Sports Authority of India on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Sports Authority of India (SAI) is the apex national sports body of India, established in 1982 by the
The Sports Authority of India (SAI) is the apex national sports body of India, established in 1982 by the
. In addition, SAI also manages
 SAI runs following two academic institutes that run graduate and post-graduate courses in sports medicine, sports and physical education to prepare coaches and allied sports support staff.SAi Academic courses
SAI runs following two academic institutes that run graduate and post-graduate courses in sports medicine, sports and physical education to prepare coaches and allied sports support staff.SAi Academic courses
*
 In 1983, a "Department of Sports Science" was established at "NSNIS Patiala". From 1987 to 1990, "Sports science centres" with "Human Performance Lab" were set up at 4 regional centres in Delhi, Bengaluru, Kolkata and Gandhinagar; basic sports science support staff scheme was implemented for National Athletes; and SAI schemes for children was introduced at various regional centres.
Sports scientists from the fields of
In 1983, a "Department of Sports Science" was established at "NSNIS Patiala". From 1987 to 1990, "Sports science centres" with "Human Performance Lab" were set up at 4 regional centres in Delhi, Bengaluru, Kolkata and Gandhinagar; basic sports science support staff scheme was implemented for National Athletes; and SAI schemes for children was introduced at various regional centres.
Sports scientists from the fields of
 This is the backbone of SAI which provides support to the National Sports Federations (NSFs) in the preparation of National Teams which participate in various International events. The TEAMS Division coordinates the Long Term Development Plan of each NSF; provides logistics and training support at various academic institutions and other Regional Centres of SAI and also at selected training centres outside SAI. The TEAMS Division draws most of its funding under the Scheme of “Assistance to National Sports Federations” from Sports Ministry. The TEAMS Division also provides support to the NSFs in the hiring of foreign coaches and selection of the national coach for each NSF, who are responsible for the training of core probables for the National teams.
With active support from TEAMS Division, good results have been achieved in the international arena in the disciplines of Badminton, Judo, Shooting, Archery, Athletics, Weightlifting, Wrestling, Wushu, Boxing and Billiards & Snooker.
Under this Scheme of “Assistance to National Sports Federations”, financial assistance is provided to recognised NSFs for training and participation of teams in international events abroad, organisation of national and international tournaments in India, coaching and training of national teams under Indian and foreign coaches with requisite technical and scientific support, procurement of equipment etc.
This is the backbone of SAI which provides support to the National Sports Federations (NSFs) in the preparation of National Teams which participate in various International events. The TEAMS Division coordinates the Long Term Development Plan of each NSF; provides logistics and training support at various academic institutions and other Regional Centres of SAI and also at selected training centres outside SAI. The TEAMS Division draws most of its funding under the Scheme of “Assistance to National Sports Federations” from Sports Ministry. The TEAMS Division also provides support to the NSFs in the hiring of foreign coaches and selection of the national coach for each NSF, who are responsible for the training of core probables for the National teams.
With active support from TEAMS Division, good results have been achieved in the international arena in the disciplines of Badminton, Judo, Shooting, Archery, Athletics, Weightlifting, Wrestling, Wushu, Boxing and Billiards & Snooker.
Under this Scheme of “Assistance to National Sports Federations”, financial assistance is provided to recognised NSFs for training and participation of teams in international events abroad, organisation of national and international tournaments in India, coaching and training of national teams under Indian and foreign coaches with requisite technical and scientific support, procurement of equipment etc.
Sportal
Sports Portal by the Government of India
Sports Authority of India official site
Lakshmibai National College of Physical Education official website
Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports official website
 The Sports Authority of India (SAI) is the apex national sports body of India, established in 1982 by the
The Sports Authority of India (SAI) is the apex national sports body of India, established in 1982 by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
The Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports is a branch of the Government of India which administers the Department of youth affairs and the Department of Sports in India. Anurag Thakur is the current Minister of Youth Affairs and Sports followed ...
of Government of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
for the development of sports in India
Sport pertains to any form of competitive physical activity or game that aims to use, maintain, or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants and, in some cases, entertainment to spectators. Sports can, th ...
