Simeon I Of Bulgaria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôtos ho Mégas) ruled over
The Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire, Oxford History of the Christian Church, J. M. Hussey, Andrew Louth, Oxford University Press, 2010, p. 100.
Halfway through his reign, Simeon assumed the title of
 Unable to effectively respond to the Bulgarian campaign due to the engagement of their forces against the Arabs, the Byzantines convinced the Magyars to attack Bulgaria, promising to transport them across the
Unable to effectively respond to the Bulgarian campaign due to the engagement of their forces against the Arabs, the Byzantines convinced the Magyars to attack Bulgaria, promising to transport them across the
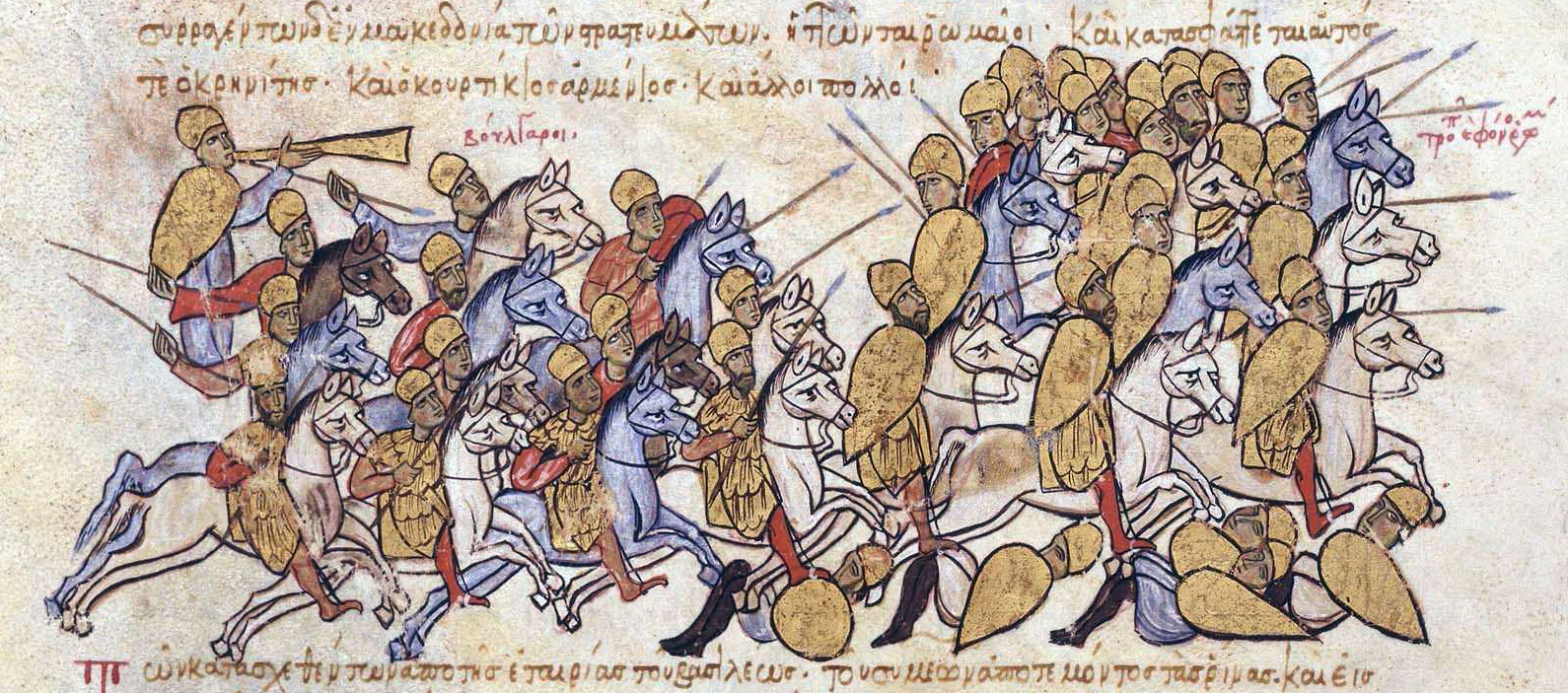 Having dealt with the pressure from the Magyars and the Byzantines, Simeon was free to plan a campaign against the Magyars looking for retribution. He negotiated a joint force with the Magyars' eastern neighbours, the
Having dealt with the pressure from the Magyars and the Byzantines, Simeon was free to plan a campaign against the Magyars looking for retribution. He negotiated a joint force with the Magyars' eastern neighbours, the  Claiming that not all prisoners had been released, Simeon once again invaded Byzantium in the summer of 896, heading directly to Constantinople. He was met in
Claiming that not all prisoners had been released, Simeon once again invaded Byzantium in the summer of 896, heading directly to Constantinople. He was met in

 By 917, Simeon was preparing for yet another war against Byzantium. He attempted to conclude an anti-Byzantine union with the Pechenegs, but his envoys could not match the financial resources of the Byzantines, who succeeded in outbidding them. The Byzantines hatched a large-scale campaign against Bulgaria and also tried to persuade the Serbian Prince Petar Gojniković to attack the Bulgarians with Magyar support.
In 917, a particularly strong Byzantine army led by Leo Phokas the Elder, son of
By 917, Simeon was preparing for yet another war against Byzantium. He attempted to conclude an anti-Byzantine union with the Pechenegs, but his envoys could not match the financial resources of the Byzantines, who succeeded in outbidding them. The Byzantines hatched a large-scale campaign against Bulgaria and also tried to persuade the Serbian Prince Petar Gojniković to attack the Bulgarians with Magyar support.
