Earth orbit—which no longer serve a useful function. These include derelict spacec ...
mitigation plan, under which the company was to:
"...implement an operations plan for the orderly de-orbit of satellites nearing the end of their useful lives (roughly five to seven years) at a rate far faster than is required under international standards. atelliteswill de-orbit by propulsively moving to a disposal orbit from which they will re-enter the Earth's atmosphere within approximately one year after completion of their mission."
 In March 2018, the FCC granted SpaceX approval for the initial 4,425 satellites, with some conditions. SpaceX would need to obtain a separate approval from the
In March 2018, the FCC granted SpaceX approval for the initial 4,425 satellites, with some conditions. SpaceX would need to obtain a separate approval from the International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
(ITU). The FCC supported a NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
request to ask SpaceX to achieve an even higher level of de-orbiting reliability than the standard that NASA had previously used for itself: reliably de-orbiting 90% of the satellites after their missions are complete.
In May 2018, SpaceX expected the total cost of development and buildout of the constellation to approach $10 billion. In mid-2018, SpaceX reorganized the satellite development division in Redmond, and terminated several members of senior management.
In November 2018, SpaceX received U.S. regulatory approval to deploy 7,518 V-band broadband satellites, in addition to the 4,425 approved earlier; however, the V-band plans were subsequently withdrawn by 2022.
At the same time, SpaceX also made new regulatory filings with the U.S. FCC to request the ability to alter its previously granted license in order to operate approximately 1,600 of the 4,425 Ka-/Ku-band satellites approved for operation at in a "new lower shell of the constellation" at only orbital altitude. These satellites would effectively operate in a third orbital shell, a orbit, while the higher and lower orbits at approximately and approximately would be used only later, once a considerably larger deployment of satellites becomes possible in the later years of the deployment process. The FCC approved the request in April 2019, giving approval to place nearly 12,000 satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioiso ...
s in three orbital shells: initially approximately 1,600 in a – altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
shell, and subsequently placing approximately 2,800 Ku- and Ka-band spectrum satellites at and approximately 7,500 V-band satellites at . In total, nearly 12,000 satellites were planned to be deployed, with (as of 2019) a possible later extension to 42,000.
In February 2019, a sister company of SpaceX, SpaceX Services Inc., filed a request with the FCC to receive a license for the operation of up to a million fixed
Fixed may refer to:
* ''Fixed'' (EP), EP by Nine Inch Nails
* ''Fixed'', an upcoming 2D adult animated film directed by Genndy Tartakovsky
* Fixed (typeface), a collection of monospace bitmap fonts that is distributed with the X Window System
* F ...
satellite Earth stations that would communicate with its non-geostationary orbit (NGSO) satellite Starlink system.
In June 2019, SpaceX applied to the FCC for a license to test up to 270 ground terminals – 70 nationwide across the United States and 200 in Washington state
Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a U.S. state, state in the Northwestern United States, Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. Named for George Washington—the first President of the United States, U.S. p ...
at SpaceX employee homes – and aircraft-borne antenna operation from four distributed United States airfields; as well as five ground-to-ground test locations.
By late 2019, SpaceX was transitioning their satellite efforts from research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in Europe as research and technological development (RTD), is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products, and improving existi ...
to manufacturing, with the planned first launch of a large group of satellites to orbit, and the clear need to achieve an average launch rate of "44 high-performance, low-cost spacecraft built and launched every month for the next 60 months" to get the 2,200 satellites launched to support their FCC spectrum allocation license assignment. SpaceX said they will meet the deadline of having half the constellation "in orbit within six years of authorization... and the full system in nine years".
On 15 October 2019, the United States FCC submitted filings to the International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
(ITU) on SpaceX's behalf to arrange spectrum for 30,000 additional Starlink satellites to supplement the 12,000 Starlink satellites already approved by the FCC.
That month, Elon Musk publicly tested the Starlink network by using an Internet connection routed through the network to post a first tweet to social media site Twitter
Twitter is an online social media and social networking service owned and operated by American company Twitter, Inc., on which users post and interact with 280-character-long messages known as "tweets". Registered users can post, like, and ...
.
In November 2020, Starlink beta internet service was opened to the public. Starlink beta testers reported speeds over 150 megabits per second, above the range announced for the public beta test.
Commercial service (2021–)
 In February 2021, SpaceX opened up pre-orders to the public. SpaceX completed raising an additional $3.5 billion in equity financing over the previous six months, to support the capital-intensive phase of the operational fielding of Starlink, plus the development of the Starship launch system. In April 2021, SpaceX clarified that they have already tested two generations of Starlink technology, with the second one having been less expensive than the first. The third generation, with laser inter-satellite links, is expected to begin launching "in the next few months nd will bemuch less expensive than earlier versions".
, SpaceX has over 3000 Starlink satellites in orbit, and announced having over one million active subscribers. They continue to launch up to 53 more satellites per Falcon 9 flight.
On 6 November 2020, Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada announced regulatory approval for the Starlink low Earth orbit satellite constellation.
The FCC initially awarded SpaceX with $885.5 million worth of federal subsidies to support rural broadband customers through the company's Starlink satellite Internet network. SpaceX won subsidies to bring service to customers in 35 U.S. states. The $885.5 million aid package was revoked in August 2022, with the FCC stating that Starlink "failed to demonstrate" its ability to deliver the promised service. SpaceX later appealed the decision saying they met or surpassed all RDOF deployment requirements that existed during bidding and that the FCC created "new standards that no bidder could meet today".
In March 2021, SpaceX put an application into FCC for mobile variations of their terminal for vehicles, vessels and aircraft.
In May 2021, SpaceX announced agreements with
In February 2021, SpaceX opened up pre-orders to the public. SpaceX completed raising an additional $3.5 billion in equity financing over the previous six months, to support the capital-intensive phase of the operational fielding of Starlink, plus the development of the Starship launch system. In April 2021, SpaceX clarified that they have already tested two generations of Starlink technology, with the second one having been less expensive than the first. The third generation, with laser inter-satellite links, is expected to begin launching "in the next few months nd will bemuch less expensive than earlier versions".
, SpaceX has over 3000 Starlink satellites in orbit, and announced having over one million active subscribers. They continue to launch up to 53 more satellites per Falcon 9 flight.
On 6 November 2020, Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada announced regulatory approval for the Starlink low Earth orbit satellite constellation.
The FCC initially awarded SpaceX with $885.5 million worth of federal subsidies to support rural broadband customers through the company's Starlink satellite Internet network. SpaceX won subsidies to bring service to customers in 35 U.S. states. The $885.5 million aid package was revoked in August 2022, with the FCC stating that Starlink "failed to demonstrate" its ability to deliver the promised service. SpaceX later appealed the decision saying they met or surpassed all RDOF deployment requirements that existed during bidding and that the FCC created "new standards that no bidder could meet today".
In March 2021, SpaceX put an application into FCC for mobile variations of their terminal for vehicles, vessels and aircraft.