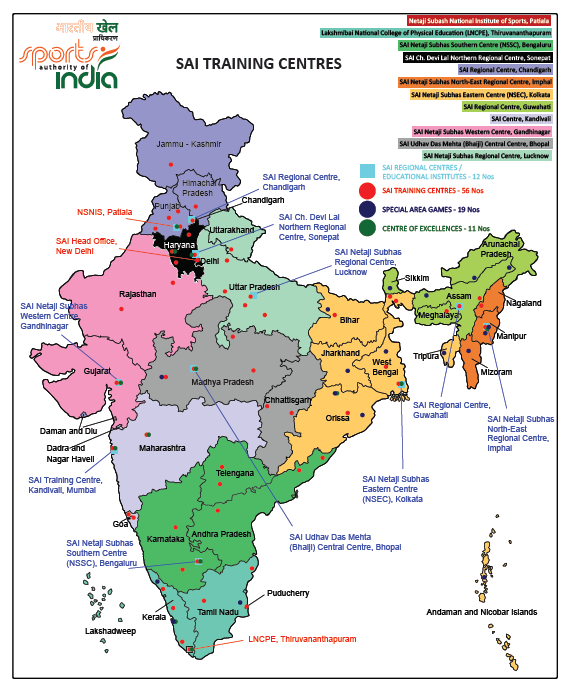
. SAI has 2 Sports Academic institutions, 11 "SAI Regional Centres" (SRC), 14 "Centre of Excellence" (COE/COX), 56 "Sports Training Centres" (STC) and 20 Special Area Games (SAG).SAI Centres of Excellence. In addition, SAI also manages
Netaji Subhash High Altitude Training Centre
Netaji Subhash High Altitude Training Centre, commonly known as High Altitude Training Centre, is one of the academic wings of the Sports Authority of India and is in Hill city of Shilaroo which is 52 km from Shimla.
The training center is ...
(Shilaroo, Himachal Pradesh) as well as 5 stadiums in the national capital of Delhi, such as Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium (also serves as national head office of SAI), Indira Gandhi Arena
The K. D. Jadhav Indoor Hall, formerly known as the Indraprashtha Stadium and Indira Gandhi Arena (officially Indira Gandhi Indoor Stadium), is located at the Indraprastha Estate in the eastern region of New Delhi. It is the largest indoor sp ...
, Major Dhyan Chand National Stadium, SPM Swimming Pool Complex
The Dr. S. P. Mukherjee Swimming Stadium or SPM Swimming Pool Complex is a swimming complex in New Delhi, India, that is hosting the aquatics events for the 2010 Commonwealth Games. The stadium is owned by the Sports Authority of India (SAI).
...
and Dr. Karni Singh Shooting Range.
Two "SAI Sports Academic" institutions are Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports
Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports, commonly known as National Institute of Sports (NIS), is the Academic Wing of the Sports Authority of India (SAI) and Asia's largest Sports Institute located in city of Patiala.
History
Founded on ...
(at Patiala in Punjab) and Lakshmibai National College of Physical Education
Lakshmibai National College of Physical Education (LNCPE) is part of the academic wing of the Sports Authority of India, and is situated at Kariavattom, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India. It was founded on 17 August 1985 under the auspices of ...
(at Thiruvananthapuram in Kerala), conducting research and running certificate to PhD PHD or PhD may refer to:
* Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), an academic qualification
Entertainment
* '' PhD: Phantasy Degree'', a Korean comic series
* '' Piled Higher and Deeper'', a web comic
* Ph.D. (band), a 1980s British group
** Ph.D. (Ph.D. al ...
level courses in physical education and sports medicine.
Eleven "SAI Regional Centres" (SRC) are located at (clockwise from north) Chandigarh
Chandigarh () is a planned city in India. Chandigarh is bordered by the state of Punjab to the west and the south, and by the state of Haryana to the east. It constitutes the bulk of the Chandigarh Capital Region or Greater Chandigarh, which al ...
, Zirakpur, Sonipat
Sonipat is a city, municipal corporation and administrative headquarter in Sonipat district of Haryana state of India. It comes under the National Capital Region and is around from New Delhi. It is also around 214 km (128 miles) southwest o ...
, Lucknow
Lucknow (, ) is the capital and the largest city of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and it is also the second largest urban agglomeration in Uttar Pradesh. Lucknow is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous district and divis ...
, Guwahati
Guwahati (, ; formerly rendered Gauhati, ) is the biggest city of the Indian state of Assam and also the largest metropolis in northeastern India. Dispur, the capital of Assam, is in the circuit city region located within Guwahati and is the ...
, Imphal
Imphal ( Meitei pronunciation: /im.pʰal/; English pronunciation: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Manipur. The metropolitan centre of the city contains the ruins of Kangla Palace (also known as Kangla Fort), the royal seat of the f ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
, Bhopal
Bhopal (; ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes'' due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It i ...
, Bengaluru
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
, Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the secon ...
and Gandhinagar
Gandhinagar (, ) is the capital of the state of Gujarat in India. Gandhinagar is located approximately 23 km north of Ahmedabad, on the west central point of the Industrial corridor between Delhi, the political capital of India, and Mum ...
. New regional centre of SAI has been inaugurated at Zirakpur, Punjab. It is the 11th regional centre of Sports Authority of India.
Fourteen "Centre of Excellences" (COE/COX) have a total of nearly 600 trainees in 18 sports (as of 2014), such as Archery, Athletics, Boxing, Cycling, Fencing, Gymnastics, Hockey, Judo, Kabaddi, Kayaking and Canoeing, Rowing, Swimming, Table Tennis, Taekwondo, Volleyball, Weightlifting, Wrestling and Wushu. These COE are at (clockwise from north) Patiala
Patiala () is a city in southeastern Punjab, northwestern India. It is the fourth largest city in the state and is the administrative capital of Patiala district. Patiala is located around the ''Qila Mubarak'' (the 'Fortunate Castle') construct ...
