Spacecraft Launched By India In 2019 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of
 A German
A German
"Shooting the duck"
''
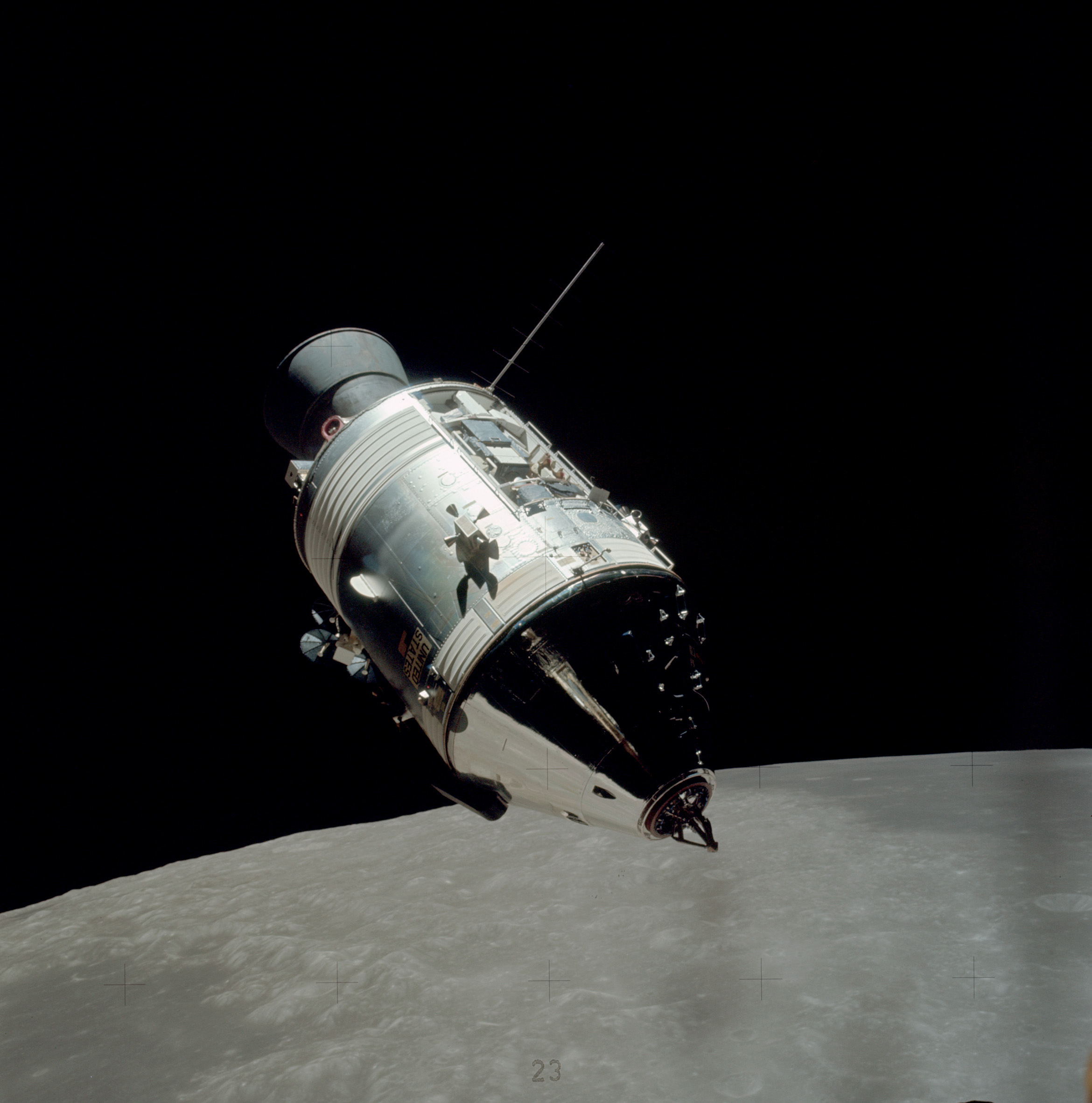 As of 2016, only three nations have flown crewed spacecraft: USSR/Russia, USA, and China.
The first crewed spacecraft was
As of 2016, only three nations have flown crewed spacecraft: USSR/Russia, USA, and China.
The first crewed spacecraft was
 A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisoto ...
, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
, Earth observation
Earth observation (EO) is the gathering of information about the physical, chemical, and biological systems of the planet Earth. It can be performed via remote-sensing technologies (Earth observation satellites) or through direct-contact sensors ...
, meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did no ...
, navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
, space colonization
Space colonization (also called space settlement or extraterrestrial colonization) is the use of outer space or celestial bodies other than Earth for permanent habitation or as extraterrestrial territory.
The inhabitation and territor ...
, planetary exploration
This is a timeline of Solar System exploration ordered by date of spacecraft launch. It includes:
*All spacecraft that have left Earth orbit for the purposes of Discovery and exploration of the Solar System, Solar System exploration (or were la ...
, and transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
of humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
and cargo
Cargo consists of bulk goods conveyed by water, air, or land. In economics, freight is cargo that is transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. ''Cargo'' was originally a shipload but now covers all types of freight, including trans ...
. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload ( spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pads, supported by a launch control center and ...
(carrier rocket).
On a sub-orbital spaceflight
A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the atmosphere or surface of the gravitating body from which it was launched, so that it will not complete one orbital re ...
, a space vehicle
A space vehicle is the combination of a spacecraft and its launch vehicle which carries it into space. The earliest space vehicles were expendable launch systems, using a single or multistage rocket to carry a relatively small spacecraft in pr ...
enters space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually cons ...
and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi) in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes days (1 sidereal year), during which time Eart ...
. For orbital spaceflight
An orbital spaceflight (or orbital flight) is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least one orbit. To do this around the Earth, it must be on a free trajectory which has an altit ...
s, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit ( space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space mission
A robotic spacecraft is an uncrewed spacecraft, usually under telerobotic control. A robotic spacecraft designed to make scientific research measurements is often called a space probe. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather ...
s operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific research are space probe
A space probe is an artificial satellite that travels through space to collect scientific data. A space probe may orbit Earth; approach the Moon; travel through interplanetary space; flyby, orbit, or land or fly on other planetary bodies; or ...
s. Robotic spacecraft that remain in orbit around a planetary body are artificial satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioi ...
s. To date, only a handful of interstellar probe
An interstellar probe is a space probe that has left—or is expected to leave—the Solar System and enter interstellar space, which is typically defined as the region beyond the heliopause. It also refers to probes capable of reaching other s ...
s, such as ''Pioneer 10
''Pioneer 10'' (originally designated Pioneer F) is an American space probe, launched in 1972 and weighing , that completed the first mission to the planet Jupiter. Thereafter, ''Pioneer 10'' became the first of five artificial objects to ach ...
