The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a
colonial empire
A colonial empire is a collective of territories (often called colonies), either contiguous with the imperial center or located overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.
Before the expansion of early mode ...
governed by Spain and its
predecessor states
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th- ...
between 1492 and 1976.
One of the
largest empires in history, it was, in conjunction with the
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the ...
, the first to usher the European
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafa ...
and achieve a global scale,
controlling vast portions of the Americas, territories in Western Europe], Africa, and various islands in
Spanish East Indies, Asia and
Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
. It was one of the most powerful empires of the
early modern period, becoming the first empire known as "
the empire on which the sun never sets
The phrase "the empire on which the sun never sets" ( es, el imperio donde nunca se pone el sol) was used to describe certain global empires that were so extensive that it seemed as though it was always daytime in at least one part of its territ ...
",
and reached its maximum extent in the 18th century.
An important element in the formation of Spain's empire was the
dynastic union between
Isabella I of Castile and
Ferdinand II of Aragon in 1469, known as the
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being bot ...
, which initiated political, religious and social cohesion but not political unification.
Castile (formed in 1230 from the
Kingdom of Leon and the
Kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias ( la, Asturum Regnum; ast, Reinu d'Asturies) was a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula founded by the Visigothic nobleman Pelagius. It was the first Christian political entity established after the Umayyad conquest of ...
) became the dominant kingdom in Iberia because of its jurisdiction over the overseas empire in the Americas. The structure of the empire was further defined under the
Spanish Habsburgs
Habsburg Spain is a contemporary historiographical term referring to the huge extent of territories (including modern-day Spain, a piece of south-east France, eventually Portugal, and many other lands outside of the Iberian Peninsula) ruled b ...
(1516–1700), and under the
Spanish Bourbon monarchs, the empire was brought under greater crown control and increased its revenues from the Indies. The crown's authority in the Indies was enlarged by the papal grant of
powers of patronage, giving it power in the religious sphere.
In the beginning, Portugal was the only serious threat to Spanish hegemony in the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
. To end the threat of Portuguese expansion, Spain invaded its Iberian neighbour in 1580, defeating Portuguese, French, and English forces. After the Spanish victory in the
War of the Portuguese Succession, Philip II of Spain obtained the Portuguese crown in 1581, and Portugal and its overseas territories came under his rule with the so-called
Iberian Union
pt, União Ibérica
, conventional_long_name =Iberian Union
, common_name =
, year_start = 1580
, date_start = 25 August
, life_span = 1580–1640
, event_start = War of the Portuguese Succession
, event_end = Portuguese Restoration War
, ...
, considered by many historians as a Spanish conquest.
[Parker, Geoffrey. Philip II. The definitive biography. Planet. 2010. : "However, the rapid and complete conquest of all of Portugal is listed as one of the most impressive military feats of the 16th century." Page 728. "Ten days after learning of Enrique's death, Felipe took off his mask and signed orders for the mobilization of troops throughout Castile for the" Jornada de Portugal ". Page 721. "In May, Felipe traveled to Mérida (...) to review an impressive army of 20,000 Italian, German and Spanish infantrymen, 1,500 cavalrymen and 136 artillery pieces." Page 725. "The seventy-three-year-old Duke (of Alba) then fought one of the most successful campaigns of the sixteenth century." Page 726. «The viceroy of India proclaimed him king (Philip II) in Goa in September 1581, followed by other outposts of the Portuguese empire, creating the first global empire in history: from Madrid and through Lisbon, Madeira, Mexico, Manila, Macao and Malacca, to India, Mozambique, Angola, Guinea, Tangier, and again to Madrid. The fifteen triumphal arches erected for the king's entry into Lisbon in June 1581 reflected this unprecedented concentration of power. ' Page 730.][Thomas, Hugh. The lord of the world. Felipe II and his empire, 2013, Planeta, : «On June 13, Felipe realized that some military action might be necessary to win the Lisbon crown and mobilized an army of 20,000 infantrymen and 1,500 cavalry under the command of the now loaded but always ready Duke of Alba. In two weeks he ordered this force to enter Portugal. Despite his defeat in the Azores, Antonio de Crato had proclaimed himself king and, had Philip not intervened, he would certainly have ruled. The main cities of Setúbal, Santarém and even Lisbon had taken sides for him. He followed a military campaign of some importance. (...) The fight was greater than expected, but anyway it ended with the victory of the Duke of Alba. The battle of Alcántara culminated the rapid and triumphant military campaign. Then all Portugal passed to the dominion of Felipe, who was declared king on September 12, 1580. Don Antonio fled but was defeated again in Terceira, in the Azores ». Page 297.][Braudel, Fernand. The Mediterranean and the Mediterranean world in the time of Felipe II, Volume II, Edit. Fondo de Cultura Económica, second edition in Spanish, 1976, , pp. 713–716: «The war in Portugal, which was no more than a simple military walk, was developed according to plans. (...) It was the speed with which the Spaniards acted, and not the weakness attributed by some to the prior, that led to the failure of the suitor. For Portugal to be entirely occupied by the Spaniards, then, four months were enough. Upon receiving the news, the Portuguese Indies submitted in turn, without combat. The only serious difficulties arose in the Azores. (...) the Azores affair in the years 1582 and 1583, where the archipelago was saved and where, at the same time, with the Strozzi disaster, the dream of a French Brazil was dispelled; (...) ». The resistance in the Azores was put down by Álvaro de Bazán and his fleet.] Phillip respected a certain degree of autonomy in its Iberian territories and, together with the other peninsular councils, established the
Council of Portugal
The Council of Portugal, officially, the Royal and Supreme Council of Portugal (Portuguese: Real e Supremo Conselho de Portugal; Spanish: Real y Supremo Consejo de Portugal), was the ruling body and a key part of the government of the Kingdom ...
, which oversaw Portugal and its empire and "preserv
dits own laws, institutions, and monetary system, and united only in sharing a common sovereign." In 1640, while Spain was fighting in
Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
,
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, and the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Portugal
revolted
In political science, a revolution ( Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically d ...
and re-established its independence under the
House of Braganza
The Most Serene House of Braganza ( pt, Sereníssima Casa de Bragança), also known as the Brigantine Dynasty (''Dinastia Brigantina''), is a dynasty of emperors, kings, princes, and dukes of Portuguese origin which reigned in Europe and the Am ...
. Iberian kingdoms retained their political identities, with particular administration and juridical configurations. Although the power of the Spanish sovereign as monarch varied from one territory to another, the monarch acted as such in a unitary manner over all the ruler's territories through a
system of councils: the unity did not mean uniformity.
The Spanish empire also included European territories, of which the
Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands ( Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the ...
were the richest. Following the
Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
against France, which concluded in 1559, Spain gained control over half of Italy (
Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
,
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
,
Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
,
Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sin ...
) with the
Treaty of Cateau-Cambresis. These territories remained under Spanish rule until the
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
.
The Spanish empire in the Americas was formed after conquering indigenous people and
claiming large stretches of land, beginning with
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
in the
Caribbean Islands
Almost all of the Caribbean islands are in the Caribbean Sea, with only a few in inland lakes. The largest island is Cuba. Other sizable islands include Hispaniola, Jamaica, Puerto Rico and Trinidad and Tobago. Some of the smaller islands a ...
. In the 16th century, the Spanish empire conquered and incorporated the
Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
and
Inca
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, ( Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The adm ...
empires, retaining indigenous elites loyal to the Spanish crown and converts to Christianity as intermediaries between their communities and royal government. After a short period of delegation of authority by the crown in the Americas, the crown asserted control over those territories and established the
Council of the Indies to oversee rule there. The crown then established viceroyalties in the two main areas of settlement,
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the A ...
and
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, both regions of dense indigenous populations and mineral wealth. The
Mayans were
finally conquered in 1697. The
Magellan-Elcano circumnavigation—the first circumnavigation of the Earth—laid the foundation for the Pacific Oceanic empire of Spain and for Spanish control over the
East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around ...
.
The structure of governance of its overseas empire was significantly
reformed in the late 18th century by the Bourbon monarchs. Although the crown attempted to keep its empire a closed economic system under Habsburg rule, Spain was unable to supply the Indies with sufficient consumer goods to meet demand. This allowed foreign merchants from
Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
,
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, and the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
to take advantage of the trade, with silver from the mines of Peru and Mexico flowing to other parts of Europe. The
merchant guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
of Seville (later Cadiz) served as middlemen in the trade. The crown's trade monopoly was broken early in the 17th century, with the crown colluding with the merchant guild for fiscal reasons in circumventing the supposedly closed system.
[Lynch, ''Bourbon Spain'', pp. 10–11.] Spain was largely able to defend its territories in the Americas, with the
Dutch,
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, and
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
taking only small Caribbean islands and outposts, using them to engage in
contraband
Contraband (from Medieval French ''contrebande'' "smuggling") refers to any item that, relating to its nature, is illegal to be possessed or sold. It is used for goods that by their nature are considered too dangerous or offensive in the eyes o ...
trade with the Spanish populace in the Indies.
Spain experienced its greatest territorial losses during the early 19th century, when its colonies in the Americas began fighting their
wars of independence. By 1900, Spain had also lost its colonies in the Caribbean and Pacific, and it was left with only its African possessions. In Spanish America among the legacies of its relationship with Iberia, Spanish is the
dominant language, Catholicism the main religion, and political traditions of representative government can be traced to the
Spanish Constitution of 1812
The Political Constitution of the Spanish Monarchy ( es, link=no, Constitución Política de la Monarquía Española), also known as the Constitution of Cádiz ( es, link=no, Constitución de Cádiz) and as ''La Pepa'', was the first Constituti ...
.
Catholic Monarchs and origins of the empire
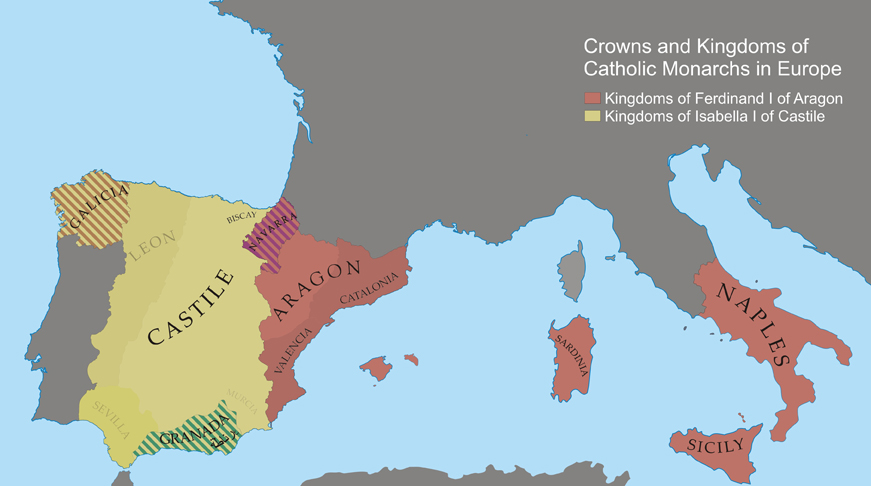
With the marriage of the heirs apparent to their respective thrones
Ferdinand of Aragon and
Isabella of Castile created a personal union that most scholars view as the foundation of the Spanish monarchy. The union of the Crowns of
Castile and
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to s ...
joined the economic and military power of Iberia under one dynasty, the
House of Trastamara. Their dynastic alliance was important for a number of reasons, ruling jointly over a number of kingdoms and other territories, mostly in the eastern mediterranean region, under their respective legal and administrative status. They successfully pursued expansion in Iberia in the Christian conquest of the Muslim
Emirate of Granada
)
, common_languages = Official language: Classical ArabicOther languages: Andalusi Arabic, Mozarabic, Berber, Ladino
, capital = Granada
, religion = Majority religion: Sunni IslamMinority religions:R ...
, completed in 1492, for which Valencia-born Pope
Alexander VI gave them the title of the
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being bot ...
. Ferdinand of Aragon was particularly concerned with expansion in France and Italy, as well as conquests in North Africa.
The concept of 'Early Modern Spain' as a subject of study is muddled. The composite monarchy of the Hapsburgs had no official name. In the Early Modern period, as a geographical (non-political) concept and following the medieval tradition, the term 'Spain' could refer to the entire Iberian Peninsula. The term 'Catholic Monarchy' (Spanish: ''Monarquía Católica'', already mentioned in a 1494 papal bull) was common during the reign of Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, insofar as the regime strived towards the realization of the idea of
universal (that is, ''Catholic'') monarchy. Later in time, other denominations such as 'Spanish Monarchy' (Spanish: ''Monarquía Española'') or 'Monarchy of Spain' (Spanish: ''Monarquía de España'', already mentioned in 1597) would also become common to refer to the composite monarchy. The official intitulation of the monarchs made no mention to monarchies nor crowns, but focused on the inherited kingdoms and other possessions.
With the Ottoman Turks controlling the choke points of the overland trade from Asia and the Middle East, both Spain and Portugal sought alternative routes. The
Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal ( la, Regnum Portugalliae, pt, Reino de Portugal) was a monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also kn ...
had an advantage over the
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accessi ...
, having earlier retaken territory from the Muslims. Following Portugal's earlier completion of the reconquest and its establishment of settled boundaries, it began to seek overseas expansion, first to the port of
Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territori ...
(1415) and then by colonizing the Atlantic islands of
Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
(1418) and the
Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
(1427–1452); it also began voyages down the west coast of Africa in the fifteenth century. Its rival Castile laid claim to the
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, :es:Canarias, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to ...
(1402) and retook territory from the Moors in 1462. The Christian rivals Castile and Portugal came to formal agreements over the division of new territories in the
Treaty of Alcaçovas (1479), as well as securing the crown of Castile for Isabella whose accession was challenged militarily by Portugal.
Following the voyage of
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
in 1492 and first major settlement in the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
in 1493, Portugal and Castile divided the world by the
Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Em ...
(1494), which gave Portugal Africa and Asia and the Western Hemisphere to Spain.
[Burkholder, Mark A. "Spanish Empire" in ] The voyage of Columbus, a
Genoese mariner, obtained the support of Isabella of Castile, sailing west in 1492, seeking a route to the Indies. Columbus unexpectedly encountered the western hemisphere, populated by peoples he named "Indians". Subsequent voyages and full-scale settlements of Spaniards followed, with gold beginning to flow into Castile's coffers. Managing the expanding empire became an administrative issue. The reign of Ferdinand and Isabella began the professionalization of the apparatus of government in Spain, which led to a demand for men of letters (''letrados'') who were university graduates (''licenciados''), of
Salamanca
Salamanca () is a city in western Spain and is the capital of the Province of Salamanca in the autonomous community of Castile and León. The city lies on several rolling hills by the Tormes River. Its Old City was declared a UNESCO World Herit ...
,
Valladolid
Valladolid () is a municipality in Spain and the primary seat of government and de facto capital of the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. It has a population around 300,000 peop ...
,
Complutense and
Alcalá. These lawyer-bureaucrats staffed the various councils of state, eventually including the
Council of the Indies and
Casa de Contratación, the two highest bodies in metropolitan Spain for the government of the empire in the New World, as well as royal government in The Indies.
Early expansion
Fall of Granada

During the last 250 years of the
Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the N ...
era, the Castilian monarchy tolerated the small Moorish ''
taifa
The ''taifas'' (singular ''taifa'', from ar, طائفة ''ṭā'ifa'', plural طوائف ''ṭawā'if'', a party, band or faction) were the independent Muslim principalities and kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula (modern Portugal and Spain), re ...
'' client-kingdom of Granada in the south-east by exacting tributes of gold—the ''
parias
In medieval Spain, ''parias'' (from medieval Latin ''pariāre'', "to make equal n account, i.e. pay) were a form of tribute paid by the ''taifas'' of al-Andalus to the Christian kingdoms of the north. ''Parias'' dominated relations between the ...
.'' In so doing, they ensured that gold from the
Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages[Queen Isabella I
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as Queen consort of Aragon from 1479 until 1504 by ...](_blank)
captured Granada in 1492, they implemented policies to maintain control of the territory. To do so, the monarchy implemented a system of encomienda.
Encomienda
The ''encomienda'' () was a Spanish labour system that rewarded conquerors with the labour of conquered non-Christian peoples. The labourers, in theory, were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they laboured, including military ...
was a method of land control and distribution based upon vassalic ties. Land would be granted to a noble family, who were then responsible for farming and defending it. This eventually led to a large land based aristocracy, a separate ruling class that the crown later tried to eliminate in its overseas colonies. By implementing this method of political organization, the crown was able to implement new forms of private property without completely replacing already existing systems, such as the communal use of resources. After the military and political conquest, there was an emphasis on religious conquest as well, leading to the creation of the
Spanish Inquisition
The Tribunal of the Holy Office of the Inquisition ( es, Tribunal del Santo Oficio de la Inquisición), commonly known as the Spanish Inquisition ( es, Inquisición española), was established in 1478 by the Catholic Monarchs, King Ferdinand ...
. Although the Inquisition was technically a part of the Catholic church, Ferdinand and Isabella formed a separate Spanish Inquisition, which led to mass expulsion of Muslims and Jews from the peninsula. This religious court system was later adopted and transported to the Americas, though they took a less effective role there due to limited jurisdiction and large territories.
Campaigns in North Africa
With the Christian reconquest completed in the Iberian peninsula, Spain began trying to take territory in Muslim North Africa. It had conquered
Melilla
Melilla ( , ; ; rif, Mřič ; ar, مليلية ) is an autonomous city of Spain located in north Africa. It lies on the eastern side of the Cape Three Forks, bordering Morocco and facing the Mediterranean Sea. It has an area of . It was pa ...
in 1497, and further expansionism policy in North Africa was developed during the regency of Ferdinand the Catholic in Castile, stimulated by the
Cardinal Cisneros
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**'' Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, th ...
. Several towns and outposts in the North African coast were conquered and occupied by Castile:
Mazalquivir (1505),
Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera
(; ) is a Spanish exclave and rocky tied island, in the western Mediterranean Sea, connected to the Moroccan shore by a sandy isthmus. It is also connected to a smaller islet to the east, La Isleta, by a rocky isthmus. The tied island was name ...
(1508),
Oran
Oran ( ar, وَهران, Wahrān) is a major coastal city located in the north-west of Algeria. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria after the capital Algiers, due to its population and commercial, industrial, and cultural ...
(1509),
Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
,
Bougie and
Tripoli (1510).
Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques d ...
was forced to pay tribute to Castile until
Ottoman intervention. On the Atlantic coast, Spain took possession of the outpost of
Santa Cruz de la Mar Pequeña (1476) with support from the
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, :es:Canarias, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to ...
, and it was retained until 1525 with the consent of the treaty of Cintra (1509).
Navarre and struggles for Italy

The Catholic Monarchs had developed a strategy of marriages for their children to isolate their long-time enemy: France. The Spanish princesses married the heirs of Portugal, England and the
House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. Following the same strategy, the Catholic Monarchs decided to support the Aragonese house of
Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
against
Charles VIII of France
Charles VIII, called the Affable (french: l'Affable; 30 June 1470 – 7 April 1498), was King of France from 1483 to his death in 1498. He succeeded his father Louis XI at the age of 13.Paul Murray Kendall, ''Louis XI: The Universal Spider'' (New ...
in the
Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
beginning in 1494. Ferdinand's general
Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba
Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba (1 September 1453 – 2 December 1515) was a Spanish general and statesman who led successful military campaigns during the Conquest of Granada and the Italian Wars. His military victories and widespread p ...
took over Naples after defeating the French at the
Battle of Cerignola
The Battle of Cerignola was fought on 28 April 1503 between Spanish and French armies outside the town of Cerignola, Apulia, Kingdom of Naples (now in modern-day Italy), approximately west of Bari.
The Spanish force under the command of G ...
and the
Battle of Garigliano in 1503. In these battles, which established the supremacy of the
Spanish Tercios in European battlefields, the forces of the kings of Spain acquired a reputation for invincibility that would last until the 1643
Battle of Rocroi
The Battle of Rocroi, fought on 19 May 1643, was a major engagement of the Thirty Years' War between a French army, led by the 21-year-old Duke of Enghien (later known as the Great Condé) and Spanish forces under General Francisco de Melo ...
.
After the death of Queen Isabella in 1504, and her exclusion of Ferdinand from a further role in Castile, Ferdinand married
Germaine de Foix
Ursula Germaine of Foix (french: Ursule-Germaine de Foix; ca, Úrsula Germana de Foix; ; c. 1488 – 15 October 1536) was an early modern French noblewoman from the House of Foix. By marriage to King Ferdinand II of Aragon, she was Queen of Ar ...
in 1505, cementing an alliance with France. Had that couple had a surviving heir, probably the
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of ...
would have been split from Castile, which was inherited by Charles, Ferdinand and Isabella's grandson. Ferdinand joined the
League of Cambrai against
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
in 1508. In 1511, he became part of the
Holy League against France, seeing a chance at taking both
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
—to which he held a dynastic claim—and
Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
. In 1516, France agreed to a truce that left Milan in its control and recognized Spanish control of
Upper Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
, which had effectively been a Spanish protectorate following a series of treaties in 1488, 1491, 1493, and 1495.
Canary Islands

Portugal obtained several
Papal bulls that acknowledged Portuguese control over the discovered territories, but Castile also obtained from the Pope the safeguard of its rights to the
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, :es:Canarias, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to ...
with the bulls ''Romani Pontifex'' dated 6 November 1436 and ''Dominatur Dominus'' dated 30 April 1437. The
conquest of the Canary Islands
The conquest of the Canary Islands by the Crown of Castille took place between 1402 and 1496 and described as the first instance of European settler colonialism in Africa. It can be divided into two periods: the Conquista señorial, carried out ...
, inhabited by
Guanche people, began in 1402 during the reign of
Henry III of Castile, by
Norman nobleman
Jean de Béthencourt
Jean de Béthencourt () (1362–1425) was a French explorer who in 1402 led an expedition to the Canary Islands, landing first on the north side of Lanzarote. From there he conquered for Castile the islands of Fuerteventura (1405) and El ...
under a feudal agreement with the crown. The conquest was completed with the campaigns of the armies of the
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accessi ...
between 1478 and 1496, when the islands of
Gran Canaria
Gran Canaria (, ; ), also Grand Canary Island, is the third-largest and second-most-populous island of the Canary Islands, an archipelago off the Atlantic coast of Northwest Africa which is part of Spain. the island had a population of that ...
(1478–1483), La Palma (1492–1493), and
Tenerife
Tenerife (; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands. It is home to 43% of the total population of the Archipelago, archipelago. With a land area of and a population of 978,100 inhabitant ...
(1494–1496) were subjugated.
Rivalry with Portugal
The Portuguese tried in vain to keep secret their discovery of the Gold Coast (1471) in the
Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is i ...
, but the news quickly caused a huge gold rush. Chronicler
Pulgar wrote that the fame of the treasures of Guinea "spread around the ports of
Andalusia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The ...
in such way that everybody tried to go there". Worthless trinkets, Moorish textiles, and above all, shells from the
Canary
Canary originally referred to the island of Gran Canaria on the west coast of Africa, and the group of surrounding islands (the Canary Islands). It may also refer to:
Animals Birds
* Canaries, birds in the genera '' Serinus'' and ''Crithagra'' ...
and
Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
islands were exchanged for gold, slaves, ivory and Guinea pepper.
The
War of the Castilian Succession (1475–79) provided the Catholic Monarchs with the opportunity not only to attack the main source of the Portuguese power, but also to take possession of this lucrative commerce. The Crown officially organized this trade with Guinea: every caravel had to secure a government license and to pay a tax on one-fifth of their profits (a receiver of the customs of Guinea was established in
Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
in 1475—the ancestor of the future and famous
Casa de Contratación).