, Sonipat
Sonipat is a city, municipal corporation and administrative headquarter in Sonipat district of Haryana state of India. It comes under the National Capital Region and is around from New Delhi. It is also around 214 km (128 miles) southwest o ...
, Hisar (Haryana), Shillong
Shillong () is a hill station and the capital of Meghalaya, a state in northeastern India, which means "The Abode of Clouds". It is the headquarters of the East Khasi Hills district. Shillong is the 330th most populous city in India with a ...
, Imphal
Imphal ( Meitei pronunciation: /im.pʰal/; English pronunciation: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Manipur. The metropolitan centre of the city contains the ruins of Kangla Palace (also known as Kangla Fort), the royal seat of the f ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
, Jagatpur (Odisha), Bhopal
Bhopal (; ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes'' due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It i ...
, Bengaluru
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
, Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populati ...
, Alappuzha
Alappuzha or Alleppey () is the administrative headquarters of Alappuzha district in state of Kerala, India. The Backwaters of Alappuzha are one of the most popular tourist attractions in India which attracts millions of domestic and interna ...
, Kandivali
Kandivali (Pronunciation: aːn̪d̪iʋəliː formerly Khandolee is a neighbourhood in the north of Mumbai, Maharashtra, India and has a large Marathi and Koli population followed by Gujarati population living in small areas. The area als ...
, Aurangabad
Aurangabad ( is a city in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarters of Aurangabad district and is the largest city in the Marathwada region. Located on a hilly upland terrain in the Deccan Traps, Aurangabad is the ...
and Gandhinagar
Gandhinagar (, ) is the capital of the state of Gujarat in India. Gandhinagar is located approximately 23 km north of Ahmedabad, on the west central point of the Industrial corridor between Delhi, the political capital of India, and Mum ...
.
Twenty "Special Area Games" (SAG) are located at (clockwise from north) Kargil
Kargil ( lbj, ) is a city and a joint capital of the union territory of Ladakh, India. It is also the headquarters of the Kargil district. It is the second-largest city in Ladakh after Leh. Kargil is located to the east of Srinagar in J ...
, Kishanganj (Bihar), Gidhaur
Gidhaur (also known as Patsanda) is a small town in the Jamui District of Bihar. In the early-modern period, it was the centre of the Gidhaur chieftaincy.
History
Raja Bir Bikram Shah who belonged to Chandel Rajput Dynasty founded this princel ...
(Bihar), Ranchi
Ranchi (, ) is the capital of the Indian state of Jharkhand. Ranchi was the centre of the Jharkhand movement, which called for a separate state for the tribal regions of South Bihar, northern Odisha, western West Bengal and the eastern area o ...
(Jharkhand), Namchi
Namchi is a city and the administrative headquarter of the Namchi district in the Indian state of Sikkim. The appellation Namchi means ''Sky (Nam) High (Chi)'' in Sikkimese.
Geography
Namchi is located at . It has an average elevation o ...
(Sikkim), Naharlagun
Naharlagun is a town situated in the foothills of Himalayas in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. It falls and is administered as a part of Itanagar Capital Complex.
Geography
It is at an altitude of 155 metres from sea level. Surrounded ...
(Arunachal Pradesh), Kokrajhar (Assam), Tinsukia
Tinsukia (Pron: ˌtɪnˈsʊkiə) is an industrial town. It is situated north-east of Guwahati and away from the border with Arunachal Pradesh.
It is the administrative headquarters of Tinsukia District of Assam, India.
History
During th ...
(Assam), Imphal
Imphal ( Meitei pronunciation: /im.pʰal/; English pronunciation: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Manipur. The metropolitan centre of the city contains the ruins of Kangla Palace (also known as Kangla Fort), the royal seat of the f ...
(Manipur), Utlou (village in Nambol, Manipur), Agartala
Agartala () is the capital city of the Indian state of Tripura, and is one of the largest cities in northeast India. The city is governed by the Agartala Municipal Corporation. The city is the seat of the Government of Tripura. It is located ...
(Tripura), Aizawl
Aizawl (; Mizo: ) is the capital of the state of Mizoram in India. Aizawl was officially established on 25 February 1890. With a population of 293,416, it is the largest city in the state. It is also the centre of administration containing all ...
(Mizoram), Bolpur
Bolpur is a city and a municipality in Birbhum district in the state of West Bengal, India. It is the headquarters of the Bolpur subdivision. Bolpur municipal area includes Santiniketan, Sriniketan and Prantik. The city is known as a Cultu ...
(West Bengal), Jagatpur (Odisha), Sundergarh
Sundergarh is a town in Sundergarh district of the Indian state of Odisha. As of 2011 census, the municipality had a population of 45,036. Sundargarh is recognized as an industrial district in Odisha. Steel, fertilizer, cement, ferrovanadium, ...
(Odisha), Dhar
Dhar is a city located in Dhar district of the Malwa region in the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. The city is the administrative headquarters of the Dhar district. Before Indian independence from Great Britain, it was the capital of the Dh ...
