Slot 1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of
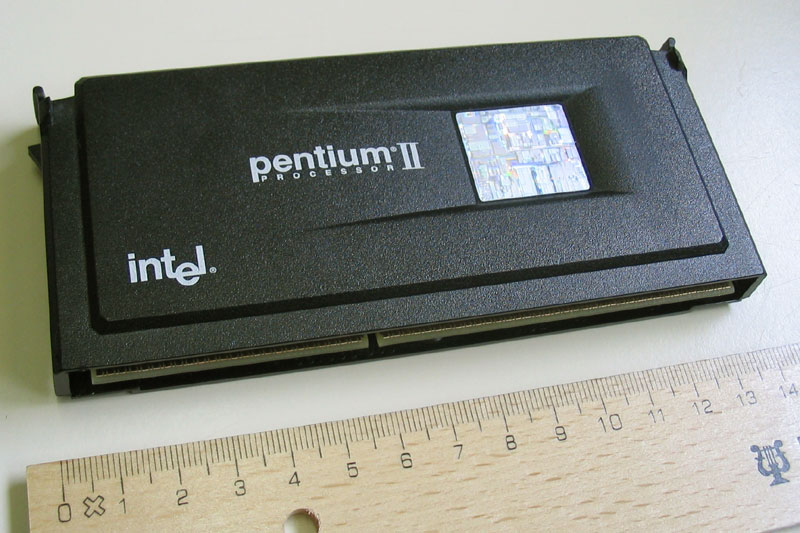

 The Single Edge Contact Cartridge, or "SECC", was used at the beginning of the Slot 1-era for Pentium II CPUs. Inside the cartridge, the CPU itself is enclosed in a hybrid plastic and metal case. The back of the housing is plastic and has several markings on it: the name, "Pentium II"; the Intel logo; a hologram; and the model number. The front consists of a black anodized aluminum plate, which is used to hold the CPU cooler. The SECC form is very solid, because the CPU itself is resting safely inside the case. As compared to socket-based CPUs, there are no pins that can be bent, and the CPU is less likely to be damaged by improper installation of a cooler.
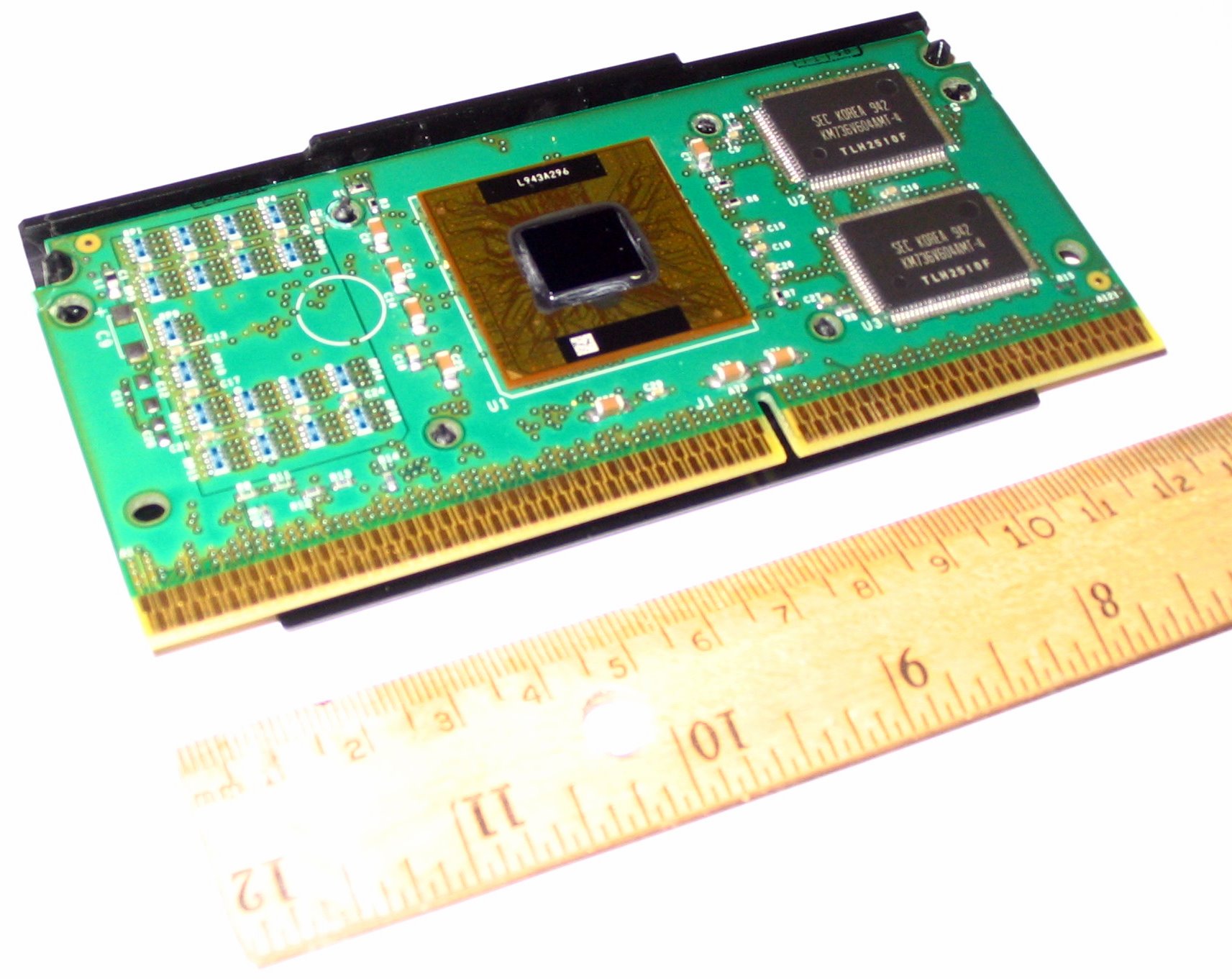
Following SECC, the SEPP-form (Single Edge Processor Package) appeared on the market. It was designed for lower-priced Celeron CPUs. This form lacks a case entirely, consisting solely of the printed-circuit board holding the components.
A form factor called SECC2 was used for late Pentium II and Pentium III CPUs for Slot 1, which was created to accommodate the switch to flip chip packaging. Only the front plate was carried over, the coolers were now mounted straight to the PCB and exposed CPU die and are, as such, incompatible with SECC cartridges.