Castilian fleets fought in the Atlantic Ocean, temporarily occupying the
Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
islands (1476), conquering the city of
Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territori ...
in the
Tingitan Peninsula
The Tingitan Peninsula, also known as the Tangier Peninsula, is a small peninsula in northwest Africa, which together with the southernmost part of mainland Spain (Iberian Peninsula), forms the Strait of Gibraltar, the Atlantic Ocean boundary with ...
in 1476 (but retaken by the Portuguese), and even attacked the
Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
islands, being defeated at
Praia
Praia (, Portuguese for "beach") is the capital and largest city of Cape Verde.[Gran Canaria
Gran Canaria (, ; ), also Grand Canary Island, is the third-largest and second-most-populous island of the Canary Islands, an archipelago off the Atlantic coast of Northwest Africa which is part of Spain. the island had a population of that ...]
lost men and ships to the Portuguese who expelled the attack, and a large Castilian armada—full of gold—was entirely captured in the decisive
Battle of Guinea
The Battle of Guinea took place on the Gulf of Guinea, in western Africa, 1478, between a Portuguese fleet and a Castilian fleet in the context of the War of the Castilian Succession.
The outcome of the battle of Guinea was decisive for Portu ...
.
The
Treaty of Alcáçovas
The Treaty of Alcáçovas (also known as Treaty or Peace of Alcáçovas-Toledo) was signed on 4 September 1479 between the Catholic Monarchs of Castile and Aragon on one side and Afonso V and his son, Prince John of Portugal, on the other side ...
(4 September 1479), while assuring the Castilian throne to the Catholic Monarchs, reflected the Castilian naval and colonial defeat: "War with Castile broke out waged savagely in the Gulf
f Guineauntil the Castilian fleet of thirty-five sail was defeated there in 1478. As a result of this naval victory, at the Treaty of Alcáçovas in 1479 Castile, while retaining her rights in the
Canaries, recognized the Portuguese monopoly of fishing and navigation along the whole west African coast and Portugal's rights over the
Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
,
Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
and
Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
islands
lus_the_right_to_conquer_the_Kingdom_of_Fez_.html" ;"title="Kingdom_of_Fez.html" ;"title="lus the right to conquer the Kingdom of Fez">lus the right to conquer the Kingdom of Fez ">Kingdom_of_Fez.html" ;"title="lus the right to conquer the Kingdom of Fez">lus the right to conquer the Kingdom of Fez " The treaty delimited the spheres of influence of the two countries, establishing the principle of the Mare clausum. It was confirmed in 1481 by the Pope Sixtus IV, in the papal bull Aeterni regis, ''Æterni regis'' (dated on 21 June 1481).
However, this experience would prove to be profitable for future Spanish overseas expansion, because as the Spaniards were excluded from the lands discovered or to be discovered from the Canaries southward—and consequently from the
road to India around Africa—they sponsored the voyage of Columbus towards the west (1492) in search of Asia to trade in its
spices
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices are ...
, encountering
the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
instead. Thus, the limitations imposed by the Alcáçovas treaty were overcome and a new and more balanced division of the world would be reached in the
Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Em ...
between both emerging maritime powers.
New World voyages and Treaty of Tordesillas


Seven months before the treaty of Alcaçovas, King
John II of Aragon died, and his son
Ferdinand II of Aragon, married to
Isabella I of Castile, inherited the thrones of the
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of ...
. The two became known as the
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being bot ...
, with their marriage a
personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
that created a relationship between the Crown of Aragon and Castile, each with their own administrations, but ruled jointly by the two monarchs.
Ferdinand and Isabella defeated the last Muslim king out of Granada in 1492 after a
ten-year war. The Catholic Monarchs then negotiated with
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
, a
Genoese sailor attempting to reach
Cipangu
The word ''Japan'' is an exonym, and is used (in one form or another) by many languages. The Japanese names for Japan are Nippon () and Nihon (). They are both written in Japanese using the kanji .
During the third-century CE Three Kingdoms peri ...
(Japan) by sailing west. Castile was already engaged in a
race of exploration with Portugal to reach the Far East by sea when Columbus made his bold proposal to Isabella. In the
Capitulations of Santa Fe
The Capitulations of Santa Fe between Christopher Columbus and the Catholic Monarchs, Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, were signed in Santa Fe, Granada on April 17, 1492. They granted Columbus the titles of admiral of ...
, dated on 17 April 1492, Christopher Columbus obtained from the Catholic Monarchs his appointment as viceroy and governor in the lands ''already discovered'' and that he might discover thenceforth; thereby, it was the first document to establish an administrative organization in the Indies. Columbus' discoveries began the
Spanish colonization of the Americas
Spain began colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish . The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions ...
. Spain's claim to these lands was solidified by the ''
Inter caetera''
papal bull dated 4 May 1493, and ''
Dudum siquidem
''Dudum siquidem'' (Latin for "A short while ago") is a papal bull issued by Pope Alexander VI Borgia on , one of the Bulls of Donation addressed to the Catholic Monarchs Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon which supplemented ...
'' on 26 September 1493, which vested the sovereignty of the territories discovered and to be discovered.
Since the Portuguese wanted to keep the line of demarcation of Alcaçovas running east and west along a latitude south of
Cape Bojador
Cape Bojador ( ar, رأس بوجادور, trans. ''Rā's Būjādūr''; ber, ⴱⵓⵊⴷⵓⵔ, ''Bujdur''; Spanish and pt, Cabo Bojador; french: Cap Boujdour) is a headland on the west coast of Western Sahara, at 26° 07' 37"N, 14° 29' 57"W ...
, a compromise was worked out and incorporated in the
Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Em ...
, dated on 7 June 1494, in which the globe was split into two hemispheres dividing Spanish and Portuguese claims. These actions gave Spain exclusive rights to establish colonies in all of the New World from north to south (later with the exception of Brazil, which Portuguese commander
Pedro Alvares Cabral encountered in 1500), as well as the easternmost parts of Asia. The treaty of Tordesillas was confirmed by
Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II ( la, Iulius II; it, Giulio II; born Giuliano della Rovere; 5 December 144321 February 1513) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 1503 to his death in February 1513. Nicknamed the Warrior Pope or the ...
in the bull ''Ea quae pro bono pacis'' on 24 January 1506.
The treaty of Tordesillas and the treaty of Cintra (18 September 1509) established the limits of the Kingdom of Fez for Portugal, and the Castilian expansion was allowed outside these limits, beginning with the
conquest of Melilla in 1497.
In 1494, Columbus launched the
transatlantic slave trade, sending at least twenty-four enslaved
Taíno
The Taíno were a historic Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the ...
s to Spain.
Papal Bulls and the Americas

Unlike the crown of Portugal, Spain had not sought papal authorization for its explorations, but with Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492, the crown sought papal confirmation of their title to the new lands.
[John F. O'Callaghan, "Line of Demarcation," in ] Since the defense of Catholicism and propagation of the faith was the papacy's primary responsibility, there were a number of papal bulls promulgated that affected the powers of the crowns of Spain and Portugal in the religious sphere. Converting the inhabitants of in the newly discovered lands was entrusted by the papacy to the rulers of Portugal and Spain, through a series of papal actions. The
Patronato real
The ''patronato'' () system in Spain (and a similar '' padroado'' system in Portugal) was the expression of royal patronage controlling major appointments of Church officials and the management of Church revenues, under terms of concordats with ...
, or power of royal patronage for ecclesiastical positions had precedents in Iberia during the
reconquest. In 1493
Pope Alexander, from the Iberian
Kingdom of Valencia
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
, issued a series of bulls. The papal bull of
Inter caetera vested the government and jurisdiction of newly found lands in the kings of Castile and León and their successors. ''Eximiae devotionis sinceritas'' granted the Catholic monarchs and their successors the same rights that the papacy had granted Portugal, in particular the right of presentation of candidates for ecclesiastical positions in the newly discovered territories.
[Nelson H. Minnich, "Papacy" and John F. O'Callaghan, "Line of Demarcation," in
*
* ]
According to the Concord of Segovia of 1475, Ferdinand was mentioned in the bulls as king of Castile, and upon his death the title of the Indies was to be incorporated into the Crown of Castile.
The territories were incorporated by the Catholic Monarchs as jointly held assets.
[
*
* ]

In the
Treaty of Villafáfila
The Treaty of Villafáfila is a treaty signed by Ferdinand the Catholic in Villafáfila on 27 June 1506 and by Philip the Handsome in Benavente, Zamora, on 28 June.
The treaty recognised the incapacity of Ferdinand's daughter and Philip's wife, ...
of 1506, Ferdinand renounced not only the government of Castile in favor of his son-in-law
Philip I of Castile
Philip the Handsome, es, Felipe, french: Philippe, nl, Filips (22 July 1478 – 25 September 1506), also called the Fair, was ruler of the Burgundian Netherlands and titular Duke of Burgundy from 1482 to 1506, as well as the first Habsburg K ...
but also the lordship of the Indies, withholding a half of the income of the ''kingdoms of the Indies''.
Joanna of Castile
Joanna (6 November 1479 – 12 April 1555), historically known as Joanna the Mad ( es, link=no, Juana la Loca), was the nominal Queen of Castile from 1504 and Queen of Aragon from 1516 to her death in 1555. She was married by arrangement to P ...
and Philip immediately added to their
titles the kingdoms of Indies, Islands and Mainland of the Ocean Sea. But the Treaty of Villafáfila did not hold for long because of the death of Philip; Ferdinand returned as regent of Castile and as "lord the Indies".
According to the domain granted by Papal bulls and the wills of queen Isabella of Castile in 1504 and king Ferdinand of Aragon in 1516, such property became held by the Crown of Castile. This arrangement was ratified by successive monarchs, beginning with Charles I in 1519
in a decree that spelled out the juridical status of the new overseas territories.
The lordship of the discovered territories conveyed by papal bulls was private to the kings of Castile and León. The political condition of the Indies were to transform from "''Lordship''" of the Catholic Monarchs to "''Kingdoms''" for the heirs of Castile. Although the Alexandrine Bulls gave full, free and omnipotent power to the Catholic Monarchs,
they did not rule them as a private property but as a public property through the public bodies and authorities from Castile, and when those territories were incorporated into the Crown of Castile the royal power was subject to the laws of Castile.
The crown was the guardian of levies for the support of the Catholic Church, in particular the tithe, which was levied on the products of agriculture and ranching. In general, Indians were exempt from the tithe. Although the crown received these revenues, they were to be used for the direct support of the ecclesiastical hierarchy and pious establishments, so that the crown itself did not benefit financially from this income. The crown's obligation to support the Church sometimes resulted in funds from the royal treasury being transferred to the Church when the tithes fell short of paying ecclesiastical expenses.
In
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the A ...
, the Franciscan Bishop of Mexico
Juan de Zumárraga
Juan de Zumárraga, OFM (1468 – June 3, 1548) was a Spanish Basque Franciscan prelate and the first Bishop of Mexico. He was also the region's first inquisitor. He wrote ''Doctrina breve'', the first book published in the Western Hemisph ...
and the first viceroy Don
Antonio de Mendoza established an institution in 1536 to train natives for ordination to the priesthood, the
Colegio de Santa Cruz de Tlatelolco. The experiment was deemed a failure, with the natives considered too new in the faith to be ordained.
Pope Paul III
Pope Paul III ( la, Paulus III; it, Paolo III; 29 February 1468 – 10 November 1549), born Alessandro Farnese, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 October 1534 to his death in November 1549.
He came to ...
did issue a bull,
Sublimis Deus (1537), declaring that natives were capable of becoming Christians, but Mexican (1555) and Peruvian (1567–68) provincial councils banned natives from ordination.
North American exploration

During the 1500s, the Spanish began to explore and colonize North America. They were looking for gold in native kingdoms. By 1511 there were rumours of undiscovered lands to the northwest of Hispaniola. Juan Ponce de León equipped three ships with at least 200 men at his own expense and set out from Puerto Rico on 4 March 1513 to Florida and surrounding coastal area. Another early motive was the search for the
Seven Cities of Gold
The myth of the Seven Cities of Gold, also known as the Seven Cities of Cibola (), was popular in the 16th century and later featured in several works of popular culture. According to legend, the seven cities of gold referred to Aztec mythology r ...
, or "Cibola", rumoured to have been built by Native Americans somewhere in the desert Southwest. In 1536
Francisco de Ulloa
Francisco de Ulloa () (died 1540) was a Spanish explorer who explored the west coast of present-day Mexico and the Baja California Peninsula under the commission of Hernán Cortés. Ulloa's voyage was among the first to disprove the cartograph ...
, the first documented European to reach the
Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. s ...
, sailed up the
Gulf of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja C ...
and a short distance into the river's delta.
In the year 1524 the Portuguese
Estevão Gomes, who'd sailed in
Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
's fleet, explored
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
, sailing South through
Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and nor ...
, where he entered
New York Harbor
New York Harbor is at the mouth of the Hudson River where it empties into New York Bay near the East River tidal estuary, and then into the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast of the United States. It is one of the largest natural harbors in ...
, the
Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
and eventually reached Florida in August 1525.
The Spaniard
Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca was the leader of the Narváez expedition of 600 men, that between 1527 and 1535 explored the mainland of North America. From Tampa Bay, Florida on 15 April 1528, they marched through Florida. Traveling mostly on foot, they crossed Texas, New Mexico and Arizona, and Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Nuevo León and Coahuila. After several months of fighting native inhabitants through wilderness and swamp, the party reached Apalachee Bay with 242 men. They believed they were near other Spaniards in Mexico, but there was in fact 1500 miles of coast between them. They followed the coast westward, until they reached the mouth of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest Drainage system (geomorphology), drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson B ...
near to
Galveston Island. Later they were enslaved for a few years by various Native American tribes of the upper Gulf Coast. They continued through Coahuila and Nueva Vizcaya; then down the Gulf of California coast to what is now Sinaloa, Mexico, over a period of roughly eight years. They spent years enslaved by the Ananarivo of the Louisiana Gulf Islands. Later they were enslaved by the Hans, the Capoques and others. In 1534 they escaped into the American interior, contacting other Native American tribes along the way. Only four men, Cabeza de Vaca,
Andrés Dorantes de Carranza,
Alonso del Castillo Maldonado, and an enslaved Moroccan Berber named
Estevanico
Estevanico ("Little Stephen"; modern spelling Estebanico; –1539), also known as Esteban de Dorantes or Mustafa Azemmouri (مصطفى الزموري), was the first African to explore North America.
Estevanico first appears as a slave in Portu ...
, survived and escaped to reach Mexico City. In 1539, Estevanico was one of four men who accompanied
Marcos de Niza
Marcos de Niza, OFM (or Marco da Nizza; 25 March 1558) was a Savoyard missionary and Franciscan friar from the County of Nice. He is credited with being the first European in what is now the State of Arizona in the United States. He is most kn ...
as a guide in search of the fabled Seven Cities of Cibola, preceding Coronado. When the others were struck ill, Estevanico continued alone, opening up what is now
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
and
Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
. He was killed at the Zuni village of Hawikuh in present-day New Mexico.
The viceroy of New Spain
Antonio de Mendoza, for who is named the
Codex Mendoza
The Codex Mendoza is an Aztec codex, believed to have been created around the year 1541. It contains a history of both the Aztec rulers and their conquests as well as a description of the daily life of pre-conquest Aztec society. The codex is wri ...
, commissioned several expeditions to explore and establish settlements in the northern lands of New Spain in 1540–42.
Francisco Vásquez de Coronado
Francisco is the Spanish and Portuguese form of the masculine given name '' Franciscus''.
Nicknames
In Spanish, people with the name Francisco are sometimes nicknamed " Paco". San Francisco de Asís was known as ''Pater Comunitatis'' (father o ...
reached
Quivira in central
Kansas
Kansas () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its Capital city, capital is Topeka, Kansas, Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita, Kansas, Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebras ...
.
Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo
Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo ( pt, João Rodrigues Cabrilho; c. 1499 – January 3, 1543) was an Iberian maritime explorer best known for investigations of the West Coast of North America, undertaken on behalf of the Spanish Empire. He was the firs ...
explored the western coastline of
Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
in 1542–43.
Francisco Vásquez de Coronado's 1540–42 expedition began as a search for the fabled Cities of Gold, but after learning from natives in New Mexico of a large river to the west, he sent
García López de Cárdenas
García López de Cárdenas y Figueroa was a Spanish conquistador who was the first European to see the Grand Canyon.
Life
Cárdenas was born in Llerena, Crown of Castile, second son to Alonso de Cárdenas, 1st Count of La Puebla del Maestre, ...
to lead a small contingent to find it. With the guidance of Hopi Indians, Cárdenas and his men became the first outsiders to see the
Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon (, yuf-x-yav, Wi:kaʼi:la, , Southern Paiute language: Paxa’uipi, ) is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a m ...
. However, Cárdenas was reportedly unimpressed with the canyon, assuming the width of the Colorado River at six feet (1.8 m) and estimating 300-foot (91 m)-tall rock formations to be the size of a man. After unsuccessfully attempting to descend to the river, they left the area, defeated by the difficult terrain and torrid weather.
In 1540,
Hernando de Alarcón
Hernando de Alarcón (born 1500) was a Spanish explorer and navigator of the 16th century, noted for having led an early expedition to the Baja California Peninsula, during which he became one of the first Europeans to ascend the Colorado River ...
and his fleet reached the mouth of the Colorado River, intending to provide additional supplies to Coronado's expedition. Alarcón may have sailed the Colorado as far upstream as the present-day California–Arizona border. However, Coronado never reached the Gulf of California, and Alarcón eventually gave up and left.
Melchior Díaz reached the delta in the same year, intending to establish contact with Alarcón, but the latter was already gone by the time of Díaz's arrival. Díaz named the Colorado River Rio del Tizon, while the name Colorado ("Red River") was first applied to a tributary of the
Gila River
The Gila River (; O'odham ima Keli Akimel or simply Akimel, Quechan: Haa Siʼil, Maricopa language: Xiil) is a tributary of the Colorado River flowing through New Mexico and Arizona in the United States. The river drains an arid watershed of ...
.
In 1540, expeditions under Hernando de Alarcon and Melchior Diaz visited the area of Yuma and immediately saw the natural crossing of the Colorado River from Mexico to California by land, as an ideal spot for a city, as the Colorado River narrows to slightly under 1000 feet wide in one small point. Later military expedition that crossed the Colorado River at the
Yuma Crossing include
Juan Bautista de Anza
Juan Bautista de Anza Bezerra Nieto (July 6 or 7, 1736 – December 19, 1788) was an expeditionary leader, military officer, and politician primarily in California and New Mexico under the Spanish Empire. He is credited as one of the founding f ...
(1774).
In 1541,
Hernando De Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and ''conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire ...
became the first explorer to cross the Mississippi River. During this expedition, the Spanish fought
Utina tribesmen in Florida,
Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classif ...
s in Mississippi, the
Coosa chiefdom
The Coosa chiefdom was a powerful Native American paramount chiefdom in what are now Gordon and Murray counties in Georgia, in the United States.[Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...]
, and Chief
Tuskaloosa at the
Battle of Mabila
Mabila (also spelled Mavila, Mavilla, Maubila, or Mauvilla, as influenced by Spanish or French transliterations) was a small fortress town known to the paramount chief Tuskaloosa in 1540, in a region of present-day central Alabama. The exact loca ...
in present-day
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = " Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,7 ...
.
The
Chamuscado and Rodríguez Expedition The Chamuscado and Rodríguez Expedition visited the land on what became present day New Mexico in 1581-1582. The expedition was led by Francisco Sánchez, called "El Chamuscado," and Fray Agustín Rodríguez, the first Spaniards known to have visi ...
explored New Mexico in 1581–82. They explored a part of the route visited by Coronado in New Mexico and other parts in the
southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, N ...
between 1540 and 1542.
The viceroy of New Spain
Don Diego García Sarmiento sent another expedition in 1648 to explore, conquer and colonize
the Californias
The Californias ( Spanish: ''Las Californias''), occasionally known as The Three Californias or Two Californias, are a region of North America spanning the United States and Mexico, consisting of the U.S. state of California and the Mexican s ...
.
First settlements in the Americas