(Madhya Pradesh), Port Blair (Andaman and Nicobar Islands), Alappuzha
Alappuzha or Alleppey () is the administrative headquarters of Alappuzha district in state of Kerala, India. The Backwaters of Alappuzha are one of the most popular tourist attractions in India which attracts millions of domestic and interna ...
(Kerala), Tellicherry
Thalassery (), formerly Tellicherry, is a municipality, Commercial City on the Malabar Coast in Kannur district, in the state of Kerala, India, bordered by the districts of Mahé (Pondicherry), Kozhikode, Wayanad, Kasaragod and Kodagu (Karnat ...
(Kerala), Mayiladuthurai
Mayiladuthurai (formerly known as Mayavaram or Mayuram) is a town and district headquarter of Mayiladuthurai district in Tamil Nadu, India. The town is located at a distance of from the state capital, Chennai.
Mayiladuthurai was ruled by Medie ...
(Tamil Nadu).
History
After independence, on 7 May 1961, theNational Institute of Sports
Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports, commonly known as National Institute of Sports (NIS), is the Academic Wing of the Sports Authority of India (SAI) and Asia's largest Sports Institute located in city of Patiala.
History
Founded on 7 ...
(NIS) was set up for the development of sports at the Motibagh Palace grounds in Patiala
Patiala () is a city in southeastern Punjab, northwestern India. It is the fourth largest city in the state and is the administrative capital of Patiala district. Patiala is located around the ''Qila Mubarak'' (the 'Fortunate Castle') construct ...
. On 23 January 1973, it was renamed Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports
Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports, commonly known as National Institute of Sports (NIS), is the Academic Wing of the Sports Authority of India (SAI) and Asia's largest Sports Institute located in city of Patiala.
History
Founded on ...
(NSNIS).
The Sports Authority of India originated with the committee formed to host the 1982 Asian Games in New Delhi
New Delhi (, , ''Naī Dillī'') is the capital of India and a part of the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, Parliament Hous ...
. On 25 January 1984, "Sports Authority of India" was established as a registered society by the "Department of Sports"" of Government of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
's Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
The Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports is a branch of the Government of India which administers the Department of youth affairs and the Department of Sports in India. Anurag Thakur is the current Minister of Youth Affairs and Sports followed ...
. On 1 May 1987, the "Society for National Institute of Physical Education and Sports" (SNIPES) was merged with SAI, and as a result, the Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports
Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports, commonly known as National Institute of Sports (NIS), is the Academic Wing of the Sports Authority of India (SAI) and Asia's largest Sports Institute located in city of Patiala.
History
Founded on ...
(NSNIS) at Patiala and its allied centres at Bhopal
Bhopal (; ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes'' due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It i ...
, Bangalore
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
and Gandhinagar
Gandhinagar (, ) is the capital of the state of Gujarat in India. Gandhinagar is located approximately 23 km north of Ahmedabad, on the west central point of the Industrial corridor between Delhi, the political capital of India, and Mum ...
and the Lakshmibai National College of Physical Education
Lakshmibai National College of Physical Education (LNCPE) is part of the academic wing of the Sports Authority of India, and is situated at Kariavattom, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India. It was founded on 17 August 1985 under the auspices of ...
at Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populati ...
also came under SAI. The Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports
Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports, commonly known as National Institute of Sports (NIS), is the Academic Wing of the Sports Authority of India (SAI) and Asia's largest Sports Institute located in city of Patiala.
History
Founded on ...
at Patiala
Patiala () is a city in southeastern Punjab, northwestern India. It is the fourth largest city in the state and is the administrative capital of Patiala district. Patiala is located around the ''Qila Mubarak'' (the 'Fortunate Castle') construct ...
and the Lakshmibai National University of Physical Education
The Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE), formerly Lakshmibai National University of Physical Education, is a higher education institute deemed-to-be-university, located in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, India. Under the aegis ...
at Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populati ...
became its academic wings. In 1995, Lakshmibai National University of Physical Education
The Lakshmibai National Institute of Physical Education (LNIPE), formerly Lakshmibai National University of Physical Education, is a higher education institute deemed-to-be-university, located in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, India. Under the aegis ...
at Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the s ...
became a separate " Deemed University."
SAI Regional Centres (SRC)s
Clockwise from north: * SAI Netaji Subhas Regional Centre, Chandigarh, Punjab * SAI Chaudhary Devi Lal Northern Regional Centre, Sonepat,Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ...
* SAI Netaji Subhas Regional Centre, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
* SAI Netaji Subhas North-East Regional Centre, Guwahati, Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
* SAI Netaji Subhas North-East Regional Centre, Imphal, Manipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of ...
* SAI Netaji Subhas Eastern Centre, Kolkata, West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
* SAI Udhav Das Mehta Bhaiji Central Centre, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
* SAI Netaji Subhas Southern Centre, Bengaluru, Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO 15919, ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reor ...
* SAI Regional Centre, Mumbai, Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India and the second-most populous country subdi ...