'' and '' 11'', ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
'' and '' 2'', and '' New Horizons'', are on trajectories that leave the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
.
Orbital spacecraft may be recoverable or not. Most are not. Recoverable spacecraft may be subdivided by a method of reentry
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the ...
to Earth into non-winged space capsule
A space capsule is an often-crewed spacecraft that uses a blunt-body reentry capsule to reenter the Earth's atmosphere without wings. Capsules are distinguished from other satellites primarily by the ability to survive reentry and return a payl ...
s and winged spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes te ...
s. Recoverable spacecraft may be reusable (can be launched again or several times, like the SpaceX Dragon
American private space transportation company SpaceX has developed and produced several spacecraft named Dragon. The first family member, now referred to as Dragon 1, flew 23 cargo missions to the ISS between 2010 and 2020 before being retired. ...
and the Space Shuttle orbiter
The Space Shuttle orbiter is the spaceplane component of the Space Shuttle, a partially reusable orbital spacecraft system that was part of the discontinued Space Shuttle program. Operated from 1977 to 2011 by NASA, the U.S. space agency, thi ...
s) or expendable (like the Soyuz Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз ( Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалис ...
). In recent years, more space agencies are tending towards reusable spacecraft.
Humanity has achieved space flight, but only a few nations have the technology for orbital launches: Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
( RSA or "Roscosmos"), the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
(NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
), the member states of the European Space Agency (ESA), Japan ( JAXA), China (CNSA
China National Space Administration (CNSA; ) is the government agency of the People's Republic of China that is responsible for civil space administration and international space cooperation, including organizing or leading foreign exchanges ...
), India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
( ISRO), Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
National Chung-Shan Institute of Science and Technology
National Chung-Shan Institute of Science and Technology (NCSIST; ) is a Taiwanese state owned corporation, formerly part of the Republic of China Ministry of National Defense's Armaments Bureau, which is active in the development, manufactur ...
, Taiwan National Space Organization (NSPO), Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
( ISA), Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
( ISA), and North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
(NADA
Nada may refer to:
Culture
*Nāda, a concept in ancient Indian metaphysics
Places
*Nada, Hainan, China
*Nada, Kentucky, an unincorporated community in the United States
*Nada, Nepal, village in Achham District, Seti Zone
*Nada, Texas, United Sta ...
). In addition, several private companies have developed or are developing the technology for orbital launches independently from government agencies. The most prominent examples of such companies are SpaceX and Blue Origin.
History
 A German
A German V-2
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name ''Aggregat 4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was develope ...
became the first spacecraft when it reached an altitude of 189 km in June 1944 in Peenemünde
Peenemünde (, en, " Peene iverMouth") is a municipality on the Baltic Sea island of Usedom in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is part of the ''Amt'' (collective municipality) of Usedom-Nord. The commu ...
, Germany. Sputnik 1 was the first artificial satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisoto ...
. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never mor ...
(LEO) by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
on 4 October 1957. The launch ushered in new political, military, technological, and scientific developments; while the Sputnik launch was a single event, it marked the start of the Space Age
The Space Age is a period encompassing the activities related to the Space Race, space exploration, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events, beginning with the launch of Sputnik 1 during 1957, and continuin ...
.Dougall, Walter A. (Winter 2010"Shooting the duck"
''
American Heritage American Heritage may refer to:
* ''American Heritage'' (magazine)
* ''The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language''
* American Heritage Rivers
* American Heritage School (disambiguation)
See also
*National Register of Historic Place ...
'' Apart from its value as a technological first, Sputnik 1 also helped to identify the upper atmospheric layer's density, through measuring the satellite's orbital changes. It also provided data on radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmi ...
-signal distribution in the ionosphere. Pressurized nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
in the satellite's false body provided the first opportunity for meteoroid
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mi ...
detection. Sputnik 1 was launched during the International Geophysical Year from Site No.1/5, at the 5th Tyuratam
Töretam ( kk, link=no, Төретам, Töretam; russian: link=no, Тюратам, Tyuratam) is a station on the main Moscow to Tashkent railway, located in Kazakhstan. The name means "Töre's grave" in the Kazakh language. Töre, or more formal ...
range, in Kazakh SSR
; kk, Қазақ Советтік Социалистік Республикасы)
*1991: Republic of Kazakhstan (russian: Республика Казахстан; kk, Қазақстан Республикасы)
, linking_name = the ...
(now at the Baikonur Cosmodrome). The satellite traveled at , taking 96.2 minutes to complete an orbit, and emitted radio signals at 20.005 and 40.002 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one he ...
While Sputnik 1 was the first spacecraft to orbit the Earth, other man-made objects had previously reached an altitude of 100 km, which is the height required by the international organization Fédération Aéronautique Internationale to count as a spaceflight. This altitude is called the Kármán line. In particular, in the 1940s there were several test launches of the V-2 rocket
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name ''Aggregat 4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was develop ...
, some of which reached altitudes well over 100 km.
Spacecraft types
Crewed spacecraft
 As of 2016, only three nations have flown crewed spacecraft: USSR/Russia, USA, and China.
The first crewed spacecraft was
As of 2016, only three nations have flown crewed spacecraft: USSR/Russia, USA, and China.
The first crewed spacecraft was Vostok 1
Vostok 1 (russian: link=no, Восток, ''East'' or ''Orient'' 1) was the first spaceflight of the Vostok programme and the first human orbital spaceflight in history. The Vostok 3KA space capsule was launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome on Apr ...
, which carried Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who became the first human to journey into outer space. T ...
into space in 1961, and completed a full Earth orbit. There were five other crewed missions which used a Vostok spacecraft
Vostok (russian: Восток, translated as "East") was a class of single-pilot crewed spacecraft built by the Soviet Union. The first human spaceflight was accomplished with Vostok 1 on April 12, 1961, by Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin.
The ...
. The second crewed spacecraft was named ''Freedom 7'', and it performed a sub-orbital spaceflight
A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the atmosphere or surface of the gravitating body from which it was launched, so that it will not complete one orbital re ...
in 1961 carrying American astronaut Alan Shepard
Alan Bartlett Shepard Jr. (November 18, 1923 – July 21, 1998) was an American astronaut, naval aviator, test pilot, and businessman. In 1961, he became the second person and the first American to travel into space and, in 1971, he beca ...
to an altitude of just over . There were five other crewed missions using Mercury spacecraft
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbit and return him safely, ideally before the Soviet Un ...