In 917, a particularly strong Byzantine army led by Leo Phokas the Elder, son of

 No longer able to climb to the Byzantine throne by diplomatic means, the infuriated Simeon once again had to wage war to impose his will. Between 920 and 922, Bulgaria increased its pressure on Byzantium, campaigning in the west through
No longer able to climb to the Byzantine throne by diplomatic means, the infuriated Simeon once again had to wage war to impose his will. Between 920 and 922, Bulgaria increased its pressure on Byzantium, campaigning in the west through
 During Simeon's reign, Bulgaria reached its cultural apogee, becoming the literary and spiritual centre of Slavic Europe.Delev, ''Zlatnijat vek na bǎlgarskata kultura''. In this respect, Simeon continued his father Boris' policy of establishing and spreading Slavic culture and attracting noted scholars and writers within Bulgaria's borders. It was in the Preslav Literary School and Ohrid Literary School, founded under Boris, that the main literary work in Bulgaria was concentrated during the reign of Simeon
Ivanova,
During Simeon's reign, Bulgaria reached its cultural apogee, becoming the literary and spiritual centre of Slavic Europe.Delev, ''Zlatnijat vek na bǎlgarskata kultura''. In this respect, Simeon continued his father Boris' policy of establishing and spreading Slavic culture and attracting noted scholars and writers within Bulgaria's borders. It was in the Preslav Literary School and Ohrid Literary School, founded under Boris, that the main literary work in Bulgaria was concentrated during the reign of Simeon
Ivanova,
Introduction
, ''Tǎržestvo na slovoto''. in the new Cyrillic alphabet which was developed there. The late 9th and early 10th centuries constitute the earliest and most productive period of medieval
 Tsar Simeon I has remained among the most highly valued Bulgarian historical figures, as indicated by popular vote in the '' Velikite Bǎlgari'' (a spin-off of ''
Tsar Simeon I has remained among the most highly valued Bulgarian historical figures, as indicated by popular vote in the '' Velikite Bǎlgari'' (a spin-off of ''
Nikolov, Angel. "The Perception of the Bulgarian Past in the Court of Preslav around 900 AD.," in ''State and Church: Studies in Medieval Bulgaria and Byzantium''. Ed. by V. Gjuzelev and K. Petkov. American Research Center in Sofia: Sofia, 2011, 157–171
Nikolov, Angel. "Making a new basileus: the case of Symeon of Bulgaria (893–927) reconsidered," in ''Rome, Constantinople and Newly converted Europe. Archeological and Historical Evidence''. Vol. I. Ed. by M. Salamon, M. Wołoszyn, A. Musin, P. Špehar. Kraków-Leipzig-Rzeszów-Warszawa, 2012, 101–108
an article by Georgi Todorov * ,
lyrics
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Simeon 01 Of Bulgaria 860s births 927 deaths 9th-century Bulgarian monarchs 10th-century Bulgarian emperors Bulgarian people of the Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars Eastern Orthodox monarchs
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, блъгарьско цѣсарьствиѥ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, Първо българско царство) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Eur ...
. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of ...
led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the '' Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages, Gold being the first and the one during which the G ...
of Bulgarian culture
A number of ancient civilizations, including the Thracians, ancient Greeks, Scythians, Celts, ancient Romans, Goths (Ostrogoths and Visigoths), Slavs ( East and West Slavs), Varangians and the Bulgars have left their mark on the culture, h ...
.
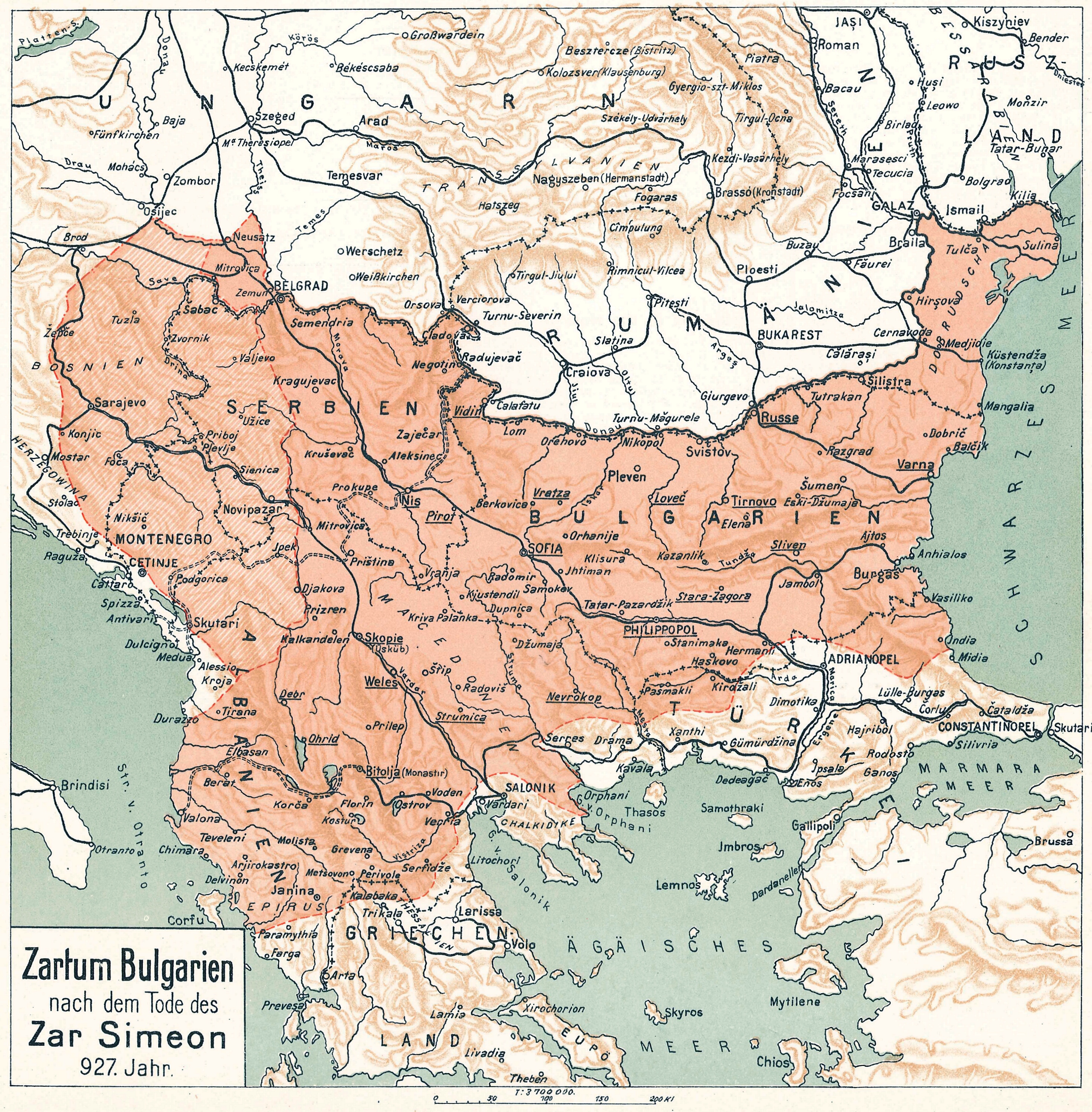
During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgars ...
became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bulgarian Glagolitic and Cyrillic translations of Christian texts spread all over the Slavic world of the time. It was at the Preslav Literary School in the 890s that the Cyrillic alphabet was developed.Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250, Cambridge Medieval Textbooks, Florin Curta, Cambridge University Press, 2006, pp. 221–222.The Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire, Oxford History of the Christian Church, J. M. Hussey, Andrew Louth, Oxford University Press, 2010, p. 100.
