Solar Dynamics Observatory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is a
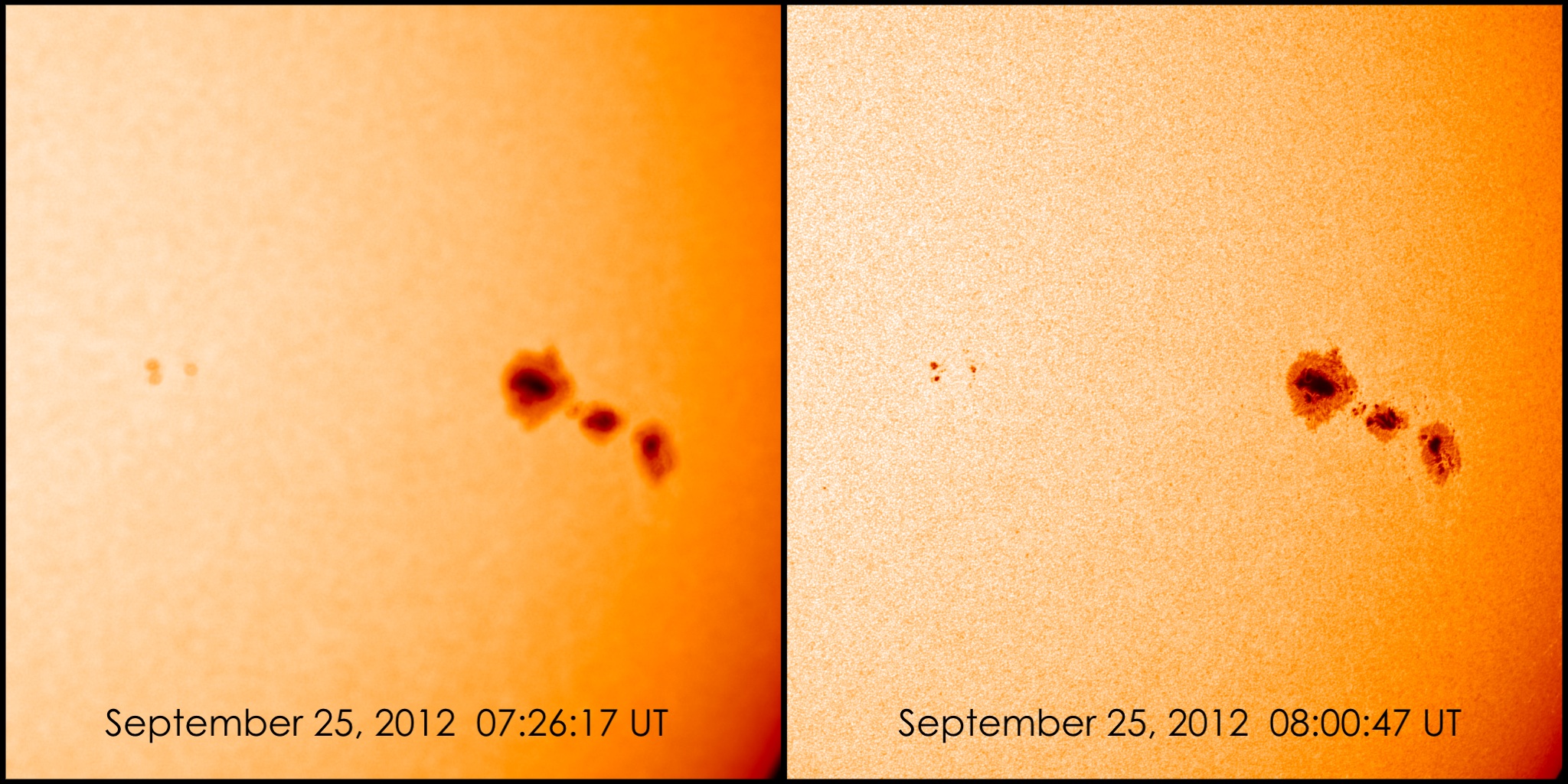 The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI), led from
The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI), led from
The Sun Today
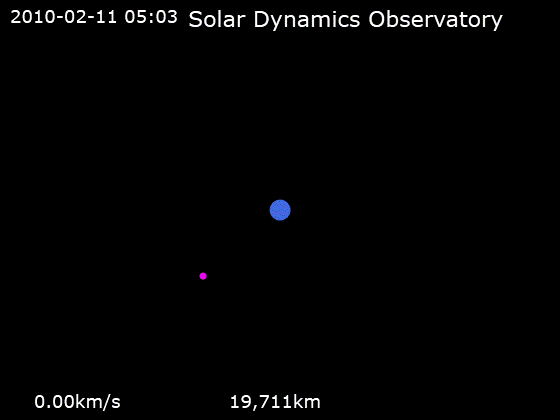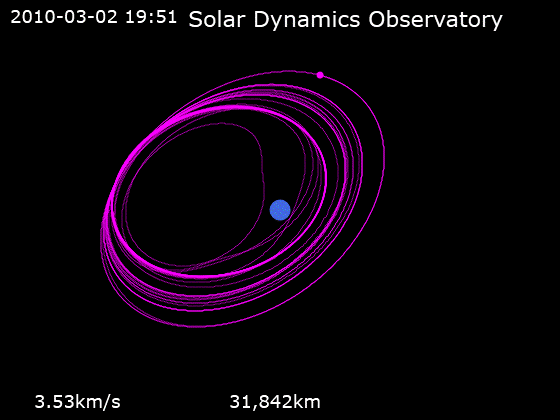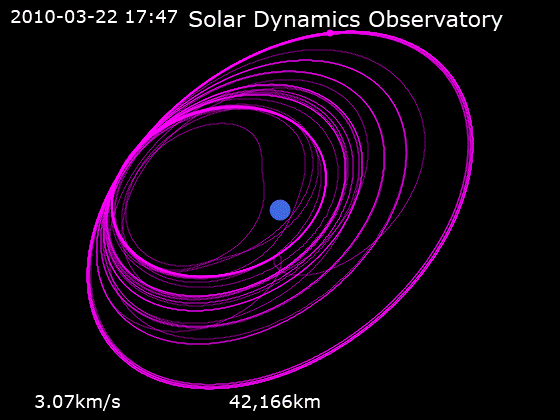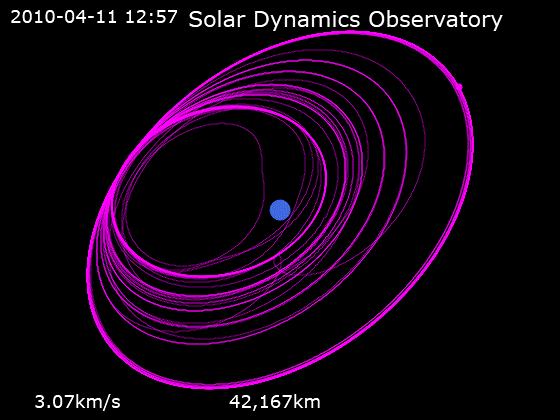 After launch, the spacecraft was placed into an
After launch, the spacecraft was placed into an
File:11742 SDO-Year 5 ProRes 1920x1080 2997.webm, SDO: Year 5
File:Camilla Corona SDO.jpg, Camilla Corona SDO
File:Solar Dynamics Observatory.png, SDO 3-D schematic
File:SDO spacecraft detailed.jpg, SDO Instruments
File:SDO from above.jpg, SDO ready to be placed on Atlas rocket for launch.
File:SDO Launch and Deployment.ogg, An animation showing the deployment of SDO.
File:SDO first light.png, First light image from the SDO showing a prominence eruption.
File:SDO's Ultra-high Definition View of 2012 Venus Transit (304 Angstrom Full Disc 02).jpg, An image of the 2012 transit of Venus taken by SDO.
File:Solar Dynamics Observatory - Argo view.ogg, This movie opens with a full-disk view of the Sun in visible wavelengths. Then the filters are applied to small pie-shaped wedges of the Sun.
File:NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory- Year 7 Ultra HD (4k).webm, SDO has now captured nearly seven years worth of ultra-high resolution solar footage. This time lapse shows that full run from two of SDO's instruments.
 NASA's images of the Sun's dynamic and dazzling beauty have captivated the attention of millions. In 2021, the U.S. Postal Service is showcasing the Sun's many faces with a series of Sun Science forever stamps that show images of solar activity captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). "I have been a stamp collector all my life and I can't wait to see NASA science highlighted in this way", said
NASA's images of the Sun's dynamic and dazzling beauty have captivated the attention of millions. In 2021, the U.S. Postal Service is showcasing the Sun's many faces with a series of Sun Science forever stamps that show images of solar activity captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). "I have been a stamp collector all my life and I can't wait to see NASA science highlighted in this way", said
Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) mission website
Where is the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) right now?