The Single Edge Contact Cartridge, or "SECC", was used at the beginning of the Slot 1-era for Pentium II CPUs. Inside the cartridge, the CPU itself is enclosed in a hybrid plastic and metal case. The back of the housing is plastic and has several markings on it: the name, "Pentium II"; the Intel logo; a hologram; and the model number. The front consists of a black anodized aluminum plate, which is used to hold the CPU cooler. The SECC form is very solid, because the CPU itself is resting safely inside the case. As compared to socket-based CPUs, there are no pins that can be bent, and the CPU is less likely to be damaged by improper installation of a cooler.
Following SECC, the SEPP-form (Single Edge Processor Package) appeared on the market. It was designed for lower-priced Celeron CPUs. This form lacks a case entirely, consisting solely of the printed-circuit board holding the components.
A form factor called SECC2 was used for late Pentium II and Pentium III CPUs for Slot 1, which was created to accommodate the switch to flip chip packaging. Only the front plate was carried over, the coolers were now mounted straight to the PCB and exposed CPU die and are, as such, incompatible with SECC cartridges.


Intel's detailed Slot 1 CPU (Coppermine) information, including Slot 1 pinoutAn image of a motherboard with Slot 1 connector
{{Intelsock Intel CPU sockets
 Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
, Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implemented.
Intel reverted to the traditional socket interface with the release of Socket 370 in 1999.