With the
Capitulations of Santa Fe
The Capitulations of Santa Fe between Christopher Columbus and the Catholic Monarchs, Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, were signed in Santa Fe, Granada on April 17, 1492. They granted Columbus the titles of admiral of ...
, the
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accessi ...
granted expansive power to
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
, including exploration, settlement, political power, and revenues, with sovereignty reserved to the Crown. The first voyage established sovereignty for the crown, and the crown acted on the assumption that Columbus's grandiose assessment of what he found was true, so Spain negotiated the
Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Em ...
with Portugal to protect their territory on the Spanish side of the line. The crown fairly quickly reassessed its relationship with Columbus and moved to assert more direct crown control over the territory and extinguish his privileges. With that lesson learned, the crown was far more prudent in the specifying the terms of exploration, conquest, and settlement in new areas.
The pattern in the Caribbean that played out over the larger Spanish Indies was exploration of an unknown area and claim of sovereignty for the crown; conquest of indigenous peoples or assumption of control without direct violence; settlement by Spaniards who were awarded the labour of indigenous people via the
encomienda
The ''encomienda'' () was a Spanish labour system that rewarded conquerors with the labour of conquered non-Christian peoples. The labourers, in theory, were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they laboured, including military ...
; and the existing settlements becoming the launch point for further exploration, conquest, and settlement, followed by the establishment institutions with officials appointed by the crown. The patterns set in the Caribbean were replicated throughout the expanding Spanish sphere, so although the importance of the Caribbean quickly faded after the
Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico or the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the eve ...
and the
Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, many of those participating in those conquests had started their exploits in the Caribbean.
The first permanent European settlements in the New World were established in the Caribbean, initially on the island of
Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
, later Cuba,
Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispa ...
and Puerto Rico. As a Genoese with the connections to Portugal, Columbus considered settlement to be on the pattern of trading forts and factories, with salaried employees to trade with locals and to identify exploitable resources. However, Spanish settlement in the New World was based on a pattern of a large, permanent settlements with the entire complex of institutions and material life to replicate Castilian life in a different venue. Columbus's second voyage in 1493 had a large contingent of settlers and goods to accomplish that. Columbus established the fort of
La Navidad in present-day Haiti; it was later destroyed by the Taínos and the Spanish garrison was wiped out.
On Hispaniola, the city of
Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total
, population_density_km2 = auto
, timezone = AST (UTC −4)
, area_code_type = Area codes
, area_code = 809, 829, 849
, postal_code_type = Postal codes
, postal_code = 10100–10699 ( Distrito Nacional)
, webs ...
was founded in 1496 by Christopher Columbus's brother
Bartholomew Columbus
Bartholomew Columbus ( lij, label= Genoese, Bertomê Corombo; pt, Bartolomeu Colombo; es, Bartolomé Colón; it, Bartolomeo Colombo; – 1515) was an Italian explorer from Genoa and the younger brother of Christopher Columbus.
Biography
Bo ...
and became a stone-built, permanent city. Non-
Castilians
Castilians (Spanish: ''castellanos'') are those people who live in certain former areas of the historical Kingdom of Castile, but the region's exact limits are disputed. A broader definition is to consider as Castilians the population belonging ...
such as
Catalans
Catalans (Catalan, French and Occitan: ''catalans''; es, catalanes, Italian: ''catalani'', sc, cadelanos) are a Romance ethnic group native to Catalonia, who speak Catalan. The current official category of "Catalans" is that of the citize ...
and
Aragonese were often forbidden to migrate to the New World. In 1508, the crown's attention shifted from Hispaniola to Cuba, where a major expedition was launched in 1511 under the leadership of
Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar
Diego Velázquez de CuéllarPronounced: (1465 – c. June 12, 1524) was a Spanish conquistador and the first governor of Cuba. In 1511 he led the successful conquest and colonization of Cuba. As the first governor of the island, he establi ...
. The invading Castilians slaughtered thousands of
Taíno
The Taíno were a historic Indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the ...
Indians. By 1515, the conquest of Cuba was complete.
Some scholars have described the initial period of the Spanish conquest of America, from 1492 until the mid 16th century, as the largest case of genocide in history, with millions of
indigenous people
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
dying from imported Eurasia diseases that travelled more quickly than the Spanish conquerors.
The death toll is estimated as high as 70 million out of a population of 80 million during this period. Diseases killed between 50% and 95% of the indigenous population.
Some scholars attribute the vast majority of indigenous deaths due to the low immunological capacity of native populations to resist exogenous diseases.
Assertion of Crown control in the Americas
Although Columbus staunchly asserted and believed that the lands he encountered were in Asia, the paucity of material wealth and the relative lack of complexity of indigenous society meant that the
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval polity in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and, some decades later, the parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accessi ...
initially was not concerned with the extensive powers granted Columbus. As the Caribbean became a draw for Spanish settlement and as Columbus and his extended Genoese family failed to be recognized as officials worthy of the titles they held, there was unrest among Spanish settlers. The crown began to curtail the expansive powers that they had granted Columbus, first by appointment of royal governors and then a high court or
Audiencia in 1511.
Columbus encountered the mainland in 1498, and the Catholic Monarchs learned of his discovery in May 1499. Taking advantage of a revolt against Columbus in
Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
, they appointed
Francisco de Bobadilla
Francisco Fernández de Bobadilla (c. 1448 – 1 July 1502) was an official under the Crown of Castile and a knight of the Order of Calatrava. He was also the brother of Beatriz de Bobadilla, marchioness (''marquesa'') of Moya and of Peñalosa ...
as governor of the Indies with civil and criminal jurisdiction over the lands discovered by Columbus. Bobadilla, however, was soon replaced by Frey
Nicolás de Ovando
Frey Nicolás de Ovando y Cáceres (1460 – 29 May 1511 or 1518) was a Spanish soldier from a noble family and a Knight of the Order of Alcántara, a military order of Spain. He was Governor of the Indies ( Hispaniola) from 1502 until 1509, s ...
in September 1501. Henceforth, the Crown would authorize to individuals voyages to discover territories in the Indies only with previous royal license, and after 1503 the monopoly of the Crown was assured by the establishment of the ''
Casa de Contratación'' (House of Trade) at Seville. The successors of Columbus, however, litigated against the Crown until 1536 for the fulfillment of the Capitulations of Santa Fe in the ''
pleitos colombinos
The ''Pleitos colombinos'' ("Colombian lawsuits") were a long series of lawsuits that the heirs of Christopher Columbus brought against the Crown of Castile and León in defense of the privileges obtained by Columbus for his discoveries in the N ...
''.
In
metropolitan
Metropolitan may refer to:
* Metropolitan area, a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories
* Metropolitan borough, a form of local government district in England
* Metropolitan county, a typ ...
Spain, the direction of the Americas was taken over by the Bishop
Fonseca between 1493 and 1516, and again between 1518 and 1524, after a brief period of rule by
Jean le Sauvage. After 1504 the figure of the secretary was added, so between 1504 and 1507 Gaspar de Gricio took charge, between 1508 and 1518
Lope de Conchillos followed him, and from 1519,
Francisco de los Cobos
Francisco de los Cobos y Molina (c. 1477 – 10 May 1547) was the secretary of State and ''Comendador'' for the kingdom of Castile under the rule of the Emperor Charles I of Spain.
Biographical data
He was born in Úbeda ca. 1477 and died on ...
.
In 1511, the
Junta
Junta may refer to:
Government and military
* Junta (governing body) (from Spanish), the name of various historical and current governments and governing institutions, including civil ones
** Military junta, one form of junta, government led by a ...
of The Indies was constituted as a standing committee belonging to the
Council of Castile
The Council of Castile ( es, Real y Supremo Consejo de Castilla), known earlier as the Royal Council ( es, Consejo Real), was a ruling body and key part of the domestic government of the Crown of Castile, second only to the monarch himself. It ...
to address issues of the Indies, and this ''junta'' constituted the origin of the
Council of the Indies, established in 1524. That same year, the crown established a permanent high court, or ''
audiencia'', in the most important city at the time, Santo Domingo, on the island of
Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
(now Haiti and the Dominican Republic). Now oversight of the Indies was based both in Castile and with officials of the new royal court in the colony. As new areas were conquered and significant Spanish settlements were established, likewise other audiencias were established.
Following the settlement of Hispaniola, Europeans began searching elsewhere to begin new settlements, since there was little apparent wealth and the numbers of indigenous were declining. Those from the less prosperous Hispaniola were eager to search for new success in a new settlement. From there
Juan Ponce de León
Juan Ponce de León (, , , ; 1474 – July 1521) was a Spanish explorer and ''conquistador'' known for leading the first official European expedition to Florida and for serving as the first governor of Puerto Rico. He was born in Santerv� ...
conquered
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
(1508) and
Diego Velázquez
Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velázquez (baptized June 6, 1599August 6, 1660) was a Spanish painter, the leading artist in the court of King Philip IV of Spain and Portugal, and of the Spanish Golden Age. He was an individualistic artist of th ...
took
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
.
In 1508, the Board of Navigators met in Burgos and concurred on the need to establish settlements on the mainland, a project entrusted to
Alonso de Ojeda and
Diego de Nicuesa as governors. They were subordinated to the governor of Hispaniola, the newly appointed
Diego Columbus, with the same legal authority as Ovando.
The first settlement on the mainland was
Santa María la Antigua del Darién in
Castilla de Oro
Castilla de Oro or del Oro () was the name given by the Spanish settlers at the beginning of the 16th century to the Central American territories from the Gulf of Urabá, near today's Colombian-Panamanian border, to the Belén River. Beyond th ...
(now
Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the coun ...
,
Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
,
Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
and
Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
), settled by
Vasco Núñez de Balboa in 1510. In 1513, Balboa crossed the
Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama ( es, Istmo de Panamá), also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien (), is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the country ...
, and led the first European expedition to see the Pacific Ocean from the West coast of the New World. In an action with enduring historical import, Balboa claimed the Pacific Ocean and all the lands adjoining it for the Spanish Crown.
The judgment of Seville of May 1511 recognized the viceregal title to Diego Columbus, but limited it to Hispaniola and to the islands discovered by his father, Christopher Columbus; his power was nevertheless limited by royal officers and magistrates constituting a dual regime of government. The crown separated the territories of the mainland, designated as
Castilla de Oro
Castilla de Oro or del Oro () was the name given by the Spanish settlers at the beginning of the 16th century to the Central American territories from the Gulf of Urabá, near today's Colombian-Panamanian border, to the Belén River. Beyond th ...
, from the viceroy of Hispaniola, establishing
Pedrarias Dávila as General Lieutenant in 1513 with functions similar to those of a viceroy, while Balboa remained but was subordinated as governor of Panama and
Coiba on the Pacific Coast; after his death, they returned to ''Castilla de Oro''. The territory of ''Castilla de Oro'' did not include
Veragua (which was comprised approximately between the
Chagres River and
cape Gracias a Dios), as it was subject to a lawsuit between the Crown and Diego Columbus, or the region farther north, towards the Yucatán peninsula, explored by
Yáñez Pinzón and
Solís in 1508–1509, due to its remoteness. The conflicts of the viceroy Columbus with the royal officers and with the ''
Audiencia'', created in Santo Domingo in 1511, caused his return to the
Peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on a ...
in 1515.
The Spanish Habsburgs (1516–1700)

As a result of the marriage politics of the
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being bot ...
(in Spanish, '), their
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
grandson
Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was " ...
inherited the Castilian empire in America and the possessions of the
Crown of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of ...
in the Mediterranean (including all of
south Italy), lands in Germany, the
Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, Franche-Comté, and Austria, starting the Spanish Habsburgs rule in Spain. The latter and the rest of the hereditary Habsburg domains were transferred to
Ferdinand, the Emperor's brother, whereas Spain and the remaining possessions were inherited by Charles's son,
Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
, at the abdication of the former in 1556.
The Habsburgs pursued several goals:
* Undermining the power of France and containing it in its eastern borders
* Defending Europe against
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
, notably the
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
in the
Ottoman–Habsburg wars
The Ottoman–Habsburg wars were fought from the 16th through the 18th centuries between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy, which was at times supported by the Kingdom of Hungary, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and Habsburg Spai ...
* Maintaining
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over oth ...
in the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
and defending the
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
against the
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
* Spreading (Catholic) Christianity to the unconverted indigenous of the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
and the Philippines
* Exploiting the resources of the Americas (gold, silver, sugar) and trading with Asia (
porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
, spices, silk)
* Excluding other European powers from the possessions it claimed in the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
"I learnt a proverb here", said a French traveler in 1603: "Everything is dear in Spain except silver". The problems caused by inflation were discussed by scholars at the
School of Salamanca and the ''
arbitrista {{italicize title
The '' arbitristas'' were a group of reformist thinkers in late 16th and 17th century Spain concerned about the decline of the economy of Spain and proposed a number of measures to reverse it. ''Arbitristas'' directed analyses of p ...
s''. The natural resource abundance provoked a decline in entrepreneurship as profits from resource extraction are less risky. The wealthy preferred to invest their fortunes in
public debt (''juros''). The Habsburg dynasty spent the Castilian and American riches in
wars across Europe on behalf of Habsburg interests, and declared moratoriums (bankruptcies) on their debt payments several times. These burdens led to a number of revolts across the Spanish Habsburg's domains, including their Spanish kingdoms, but the rebellions were put down.
Imperial economic policy


The Spanish Empire benefited from favorable
factor endowments
A factor endowment, in economics, is commonly understood to be the amount of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship that a country possesses and can exploit for manufacturing. Countries with a large endowment of resources tend to be more prosp ...
in its overseas possessions with their large, exploitable, indigenous populations and rich mining areas.
Given that, the crown attempted to create and maintain a classic closed
mercantile system
Mercantilism is an economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports for an economy. It promotes imperialism, colonialism, tariffs and subsidies on traded goods to achieve that goal. The policy aims to reduce a ...
, warding off competitors and keeping wealth within the empire. While the Habsburgs were committed to maintaining a state monopoly in theory, in reality the Empire was a porous economic realm and smuggling was widespread. In the 16th and 17th century under the Habsburgs, Spain experienced a gradual decline in economic conditions, especially relative to the industrial development of its French, Dutch, and English rivals. Many of the goods being exported to the Empire originated from manufacturers in northwest Europe, rather than in Spain. But illicit commercial activities became a part of the Empire's administrative structure. Supported by large flows of silver from America, trade prohibited by Spanish mercantilist trade restrictions flourished, because it provided a source of income to both crown officials and private merchants. The local administrative structure in
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, for example, was established through its oversight of both legal and illegal commerce. The crown's pursuit of wars to maintain and expand territory, defend the Catholic faith and stamp out Protestantism, and beat back Ottoman Turkish strength outstripped its ability to pay for it all, despite the huge production of silver in Peru and Mexico. Most of that flow paid mercenary soldiers in the European religious wars in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries and into foreign merchants' hands to pay for the consumer goods manufactured in northern Europe. Paradoxically the wealth of the Indies impoverished Spain and enriched northern Europe, a course the Bourbon monarchs would later attempt to reverse in the eighteenth century.
This was well recognized in Spain, with writers on political economy, the ''
arbitristas'' sending the crown lengthy analyses in the form of "memorials, of the perceived problems and with proposed solutions." According to these thinkers, "Royal expenditure must be regulated, the sale of office halted, the growth of the church checked. The tax system must be overhauled, special concessions be made to agricultural laborers, rivers be made navigable and dry lands irrigated. In this way alone could Castile's productivity increased, its commerce restored, and its humiliating dependence on foreigners, on the Dutch and the Genoese, be brought to an end."
From the early days of the Caribbean and conquest era, the crown attempted to control trade between Spain and the Indies with restrictive policies enforced by the House of Trade (est. 1503) in Seville. Shipping was through particular ports in Spain (Seville, subsequently Cadiz), Spanish America (Veracruz, Acapulco, Havana, Cartagena de Indias, and Callao/Lima) and the Philippines (Manila). Spanish settlers in the Indies in the very early period were few and Spain could supply sufficient goods to them. But as the Aztec and Inca empires were conquered in the early sixteenth century and then large deposits of silver found in both Mexico and Peru, the regions of those major empires, Spanish immigration increased and demand for goods rose far beyond Spain's ability to supply it. Since Spain had little capital to invest in the expanding trade and no significant commercial group, bankers and commercial houses in Genoa, Germany, The Netherlands, France, and England supplied both investment capital and goods in a supposedly closed system. Even in the sixteenth century, Spain recognized that the idealized closed system did not function in reality. Despite that the crown did not alter its restrictive structure or advocacy of fiscal prudence, despite the pleas of the ''arbitristas'', the Indies trade remained nominally in the hands of Spain, but in fact enriched the other European countries.

The crown established the system of
treasure fleets ( es, link=no, flota) to protect the conveyance of silver to Seville (later Cadiz). Merchants in Seville conveyed consumer goods that were registered and taxed by the House of Trade were sent to the Indies were produced in other European countries. Other European commercial interests came to dominate supply, with Spanish merchant houses and their guilds (''
consulados'') in Spain and the Indies acting as mere middlemen, reaping profits a slice of the profits. However, those profits did not promote Spanish economic development of a manufacturing sector, with its economy continuing to be based on agriculture. The wealth of the Indies led to prosperity in northern Europe, particularly The Netherlands and England, both Protestant. As Spain's power weakened in the seventeenth century, England, The Netherlands, and the French took advantage overseas by seizing islands in the Caribbean, which became bases for a burgeoning contraband trade in Spanish America. Crown officials who were supposed to suppress contraband trade were quite often in cahoots with the foreigners, since it was a source of personal enrichment. In Spain, the crown itself participated in collusion with foreign merchant houses, since they paid fines, "meant to establish a compensation to the state for losses through fraud." it became for merchant houses a calculated risk for doing business; for the crown it gained income it would have lost otherwise. Foreigner merchants were part of the supposed monopoly system of trade. The transfer of the House of Trade from Seville to Cadiz meant even easier access of foreign merchant houses to the Spanish trade.
The motor of the Spanish imperial economy that had a
global impact was
silver mining
Silver mining is the extraction of silver from minerals, starting with mining. Because silver is often found in intimate combination with other metals, its extraction requires elaborate technologies. In 2008, ca.25,900 metric tons were consumed ...
. The mines in
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
and Mexico were in the hands of a few elite mining entrepreneurs, with access to capital and a stomach for the risk mining entailed. They operated under a system of royal licensing, since the crown held the rights to subsoil wealth. Mining entrepreneurs assumed all the risk of the enterprise, while the crown gained a 20% slice of the profits, the
royal fifth
The royal fifth ( Spanish and pt, quinto real / quinto del rey) is an old royal tax that reserves to the monarch 20% of all precious metals and other commodities (including slaves) acquired by his subjects as war loot, found as treasure or extr ...
("Quinto"). Further adding to the crown's revenues was mining was that it crown held a monopoly on the supply of mercury, used for separating pure silver from silver ore in the
patio process. The crown kept the price high, thereby depressing the volume of silver production.
[Bakewell, Peter and Kendall W. Brown, "Mining: Colonial Spanish America" in ] Protecting its flow from Mexico and Peru as it transited to ports for shipment to Spain resulted early on in a convoy system (the flota) sailing twice a year. Its success can be judged by the fact that the silver fleet was captured only once, in 1628 by Dutch privateer
Piet Hein. That loss resulted in the bankruptcy of the Spanish crown and an extended period of economic depression in Spain.
One practice used by the Spanish to gather workers for the mines was called ''repartimiento''. This was a rotational forced labor system where indigenous pueblos were obligated to send laborers to work in Spanish mines and plantations for a set number of days out of the year. Repartimiento was not implemented to replace slave labor but instead existed alongside free wage labor, slavery, and indentured labor. It was, however, a way for the Spanish to procure cheap labor thus boosting the mining-driven economy. It is important to note that the men who worked as repartimiento laborers were not always resistant to the practice. Some were drawn to the labor as a way to supplement the wages they earned cultivating fields so as to support their families and, of course, pay tributes. At first, a Spaniard could get repartimiento laborers to work for them with permission from a crown official, such as a viceroy, only on the basis that this labor was absolutely necessary to provide the country with important resources. This condition became laxer as the years went on and various enterprises had repartimiento laborers where they would work in dangerous conditions for long hours and low wages.