* SAI Netaji Subhas Western Centre, Gandhinagar, Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
SAI Academies

 SAI runs following two academic institutes that run graduate and post-graduate courses in sports medicine, sports and physical education to prepare coaches and allied sports support staff.SAi Academic courses
SAI runs following two academic institutes that run graduate and post-graduate courses in sports medicine, sports and physical education to prepare coaches and allied sports support staff.SAi Academic courses*
Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports
Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports, commonly known as National Institute of Sports (NIS), is the Academic Wing of the Sports Authority of India (SAI) and Asia's largest Sports Institute located in city of Patiala.
History
Founded on ...
(NSNIS) at Patiala
:** Refresher Courses
:** Certificate Course in Sports Coaching
A sports coach is a person coaching in sport, involved in the direction, instruction and training of a sports team or athlete.
History
The original sense of the word ''coach'' is that of a horse-drawn carriage, deriving ultimately from the Hung ...
via SAI Regional Centres (SRC)s
:** Diploma in Sports Coaching
:** Post-graduate Diploma Course in Sports medicine
Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. Although most sports teams have employed team physicians for many years, it is only since the ...
:** Master's degree in Sports Coaching
* Lakshmibai National College of Physical Education
Lakshmibai National College of Physical Education (LNCPE) is part of the academic wing of the Sports Authority of India, and is situated at Kariavattom, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India. It was founded on 17 August 1985 under the auspices of ...
(LNCPE) at Thiruvananthapuram
:** Bachelor of Physical Education
A Bachelor of Physical Education (BPE or BPhEd) is a bachelor degree granted by some universities. In many Canadian universities it has been replaced by a Bachelor of Kinesiology. The degree can include topics such as sport science, coaching, and ...
(BPE)
:** Master of Physical Education The Master of Physical Education (M.P.Ed or MPhEd) is a postgraduate academic degree in physical education awarded by universities.
Specialization
Sports Specialization curriculum.
* Athletics
* Gymnastics
* Team Game
* Individual game
See also
* ...
(MPE)
:** Doctor of Philosophy
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: or ') is the most common degree at the highest academic level awarded following a course of study. PhDs are awarded for programs across the whole breadth of academic fields. Because it is ...
(PhD) Regular and Part-time
Sports Sciences and Sports Medicine
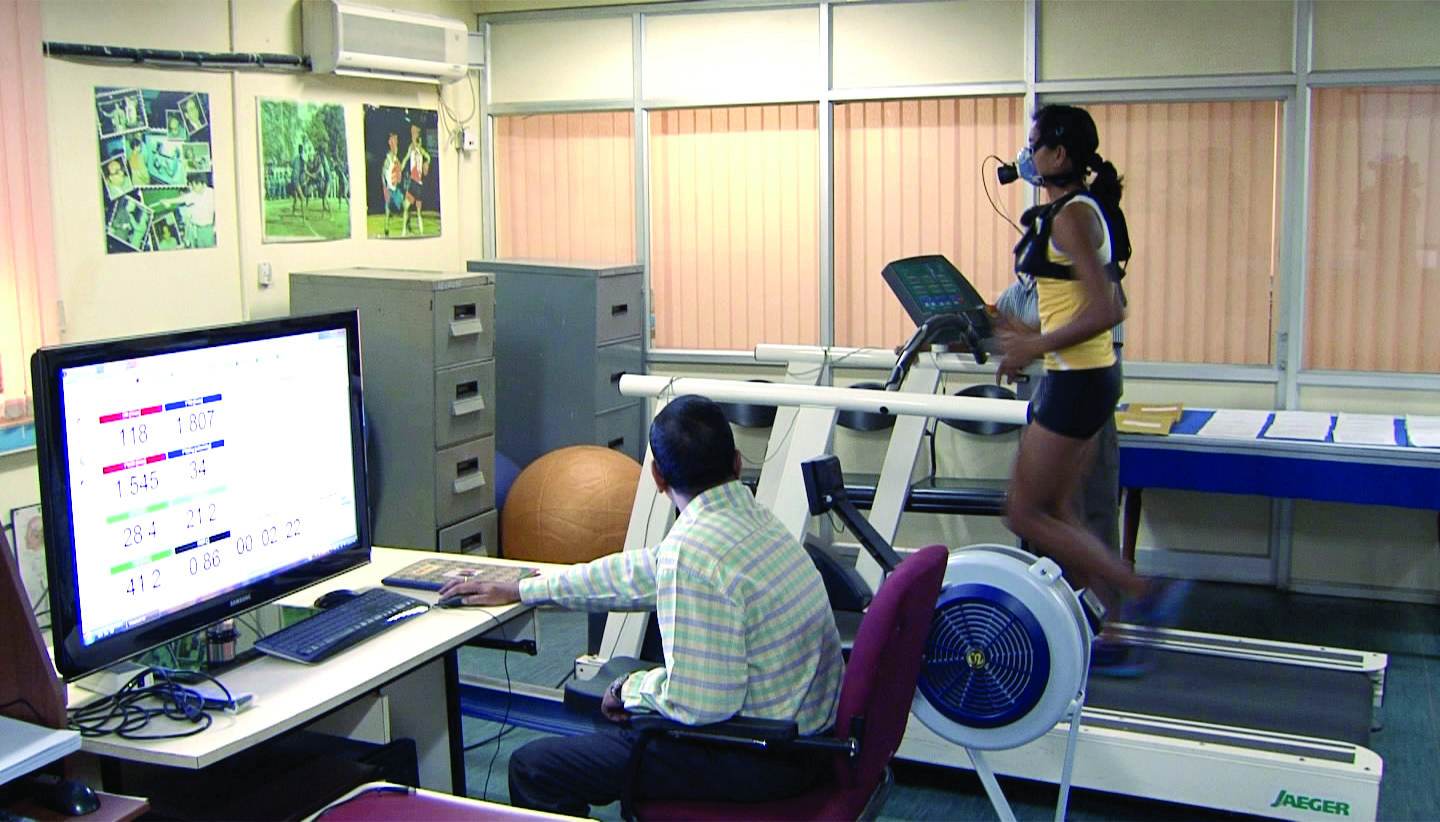
 In 1983, a "Department of Sports Science" was established at "NSNIS Patiala". From 1987 to 1990, "Sports science centres" with "Human Performance Lab" were set up at 4 regional centres in Delhi, Bengaluru, Kolkata and Gandhinagar; basic sports science support staff scheme was implemented for National Athletes; and SAI schemes for children was introduced at various regional centres.