Halfway through his reign, Simeon assumed the title of
Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( ...
('' Tsar''), having prior to that been styled Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. ...
('' Knyaz'').Zlatarski, ''Istorija na Pǎrvoto bǎlgarsko carstvo'', p. 280.
Background and early life
Simeon was born in 864 or 865, as the third son of KnyazBoris I
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, Борисъ А҃ / Борисъ-Михаилъ bg, Борис I / Борис-Михаил; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At ...
of Krum
Krum ( bg, Крум, el, Κροῦμος/Kroumos), often referred to as Krum the Fearsome ( bg, Крум Страшни) was the Khan of Bulgaria from sometime between 796 and 803 until his death in 814. During his reign the Bulgarian territor ...
's dynasty. As Boris was the ruler who Christianized Bulgaria in 865, Simeon was a Christian all his life.Fine, ''The Early Medieval Balkans'', p. 132. Because his eldest brother Vladimir was designated heir to the Bulgarian throne, Boris intended Simeon to become a high-ranking cleric,Delev, ''Bǎlgarskata dǎržava pri car Simeon''. possibly Bulgarian archbishop, and sent him to the leading University of Constantinople to receive theological education when he was thirteen or fourteen. He took the name Simeon as a novice in a monastery in Constantinople. During the decade (ca. 878–888) he spent in the Byzantine capital, he received excellent education and studied the rhetoric of Demosthenes
Demosthenes (; el, Δημοσθένης, translit=Dēmosthénēs; ; 384 – 12 October 322 BC) was a Greek statesman and orator in ancient Athens. His orations constitute a significant expression of contemporary Athenian intellectual pr ...
and Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
. He also learned fluent Greek, to the extent that he was referred to as "the half-Greek" in Byzantine chronicles. He is speculated to have been tutored by Patriarch Photios I of Constantinople, but this is not supported by any source.
Around 888, Simeon returned to Bulgaria and settled at the newly established royal monastery of Preslav "at the mouth of the Tiča", where, under the guidance of Naum of Preslav, he engaged in active translation of important religious works from Greek to Medieval Bulgarian (currently referred to as Church Slavonic), aided by other students from Constantinople. Meanwhile, Vladimir had succeeded Boris, who had retreated to a monastery, as ruler of Bulgaria. Vladimir attempted to reintroduce paganism
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. I ...
in the empire and possibly signed an anti-Byzantine pact with Arnulf of Carinthia
Arnulf of Carinthia ( 850 – 8 December 899) was the duke of Carinthia who overthrew his uncle Emperor Charles the Fat to become the Carolingian king of East Francia from 887, the disputed king of Italy from 894 and the disputed emperor from ...
, forcing Boris to re-enter political life. Boris had Vladimir imprisoned and blinded, and then appointed Simeon as the new ruler. This was done at an assembly in Preslav which also proclaimed Bulgarian as the only language of state and church and moved the Bulgarian capital from Pliska to Preslav, to better cement the recent conversion. It is not known why Boris did not place his second son, Gavril, on the throne, but instead preferred Simeon.
Reign
Trade War with Byzantium and Magyar invasions
With Simeon on the throne, the long-lasting peace with the Byzantine Empire established by his father was about to end. A conflict arose whenByzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
Leo VI the Wise, allegedly acting under pressure from his mistress Zoe Zaoutzaina and her father Stylianos Zaoutzes, moved the marketplace for Bulgarian goods from Constantinople to Thessaloniki, where the Bulgarian merchants were heavily taxed. The Bulgarians sought protection by Simeon, who in turn complained to Leo. However, the Byzantine emperor ignored his embassy.