.
Other Soviet crewed spacecraft include the Voskhod, Soyuz Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз ( Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалис ...
, flown uncrewed as Zond/L1, L3, TKS
The TK (TK-3) and TKS were Polish tankettes developed during the 1930s and used in the Second World War.
Design and development
The TK (also known as the TK-3) tankette was a Polish design produced from 1931 based on the chassis of the British ...
, and the Salyut
The ''Salyut'' programme (russian: Салют, , meaning "salute" or "fireworks") was the first space station programme, undertaken by the Soviet Union. It involved a series of four crewed scientific research space stations and two crewed ...
and ''Mir
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to&n ...
'' crewed space stations. Other American crewed spacecraft include the Gemini spacecraft
Project Gemini () was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual ...
, the Apollo spacecraft
The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft ...
including the Apollo Lunar Module, the Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations ...
space station, the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program ...
with undetached European Spacelab
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by European Space Agency (ESA) and used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory comprised multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier, ...
and private US Spacehab
Astrotech Corporation, formerly Spacehab Inc., is a technology incubator headquartered in Austin, Texas. Astrotech uses technology sourced internally and from research institutions, government laboratories, and universities to fund, manage and s ...
space stations-modules, and the SpaceX Crew Dragon configuration of their Dragon 2
Dragon 2 is a class of partially reusable spacecraft developed and manufactured by American aerospace manufacturer SpaceX, primarily for flights to the International Space Station (ISS). SpaceX has also launched private missions such as Ins ...
. US company Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and p ...
also developed and flown a spacecraft of their own, the CST-100
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner
is a class of two partially Starliner, but a crewed flight is yet to occur. China developed, but did not fly Shuguang, and is currently using Shenzhou (its first crewed mission was in 2003). Except for the Space Shuttle, all of the recoverable crewed orbital spacecraft were
File:NASA spacecraft comparison.jpg, alt=Drawings of Mercury, Gemini capsules and Apollo spacecraft, with their launch vehicles, American Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo spacecraft
File:Vostok Spacecraft Diagram.svg, Soviet Vostok capsule
File:Voskhod 1 and 2.svg, alt=Line drawing of Voskhod capsules, Soviet Voskhod (variant of Vostok)
File:Soyuz 7K-OK(A) drawing.svg, alt=Soyuz 7K-OK(A) drawing, 1967 Soviet/Russian Soyuz spacecraft
File:Post S-7 Shenzhou spacecraft.png, alt=Drawing of Shenzhou spacecraft, Chinese Shenzhou spacecraft
The
 Spaceplanes are spacecraft are built in the shape of, and function as,
Spaceplanes are spacecraft are built in the shape of, and function as,



 *''Akatsuki (spacecraft), Akatsuki'' JPN – a Venus orbiter
*''Cassini–Huygens'' – first Saturn orbiter and Titan (moon), Titan lander
*Curiosity (rover), ''Curiosity'' – Rover sent to Mars by NASA in 2012
*Galileo spacecraft, ''Galileo'' – first Jupiter orbiter and descent probe
*IKAROS JPN – first solar-sail spacecraft
*Mariner 4 – first Mars flyby, first close and high resolution images of Mars
*Mariner 9 – first Mars orbiter
*Mariner 10 – first Mercury (planet), Mercury flyby, first close up images
*Mars Exploration Rovers (''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'')– Mars rovers
*''Mars Express'' – Mars orbiter
*''Mars Global Surveyor'' – Mars orbiter
*Mars Orbiter Mission (''Mangalyaan'') - India's first Interplanetary probe
*''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' – an advanced climate, imaging, sub-surface radar, and telecommunications Mars orbiter
*''MESSENGER'' – first Mercury orbiter (arrival 2011)
*''Mars Pathfinder'' – Mars lander, carrying the ''Sojourner (rover), Sojourner'' rover
*'' New Horizons'' – first Pluto flyby (arrival 2015)
*''
*''Akatsuki (spacecraft), Akatsuki'' JPN – a Venus orbiter
*''Cassini–Huygens'' – first Saturn orbiter and Titan (moon), Titan lander
*Curiosity (rover), ''Curiosity'' – Rover sent to Mars by NASA in 2012
*Galileo spacecraft, ''Galileo'' – first Jupiter orbiter and descent probe
*IKAROS JPN – first solar-sail spacecraft
*Mariner 4 – first Mars flyby, first close and high resolution images of Mars
*Mariner 9 – first Mars orbiter
*Mariner 10 – first Mercury (planet), Mercury flyby, first close up images
*Mars Exploration Rovers (''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'')– Mars rovers
*''Mars Express'' – Mars orbiter
*''Mars Global Surveyor'' – Mars orbiter
*Mars Orbiter Mission (''Mangalyaan'') - India's first Interplanetary probe
*''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' – an advanced climate, imaging, sub-surface radar, and telecommunications Mars orbiter
*''MESSENGER'' – first Mercury orbiter (arrival 2011)
*''Mars Pathfinder'' – Mars lander, carrying the ''Sojourner (rover), Sojourner'' rover
*'' New Horizons'' – first Pluto flyby (arrival 2015)
*''

 ; Attitude control
: A Spacecraft needs an attitude control subsystem to be correctly oriented in space and respond to external torques and forces properly. The attitude control subsystem consists of sensors and actuators, together with controlling algorithms. The attitude-control subsystem permits proper pointing for the science objective, sun pointing for power to the solar arrays and earth pointing for communications.
; GNC
: Guidance refers to the calculation of the commands (usually done by the CDH subsystem) needed to steer the spacecraft where it is desired to be. Navigation means determining a spacecraft's orbital elements or position. Control means adjusting the path of the spacecraft to meet mission requirements.
; Command and data handling
: The C&DH subsystem receives commands from the communications subsystem, performs validation and decoding of the commands, and distributes the commands to the appropriate spacecraft subsystems and components. The CDH also receives housekeeping data and science data from the other spacecraft subsystems and components, and packages the data for storage on a data recorder or transmission to the ground via the communications subsystem. Other functions of the CDH include maintaining the spacecraft clock and state-of-health monitoring.
; Communications
: Spacecraft, both Robotic spacecraft, robotic and Human spaceflight, crewed, utilize various communications systems for communication with terrestrial stations as well as for communication between spacecraft in space. Technologies utilized include Radio-frequency communication, RF and Free-space optical communication, optical communication. In addition, some spacecraft payloads are explicitly for the purpose of ground–ground Commsat, communication using Bent pipe, receiver/retransmitter electronic technologies.
