Social Impact Incentives on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
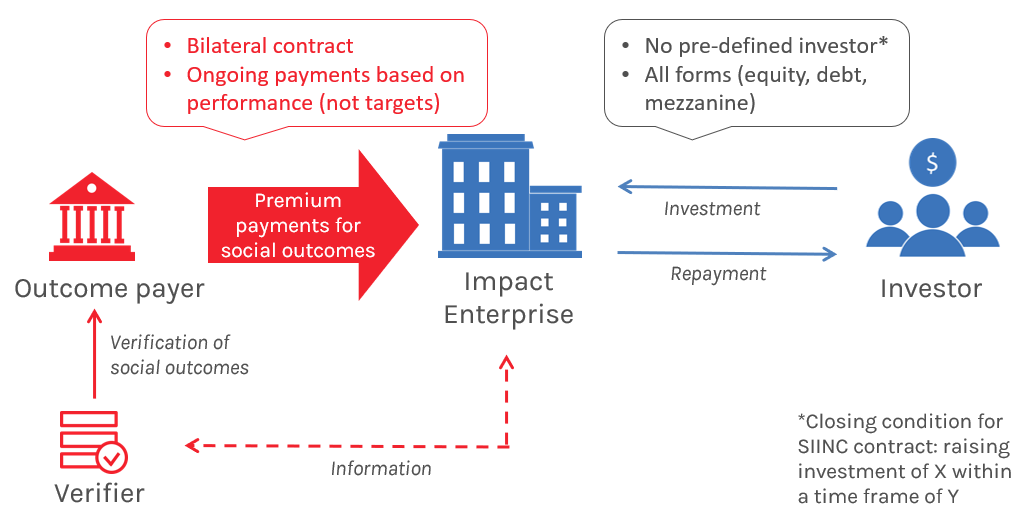
The Social Impact Incentives (SIINC) model is a blended finance instrument introduced for the first time in 2016. In the SIINC model, enterprises are provided with time-limited premium payments for achieving social impact, thus aligning profitability with their social impact and enabling them to attract growth capital. The SIINC agreement is a bilateral contract between an outcome funder (e.g. a development agency or a philanthropic organization) and an enterprise; an independent verifier assesses the impact performance and clears payments for disbursement; the investment between the enterprise and its investor is arranged via a separate contract.

History
SIINC was co-created by Roots of Impact and theSwiss Agency for Development and Cooperation
The Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) is an office-level agency in the federal administration of Switzerland, and a part of the Federal Department of Foreign Affairs. Together with other federal offices, SDC is responsible for ...
in 2016 by exploring how to adapt pay-for-success models like impact bonds for market-based organizations. The Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation funded a pilot program in Latin America and the Caribbean which launched in 2016, led by a collaborative with Roots of Impact, the Inter-American Development Bank
The Inter-American Development Bank (IDB or IADB) is an international development finance institution headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States of America. It serves as one of the leading sources of development financing for the countri ...
, New Ventures, and Ashoka (non-profit organization)
Ashoka (formerly branded Ashoka: Innovators for the Public) is an American-based nonprofit organization that promotes social entrepreneurship by connecting and supporting individual social entrepreneurs. Ashoka invests in over 3,800 social entre ...
.
Structure
SIINC is a blended finance model that seeks to align the interests of development funders, enterprises, and investors around social impact. A SIINC transaction can be understood as a pre-order for the impact made by a development funder with an enterprise. The enterprise uses this pre-order to secure investment, using that investment to expand operations and deliver the desired impact. In the basic model, there is a time-limited payment agreement between the outcome payer and the social enterprise along with predefined social performance indicators. The investment contract between the social enterprise and the investor is structured individually to meet the specific needs of both. In the second step, an impact base-line is established, with payments triggered by organizational metrics directly related to the impact performance or externally generated impact metrics. Finally, the ongoing payments are structured and linked to impact, while an independent verification of the impact assessment system ensures that the results are as reliable as possible. A report from theBoston Consulting Group
Boston Consulting Group, Inc. (BCG) is an American global management consulting firm founded in 1963 and headquartered in Boston, Massachusetts. It is one of the "Big Three (management consultancies), Big Three" (or MBB, the world's three large ...
highlighted that SIINC is a form of Impact-Linked Finance as it fulfills the criteria of focusing on outcomes as opposed to outputs, and incentives are paid only to the value creator for additional impact.
Benefits and costs
SIINC has been described as an innovation due to the fact that the model is more streamlined than comparable approaches. SIINC was developed for supporting market-based organizations (enterprises), while comparable models such as thesocial impact bond
A social impact bond (SIB), also known as pay-for-success financing, pay-for-success bond (US), social benefit bond (Australia), pay-for-benefit bond (Australia), social outcomes contract (UK), social impact partnership (Europe), social impact ...
(SIB) and development impact bond Development impact bonds (DIBs) are a performance-based investment instrument intended to finance development programmes in low resource countries, which are built off the model of social impact bond (SIB) model. In general, the model works the same ...
(DIB) were originally developed for non-profit interventions. The SIINC model can be utilized to catalyze investment into an enterprise in an impact-focused manner, or it can lead to deeper levels of impact being generated.
The need for independent verification of results has been singled out as a drawback, with the costs needing to be covered by potential savings in order to ensure a transaction is cost effective.
Implementing organizations
To date, the SIINC model has been implemented by the German firm Roots of Impact, with funding from theSwiss Agency for Development and Cooperation
The Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) is an office-level agency in the federal administration of Switzerland, and a part of the Federal Department of Foreign Affairs. Together with other federal offices, SDC is responsible for ...
, and in collaboration with the Inter-American Development Bank
The Inter-American Development Bank (IDB or IADB) is an international development finance institution headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States of America. It serves as one of the leading sources of development financing for the countri ...
, New Ventures, and Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
.
References
{{Reflist Social impact Sustainable development