 Unable to effectively respond to the Bulgarian campaign due to the engagement of their forces against the Arabs, the Byzantines convinced the Magyars to attack Bulgaria, promising to transport them across the
Unable to effectively respond to the Bulgarian campaign due to the engagement of their forces against the Arabs, the Byzantines convinced the Magyars to attack Bulgaria, promising to transport them across the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
using the Byzantine navy
The Byzantine navy was the naval force of the East Roman or Byzantine Empire. Like the empire it served, it was a direct continuation from its Imperial Roman predecessor, but played a far greater role in the defence and survival of the state than ...
.Canev, ''Bǎlgarski hroniki'', p. 198. Leo VI may have also concluded an agreement with Arnulf to make sure that the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
did not support Simeon against the Magyars. In addition, the talented commander Nikephoros Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
was called back from southern Italy to lead a separate army against Bulgaria in 895 with the mere intention to overawe the Bulgarians.Runciman, ''A history of the First Bulgarian Empire'', p. 146. Simeon, unaware of the threat from the north, rushed to meet Phokas' forces, but the two armies did not engage in a fight. Instead, the Byzantines offered peace, informing him of both the Byzantine foot and maritime campaign, but intentionally did not notify him of the planned Magyar attack. Simeon did not trust the envoy and, after sending him to prison, ordered the Byzantine navy's route into the Danube closed off with ropes and chains, intending to hold it until he had dealt with Phokas.
Despite the problems they encountered because of the fencing, the Byzantines ultimately managed to ferry the Magyar forces led by Árpád's son Liüntika across the Danube, possibly near modern Galaţi, and assisted them in pillaging the nearby Bulgarian lands. Once notified of the surprise invasion, Simeon headed north to stop the Magyars, leaving some of his troops at the southern border to prevent a possible attack by Phokas.Zlatarski, ''Istorija na Pǎrvoto bǎlgarsko carstvo'', pp. 298–299. Simeon's two encounters with the enemy in Northern Dobruja
Northern Dobruja ( ro, Dobrogea de Nord or simply ; bg, Северна Добруджа, ''Severna Dobrudzha'') is the part of Dobruja within the borders of Romania. It lies between the lower Danube river and the Black Sea, bordered in the south ...
resulted in Magyar victories, forcing him to retreat to Drǎstǎr. After pillaging much of Bulgaria and reaching Preslav, the Magyars returned to their lands, but not before Simeon had concluded an armistice with Byzantium towards the summer of 895. A complete peace was delayed, as Leo VI required the release of the Byzantine captives from the Trade War.
Anti-Magyar campaign and further wars with Byzantium
 Having dealt with the pressure from the Magyars and the Byzantines, Simeon was free to plan a campaign against the Magyars looking for retribution. He negotiated a joint force with the Magyars' eastern neighbours, the
Having dealt with the pressure from the Magyars and the Byzantines, Simeon was free to plan a campaign against the Magyars looking for retribution. He negotiated a joint force with the Magyars' eastern neighbours, the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
, and imprisoned the Byzantine envoy Leo Choirosphaktes in order to delay the release of the captives until after the campaign against the Magyars. This would allow him to renegotiate the peace conditions in his favour. In an exchange of letters with the envoy, Simeon refused to release the captives and ridiculed Leo VI's astrological abilities.
Using a Magyar invasion in the lands of the neighbouring Slavs in 896 as a ''casus belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one ...
'', Simeon headed against the Magyars together with his Pecheneg allies, defeating them completelyRunciman, ''A history of the First Bulgarian Empire'', p. 147. in the Battle of Southern Buh and making them leave Etelköz forever and settle in Pannonia. Following the defeat of the Magyars, Simeon finally released the Byzantine prisoners in exchange for Bulgarians captured in 895.
 Claiming that not all prisoners had been released, Simeon once again invaded Byzantium in the summer of 896, heading directly to Constantinople. He was met in
Claiming that not all prisoners had been released, Simeon once again invaded Byzantium in the summer of 896, heading directly to Constantinople. He was met in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
by a hastily assembled Byzantine army, but annihilated the Byzantine forces in the Battle of Bulgarophygon
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
(at modern Babaeski
Babaeski is a town and district of Kırklareli Province in the Marmara region of Turkey. The countyship has a population of 29,342 and the total area of the district is 652 km2.
Name
The name Babaeski is believed to have originated accordin ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
). Arming Arab captives and sending them to fight with the Bulgarians as a desperate measure, Leo VI managed to repel the Bulgarians from Constantinople, which they had besieged. The war ended with a peace treaty which formally lasted until around Leo VI's death in 912 and under which Byzantium was obliged to pay Bulgaria an annual tribute. Under the treaty, the Byzantines also ceded an area between the Black Sea and Strandža to the Bulgarian Empire. Meanwhile, Simeon had also imposed his authority over Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia ( Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hu ...
in return for recognizing Petar Gojniković as their ruler.