HELAS
(Cometal 14 July 2011)
History of SDO patch
Facebook
( )
)
Album
of images and videos by Seán Doran, based on SDO imagery, and a longer (24 min.) YouTube video
''Sun Dance''
SDO 5-year timelapse video of the Sun
SDO 10-year timelapse video of the Sun
Extreme Ultraviolet Variability Experiment (EVE)
,
ATMOSPHERIC IMAGING ASSEMBLY (AIA)
Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI)
Joint Science Operations Center – Science Data Processing HMI – AIA
{{Authority control Space probes launched in 2010 NASA space probes Living With a Star Missions to the Sun Solar space observatories Solar telescopes Space weather Articles containing video clips Spacecraft launched by Atlas rockets
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
mission which has been observing the Sun since 2010. Launched on 11 February 2010, the observatory is part of the Living With a Star
Living With a Star (LWS) is a NASA scientific program to study those aspects of the connected Sun-Earth system that directly affect life and society. LWS is a crosscutting initiative with goals and objectives relevant to NASA's Exploration Initiat ...
(LWS) program.
The goal of the LWS program is to develop the scientific understanding necessary to effectively address those aspects of the connected Sun–Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
system directly affecting life and society. The goal of the SDO is to understand the influence of the Sun on the Earth and near-Earth space by studying the solar atmosphere on small scales of space and time and in many wavelengths simultaneously. SDO has been investigating how the Sun's magnetic field is generated and structured, how this stored magnetic energy is converted and released into the heliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstell ...
and geospace
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, pred ...
in the form of solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
, energetic particles, and variations in the solar irradiance
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area ( surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre ...
.
General
The SDO spacecraft was developed at NASA'sGoddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
in Greenbelt, Maryland
Greenbelt is a city in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States, and a suburb of Washington, D.C. At the 2020 census, the population was 24,921.
Greenbelt is the first and the largest of the three experimental and controversial New Dea ...
, and launched on 11 February 2010, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station ( CCAFS). The primary mission lasted five years and three months, with expendables expected to last at least ten years. Some consider SDO to be a follow-on mission to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory
The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) is a European Space Agency (ESA) spacecraft built by a European industrial consortium led by Matra Marconi Space (now Airbus Defence and Space) that was launched on a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIAS lau ...
(SOHO).
SDO is a three-axis stabilized spacecraft, with two solar arrays, and two high-gain antennas, in an inclined geosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbita ...
around Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
.
The spacecraft includes three instruments:
* the Extreme Ultraviolet Variability Experiment (EVE) built in partnership with the University of Colorado Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a public research university in Boulder, Colorado. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a state, it is the flagship university of the University of Colorado sy ...
's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP),
* the Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) built in partnership with Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is conside ...
, and
* the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) built in partnership with the Lockheed Martin Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory (LMSAL).
Data which is collected by the craft is made available as soon as possible, after it is received.
As of February 2020, SDO is expected to remain operational until 2030.
Instruments
Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI)
 The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI), led from
The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI), led from Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is conside ...
in Stanford, California
Stanford is a census-designated place (CDP) in the northwest corner of Santa Clara County, California, United States. It is the home of Stanford University. The population was 21,150 at the 2020 census.
Stanford is an unincorporated area of ...
, studies solar variability and characterizes the Sun's interior and the various components of magnetic activity. HMI takes high-resolution measurements of the longitudinal and vector magnetic field over the entire visible solar disk thus extending the capabilities of SOHO
Soho is an area of the City of Westminster, part of the West End of London. Originally a fashionable district for the aristocracy, it has been one of the main entertainment districts in the capital since the 19th century.
The area was deve ...
's MDI instrument.
HMI produces data to determine the interior sources and mechanisms of solar variability and how the physical processes inside the Sun are related to surface magnetic field and activity. It also produces data to enable estimates of the coronal magnetic field for studies of variability in the extended solar atmosphere. HMI observations will enable establishing the relationships between the internal dynamics and magnetic activity in order to understand solar variability and its effects.
Extreme Ultraviolet Variability Experiment (EVE)
The Extreme Ultraviolet Variability Experiment (EVE) measures the Sun'sextreme ultraviolet
Extreme ultraviolet radiation (EUV or XUV) or high-energy ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum spanning wavelengths from 124 nm down to 10 nm, and therefore (by the Planck–E ...
irradiance with improved spectral resolution The spectral resolution of a spectrograph, or, more generally, of a frequency spectrum, is a measure of its ability to resolve features in the electromagnetic spectrum. It is usually denoted by \Delta\lambda, and is closely related to the resolvi ...
