Skeletal animation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
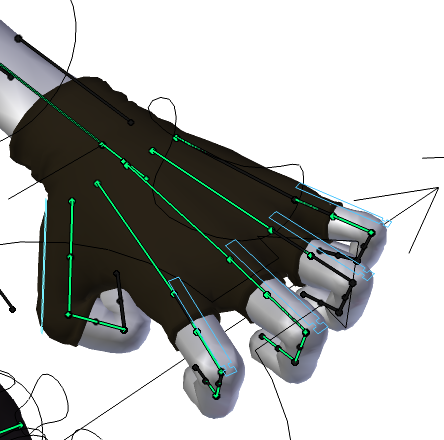 Skeletal animation or rigging is a technique in
Skeletal animation or rigging is a technique in
 Skeletal animation or rigging is a technique in
Skeletal animation or rigging is a technique in computer animation
Computer animation is the process used for digitally generating animations. The more general term computer-generated imagery (CGI) encompasses both static scenes ( still images) and dynamic images ( moving images), while computer animation re ...
in which a character
Character or Characters may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''Character'' (novel), a 1936 Dutch novel by Ferdinand Bordewijk
* ''Characters'' (Theophrastus), a classical Greek set of character sketches attributed to The ...
(or other articulated object) is represented in two parts: a surface representation used to draw the character (called the ''mesh
A mesh is a barrier made of connected strands of metal, fiber, or other flexible or ductile materials. A mesh is similar to a web or a net in that it has many attached or woven strands.
Types
* A plastic mesh may be extruded, oriented, exp ...
'' or ''skin'') and a hierarchical set of interconnected parts (called ''bones'', and collectively forming the ''skeleton'' or ''rig''), a virtual armature used to animate (''pose'' and ''keyframe'') the mesh. While this technique is often used to animate humans and other organic figures, it only serves to make the animation process more intuitive, and the same technique can be used to control the deformation of any object—such as a door, a spoon, a building, or a galaxy. When the animated object is more general than, for example, a humanoid character, the set of "bones" may not be hierarchical or interconnected, but simply represent a higher-level description of the motion of the part of mesh it is influencing.
The technique was introduced in 1988 by Nadia Magnenat Thalmann, Richard Laperrière, and Daniel Thalmann. This technique is used in virtually all animation systems where simplified user interfaces allows animators to control often complex algorithms and a huge amount of geometry; most notably through inverse kinematics
In computer animation and robotics, inverse kinematics is the mathematical process of calculating the variable joint parameters needed to place the end of a kinematic chain, such as a robot manipulator or animation character's skeleton, in a ...
and other "goal-oriented" techniques. In principle, however, the intention of the technique is never to imitate real anatomy or physical processes, but only to control the deformation of the mesh data.
Technique
As described in an instructional article by Josh Petty: This technique constructs a series of ''bones'' (which need not correspond to any real-world anatomical feature), sometimes also referred to as ''rigging'' in the noun sense. Each bone has a three-dimensional transformation from the default bind pose (which includes its position, scale and orientation), and an optional parent bone. The bones therefore form ahierarchy
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
. The full transform of a child node is the product of its parent transform and its own transform. So moving a thigh-bone will move the lower leg too. As the character is animated, the bones change their transformation over time, under the influence of some animation controller. A rig is generally composed of both forward kinematics
In robot kinematics, forward kinematics refers to the use of the kinematic equations of a robot to compute the position of the end-effector from specified values for the joint parameters.
The kinematics equations of the robot are used in robo ...
and inverse kinematics
In computer animation and robotics, inverse kinematics is the mathematical process of calculating the variable joint parameters needed to place the end of a kinematic chain, such as a robot manipulator or animation character's skeleton, in a ...
parts that may interact with each other. Skeletal animation is referring to the forward kinematics part of the rig, where a complete set of bone configurations identifies a unique pose.
Each bone in the skeleton is associated with some portion of the character's visual representation (the mesh
A mesh is a barrier made of connected strands of metal, fiber, or other flexible or ductile materials. A mesh is similar to a web or a net in that it has many attached or woven strands.