Simeon often violated the peace treaty with Byzantium, attacking and conquering Byzantine territory on several occasions, such as in 904, when the Bulgarian raids were used by Arabs led by the Byzantine renegade Leo of Tripoli
Leo of Tripoli ( el, Λέων ὸ Τριπολίτης), known in Arabic as Rashīq al-Wardāmī (), and Ghulām Zurāfa (), was a Greek renegade and fleet commander for the Abbasid Caliphate in the early tenth century. He is most notable for ...
to undertake a maritime campaign and seize Thessaloniki. After the Arabs plundered the city, it was an easy target for Bulgaria and the nearby Slavic tribes. In order to dissuade Simeon from capturing the city and populating it with Slavs, Leo VI was forced to make further territorial concessions to the Bulgarians in the modern region of Macedonia. With the treaty of 904, all Slavic-inhabited lands in modern southern Macedonia and southern Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
were ceded to the Bulgarian Empire, with the border line running some 20 kilometres north of Thessaloniki.
Recognition as Emperor
The death of Leo VI on 11 May 912 and the accession of his infant sonConstantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe ...
under the guidance of Leo's brother Alexander, who expelled Leo's wife Zoe from the palace, constituted a great opportunity for Simeon to attempt another campaign against Constantinople, the conquest of which remained the dream of his life. In the spring of 913, Simeon's envoys, who had arrived in Constantinople to renew the peace of 896, were sent away by Alexander, who refused to pay the annual tribute, urging Simeon to prepare for war.
Before Simeon could attack, Alexander died on 6 June 913, leaving the empire in the hands of a regency council headed by Patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in c ...
Nicholas Mystikos. Many residents of Constantinople did not recognize the young emperor and instead supported the pretender Constantine Doukas, which, exacerbated by revolts in southern Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and the planned Arab invasion in eastern Anatolia, was all to Simeon's advantage. Nicholas Mystikos tried to discourage Simeon from invading Byzantium in a long series of pleading letters, but the Bulgarian ruler nevertheless attacked in full force in late July or August 913, reaching Constantinople without any serious resistance.''Bǎlgarite i Bǎlgarija'', 1.2.
The anarchy in Constantinople had ceased after the murder of the pretender Constantine Doukas, however, and a government had promptly been formed with Patriarch Nicholas at the helm.Zlatarski, ''Istorija na Pǎrvoto bǎlgarsko carstvo'', p. 359. This urged Simeon to raise his siege and enter peace negotiations, to the joy of the Byzantines. The protracted negotiations resulted in the payment of the arrears of Byzantine tribute,Runciman, ''A history of the First Bulgarian Empire'', p. 157. the promise that Constantine VII would marry one of Simeon's daughters, and, most importantly, Simeon's official recognition as Emperor of the Bulgarians by Patriarch Nicholas in the Blachernae Palace.
Shortly after Simeon visited Constantinople, Constantine's mother Zoe returned to the palace on the insistence of the young emperor and immediately proceeded to eliminate the regents. Through a plot, she managed to assume power in February 914, practically removing Patriarch Nicholas from the government, disowning and obscuring his recognition of Simeon's imperial title, and rejecting the planned marriage of her son to one of Simeon's daughters. Simeon had to resort to war to achieve his goals. He invaded Thrace in the summer of 914 and captured Adrianople. Zoe was quick to send Simeon numerous presents in order to conciliate him, and she managed to convince him to cede back Adrianople and withdraw his army. In the following years, Simeon's forces were engaged in the northwestern Byzantine provinces, around Drač ( Durrës) and Thessaloniki, but did not make a move against Constantinople.
Victories at Acheloos and Katasyrtai
 By 917, Simeon was preparing for yet another war against Byzantium. He attempted to conclude an anti-Byzantine union with the Pechenegs, but his envoys could not match the financial resources of the Byzantines, who succeeded in outbidding them. The Byzantines hatched a large-scale campaign against Bulgaria and also tried to persuade the Serbian Prince Petar Gojniković to attack the Bulgarians with Magyar support.
In 917, a particularly strong Byzantine army led by Leo Phokas the Elder, son of
By 917, Simeon was preparing for yet another war against Byzantium. He attempted to conclude an anti-Byzantine union with the Pechenegs, but his envoys could not match the financial resources of the Byzantines, who succeeded in outbidding them. The Byzantines hatched a large-scale campaign against Bulgaria and also tried to persuade the Serbian Prince Petar Gojniković to attack the Bulgarians with Magyar support.
In 917, a particularly strong Byzantine army led by Leo Phokas the Elder, son of Nikephoros Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
, invaded Bulgaria accompanied by the Byzantine navy under the command of Romanos Lekapenos, which sailed to the Bulgarian Black Sea ports. En route to Mesembria ( Nesebǎr), where they were supposed to be reinforced by troops transported by the navy, Phokas' forces stopped to rest near the river of Acheloos, not far from the port of Anchialos ( Pomorie).Runciman, ''A history of the First Bulgarian Empire'', pp. 160–161. Once informed of the invasion, Simeon rushed to intercept the Byzantines, and attacked them from the nearby hills while they were resting disorganized. In the Battle of Acheloos of 20 August 917, one of the largest in medieval history, the Bulgarians completely routed the Byzantines and killed many of their commanders, although Phokas managed to escape to Mesembria. Decades later, Leo the Deacon would write that "piles of bones can still be seen today at the river Acheloos, where the fleeing army of the Romans was then infamously slain".
The planned Pecheneg attack from the north also failed, as the Pechenegs quarrelled with admiral Lekapenos, who refused to transport them across the Danube to aid the main Byzantine army. The Byzantines were not aided by Serbs and Magyars either: the Magyars were engaged in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
as Frankish allies, and the Serbs under Petar Gojniković were reluctant to attack Bulgaria because Michael of Zahumlje, an ally of Bulgaria, had notified Simeon of their plans.