During the Bourbon era, economic reforms sought to reverse the pattern that left Spain impoverished with no manufacturing sector and its colonies' need for manufactured goods supplied by other nations. It attempted to restructure to establish as closed trading system, but it was hampered by the terms of the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht. The treaty ending the War of the Spanish Succession with a victory for the Bourbon French candidate for the throne had a provision for British merchants to legally sell by a license (''
Asiento de Negros
The () was a monopoly contract between the Spanish Crown and various merchants for the right to provide African slaves to colonies in the Spanish Americas. The Spanish Empire rarely engaged in the trans-Atlantic slave trade directly from Afr ...
'')
slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
to Spanish America. The provision undermined the possibility of a revamped Spanish monopoly system. The merchants also used the opportunity to engage in contraband trade of their manufactured goods. Crown policy sought to make legal trade more appealing than contraband by instituting free commerce (''comercio libre'') in 1778 whereby Spanish American ports could trade with each other and they could trade with any port in Spain. It was aimed at revamping a closed Spanish system and outflanking the increasingly powerful British. Silver production revived in the eighteenth century, with production far surpassing the earlier output. The crown reducing the taxes on mercury, meaning that a greater volume of pure silver could be refined. Silver mining absorbed most available capital in Mexico and Peru, and the crown emphasized the production of precious metals that was sent to Spain. There was some economic development in the Indies to supply food, but a diversified economy did not emerge.
[ The economic reforms of the Bourbon era both shaped and were themselves impacted by geopolitical developments in Europe. The Bourbon Reforms arose out of the ]War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
. In turn, the crown's attempt to tighten its control over its colonial markets in the Americas led to further conflict with other European powers who were vying for access to them. After a sparking a series of skirmishes throughout the 1700s over its stricter policies, Spain's reformed trade system led to war with Britain in 1796. In the Americas, meanwhile, economic policies enacted under the Bourbons had different impacts in different regions. On one hand, silver production in New Spain greatly increased and led to economic growth. But much of the profits of the revitalized mining sector went to mining elites and state officials, while in rural areas of New Spain conditions for rural workers deteriorated, contributing to social unrest that would impact subsequent revolts.
Pacific exploration and trade
In 1525, King Charles I of Spain ordered an expedition led by friar García Jofre de Loaísa to go to Asia by the western route to colonize the Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located ...
(known as Spice Islands, now part of Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
), thus crossing first the Atlantic and then the Pacific oceans. Ruy López de Villalobos sailed to the Philippines in 1542–43. From 1546 to 1547 Francis Xavier
Francis Xavier (born Francisco de Jasso y Azpilicueta; Latin: ''Franciscus Xaverius''; Basque: ''Frantzisko Xabierkoa''; French: ''François Xavier''; Spanish: ''Francisco Javier''; Portuguese: ''Francisco Xavier''; 7 April 15063 December ...
worked in Maluku among the peoples of Ambon Island
Ambon Island is part of the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. The island has an area of and is mountainous, well watered, and fertile. Ambon Island consists of two territories: the city of Ambon to the south and various districts (''kecamatan'') o ...
, Ternate
Ternate is a city in the Indonesian province of North Maluku and an island in the Maluku Islands. It was the ''de facto'' provincial capital of North Maluku before Sofifi on the nearby coast of Halmahera became the capital in 2010. It is off the ...
, and Morotai
Morotai Island ( id, Pulau Morotai) is an island in the Halmahera group of eastern Indonesia's Maluku Islands (Moluccas). It is one of Indonesia's northernmost islands.
Morotai is a rugged, forested island lying to the north of Halmahera. It ha ...
, and laid the foundations for the Christian religion there.
In 1564, Miguel López de Legazpi
Miguel López de Legazpi (12 June 1502 – 20 August 1572), also known as '' El Adelantado'' and ''El Viejo'' (The Elder), was a Spaniard who, from the age of 26, lived and built a career in Mexico (then the Viceroyalty of New Spain) and, ...
was commissioned by the viceroy of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the A ...
, Luis de Velasco, to explore the Maluku Islands where Magellan and Ruy López de Villalobos had landed in 1521 and 1543, respectively. The expedition was ordered by King Philip II of Spain, after whom the Philippines had earlier been named by Villalobos. El Adelantado Legazpi established settlements in the East Indies and the Pacific Islands in 1565. He was the first governor-general of the Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies ( es , Indias orientales españolas ; fil, Silangang Indiyas ng Espanya) were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1898, governed for the Spanish Crown from Mexico City and Madri ...
. After obtaining peace with various indigenous tribes, López de Legazpi made Manila the capital in 1571.
The Spanish settled and took control of Tidore
Tidore ( id, Kota Tidore Kepulauan, lit. "City of Tidore Islands") is a city, island, and archipelago in the Maluku Islands of eastern Indonesia, west of the larger island of Halmahera. Part of North Maluku Province, the city includes the island ...
in 1603 to trade spices and counter Dutch encroachment in the archipelago of Maluku. The Spanish presence lasted until 1663, when the settlers and military were moved back to the Philippines. Part of the Ternatean population chose to leave with the Spanish, settling near Manila in what later became the municipality of Ternate.
Spanish galleon
Galleons were large, multi-decked sailing ships first used as armed cargo carriers by European states from the 16th to 18th centuries during the age of sail and were the principal vessels drafted for use as warships until the Anglo-Dutch ...
s travelled across the Pacific Ocean annually between Acapulco
Acapulco de Juárez (), commonly called Acapulco ( , also , nah, Acapolco), is a city and major seaport in the state of Guerrero on the Pacific Coast of Mexico, south of Mexico City. Acapulco is located on a deep, semicircular bay and has ...
in Mexico and Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
, and from there the primary Asian destination for silver from the Americas was China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
.
In 1542, Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo
Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo ( pt, João Rodrigues Cabrilho; c. 1499 – January 3, 1543) was an Iberian maritime explorer best known for investigations of the West Coast of North America, undertaken on behalf of the Spanish Empire. He was the firs ...
traversed the coast of California and named many of its features. In 1601, Sebastián Vizcaíno
Sebastián Vizcaíno (1548–1624) was a Spanish soldier, entrepreneur, explorer, and diplomat whose varied roles took him to New Spain, the Baja California peninsula, the California coast and Asia.
Early career
Vizcaíno was born in 154 ...
mapped the coastline in detail and gave new names to many features. Martín de Aguilar, lost from the expedition led by Sebastián Vizcaíno, explored the Pacific coast as far north as Coos Bay
Coos Bay is an estuary where the Coos River enters the Pacific Ocean, the estuary is approximately 12 miles long and up to two miles wide. It is the largest estuary completely within Oregon state lines. The Coos Bay watershed covers an area of abou ...
in present-day Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
.
Since the 1549 arrival to Kagoshima
, abbreviated to , is the capital city of Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. Located at the southwestern tip of the island of Kyushu, Kagoshima is the largest city in the prefecture by some margin. It has been nicknamed the "Naples of the Eastern wor ...
(Kyushu) of a group of Jesuits with St. Francis Xavier missionary and Portuguese traders, Spain was interested in Japan. In this first group of Jesuit missionaries were included Spaniards Cosme de Torres and Juan Fernández.
In 1611, Sebastián Vizcaíno surveyed the east coast of Japan and from the year of 1611 to 1614 he was ambassador of King Philip III in Japan returning to Acapulco in the year of 1614. In 1608, he was sent to search for two mythical islands called Rico de Oro (island of gold) and Rico de Plata (island of silver).
Spain expanded its Pacific empire in 1668 when Jesuit missionary Diego Luis de San Vitores
Diego Luis de San Vitores, SJ (November 12, 1627 – April 2, 1672) was a Spanish Jesuit missionary who founded the first Catholic church on the island of Guam. He is responsible for establishing the Christian presence in the Mariana Islands. ...
established a mission on Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
. San Vitores was killed by the native Chamorros in 1672, sparking the Spanish-Chamorro Wars.
The Spanish Bourbons (1700–1808)
 With the 1700 death of the childless
With the 1700 death of the childless Charles II of Spain
Charles II of Spain (''Spanish: Carlos II,'' 6 November 1661 – 1 November 1700), known as the Bewitched (''Spanish: El Hechizado''), was the last Habsburg ruler of the Spanish Empire. Best remembered for his physical disabilities and the War ...
, the crown of Spain was contested in the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
.
Under the Treaties of Utrecht (11 April 1713) ending the war, the French prince of the House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spani ...
, Philippe of Anjou, grandchild of Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of ...
, became the king Philip V. He retained the Spanish overseas empire in the Americas and the Philippines. The settlement gave spoils to those who had backed a Habsburg for the Spanish monarchy, ceding European territory of the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands ( Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a '' pars pro toto'') was the ...
, Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
, and Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
to Austria; Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
and parts of Milan to the Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy ( it, Ducato di Savoia; french: Duché de Savoie) was a country in Western Europe that existed from 1416.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy for Amadeus VIII. The du ...
, and Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
and Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its cap ...
to the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, wh ...
. The treaty also granted British merchants the exclusive right to sell slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
in Spanish America for thirty years, the ''asiento de negros'', as well as licensed voyages to ports in Spanish colonial dominions and openings.
Spain's economic and demographic recovery had begun slowly in the last decades of the Habsburg reign, as was evident from the growth of its trading convoys and the much more rapid growth of illicit trade during the period. (This growth was slower than the growth of illicit trade by northern rivals in the empire's markets.) However, this recovery was not then translated into institutional improvement, rather the "proximate solutions to permanent problems." This legacy of neglect was reflected in the early years of Bourbon rule in which the military was ill-advisedly pitched into battle in the War of the Quadruple Alliance (1718–20). Spain was defeated in Italy by an alliance of Britain, France, Savoy, and Austria. Following the war, the new Bourbon monarchy took a much more cautious approach to international relations, relying on a family alliance with Bourbon France, and continuing to follow a program of institutional renewal.
The crown program to enact reforms that promoted administrative control and efficiency in the metropole to the detriment of interests in the colonies undermined creole elites' loyalty to the crown. When French forces of Napoleon Bonaparte invaded the Iberian peninsula in 1808, Napoleon ousted the Spanish Bourbon monarchy, placing his brother Joseph Bonaparte on the Spanish throne. There was a crisis of legitimacy of crown rule in Spanish America, leading to the Spanish American wars of independence (1808–1826).
Bourbon reforms
 The Spanish Bourbons' broadest intentions were to reorganize the institutions of empire to better administer it for the benefit of Spain and the crown. It sought to increase revenues and to assert greater crown control, including over the Catholic Church. Centralization of power was to be for the benefit of the crown and the metropole and for the defense of its empire against foreign incursions.
The Spanish Bourbons' broadest intentions were to reorganize the institutions of empire to better administer it for the benefit of Spain and the crown. It sought to increase revenues and to assert greater crown control, including over the Catholic Church. Centralization of power was to be for the benefit of the crown and the metropole and for the defense of its empire against foreign incursions.[Kuethe, Allan J. "The Bourbon Reforms" in ] From the viewpoint of Spain, the structures of colonial rule under the Habsburgs were no longer functioning to the benefit of Spain, with much wealth being retained in Spanish America and going to other European powers. The presence of other European powers in the Caribbean, with the English in Barbados (1627), St Kitts (1623–25), and Jamaica (1655); the Dutch in Curaçao, and the French in Saint Domingue (Haiti) (1697), Martinique, and Guadeloupe had broken the integrity of the closed Spanish mercantile system and established thriving sugar colonies.Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
to Cadiz, where foreign merchant houses had easier access to the Indies trade. Cadiz became the one port for all Indies trading (see flota system). Individual sailings at regular intervals were slow to displace the traditional armed convoys, but by the 1760s there were regular ships plying the Atlantic from Cadiz to Havana and Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, and at longer intervals to the Río de la Plata, where an additional viceroyalty was created in 1776. The contraband trade that was the lifeblood of the Habsburg empire declined in proportion to registered shipping (a shipping registry having been established in 1735).
Two upheavals registered unease within Spanish America and at the same time demonstrated the renewed resiliency of the reformed system: the Túpac Amaru II, Tupac Amaru uprising in Peru in 1780 and the Revolt of the Comuneros (New Granada), rebellion of the ''comuneros'' of Viceroyalty of New Granada, New Granada, both in part reactions to tighter, more efficient control.
18th-century economic conditions
 The 18th century was a century of prosperity for the overseas Spanish Empire as trade within grew steadily, particularly in the second half of the century, under the Bourbon reforms. Spain's victory in the Battle of Cartagena de Indias against a British expedition in the Caribbean port of Cartagena de Indias helped Spain secure its dominance of its possessions in America until the 19th century. But different regions fared differently under Bourbon rule, and even while New Spain was particularly prosperous, it was also marked by steep wealth inequality. Silver production boomed in New Spain during the 18th century, with output more than tripling between the start of the century and the 1750s. The economy and the population both grew, both centered around Mexico City. But while mine owners and the crown benefited from the flourishing silver economy, most of the population in the rural Bajío faced rising land prices, falling wages. Eviction of many from their lands resulted.
The 18th century was a century of prosperity for the overseas Spanish Empire as trade within grew steadily, particularly in the second half of the century, under the Bourbon reforms. Spain's victory in the Battle of Cartagena de Indias against a British expedition in the Caribbean port of Cartagena de Indias helped Spain secure its dominance of its possessions in America until the 19th century. But different regions fared differently under Bourbon rule, and even while New Spain was particularly prosperous, it was also marked by steep wealth inequality. Silver production boomed in New Spain during the 18th century, with output more than tripling between the start of the century and the 1750s. The economy and the population both grew, both centered around Mexico City. But while mine owners and the crown benefited from the flourishing silver economy, most of the population in the rural Bajío faced rising land prices, falling wages. Eviction of many from their lands resulted.
Scientific investigations and expeditions
 The Spanish American Enlightenment produced a huge body of information on Spain's overseas empire via scientific expeditions. The most famous traveler in Spanish America was Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt, whose travel writings, especially ''Political Essay on the Kingdom of New Spain'' and scientific observations remain important sources for the history of Spanish America. Humboldt's expedition was authorized by the crown, but was self-funded from his personal fortune. The Bourbon crown promoted state-funded scientific work prior to the famous Humboldt expedition. Eighteenth-century clerics contributed to the expansion of scientific knowledge. These include José Antonio de Alzate y Ramírez, and José Celestino Mutis.
The Spanish crown funded a number of important scientific expeditions: Botanical Expedition to the Viceroyalty of Peru (1777–78); Royal Botanical Expedition to New Granada (1783–1816); the Royal Botanical Expedition to New Spain (1787–1803); which scholars are now examining afresh. Although the crown funded a number of Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest to bolster claims to territory, lengthy transatlantic and transpacific Malaspina Expedition, Malaspina-Bustamante Expedition was for scientific purposes. The crown also funded the Balmis Expedition in 1804 to vaccinate colonial populations against smallpox.
Much of the research done in the eighteenth century was never published or otherwise disseminated, in part due to budgetary constraints on the crown. Starting in the late twentieth century, research on the history of science in Spain and the Spanish empire has blossomed, with primary sources being published in scholarly editions or reissued, as well the publication of a considerable number of important scholarly studies.
The Spanish American Enlightenment produced a huge body of information on Spain's overseas empire via scientific expeditions. The most famous traveler in Spanish America was Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt, whose travel writings, especially ''Political Essay on the Kingdom of New Spain'' and scientific observations remain important sources for the history of Spanish America. Humboldt's expedition was authorized by the crown, but was self-funded from his personal fortune. The Bourbon crown promoted state-funded scientific work prior to the famous Humboldt expedition. Eighteenth-century clerics contributed to the expansion of scientific knowledge. These include José Antonio de Alzate y Ramírez, and José Celestino Mutis.
The Spanish crown funded a number of important scientific expeditions: Botanical Expedition to the Viceroyalty of Peru (1777–78); Royal Botanical Expedition to New Granada (1783–1816); the Royal Botanical Expedition to New Spain (1787–1803); which scholars are now examining afresh. Although the crown funded a number of Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest to bolster claims to territory, lengthy transatlantic and transpacific Malaspina Expedition, Malaspina-Bustamante Expedition was for scientific purposes. The crown also funded the Balmis Expedition in 1804 to vaccinate colonial populations against smallpox.
Much of the research done in the eighteenth century was never published or otherwise disseminated, in part due to budgetary constraints on the crown. Starting in the late twentieth century, research on the history of science in Spain and the Spanish empire has blossomed, with primary sources being published in scholarly editions or reissued, as well the publication of a considerable number of important scholarly studies.
Contesting with other empires
The Spanish empire had still not returned to first-rate power status, but it had recovered and even extended its territories considerably from the dark days at the beginning of the eighteenth century when it was, particularly in continental matters, at the mercy of other powers' political deals. The relatively more peaceful century under the new monarchy had allowed it to rebuild and start the long process of modernizing its institutions and economy, and the demographic decline of the 17th century had been reversed. It was a middle-ranking power with great power pretensions that could not be ignored. But time was to be against it.
Military recovery