In May 2021, SpaceX announced agreements with Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offered by Google, is a suite of cloud computing services that runs on the same infrastructure that Google uses internally for its end-user products, such as Google Search, Gmail, Google Drive, and YouTube. Alongsi ...
and Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure, often referred to as Azure ( , ), is a cloud computing platform operated by Microsoft for application management via around the world-distributed data centers. Microsoft Azure has multiple capabilities such as software as a ...
to provide on-ground compute and networking services for Starlink. Viasat
Viasat may refer to:
*Viasat (American company) (founded 1986)
*Viasat (Nordic television service) (founded 1991)
* Danish 1st Division, officially Viasat Divisionen, second-highest football league in Denmark
* Viasat Cup, 2006 Danish football tour ...
made a legal attempt to temporarily halt Starlink launches.
In June 2021, SpaceX applied to the FCC to use mobile Starlink transceivers on launch vehicles flying to Earth orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi) in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes days (1 sidereal year), during which time E ...
, after having previously tested high-altitude low-velocity mobile use on a rocket prototype in May 2021.
By 1 October 2021, SpaceX had sold 5000 Starlink preorders in India, and announced that Sanjay Bhargava, who had worked with Elon Musk as part of a team that founded electronic payment firm PayPal, would head the tech billionaire entrepreneur's Starlink satellite broadband venture in India. Three months later, Bhargava resigned "for personal reasons" following the Indian government
The Government of India (ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
ordering SpaceX to halt selling preorders for Starlink service until SpaceX gains regulatory approval
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. For ...
for providing satellite internet services in the country.
In 2022 SpaceX announced the '' Starlink Business'' service tier. The FCC also approved the licensing of Starlink services to boats, aircraft, and moving vehicles.
In May 2022, Starlink entered the Philippine market, and is the company's first Asian deployment, due to a landmark legislative change (RA 11659, Public Services Act) about all-foreign allowance of company ownership in regards to utility entities such as internet and telco companies. Starlink was able to obtain a provisional permission from the country's Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DICT), National Telecommunications Commission (NTC) and Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) and will soon start commercial services, aimed at regions with lower internet connectivity.
In May 2022, Chinese military researchers published an article in a peer-reviewed journal describing a strategy for destroying the Starlink constellation if they threaten national security. The researchers specifically highlight concerns with reported Starlink military capabilities. Musk later announced that "Starlink is meant for peaceful use... to mend the fault in our stars". The head of Russia's space agency, Dmitry Rogozin, had earlier warned Musk that "you will have to answer in an adult way, Elon, no matter how you play the fool."
In August 2022, SpaceX secured its first contract for services in the passenger shipping industry. Royal Caribbean Group has added Starlink internet to Freedom of the Seas and plans to offer the service on 50 ships under its Royal Caribbean International, Celebrity Cruises
Celebrity Cruises is a cruise line headquartered in Miami, Florida and a wholly owned subsidiary of Royal Caribbean Group. Celebrity Cruises was founded in 1988 by the Greece-based Chandris Group, and merged with Royal Caribbean Cruise Line in ...
, and Silversea Cruises brands by March 2023. Starlink services on private jet charter flights in the US by JSX are expected to begin in late 2022, and Hawaiian Airlines has contracted to provide "Starlink services on transpacific flights to and from Hawaii in 2023."
According to Ookla
}
Speedtest.net, also known as Speedtest by Ookla, is a web service that provides free analysis of Internet access performance metrics, such as connection data rate and latency. It is the flagship product of Ookla, a web testing and network diag ...
, between Q1 and Q2 2022, Starlink speeds decreased worldwide as more people signed up for Starlink, although SpaceX has said that Starlink speeds will improve once more satellites are operational.
On 1 December 2022, the FCC issued an approval for SpaceX to launch the initial 7500 satellites for its second generation (Gen2) constellation, in three low-Earth-orbit orbital shell
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any ...
s, at 525, 530, and 535 km altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
. Overall, SpaceX had requested approval for as many as 29,988 Gen2 satellites, with approximately 10,000 in the 525–535 km altitude shells, plus ~20,000 in 340–360 km shells and nearly 500 in 604–614-km shells. However, the FCC noted that this is not a net increase in approved on-orbit satellites for SpaceX since SpaceX is no longer planning to deploy 7518 V-band satellites at altitude that had previously been authorized.
Services
Satellite internet
Starlink provides satellite internet connectivity to underserved areas of the planet, as well as competitively priced service in more urbanized areas. The company has stated that the positive cash flow from selling satellite internet services would be necessary to fund their Mars plans. Furthermore, SpaceX has long-term plans to develop and deploy a version of the satellite communication system to serveMars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
.
In October 2020, SpaceX launched a paid-for beta service in the U.S. called "Better Than Nothing Beta", charging $499 for a user terminal, with an expected service of "50 Mbps to 150 Mbps and latency from 20 ms to 40 ms over the next several months". From January 2021, the paid-for beta service was extended to other countries, starting with the United Kingdom.
The initial version of Starlink was limited to working within a few miles of the customers' registered address. In April 2021, Musk tweeted that users would be able to move the Starlink unit anywhere by the end of the year after more satellite launches and software updates.
In February 2022, SpaceX announced ''Starlink Business'', a higher performance edition of the service. It provides a larger high-performance antenna and listed speeds of between 150 and 500Mbit/s, with a cost of $2500 for the antenna and a $500 monthly service fee. The service includes 24/7, prioritized support. Deliveries are advertised to begin in the second quarter of 2022.
On 23 May 2022, SpaceX rolled out ''Starlink For RVs'', a new edition of the service that lets customers pay more to skip waitlists to connect to its broadband satellites without a fixed address, although connection speeds for other users will be prioritized.
On 7 July 2022 SpaceX announced ''Starlink Maritime'', a new addition to help support users, and companies, on the ocean. Only working on the water, unable to work on land, the advertised speed for the service is set up to 350 Mbps. However it comes at the one time price of $10,000 for the two user terminals, and $5,000 monthly price.
In August 2022 SpaceX lowered monthly service costs for users in select countries. Users in Brazil and Chile are reporting decreases of about 50%.
In September 2022, SpaceX sent out an email to users with pre-orders about a service called ''Best Effort''. It allows those still waiting in a full capacity cell to receive the unused bandwidth of their cell, while still being on the waiting list for more prioritized service. The price and equipment are the same as the residential service coming in at $110 per month.
Satellite cellular service
In August 2022,T-Mobile US
T-Mobile US, Inc. is an American wireless network operator headquartered in Overland Park, Kansas and Bellevue, Washington, U.S. Its largest shareholder is a multinational telecommunications company Deutsche Telekom AG, which , holds 48.4 pe ...
and SpaceX announced a partnership to add satellite cellular service to Starlink Gen2 satellites, and provide dead-zone cell phone coverage across the US using existing midband PCS
A personal communications service (PCS) is set of communications capabilities that provide a combination of terminal mobility, personal mobility, and service profile management. This class of services comprises several types of wireless voice o ...
spectrum that T-Mobile owns. Cell coverage will begin with messaging and expand to include voice and limited data services later, with testing to begin in 2023. With Starlink Gen2 sats in low-Earth orbit using existing PCS
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or techn ...
spectrum, T-Mobile plans to be able to connect by satellite to ordinary mobile devices, unlike previous generations of satellite phone
A satellite telephone, satellite phone or satphone is a type of mobile phone that connects to other phones or the telephone network by radio through orbiting satellites instead of terrestrial cell sites, as cellphones do. The advantage of a sa ...
s which used specialized Earth-bound radios to connect to geosynchronous satellites with characteristic long communications lag time. T-Mobile has offered to extend the offering globally if cellular carriers in other countries wish to exchange roaming services via the T-Mobile partnership with SpaceX, with other carriers responsible for working with their regulators to enable midband data communication landing rights on a country-by-country basis. Bandwidth will be limited to approximately 2 to 4 megabits per second spread across a very large cell coverage area; so limited to approximately 1000 to 2000 voice calls, or millions of text messages, across an entire cell. The size of a single coverage cell has not yet been publicly released, but the satellites are 7 meters long, and the antenna would fold out to be "roughly 25 square meters".