Simeon's army quickly followed up the victory of Acheloos with another success. The Bulgarians sent to pursue the remnants of the Byzantine army approached Constantinople and encountered Byzantine forces under Leo Phokas, who had returned to the capital, at the village of Katasyrtai in the immediate proximity of Constantinople. The Bulgarian regiments attacked and again defeated the Byzantines, destroying some of their last units before returning to Bulgaria.
Suppression of Serbian unrest and late campaigns against Byzantium
Immediately after that campaign, Simeon sought to punish the Serbian ruler Petar Gojniković who had attempted to betray him by concluding an alliance with the Byzantines. Simeon sent an army led by two of his commanders, Theodore Sigrica andMarmais Marmais ( bg, Мармаис; died 924) was a Bulgarian military commander, nobleman and ''komita'' (duke) of a western Bulgarian region ( Sredets or Macedonia) during the reign of Emperor Simeon I (893–927). He was a descendant of an ancient B ...
, to Serbia. The two managed to persuade Petar to attend a personal meeting, during which he was enchained and carried off to Bulgaria, where he died in a dungeon. Simeon put Pavle Branović, prior to that an exile in Bulgaria, on the Serbian throne, thus restoring the Bulgarian influence in Serbia for a while.
Meanwhile, the Byzantine military failures forced another change of government in Constantinople: the admiral Romanos Lekapenos replaced Zoe as regent of the young Constantine VII in 919, forcing her back into a convent. Romanos betrothed his daughter Helena Lekapene to Constantine and advanced to the rank of co-emperor in December 920, effectively assuming the government of the empire, which was largely what Simeon had planned to do.

 No longer able to climb to the Byzantine throne by diplomatic means, the infuriated Simeon once again had to wage war to impose his will. Between 920 and 922, Bulgaria increased its pressure on Byzantium, campaigning in the west through
No longer able to climb to the Byzantine throne by diplomatic means, the infuriated Simeon once again had to wage war to impose his will. Between 920 and 922, Bulgaria increased its pressure on Byzantium, campaigning in the west through Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
reaching the Isthmus of Corinth and in the east in Thrace, reaching and crossing the Dardanelles to lay siege on the town of Lampsacus. Simeon's forces appeared before Constantinople in 921, when they demanded the deposition of Romanos and captured Adrianople, and 922, when they were victorious at Pigae, burned much of the Golden Horn and seized Bizye.Runciman, ''A history of the First Bulgarian Empire'', pp. 164–165. In the meantime, the Byzantines attempted to ignite Serbia against Simeon, but he substituted Pavle with Zaharije Pribisavljević, a former refugee at Constantinople that he had captured.
Desperate to conquer Constantinople, Simeon planned a large campaign in 924 and sent envoys to the Fatimid caliph Ubayd Allah al-Mahdi Billah
Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh/ʿUbayd Allāh ibn al-Ḥusayn (), 873 – 4 March 934, better known by his regnal name al-Mahdi Billah, was the founder of the Isma'ili Fatimid Caliphate, the only major Shi'a caliphate in Islamic history, and the ...
, who possessed a powerful navy which Simeon needed. The caliph agreed and sent his own representatives back with the Bulgarians to arrange the alliance. However, the envoys were captured by the Byzantines at Calabria. Romanos offered peace to the Arabs, supplementing this offer with generous gifts, and ruined their union with Bulgaria.
In Serbia, Zaharije was persuaded by the Byzantines to revolt against Simeon. Zaharije was supported by many Bulgarians exhausted from Simeon's endless campaigns against Byzantium. The Bulgarian emperor sent his troops under Sigrica and Marmais, but they were routed and the two commanders beheaded, which forced Simeon to conclude an armistice with Byzantium in order to concentrate on the suppression of the uprising. Simeon sent an army led by Časlav Klonimirović in 924 to depose Zaharije. He was successful, as Zaharije fled to Croatia. After this victory, the Serbian nobility was invited to come to Bulgaria and bow to the new Prince. However, he did not appear at the supposed meeting and all of them were beheaded. Bulgaria annexed Serbia directly.
In the summer of 924, Simeon nevertheless arrived at Constantinople and demanded to see the patriarch and the emperor. He conversed with Romanos on the Golden Horn on 9 September 924 and arranged a truce, according to which Byzantium would pay Bulgaria an annual tax, but would be ceded back some cities on the Black Sea coast. During the interview of the two monarchs, two eagles are said to have met in the skies above and then to have parted, one of them flying over Constantinople and the other heading to Thrace, as a sign of the irreconcilability of the two rulers. In his description of this meeting, Theophanes Continuatus mentions that "the two ''emperors''... conversed", which may indicate renewed Byzantine recognition of Simeon's imperial claims.
War with Croatia and death
Most likely after (or possibly at the time of) Patriarch Nicholas' death in 925, Simeon raised the status of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church to a patriarchate. This may be linked to Simeon's diplomatic relations with thePapacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
between 924 and 926, during which he demanded and received Pope John X
Pope John X ( la, Ioannes X; died 28 May 928) was the bishop of Rome and nominal ruler of the Papal States from March 914 to his death. A candidate of the counts of Tusculum, he attempted to unify Italy under the leadership of Berengar of Friul ...
's recognition of his title as "Emperor of the Romans", truly equal to the Byzantine emperor, and possibly the confirmation of a patriarchal dignity for the head of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church.
In 926, Simeon's troops under Alogobotur invaded Croatia, at the time a Byzantine ally, but were completely defeated by the army of King Tomislav in the Battle of the Bosnian Highlands
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
. Fearing a Bulgarian retribution, Tomislav agreed to abandon his union with Byzantium and make peace on the basis of the '' status quo'', negotiated by the papal legate Madalbert. In the last months of his life, Simeon prepared for another conflict with Constantinople despite Romanos' desperate pleas for peace.