 Bourbon institutional reforms under Philip V bore fruit militarily when Spanish forces easily retook
Bourbon institutional reforms under Philip V bore fruit militarily when Spanish forces easily retook Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily from the Austrians at the Battle of Bitonto in 1734 during the War of the Polish Succession, and during the War of Jenkins' Ear (1739–42) thwarted British efforts to capture the strategic cities of Battle of Cartagena de Indias, Cartagena de Indias and Invasion of Cuba (1741), Santiago de Cuba by defeating a massive British army and navy, although Spain's Invasion of Georgia (1742), invasion of Georgia also failed.
In 1742, the War of Jenkins' Ear merged with the larger War of the Austrian Succession, and King George's War in North America. The British, also occupied with France, were unable to capture Spanish convoys, and Spanish privateers captured British merchant shipping along the Triangle Trade routes and attacked the coast of Province of North Carolina, North Carolina, levying tribute on the inhabitants. In Europe, Spain had been trying to divest Maria Theresa of Lombardy in northern Italy since 1741, but faced the opposition of Charles Emmanuel III of Sardinia, and warfare in northern Italy remained indecisive throughout the period up to 1746. By the 1748 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748), Treaty of Aix-la-Chappelle, Spain gained Parma, Piacenza, and Guastalla in northern Italy.
Spain was defeated during the Spanish invasion of Portugal (1762), invasion of Portugal and lost both Siege of Havana, Havana and Battle of Manila (1762), Manila to British forces towards the end of the Seven Years' War (1756–63), but it promptly recovered these losses and seized British forts in British West Florida, West Florida and the British naval base in the Bahamas during the American Revolutionary War (1775–83).
In North Africa, Spain captured Oran
Oran ( ar, وَهران, Wahrān) is a major coastal city located in the north-west of Algeria. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria after the capital Algiers, due to its population and commercial, industrial, and cultural ...
from the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
in 1732 at the cost of only 30 killed. In 1775, Spain :es:Invasión española de Argel de 1775, unsuccessfully invaded Ottoman Algeria, Ottoman Algiers, killing 5,000–6,000 Algerians and Turks while suffering 500 dead. In 1783 and 1784, the Spanish navy bombarded Algiers to end piracy in the Mediterranean. The :es:Bombardeo de Argel (1784), second bombardment under Admiral Antonio Barceló damaged the city so severely that the Dey of Algiers negotiated a peace treaty.
During most of the 18th century, Spanish privateers, particularly from Santo Domingo, were the scourge of the Antilles, with Dutch, British, French and Danish vessels as their Prize (law), prizes.
Role in the American Revolution
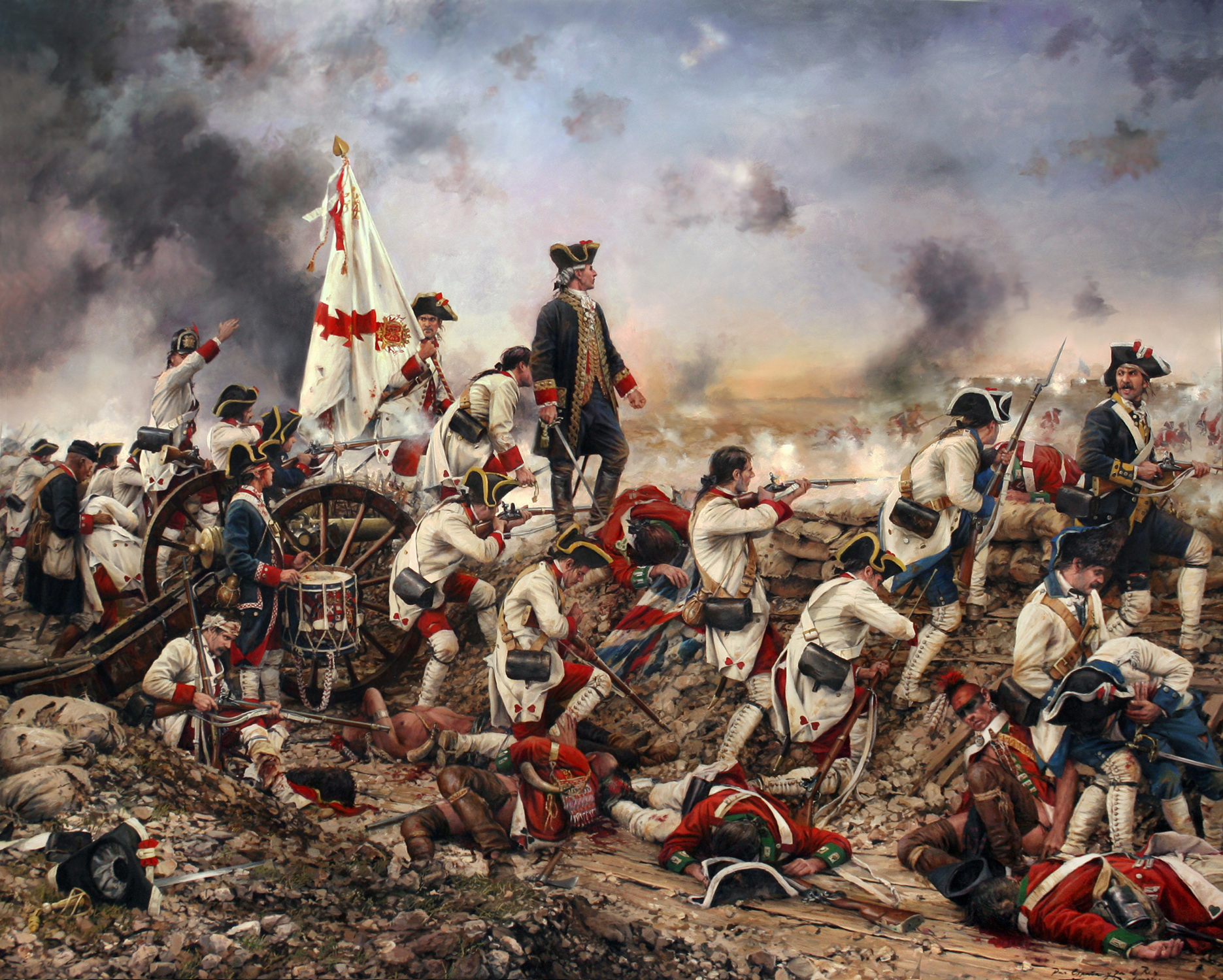 Spain contributed to the independence of the Thirteen Colonies, thirteen American colonies (which formed the United States) together with France. Spain and France were allies because of the Bourbon "Pacte de Famille, Family Pact" carried out by both countries against Britain.
Great Siege of Gibraltar, Gibraltar was besieged for more than three years, but the British garrison stubbornly resisted and was resupplied twice: once after Admiral George Rodney's victory over Juan de Lángara in the 1780 Battle of Cape St. Vincent (1780), Battle of Cape St. Vincent, and again by Admiral Richard Howe in 1782. Further Franco-Spanish efforts to capture Gibraltar were unsuccessful. One notable success took place on 5 February 1782, when the Spanish Invasion of Minorca (1781), recaptured Minorca. Ambitious plans for an Armada of 1779, invasion of Britain in 1779 had to be abandoned. Admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova captured two British convoys totaling seventy-nine ships, including a fleet of fifty-five merchantmen and frigates in the action of 9 August 1780.
The Spanish governor of Louisiana (New Spain), Louisiana Bernardo de Gálvez launched several Gulf Coast campaign, successful offensives against British Florida (1779–81), capturing the entirety of West Florida from Britain. Gálvez also Capture of the Bahamas (1782), conquered the island New Providence in the Bahamas. Colony of Jamaica, Jamaica was the last British stronghold of importance in the Caribbean. Gálvez attempted to organize an expedition to capture the island; however, the Peace of Paris (1783), 1783 Peace of Paris was concluded and the invasion cancelled.
Under royal order from Charles III of Spain Gálvez continued the aid operations to supply the American rebels. The British blockaded the colonial ports of the Thirteen Colonies, and the route from Spanish-controlled New Orleans up to the Mississippi river was an effective alternative to supply the American rebels. Spain actively supported the thirteen colonies throughout the American Revolutionary War, beginning in 1776 by jointly funding Roderigue Hortalez and Company, a trading company that provided critical military supplies, throughout financing the final Siege of Yorktown (1781), Siege of Yorktown in 1781 with a collection of gold and silver from Havana. Spanish aid was supplied to the colonies via four main routes: from French ports with the funding of ''Roderigue Hortalez and Company''; through the port of New Orleans and up the Mississippi river; from warehouses in Havana; and (4)from the northwestern Spanish port of Bilbao, through the Gardoqui family trading company which supplied significant war materiel.
Spain contributed to the independence of the Thirteen Colonies, thirteen American colonies (which formed the United States) together with France. Spain and France were allies because of the Bourbon "Pacte de Famille, Family Pact" carried out by both countries against Britain.
Great Siege of Gibraltar, Gibraltar was besieged for more than three years, but the British garrison stubbornly resisted and was resupplied twice: once after Admiral George Rodney's victory over Juan de Lángara in the 1780 Battle of Cape St. Vincent (1780), Battle of Cape St. Vincent, and again by Admiral Richard Howe in 1782. Further Franco-Spanish efforts to capture Gibraltar were unsuccessful. One notable success took place on 5 February 1782, when the Spanish Invasion of Minorca (1781), recaptured Minorca. Ambitious plans for an Armada of 1779, invasion of Britain in 1779 had to be abandoned. Admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova captured two British convoys totaling seventy-nine ships, including a fleet of fifty-five merchantmen and frigates in the action of 9 August 1780.
The Spanish governor of Louisiana (New Spain), Louisiana Bernardo de Gálvez launched several Gulf Coast campaign, successful offensives against British Florida (1779–81), capturing the entirety of West Florida from Britain. Gálvez also Capture of the Bahamas (1782), conquered the island New Providence in the Bahamas. Colony of Jamaica, Jamaica was the last British stronghold of importance in the Caribbean. Gálvez attempted to organize an expedition to capture the island; however, the Peace of Paris (1783), 1783 Peace of Paris was concluded and the invasion cancelled.
Under royal order from Charles III of Spain Gálvez continued the aid operations to supply the American rebels. The British blockaded the colonial ports of the Thirteen Colonies, and the route from Spanish-controlled New Orleans up to the Mississippi river was an effective alternative to supply the American rebels. Spain actively supported the thirteen colonies throughout the American Revolutionary War, beginning in 1776 by jointly funding Roderigue Hortalez and Company, a trading company that provided critical military supplies, throughout financing the final Siege of Yorktown (1781), Siege of Yorktown in 1781 with a collection of gold and silver from Havana. Spanish aid was supplied to the colonies via four main routes: from French ports with the funding of ''Roderigue Hortalez and Company''; through the port of New Orleans and up the Mississippi river; from warehouses in Havana; and (4)from the northwestern Spanish port of Bilbao, through the Gardoqui family trading company which supplied significant war materiel.
Contestation in Brazil
The majority of the territory of today's Brazil had been claimed as Spanish when exploration began with the navigation of the length of the Amazon River in 1541–42 by Francisco de Orellana. Many Spanish expeditions explored large parts of this vast region, especially those close to Spanish settlements. During the 16th and 17th centuries, Spanish soldiers, missionaries and adventurers also established pioneering communities, primarily in Paraná (state), Paraná, Santa Catarina, and São Paulo, and forts on the northeastern coast threatened by the French and Dutch.
 As Portuguese-Brazilian settlement expanded, following in the trail of the Bandeirantes exploits, these isolated Spanish groups were eventually integrated into Brazilian society. Only some Castilians who were displaced from the disputed areas of the Pampas of Rio Grande do Sul have left a significant influence on the formation of the gaucho, when they mixed with Indian groups, Portuguese and blacks who arrived in the region during the 18th century. The Spanish were barred by their laws from slaving of indigenous people, leaving them without a commercial interest deep in the interior of the Amazon basin. The Laws of Burgos (1512) and the New Laws (1542) had been intended to protect the interests of indigenous people. The Portuguese-Brazilian slavers, the Bandeirantes, had the advantage of access from the mouth of the Amazon River, which was on the Portuguese side of the line of Tordesillas. One famous attack upon a Spanish mission in 1628 resulted in the enslavement of about 60,000 indigenous people.
In time, there was in effect a self-funding force of occupation. By the 18th century, much of the Spanish territory was under de facto control of Portuguese-Brazil. This reality was recognized with the legal transfer of sovereignty in 1750 of most of the Amazon basin and surrounding areas to Portugal in the Treaty of Madrid (13 January 1750), Treaty of Madrid. This settlement sowed the seeds of the Guaraní War in 1756.
As Portuguese-Brazilian settlement expanded, following in the trail of the Bandeirantes exploits, these isolated Spanish groups were eventually integrated into Brazilian society. Only some Castilians who were displaced from the disputed areas of the Pampas of Rio Grande do Sul have left a significant influence on the formation of the gaucho, when they mixed with Indian groups, Portuguese and blacks who arrived in the region during the 18th century. The Spanish were barred by their laws from slaving of indigenous people, leaving them without a commercial interest deep in the interior of the Amazon basin. The Laws of Burgos (1512) and the New Laws (1542) had been intended to protect the interests of indigenous people. The Portuguese-Brazilian slavers, the Bandeirantes, had the advantage of access from the mouth of the Amazon River, which was on the Portuguese side of the line of Tordesillas. One famous attack upon a Spanish mission in 1628 resulted in the enslavement of about 60,000 indigenous people.
In time, there was in effect a self-funding force of occupation. By the 18th century, much of the Spanish territory was under de facto control of Portuguese-Brazil. This reality was recognized with the legal transfer of sovereignty in 1750 of most of the Amazon basin and surrounding areas to Portugal in the Treaty of Madrid (13 January 1750), Treaty of Madrid. This settlement sowed the seeds of the Guaraní War in 1756.
Rival empires in the Pacific Northwest
 Spain claimed all of North America in the Age of Discovery, but claims were not translated into occupation until a major resource was discovered and Spanish settlement and crown rule put in place. The French had established an French America, empire in northern North America and took some islands in the Caribbean. The English established colonies on the eastern seaboard of North America and in northern North America and some Caribbean islands as well. In the eighteenth century, the Spanish crown realized that its territorial claims needed to be defended, particularly in the wake of its visible weakness during the Seven Years' War when Britain captured the important Spanish ports of Havana and Manila. Another important factor was that the Russian America, Russian empire had expanded into North America from the mid-eighteenth century, with Maritime fur trade, fur trading settlements in what is now Alaska and forts as far south as Fort Ross, California. Great Britain was also expanding into areas that Spain claimed as its territory on the Pacific coast. Taking steps to shore up its fragile claims to California, Spain began planning Spanish missions in California, California missions in 1769. Spain also began a series of voyages to the Pacific Northwest, where Russia and Great Britain were encroaching on claimed territory. The Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, with Alessandro Malaspina and others sailing for Spain, came too late for Spain to assert its sovereignty in the Pacific Northwest.
The Nootka Crisis (1789–1791) nearly brought Spain and Britain to war. It was a dispute over claims in the Pacific Northwest, where neither nation had established permanent settlements. The crisis could have led to war, but without French support Spain capitulated to British terms and negotiations took place with the Nootka Convention. Spain and Great Britain agreed to not establish settlements and allowed free access to Nootka Sound on the west coast of what is now Vancouver Island. Nevertheless, the outcome of the crisis was a humiliation for Spain and a triumph for Britain, as Spain had practically renounced all sovereignty on the North Pacific coast.
In 1806, Baron Nikolai Rezanov attempted to negotiate a treaty between the Russian-American Company and the Viceroyalty of New Spain, but his unexpected death in 1807 ended any treaty hopes. Spain gave up its claims in the West of North America in the Adams-Onis Treaty of 1819, ceding its rights there to the United States, allowing the U.S. to purchase Florida, and establishing a boundary between New Spain and the U.S. When the negotiations between the two nations were taking place, Spain's resources were stretched due to the Spanish American wars of independence. Much of the present-day American Southwest later became part of Mexico after its independence from Spain; after the Mexican–American War, Mexico ceded to the U.S. present-day California, Texas, New Mexico, Utah, Nevada, Arizona, and parts of Colorado, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska and Wyoming for $15 million.
Spain claimed all of North America in the Age of Discovery, but claims were not translated into occupation until a major resource was discovered and Spanish settlement and crown rule put in place. The French had established an French America, empire in northern North America and took some islands in the Caribbean. The English established colonies on the eastern seaboard of North America and in northern North America and some Caribbean islands as well. In the eighteenth century, the Spanish crown realized that its territorial claims needed to be defended, particularly in the wake of its visible weakness during the Seven Years' War when Britain captured the important Spanish ports of Havana and Manila. Another important factor was that the Russian America, Russian empire had expanded into North America from the mid-eighteenth century, with Maritime fur trade, fur trading settlements in what is now Alaska and forts as far south as Fort Ross, California. Great Britain was also expanding into areas that Spain claimed as its territory on the Pacific coast. Taking steps to shore up its fragile claims to California, Spain began planning Spanish missions in California, California missions in 1769. Spain also began a series of voyages to the Pacific Northwest, where Russia and Great Britain were encroaching on claimed territory. The Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, with Alessandro Malaspina and others sailing for Spain, came too late for Spain to assert its sovereignty in the Pacific Northwest.
The Nootka Crisis (1789–1791) nearly brought Spain and Britain to war. It was a dispute over claims in the Pacific Northwest, where neither nation had established permanent settlements. The crisis could have led to war, but without French support Spain capitulated to British terms and negotiations took place with the Nootka Convention. Spain and Great Britain agreed to not establish settlements and allowed free access to Nootka Sound on the west coast of what is now Vancouver Island. Nevertheless, the outcome of the crisis was a humiliation for Spain and a triumph for Britain, as Spain had practically renounced all sovereignty on the North Pacific coast.
In 1806, Baron Nikolai Rezanov attempted to negotiate a treaty between the Russian-American Company and the Viceroyalty of New Spain, but his unexpected death in 1807 ended any treaty hopes. Spain gave up its claims in the West of North America in the Adams-Onis Treaty of 1819, ceding its rights there to the United States, allowing the U.S. to purchase Florida, and establishing a boundary between New Spain and the U.S. When the negotiations between the two nations were taking place, Spain's resources were stretched due to the Spanish American wars of independence. Much of the present-day American Southwest later became part of Mexico after its independence from Spain; after the Mexican–American War, Mexico ceded to the U.S. present-day California, Texas, New Mexico, Utah, Nevada, Arizona, and parts of Colorado, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska and Wyoming for $15 million.
Loss of Spanish Louisiana
 The growth of trade and wealth in the colonies caused increasing political tensions as frustration grew with the improving but still restrictive trade with Spain. Alessandro Malaspina's recommendation to turn the empire into a looser confederation to help improve governance and trade so as to quell the growing political tensions between the élites of the empire's periphery and center was suppressed by a monarchy afraid of losing control. All was to be swept away by the tumult that was to overtake Europe at the turn of the 19th century with the French Revolutionary Wars, French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
The first major territory Spain was to lose in the 19th century was the vast Louisiana (New Spain), Louisiana Territory, which had few European settlers. It stretched north to Canada and was ceded by France in 1763 under the terms of the Treaty of Fontainebleau (1762), Treaty of Fontainebleau. The French, under Napoleon, took back possession as part of the Third Treaty of San Ildefonso, Treaty of San Ildefonso in 1800 and sold it to the United States in the Louisiana Purchase of 1803. Napoleon's sale of the Louisiana Territory to the United States in 1803 caused border disputes between the United States and Spain that, with rebellions in West Florida (1810) and in the remainder of Louisiana at the mouth of the Mississippi river, Mississippi, led to their eventual cession to the United States.
The growth of trade and wealth in the colonies caused increasing political tensions as frustration grew with the improving but still restrictive trade with Spain. Alessandro Malaspina's recommendation to turn the empire into a looser confederation to help improve governance and trade so as to quell the growing political tensions between the élites of the empire's periphery and center was suppressed by a monarchy afraid of losing control. All was to be swept away by the tumult that was to overtake Europe at the turn of the 19th century with the French Revolutionary Wars, French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
The first major territory Spain was to lose in the 19th century was the vast Louisiana (New Spain), Louisiana Territory, which had few European settlers. It stretched north to Canada and was ceded by France in 1763 under the terms of the Treaty of Fontainebleau (1762), Treaty of Fontainebleau. The French, under Napoleon, took back possession as part of the Third Treaty of San Ildefonso, Treaty of San Ildefonso in 1800 and sold it to the United States in the Louisiana Purchase of 1803. Napoleon's sale of the Louisiana Territory to the United States in 1803 caused border disputes between the United States and Spain that, with rebellions in West Florida (1810) and in the remainder of Louisiana at the mouth of the Mississippi river, Mississippi, led to their eventual cession to the United States.
End of the global empire (1808–1899)
Destabilization of the empire (1808–1814)
 Spain was caught up in European events of the Napoleonic era that led to its loss of empire in Spanish America. Spain was France's ally, but it had tried to avoid being drawn directly into the ongoing conflict between Napoleon's France and Britain. Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), War broke out in 1804 after a British squadron Action of 5 October 1804, captured a Spanish convoy off Cape Santa Maria, Portugal. The British navy defeated the Spanish navy in the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. The following year, the British British invasions of the River Plate, attempted to seize the Río de la Plata estuary. The viceroy retreated hastily inland when defeated by a small British force. However, the ''Criollo people, Criollos militias and colonial army repulsed the now reinforced British force in 1807.
In 1808, the Spanish king was tricked and Spain was taken over by Napoleon without firing a shot, but the French provoked a popular uprising from the Spanish people and the grinding guerrilla warfare, which Napoleon dubbed his "ulcer," the Peninsular War, (famously depicted by the painter Goya) ensued. Spain gave the Napoleonic army their first open-field defeat at the Battle of Bailén (July 1808), which inspired Austria and Britain to form the War of the Fifth Coalition, Fifth Coalition against France.
Spain was caught up in European events of the Napoleonic era that led to its loss of empire in Spanish America. Spain was France's ally, but it had tried to avoid being drawn directly into the ongoing conflict between Napoleon's France and Britain. Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), War broke out in 1804 after a British squadron Action of 5 October 1804, captured a Spanish convoy off Cape Santa Maria, Portugal. The British navy defeated the Spanish navy in the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. The following year, the British British invasions of the River Plate, attempted to seize the Río de la Plata estuary. The viceroy retreated hastily inland when defeated by a small British force. However, the ''Criollo people, Criollos militias and colonial army repulsed the now reinforced British force in 1807.
In 1808, the Spanish king was tricked and Spain was taken over by Napoleon without firing a shot, but the French provoked a popular uprising from the Spanish people and the grinding guerrilla warfare, which Napoleon dubbed his "ulcer," the Peninsular War, (famously depicted by the painter Goya) ensued. Spain gave the Napoleonic army their first open-field defeat at the Battle of Bailén (July 1808), which inspired Austria and Britain to form the War of the Fifth Coalition, Fifth Coalition against France.
 The Napoleonic invasion provoked a crisis of sovereignty and legitimacy to rule, a new political framework, and the loss of most of Spanish America. In Spain, political uncertainty lasted over a decade and turmoil for several decades, civil wars on succession disputes, a republic, and finally a liberal democracy. Resistance coalesced around junta (Peninsular War), juntas, emergency ad hoc governments. A Supreme Central and Governing Junta of the Kingdom, Supreme Central Junta, ruling in the name of Ferdinand VII, was created on 25 September 1808 to coordinate efforts among the various juntas. Subsequently, a wikt:cortes, cortes or parliament was called, with representatives not only from Spain, but also Spanish America and the Philippines. In 1812, the Cortes of Cádiz drafted the
The Napoleonic invasion provoked a crisis of sovereignty and legitimacy to rule, a new political framework, and the loss of most of Spanish America. In Spain, political uncertainty lasted over a decade and turmoil for several decades, civil wars on succession disputes, a republic, and finally a liberal democracy. Resistance coalesced around junta (Peninsular War), juntas, emergency ad hoc governments. A Supreme Central and Governing Junta of the Kingdom, Supreme Central Junta, ruling in the name of Ferdinand VII, was created on 25 September 1808 to coordinate efforts among the various juntas. Subsequently, a wikt:cortes, cortes or parliament was called, with representatives not only from Spain, but also Spanish America and the Philippines. In 1812, the Cortes of Cádiz drafted the Spanish Constitution of 1812
The Political Constitution of the Spanish Monarchy ( es, link=no, Constitución Política de la Monarquía Española), also known as the Constitution of Cádiz ( es, link=no, Constitución de Cádiz) and as ''La Pepa'', was the first Constituti ...
. When Ferdinand VII was restored to the throne in 1814, he repudiated the constitution and re-asserted absolutist rule. A military coup in 1820 led by Rafael del Riego forced Ferdinand to accept the constitution again, which went back into force until Ferdinand raised troops in 1823, and re-asserted absolutist rule again. The reinstatement of the constitution was a major factor in propelling New Spain's elites to support Mexican War of Independence, independence in 1821.
Spanish American conflicts and independence (1810–1833)
 The idea of a separate identity for Spanish America has been developed in the modern historical literature, but the idea of complete Spanish American independence from the Spanish Empire was not general at the time and political independence was not inevitable. Historian Brian Hamnett argues that had the Spanish monarchy and Spanish liberals been more flexible regarding the place of the overseas components, the empire would not have collapsed. Juntas emerged in Spanish America as Spain faced a political crisis due to the invasion and occupation by Napoleon Bonaparte and abdication of Ferdinand VII. Spanish Americans reacted in much the same way the Peninsular Spanish did, legitimizing their actions through traditional law, which held that sovereignty reverted to the people in the absence of a legitimate king.
The majority of Spanish Americans continued to support the idea of maintaining a monarchy, but did not support retaining absolute monarchy under Ferdinand VII. Spanish Americans wanted self-government. The juntas in the Americas did not accept the governments of the Europeans—neither the government set up for Spain by the French nor the various Spanish governments set up in response to the French invasion. The juntas did not accept the Spanish regency, isolated under Siege of Cádiz, siege in the city of Cadiz (1810–1812). They also rejected the
The idea of a separate identity for Spanish America has been developed in the modern historical literature, but the idea of complete Spanish American independence from the Spanish Empire was not general at the time and political independence was not inevitable. Historian Brian Hamnett argues that had the Spanish monarchy and Spanish liberals been more flexible regarding the place of the overseas components, the empire would not have collapsed. Juntas emerged in Spanish America as Spain faced a political crisis due to the invasion and occupation by Napoleon Bonaparte and abdication of Ferdinand VII. Spanish Americans reacted in much the same way the Peninsular Spanish did, legitimizing their actions through traditional law, which held that sovereignty reverted to the people in the absence of a legitimate king.
The majority of Spanish Americans continued to support the idea of maintaining a monarchy, but did not support retaining absolute monarchy under Ferdinand VII. Spanish Americans wanted self-government. The juntas in the Americas did not accept the governments of the Europeans—neither the government set up for Spain by the French nor the various Spanish governments set up in response to the French invasion. The juntas did not accept the Spanish regency, isolated under Siege of Cádiz, siege in the city of Cadiz (1810–1812). They also rejected the Spanish Constitution of 1812
The Political Constitution of the Spanish Monarchy ( es, link=no, Constitución Política de la Monarquía Española), also known as the Constitution of Cádiz ( es, link=no, Constitución de Cádiz) and as ''La Pepa'', was the first Constituti ...
although the Constitution gave Spanish citizenship to those in the territories that had belonged to the Spanish monarchy in both hemispheres.
The liberal Spanish Constitution of 1812 recognized indigenous peoples of the Americas as Spanish citizens. But the acquisition of citizenship for any casta of Afro-American peoples of the Americas was through naturalization—excluding slaves.
A long period of wars followed in America, and the lack of Spanish troops in the colonies led to civil war between Patriot Governments (Spanish American independence), patriotic rebels and local Royalists. In South America this period of wars led to the independence of Argentina (1810), Venezuela (1810), Chile (1810), Paraguay (1811) and Uruguay (1815, but subsequently ruled by Brazil until 1828). José de San Martín campaigned for independence in Chile (1818) and in Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
(1821). Further north, Simón Bolívar led forces that won independence between 1811 and 1826 for the area that became Venezuela, Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
, Ecuador, Perú and Bolivia (then Alto Perú). Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
declared independence in 1821 and merged with the Republic of Gran Colombia (from 1821 to 1903).
In the Viceroyalty of New Spain, Miguel Hidalgo wanted freedom and liberty for Mexico in 1810 in the Grito de Dolores. Independence was actually won in 1821 by a royalist army officer turned insurgent, Agustín de Iturbide, in alliance with insurgent Vicente Guerrero and under the Plan of Iguala. The conservative Catholic hierarchy in New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the A ...
supported Mexican independence largely because it found the liberal Spanish Constitution of 1812 abhorrent. Central America provinces became independent via Mexico's independence in 1821 and Central America under Mexican rule, joined Mexico for a brief time (1822–23), but they chose their own path when Mexico became a republic in 1824.