; Power
: Spacecraft need an electrical power generation and distribution subsystem for powering the various spacecraft subsystems. For spacecraft near the Sun, Solar panels on spacecraft, solar panels are frequently used to generate electrical power. Spacecraft designed to operate in more distant locations, for example Jupiter, might employ a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) to generate electrical power. Electrical power is sent through power conditioning equipment before it passes through a power distribution unit over an electrical bus to other spacecraft components. Batteries are typically connected to the bus via a battery charge regulator, and the batteries are used to provide electrical power during periods when primary power is not available, for example when a low Earth orbit spacecraft is eclipsed by Earth.
; Thermal control
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand transit through Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and the space environment. They must operate in a vacuum with temperatures potentially ranging across hundreds of degrees Celsius as well as (if subject to reentry) in the presence of plasmas. Material requirements are such that either high melting temperature, low density materials such as beryllium and reinforced carbon–carbon or (possibly due to the lower thickness requirements despite its high density) tungsten or Ablation, ablative carbon–carbon composites are used. Depending on mission profile, spacecraft may also need to operate on the surface of another planetary body. The thermal control subsystem can be passive, dependent on the selection of materials with specific radiative properties. Active thermal control makes use of electrical heaters and certain actuators such as louvers to control temperature ranges of equipments within specific ranges.
; Spacecraft propulsion
: Spacecraft may or may not have a Spacecraft propulsion, propulsion subsystem, depending on whether or not the mission profile calls for propulsion. The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission, ''Swift'' spacecraft is an example of a spacecraft that does not have a propulsion subsystem. Typically though, LEO spacecraft include a propulsion subsystem for altitude adjustments (drag make-up maneuvers) and inclination adjustment maneuvers. A propulsion system is also needed for spacecraft that perform momentum management maneuvers. Components of a conventional propulsion subsystem include fuel, tankage, valves, pipes, and Rocket engine, thrusters. The thermal control system interfaces with the propulsion subsystem by monitoring the temperature of those components, and by preheating tanks and thrusters in preparation for a spacecraft maneuver.
; Structures
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand launch loads imparted by the launch vehicle, and must have a point of attachment for all the other subsystems. Depending on mission profile, the structural subsystem might need to withstand loads imparted by entry into the Celestial body atmosphere, atmosphere of another planetary body, and landing on the surface of another planetary body.
; Payload
: The payload depends on the mission of the spacecraft, and is typically regarded as the part of the spacecraft "that pays the bills". Typical payloads could include scientific instruments (cameras, telescopes, or particle detectors, for example), cargo, or a Human spaceflight, human crew.
; Ground segment
: The ground segment, though not technically part of the spacecraft, is vital to the operation of the spacecraft. Typical components of a ground segment in use during normal operations include a mission operations facility where the flight operations team conducts the operations of the spacecraft, a data processing and storage facility, Earth station, ground stations to radiate signals to and receive signals from the spacecraft, and a voice and data communications network to connect all mission elements.
; Launch vehicle
: The
; Attitude control
: A Spacecraft needs an attitude control subsystem to be correctly oriented in space and respond to external torques and forces properly. The attitude control subsystem consists of sensors and actuators, together with controlling algorithms. The attitude-control subsystem permits proper pointing for the science objective, sun pointing for power to the solar arrays and earth pointing for communications.
; GNC
: Guidance refers to the calculation of the commands (usually done by the CDH subsystem) needed to steer the spacecraft where it is desired to be. Navigation means determining a spacecraft's orbital elements or position. Control means adjusting the path of the spacecraft to meet mission requirements.
; Command and data handling
: The C&DH subsystem receives commands from the communications subsystem, performs validation and decoding of the commands, and distributes the commands to the appropriate spacecraft subsystems and components. The CDH also receives housekeeping data and science data from the other spacecraft subsystems and components, and packages the data for storage on a data recorder or transmission to the ground via the communications subsystem. Other functions of the CDH include maintaining the spacecraft clock and state-of-health monitoring.
; Communications
: Spacecraft, both Robotic spacecraft, robotic and Human spaceflight, crewed, utilize various communications systems for communication with terrestrial stations as well as for communication between spacecraft in space. Technologies utilized include Radio-frequency communication, RF and Free-space optical communication, optical communication. In addition, some spacecraft payloads are explicitly for the purpose of ground–ground Commsat, communication using Bent pipe, receiver/retransmitter electronic technologies.
; Power
: Spacecraft need an electrical power generation and distribution subsystem for powering the various spacecraft subsystems. For spacecraft near the Sun, Solar panels on spacecraft, solar panels are frequently used to generate electrical power. Spacecraft designed to operate in more distant locations, for example Jupiter, might employ a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) to generate electrical power. Electrical power is sent through power conditioning equipment before it passes through a power distribution unit over an electrical bus to other spacecraft components. Batteries are typically connected to the bus via a battery charge regulator, and the batteries are used to provide electrical power during periods when primary power is not available, for example when a low Earth orbit spacecraft is eclipsed by Earth.
; Thermal control
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand transit through Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and the space environment. They must operate in a vacuum with temperatures potentially ranging across hundreds of degrees Celsius as well as (if subject to reentry) in the presence of plasmas. Material requirements are such that either high melting temperature, low density materials such as beryllium and reinforced carbon–carbon or (possibly due to the lower thickness requirements despite its high density) tungsten or Ablation, ablative carbon–carbon composites are used. Depending on mission profile, spacecraft may also need to operate on the surface of another planetary body. The thermal control subsystem can be passive, dependent on the selection of materials with specific radiative properties. Active thermal control makes use of electrical heaters and certain actuators such as louvers to control temperature ranges of equipments within specific ranges.
; Spacecraft propulsion
: Spacecraft may or may not have a Spacecraft propulsion, propulsion subsystem, depending on whether or not the mission profile calls for propulsion. The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission, ''Swift'' spacecraft is an example of a spacecraft that does not have a propulsion subsystem. Typically though, LEO spacecraft include a propulsion subsystem for altitude adjustments (drag make-up maneuvers) and inclination adjustment maneuvers. A propulsion system is also needed for spacecraft that perform momentum management maneuvers. Components of a conventional propulsion subsystem include fuel, tankage, valves, pipes, and Rocket engine, thrusters. The thermal control system interfaces with the propulsion subsystem by monitoring the temperature of those components, and by preheating tanks and thrusters in preparation for a spacecraft maneuver.
