Space Telescope on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
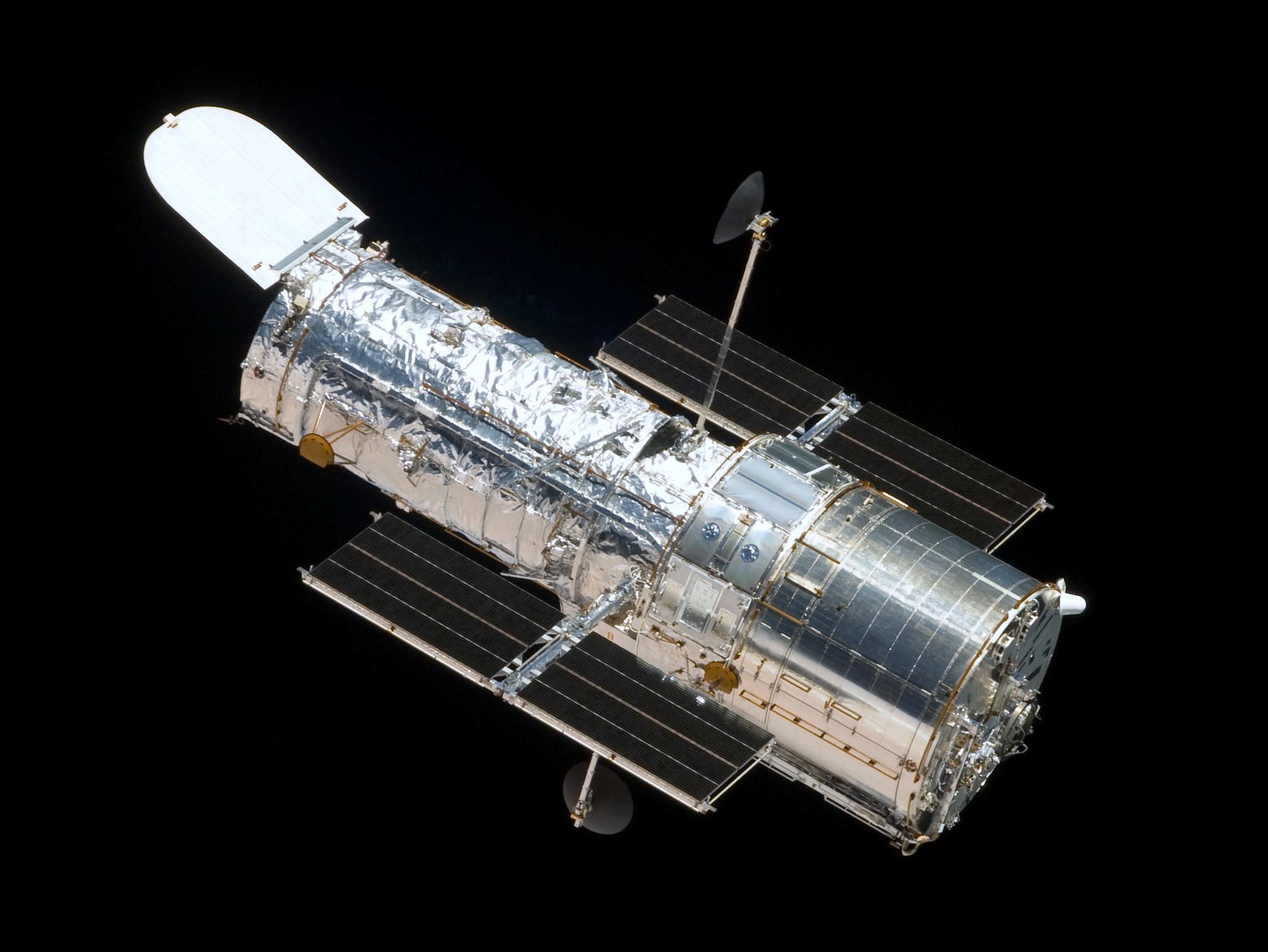 A space telescope or space observatory is a
A space telescope or space observatory is a
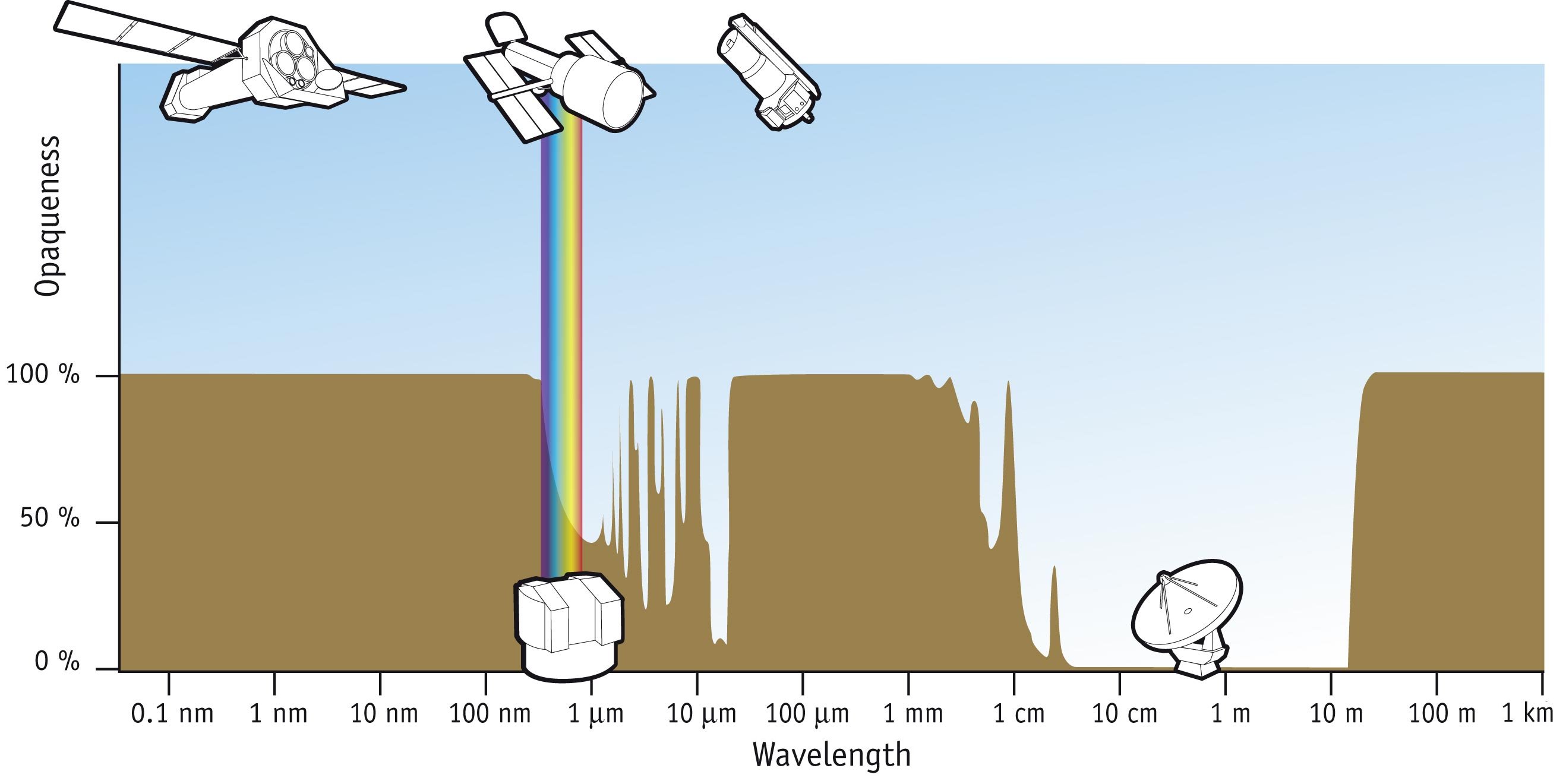 Space-based astronomy is more important for frequency ranges that are outside the optical window and the radio window, the only two wavelength ranges of the
Space-based astronomy is more important for frequency ranges that are outside the optical window and the radio window, the only two wavelength ranges of the

 A space telescope or space observatory is a
A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to obse ...
in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope aboard space station Salyut 1 in 1971. Space telescopes avoid the filtering and distortion ( scintillation) of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visib ...
which they observe, and avoid light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive use of artificial lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting, during the day or night. Light po ...
which ground-based observatories encounter. They are divided into two types: Satellites which map the entire sky (astronomical survey
An astronomical survey is a general map or image of a region of the sky (or of the whole sky) that lacks a specific observational target. Alternatively, an astronomical survey may comprise a set of images, spectra, or other observations of obj ...