The Spanish coastal fortifications in Veracruz, Callao and Chiloé were the footholds that resisted until 1825 and 1826 respectively. In Spanish America, Royalist guerrillas continued the war in several countries, and Spain launched attempts to Battle of Lake Maracaibo, retake Venezuela in 1823 Spanish attempts to reconquer Mexico, and Mexico in 1829. Spain abandoned all plans of military re-conquest at the death of King Ferdinand VII in 1833. Finally the Spanish government went so far as to renounce sovereignty over all of continental America in 1836.
Santo Domingo and Cuba
Dominican Republic, Santo Domingo (which had previously gone to war against the French to Spanish reconquest of Santo Domingo, restore Spanish rule) likewise declared independence in 1821 and began negotiating for inclusion in Bolivar's Republic of Gran Colombia, but was quickly occupied by the former French colony of Haiti, which ruled it until an 1844 revolution. After 17 years of independence, in 1861, Santo Domingo was again made a Spanish colony due to Haitian aggression. It was the only time that a Spanish colonial possession would return to Spain after having gained independence.
By 1862, Spain was contending with a limited insurgency and losing hundreds of soldiers.[ In September 1863, the besieged Spanish garrison of Santiago abandoned the city and marched to Puerto Plata, harassed by Dominicans all the way. There they joined the garrison in the fort, leaving the city to be pillaged by the rebels. Eventually six hundred Spanish sallied out, and after a severe fight, drove off the rebels with help from the cannon of the fort, but by then the city had been plundered and burnt almost out of existence. The damage to Santiago and Puerto Plata was estimated at $5,000,000.
] During the Dominican Restoration War, the rebel leadership had changed frequently, only to be deposed in coups for corruption, politics or in the case of Gaspar Polanco (who lasted three months) leading a disastrous direct attack on the Spanish at Monte Cristi in December 1864. Thus by the end of 1864, it could be said the Spanish were winning. However, military victory was trumped by political defeat. The price of war in terms of money and lives had been huge, disease and the hardy guerrilla fighters of the island causing many casualties that Spain could ill afford, and in 1865, the Bourbon Queen Isabella II signed a decree annulling the annexation.
During the Dominican Restoration War, the rebel leadership had changed frequently, only to be deposed in coups for corruption, politics or in the case of Gaspar Polanco (who lasted three months) leading a disastrous direct attack on the Spanish at Monte Cristi in December 1864. Thus by the end of 1864, it could be said the Spanish were winning. However, military victory was trumped by political defeat. The price of war in terms of money and lives had been huge, disease and the hardy guerrilla fighters of the island causing many casualties that Spain could ill afford, and in 1865, the Bourbon Queen Isabella II signed a decree annulling the annexation.
 A few years later, the Ten Years' War (1868–78) would begin in Cuba. The Virginius Affair (31 October 1873), in which Spanish naval forces seized a filibustering ship flying the U.S. flag off Jamaica and executed more than fifty of its officers, crew, and passengers, seriously strained relations with the United States, but U.S. intervention in Cuba was averted by the diplomatic pressure of Britain. The Cubans defeated the Spanish in several battles, most notably at the Battle of Las Guasimas (1874), Battle of Las Guasimas in 1874, but Cuba's first war of independence ended inconclusively. Both sides sustained heavy casualties and the island sustained over $300 million in property damage. After the Cuban War of Independence broke out in 1895, Spain sent more than two hundred thousand soldiers to Cuba, the largest army ever to cross the Atlantic until World War II. Reconcentration policy, Spanish atrocities in Cuba and the sinking of an American battleship in Havana Harbor caused the U.S. to declare war on Spain in April 1898.
A few years later, the Ten Years' War (1868–78) would begin in Cuba. The Virginius Affair (31 October 1873), in which Spanish naval forces seized a filibustering ship flying the U.S. flag off Jamaica and executed more than fifty of its officers, crew, and passengers, seriously strained relations with the United States, but U.S. intervention in Cuba was averted by the diplomatic pressure of Britain. The Cubans defeated the Spanish in several battles, most notably at the Battle of Las Guasimas (1874), Battle of Las Guasimas in 1874, but Cuba's first war of independence ended inconclusively. Both sides sustained heavy casualties and the island sustained over $300 million in property damage. After the Cuban War of Independence broke out in 1895, Spain sent more than two hundred thousand soldiers to Cuba, the largest army ever to cross the Atlantic until World War II. Reconcentration policy, Spanish atrocities in Cuba and the sinking of an American battleship in Havana Harbor caused the U.S. to declare war on Spain in April 1898.
Philippine Revolution
The Philippine Revolution began in August 1896, when the Spanish authorities discovered the Katipunan, an anti-colonial secret organization. The Katipunan, led by Andrés Bonifacio, began to influence much of the Philippines. During a mass gathering in Caloocan, the leaders of the Katipunan organized into a revolutionary government, named the newly established government "Haring Bayang Katagalugan", and openly declared a nationwide armed revolution.Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
. This attack failed; however, the surrounding provinces began to revolt. In particular, rebels in Cavite led by Mariano Álvarez and Baldomero Aguinaldo (who were leaders from two different factions of the Katipunan) won early major victories. A power struggle among the revolutionaries led to a Katipunan#Schism, transfer of authority and dissolution, schism among Katipunan leadership followed by Andrés Bonifacio#Trial and death, Bonifacio's execution in 1897. With command having shifted to Emilio Aguinaldo, who led the newly formed Tejeros Convention, revolutionary government. That year, revolutionaries and the Spanish signed the Pact of Biak-na-Bato, which temporarily reduced hostilities. Filipino revolutionary officers Hong Kong Junta, exiled themselves to British Hong Kong, Hong Kong. However, the hostilities never completely ceased.[.]
On April 21, 1898, after the sinking of in Havana Harbor and prior to its declaration of war on April 25, the United States launched a naval blockade of the Spanish colonial island of Captaincy General of Cuba, Cuba, off its southern coast of the peninsula of Florida. This was the first military action of the Spanish–American War of 1898. On May 1, the U.S. Navy's Asiatic Squadron, under Commodore George Dewey, decisively defeated the Spanish Navy in the Battle of Manila Bay, effectively seizing control of Manila. On May 19, Aguinaldo, unofficially allied with the United States, returned to the Philippines and resumed attacks against the Spaniards. By June, the rebels had gained control of nearly all of the Philippines, with the exception of Manila. On June 12, Aguinaldo issued the Philippine Declaration of Independence. Although this signified the end date of the revolution, neither Spain nor the United States recognized Philippine independence.
The Spanish rule of the Philippines officially ended with the Treaty of Paris (1898), Treaty of Paris of 1898, which also ended the Spanish–American War. In the treaty, Spain ceded control of the Philippines and other territories to the United States.
Spanish–American War
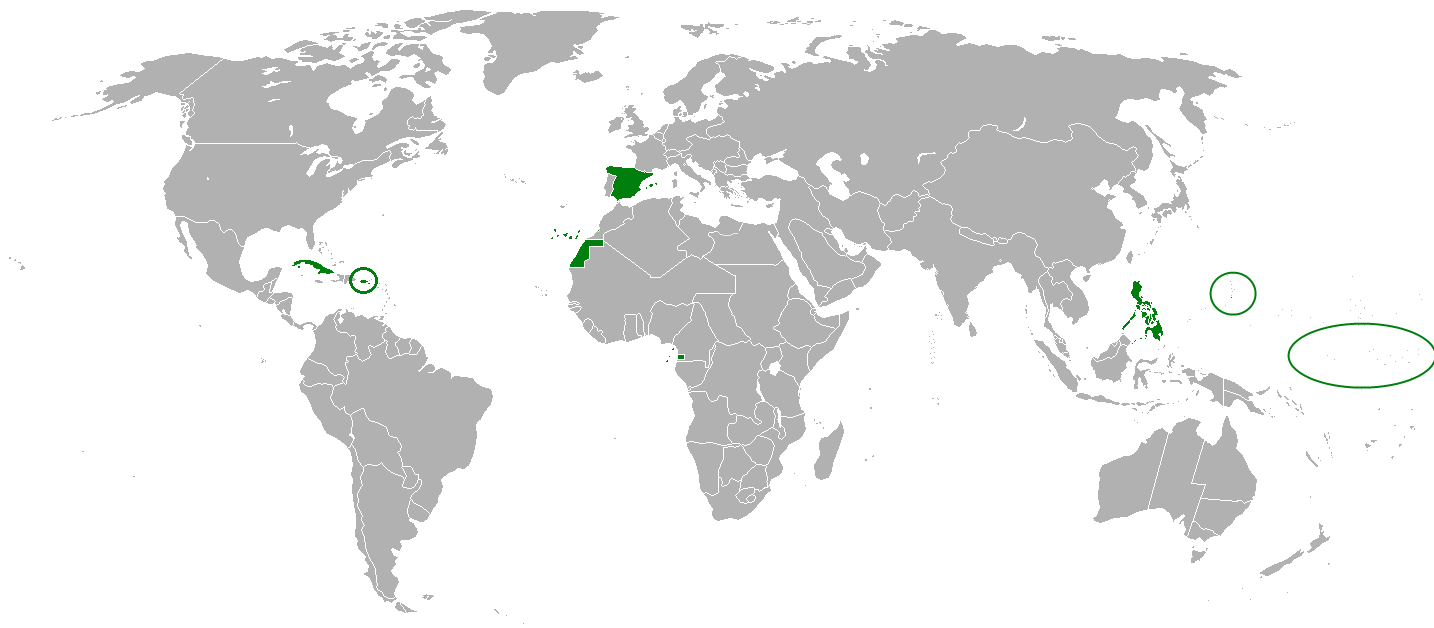 The uprisings in Cuba and the Philippine Islands culminated with the Spanish–American War of 1898. On 1 May, the American navy destroyed the Spanish Pacific fleet at the Battle of Manila Bay in the first List of battles of the Spanish–American War, battle of the Spanish–American War. The Battle of Las Guasimas, Battle of El Caney, and Battle of San Juan Hill were counted as American victories but saw the Spanish Army inflict heavier casualties. After isolating and defeating the Spanish garrisons in Cuba, the American navy destroyed the Spanish Caribbean fleet on 3 July at the Battle of Santiago de Cuba. A more modern Spanish fleet, which had been sent to try and recover Manila, was recalled to protect the Spanish coasts from a possible American attack. Thus ended any Spanish attempt to recapture or even to protect its colonies.
Military defeat was followed by the United States Military Government in Cuba, U.S. occupation of Cuba and the cession of
The uprisings in Cuba and the Philippine Islands culminated with the Spanish–American War of 1898. On 1 May, the American navy destroyed the Spanish Pacific fleet at the Battle of Manila Bay in the first List of battles of the Spanish–American War, battle of the Spanish–American War. The Battle of Las Guasimas, Battle of El Caney, and Battle of San Juan Hill were counted as American victories but saw the Spanish Army inflict heavier casualties. After isolating and defeating the Spanish garrisons in Cuba, the American navy destroyed the Spanish Caribbean fleet on 3 July at the Battle of Santiago de Cuba. A more modern Spanish fleet, which had been sent to try and recover Manila, was recalled to protect the Spanish coasts from a possible American attack. Thus ended any Spanish attempt to recapture or even to protect its colonies.
Military defeat was followed by the United States Military Government in Cuba, U.S. occupation of Cuba and the cession of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, and the Philippines to the United States, receiving US$20 million in compensation for the Philippines.
Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War][ or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an armed conflict between the First Philippine Republic and the United States that started on February 4, 1899, and ended on July 2, 1902. The conflict arose in 1898 when the United States, rather than acknowledging the Philippines' Philippine Declaration of Independence, declaration of independence, annexed the Philippines under the Treaty of Paris (1898), Treaty of Paris at the conclusion of the Spanish–American War. The war can be seen as a continuation of the Philippine struggle for independence that began in 1896 with the Philippine Revolution against Spanish East Indies, Spanish rule.
Fighting erupted between forces of the United States and those of the Philippine Republic on February 4, 1899, in what became known as the Battle of Manila (1899), 1899 Battle of Manila. On June 2, 1899, the First Philippine Republic officially declared war against the United States.][ The Philippine President Emilio Aguinaldo was captured on March 23, 1901, and the war was officially declared ended by the American government on July 2, 1902, with a victory for the United States. However, some Philippine groups—some led by veterans of the Katipunan, a Philippine revolutionary society that had launched the revolution against Spain—continued to battle the American forces for several more years. Among those leaders was Macario Sakay, a veteran Katipunan member who established Tagalog Republic#Bonifacio, (or re-established) the Tagalog Republic#Sakay, Tagalog Republic in 1902 along Katipunan lines in contrast to Aguinaldo's Republic, with himself as president. Other groups, including the Islam in the Philippines, Muslim Moro people, Moro peoples of the southern Philippines and Folk Catholicism, quasi-Catholic Pulahan religious movements, continued hostilities in remote areas. The resistance in the Moro-dominated provinces in the south, called the Moro Rebellion by the Americans, ended with their final defeat at the Battle of Bud Bagsak on June 15, 1913. The war resulted in at least 200,000 Filipino civilian deaths, mostly due to famine and disease.][ Some estimates for total civilian dead reach up to a million.]
Territories in Africa (1885–1975)
 By the end of the 17th century, only Melilla, Alhucemas, Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera (which had been taken again in 1564),
By the end of the 17th century, only Melilla, Alhucemas, Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera (which had been taken again in 1564), Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ar, سَبْتَة, Sabtah) is a Spanish autonomous city on the north coast of Africa.
Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. It is one of several Spanish territori ...
(part of the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the ...
since 1415, had chosen to retain its links to Spain once the Iberian Union
pt, União Ibérica
, conventional_long_name =Iberian Union
, common_name =
, year_start = 1580
, date_start = 25 August
, life_span = 1580–1640
, event_start = War of the Portuguese Succession
, event_end = Portuguese Restoration War
, ...
ended; the formal allegiance of Ceuta to Spain was recognized by the Treaty of Lisbon (1668), Treaty of Lisbon in 1668), Oran and Mers El Kébir remained as Spanish territory in Africa. The latter cities were lost in 1708, Spanish conquest of Oran (1732), reconquered in 1732 and sold by Charles IV of Spain, Charles IV in 1792.
In 1778, Fernando Poo (island), Fernando Poo Island (now Bioko), adjacent islets, and commercial rights to the mainland between the Niger river, Niger and Ogooué Rivers were ceded to Spain by the Portuguese in exchange for territory in South America (Treaty of El Pardo (1778), Treaty of El Pardo). In the 19th century, some Spanish explorers and missionaries would cross this zone, among them Manuel Iradier.
In 1848, Spanish troops occupied the uninhabited Chafarinas Islands, anticipating a French move on the rocks located off the North-African coast.
 In 1860, after the Spanish-Moroccan War (1859), Tetuan War, Morocco paid Spain 100 million pesetas as war reparations and ceded Sidi Ifni to Spain as a part of the Treaty of Tangiers, on the basis of the old outpost of Santa Cruz de la Mar Pequeña, thought to be Sidi Ifni. The following decades of Franco-Spanish collaboration resulted in the establishment and extension of Spanish protectorates south of the city, and Spanish influence obtained international recognition in the Berlin Conference of 1884: Spain administered Sidi Ifni and Western Sahara jointly. Spain claimed a protectorate over the coast of Guinea from
In 1860, after the Spanish-Moroccan War (1859), Tetuan War, Morocco paid Spain 100 million pesetas as war reparations and ceded Sidi Ifni to Spain as a part of the Treaty of Tangiers, on the basis of the old outpost of Santa Cruz de la Mar Pequeña, thought to be Sidi Ifni. The following decades of Franco-Spanish collaboration resulted in the establishment and extension of Spanish protectorates south of the city, and Spanish influence obtained international recognition in the Berlin Conference of 1884: Spain administered Sidi Ifni and Western Sahara jointly. Spain claimed a protectorate over the coast of Guinea from Cape Bojador
Cape Bojador ( ar, رأس بوجادور, trans. ''Rā's Būjādūr''; ber, ⴱⵓⵊⴷⵓⵔ, ''Bujdur''; Spanish and pt, Cabo Bojador; french: Cap Boujdour) is a headland on the west coast of Western Sahara, at 26° 07' 37"N, 14° 29' 57"W ...
to Ras Nouadhibou, Cap Blanc, too, and even try to press a claim over the Adrar (region), Adrar and Tiris Zemmour Region, Tiris regions in Mauritania. Río Muni became a protectorate in 1885 and a colony in 1900. Conflicting claims to the Guinea mainland were settled in 1900 by the Treaty of Paris (1900), Treaty of Paris, because of which Spain was left with a mere 26,000 km2 out of the 300,000 stretching east to the Ubangi River which they initially claimed.[William Gervase Clarence-Smith, 1986 "Spanish Equatorial Guinea, 1898–1940", in ''The Cambridge History of Africa: From 1905 to 1940'' Ed. J. D. Fage, A. D. Roberts, & Roland Anthony Oliver. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press>]
 Following a Rif War (1893), brief war in 1893, Morocco paid war reparations of 20 million pesetas and Spain expanded its influence south from Melilla. In 1911, Morocco was divided between the French and Spanish. The Riffians rebelled, led by Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Karim al-Khattabi, Abdelkrim, a former officer for the Spanish administration. The Battle of Annual (1921) during the Rif War was a major military defeat suffered by the Spanish army against Moroccan insurgents. A leading Spanish politician emphatically declared: "''We are at the most acute period of Spanish decadence''". After the disaster of Annual, Spain began Spanish use of chemical weapons in the Rif War, using German chemical weapons against the Moroccans. In September 1925, the Alhucemas landing by the Spanish Army and Navy with a small collaboration of an allied French contingent put an end to the Rif War. It is considered the first successful amphibious landing in history supported by seaborne air power and tanks.
In 1923, Tangier International Zone, Tangier was declared an international city under French, Spanish, British, and later Italian condominium (international law), joint administration.
Following a Rif War (1893), brief war in 1893, Morocco paid war reparations of 20 million pesetas and Spain expanded its influence south from Melilla. In 1911, Morocco was divided between the French and Spanish. The Riffians rebelled, led by Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Karim al-Khattabi, Abdelkrim, a former officer for the Spanish administration. The Battle of Annual (1921) during the Rif War was a major military defeat suffered by the Spanish army against Moroccan insurgents. A leading Spanish politician emphatically declared: "''We are at the most acute period of Spanish decadence''". After the disaster of Annual, Spain began Spanish use of chemical weapons in the Rif War, using German chemical weapons against the Moroccans. In September 1925, the Alhucemas landing by the Spanish Army and Navy with a small collaboration of an allied French contingent put an end to the Rif War. It is considered the first successful amphibious landing in history supported by seaborne air power and tanks.
In 1923, Tangier International Zone, Tangier was declared an international city under French, Spanish, British, and later Italian condominium (international law), joint administration.
 In 1926 Bioko and Rio Muni were united as the colony of Spanish Guinea, a status that would last until 1959. In 1931, following the fall of the monarchy, the African colonies became part of the Second Spanish Republic. In 1934, during the government of Prime Minister Alejandro Lerroux, Spanish troops led by General Osvaldo Capaz landed in Sidi Ifni and carried out the occupation of the territory, ceded ''de jure'' by Morocco in 1860. Two years later, Francisco Franco, a general of the Army of Africa (Spain), Army of Africa, rebelled against the republican government and started the Spanish Civil War (1936–39). During the Second World War the Vichy French presence in Tangier was overcome by that of Francoist Spain.
Spain lacked the wealth and the interest to develop an extensive economic infrastructure in its African colonies during the first half of the 20th century. However, through a Paternalism, paternalistic system, particularly on Bioko Island, Spain developed large Cocoa bean, cocoa plantations for which thousands of Nigerian workers were imported as laborers.
In 1926 Bioko and Rio Muni were united as the colony of Spanish Guinea, a status that would last until 1959. In 1931, following the fall of the monarchy, the African colonies became part of the Second Spanish Republic. In 1934, during the government of Prime Minister Alejandro Lerroux, Spanish troops led by General Osvaldo Capaz landed in Sidi Ifni and carried out the occupation of the territory, ceded ''de jure'' by Morocco in 1860. Two years later, Francisco Franco, a general of the Army of Africa (Spain), Army of Africa, rebelled against the republican government and started the Spanish Civil War (1936–39). During the Second World War the Vichy French presence in Tangier was overcome by that of Francoist Spain.
Spain lacked the wealth and the interest to develop an extensive economic infrastructure in its African colonies during the first half of the 20th century. However, through a Paternalism, paternalistic system, particularly on Bioko Island, Spain developed large Cocoa bean, cocoa plantations for which thousands of Nigerian workers were imported as laborers.
 In 1956, when French Morocco became independent, Spain surrendered Spanish Morocco to the new nation, but retained control of Sidi Ifni, the Tarfaya region and Spanish Sahara. Moroccan Sultan (later King) Mohammed V of Morocco, Mohammed V was interested in these territories and unsuccessfully invaded Spanish Sahara in 1957, in the Ifni War, or in Spain, the Forgotten War ('). In 1958, Spain ceded Tarfaya to Mohammed V and joined the previously separate districts of Saguia el-Hamra (in the north) and Río de Oro (in the south) to form the province of Spanish Sahara.
In 1959, the Spanish territory on the
In 1956, when French Morocco became independent, Spain surrendered Spanish Morocco to the new nation, but retained control of Sidi Ifni, the Tarfaya region and Spanish Sahara. Moroccan Sultan (later King) Mohammed V of Morocco, Mohammed V was interested in these territories and unsuccessfully invaded Spanish Sahara in 1957, in the Ifni War, or in Spain, the Forgotten War ('). In 1958, Spain ceded Tarfaya to Mohammed V and joined the previously separate districts of Saguia el-Hamra (in the north) and Río de Oro (in the south) to form the province of Spanish Sahara.
In 1959, the Spanish territory on the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is i ...
was established with a status similar to the provinces of metropolitan Spain. As the Spanish Equatorial Region, it was ruled by a governor general exercising military and civilian powers. The first local elections were held in 1959, and the first Equatoguinean representatives were seated in the Cortes Generales, Spanish parliament. Under the Basic Law of December 1963, limited autonomy was authorized under a joint legislative body for the territory's two provinces. The name of the country was changed to Equatorial Guinea. In March 1968, under pressure from Equatoguinean nationalists and the United Nations, Spain announced that it would grant the country independence.
In 1969, under international pressure, Spain returned Sidi Ifni to Morocco. Spanish control of Spanish Sahara endured until the 1975 Green March prompted a withdrawal, under Moroccan military pressure. The future of this former Spanish colony remains uncertain.
The Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, :es:Canarias, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to ...
and Spanish cities in the African mainland are considered an equal part of Spain and the European Union but have a different tax system.
Morocco still claims Ceuta, Melilla, and ' even though they are internationally recognized as administrative divisions of Spain. Isla Perejil Perejil Island crisis, was occupied on 11 July 2002 by Moroccan Gendarmerie and troops, who were evicted by Spanish Navy, Spanish naval forces in a bloodless operation.
Legacy
Although the Spanish Empire declined from its apogee in the middle seventeenth century, it remained a wonder for other Europeans for its sheer geographical span. London (Samuel Johnson poem), Writing in 1738, English author Samuel Johnson questioned, "Has heaven reserved, in pity to the poor,/No pathless waste or undiscovered shore,/No secret island in the boundless main,/No peaceful desert yet unclaimed by Spain?"
The Spanish Empire left a huge linguistic, religious, political, cultural, and urban architectural legacy in the Western Hemisphere. With over 470 million native speakers today, Spanish is the second List of languages by number of native speakers, most spoken native language in the world, as result of the introduction of the language of Castile—Castilian, "''Castellano''" —from Iberia to Spanish America, later expanded by the governments of successor independent republics. In the Philippines, the Spanish–American War (1898) brought the islands under U.S. jurisdiction, with English being imposed in schools and Spanish becoming Languages of the Philippines, a secondary official language. Many indigenous languages throughout the empire were often lost either as indigenous populations were decimated by war and disease, or as indigenous people mixed with colonists, and the Spanish language was taught and spread over time.
Gallery
File:Cathedral, City of Mexico. (15719792402).jpg, A photo of Metropolitan Cathedral of Mexico City, Cathedral of Mexico City, it is one of the largest cathedrals in Americas, built on the ruins of the Aztec main square.
File:Clock of Comayagua.jpg, The clock of Immaculate Conception Cathedral, Comayagua, Comaygua Cathedral's bell tower in Honduras is one of the oldest clocks in Americas and the oldest still working in the world.
See also
* Black legend (Spain)
* Cartography of Latin America
* Colonialism
* Creole nationalism
* Governor-General of the Philippines
* Historiography of Colonial Spanish America
* History of Spain
* History of the Americas
* List of countries that gained independence from Spain
* List of oldest buildings in the Americas
* Criollo people#Spanish colonial caste system, Society in the Spanish Colonial Americas
* Spain
** Columbian Viceroyalty
** Captaincy General of the Philippines, Las Islas Filipinas
** Spain in the 17th century
** Spain in the 18th century
** Spanish North Africa (disambiguation)
** Spanish West Africa
** Spanish West Indies
* Spanish Colonial architecture
* List of Spanish Viceroys of Aragon, Spanish Viceroys of Aragon
* List of Spanish Viceroys of Catalonia, Spanish Viceroys of Catalonia
* List of Spanish Viceroys of Naples, Spanish Viceroys of Naples
* List of Spanish Viceroys of Navarre, Spanish Viceroys of Navarre
* List of Spanish Viceroys of Sardinia, Spanish Viceroys of Sardinia
* List of Spanish Viceroys of Sicily, Spanish Viceroys of Sicily
* List of Spanish Viceroys of Valencia, Spanish Viceroys of Valencia
* List of Viceroys of New Granada, Viceroys of New Granada
* List of viceroys of New Spain, Viceroys of New Spain
* List of Viceroys of Peru, Viceroys of Peru
* Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata#List of viceroys, Viceroys of Río de la Plata
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* 5 volumes
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Kamen, Henry. ''Empire: How Spain Became a World Power, 1493–1763''. New York: HarperCollins 2003.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Library of Iberian Resources Online, Stanley G Payne ''A History of Spain and Portugal'' vol 1 Ch 13 "The Spanish Empire"
Documentary Film, ''Villa de Albuquerque''
The last Spanish colonies
*
at the Library of Congress contains primary materials on Spanish colonialism.
{{Authority control
Spanish Empire,
States and territories established in 1492
States and territories disestablished in 1976
Christian states
Former empires
History of European colonialism
House of Habsburg, Spain
Overseas empires
Spanish colonization of the Americas
1492 establishments in the Spanish Empire, .
1492 establishments in Spain, .
1976 disestablishments in Spain, .
2nd millennium in Spain
Historical transcontinental empires
 With the marriage of the heirs apparent to their respective thrones Ferdinand of Aragon and Isabella of Castile created a personal union that most scholars view as the foundation of the Spanish monarchy. The union of the Crowns of Castile and
With the marriage of the heirs apparent to their respective thrones Ferdinand of Aragon and Isabella of Castile created a personal union that most scholars view as the foundation of the Spanish monarchy. The union of the Crowns of Castile and  During the last 250 years of the
During the last 250 years of the  The Catholic Monarchs had developed a strategy of marriages for their children to isolate their long-time enemy: France. The Spanish princesses married the heirs of Portugal, England and the
The Catholic Monarchs had developed a strategy of marriages for their children to isolate their long-time enemy: France. The Spanish princesses married the heirs of Portugal, England and the  Portugal obtained several Papal bulls that acknowledged Portuguese control over the discovered territories, but Castile also obtained from the Pope the safeguard of its rights to the
Portugal obtained several Papal bulls that acknowledged Portuguese control over the discovered territories, but Castile also obtained from the Pope the safeguard of its rights to the 
 Seven months before the treaty of Alcaçovas, King John II of Aragon died, and his son Ferdinand II of Aragon, married to Isabella I of Castile, inherited the thrones of the
Seven months before the treaty of Alcaçovas, King John II of Aragon died, and his son Ferdinand II of Aragon, married to Isabella I of Castile, inherited the thrones of the  Unlike the crown of Portugal, Spain had not sought papal authorization for its explorations, but with Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492, the crown sought papal confirmation of their title to the new lands.John F. O'Callaghan, "Line of Demarcation," in Since the defense of Catholicism and propagation of the faith was the papacy's primary responsibility, there were a number of papal bulls promulgated that affected the powers of the crowns of Spain and Portugal in the religious sphere. Converting the inhabitants of in the newly discovered lands was entrusted by the papacy to the rulers of Portugal and Spain, through a series of papal actions. The
Unlike the crown of Portugal, Spain had not sought papal authorization for its explorations, but with Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492, the crown sought papal confirmation of their title to the new lands.John F. O'Callaghan, "Line of Demarcation," in Since the defense of Catholicism and propagation of the faith was the papacy's primary responsibility, there were a number of papal bulls promulgated that affected the powers of the crowns of Spain and Portugal in the religious sphere. Converting the inhabitants of in the newly discovered lands was entrusted by the papacy to the rulers of Portugal and Spain, through a series of papal actions. The  In the
In the  During the 1500s, the Spanish began to explore and colonize North America. They were looking for gold in native kingdoms. By 1511 there were rumours of undiscovered lands to the northwest of Hispaniola. Juan Ponce de León equipped three ships with at least 200 men at his own expense and set out from Puerto Rico on 4 March 1513 to Florida and surrounding coastal area. Another early motive was the search for the
During the 1500s, the Spanish began to explore and colonize North America. They were looking for gold in native kingdoms. By 1511 there were rumours of undiscovered lands to the northwest of Hispaniola. Juan Ponce de León equipped three ships with at least 200 men at his own expense and set out from Puerto Rico on 4 March 1513 to Florida and surrounding coastal area. Another early motive was the search for the 