; Structures
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand launch loads imparted by the launch vehicle, and must have a point of attachment for all the other subsystems. Depending on mission profile, the structural subsystem might need to withstand loads imparted by entry into the Celestial body atmosphere, atmosphere of another planetary body, and landing on the surface of another planetary body.
; Payload
: The payload depends on the mission of the spacecraft, and is typically regarded as the part of the spacecraft "that pays the bills". Typical payloads could include scientific instruments (cameras, telescopes, or particle detectors, for example), cargo, or a Human spaceflight, human crew.
; Ground segment
: The ground segment, though not technically part of the spacecraft, is vital to the operation of the spacecraft. Typical components of a ground segment in use during normal operations include a mission operations facility where the flight operations team conducts the operations of the spacecraft, a data processing and storage facility, Earth station, ground stations to radiate signals to and receive signals from the spacecraft, and a voice and data communications network to connect all mission elements.
; Launch vehicle
: The
NASA: Space Science Spacecraft Missions
NSSDC Master Catalog Spacecraft Query FormBasics of Spaceflight tutorial from JPL/CaltechInternational Spaceflight Museum
{{Authority control Spacecraft, Astronautics Pressure vessels
is a class of two partially Starliner, but a crewed flight is yet to occur. China developed, but did not fly Shuguang, and is currently using Shenzhou (its first crewed mission was in 2003). Except for the Space Shuttle, all of the recoverable crewed orbital spacecraft were
space capsule
A space capsule is an often-crewed spacecraft that uses a blunt-body reentry capsule to reenter the Earth's atmosphere without wings. Capsules are distinguished from other satellites primarily by the ability to survive reentry and return a payl ...
s.
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA ( ...
, crewed since November 2000, is a joint venture between Russia, the United States, Canada and several other countries.
Spaceplanes
 Spaceplanes are spacecraft are built in the shape of, and function as,
Spaceplanes are spacecraft are built in the shape of, and function as, airplane
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, Propeller (aircraft), propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurat ...
s. The first example of such was the North American X-15 spaceplane, which conducted two crewed flights which reached an altitude of over 100 km in the 1960s. This first reusable spacecraft was air-launched on a suborbital trajectory on July 19, 1963.
The first partially reusable orbital spacecraft, a winged non-capsule, the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program ...
, was launched by the USA on the 20th anniversary of Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who became the first human to journey into outer space. T ...
's flight, on April 12, 1981. During the Shuttle era, six orbiters were built, all of which have flown in the atmosphere and five of which have flown in space. ''Enterprise
Enterprise (or the archaic spelling Enterprize) may refer to:
Business and economics
Brands and enterprises
* Enterprise GP Holdings, an energy holding company
* Enterprise plc, a UK civil engineering and maintenance company
* Enterpris ...
'' was used only for approach and landing tests, launching from the back of a Boeing 747 SCA and gliding to deadstick landings at Edwards AFB, California. The first Space Shuttle to fly into space was '' Columbia'', followed by '' Challenger'', ''Discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discover ...
'', ''Atlantis
Atlantis ( grc, Ἀτλαντὶς νῆσος, , island of Atlas) is a fictional island mentioned in an allegory on the hubris of nations in Plato's works '' Timaeus'' and '' Critias'', wherein it represents the antagonist naval power that b ...
'', and '' Endeavour''. ''Endeavour'' was built to replace ''Challenger'' when it was lost
Lost may refer to getting lost, or to:
Geography
*Lost, Aberdeenshire, a hamlet in Scotland
* Lake Okeechobee Scenic Trail, or LOST, a hiking and cycling trail in Florida, US
History
*Abbreviation of lost work, any work which is known to have bee ...
in January 1986. ''Columbia'' broke up
A relationship breakup, breakup, or break-up is the termination of a relationship. The act is commonly termed "dumping omeone in slang when it is initiated by one partner. The term is less likely to be applied to a married couple, where a bre ...
during reentry in February 2003.
The first automatic partially reusable spacecraft was the ''Buran''-class shuttle, launched by the USSR on November 15, 1988, although it made only one flight and this was uncrewed. This spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes te ...
was designed for a crew and strongly resembled the U.S. Space Shuttle, although its drop-off boosters used liquid propellants and its main engines were located at the base of what would be the external tank in the American Shuttle. Lack of funding, complicated by the dissolution of the USSR
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
, prevented any further flights of Buran. The Space Shuttle was subsequently modified to allow for autonomous re-entry in case of necessity.
Per the Vision for Space Exploration, the Space Shuttle was retired in 2011 mainly due to its old age and high cost of program reaching over a billion dollars per flight. The Shuttle's human transport role is to be replaced by SpaceX's SpaceX Dragon 2 and Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and p ...
's CST-100 Starliner. Dragon 2's first crewed flight occurred on May 30, 2020. The Shuttle's heavy cargo transport role is to be replaced by expendable rockets such as the Space Launch System and United Launch Alliance, ULA's Vulcan (rocket), Vulcan rocket, as well as the commercial launch vehicles.
Scaled Composites' SpaceShipOne was a reusable suborbital spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes te ...
that carried pilots Mike Melvill and Brian Binnie on consecutive flights in 2004 to win the Ansari X Prize. The Spaceship Company will build its successor SpaceShipTwo. A fleet of SpaceShipTwos operated by Virgin Galactic was planned to begin reusable private spaceflight carrying paying passengers in 2014, but was delayed after the VSS Enterprise crash, crash of VSS ''Enterprise''.
Uncrewed spacecraft


Semi-crewed – crewed as space stations or part of space stations
* Progress spacecraft, Progress – uncrewed USSR/Russia cargo spacecraft *TKS
The TK (TK-3) and TKS were Polish tankettes developed during the 1930s and used in the Second World War.
Design and development
The TK (also known as the TK-3) tankette was a Polish design produced from 1931 based on the chassis of the British ...
– uncrewed USSR/Russia cargo spacecraft and space station module
* Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) – uncrewed European cargo spacecraft
* H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV) – uncrewed Japanese cargo spacecraft
* SpaceX Dragon
American private space transportation company SpaceX has developed and produced several spacecraft named Dragon. The first family member, now referred to as Dragon 1, flew 23 cargo missions to the ISS between 2010 and 2020 before being retired. ...