), and satellites which focus on selected astronomical objects or parts of the sky and beyond. Space telescopes are distinct from Earth imaging satellites
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface ...
, which point toward Earth for satellite imaging, applied for weather analysis, espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tang ...
, and other types of information gathering.
History
Wilhelm Beer and Johann Heinrich Mädler in 1837 discussed the advantages of an observatory on the Moon. In 1946, American theoretical astrophysicist Lyman Spitzer proposed a telescope in space. Spitzer's proposal called for a large telescope that would not be hindered by Earth's atmosphere. After lobbying in the 1960s and 70s for such a system to be built, Spitzer's vision ultimately materialized into theHubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
, which was launched on April 24, 1990 by the Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' (STS-31).
The first operational space telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope aboard space station Salyut 1 in 1971.
Advantages
Performingastronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
from ground-based observatories on Earth is limited by the filtering and distortion of electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visib ...
( scintillation or twinkling) due to the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A ...
. A telescope orbiting Earth outside the atmosphere is subject neither to twinkling nor to light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive use of artificial lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting, during the day or night. Light po ...
from artificial light sources on Earth. As a result, the angular resolution
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major determinant of image resolut ...
of space telescopes is often much higher than a ground-based telescope with a similar aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane.
An ...
. Many larger terrestrial telescopes, however, reduce atmospheric effects with adaptive optics
Adaptive optics (AO) is a technology used to improve the performance of optical systems by reducing the effect of incoming wavefront distortions by deforming a mirror in order to compensate for the distortion. It is used in astronomical tele ...
.
 Space-based astronomy is more important for frequency ranges that are outside the optical window and the radio window, the only two wavelength ranges of the
Space-based astronomy is more important for frequency ranges that are outside the optical window and the radio window, the only two wavelength ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging fro ...
that are not severely attenuated by the atmosphere. For example, X-ray astronomy is nearly impossible when done from Earth, and has reached its current importance in astronomy only due to orbiting X-ray telescopes such as the Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources ...
and the XMM-Newton observatory. Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
and ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
are also largely blocked.
Disadvantages
Space telescopes are much more expensive to build than ground-based telescopes. Due to their location, space telescopes are also extremely difficult to maintain. The Hubble Space Telescope was serviced by theSpace Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program n ...
, but most space telescopes cannot be serviced at all.
Future of space observatories
Satellites have been launched and operated byNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
, ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman o ...
, ESA, CNSA, JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into o ...
and the Soviet space program (later succeeded by Roscosmos of Russia). As of 2022, many space observatories have already completed their missions, while others continue operating on extended time. However, the future availability of space telescopes and observatories depends on timely and sufficient funding. While future space observatories are planned by NASA, JAXA and the CNSA, scientists fear that there would be gaps in coverage that would not be covered immediately by future projects and this would affect research in fundamental science. For example, there was a fear that there would be a gap in coverage between the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most vers ...
and the James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Sp ...
(JWST).
List of space telescopes

See also
*Airborne observatory
An airborne observatory is an airplane, airship, or balloon with an astronomical telescope. By carrying the telescope to a sufficiently high altitude, the telescope can avoid cloud cover, pollution, and carry out observations in the infrared spec ...
* Earth observation satellite
An Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, ...
* List of telescope types
The following are lists of devices categorized as types of telescopes or devices associated with telescopes. They are broken into major classifications with many variations due to professional, amateur, and commercial sub-types. Telescopes can be ...
* Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. ...
* Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes
* Timeline of telescopes, observatories, and observing technology
* Ultraviolet astronomy
* X-ray astronomy satellite
An X-ray astronomy satellite studies X-ray emissions from celestial objects, as part of a branch of space science known as X-ray astronomy. Satellites are needed because X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect ...
References
Further reading
* Neil English: ''Space Telescopes - Capturing the Rays of the Electromagnetic Spectrum.'' Springer, Cham 2017, .External links
* · {{DEFAULTSORT:Space Observatory American inventions Astronomical observatories Telescope types Uncrewed spacecraft