Sports scientists from the fields of
In 1983, a "Department of Sports Science" was established at "NSNIS Patiala". From 1987 to 1990, "Sports science centres" with "Human Performance Lab" were set up at 4 regional centres in Delhi, Bengaluru, Kolkata and Gandhinagar; basic sports science support staff scheme was implemented for National Athletes; and SAI schemes for children was introduced at various regional centres.
Sports scientists from the fields of anthropometry
Anthropometry () refers to the measurement of the human individual. An early tool of physical anthropology, it has been used for identification, for the purposes of understanding human physical variation, in paleoanthropology and in various atte ...
, sports biomechanics, sports nutrition, sport psychology
Sport psychology was defined by the European Federation of Sport in 1996, as the study of the psychological basis, processes, and effects of sport. Otherwise, sport is considered as any physical activity where the individuals engage for competi ...
, sports physiology, physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patie ...
, and physical education
Physical education, often abbreviated to Phys Ed. or P.E., is a subject taught in schools around the world. It is usually taught during primary and secondary education, and encourages psychomotor learning by using a play and movement explorat ...
(GTMT) undertake the research work to improve the performance of sportsperson in competitions. SAI has technical and research collaboration with various reputed Indian and foreign sports science and medical institutes. Doctors, physiotherapists, psychologists, nutritionists, coaches and experts from these friends are also deployed at SAI academies, regional centres, sports training centres and centre of excellences. SPARRC institute and Indian Institute of Sports Medicine recognized by Indian Government aim to provide non-invasive procedures for sorts injuries with advanced research in sports science.
Training of Elite Athlete Management Support (Teams) Division
 This is the backbone of SAI which provides support to the National Sports Federations (NSFs) in the preparation of National Teams which participate in various International events. The TEAMS Division coordinates the Long Term Development Plan of each NSF; provides logistics and training support at various academic institutions and other Regional Centres of SAI and also at selected training centres outside SAI. The TEAMS Division draws most of its funding under the Scheme of “Assistance to National Sports Federations” from Sports Ministry. The TEAMS Division also provides support to the NSFs in the hiring of foreign coaches and selection of the national coach for each NSF, who are responsible for the training of core probables for the National teams.
With active support from TEAMS Division, good results have been achieved in the international arena in the disciplines of Badminton, Judo, Shooting, Archery, Athletics, Weightlifting, Wrestling, Wushu, Boxing and Billiards & Snooker.
Under this Scheme of “Assistance to National Sports Federations”, financial assistance is provided to recognised NSFs for training and participation of teams in international events abroad, organisation of national and international tournaments in India, coaching and training of national teams under Indian and foreign coaches with requisite technical and scientific support, procurement of equipment etc.
This is the backbone of SAI which provides support to the National Sports Federations (NSFs) in the preparation of National Teams which participate in various International events. The TEAMS Division coordinates the Long Term Development Plan of each NSF; provides logistics and training support at various academic institutions and other Regional Centres of SAI and also at selected training centres outside SAI. The TEAMS Division draws most of its funding under the Scheme of “Assistance to National Sports Federations” from Sports Ministry. The TEAMS Division also provides support to the NSFs in the hiring of foreign coaches and selection of the national coach for each NSF, who are responsible for the training of core probables for the National teams.
With active support from TEAMS Division, good results have been achieved in the international arena in the disciplines of Badminton, Judo, Shooting, Archery, Athletics, Weightlifting, Wrestling, Wushu, Boxing and Billiards & Snooker.