Military satellites
In March 2018, the Space Development Agency (SDA) was formed by Under Secretary of Defense Michael D. Griffin as part of aTrump Administration
Donald Trump's tenure as the List of presidents of the United States, 45th president of the United States began with Inauguration of Donald Trump, his inauguration on January 20, 2017, and ended on January 20, 2021. Trump, a Republican Party ...
initiative to resurrect the Strategic Defense Initiative
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisively nicknamed the "''Star Wars'' program", was a proposed missile defense system intended to protect the United States from attack by ballistic strategic nuclear weapons ( intercontinental ballist ...
(SDI). SDA accelerates development of missile defense
Missile defense is a system, weapon, or technology involved in the detection, tracking, interception, and also the destruction of attacking missiles. Conceived as a defense against nuclear-armed intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), ...
capabilities using industry-procured low-cost low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
satellite platforms.
In October 2020, SDA awarded SpaceX an initial $150 million dual-use
In politics, diplomacy and export control, dual-use items refers to goods, software and technology that can be used for both civilian and military applications.
contract to develop a deluxe military version of the Starlink satellite bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held.
Bus-derived satellites are opposed to specially produced satellites. Bus- ...
. The first tranche of satellites were originally scheduled to launch September 2022 to form part of the Tracking Layer of the Space Force's National Defense Space Architecture
The Space Development Agency (SDA) began as a directorate of the United States Department of Defense's office of the under secretary of defense for research and engineering ( OUSD (R&E)) which supports space development in the interests of U.S. ...
(NDSA). However, the launch schedule slipped to mid-December 2022 after supply-chain difficulties arose procuring "space qualified microelectronics for components such as radios."
The NDSA will be composed of seven layers with specific functions: data transport, battle management, missile tracking
Measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) is a technical branch of intelligence gathering, which serves to detect, track, identify or describe the distinctive characteristics (signatures) of fixed or dynamic target sources. This often incl ...
, custody/weapons targeting, navigation/PNT, deterrence, and ground support. Historically, space-based missile defense
Missile defense is a system, weapon, or technology involved in the detection, tracking, interception, and also the destruction of attacking missiles. Conceived as a defense against nuclear-armed intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), ...
concepts (e.g., Brilliant Pebbles
Brilliant Pebbles was a ballistic missile defense (BMD) system proposed by Lowell Wood and Edward Teller of the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) in 1987, near the end of the Cold War. The system would consist of thousands of small ...
) were expensive, but reusable launch systems have mitigated costs according to a 2019 Congressional Budget Office analysis. NSDA leverages existing commercial satellite bus development such as Starlink to reduce costs, including free-space optical laser terminals for a secure command and control mesh network. The 2019 Missile Defense Review notes space-based sensing enables "improved tracking and potentially targeting of advanced threats, including HGVs and hypersonic cruise missiles". " However, the Union of Concerned Scientists
The Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS) is a nonprofit science advocacy organization based in the United States. The UCS membership includes many private citizens in addition to professional scientists. Anne Kapuscinski, Professor of Environmenta ...
warns developments could escalate tensions with Russia and China and called the project "fundamentally destabilizing". The Carnegie Endowment for International Peace
The Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (CEIP) is a nonpartisan international affairs think tank headquartered in Washington D.C. with operations in Europe, South and East Asia, and the Middle East as well as the United States. Founded i ...
later advocated for a treaty halting development to prevent an arms race
An arms race occurs when two or more groups compete in military superiority. It consists of a competition between two or more states to have superior armed forces; a competition concerning production of weapons, the growth of a military, and ...
in space.
Starlink's military satellite development is overseen internally at SpaceX by retired four-star general Terrence J. O'Shaughnessy. O'Shaughnessy advocated before the United States Senate Committee on Armed Services for a layered capability with lethal follow-on that incorporates machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
and artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech ...
to gather and act upon sensor data quickly.
Starshield program
In December 2022, SpaceX announced Starshield, a program to incorporate military or government entity payloads onboard a Starshield satellite bus (based on Starlink Block v1.5 and v2.0 technology). These satellites are heavier, with twice the area as a single Starlink v1.5 and have two pair of solar arrays as opposed to one on Starlink Block v1.5. While Starlink is designed for consumer and commercial use, Starshield is designed for US government use, with an initial focus on three areas, namely, earth observation, communications and hosting payloads. Designed to meet diverse mission requirements, Starshield satellites are capable of integrating a wide variety of payloads, offering unique versatility to users. Starshield will be compatible with the Starlink constellation to interoperate. “Starlink's inter-satellite laser communications terminal, which is the only communications laser operating at scale in orbit today, can be integrated onto partner satellites to enable incorporation into the Starshield network. In January 2022, SpaceX deployed fournational security
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military att ...
satellites for the US government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a feder ...
on their Transporter-3 rideshare mission. In the same year they launched another group of four US satellites with a single on-orbit spare Globalstar FM-15 satellite in June. Their purpose was not disclosed at the time of launch, but was considered likely either technical demonstration, communications, earth observation or signals intelligence.
It is likely the four SpaceX-built Tranche 0 Tracking Layer satellites due to launch in Q1 2023 are also based on the Starshield satellite bus.
Military communications
In 2019, tests by the United States Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) demonstrated a 610 Mbit/s data link through Starlink to a Beechcraft C-12 Huron aircraft in flight. Additionally, in late 2019, theUnited States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
successfully tested a connection with Starlink on an AC-130 Gunship
The Lockheed AC-130 gunship is a heavily armed, long-endurance, ground-attack variant of the C-130 Hercules transport, fixed-wing aircraft. It carries a wide array of ground-attack weapons that are integrated with sophisticated sensors, n ...
.
In 2020, United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
utilized Starlink in support of its Advanced Battlefield management system during a live-fire exercise. They demonstrated Starlink connected to a "variety of air and terrestrial assets" including the Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker
The Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker is an American military aerial refueling aircraft that was developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype, alongside the Boeing 707 airliner. It is the predominant variant of the C-135 Stratolifter family of trans ...
.