– uncrewed private spacecraft
* ''Tianzhou (spacecraft), Tianzhou'' – China's uncrewed cargo spacecraft
* Cygnus (spacecraft), Northrop Grumman Cygnus – uncrewed commercial spacecraft
Earth-orbit satellites
* Explorer 1 – first US satellite * Project SCORE – first communications satellite * Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) - orbits the Sun near L1 * Sputnik 1 – world's first artificial satellite * Sputnik 2 – first animal in orbit (Laika) * Korabl-Sputnik 2 – first capsule recovered from orbit (Vostok programme, Vostok precursor) – animals survived * Syncom – first geosynchronous communications satellite * Hubble Space Telescope – largest orbital observatory * Boeing X-37, X-37 – spaceplaneLunar probes
* Clementine probe, Clementine – US Navy mission, orbited Moon, detected hydrogen at the poles * Kaguya (SELENE), Kaguya JPN – lunar orbiter * Luna 1 – first lunar flyby * Luna 2 – first lunar impact * Luna 3 – first images of lunar far side * Luna 9 – first soft landing on the Moon * Luna 10 – first lunar orbiter * Luna 16 – first uncrewed lunar sample retrieval * Lunar Orbiter – very successful series of lunar mapping spacecraft * Lunar Prospector – confirmed detection of hydrogen at the lunar poles * Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter – Identifies safe landing sites and locates Moon resources * Lunokhod - Soviet lunar rovers * SMART-1 ESA – Lunar Impact * Surveyor program, Surveyor – USA's first soft lander * Chang'e 1 – China's first lunar mission * Chang'e 2 – China's second lunar mission * Chang'e 3 – China's first soft landing on the Moon * Chang'e 4 – first soft landing on far side of the Moon * Chang'e 5 – China's first lunar probe which completed a sample-return mission * Chandrayaan 1 – first Indian Lunar mission * Chandrayaan 2 – second Indian Lunar missionPlanetary probes

 *''Akatsuki (spacecraft), Akatsuki'' JPN – a Venus orbiter
*''Cassini–Huygens'' – first Saturn orbiter and Titan (moon), Titan lander
*Curiosity (rover), ''Curiosity'' – Rover sent to Mars by NASA in 2012
*Galileo spacecraft, ''Galileo'' – first Jupiter orbiter and descent probe
*IKAROS JPN – first solar-sail spacecraft
*Mariner 4 – first Mars flyby, first close and high resolution images of Mars
*Mariner 9 – first Mars orbiter
*Mariner 10 – first Mercury (planet), Mercury flyby, first close up images
*Mars Exploration Rovers (''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'')– Mars rovers
*''Mars Express'' – Mars orbiter
*''Mars Global Surveyor'' – Mars orbiter
*Mars Orbiter Mission (''Mangalyaan'') - India's first Interplanetary probe
*''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' – an advanced climate, imaging, sub-surface radar, and telecommunications Mars orbiter
*''MESSENGER'' – first Mercury orbiter (arrival 2011)
*''Mars Pathfinder'' – Mars lander, carrying the ''Sojourner (rover), Sojourner'' rover
*'' New Horizons'' – first Pluto flyby (arrival 2015)
*''
*''Akatsuki (spacecraft), Akatsuki'' JPN – a Venus orbiter
*''Cassini–Huygens'' – first Saturn orbiter and Titan (moon), Titan lander
*Curiosity (rover), ''Curiosity'' – Rover sent to Mars by NASA in 2012
*Galileo spacecraft, ''Galileo'' – first Jupiter orbiter and descent probe
*IKAROS JPN – first solar-sail spacecraft
*Mariner 4 – first Mars flyby, first close and high resolution images of Mars
*Mariner 9 – first Mars orbiter
*Mariner 10 – first Mercury (planet), Mercury flyby, first close up images
*Mars Exploration Rovers (''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'')– Mars rovers
*''Mars Express'' – Mars orbiter
*''Mars Global Surveyor'' – Mars orbiter
*Mars Orbiter Mission (''Mangalyaan'') - India's first Interplanetary probe
*''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' – an advanced climate, imaging, sub-surface radar, and telecommunications Mars orbiter
*''MESSENGER'' – first Mercury orbiter (arrival 2011)
*''Mars Pathfinder'' – Mars lander, carrying the ''Sojourner (rover), Sojourner'' rover
*'' New Horizons'' – first Pluto flyby (arrival 2015)
*''Pioneer 10
''Pioneer 10'' (originally designated Pioneer F) is an American space probe, launched in 1972 and weighing , that completed the first mission to the planet Jupiter. Thereafter, ''Pioneer 10'' became the first of five artificial objects to ach ...
'' – first Jupiter flyby, first close up images
*''Pioneer 11'' – second Jupiter flyby and first Saturn flyby (first close up images of Saturn)
*Pioneer Venus – first Venus orbiter and landers
*Vega 1 – Balloon release into Venus atmosphere and lander, mothership continued on to fly by Halley's Comet. Joint mission with Vega 2.
*Venera 4 – first soft landing on another planet (Venus)
*''Viking 1'' – first soft landing on Mars
*''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
'' - flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, and Saturn's moon Titan (moon), Titan
*''Voyager 2'' – Jupiter flyby, Saturn flyby, and first flybys/images of Neptune and Uranus
* ''Emirates Mars Mission, Hope'' - Mars orbiter of the United Arab Emirates in 2020
* ''Tianwen-1 '' - China's orbiter, lander and rover mission to Mars in 2020
* Perseverance (rover), Perseverance - Rover sent to Mars in 2020
* Ingenuity (helicopter), Ingenuity - experimental rotorcraft sent to Mars in 2020
Other – deep space
* Cluster mission, Cluster * Deep Space 1 * ''Deep Impact (spacecraft), Deep Impact'' * ''Genesis (spacecraft), Genesis'' * ''Hayabusa (spacecraft), Hayabusa'' * NEAR Shoemaker, Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous * Rosetta (spacecraft), Rosetta * ''Stardust (spacecraft), Stardust'' * STEREO – Heliospheric and solar sensing; first images of the entire Sun * WMAPFastest spacecraft
*Parker Solar Probe, Parker ''Solar Probe'' (estimated at first sun close pass, will reach at final perihelion) *Helios probes, Helios I and II ''Solar Probes'' ()Furthest spacecraft from the Sun
* ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin ''Voyager 2'', ''Voya ...
'' at 156.13 Astronomical unit, AU as of April 2022, traveling outward at about
* ''Pioneer 10
''Pioneer 10'' (originally designated Pioneer F) is an American space probe, launched in 1972 and weighing , that completed the first mission to the planet Jupiter. Thereafter, ''Pioneer 10'' became the first of five artificial objects to ach ...