Under this Scheme of “Assistance to National Sports Federations”, financial assistance is provided to recognised NSFs for training and participation of teams in international events abroad, organisation of national and international tournaments in India, coaching and training of national teams under Indian and foreign coaches with requisite technical and scientific support, procurement of equipment etc.
Engagement of Foreign Coaches and Experts
It is SAI's constant endeavor to engage expert foreign coaches on short term and long-term basis to train and coach national coaching campers and also to facilitate knowledge exchange with Indian coaches.National Coaching Camps
In a year, SAI organises a number of national coaching camps in different disciplines in SAI centres and other centres for preparation of Indian teams for various national and international tournaments.Long Term Development Plan (LTDP)
SAI Long Term Development Plan ( SAI LTDP) aims at the joint preparation of long term sports-specific development plans by National Sports governing bodies and federations of India (NSFs) based on a four-year cycle with yearly review. The plans cover all aspects of sports including development of sportsperson, coaching, participation, promotion, tournament schedule, hosting of major events and sports sciences.Operations Division
Different sports promotion schemes of SAI, aimed at spotting and nurturing talent are being implemented and monitored through the networks of SAI centres. SAI Schemes:SAI Sports Promotional Schemes
The Sports Authority of India conducts various activities and schemes to promote sports in India. they include:(i) National Sports Talent Contest Scheme (NSTC)
SAI National Sports Talent Contest Scheme (SAI NSTC) provides the school environment to play and study for talented 8-14 year olds who are at the right age for higher level training in competitive sports. The selection of trainees is done on the basis of performance and potential, and they are admitted to schools on a non-residential basis. The main objectives of the scheme are to: • Identify educational institutions having good sports infrastructure • Scientifically scout for optimum-aged talent • Convert the genetically and physiologically gifted children into future champions • Ensure availability of trained coaches • Ensure financial assistance for consumables • Provide adequate competition exposure and sports equipment to sports institutes andAkhara
Akhara or Akhada ( Sanskrit and Hindi: अखाड़ा, shortened to ''khara'' Hindi: खाड़ा) is an Indian word for a place of practice with facilities for boarding, lodging and training, both in the context of Indian martial artist ...
s to create a broader base for modern wrestling
The disciplines covered under SAI NSTC are
* 14 Regular schools with 11 disciplines namely Athletics, Basketball, Football, Gymnastics, Hockey, Kho-Kho, Kabaddi, Swimming, Table Tennis, Volleyball and Wrestling.
* 10 Indigenous Games & Martial Arts (IGMA) with 9 disciplines, namely, Archery, Kabaddi, Kalaripayatu, Mukna, Thang-Ta, Silambam, Khomlainai, Malkhamb & Gatka.
* Akhara
Akhara or Akhada ( Sanskrit and Hindi: अखाड़ा, shortened to ''khara'' Hindi: खाड़ा) is an Indian word for a place of practice with facilities for boarding, lodging and training, both in the context of Indian martial artist ...
s for wrestling
(ii) Army Boys Sports Company (ABSC)
SAI Army Boys Sports Company (SAI ABSC) is a scheme run in collaboration with theIndian Army
The Indian Army is the Land warfare, land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Arm ...
to nurture and groom talented boys in the age group of 8 to 14 years. These companies act as virtual sports schools where training is scientifically backed up and support facility is provided throughout the training period. The trainees are entitled to an assured career in the Armed Forces at 17½ years. The selection of trainees is done on the basis of performance and potential assessed through a battery of tests. Objectives of this scheme include:
* Nurturing budding talent
* Improving the achievements tally in international sports competitions
* Using the Army's excellent infrastructure and disciplined administrative environment
(iii) SAI Training Centers Scheme (STC)
file:SAINSA-Swimming_Academy.jpg, "SAI National Swimming Academy" (SAINSA) atSPM Swimming Pool Complex
The Dr. S. P. Mukherjee Swimming Stadium or SPM Swimming Pool Complex is a swimming complex in New Delhi, India, that is hosting the aquatics events for the 2010 Commonwealth Games. The stadium is owned by the Sports Authority of India (SAI).
...
in Delhi.
SAI Training Centre Scheme (SAI STC) was created in 1995 by merging "Sports Project Development Area Centres" (SPDA) and "Sports Hostel Scheme". It is run collaboration with the State Government and Union Territory Administrations. The trainees are admitted into the scheme on residential and non-residential basis where they are funded by the government. The main objectives of the scheme are to:
* Train talented young sportspersons aged 12–18 years (Sub-Junior/Junior)
* Identify those who have attained advanced levels of proficiency in sports.
* Identify those who show natural potential in the Olympic disciplines, indigenous and other sports.
* Provide in-house coaching, training and nutritional support to sportspersons.