Use in Ukraine
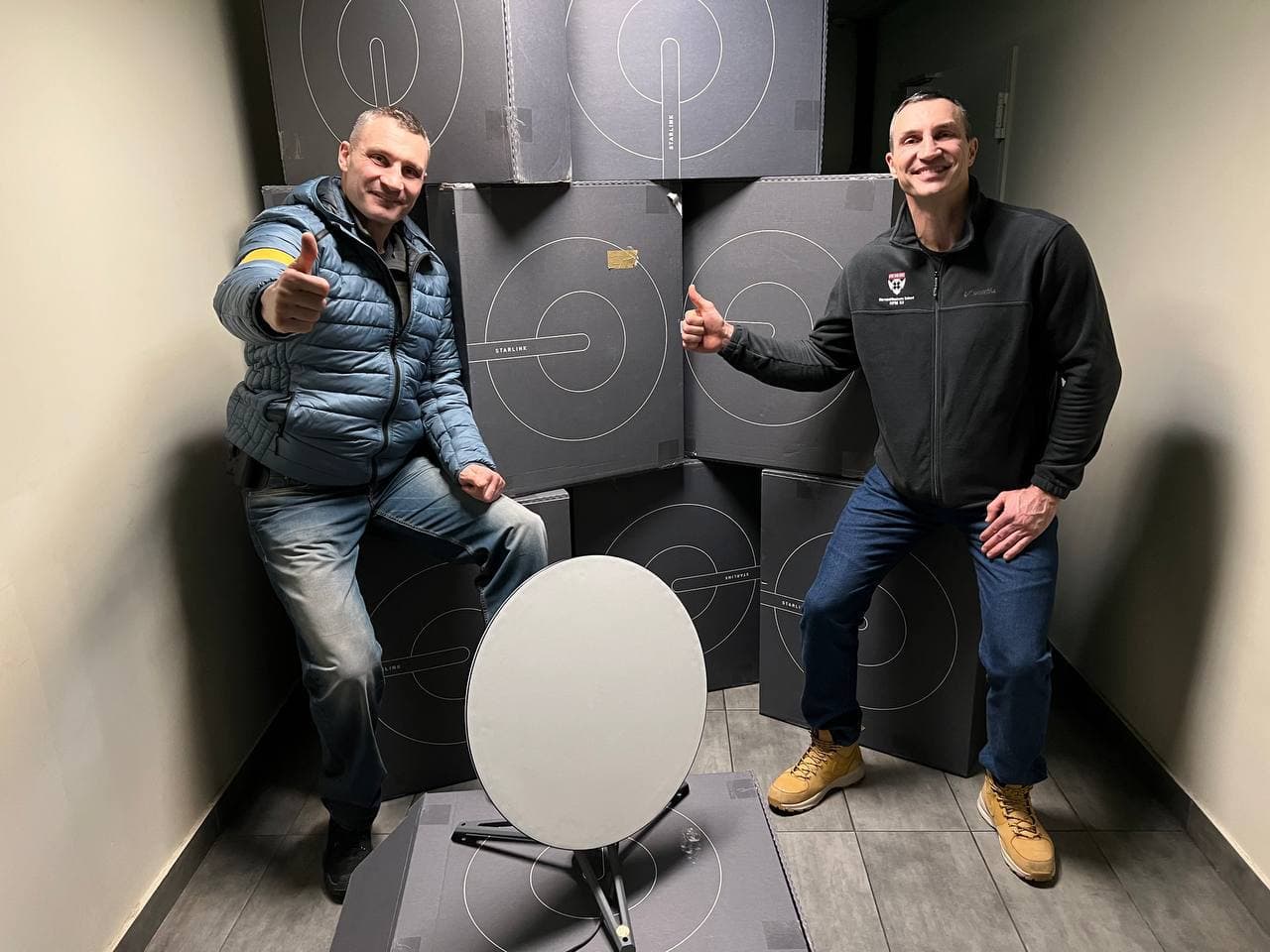
 On 26 February 2022, Elon Musk announced that the Starlink satellites had become active over
On 26 February 2022, Elon Musk announced that the Starlink satellites had become active over Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
after a request from the Ukrainian government to replace internet services destroyed during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. A ...
.Elon Musk says SpaceX's Starlink satellites active over Ukraine after request from embattled country's leadersThe Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publish ...
(26 February 2022) By 6 April 2022, SpaceX had sent over 5000 Starlink terminals to Ukraine to allow Ukrainians access to the Starlink network; SpaceX had donated 3667 or 73% of the 5000 terminals and removed the monthly service fees, and USAID had purchased the balance of the terminals. According to ''The Washington Post'', The Starlink equipment sent to Ukraine was funded by SpaceX including partial funding by the U.S. Agency for International Development, as well as the governments of France and Poland. By mid August, Ukraine internet service was being provided by more than 20,000 Starlink terminals, some from foreign partners and volunteers, in addition to many provided directly by SpaceX. During the war, Ukrainians can use Starlink terminals without paying the normal monthly subscription fee; by year-end, Musk estimated the cost of Starlink's donation at $20 million per month.
In May 2022 a Starlink-enabled Ukrainian Internet App was the key component of a successful new artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
fire coordination system. While military and government use of the Starlink has been the most important aspect of opening Ukraine to low-altitude satellite internet services in early 2022, civilians are also heavily using the technology "to keep in touch with the outside world and tell loved ones that they are alive."
On September 30, Ukrainian forces reported major Starlink outages across the frontline, resulting in "catastrophic" losses of communication. CNN reported Starlink services had to be requested by Ukrainian forces as new areas were liberated.
Promotion at
2022 FIFA World Cup
The 2022 FIFA World Cup is an international football tournament contested by the men's national teams of FIFA's member associations. The 22nd FIFA World Cup is taking place in Qatar from 20 November to 18 December 2022; it is the first Wor ...
FIFA
FIFA (; stands for ''Fédération Internationale de Football Association'' (French), meaning International Association Football Federation ) is the international governing body of association football, beach football and futsal. It was found ...
and Qatar Airways partnered with SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal o ...
on a falcon 9 mission. On Eutelsat
Eutelsat S.A. is a French satellite operator. Providing coverage over the entire European continent, the Middle East, Africa, Asia and the Americas, it is the world's third-largest satellite operator in terms of revenues.
Eutelsat's satellite ...
Hotbird 13F mission (launched in October 2022), the first stage B1069.3 included a hosted promotional payload by FIFA
FIFA (; stands for ''Fédération Internationale de Football Association'' (French), meaning International Association Football Federation ) is the international governing body of association football, beach football and futsal. It was found ...
, that was a box powered by starlink containing 2 Adidas Al Rihla balls, that were to be used in 2022 FIFA World Cup
The 2022 FIFA World Cup is an international football tournament contested by the men's national teams of FIFA's member associations. The 22nd FIFA World Cup is taking place in Qatar from 20 November to 18 December 2022; it is the first Wor ...
in Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
. These match balls were launched and brought back by landing on the droneship surviving the stresses of the booster. Later, they were taken out and shipped back to Qatar for the world cup. This was actually the first payload on a Falcon 9 booster and thus showed the ease of reusability.
The balls' flight by SpaceX was, in part, a promotion for the company's Starlink satellite internet service. An associated website invited World Cup attendees to visit the Starlink office in Doha.
Availability and regulatory approval by country
International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
(ITU) regulations and long-standing international treaties require that landing rights be granted by each country jurisdiction, and within a country, by the national communications regulators. As a result, even though the Starlink network has near-global reach at latitudes below approximately 60°, broadband services can only be provided in 40 countries as of September 2022. SpaceX can also have business operation and economic considerations that may make a difference in which countries Starlink service is offered, in which order, and how soon. For example, SpaceX formally requested authorization for Canada only in June 2020, the Canadian regulatory authority approved it in November 2020, and SpaceX rolled out service two months later, in January 2021. As of September 2022, Starlink services were on offer in 40 countries, with applications pending regulatory approval in many more.