 As a result of the marriage politics of the
As a result of the marriage politics of the 
 The Spanish Empire benefited from favorable
The Spanish Empire benefited from favorable  The crown established the system of treasure fleets ( es, link=no, flota) to protect the conveyance of silver to Seville (later Cadiz). Merchants in Seville conveyed consumer goods that were registered and taxed by the House of Trade were sent to the Indies were produced in other European countries. Other European commercial interests came to dominate supply, with Spanish merchant houses and their guilds ('' consulados'') in Spain and the Indies acting as mere middlemen, reaping profits a slice of the profits. However, those profits did not promote Spanish economic development of a manufacturing sector, with its economy continuing to be based on agriculture. The wealth of the Indies led to prosperity in northern Europe, particularly The Netherlands and England, both Protestant. As Spain's power weakened in the seventeenth century, England, The Netherlands, and the French took advantage overseas by seizing islands in the Caribbean, which became bases for a burgeoning contraband trade in Spanish America. Crown officials who were supposed to suppress contraband trade were quite often in cahoots with the foreigners, since it was a source of personal enrichment. In Spain, the crown itself participated in collusion with foreign merchant houses, since they paid fines, "meant to establish a compensation to the state for losses through fraud." it became for merchant houses a calculated risk for doing business; for the crown it gained income it would have lost otherwise. Foreigner merchants were part of the supposed monopoly system of trade. The transfer of the House of Trade from Seville to Cadiz meant even easier access of foreign merchant houses to the Spanish trade.
The motor of the Spanish imperial economy that had a global impact was
The crown established the system of treasure fleets ( es, link=no, flota) to protect the conveyance of silver to Seville (later Cadiz). Merchants in Seville conveyed consumer goods that were registered and taxed by the House of Trade were sent to the Indies were produced in other European countries. Other European commercial interests came to dominate supply, with Spanish merchant houses and their guilds ('' consulados'') in Spain and the Indies acting as mere middlemen, reaping profits a slice of the profits. However, those profits did not promote Spanish economic development of a manufacturing sector, with its economy continuing to be based on agriculture. The wealth of the Indies led to prosperity in northern Europe, particularly The Netherlands and England, both Protestant. As Spain's power weakened in the seventeenth century, England, The Netherlands, and the French took advantage overseas by seizing islands in the Caribbean, which became bases for a burgeoning contraband trade in Spanish America. Crown officials who were supposed to suppress contraband trade were quite often in cahoots with the foreigners, since it was a source of personal enrichment. In Spain, the crown itself participated in collusion with foreign merchant houses, since they paid fines, "meant to establish a compensation to the state for losses through fraud." it became for merchant houses a calculated risk for doing business; for the crown it gained income it would have lost otherwise. Foreigner merchants were part of the supposed monopoly system of trade. The transfer of the House of Trade from Seville to Cadiz meant even easier access of foreign merchant houses to the Spanish trade.
The motor of the Spanish imperial economy that had a global impact was  During the Bourbon era, economic reforms sought to reverse the pattern that left Spain impoverished with no manufacturing sector and its colonies' need for manufactured goods supplied by other nations. It attempted to restructure to establish as closed trading system, but it was hampered by the terms of the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht. The treaty ending the War of the Spanish Succession with a victory for the Bourbon French candidate for the throne had a provision for British merchants to legally sell by a license (''
During the Bourbon era, economic reforms sought to reverse the pattern that left Spain impoverished with no manufacturing sector and its colonies' need for manufactured goods supplied by other nations. It attempted to restructure to establish as closed trading system, but it was hampered by the terms of the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht. The treaty ending the War of the Spanish Succession with a victory for the Bourbon French candidate for the throne had a provision for British merchants to legally sell by a license ('' With the 1700 death of the childless
With the 1700 death of the childless  The Spanish Bourbons' broadest intentions were to reorganize the institutions of empire to better administer it for the benefit of Spain and the crown. It sought to increase revenues and to assert greater crown control, including over the Catholic Church. Centralization of power was to be for the benefit of the crown and the metropole and for the defense of its empire against foreign incursions.Kuethe, Allan J. "The Bourbon Reforms" in From the viewpoint of Spain, the structures of colonial rule under the Habsburgs were no longer functioning to the benefit of Spain, with much wealth being retained in Spanish America and going to other European powers. The presence of other European powers in the Caribbean, with the English in Barbados (1627), St Kitts (1623–25), and Jamaica (1655); the Dutch in Curaçao, and the French in Saint Domingue (Haiti) (1697), Martinique, and Guadeloupe had broken the integrity of the closed Spanish mercantile system and established thriving sugar colonies.
At the beginning of his reign, the first Spanish Bourbon, King Philip V, reorganized the government to strengthen the executive power of the monarch as was done in France, in place of the deliberative, Polysynodial System of Councils.
Philip's government set up a ministry of the Navy and the Indies (1714) and established commercial companies, the History of Honduras, Honduras Company (1714), a Caracas company, the Guipuzcoana Company (1728), and the most successful one, the History of Cuba, Havana Company (1740).
In 1717–18, the structures for governing the Indies, the ' and the ', which governed investments in the cumbersome Spanish treasure fleets, were transferred from
The Spanish Bourbons' broadest intentions were to reorganize the institutions of empire to better administer it for the benefit of Spain and the crown. It sought to increase revenues and to assert greater crown control, including over the Catholic Church. Centralization of power was to be for the benefit of the crown and the metropole and for the defense of its empire against foreign incursions.Kuethe, Allan J. "The Bourbon Reforms" in From the viewpoint of Spain, the structures of colonial rule under the Habsburgs were no longer functioning to the benefit of Spain, with much wealth being retained in Spanish America and going to other European powers. The presence of other European powers in the Caribbean, with the English in Barbados (1627), St Kitts (1623–25), and Jamaica (1655); the Dutch in Curaçao, and the French in Saint Domingue (Haiti) (1697), Martinique, and Guadeloupe had broken the integrity of the closed Spanish mercantile system and established thriving sugar colonies.
At the beginning of his reign, the first Spanish Bourbon, King Philip V, reorganized the government to strengthen the executive power of the monarch as was done in France, in place of the deliberative, Polysynodial System of Councils.
Philip's government set up a ministry of the Navy and the Indies (1714) and established commercial companies, the History of Honduras, Honduras Company (1714), a Caracas company, the Guipuzcoana Company (1728), and the most successful one, the History of Cuba, Havana Company (1740).
In 1717–18, the structures for governing the Indies, the ' and the ', which governed investments in the cumbersome Spanish treasure fleets, were transferred from  The Spanish American Enlightenment produced a huge body of information on Spain's overseas empire via scientific expeditions. The most famous traveler in Spanish America was Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt, whose travel writings, especially ''Political Essay on the Kingdom of New Spain'' and scientific observations remain important sources for the history of Spanish America. Humboldt's expedition was authorized by the crown, but was self-funded from his personal fortune. The Bourbon crown promoted state-funded scientific work prior to the famous Humboldt expedition. Eighteenth-century clerics contributed to the expansion of scientific knowledge. These include José Antonio de Alzate y Ramírez, and José Celestino Mutis.
The Spanish crown funded a number of important scientific expeditions: Botanical Expedition to the Viceroyalty of Peru (1777–78); Royal Botanical Expedition to New Granada (1783–1816); the Royal Botanical Expedition to New Spain (1787–1803); which scholars are now examining afresh. Although the crown funded a number of Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest to bolster claims to territory, lengthy transatlantic and transpacific Malaspina Expedition, Malaspina-Bustamante Expedition was for scientific purposes. The crown also funded the Balmis Expedition in 1804 to vaccinate colonial populations against smallpox.
Much of the research done in the eighteenth century was never published or otherwise disseminated, in part due to budgetary constraints on the crown. Starting in the late twentieth century, research on the history of science in Spain and the Spanish empire has blossomed, with primary sources being published in scholarly editions or reissued, as well the publication of a considerable number of important scholarly studies.
The Spanish American Enlightenment produced a huge body of information on Spain's overseas empire via scientific expeditions. The most famous traveler in Spanish America was Prussian scientist Alexander von Humboldt, whose travel writings, especially ''Political Essay on the Kingdom of New Spain'' and scientific observations remain important sources for the history of Spanish America. Humboldt's expedition was authorized by the crown, but was self-funded from his personal fortune. The Bourbon crown promoted state-funded scientific work prior to the famous Humboldt expedition. Eighteenth-century clerics contributed to the expansion of scientific knowledge. These include José Antonio de Alzate y Ramírez, and José Celestino Mutis.
The Spanish crown funded a number of important scientific expeditions: Botanical Expedition to the Viceroyalty of Peru (1777–78); Royal Botanical Expedition to New Granada (1783–1816); the Royal Botanical Expedition to New Spain (1787–1803); which scholars are now examining afresh. Although the crown funded a number of Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest to bolster claims to territory, lengthy transatlantic and transpacific Malaspina Expedition, Malaspina-Bustamante Expedition was for scientific purposes. The crown also funded the Balmis Expedition in 1804 to vaccinate colonial populations against smallpox.
Much of the research done in the eighteenth century was never published or otherwise disseminated, in part due to budgetary constraints on the crown. Starting in the late twentieth century, research on the history of science in Spain and the Spanish empire has blossomed, with primary sources being published in scholarly editions or reissued, as well the publication of a considerable number of important scholarly studies.