General
With the introduction of the Pentium II CPU, the need for greater access for testing had made the transition from socket to slot necessary. Previously with the Pentium Pro, Intel had combined processor and cache dies in the same Socket 8 package. These were connected by a full-speed bus, resulting in significant performance benefits. Unfortunately, this method required that the two components be bonded together early in the production process, before testing was possible. As a result, a single, tiny flaw in either die made it necessary to discard the entire assembly, causing low production yield and high cost. Intel subsequently designed a circuit board where the CPU and cache remained closely integrated, but were mounted on aprinted circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
, called a Single-Edged Contact Cartridge (SECC). The CPU and cache could be tested separately, before final assembly into a package, reducing cost and making the CPU more attractive to markets other than that of high-end servers. These cards could also be easily plugged into a Slot 1, thereby eliminating the chance for pins of a typical CPU to be bent or broken when installing in a socket.
The form factor used for Slot 1 was a 5-inch-long, 242-contact edge connector named SC242. To prevent the cartridge from being inserted the wrong way, the slot was keyed to allow installation in only one direction. The SC242 was later used for AMD's Slot A as well, and while the two slots were identical mechanically, they were electrically incompatible. To discourage Slot A users from trying to install a Slot 1 CPU, the connector was rotated 180 degrees on Slot A motherboards. This also allowed motherboard manufacturers to save costs by stocking the same part for both Slot 1 and Slot A assemblies.
With the new Slot 1, Intel added support for symmetric multiprocessing (SMP). A maximum of two Pentium II or Pentium III CPUs can be used in a dual slot motherboard. The Celeron does not have official SMP support.
There are also converter cards, known as Slotkets, which hold a Socket 8 so that a Pentium Pro CPU can be used with Slot 1 motherboards. These specific converters, however, are rare. Another kind of slotket allows using a Socket 370 CPU in a Slot 1. These are generally more common than Socket 8 to Slot 1 slotkets. Many of these latter devices are equipped with their own voltage regulator modules, in order to supply the new CPU with a lower core voltage, which the motherboard would not otherwise allow.
Form factors


 The Single Edge Contact Cartridge, or "SECC", was used at the beginning of the Slot 1-era for Pentium II CPUs. Inside the cartridge, the CPU itself is enclosed in a hybrid plastic and metal case. The back of the housing is plastic and has several markings on it: the name, "Pentium II"; the Intel logo; a hologram; and the model number. The front consists of a black anodized aluminum plate, which is used to hold the CPU cooler. The SECC form is very solid, because the CPU itself is resting safely inside the case. As compared to socket-based CPUs, there are no pins that can be bent, and the CPU is less likely to be damaged by improper installation of a cooler.
Following SECC, the SEPP-form (Single Edge Processor Package) appeared on the market. It was designed for lower-priced Celeron CPUs. This form lacks a case entirely, consisting solely of the printed-circuit board holding the components.
A form factor called SECC2 was used for late Pentium II and Pentium III CPUs for Slot 1, which was created to accommodate the switch to flip chip packaging. Only the front plate was carried over, the coolers were now mounted straight to the PCB and exposed CPU die and are, as such, incompatible with SECC cartridges.
The Single Edge Contact Cartridge, or "SECC", was used at the beginning of the Slot 1-era for Pentium II CPUs. Inside the cartridge, the CPU itself is enclosed in a hybrid plastic and metal case. The back of the housing is plastic and has several markings on it: the name, "Pentium II"; the Intel logo; a hologram; and the model number. The front consists of a black anodized aluminum plate, which is used to hold the CPU cooler. The SECC form is very solid, because the CPU itself is resting safely inside the case. As compared to socket-based CPUs, there are no pins that can be bent, and the CPU is less likely to be damaged by improper installation of a cooler.
Following SECC, the SEPP-form (Single Edge Processor Package) appeared on the market. It was designed for lower-priced Celeron CPUs. This form lacks a case entirely, consisting solely of the printed-circuit board holding the components.