Japan's major mobile provider, KDDI
() is a Japanese telecommunications operator formed on October 1, 2000 through the merger of DDI Corp. (Daini-Denden Inc.), KDD (Kokusai Denshin Denwa) Corp. (itself a former listed state-owned enterprise privatized in 1998), and IDO Corp. It ...
, announced a partnership with SpaceX to begin offering in 2022 expanded connectivity for its rural mobile customers via 1,200 remote mobile towers.
On 25 April 2022, Hawaiian Airlines announced an agreement with Starlink to provide free internet access on its aircraft, becoming the first airline to use Starlink. By July 2022, Starlink internet service was available in 36 countries and 41 markets.
In May 2022, it was announced that regulatory approval had been granted for Nigeria, Mozambique, and the Philippines.
Technology
Satellite hardware
The Internet communication satellites were expected to be in the smallsat-class of -mass, and were intended to be inlow Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
(LEO) at an altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
of approximately , according to early public releases of information in 2015. In the event, the first large deployment of 60 satellites in May 2019 were and SpaceX decided to place the satellites at a relatively low , due to concerns about the space environment. Initial plans were for the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the earliest constellation ...
to be made up of approximately 4,000 cross-linked satellites, more than twice as many operational satellites as were in orbit in January 2015.
The satellites will employ optical inter-satellite links and phased array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving th ...
beam-forming and digital processing technologies in the Ku and Ka microwave bands ''(super high frequency HFto extremely high frequency HF'', according to documents filed with the U.S. FCC. While specifics of the phased array technologies have been disclosed as part of the frequency application, SpaceX enforced confidentiality regarding details of the optical inter-satellite links. Early satellites were launched without laser links. The inter-satellite laser links were successfully tested in late 2020.
The satellites will be mass-produced, at a much lower cost per unit of capability than previously existing satellites. Musk said, "We're going to try and do for satellites what we've done for rockets." "In order to revolutionize space, we have to address both satellites and rockets." "Smaller satellites are crucial to lowering the cost of space-based Internet and communications".
In February 2015, SpaceX asked the FCC to consider future innovative uses of the Ka-band spectrum before the FCC commits to 5G communications regulations that would create barriers to entry
In theories of competition in economics, a barrier to entry, or an economic barrier to entry, is a fixed cost that must be incurred by a new entrant, regardless of production or sales activities, into a market that incumbents do not have or ha ...
, since SpaceX is a new entrant to the satellite communications
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. ...
market. The SpaceX non-geostationary orbit communications satellite constellation will operate in the high-frequency bands above 24 GHz, "where steerable Earth station transmit antennas would have a wider geographic impact, and significantly lower satellite altitudes magnify the impact of aggregate interference from terrestrial transmissions".
Internet traffic via a geostationary
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitud ...
satellite has a minimum theoretical round-trip latency of at least 477 milliseconds (ms; between user and ground gateway), but in practice, current satellites have latencies of 600 ms or more. Starlink satellites are orbiting at to of the height of geostationary orbits, and thus offer more practical Earth-to-sat latencies of around 25 to 35 ms, comparable to existing cable and fiber networks. The system will use a peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network. They are said to form a peer-to-peer ...
protocol claimed to be "simpler than IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. I ...
", it will also incorporate end-to-end encryption natively.
Starlink satellites use Hall-effect thrusters with krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is of ...
gas as the reaction mass for orbit raising and station keeping. Krypton Hall thrusters tend to exhibit significantly higher erosion of the flow channel compared to a similar electric propulsion system operated with xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
, but krypton is much more abundant and has a lower market price.
User terminals
 The system does not directly connect from its satellites to handsets (like the constellations from
The system does not directly connect from its satellites to handsets (like the constellations from Iridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density o ...
, Globalstar, Thuraya and Inmarsat). Instead, it is linked to flat user terminals the size of a pizza box, which will have phased array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving th ...
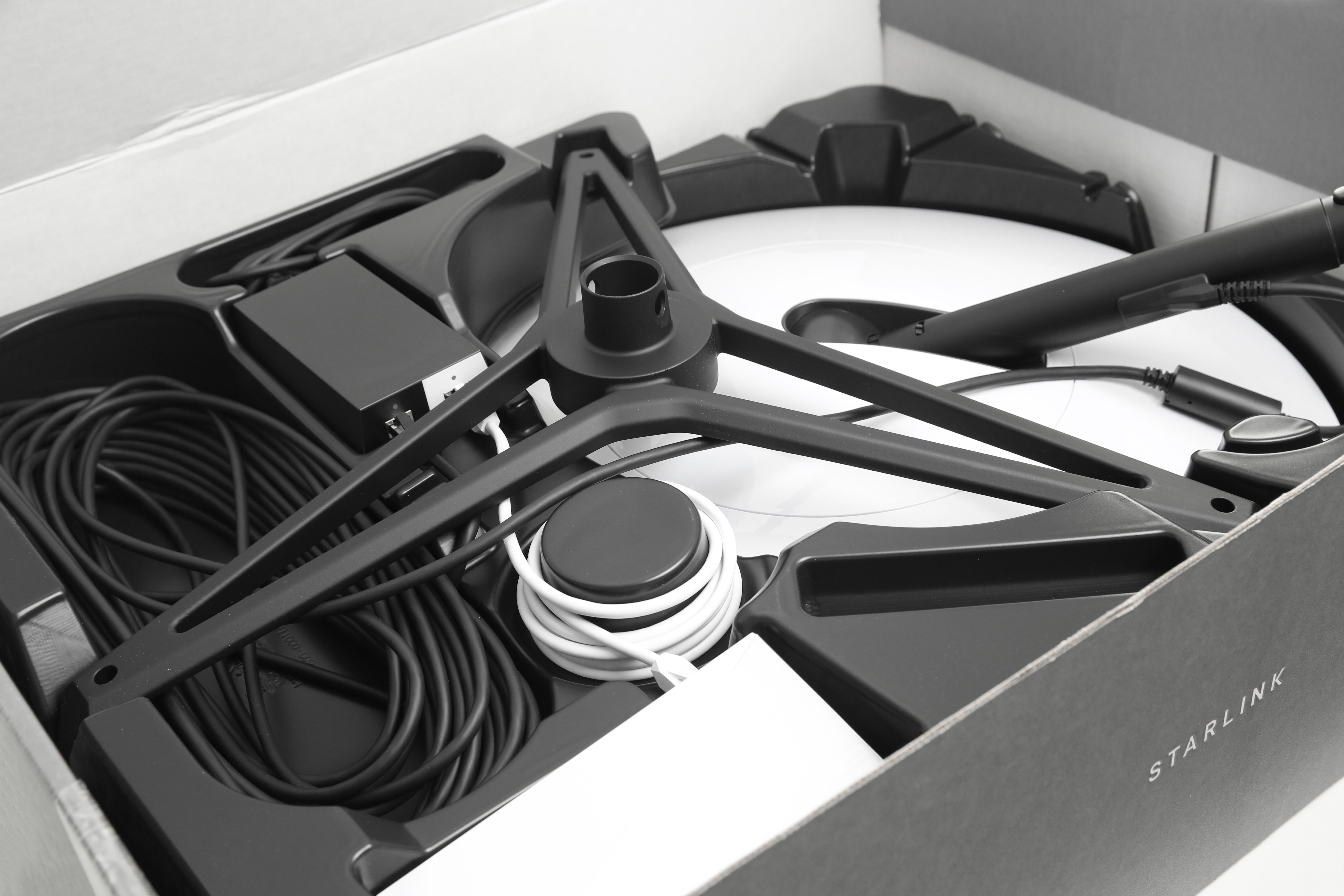
antennas and track the satellites. The terminals can be mounted anywhere, as long as they can see the sky. This includes fast-moving objects like trains. Photographs of the customer antennas were first seen on the internet in June 2020, supporting earlier statements by SpaceX CEO Musk that the terminals would look like a "UFO on a stick. Starlink Terminal has motors to self-adjust optimal angle to view sky". The antenna is known internally as "Dishy McFlatface".
