Shovel-shaped incisors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Shovel-shaped incisors (or, more simply, shovel incisors) are
Shovel-shaped incisors (or, more simply, shovel incisors) are
 It is hypothesized that other
It is hypothesized that other
 The first description of shovel-shaped incisors was in 1870. During the 20th century, it was accepted that incisor shoveling yielded a direct advantage to the possessor. The proposed explanation for this at the time was that shovel-shaped incisors were stronger than non-shovel shaped incisors, resulting in the evolution of shovel-shaped incisors in regions where having stronger teeth would provide an evolutionary advantage. The greater size and mass of shoveled incisors was said to have provided increased strength and durability as a means to prevent breakage. However, current research shows that part of the
The first description of shovel-shaped incisors was in 1870. During the 20th century, it was accepted that incisor shoveling yielded a direct advantage to the possessor. The proposed explanation for this at the time was that shovel-shaped incisors were stronger than non-shovel shaped incisors, resulting in the evolution of shovel-shaped incisors in regions where having stronger teeth would provide an evolutionary advantage. The greater size and mass of shoveled incisors was said to have provided increased strength and durability as a means to prevent breakage. However, current research shows that part of the
 Shovel-shaped incisors (or, more simply, shovel incisors) are
Shovel-shaped incisors (or, more simply, shovel incisors) are incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...
s whose lingual surfaces are scooped as a consequence of lingual marginal ridges, crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, parti ...
curvature, or basal tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal.
In plants
A tubercle is generally a wart-like projectio ...
s, either alone or in combination.
Shovel-shaped incisors are significantly common in Amerindians
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of ...
from North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
, Central, and South America. They are also common in East Asians
East Asian people (also East Asians) are the people from East Asia, which consists of China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. The total population of all countries within this region is estimated to be 1.677 billion and 21% ...
and Central Asians, Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
, and Aleut
Aleuts ( ; (west) or (east) ) are the Indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleuts and the islands are politically divided between the US state of Alaska ...
peoples of Northeast Asia
Northeast Asia or Northeastern Asia is a geographical Subregion#Asia, subregion of Asia. Its northeastern landmass and islands are bounded by the Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean.
The term Northeast Asia was popularized during the 1930s by Ame ...
and North America (including but not limited to Inuit in eastern Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, Arctic Canada
Northern Canada (), colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada, variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories a ...
, and Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
). In certain European and African groups, shovel-shaped upper incisors are uncommon or not present. There is a spectrum of the degree of shoveled-ness, ranging on a scale from 0 to 7 of spatulate incisors to shoveled incisors. It was theorized that positive selection for shovel-shaped incisors over the spatulate incisors is more commonly found within cultures that used their teeth as tools due to a greater structural strength in increased shovel-shaped incisors.
In some instances, incisors can present a more pronounced version of this called double shovel-shaped. When present, shovel-shaped incisors can indicate correlation among populations and are considered to be one of the non-metrical traits in osteology
Osteology () is the scientific study of bones, practiced by osteologists . A subdiscipline of anatomy, anthropology, archaeology and paleontology, osteology is the detailed study of the structure of bones, skeletal elements, teeth, microbone mo ...
. Structurally resembling the shovel-shaped incisors, double shovel-shaped incisors are distinguished by a more pronounced mesial
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body.
Terms
...
ridge compared to the distal ridge. Similarly, the grades for both shovel-shaped incisors and the double shovel-shaped incisors in females are significantly greater than that in males.
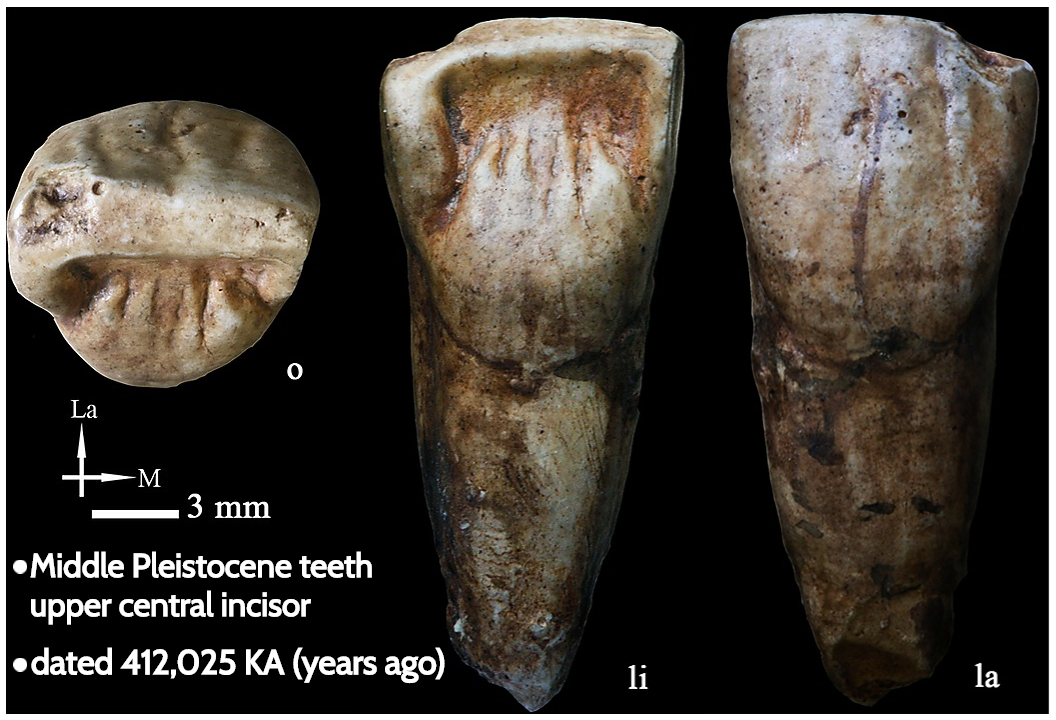
Shovel-shaped dental characteristics are also observed in ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' ( ) is an extinction, extinct species of Homo, archaic human from the Pleistocene, spanning nearly 2 million years. It is the first human species to evolve a humanlike body plan and human gait, gait, to early expansions of h ...