A form factor called SECC2 was used for late Pentium II and Pentium III CPUs for Slot 1, which was created to accommodate the switch to flip chip packaging. Only the front plate was carried over, the coolers were now mounted straight to the PCB and exposed CPU die and are, as such, incompatible with SECC cartridges.
History
Historically, there are three platforms for the Intel P6 CPUs: Socket 8, Slot 1 and Socket 370. Slot 1 is a successor to Socket 8. While the Socket 8 CPUs (Pentium Pro) directly had the L2-cache embedded into the CPU, it is located (outside of the core) on a circuit board shared with the core itself. The exception is later Slot 1 CPUs with the Coppermine core which have the L2-cache embedded into the die. In the beginning of 2000, around the time the Coppermine Pentium III CPUs with FC-PGA housing were already commonplace, Slot 1 was being gradually phased out in favor of Socket 370, well after Intel started to offer both Socket 370 and Slot 1 CPUs at the same time since late 1998. Socket 370 was initially made for low-cost Celeron processors starting with the Mendocino Celerons, while Slot 1 was thought of as a platform for the more expensive Pentium II and early Pentium III models. Both cache and core were embedded into the die. Slot 1 also obsoleted the old Socket 7 as the standard platform for home users, at least regarding Intel. After superseding the Intel P5 Pentium MMX CPU in the late 1990s, Intel had completely left the Socket 7 market.Chipsets and officially supported CPUs


Intel 440FX
* Introduced in: May 6, 1996 * FSB: 66 MHz * PIO/ WDMA * Supported RAM type: EDO-DRAM * Supported CPUs: ** Pentium Pro **Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
with 66 MHz FSB
** Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Covington, Mendocino)
* Used in both Socket 8 (Pentium Pro) and Slot 1 (Pentium II, early Celerons)
* Does not support AGP or SDRAM, as it predates the introduction of said technologies
* Allowed up to two CPUs for SMP
Intel 440LX
* Introduced in: August 27, 1997 * FSB: 66 MHz * Supported RAM type: EDO-DRAM, SDRAM * Supported CPUs: Pentium II, Celeron * AGP 2× Mode * UDMA/33 **Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
with 66 MHz FSB
** Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Covington, Mendocino)
* Introduced support for AGP and SDRAM
* Allowed up to two CPUs for SMP
Intel 440EX
* Introduced in: April, 1998 * FSB: 66 MHz * Supported RAM type: EDO-DRAM, SDRAM * Supported CPUs: Pentium II, Celeron * AGP 2× Mode * UDMA/33 **Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
with 66 MHz FSB
** Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Covington, Mendocino)
* Same specifications as 440LX, but memory support limited to 256 MB and no SMP support.
Intel 440BX Intel Corporation:
440BX AGPset Design Guide
''
Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
with 66 and 100 MHz FSB
** Pentium III with 100 MHz FSB (133 with overclocking)
** Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Covington, Mendocino, Coppermine)
* Allowed up to two CPUs for SMP
Intel 440ZX
* Introduced in: November 1998 * FSB: 66 and 100 MHz (some motherboards supported overclocking to 133 MHz, allowing usage of Socket 370 CPUs using a Slocket) * AGP 2× Mode * UDMA/33 * Supported RAM types: SDRAM ( PC66 and PC100, PC133 with overclocking), up to 2 DIMMs of 256 MB * Supported CPUs: **Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
with 66 and 100 MHz FSB
** Pentium III with 100 MHz FSB (133 with overclocking)
** Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Covington, Mendocino, Coppermine)
Intel 810
* Introduced in: 1999 * FSB: 66 and 100 MHz * No external AGP * Intel i752 based graphics * UDMA/66 (UDMA/33 with ICH0) * Supported RAM types: PC100 SDRAM * Supported CPUs: **Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
with 66 and 100 MHz FSB
** Pentium III with 100 MHz FSB (133 with overclocking)
** Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Covington, Mendocino, Coppermine)
Intel 820/820E (Camino)
* Introduced in: November 1999 * FSB: 100 and 133 MHz * AGP 4× Mode * UDMA/66 (i820), UDMA/100 (i820E) * Supported RAM types:RDRAM
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM), and its successors Concurrent Rambus DRAM (CRDRAM) and Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM), are types of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) developed by Rambus from the 1990s through to the early 2000s. The third-generati ...