In October 2020, SpaceX launched a paid-for beta service in the U.S. called "Better Than Nothing Beta", charging $499 for a user terminal, with an expected service of "50 Mbps to 150 Mbps and latency from 20 ms to 40 ms over the next several months". From January 2021, the paid-for beta service was extended to other continents, starting with the United Kingdom.
A larger, high-performance version of the antenna is available for use with the '' Starlink Business'' service tier.
In September 2020, SpaceX applied for permission to put terminals on 10 of its ships with the expectation of entering the maritime market in the future.
Ground stations
SpaceX has made applications to the FCC for at least 32ground station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves f ...
s in United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, and has approvals for five of them (in five states). Starlink uses the Ka-band to connect with ground stations.
A typical ground station right now has nine 2.86m antennas in a 400 sqm fenced in area.
According to their filing, SpaceX's ground stations would also be installed on-site at Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
data-centers world-wide.
Satellite revisions
MicroSat MicroSat-1a and MicroSat-1b were originally slated to be launched into circular orbits at approximately 86.4° inclination, and to include panchromatic video imager cameras to film images of Earth and the satellite. The two satellites, "MicroSat-1a" and "MicroSat-1b" were meant to be launched together as secondary payloads on one of the Iridium-NEXT flights, but they were instead used for ground-based tests. Tintin At the time of the June 2015 announcement, SpaceX had stated plans to launch the first two demonstration satellites in 2016, but the target date was subsequently moved out to 2018. SpaceX began flight testing their satellite technologies in 2018 with the launch of two test satellites. The two identical satellites were called MicroSat-2a and MicroSat-2b during development but were renamed Tintin A and Tintin B upon orbital deployment on 22 February 2018. The satellites were launched by a Falcon 9 rocket, and they were piggy-pack payloads launching with the Paz satellite. Tintin A and B were inserted into a orbit. Per FCC filings, they were intended to raise themselves to an orbit, the operational altitude for Starlink LEO satellites per the earliest regulatory filings, but stayed close to their original orbits. SpaceX announced in November 2018 that they would like to operate an initial shell of about 1600 satellites in the constellation at about orbital altitude, at an altitude similar to the orbits Tintin A and B stayed in. The satellites orbit in a circularlow Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never m ...
at about altitude in a high-inclination orbit for a planned six to twelve-month duration. The satellites communicate with three testing ground stations in Washington State
Washington (), officially the State of Washington, is a U.S. state, state in the Northwestern United States, Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. Named for George Washington—the first President of the United States, U.S. p ...
and California for short-term experiments of less than ten minutes duration, roughly daily.
v0.9 (test)
The 60 Starlink v0.9 satellites, launched in May 2019, have the following characteristics:
* Flat-panel design with multiple high-throughput antennas and a single solar array
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and ...
* Mass:
* Hall-effect thrusters using krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is of ...
as the reaction mass, for position adjustment on orbit, altitude maintenance, and deorbit
* Star tracker navigation system for precision pointing
* Able to use Department of Defense Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philipp ...
-provided debris data to autonomously avoid collision
* Altitude of
* 95% of "all components of this design will quickly burn in Earth's atmosphere at the end of each satellite's lifecycle".
v1.0 (operational)
The Starlink v1.0 satellites, launched since November 2019, have the following additional characteristics:
* 100% of all components of this design will completely demise, or burn up, in Earth's atmosphere at the end of each satellite's life.
* Ka-band added
* Mass:
* One of them, numbered 1130 and called DarkSat, had its albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that refle ...
reduced using a special coating but the method was abandoned due to thermal issues and IR reflectivity.
* All satellites launched since the ninth launch at August 2020 have visors to block sunlight from reflecting from parts of the satellite to reduce its albedo further.
v1.5 (operational)
The Starlink v1.5 satellites, launched since 24 January 2021, have the following additional characteristics:
* Lasers for inter-satellite communication
* Mass: ∼
* Visors that blocked sunlight were removed from satellites launched from September 2021 onwards.
Starshield (operational)
These are satellites buses with two solar arrays derived from starlinks v1.5 and v2.0 for military use and can host classified government or military payloads.
v2.0 (planned)
SpaceX was preparing for the production of Starlink v2.0 satellites by early 2021. Starlink v2.0 satellites will be "almost an order of magnitude
An order of magnitude is an approximation of the logarithm of a value relative to some contextually understood reference value, usually 10, interpreted as the base of the logarithm and the representative of values of magnitude one. Logarithmic di ...
more capable than v1.0" in terms of communications bandwidth.
SpaceX hopes to begin launching Starlink v2.0 in 2022. , SpaceX said publicly that all Gen2 Starlink sats would need to be launched on Starship
A starship, starcraft, or interstellar spacecraft is a theoretical spacecraft designed for traveling between planetary systems.
The term is mostly found in science fiction. Reference to a "star-ship" appears as early as 1882 in '' Oahspe: A Ne ...
, as they are too large to fit inside a Falcon 9 fairing. However, in August 2022, SpaceX made formal regulatory filings with the FCC that indicated they would build the Gen2 Starlinks in two different form factors: one with the components laid out in such a way that they could be launched in Falcon 9, and one laid out in the 7-meter long form factor that could only be launched on Starship. The smaller one is being planned as a backup, in the event that regular operational payload-delivery Starship launches do not occur as soon as SpaceX would like.SpaceX supplemental filing on IBFS File Nos. SAT-LOA-20200526-00055 and SAT-AMD-20210818-00105FCC documents website, PDF, 19 August 2022. Starlink v2.0 is both larger and heavier than Starlink v1 satellites: * Lasers for inter-satellite communication * Mass: ∼ * Length: ∼ (Starship form factor)
TBD, <7m (Falcon 9 form factor) * Further improvements to reduce its brightness, including the use of a
dielectric mirror
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of mirror composed of multiple thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type and thickne ...
film.
* Gen2 Starlink satellites will also include a very large antenna to communicate in the existing midband PCS
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or techn ...
spectrum, one that will allow cell phone network customers to be able to connect by satellite through their regular mobile devices. This communication is supplemental to the existing Ku-band and Ka-band antennas, and intersatellite laser links, that have been on the first generation satellites launching as of mid-2022.
*German-licensed hosted payloads by T-mobile together with SpaceX direct wholly-owned subsidiary, IoT
The Internet of things (IoT) describes physical objects (or groups of such objects) with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other comm ...
Swarm Technologies' connectivity solutions to be implemented and flown on a subset of 2,016 of these satellites for its direct-to-cellular connectivity system.