 Bourbon institutional reforms under Philip V bore fruit militarily when Spanish forces easily retook
Bourbon institutional reforms under Philip V bore fruit militarily when Spanish forces easily retook  Spain contributed to the independence of the Thirteen Colonies, thirteen American colonies (which formed the United States) together with France. Spain and France were allies because of the Bourbon "Pacte de Famille, Family Pact" carried out by both countries against Britain.
Great Siege of Gibraltar, Gibraltar was besieged for more than three years, but the British garrison stubbornly resisted and was resupplied twice: once after Admiral George Rodney's victory over Juan de Lángara in the 1780 Battle of Cape St. Vincent (1780), Battle of Cape St. Vincent, and again by Admiral Richard Howe in 1782. Further Franco-Spanish efforts to capture Gibraltar were unsuccessful. One notable success took place on 5 February 1782, when the Spanish Invasion of Minorca (1781), recaptured Minorca. Ambitious plans for an Armada of 1779, invasion of Britain in 1779 had to be abandoned. Admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova captured two British convoys totaling seventy-nine ships, including a fleet of fifty-five merchantmen and frigates in the action of 9 August 1780.
The Spanish governor of Louisiana (New Spain), Louisiana Bernardo de Gálvez launched several Gulf Coast campaign, successful offensives against British Florida (1779–81), capturing the entirety of West Florida from Britain. Gálvez also Capture of the Bahamas (1782), conquered the island New Providence in the Bahamas. Colony of Jamaica, Jamaica was the last British stronghold of importance in the Caribbean. Gálvez attempted to organize an expedition to capture the island; however, the Peace of Paris (1783), 1783 Peace of Paris was concluded and the invasion cancelled.
Under royal order from Charles III of Spain Gálvez continued the aid operations to supply the American rebels. The British blockaded the colonial ports of the Thirteen Colonies, and the route from Spanish-controlled New Orleans up to the Mississippi river was an effective alternative to supply the American rebels. Spain actively supported the thirteen colonies throughout the American Revolutionary War, beginning in 1776 by jointly funding Roderigue Hortalez and Company, a trading company that provided critical military supplies, throughout financing the final Siege of Yorktown (1781), Siege of Yorktown in 1781 with a collection of gold and silver from Havana. Spanish aid was supplied to the colonies via four main routes: from French ports with the funding of ''Roderigue Hortalez and Company''; through the port of New Orleans and up the Mississippi river; from warehouses in Havana; and (4)from the northwestern Spanish port of Bilbao, through the Gardoqui family trading company which supplied significant war materiel.
Spain contributed to the independence of the Thirteen Colonies, thirteen American colonies (which formed the United States) together with France. Spain and France were allies because of the Bourbon "Pacte de Famille, Family Pact" carried out by both countries against Britain.
Great Siege of Gibraltar, Gibraltar was besieged for more than three years, but the British garrison stubbornly resisted and was resupplied twice: once after Admiral George Rodney's victory over Juan de Lángara in the 1780 Battle of Cape St. Vincent (1780), Battle of Cape St. Vincent, and again by Admiral Richard Howe in 1782. Further Franco-Spanish efforts to capture Gibraltar were unsuccessful. One notable success took place on 5 February 1782, when the Spanish Invasion of Minorca (1781), recaptured Minorca. Ambitious plans for an Armada of 1779, invasion of Britain in 1779 had to be abandoned. Admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova captured two British convoys totaling seventy-nine ships, including a fleet of fifty-five merchantmen and frigates in the action of 9 August 1780.
The Spanish governor of Louisiana (New Spain), Louisiana Bernardo de Gálvez launched several Gulf Coast campaign, successful offensives against British Florida (1779–81), capturing the entirety of West Florida from Britain. Gálvez also Capture of the Bahamas (1782), conquered the island New Providence in the Bahamas. Colony of Jamaica, Jamaica was the last British stronghold of importance in the Caribbean. Gálvez attempted to organize an expedition to capture the island; however, the Peace of Paris (1783), 1783 Peace of Paris was concluded and the invasion cancelled.
Under royal order from Charles III of Spain Gálvez continued the aid operations to supply the American rebels. The British blockaded the colonial ports of the Thirteen Colonies, and the route from Spanish-controlled New Orleans up to the Mississippi river was an effective alternative to supply the American rebels. Spain actively supported the thirteen colonies throughout the American Revolutionary War, beginning in 1776 by jointly funding Roderigue Hortalez and Company, a trading company that provided critical military supplies, throughout financing the final Siege of Yorktown (1781), Siege of Yorktown in 1781 with a collection of gold and silver from Havana. Spanish aid was supplied to the colonies via four main routes: from French ports with the funding of ''Roderigue Hortalez and Company''; through the port of New Orleans and up the Mississippi river; from warehouses in Havana; and (4)from the northwestern Spanish port of Bilbao, through the Gardoqui family trading company which supplied significant war materiel.
 Spain claimed all of North America in the Age of Discovery, but claims were not translated into occupation until a major resource was discovered and Spanish settlement and crown rule put in place. The French had established an French America, empire in northern North America and took some islands in the Caribbean. The English established colonies on the eastern seaboard of North America and in northern North America and some Caribbean islands as well. In the eighteenth century, the Spanish crown realized that its territorial claims needed to be defended, particularly in the wake of its visible weakness during the Seven Years' War when Britain captured the important Spanish ports of Havana and Manila. Another important factor was that the Russian America, Russian empire had expanded into North America from the mid-eighteenth century, with Maritime fur trade, fur trading settlements in what is now Alaska and forts as far south as Fort Ross, California. Great Britain was also expanding into areas that Spain claimed as its territory on the Pacific coast. Taking steps to shore up its fragile claims to California, Spain began planning Spanish missions in California, California missions in 1769. Spain also began a series of voyages to the Pacific Northwest, where Russia and Great Britain were encroaching on claimed territory. The Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, with Alessandro Malaspina and others sailing for Spain, came too late for Spain to assert its sovereignty in the Pacific Northwest.
The Nootka Crisis (1789–1791) nearly brought Spain and Britain to war. It was a dispute over claims in the Pacific Northwest, where neither nation had established permanent settlements. The crisis could have led to war, but without French support Spain capitulated to British terms and negotiations took place with the Nootka Convention. Spain and Great Britain agreed to not establish settlements and allowed free access to Nootka Sound on the west coast of what is now Vancouver Island. Nevertheless, the outcome of the crisis was a humiliation for Spain and a triumph for Britain, as Spain had practically renounced all sovereignty on the North Pacific coast.
In 1806, Baron Nikolai Rezanov attempted to negotiate a treaty between the Russian-American Company and the Viceroyalty of New Spain, but his unexpected death in 1807 ended any treaty hopes. Spain gave up its claims in the West of North America in the Adams-Onis Treaty of 1819, ceding its rights there to the United States, allowing the U.S. to purchase Florida, and establishing a boundary between New Spain and the U.S. When the negotiations between the two nations were taking place, Spain's resources were stretched due to the Spanish American wars of independence. Much of the present-day American Southwest later became part of Mexico after its independence from Spain; after the Mexican–American War, Mexico ceded to the U.S. present-day California, Texas, New Mexico, Utah, Nevada, Arizona, and parts of Colorado, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska and Wyoming for $15 million.
Spain claimed all of North America in the Age of Discovery, but claims were not translated into occupation until a major resource was discovered and Spanish settlement and crown rule put in place. The French had established an French America, empire in northern North America and took some islands in the Caribbean. The English established colonies on the eastern seaboard of North America and in northern North America and some Caribbean islands as well. In the eighteenth century, the Spanish crown realized that its territorial claims needed to be defended, particularly in the wake of its visible weakness during the Seven Years' War when Britain captured the important Spanish ports of Havana and Manila. Another important factor was that the Russian America, Russian empire had expanded into North America from the mid-eighteenth century, with Maritime fur trade, fur trading settlements in what is now Alaska and forts as far south as Fort Ross, California. Great Britain was also expanding into areas that Spain claimed as its territory on the Pacific coast. Taking steps to shore up its fragile claims to California, Spain began planning Spanish missions in California, California missions in 1769. Spain also began a series of voyages to the Pacific Northwest, where Russia and Great Britain were encroaching on claimed territory. The Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, with Alessandro Malaspina and others sailing for Spain, came too late for Spain to assert its sovereignty in the Pacific Northwest.
The Nootka Crisis (1789–1791) nearly brought Spain and Britain to war. It was a dispute over claims in the Pacific Northwest, where neither nation had established permanent settlements. The crisis could have led to war, but without French support Spain capitulated to British terms and negotiations took place with the Nootka Convention. Spain and Great Britain agreed to not establish settlements and allowed free access to Nootka Sound on the west coast of what is now Vancouver Island. Nevertheless, the outcome of the crisis was a humiliation for Spain and a triumph for Britain, as Spain had practically renounced all sovereignty on the North Pacific coast.
In 1806, Baron Nikolai Rezanov attempted to negotiate a treaty between the Russian-American Company and the Viceroyalty of New Spain, but his unexpected death in 1807 ended any treaty hopes. Spain gave up its claims in the West of North America in the Adams-Onis Treaty of 1819, ceding its rights there to the United States, allowing the U.S. to purchase Florida, and establishing a boundary between New Spain and the U.S. When the negotiations between the two nations were taking place, Spain's resources were stretched due to the Spanish American wars of independence. Much of the present-day American Southwest later became part of Mexico after its independence from Spain; after the Mexican–American War, Mexico ceded to the U.S. present-day California, Texas, New Mexico, Utah, Nevada, Arizona, and parts of Colorado, Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska and Wyoming for $15 million.
 Spain was caught up in European events of the Napoleonic era that led to its loss of empire in Spanish America. Spain was France's ally, but it had tried to avoid being drawn directly into the ongoing conflict between Napoleon's France and Britain. Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), War broke out in 1804 after a British squadron Action of 5 October 1804, captured a Spanish convoy off Cape Santa Maria, Portugal. The British navy defeated the Spanish navy in the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. The following year, the British British invasions of the River Plate, attempted to seize the Río de la Plata estuary. The viceroy retreated hastily inland when defeated by a small British force. However, the ''Criollo people, Criollos militias and colonial army repulsed the now reinforced British force in 1807.
In 1808, the Spanish king was tricked and Spain was taken over by Napoleon without firing a shot, but the French provoked a popular uprising from the Spanish people and the grinding guerrilla warfare, which Napoleon dubbed his "ulcer," the Peninsular War, (famously depicted by the painter Goya) ensued. Spain gave the Napoleonic army their first open-field defeat at the Battle of Bailén (July 1808), which inspired Austria and Britain to form the War of the Fifth Coalition, Fifth Coalition against France.
Spain was caught up in European events of the Napoleonic era that led to its loss of empire in Spanish America. Spain was France's ally, but it had tried to avoid being drawn directly into the ongoing conflict between Napoleon's France and Britain. Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), War broke out in 1804 after a British squadron Action of 5 October 1804, captured a Spanish convoy off Cape Santa Maria, Portugal. The British navy defeated the Spanish navy in the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. The following year, the British British invasions of the River Plate, attempted to seize the Río de la Plata estuary. The viceroy retreated hastily inland when defeated by a small British force. However, the ''Criollo people, Criollos militias and colonial army repulsed the now reinforced British force in 1807.
In 1808, the Spanish king was tricked and Spain was taken over by Napoleon without firing a shot, but the French provoked a popular uprising from the Spanish people and the grinding guerrilla warfare, which Napoleon dubbed his "ulcer," the Peninsular War, (famously depicted by the painter Goya) ensued. Spain gave the Napoleonic army their first open-field defeat at the Battle of Bailén (July 1808), which inspired Austria and Britain to form the War of the Fifth Coalition, Fifth Coalition against France.
 The Napoleonic invasion provoked a crisis of sovereignty and legitimacy to rule, a new political framework, and the loss of most of Spanish America. In Spain, political uncertainty lasted over a decade and turmoil for several decades, civil wars on succession disputes, a republic, and finally a liberal democracy. Resistance coalesced around junta (Peninsular War), juntas, emergency ad hoc governments. A Supreme Central and Governing Junta of the Kingdom, Supreme Central Junta, ruling in the name of Ferdinand VII, was created on 25 September 1808 to coordinate efforts among the various juntas. Subsequently, a wikt:cortes, cortes or parliament was called, with representatives not only from Spain, but also Spanish America and the Philippines. In 1812, the Cortes of Cádiz drafted the
The Napoleonic invasion provoked a crisis of sovereignty and legitimacy to rule, a new political framework, and the loss of most of Spanish America. In Spain, political uncertainty lasted over a decade and turmoil for several decades, civil wars on succession disputes, a republic, and finally a liberal democracy. Resistance coalesced around junta (Peninsular War), juntas, emergency ad hoc governments. A Supreme Central and Governing Junta of the Kingdom, Supreme Central Junta, ruling in the name of Ferdinand VII, was created on 25 September 1808 to coordinate efforts among the various juntas. Subsequently, a wikt:cortes, cortes or parliament was called, with representatives not only from Spain, but also Spanish America and the Philippines. In 1812, the Cortes of Cádiz drafted the  The idea of a separate identity for Spanish America has been developed in the modern historical literature, but the idea of complete Spanish American independence from the Spanish Empire was not general at the time and political independence was not inevitable. Historian Brian Hamnett argues that had the Spanish monarchy and Spanish liberals been more flexible regarding the place of the overseas components, the empire would not have collapsed. Juntas emerged in Spanish America as Spain faced a political crisis due to the invasion and occupation by Napoleon Bonaparte and abdication of Ferdinand VII. Spanish Americans reacted in much the same way the Peninsular Spanish did, legitimizing their actions through traditional law, which held that sovereignty reverted to the people in the absence of a legitimate king.
The majority of Spanish Americans continued to support the idea of maintaining a monarchy, but did not support retaining absolute monarchy under Ferdinand VII. Spanish Americans wanted self-government. The juntas in the Americas did not accept the governments of the Europeans—neither the government set up for Spain by the French nor the various Spanish governments set up in response to the French invasion. The juntas did not accept the Spanish regency, isolated under Siege of Cádiz, siege in the city of Cadiz (1810–1812). They also rejected the
The idea of a separate identity for Spanish America has been developed in the modern historical literature, but the idea of complete Spanish American independence from the Spanish Empire was not general at the time and political independence was not inevitable. Historian Brian Hamnett argues that had the Spanish monarchy and Spanish liberals been more flexible regarding the place of the overseas components, the empire would not have collapsed. Juntas emerged in Spanish America as Spain faced a political crisis due to the invasion and occupation by Napoleon Bonaparte and abdication of Ferdinand VII. Spanish Americans reacted in much the same way the Peninsular Spanish did, legitimizing their actions through traditional law, which held that sovereignty reverted to the people in the absence of a legitimate king.
The majority of Spanish Americans continued to support the idea of maintaining a monarchy, but did not support retaining absolute monarchy under Ferdinand VII. Spanish Americans wanted self-government. The juntas in the Americas did not accept the governments of the Europeans—neither the government set up for Spain by the French nor the various Spanish governments set up in response to the French invasion. The juntas did not accept the Spanish regency, isolated under Siege of Cádiz, siege in the city of Cadiz (1810–1812). They also rejected the  During the Dominican Restoration War, the rebel leadership had changed frequently, only to be deposed in coups for corruption, politics or in the case of Gaspar Polanco (who lasted three months) leading a disastrous direct attack on the Spanish at Monte Cristi in December 1864. Thus by the end of 1864, it could be said the Spanish were winning. However, military victory was trumped by political defeat. The price of war in terms of money and lives had been huge, disease and the hardy guerrilla fighters of the island causing many casualties that Spain could ill afford, and in 1865, the Bourbon Queen Isabella II signed a decree annulling the annexation.
During the Dominican Restoration War, the rebel leadership had changed frequently, only to be deposed in coups for corruption, politics or in the case of Gaspar Polanco (who lasted three months) leading a disastrous direct attack on the Spanish at Monte Cristi in December 1864. Thus by the end of 1864, it could be said the Spanish were winning. However, military victory was trumped by political defeat. The price of war in terms of money and lives had been huge, disease and the hardy guerrilla fighters of the island causing many casualties that Spain could ill afford, and in 1865, the Bourbon Queen Isabella II signed a decree annulling the annexation.
 A few years later, the Ten Years' War (1868–78) would begin in Cuba. The Virginius Affair (31 October 1873), in which Spanish naval forces seized a filibustering ship flying the U.S. flag off Jamaica and executed more than fifty of its officers, crew, and passengers, seriously strained relations with the United States, but U.S. intervention in Cuba was averted by the diplomatic pressure of Britain. The Cubans defeated the Spanish in several battles, most notably at the Battle of Las Guasimas (1874), Battle of Las Guasimas in 1874, but Cuba's first war of independence ended inconclusively. Both sides sustained heavy casualties and the island sustained over $300 million in property damage. After the Cuban War of Independence broke out in 1895, Spain sent more than two hundred thousand soldiers to Cuba, the largest army ever to cross the Atlantic until World War II. Reconcentration policy, Spanish atrocities in Cuba and the sinking of an American battleship in Havana Harbor caused the U.S. to declare war on Spain in April 1898.
A few years later, the Ten Years' War (1868–78) would begin in Cuba. The Virginius Affair (31 October 1873), in which Spanish naval forces seized a filibustering ship flying the U.S. flag off Jamaica and executed more than fifty of its officers, crew, and passengers, seriously strained relations with the United States, but U.S. intervention in Cuba was averted by the diplomatic pressure of Britain. The Cubans defeated the Spanish in several battles, most notably at the Battle of Las Guasimas (1874), Battle of Las Guasimas in 1874, but Cuba's first war of independence ended inconclusively. Both sides sustained heavy casualties and the island sustained over $300 million in property damage. After the Cuban War of Independence broke out in 1895, Spain sent more than two hundred thousand soldiers to Cuba, the largest army ever to cross the Atlantic until World War II. Reconcentration policy, Spanish atrocities in Cuba and the sinking of an American battleship in Havana Harbor caused the U.S. to declare war on Spain in April 1898.
 The uprisings in Cuba and the Philippine Islands culminated with the Spanish–American War of 1898. On 1 May, the American navy destroyed the Spanish Pacific fleet at the Battle of Manila Bay in the first List of battles of the Spanish–American War, battle of the Spanish–American War. The Battle of Las Guasimas, Battle of El Caney, and Battle of San Juan Hill were counted as American victories but saw the Spanish Army inflict heavier casualties. After isolating and defeating the Spanish garrisons in Cuba, the American navy destroyed the Spanish Caribbean fleet on 3 July at the Battle of Santiago de Cuba. A more modern Spanish fleet, which had been sent to try and recover Manila, was recalled to protect the Spanish coasts from a possible American attack. Thus ended any Spanish attempt to recapture or even to protect its colonies.
Military defeat was followed by the United States Military Government in Cuba, U.S. occupation of Cuba and the cession of
The uprisings in Cuba and the Philippine Islands culminated with the Spanish–American War of 1898. On 1 May, the American navy destroyed the Spanish Pacific fleet at the Battle of Manila Bay in the first List of battles of the Spanish–American War, battle of the Spanish–American War. The Battle of Las Guasimas, Battle of El Caney, and Battle of San Juan Hill were counted as American victories but saw the Spanish Army inflict heavier casualties. After isolating and defeating the Spanish garrisons in Cuba, the American navy destroyed the Spanish Caribbean fleet on 3 July at the Battle of Santiago de Cuba. A more modern Spanish fleet, which had been sent to try and recover Manila, was recalled to protect the Spanish coasts from a possible American attack. Thus ended any Spanish attempt to recapture or even to protect its colonies.
Military defeat was followed by the United States Military Government in Cuba, U.S. occupation of Cuba and the cession of  By the end of the 17th century, only Melilla, Alhucemas, Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera (which had been taken again in 1564),
By the end of the 17th century, only Melilla, Alhucemas, Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera (which had been taken again in 1564),  In 1860, after the Spanish-Moroccan War (1859), Tetuan War, Morocco paid Spain 100 million pesetas as war reparations and ceded Sidi Ifni to Spain as a part of the Treaty of Tangiers, on the basis of the old outpost of Santa Cruz de la Mar Pequeña, thought to be Sidi Ifni. The following decades of Franco-Spanish collaboration resulted in the establishment and extension of Spanish protectorates south of the city, and Spanish influence obtained international recognition in the Berlin Conference of 1884: Spain administered Sidi Ifni and Western Sahara jointly. Spain claimed a protectorate over the coast of Guinea from
In 1860, after the Spanish-Moroccan War (1859), Tetuan War, Morocco paid Spain 100 million pesetas as war reparations and ceded Sidi Ifni to Spain as a part of the Treaty of Tangiers, on the basis of the old outpost of Santa Cruz de la Mar Pequeña, thought to be Sidi Ifni. The following decades of Franco-Spanish collaboration resulted in the establishment and extension of Spanish protectorates south of the city, and Spanish influence obtained international recognition in the Berlin Conference of 1884: Spain administered Sidi Ifni and Western Sahara jointly. Spain claimed a protectorate over the coast of Guinea from  Following a Rif War (1893), brief war in 1893, Morocco paid war reparations of 20 million pesetas and Spain expanded its influence south from Melilla. In 1911, Morocco was divided between the French and Spanish. The Riffians rebelled, led by Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Karim al-Khattabi, Abdelkrim, a former officer for the Spanish administration. The Battle of Annual (1921) during the Rif War was a major military defeat suffered by the Spanish army against Moroccan insurgents. A leading Spanish politician emphatically declared: "''We are at the most acute period of Spanish decadence''". After the disaster of Annual, Spain began Spanish use of chemical weapons in the Rif War, using German chemical weapons against the Moroccans. In September 1925, the Alhucemas landing by the Spanish Army and Navy with a small collaboration of an allied French contingent put an end to the Rif War. It is considered the first successful amphibious landing in history supported by seaborne air power and tanks.
In 1923, Tangier International Zone, Tangier was declared an international city under French, Spanish, British, and later Italian condominium (international law), joint administration.
Following a Rif War (1893), brief war in 1893, Morocco paid war reparations of 20 million pesetas and Spain expanded its influence south from Melilla. In 1911, Morocco was divided between the French and Spanish. The Riffians rebelled, led by Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Karim al-Khattabi, Abdelkrim, a former officer for the Spanish administration. The Battle of Annual (1921) during the Rif War was a major military defeat suffered by the Spanish army against Moroccan insurgents. A leading Spanish politician emphatically declared: "''We are at the most acute period of Spanish decadence''". After the disaster of Annual, Spain began Spanish use of chemical weapons in the Rif War, using German chemical weapons against the Moroccans. In September 1925, the Alhucemas landing by the Spanish Army and Navy with a small collaboration of an allied French contingent put an end to the Rif War. It is considered the first successful amphibious landing in history supported by seaborne air power and tanks.
In 1923, Tangier International Zone, Tangier was declared an international city under French, Spanish, British, and later Italian condominium (international law), joint administration.
 In 1926 Bioko and Rio Muni were united as the colony of Spanish Guinea, a status that would last until 1959. In 1931, following the fall of the monarchy, the African colonies became part of the Second Spanish Republic. In 1934, during the government of Prime Minister Alejandro Lerroux, Spanish troops led by General Osvaldo Capaz landed in Sidi Ifni and carried out the occupation of the territory, ceded ''de jure'' by Morocco in 1860. Two years later, Francisco Franco, a general of the Army of Africa (Spain), Army of Africa, rebelled against the republican government and started the Spanish Civil War (1936–39). During the Second World War the Vichy French presence in Tangier was overcome by that of Francoist Spain.
Spain lacked the wealth and the interest to develop an extensive economic infrastructure in its African colonies during the first half of the 20th century. However, through a Paternalism, paternalistic system, particularly on Bioko Island, Spain developed large Cocoa bean, cocoa plantations for which thousands of Nigerian workers were imported as laborers.
In 1926 Bioko and Rio Muni were united as the colony of Spanish Guinea, a status that would last until 1959. In 1931, following the fall of the monarchy, the African colonies became part of the Second Spanish Republic. In 1934, during the government of Prime Minister Alejandro Lerroux, Spanish troops led by General Osvaldo Capaz landed in Sidi Ifni and carried out the occupation of the territory, ceded ''de jure'' by Morocco in 1860. Two years later, Francisco Franco, a general of the Army of Africa (Spain), Army of Africa, rebelled against the republican government and started the Spanish Civil War (1936–39). During the Second World War the Vichy French presence in Tangier was overcome by that of Francoist Spain.
Spain lacked the wealth and the interest to develop an extensive economic infrastructure in its African colonies during the first half of the 20th century. However, through a Paternalism, paternalistic system, particularly on Bioko Island, Spain developed large Cocoa bean, cocoa plantations for which thousands of Nigerian workers were imported as laborers.
 In 1956, when French Morocco became independent, Spain surrendered Spanish Morocco to the new nation, but retained control of Sidi Ifni, the Tarfaya region and Spanish Sahara. Moroccan Sultan (later King) Mohammed V of Morocco, Mohammed V was interested in these territories and unsuccessfully invaded Spanish Sahara in 1957, in the Ifni War, or in Spain, the Forgotten War ('). In 1958, Spain ceded Tarfaya to Mohammed V and joined the previously separate districts of Saguia el-Hamra (in the north) and Río de Oro (in the south) to form the province of Spanish Sahara.
In 1959, the Spanish territory on the
In 1956, when French Morocco became independent, Spain surrendered Spanish Morocco to the new nation, but retained control of Sidi Ifni, the Tarfaya region and Spanish Sahara. Moroccan Sultan (later King) Mohammed V of Morocco, Mohammed V was interested in these territories and unsuccessfully invaded Spanish Sahara in 1957, in the Ifni War, or in Spain, the Forgotten War ('). In 1958, Spain ceded Tarfaya to Mohammed V and joined the previously separate districts of Saguia el-Hamra (in the north) and Río de Oro (in the south) to form the province of Spanish Sahara.
In 1959, the Spanish territory on the