'' at 122.48 Astronomical unit, AU as of December 2018, traveling outward at about
*''Voyager 2'' at 122.82 Astronomical unit, AU as of January 2020, traveling outward at about
*''Pioneer 11'' at 101.17 Astronomical unit, AU as of December 2018, traveling outward at about
Unfunded and canceled programs

Crewed spacecraft
* Chinese Shuguang capsule * Soviet Zond/L1 – lunar flyby capsule * Soviet L3 – capsule and lunar lander * Soviet LK (spacecraft), LK – lunar lander * SovietTKS
The TK (TK-3) and TKS were Polish tankettes developed during the 1930s and used in the Second World War.
Design and development
The TK (also known as the TK-3) tankette was a Polish design produced from 1931 based on the chassis of the British ...
– space station resupply capsule
* Soviet Buran (spacecraft), ''Buran''-class shuttle – spaceplane
* Soviet Soyuz Kontakt capsule
* Soviet Almaz space station
* US Manned Orbiting Laboratory space station
* US Altair (spacecraft), Altair lunar lander
Multi-stage spaceplanes
* US Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar, X-20 spaceplane * Soviet Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-105, Spiral shuttle * Soviet/Russian ''Buran''-class shuttle * ESA Hermes (shuttle), Hermes shuttle * Kliper Russian semi-shuttle/semi-capsule * Japanese HOPE-X shuttle * Chinese Shuguang Project 921-3 shuttleSSTO spacecraft
* RR/British Aerospace HOTOL * ESA Hopper (spacecraft), Hopper Orbiter * US McDonnell Douglas DC-X, DC-X (Delta Clipper) * US Rotary Rocket, Roton Rotored-Hybrid * US VentureStarSpacecraft under development

Crewed
* (US-NASA; Europe-ESA) Orion (spacecraft), Orion – capsule * (US- SpaceX) SpaceX Starship, Starship – VTVL spacecraft * (US-Boeing) CST-100 – capsule * (US-Sierra Nevada Corporation) Dream Chaser – orbitalspaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes te ...
* (US-The SpaceShip company) SpaceShipTwo suborbital spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes te ...
* (US- Blue Origin) New Shepard – VTVL capsule
* (US-XCOR) Lynx rocketplane – suborbital spaceplane
* (India-DRDO) Avatar RLV -Under development, First demonstration flight in 2015.
* (India-ISRO) ISRO Orbital Vehicle, Gaganyaan – capsule
* (India-ISRO) RLV Technology Demonstration Programme – spacecraft
* (Russia-RKA) Orel (spacecraft), Orel – capsule
* (Europe-ESA) Smart Upper Stage for Innovative Exploration – capsule
* (Iranian Space Agency) Iranian crewed spacecraft – capsule
Uncrewed
* CNES Mars Netlander * ''Darwin (ESA), Darwin14'' ESA probe * Sierra Nevada Corporation Dream Chaser – orbital cargo spaceplane * Skylon (spacecraft), Skylon spaceplane * ''StarChip'' and ''Breakthrough Starshot#StarChip, Sprites'' - miniaturized interstellar spacecraft * System F6—a DARPA Fractionated Spacecraft demonstratorSubsystems
A spacecraft astrionics system comprises different subsystems, depending on the mission profile. Spacecraft subsystems comprise the spacecraft's Spacecraft bus, bus and may include attitude determination and control (variously called ADAC, ADC, or ACS), guidance, navigation and control (GNC or GN&C), communications (comms), command and data handling (CDH or C&DH), power (EPS), spacecraft thermal control, thermal control (TCS), propulsion, and structures. Attached to the bus are typically payloads. ; Life support : Spacecraft intended for human spaceflight must also include a life support system for the crew. ; Attitude control
: A Spacecraft needs an attitude control subsystem to be correctly oriented in space and respond to external torques and forces properly. The attitude control subsystem consists of sensors and actuators, together with controlling algorithms. The attitude-control subsystem permits proper pointing for the science objective, sun pointing for power to the solar arrays and earth pointing for communications.
; GNC
: Guidance refers to the calculation of the commands (usually done by the CDH subsystem) needed to steer the spacecraft where it is desired to be. Navigation means determining a spacecraft's orbital elements or position. Control means adjusting the path of the spacecraft to meet mission requirements.
; Command and data handling
: The C&DH subsystem receives commands from the communications subsystem, performs validation and decoding of the commands, and distributes the commands to the appropriate spacecraft subsystems and components. The CDH also receives housekeeping data and science data from the other spacecraft subsystems and components, and packages the data for storage on a data recorder or transmission to the ground via the communications subsystem. Other functions of the CDH include maintaining the spacecraft clock and state-of-health monitoring.
; Communications
: Spacecraft, both Robotic spacecraft, robotic and Human spaceflight, crewed, utilize various communications systems for communication with terrestrial stations as well as for communication between spacecraft in space. Technologies utilized include Radio-frequency communication, RF and Free-space optical communication, optical communication. In addition, some spacecraft payloads are explicitly for the purpose of ground–ground Commsat, communication using Bent pipe, receiver/retransmitter electronic technologies.
; Power
: Spacecraft need an electrical power generation and distribution subsystem for powering the various spacecraft subsystems. For spacecraft near the Sun, Solar panels on spacecraft, solar panels are frequently used to generate electrical power. Spacecraft designed to operate in more distant locations, for example Jupiter, might employ a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) to generate electrical power. Electrical power is sent through power conditioning equipment before it passes through a power distribution unit over an electrical bus to other spacecraft components. Batteries are typically connected to the bus via a battery charge regulator, and the batteries are used to provide electrical power during periods when primary power is not available, for example when a low Earth orbit spacecraft is eclipsed by Earth.
; Thermal control
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand transit through Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and the space environment. They must operate in a vacuum with temperatures potentially ranging across hundreds of degrees Celsius as well as (if subject to reentry) in the presence of plasmas. Material requirements are such that either high melting temperature, low density materials such as beryllium and reinforced carbon–carbon or (possibly due to the lower thickness requirements despite its high density) tungsten or Ablation, ablative carbon–carbon composites are used. Depending on mission profile, spacecraft may also need to operate on the surface of another planetary body. The thermal control subsystem can be passive, dependent on the selection of materials with specific radiative properties. Active thermal control makes use of electrical heaters and certain actuators such as louvers to control temperature ranges of equipments within specific ranges.