Due to delays in starship launch, SpaceX redefined some early v2.0s so there are 3 different busses of v2.0s:
* Bus F9-1, 303 kg mass, having roughly the same dimensions and mass as the current V1.5 satellites
* Bus F9-2 (dubbed as Starlink V2 Mini), 800 kg mass and measuring by with a total array of . It could offer around 3-4 times more usable bandwidth per satellite.
* Bus Starship, 2000 kg mass being the original v2.0 satellites
Launches
Between February 2018 and 2022, SpaceX successfully launched 2,091 satellites into orbit. In March 2020, SpaceX reported producing six satellites per day. The deployment of the first 1,440 satellites was planned in 72 orbital planes of 20 satellites each, with a requested lower minimum elevation angle of beams to improve reception: 25° rather than the 40° of the other two orbital shells. SpaceX launched the first 60 satellites of the constellation in May 2019 into a orbit and expected up to six launches in 2019 at that time, with 720 satellites (12 × 60) for continuous coverage in 2020. Starlink satellites are also planned to launch onStarship
A starship, starcraft, or interstellar spacecraft is a theoretical spacecraft designed for traveling between planetary systems.
The term is mostly found in science fiction. Reference to a "star-ship" appears as early as 1882 in '' Oahspe: A Ne ...
, an under-development rocket of SpaceX with a much larger payload capability. The initial announcement included plans to launch 400 Starlink (version 1.0) satellites at a time. Current plans now call for Starship to be the only launch vehicle to be used to launch fewer of the much larger Starlink version 2.0.

Constellation design and status
Contains all v0.9 and higher satellite generations. Tintin A and Tintin B as test satellites are not included. Early designs had all phase 1 satellites in altitudes of around . SpaceX initially requested to lower the first 1584 satellites, and in April 2020 requested to lower all other higher satellite orbits to about . In April 2020, SpaceX modified the architecture of the Starlink network. SpaceX submitted an application to the FCC proposing to operate more satellites in lower orbits in the first phase than the FCC previously authorized. The first phase will still include 1,440 satellites in the first shell orbiting at in planes inclined 53.0°, with no change to the first shell of the constellation launched largely in 2020. SpaceX also applied in the United States for use of the E-band in their constellation The FCC approved the application in April 2021. * First shell: 1,440 in aaltitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
shell at 53.0° inclination
* Second shell: 1,440 in a shell at 53.2° inclination
* Third shell: 720 in a shell at 70° inclination
* Fourth shell: 336 in a shell at 97.6° inclination
* Fifth shell: 172 satellites in a shell at 97.6° inclination
SpaceX previously had regulatory approval from the FCC to operate another 2,825 satellites in higher orbits between and , in orbital planes inclined at 53.8°, 70.0°, 74.0° and 81.0°.
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal o ...
released a new group of 10 Starlink satellites on 24 January 2021, the first Starlink satellites in polar orbits. The launch also surpassed ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman o ...
's record of launching the most satellites in one mission (143), taking to 1,025 the cumulative number of satellites deployed for Starlink to that date.
On 3 February 2022, 49 satellites were launched as Starlink Group 47. A G2-rated geomagnetic storm occurred on 4 February, caused the atmosphere to warm and density at the low deployment altitudes to increase. Predictions were that up to 40 of the 49 satellites might be lost to drag. In the event, 38 satellites reentered the atmosphere by 12 February while the remaining 11 were able to raise their orbits and avoid loss due to the storm.
Impact on astronomy


 The planned large number of satellites has been met with criticism from the astronomical community because of concerns over
The planned large number of satellites has been met with criticism from the astronomical community because of concerns over light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive use of artificial lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting, during the day or night. Light po ...
. Astronomers claim that the number of visible satellites will outnumber visible stars and that their brightness in both optical and radio wavelengths will severely impact scientific observations. While astronomers can schedule observations to avoid pointing where satellites currently orbit, it is "getting more difficult" as more satellites come online. The International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
(IAU), National Radio Astronomy Observatory
The National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) is a federally funded research and development center of the United States National Science Foundation operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc. for the purpose of radio a ...
(NRAO), and Square Kilometre Array Organization (SKAO) have released official statements expressing concern on the matter.
On 20 November 2019, the four-meter (13') Blanco telescope of the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO) recorded strong signal loss and the appearance of 19 white lines on a DECam
The Dark Energy Survey (DES) is an astronomical survey designed to constrain the properties of dark energy. It uses images taken in the near-ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared to measure the expansion of the universe using Type Ia supernova ...
shot (right image). This image noise was correlated to the transit of a Starlink satellite train, launched a week earlier.
SpaceX representatives and Musk have claimed that the satellites will have minimal impact, being easily mitigated by pixel masking and image stacking. However, professional astronomers have disputed these claims based on initial observation of the Starlink v0.9 satellites on the first launch, shortly after their deployment from the launch vehicle. In later statements on Twitter, Musk stated that SpaceX will work on reducing the albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that refle ...
of the satellites and will provide on-demand orientation adjustments for astronomical experiments, if necessary. One Starlink satellite (Starlink 1130 / DarkSat) launched with an experimental coating to reduce its albedo. The reduction in g-band magnitude is 0.8 magnitude (55%). Despite these measures, astronomers found that the satellites were still too bright thus making DarkSat essentially a "dead end".
On 17 April 2020, SpaceX wrote in an FCC filing that it would test new methods of mitigating light pollution, and also provide access to satellite tracking data for astronomers to "better coordinate their observations with our satellites". On 27 April 2020, Musk announced that the company would introduce a new sunshade designed to reduce the brightness of Starlink satellites. , over 200 Starlink satellites had a sunshade. An October 2020 analysis found them to be only marginally fainter than DarkSat. A January 2021 study pinned the brightness at 31% of the original design.
According to a May 2021 study, "The large number of fast-moving transmitting stations (i.e. satellites) will cause further interference. New analysis methods could mitigate some of these effects, but data loss is inevitable, increasing the time needed for each study and limiting the overall amount of science done".
In February 2022, the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
(IAU) established a center to help astronomers deal with the adverse effects of satellite constellations such as Starlink. Work will include the development of software tools for astronomers, advancement of national and international policies, community outreach and work with industry on relevant technologies.
In June 2022, the IAU released a website for astronomers to deal with some adverse effects via satellite tracking. This will enable astronomers to be able to track satellites to be able to avoid and time them for minimal impact on current work.
Increased risk of satellite collision
The large number of satellites employed by Starlink may create long-term danger ofspace debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, or space garbage) are defunct human-made objects in space—principally in Earth orbit—which no longer serve a useful function. These include derelict spacec ...
resulting from placing thousands of satellites in orbit and the risk of causing a satellite collision, potentially triggering a phenomenon known as Kessler syndrome. SpaceX has said that most of the satellites are launched at a lower altitude, and failed satellites are expected to deorbit within five years without propulsion.
Early in the program, a near-miss occurred when SpaceX did not move a satellite that had a 1 in 1,000 chance of colliding with a European one, ten times higher than ESA's threshold for avoidance maneuvers. SpaceX subsequently fixed an issue with its paging system that had disrupted emails between ESA and SpaceX. ESA said it plans to invest in technologies to automate satellite collision avoidance maneuvers. In 2021, Chinese authorities lodged a complaint with the United Nations, saying their space station had performed evasive maneuvers that year to avoid Starlink satellites. In the document, Chinese delegates said that the continuously maneuvering Starlink satellites posed a risk of collision, and two close encounters with the satellites in July and October constituted dangers to the life or health of astronauts aboard the Chinese Tiangong space station.