, SDRAM (PC100 via MTH)
* Supported CPUs: All FSB 100/133 Slot 1 CPUs
* Allowed up to two CPUs for SMP
Intel 840
* Introduced in: November 1999 * FSB: 100 and 133 MHz * AGP 4× Mode * UDMA/66 (i820), UDMA/100 (i820E) * Supported RAM types: Dual ChannelRDRAM
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM), and its successors Concurrent Rambus DRAM (CRDRAM) and Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM), are types of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) developed by Rambus from the 1990s through to the early 2000s. The third-generati ...
, SDRAM (PC100 via MTH)
* Supported CPUs: All FSB 100/133 Slot 1 CPUs
* Allowed up to two CPUs for SMP
VIA Apollo Pro / Pro II / Pro+
* Introduced in: May 1998 (Pro Plus: Dec 1998) * FSB: 66, 100 MHz (some motherboards supported overclocking to 133 MHz, allowing usage of Socket 370 CPUs using a Slocket) * AGP 2× Mode * UDMA/33 (VT82C586B/VT82C596A), UDMA/66 (VT82C596B) *Supported RAM types: PC66/100 SDRAM up to 1536 MB * Supported CPUs: ** Pentium Pro with 66 MHz FSB **Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
with 66 and 100 MHz FSB
** Pentium III with 100 MHz FSB (133 with overclocking)
** Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Covington, Mendocino, Coppermine)
VIA Apollo Pro 133
* Introduced in: July 1999 * FSB: 66, 100, and 133 MHz * AGP 2× Mode * UDMA/33 (VT82C596A), UDMA/66 (VT82C596B/VT82C686A), UDMA/100 (VT82C686B) *Supported RAM types: PC66/100/133 SDRAM up to 1536 MB * Supported CPUs: All Slot 1 CPUsVIA Apollo Pro 133A
* Introduced in: Oct 1999 * FSB: 66, 100, and 133 MHz * AGP 4× Mode * UDMA/66 (VT82C596B/VT82C686A), UDMA/100 (VT82C686B) *Supported RAM types: PC66/100/133 SDRAM up to 2048 MB * Supported CPUs: All Slot 1 CPUs * Allowed up to two CPUs for SMPSiS 5600 (SiS 600)
* Introduced in: November 1998 * FSB: 66 and 100 MHz * AGP 2× Mode * UDMA/33 * Supported RAM types: PC66/100 SDRAM up to 1536 MB * Supported CPUs: **Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
with 66 and 100 MHz FSB
** Pentium III with 100 MHz FSB
** Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Covington, Mendocino, Coppermine)
SiS 620
* Introduced in: April 1999 * FSB: 66 and 100 MHz * No external AGP port *SiS 6326 based Integrated Graphics * UDMA/33 * Supported RAM types: PC66/100 SDRAM up to 1536 MB * Supported CPUs: **Pentium II
The Pentium II is a brand of sixth-generation Intel x86 microprocessors based on the P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture, introduced on May 7, 1997. It combined the ''P6'' microarchitecture seen on the Pentium Pro with the MMX (instruc ...
with 66 and 100 MHz FSB
** Pentium III with 100 MHz FSB
** Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023.
The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, ...
(Covington, Mendocino, Coppermine)
See also
* Slot A * Slot 2 * List of Intel microprocessors * SlotketReferences
External links
Intel's detailed Slot 1 CPU (Coppermine) information, including Slot 1 pinout
{{Intelsock Intel CPU sockets