; Spacecraft propulsion
: Spacecraft may or may not have a Spacecraft propulsion, propulsion subsystem, depending on whether or not the mission profile calls for propulsion. The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission, ''Swift'' spacecraft is an example of a spacecraft that does not have a propulsion subsystem. Typically though, LEO spacecraft include a propulsion subsystem for altitude adjustments (drag make-up maneuvers) and inclination adjustment maneuvers. A propulsion system is also needed for spacecraft that perform momentum management maneuvers. Components of a conventional propulsion subsystem include fuel, tankage, valves, pipes, and Rocket engine, thrusters. The thermal control system interfaces with the propulsion subsystem by monitoring the temperature of those components, and by preheating tanks and thrusters in preparation for a spacecraft maneuver.
; Structures
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand launch loads imparted by the launch vehicle, and must have a point of attachment for all the other subsystems. Depending on mission profile, the structural subsystem might need to withstand loads imparted by entry into the Celestial body atmosphere, atmosphere of another planetary body, and landing on the surface of another planetary body.
; Payload
: The payload depends on the mission of the spacecraft, and is typically regarded as the part of the spacecraft "that pays the bills". Typical payloads could include scientific instruments (cameras, telescopes, or particle detectors, for example), cargo, or a Human spaceflight, human crew.
; Ground segment
: The ground segment, though not technically part of the spacecraft, is vital to the operation of the spacecraft. Typical components of a ground segment in use during normal operations include a mission operations facility where the flight operations team conducts the operations of the spacecraft, a data processing and storage facility, Earth station, ground stations to radiate signals to and receive signals from the spacecraft, and a voice and data communications network to connect all mission elements.
; Launch vehicle
: The
; Attitude control
: A Spacecraft needs an attitude control subsystem to be correctly oriented in space and respond to external torques and forces properly. The attitude control subsystem consists of sensors and actuators, together with controlling algorithms. The attitude-control subsystem permits proper pointing for the science objective, sun pointing for power to the solar arrays and earth pointing for communications.
; GNC
: Guidance refers to the calculation of the commands (usually done by the CDH subsystem) needed to steer the spacecraft where it is desired to be. Navigation means determining a spacecraft's orbital elements or position. Control means adjusting the path of the spacecraft to meet mission requirements.
; Command and data handling
: The C&DH subsystem receives commands from the communications subsystem, performs validation and decoding of the commands, and distributes the commands to the appropriate spacecraft subsystems and components. The CDH also receives housekeeping data and science data from the other spacecraft subsystems and components, and packages the data for storage on a data recorder or transmission to the ground via the communications subsystem. Other functions of the CDH include maintaining the spacecraft clock and state-of-health monitoring.
; Communications
: Spacecraft, both Robotic spacecraft, robotic and Human spaceflight, crewed, utilize various communications systems for communication with terrestrial stations as well as for communication between spacecraft in space. Technologies utilized include Radio-frequency communication, RF and Free-space optical communication, optical communication. In addition, some spacecraft payloads are explicitly for the purpose of ground–ground Commsat, communication using Bent pipe, receiver/retransmitter electronic technologies.
; Power
: Spacecraft need an electrical power generation and distribution subsystem for powering the various spacecraft subsystems. For spacecraft near the Sun, Solar panels on spacecraft, solar panels are frequently used to generate electrical power. Spacecraft designed to operate in more distant locations, for example Jupiter, might employ a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) to generate electrical power. Electrical power is sent through power conditioning equipment before it passes through a power distribution unit over an electrical bus to other spacecraft components. Batteries are typically connected to the bus via a battery charge regulator, and the batteries are used to provide electrical power during periods when primary power is not available, for example when a low Earth orbit spacecraft is eclipsed by Earth.
; Thermal control
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand transit through Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and the space environment. They must operate in a vacuum with temperatures potentially ranging across hundreds of degrees Celsius as well as (if subject to reentry) in the presence of plasmas. Material requirements are such that either high melting temperature, low density materials such as beryllium and reinforced carbon–carbon or (possibly due to the lower thickness requirements despite its high density) tungsten or Ablation, ablative carbon–carbon composites are used. Depending on mission profile, spacecraft may also need to operate on the surface of another planetary body. The thermal control subsystem can be passive, dependent on the selection of materials with specific radiative properties. Active thermal control makes use of electrical heaters and certain actuators such as louvers to control temperature ranges of equipments within specific ranges.
; Spacecraft propulsion
: Spacecraft may or may not have a Spacecraft propulsion, propulsion subsystem, depending on whether or not the mission profile calls for propulsion. The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission, ''Swift'' spacecraft is an example of a spacecraft that does not have a propulsion subsystem. Typically though, LEO spacecraft include a propulsion subsystem for altitude adjustments (drag make-up maneuvers) and inclination adjustment maneuvers. A propulsion system is also needed for spacecraft that perform momentum management maneuvers. Components of a conventional propulsion subsystem include fuel, tankage, valves, pipes, and Rocket engine, thrusters. The thermal control system interfaces with the propulsion subsystem by monitoring the temperature of those components, and by preheating tanks and thrusters in preparation for a spacecraft maneuver.
; Structures
: Spacecraft must be engineered to withstand launch loads imparted by the launch vehicle, and must have a point of attachment for all the other subsystems. Depending on mission profile, the structural subsystem might need to withstand loads imparted by entry into the Celestial body atmosphere, atmosphere of another planetary body, and landing on the surface of another planetary body.
; Payload
: The payload depends on the mission of the spacecraft, and is typically regarded as the part of the spacecraft "that pays the bills". Typical payloads could include scientific instruments (cameras, telescopes, or particle detectors, for example), cargo, or a Human spaceflight, human crew.
; Ground segment
: The ground segment, though not technically part of the spacecraft, is vital to the operation of the spacecraft. Typical components of a ground segment in use during normal operations include a mission operations facility where the flight operations team conducts the operations of the spacecraft, a data processing and storage facility, Earth station, ground stations to radiate signals to and receive signals from the spacecraft, and a voice and data communications network to connect all mission elements.
; Launch vehicle
: The launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload ( spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pads, supported by a launch control center and ...
propels the spacecraft from Earth's surface, through the atmosphere, and into an orbit, the exact orbit being dependent on the mission configuration. The launch vehicle may be Expendable launch system, expendable or Reusable launch system, reusable.
See also
*Astrionics *Commercial astronaut *Flying saucer *List of crewed spacecraft *List of fictional spacecraft *NewSpace *Spacecraft design *Space exploration *Space launch *Spaceships in science fiction *Space suit *List of spaceflight records, Spaceflight records *Starship *Timeline of Solar System exploration *U.S. Space Exploration History on U.S. StampsNotes
References
Citations
Sources
* *External links
NASA: Space Science Spacecraft Missions
NSSDC Master Catalog Spacecraft Query Form
{{Authority control Spacecraft, Astronautics Pressure vessels