All these reported issues, plus current plans for the extension of the constellation, motivated a formal letter from National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) on behalf of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the
National Science Foundation (NSF), submitted to FCC on 8 February 2022, warning about the potential impact on LEO orbit, increased collision risk, impact on science missions, rocket launches, International Space Station and Radio frequencies Interferences. Resting credibility on the arguments for collision self-avoidance reported by SpaceX.
Competition and market effects
In addition to the OneWeb constellation, announced nearly concurrently with the SpaceX constellation, a 2015 proposal fromSamsung
The Samsung Group (or simply Samsung) ( ko, 삼성 ) is a South Korean multinational manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea. It comprises numerous affiliated businesses, most of them united under the ...
outlined a 4,600-satellite constellation orbiting at that could provide a zettabyte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable uni ...
per month capacity worldwide, an equivalent of 200 gigabytes per month for 5 billion users of Internet data, but by 2020, no more public information had been released about the Samsung constellation. Telesat announced a smaller 117 satellite constellation in 2015 with plans to deliver initial service in 2021. Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
announced a large broadband internet satellite constellation in April 2019, planning to launch 3,236 satellites in the next decade in what the company calls "Project Kuiper
Kuiper Systems LLC is a subsidiary of Amazon that was set up in 2019 to deploy a large broadband satellite internet constellation to provide broadband internet connectivity. The deployment is also referred to by its project name "Project Kuipe ...
", a satellite constellation
A satellite constellation is a group of artificial satellites working together as a system. Unlike a single satellite, a constellation can provide permanent global or near-global coverage, such that at any time everywhere on Earth at least one s ...
that will work in concert with Amazon's previously announced large network of twelve satellite ground station facilities (the "AWS
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon that provides on-demand cloud computing platforms and APIs to individuals, companies, and governments, on a metered pay-as-you-go basis. These cloud computing web services provide d ...
ground station unit") announced in November 2018.
In February 2015, financial analysts questioned established geosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbita ...
communications satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth ...
fleet operators as to how they intended to respond to the competitive threat of SpaceX and OneWeb LEO communication satellites. In October 2015, SpaceX President Gwynne Shotwell indicated that while development continues, the business case for the long-term rollout of an operational satellite network was still in an early phase.
By October 2017, the expectation for large increases in satellite network capacity from emerging lower-altitude broadband constellations caused market players to cancel some planned investments in new geosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbita ...
broadband communications satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth ...
s.
SpaceX was challenged regarding Starlink in February 2021 when the National Rural Electric Cooperative Association (NRECA), a political interest group representing traditional rural internet service providers, urged the U.S. Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdicti ...
(FCC) to "actively, and aggressively, and thoughtfully vet" the subsidy
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector (business, or individual) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Although commonly extended from the government, the ter ...
applications of SpaceX and other broadband providers. At the time, SpaceX had provisionally won $886 million for a commitment to provide service to approximately 643,000 locations in 35 states as part of the Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF). The NRECA criticisms included that the funding allocation to Starlink would include service to locations—such as Harlem
Harlem is a neighborhood in Upper Manhattan, New York City. It is bounded roughly by the Hudson River on the west; the Harlem River and 155th Street on the north; Fifth Avenue on the east; and Central Park North on the south. The greater Ha ...
and terminals at Newark Liberty International Airport
Newark Liberty International Airport , originally Newark Metropolitan Airport and later Newark International Airport, is an international airport straddling the boundary between the cities of Newark in Essex County and Elizabeth in Union Cou ...
and Miami International Airport
Miami International Airport , also known as MIA and historically as Wilcox Field, is the primary airport serving the greater Miami metropolitan area with over 1,000 daily flights to 167 domestic and international destinations, including most c ...
—that are not rural, and because SpaceX was planning to build the infrastructure and serve any customers who request service with or without the FCC subsidy. Additionally, Jim Matheson, chief executive officer of the NRECA voiced concern about technologies that had not yet been proven to meet the high speeds required for the award category. Starlink was specifically criticized for being still in beta testing and an unproven technology.
Similar or competitive systems
* OneWeb satellite constellation – a satellite constellation project that began operational deployment of satellites in 2020. * China national satellite internet project – a planned satellite internet offering for the Chinese market. * Kuiper Systems – a planned 3,236 LEO satellite Internet constellation by an Amazon subsidiary. * Hughes Network Systems – a current broadband satellite provider providing fixed, cellular backhaul, and airborne antennas. * Viasat, Inc. – a current broadband satellite provider providing fixed, ground mobile, and airborne antennas. *O3b
O3b is a satellite constellation in Medium Earth orbit (MEO) owned and operated by SES, and designed to provide low-latency broadband connectivity to remote locations for mobile network operators and internet service providers, maritime, aviat ...
– Medium Earth orbit
A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between above sea level.
constellation that provides access to mobile phone operators and internet service providers. It covers only the equatorial region.
See also
* AST SpaceMobile – a satellite-to-mobile-phone satellite constellation working with large mobile network operators such as Vodafone, AT&T, Orange, Rakuten, Telestra, Telefonica, etc. with the objective to provide broadband internet coverage to existing unmodified mobile phones *Orbcomm
''ORBCOMM'' is an American company that offers industrial Internet of things (IoT) and machine to machine (M2M) communications hardware, software and services designed to track, monitor, and control fixed and mobile assets in markets including ...
– an operational constellation used to provide global asset monitoring and messaging services from its constellation of 29 LEO communications satellites orbiting at 775 km
* Globalstar – an operational low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellation for satellite phone and low-speed data communications, covering most of the world's landmass
* Iridium
Iridium is a chemical element with the symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, it is considered the second-densest naturally occurring metal (after osmium) with a density o ...
– an operational constellation of 66 cross-linked satellites in a polar orbit, used to provide satellite phone and low-speed data services over the entire surface of Earth
* Lynk Global – a satellite-to-mobile-phone satellite constellation with the objective to coverage to traditional low-cost mobile devices
* Teledesic – a former (1990s) venture to accomplish broadband satellite internet services
* Project Loon – former concept to provide internet access via balloons in the stratosphere
References
External links
*Official Starlink Availability Map
Starlink Satellite and Groundstation Locations, Data Links, path projection, environmental Information etc. (starlink.sx)
Starlink Coverage Area, Satellite and Groundstation Locations for Starlink, OneWeb and GPS constellations (satellitemap.space)
Complete Starlink Satellite Catalog allowing tracking location details from user location.
Starlink Satellite Locations and Information on individual coverage area, connections, etc.
See A Satellite Tonight
shows when Starlink satellites can be seen.
Shows real-time Starlink satellites position
Starlink Professional Installers Directory
List of Starlink dish firmware updates
''A User Friendly Real-Time SpaceX Satellite Locator''
{{Portal bar, Spaceflight Articles containing video clips Communications satellite constellations Communications satellites in low Earth orbit Communications satellites of the United States Communications satellite operators High throughput satellites Internet service providers Internet service providers of the United States Satellite Internet access SpaceX satellites Spacecraft launched in 2019 Spacecraft launched in 2020 Spacecraft launched in 2021 Spacecraft launched in 2022 Space hazards