, "temporal cadence", accuracy, and precision over preceding measurements made by TIMED
timed (time daemon) is an operating system program that maintains the system time in synchronization with time servers using the Time Synchronization Protocol (TSP) developed by Riccardo Gusella and Stefano Zatti. Gusella and Zatti had done e ...
SEE, SOHO
Soho is an area of the City of Westminster, part of the West End of London. Originally a fashionable district for the aristocracy, it has been one of the main entertainment districts in the capital since the 19th century.
The area was deve ...
, and SORCE
The Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE) was a NASA-sponsored satellite mission that measured incoming X-ray, ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, and total solar radiation. These measurements specifically addressed long-term climate ...
XPS. The instrument incorporates physics-based models in order to further scientific understanding of the relationship between solar EUV variations and magnetic variation changes in the Sun.
The Sun's output of energetic extreme ultraviolet photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they alwa ...
s is primarily what heats the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
's upper atmosphere Upper atmosphere is a collective term that refers to various layers of the atmosphere of the Earth above the troposphere and corresponding regions of the atmospheres of other planets, and includes:
* The mesosphere, which on Earth lies between th ...
and creates the ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays ...
. Solar EUV radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visi ...
output undergoes constant changes, both moment to moment and over the Sun's 11-year solar cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surf ...
, and these changes are important to understand because they have a significant impact on atmospheric heating, satellite drag, and communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inqui ...
s system degradation, including disruption of the Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite ...
.
The EVE instrument package was built by the University of Colorado Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a public research university in Boulder, Colorado. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a state, it is the flagship university of the University of Colorado sy ...
's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP), with Dr. Tom Woods as principal investigator
In many countries, the term principal investigator (PI) refers to the holder of an independent grant and the lead researcher for the grant project, usually in the sciences, such as a laboratory study or a clinical trial. The phrase is also often u ...
, and was delivered to NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
on 7 September 2007. The instrument provides improvements of up to 70% in spectral resolution measurements in the wavelengths below 30 nm, and a 30% improvement in "time cadence" by taking measurements every 10 seconds over a 100% duty cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a form ...
.
Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA)
The Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA), led from the Lockheed Martin Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory (LMSAL), provides continuous full-disk observations of the solarchromosphere
A chromosphere ("sphere of color") is the second layer of a star's atmosphere, located above the photosphere and below the solar transition region and corona. The term usually refers to the Sun's chromosphere, but not exclusively.
In the ...
and corona
Corona (from the Latin for 'crown') most commonly refers to:
* Stellar corona, the outer atmosphere of the Sun or another star
* Corona (beer), a Mexican beer
* Corona, informal term for the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which causes the COVID-19 di ...
in seven extreme ultraviolet
Extreme ultraviolet radiation (EUV or XUV) or high-energy ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum spanning wavelengths from 124 nm down to 10 nm, and therefore (by the Planck–E ...
(EUV) channels, spanning a temperature range from approximately 20,000 Kelvin to in excess of 20 million Kelvin. The 12-second cadence of the image stream with 4096 by 4096 pixel images at 0.6 arcsec/pixel provides unprecedented views of the various phenomena that occur within the evolving solar outer atmosphere.
The AIA science investigation is led by LMSAL, which also operates the instrument and – jointly with Stanford University – runs the Joint Science Operations Center from which all of the data are served to the worldwide scientific community, as well as the general public. LMSAL designed the overall instrumentation and led its development and integration. The four telescopes providing the individual light feeds for the instrument were designed and built at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) is a research institute of the Smithsonian Institution, concentrating on astrophysical studies including galactic and extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, solar, earth and planetary sciences, the ...
(SAO). Since beginning its operational phase on 1 May 2010, AIA has operated successfully with unprecedented EUV image quality.
Photographs of the Sun in these various regions of the spectrum can be seen at NASA's SDO Data website. Images and movies of the Sun seen on any day of the mission, including within the last half-hour, can be found aThe Sun Today
Communications
SDO down-links science data ( K-band) from its two onboard high-gain antennas, andtelemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", an ...
(S-band
The S band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a part of the microwave radio band, band of the electromagnetic spectrum covering frequency, frequencies from 2 to 4 gigahertz (GHz). Thus it c ...