Types
* A plastic mesh may be extruded, oriented, exp ...
) in a process called ''skinning''. In the most common case of a polygonal mesh character, the bone is associated with a group of vertices; for example, in a model of a human being, the bone for the thigh would be associated with the vertices making up the polygons in the model's thigh. Portions of the character's skin can normally be associated with multiple bones, each one having a scaling factors called vertex weights, or blend weights. The movement of skin near the joints of two bones, can therefore be influenced by both bones. In most state-of-the-art graphical engines, the skinning process is done on the GPU thanks to a shader program.
For a polygonal mesh, each vertex can have a blend weight for each bone. To calculate the final position of the vertex, a transformation matrix is created for each bone which, when applied to the vertex, first puts the vertex in bone space then puts it back into mesh space. After applying a matrix to the vertex, it is scaled by its corresponding weight. This algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
is called ''matrix-palette skinning'' or ''linear-blend skinning'', because the set of bone transformations (stored as transform matrices) form a palette for the skin vertex to choose from.
Benefits and drawbacks
Strengths
* A bone represents a set of vertices (or some other object which represents something, such as a leg), ** The animator needs to control fewer characteristics of the model, *** The animator can focus on the large-scale motion, ** Bones are independently movable. * An animation can be defined by simple movements of the bones, instead of vertex by vertex (in the case of a polygonal mesh).Weaknesses
* A bone does only represent a set of vertices (or some other precisely defined object), and is not more abstract or conceptual. ** Does not provide realisticmuscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of mus ...
movement and skin motion. Possible solutions to this problem:
*** Special muscle controllers attached to the bones.
*** Consultation with physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemic ...
experts, to increase accuracy of musculoskeletal realism with more thorough virtual anatomy simulations.
Applications
Skeletal animation is the standard way to animate characters or mechanical objects for a prolonged period of time (usually over 100 frames). It is commonly used by video game artists and in themovie industry
The film industry or motion picture industry comprises the technological and commercial institutions of filmmaking, i.e., film production companies, film studios, cinematography, animation, film production, screenwriting, pre-production, post ...
, and can also be applied to mechanical objects and any other object made up of rigid elements and joints.
Performance capture (or motion capture
Motion capture (sometimes referred as mo-cap or mocap, for short) is the process of recording the movement of objects or people. It is used in military, entertainment, sports, medical applications, and for validation of computer vision and robo ...
) can speed up development time of skeletal animation, as well as increasing the level of realism.
For motion that is too dangerous for performance capture, there are computer simulation
Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be deter ...
s that automatically calculate physics of motion and resistance with skeletal frames. Virtual anatomy properties such as weight of limbs, muscle reaction, bone strength, and joint constraints may be added for realistic bouncing, buckling, fracture, and tumbling effects known as virtual stunt
A stunt is an unusual and difficult physical feat or an act requiring a special skill, performed for artistic purposes usually on television, theaters, or cinema. Stunts are a feature of many action films. Before computer generated imagery sp ...
s. However, there are other applications of virtual anatomy simulations such as military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
and emergency
An emergency is an urgent, unexpected, and usually dangerous situation that poses an immediate risk to health, life, property, or environment and requires immediate action. Most emergencies require urgent intervention to prevent a worsening ...
response. Virtual soldiers, rescue workers, patients, passengers, and pedestrians can be used for training, virtual engineering and virtual testing of equipment. Virtual anatomy technology may be combined with artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech ...
for further enhancement of animation and simulation technology.
See also
*3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, or “3D graphics,” sometimes called CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for th ...
* Morph target animation
* Interactive skeleton-driven simulation
* Cutout animation
Cutout animation is a form of stop-motion animation using flat characters, props and backgrounds cut from materials such as paper, card, stiff fabric or photographs. The props would be cut out and used as puppets for stop motion. The world's e ...
References
{{Authority control Computer animation Computer graphic techniques 3D computer graphics Animation techniques Anatomical simulation