(iv) Special Area Games Scheme (SAG)
SAI Special Area Games (SAI SAG) are similar to STC, except that the focus of the SAG Centres is on popular indigenous sports of India bu spotting and nurturing talent in specific disciplines in tribal, coastal and hilly areas, to grooms them to achieve excellence in the related modern competitive games and sports. The SAG Centres are fully funded by SAI, and land is to be provided by the respective State Governments or other institutions such as universities and schools. "Special Area Games" (SAG) are located at (clockwise from north):(v) Extension Centres of STCs/SAGs
SAI Extension Centres of STCs/SAG (SAI ESTC/ESAG) scheme commenced in 2005 to develop sports in schools, colleges and universities having commendable sporting performance and adequate infrastructure. The Extension Centres are monitored by the nearest STC or SAG and Regional Centre Head for their adherence to SAI regulations. Authority to approve these Extension Centres lies with theDirector general
A director general or director-general (plural: ''directors general'', ''directors-general'', ''director generals'' or ''director-generals''
) or general director is a senior executive officer, often the chief executive officer, within a government ...
of SAI.
(vi) Centres of Excellence (CoE)
SAI Centres of Excellence (SAI CoE) identify and train the talented sportspersons in the age group of 12–25 years who have shown promise at the sub-junior, junior and senior National Sports Competitions for 330 days in a year. "Centre of Excellences" (COE/COX) have a total of nearly 600 trainees in 18 sports (2014 figure), such asarchery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In ...
, athletics
Athletics may refer to:
Sports
* Sport of athletics, a collection of sporting events that involve competitive running, jumping, throwing, and walking
** Track and field, a sub-category of the above sport
* Athletics (physical culture), competi ...
, boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
, cycling
Cycling, also, when on a two-wheeled bicycle, called bicycling or biking, is the use of cycles for transport, recreation, exercise or sport. People engaged in cycling are referred to as "cyclists", "bicyclists", or "bikers". Apart from ...
, fencing
Fencing is a group of three related combat sports. The three disciplines in modern fencing are the foil, the épée, and the sabre (also ''saber''); winning points are made through the weapon's contact with an opponent. A fourth discipline, ...
, gymnastics
Gymnastics is a type of sport that includes physical exercises requiring balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination, dedication and endurance. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, s ...
, hockey
Hockey is a term used to denote a family of various types of both summer and winter team sports which originated on either an outdoor field, sheet of ice, or dry floor such as in a gymnasium. While these sports vary in specific rules, numbers o ...
, judo
is an unarmed modern Japanese martial art, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyclopedia Nipponica, "Judo") ...
, kabaddi
Kabaddi is a contact team sport. Played between two teams of seven players, the objective of the game is for a single player on offence, referred to as a "raider", to run into the opposing team's half of the court, touch out as many of their ...
, kayaking
Kayaking is the use of a kayak for moving over water. It is distinguished from canoeing by the sitting position of the paddler and the number of blades on the paddle. A kayak is a low-to-the-water, canoe-like boat in which the paddler sits faci ...
and canoeing
Canoeing is an activity which involves paddling a canoe with a single-bladed paddle. Common meanings of the term are limited to when the canoeing is the central purpose of the activity. Broader meanings include when it is combined with other act ...
, rowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically ...
, swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
, table tennis
Table tennis, also known as ping-pong and whiff-whaff, is a sport in which two or four players hit a lightweight ball, also known as the ping-pong ball, back and forth across a table using small solid rackets. It takes place on a hard table div ...
, taekwondo
''Taekwondo'', ''Tae Kwon Do'' or ''Taekwon-Do'' (; ko, 태권도/跆拳道 ) is a Korean martial arts, Korean form of martial arts involving punching and kicking techniques, with emphasis on head-height kicks, spinning jump kicks, and fast k ...
, volleyball
Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules. It has been a part of the official program of the Sum ...
, weightlifting
Weightlifting generally refers to activities in which people lift weights, often in the form of dumbbells or barbells. People lift various kinds of weights for a variety of different reasons. These may include various types of competition; pro ...
, wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat s ...
, and wushu.
COE are located at (clockwise from north):
(vii) Come and Play Scheme
SAI Come and Play Scheme (SAI CPS) serves the purpose of talent scouting. Meritorious talent emerging from this scheme forms a pool for induction into regular residential and non-residential sports promotional schemes of STC and SAG. The scheme was introduced in May 2011 for optimum utilisation of its 5 stadia in Delhi by throwing open the designated areas in the SAI Stadia for community sports. After this scheme received an excellent public response by registering to use the sports facilities in Delhi in disciplines such as Badminton, Boxing, Basketball, Cricket, Cycling, Football, Hockey, Gymnastics, Judo, Shooting, Swimming, Table Tennis, Volleyball, Weightlifting and Wrestling, SAI then extended this scheme to all centres of SAI across India to encourage the youth in the local areas to use sports facilities available at these centres. SAI participated in 2015-16 Calcutta Premier League with a team named SAI Darjeeling.See also
* Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award * * List of sports events in India * * Sports in AsiaExternal links
Sportal
Sports Portal by the Government of India
Sports Authority of India official site
Lakshmibai National College of Physical Education official website
Netaji Subhas National Institute of Sports official website
References
{{India topics Sports governing bodies in India Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports Organisations based in Delhi Sports organizations established in 1984 1984 establishments in Delhi