) from its two onboard omnidirectional antenna
In radio communication, an omnidirectional antenna is a class of antenna which radiates equal radio power in all directions perpendicular to an axis (azimuthal directions), with power varying with angle to the axis ( elevation angle), declining ...
s. The ground station consists of two dedicated (redundant) 18-meter radio antennas in White Sands Missile Range
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established as the White Sands Proving Ground on 9July 1945. White Sands National P ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, constructed specifically for SDO. Mission controllers operate the spacecraft remotely from the Mission Operations Center at NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
. The combined data rate is about 130 Mbit/s (150 Mbit/s with overhead, or 300 Msymbols/s with rate 1/2 convolutional encoding), and the craft generates approximately 1.5 Terabytes
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable uni ...
of data per day (equivalent to downloading around 500,000 songs).
Launch
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
's Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC, originally known as the NASA Launch Operations Center), located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since December 196 ...
managed the payload integration and launch. The SDO launched from Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 41
Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41), previously Launch Complex 41 (LC-41), is an active launch site at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. As of 2020, the site is used by United Launch Alliance (ULA) for Atlas V launches. Previously, it had been us ...
(SLC-41), utilizing an Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Mart ...
-401 rocket with a RD-180
The RD-180 ( rus, РД-180, Ракетный Двигатель-180, Raketnyy Dvigatel-180) is a rocket engine designed and built in Russia. It features a dual combustion chamber, dual- nozzle design and is fueled by a RP-1/ LOX mixture. The RD ...
powered Common Core Booster
The Common Core Booster (CCB) is an American rocket stage, which is used as the first stage of the Atlas V rocket as part of its modular design. It was also intended that two additional CCBs would be used as boosters on the Atlas V Heavy, however ...
, which has been developed to meet the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle
National Security Space Launch (NSSL) — formerly Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) from 1994 to 2019 — is a program of the United States Space Force (USSF) intended to assure access to space for United States Department of Defense and o ...
(EELV) program requirements.
Orbit
 After launch, the spacecraft was placed into an
After launch, the spacecraft was placed into an orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
around the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
with an initial perigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any el ...
of about . SDO then underwent a series of orbit-raising maneuvers which adjusted its orbit until the spacecraft reached its planned circular
Circular may refer to:
* The shape of a circle
* ''Circular'' (album), a 2006 album by Spanish singer Vega
* Circular letter (disambiguation)
** Flyer (pamphlet), a form of advertisement
* Circular reasoning, a type of logical fallacy
* Circular ...
, geosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbita ...
at an altitude of , at 102° West longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek let ...
, inclined at 28.5°. This orbit was chosen to allow 24/7 communications to/from the fixed ground station, and to minimise solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six mon ...
s to about an hour a day for only a few weeks a year.
Sun dog phenomenon
Moments after launch, SDO's Atlas V rocket penetrated acirrus cloud
Cirrus ( cloud classification symbol: Ci) is a genus of high cloud made of ice crystals. Cirrus clouds typically appear delicate and wispy with white strands. Cirrus are usually formed when warm, dry air rises, causing water vapor deposition on ...
which created visible shock wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
s in the sky and destroyed the alignment of ice crystals that were forming a sun dog
A sun dog (or sundog) or mock sun, also called a parhelion (plural parhelia) in meteorology, is an atmospheric optical phenomenon that consists of a bright spot to one or both sides of the Sun. Two sun dogs often flank the Sun within a 22° ...
visible to onlookers.
Mission mascot - Camilla
Camilla Corona is a rubber chicken (similar to a children's toy), and is the missionmascot
A mascot is any human, animal, or object thought to bring luck, or anything used to represent a group with a common public identity, such as a school, professional sports team, society, military unit, or brand name. Mascots are also used as ...
for SDO. It is part of the Education and public outreach
Science outreach, also called Education and Public Outreach (EPO or E/PO) or simply public outreach, is an umbrella term for a variety of activities by research institutes, universities, and institutions such as science museums, aimed at promoting ...
team and assists with various functions to help educate the public, mainly children, about the SDO mission, facts about the Sun and Space weather
Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the ...
. Camilla also assists in cross-informing the public about other NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
missions and space related projects. Camilla Corona SDO uses social media
Social media are interactive media technologies that facilitate the creation and sharing of information, ideas, interests, and other forms of expression through virtual communities and networks. While challenges to the definition of ''social me ...
to interact with fans.
Image gallery
Stamps
 NASA's images of the Sun's dynamic and dazzling beauty have captivated the attention of millions. In 2021, the U.S. Postal Service is showcasing the Sun's many faces with a series of Sun Science forever stamps that show images of solar activity captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). "I have been a stamp collector all my life and I can't wait to see NASA science highlighted in this way", said
NASA's images of the Sun's dynamic and dazzling beauty have captivated the attention of millions. In 2021, the U.S. Postal Service is showcasing the Sun's many faces with a series of Sun Science forever stamps that show images of solar activity captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). "I have been a stamp collector all my life and I can't wait to see NASA science highlighted in this way", said Thomas Zurbuchen
Thomas Hansueli Zurbuchen (born 1968) is a Swiss-American astrophysicist. From October 2016 until the end of 2022, he was the longest continually running Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA. Prior to this, he was ...
, associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate
The Science Mission Directorate (SMD) of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) engages the United States’ science community, sponsors scientific research, and develops and deploys satellites and probes in collaboration with NA ...
(SMD) in Washington, D.C. "I feel that the natural world around us is as beautiful as art, and it is inspiring to be able to share the import and excitement of studying the Sun with people around the country".
The 20-stamp set features ten images that celebrate the science behind NASA's ongoing exploration of our nearest star. The images display common events on the Sun, such as solar flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other sol ...
s, sunspot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. S ...
s and coronal loop
In solar physics, a coronal loop is a well-defined arch-like structure in the Sun's atmosphere made up of relatively dense plasma confined and isolated from the surrounding medium by magnetic flux tubes. Coronal loops begin and end at two f ...
s. SDO has kept a constant eye on the Sun for over a decade. Outfitted with equipment to capture images of the Sun in multiple wavelengths of visible, ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
, and extreme ultraviolet
Extreme ultraviolet radiation (EUV or XUV) or high-energy ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation in the part of the electromagnetic spectrum spanning wavelengths from 124 nm down to 10 nm, and therefore (by the Planck–E ...
light, SDO has gathered hundreds of millions of images during its tenure to help scientists learn about how our star works and how its constantly churning magnetic fields create the solar activity we see.
That solar activity can drive space weather
Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the ...
closer to Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
that can interfere with technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
and radio communications
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmi ...
in space. In addition to this immediate relevancy to our high-tech daily lives, the study of the Sun and its influence on the planets and space surrounding it – a field of research known as heliophysics – holds profound implications for the understanding of our Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
and the thousands of solar systems that have been discovered beyond our own. As our closest star, the Sun is the only nearby star that humans are able to study in great detail, making it a vital source of data.
See also
*Heliophysics
Heliophysics (from the prefix " helio", from Attic Greek ''hḗlios'', meaning Sun, and the noun "physics": the science of matter and energy and their interactions) is the physics of the Sun and its connection with the Solar System. NASA define ...
* Advanced Composition Explorer
* Parker Solar Probe
The Parker Solar Probe (PSP; previously Solar Probe, Solar Probe Plus or Solar Probe+) is a NASA space probe launched in 2018 with the mission of making observations of the outer corona of the Sun. It will approach to within 9.86 solar radii ...
* Radiation Belt Storm Probes (Van Allen Probes)
* Richard R. Fisher
Richard R. Fisher is an American astrophysicist who worked in academia and at NASA. He retired in 2012.
Fisher received his BA with honors from Grinnell College in 1961 and his PhD in astrogeophysics from University of Colorado in 1965. In May ...
* Solar and Heliospheric Observatory
The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) is a European Space Agency (ESA) spacecraft built by a European industrial consortium led by Matra Marconi Space (now Airbus Defence and Space) that was launched on a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIAS lau ...
(SOHO)
* STEREO
Stereophonic sound, or more commonly stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration ...
(Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory), launched 2006, 1 of 2 spacecraft still operational.
* Wind (spacecraft), launched 1994, still operational.
* List of heliophysics missions
References
External links
Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) mission website
Where is the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) right now?
HELAS
(Cometal 14 July 2011)
History of SDO patch
(
Album
of images and videos by Seán Doran, based on SDO imagery, and a longer (24 min.) YouTube video
''Sun Dance''
SDO 5-year timelapse video of the Sun
SDO 10-year timelapse video of the Sun
Instruments
Extreme Ultraviolet Variability Experiment (EVE)
,
University of Colorado
The University of Colorado (CU) is a system of public universities in Colorado. It consists of four institutions: University of Colorado Boulder, University of Colorado Colorado Springs, University of Colorado Denver, and the University o ...
ATMOSPHERIC IMAGING ASSEMBLY (AIA)
Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI)
Stanford
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. S ...
Joint Science Operations Center – Science Data Processing HMI – AIA
{{Authority control Space probes launched in 2010 NASA space probes Living With a Star Missions to the Sun Solar space observatories Solar telescopes Space weather Articles containing video clips Spacecraft launched by Atlas rockets