On 27 May 927, Simeon died of heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
in his palace in Preslav. Byzantine chroniclers tie his death to a legend, according to which Romanos decapitated a statue which was Simeon's inanimate double, and he died at that very hour.
He was succeeded by his son Peter I Peter I may refer to:
Religious hierarchs
* Saint Peter (c. 1 AD – c. 64–88 AD), a.k.a. Simon Peter, Simeon, or Simon, apostle of Jesus
* Pope Peter I of Alexandria (died 311), revered as a saint
* Peter I of Armenia (died 1058), Catholicos ...
, with George Sursubul, the new emperor's maternal uncle, initially acting as a regent.Runciman, ''A history of the First Bulgarian Empire'', p. 177. As part of the peace treaty signed in October 927 and reinforced by Peter's marriage to Maria (Eirene), Romanos' granddaughter, the existing borders were confirmed, as were the Bulgarian ruler's imperial dignity and the head of the Bulgarian Church's patriarchal status.
H.H.Howorth opined "If he had lived, or if he had been succeeded by princes of the same martial character, it is very probable that a great Slav state reaching from the Adriatic to the Black Sea, which would have been a barrier to the Turks, might have been formed south of the Danube."
Culture and religion
 During Simeon's reign, Bulgaria reached its cultural apogee, becoming the literary and spiritual centre of Slavic Europe.Delev, ''Zlatnijat vek na bǎlgarskata kultura''. In this respect, Simeon continued his father Boris' policy of establishing and spreading Slavic culture and attracting noted scholars and writers within Bulgaria's borders. It was in the Preslav Literary School and Ohrid Literary School, founded under Boris, that the main literary work in Bulgaria was concentrated during the reign of Simeon
Ivanova,
During Simeon's reign, Bulgaria reached its cultural apogee, becoming the literary and spiritual centre of Slavic Europe.Delev, ''Zlatnijat vek na bǎlgarskata kultura''. In this respect, Simeon continued his father Boris' policy of establishing and spreading Slavic culture and attracting noted scholars and writers within Bulgaria's borders. It was in the Preslav Literary School and Ohrid Literary School, founded under Boris, that the main literary work in Bulgaria was concentrated during the reign of Simeon
Ivanova,Introduction
, ''Tǎržestvo na slovoto''. in the new Cyrillic alphabet which was developed there. The late 9th and early 10th centuries constitute the earliest and most productive period of medieval
Bulgarian literature
Bulgarian literature is literature written by Bulgarians or residents of Bulgaria, or written in the Bulgarian language; usually the latter is the defining feature. Bulgarian literature can be said to be one of the oldest among the Slavic peopl ...
. Having spent his early years in Constantinople, Simeon introduced Byzantine culture to the Bulgarian court, but eliminated its assimilative effect by means of military power and religious autonomy. The disciples of Cyril and Methodius
Cyril (born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (815–885) were two brothers and Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs".
They are credited w ...
, among whom were Clement of Ohrid, Naum and Constantine of Preslav
Constantine of Preslav () was a medieval Bulgarian scholar, writer and translator, one of the most important men of letters working at the Preslav Literary School at the end of the 9th and the beginning of the 10th century. Biographical eviden ...
, continued their educational work in Bulgaria, actively translating Christian texts, such as the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
and the works of John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; gr, Ἰωάννης ὁ Χρυσόστομος; 14 September 407) was an important Early Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of ...
, Basil of Caesarea, Cyril of Alexandria, Gregory of Nazianzus
Gregory of Nazianzus ( el, Γρηγόριος ὁ Ναζιανζηνός, ''Grēgorios ho Nazianzēnos''; ''Liturgy of the Hours'' Volume I, Proper of Saints, 2 January. – 25 January 390,), also known as Gregory the Theologian or Gregory N ...
, and Athanasius of Alexandria
Athanasius I of Alexandria, ; cop, ⲡⲓⲁⲅⲓⲟⲥ ⲁⲑⲁⲛⲁⲥⲓⲟⲩ ⲡⲓⲁⲡⲟⲥⲧⲟⲗⲓⲕⲟⲥ or Ⲡⲁⲡⲁ ⲁⲑⲁⲛⲁⲥⲓⲟⲩ ⲁ̅; (c. 296–298 – 2 May 373), also called Athanasius the Great, ...
, as well as historic chronicles such as those of John Malalas and George Hamartolus
George Hamartolos or Hamartolus ( el, ) was a monk at Constantinople under Michael III (842–867) and the author of a chronicle of some importance. Hamartolus is not his name but the epithet he gives to himself in the title of his work: "A compe ...
, to Bulgarian. The reign of Simeon also witnessed the production of a number of original theological and secular works, such as John Exarch's ''Six Days'' (''Šestodnev''), Constantine of Preslav's ''Alphabetical Prayer'' and ''Proclamation of the Holy Gospels'', and Černorizec Hrabǎr's ''An Account of Letters''. Simeon's own contribution to this literary blossoming was praised by his contemporaries, for example in the ''Praise to Tsar Simeon'' preserved in the ''Zlatostruj'' collection and ''Simeon's Collection'', to which the tsar personally wrote an addendum.
Simeon turned the new Bulgarian capital Preslav into a magnificent religious and cultural centre, intended more as a display of his realm's heyday and as a royal residence than as a military fortress. With its more than twenty cross-domed churches and numerous monasteries, its impressive royal palace and the Golden (or Round) Church, Preslav was a true imperial capital. The development of Bulgarian art in the period is demonstrated by a ceramic icon of Theodore Stratelates and the Preslav-style illustrated ceramics.
Family
Simeon was married twice. By his first wife, whose identity is unknown, Simeon had a son calledMichael
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name "Michael"
* Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and ...
. Possibly because his mother was of inferior birth, he was excluded from the succession and sent to a monastery.
By his second wife, the sister of the influential noble George Sursubul, he had three sons: Peter, who succeeded as Emperor of Bulgaria in 927 and ruled until 969; Ivan, who unsuccessfully conspired against Peter in 929 and then fled to Byzantium; and Benjamin (Bajan), who, according to Lombard historian Liutprand of Cremona, "possessed the power to transform himself suddenly into a wolf or other strange animal".
Simeon also had several daughters, including one who was arranged to marry Constantine VII in 913. The marriage was annulled by Constantine's mother Zoe once she had returned to the court.
Legacy and popular culture
 Tsar Simeon I has remained among the most highly valued Bulgarian historical figures, as indicated by popular vote in the '' Velikite Bǎlgari'' (a spin-off of ''
Tsar Simeon I has remained among the most highly valued Bulgarian historical figures, as indicated by popular vote in the '' Velikite Bǎlgari'' (a spin-off of ''100 Greatest Britons
''100 Greatest Britons'' is a television series that was broadcast by the BBC in 2002. It was based on a television poll conducted to determine who the British people at that time considered the greatest Britons in history. The series included in ...
'') television programme, which in February 2007 placed him fourth among the greatest Bulgarians ever. Simeon the Great
This is a list of people known as the Great, or the equivalent, in their own language. Other languages have their own suffixes, such as Persian ''e Bozorg'' and Urdu ''e Azam''.
In Persia, the title "the Great" at first seems to have been a co ...
has been regularly featured in fiction. Bulgarian national writer Ivan Vazov dedicated a children's patriotic poem to him, "Tsar Simeon", and it was later arranged as a song, "Kray Bosfora šum se vdiga" ("A Clamour Rises by the Bosphorus"). An eleven-episode drama series filmed in 1984, ''Zlatniyat vek
''Zlatniyat vek'' is a Bulgarian historical and drama TV series produced in 1984.
History
The movie was dedicated to 1300 anniversary of foundation of Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of ...
'' (''The Golden Age''), retells the story of Simeon's reign. In the series, the tsar is played by Marius Donkin. A historical drama play called ''Tsar Simeon Veliki – Zlatniyat vek'' produced by Stefan Staychev, director of the Silistra
Silistra ( bg, Силистра ; tr, Silistre; ro, Silistra) is a town in Northeastern Bulgaria. The town lies on the southern bank of the lower Danube river, and is also the part of the Romanian border where it stops following the Danube. Si ...
Theatre, premiered in December 2006. Ivan Samokovliev stars in the part of Simeon.
The painting, "The Bulgarian Tsar Simeon" is part of the 20-canvas work by Alfons Mucha
Alfons Maria Mucha (; 24 July 1860 – 14 July 1939), known internationally as Alphonse Mucha, was a Czech painter, illustrator and graphic artist, living in Paris during the Art Nouveau period, best known for his distinctly stylized and decorat ...
, ''The Slav Epic
''The Slav Epic'' ( cs, Slovanská epopej) is a cycle of 20 large canvases painted by Czechs, Czech Art Nouveau painter Alphonse Mucha between 1910 and 1928. The cycle depicts the mythology and history of Czechs and other Slavic peoples. In 19 ...
''.
The last Bulgarian monarch, Simeon Saxe-Coburg-Gotha, was named after Simeon I. A brand of high-quality grape rakija, ''Car Simeon Veliki'', also bears his name, and an Antarctic peak on Livingston Island
Livingston Island (Russian name ''Smolensk'', ) is an Antarctic island in the Southern Ocean, part of the South Shetlands Archipelago, a group of Antarctic islands north of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was the first land discovered south of 60 ...
of the South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1 ...
was named Simeon Peak
Simeon Peak ( bg, връх Симеон, vrah Simeon, ) rises to 1,580 mD. Boyanov and N. PetkovThe Peaks of Tangra Mountains: Project Report Part Two 2016/17.Sofia, February 2017 (in Bulgarian) in Friesland Ridge, Tangra Mountains, Livingsto ...
in his honour by the Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria.
The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in ...
.
Timeline
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * Todorov, Boris. "The value of empire: tenth-century Bulgaria between Magyars, Pechenegs and Byzantium," Journal of Medieval History (2010) 36#4 pp 312–326Nikolov, Angel. "The Perception of the Bulgarian Past in the Court of Preslav around 900 AD.," in ''State and Church: Studies in Medieval Bulgaria and Byzantium''. Ed. by V. Gjuzelev and K. Petkov. American Research Center in Sofia: Sofia, 2011, 157–171
Nikolov, Angel. "Making a new basileus: the case of Symeon of Bulgaria (893–927) reconsidered," in ''Rome, Constantinople and Newly converted Europe. Archeological and Historical Evidence''. Vol. I. Ed. by M. Salamon, M. Wołoszyn, A. Musin, P. Špehar. Kraków-Leipzig-Rzeszów-Warszawa, 2012, 101–108
In Bulgarian
* * * * * * * * *External links
*an article by Georgi Todorov * ,
lyrics
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Simeon 01 Of Bulgaria 860s births 927 deaths 9th-century Bulgarian monarchs 10th-century Bulgarian emperors Bulgarian people of the Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars Eastern Orthodox monarchs