'' like the Peking Man
Peking Man (''Homo erectus pekinensis'', originally "''Sinanthropus pekinensis''") is a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' which inhabited what is now northern China during the Middle Pleistocene. Its fossils have been found in a cave some southw ...
and in Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
s, although the morphology of these shoveled incisors is distinct from the modern human form of shoveling. The morphology of Neanderthal's anterior teeth has been seen as an adaptation to the heavy use of their canines and incisors in processing and chewing food, and the use of their teeth for activities other than feeding.
Genetics
Variation in modern human incisor shoveling has been associated with the presence/absence of the V370Aallele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule.
Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), ...
of the ''Ectodysplasin A Receptor'' (''EDAR'') gene. The EDAR V370A isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have uniqu ...
arises from a single nucleotide polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in ...
/missense mutation which changes the 370 Valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deproton ...
residue to an Alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group sid ...
on the EDAR gene. The effect is approximately additive, where individuals with one copy of the allele have intermediate expression of shovel-shaped incisors and homozygotes
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
have more strongly shoveled incisors. The trait is pleiotropically related to thicker and straighter hair shafts, other dental traits, sweat glands, and mammary gland ductal branching. An earlier quantitative genetic analysis of a Finnish population also revealed that inheritance of incisor shoveling is monogenic. The 1540C allele of EDAR is also strongly correlated with the presence of shovel-shaped incisors and hair thickness, as found in a study conducted on the DNA from Japanese populations. People with Amerindian
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of ...
or Asian ancestry have thicker and straighter hair.
 It is hypothesized that other
It is hypothesized that other pleiotropic
Pleiotropy () is a condition in which a single gene or genetic variant influences multiple phenotypic traits. A gene that has such multiple effects is referred to as a ''pleiotropic gene''. Mutations in pleiotropic genes can impact several trait ...
effects associated with the V370A allele were favored by natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
to help promote the presence of the allele and thus the emergence of shovel-shaped incisors. One of these associated traits is increased ductal branching in the mammary gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, human ...
, which improves nutrient transport in breastmilk. This may likely have conferred a survival advantage to those with the allele during the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
in certain environments with high altitudes and low Vitamin D.
History
 The first description of shovel-shaped incisors was in 1870. During the 20th century, it was accepted that incisor shoveling yielded a direct advantage to the possessor. The proposed explanation for this at the time was that shovel-shaped incisors were stronger than non-shovel shaped incisors, resulting in the evolution of shovel-shaped incisors in regions where having stronger teeth would provide an evolutionary advantage. The greater size and mass of shoveled incisors was said to have provided increased strength and durability as a means to prevent breakage. However, current research shows that part of the
The first description of shovel-shaped incisors was in 1870. During the 20th century, it was accepted that incisor shoveling yielded a direct advantage to the possessor. The proposed explanation for this at the time was that shovel-shaped incisors were stronger than non-shovel shaped incisors, resulting in the evolution of shovel-shaped incisors in regions where having stronger teeth would provide an evolutionary advantage. The greater size and mass of shoveled incisors was said to have provided increased strength and durability as a means to prevent breakage. However, current research shows that part of the genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
, the EDAR gene, which was selected for because of its role in nutrient transfer in breast milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by the mammary glands in the breasts of women. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborn infants, comprising fats, proteins, carbohydrates, and a var ...
during the era of the Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 70th parallel north, 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south ...
n refugium, also determines the degree to which teeth shovel. In an interview, Dr. Hlusko suggests that human populations who had the trait migrated from Asia to the Americas, thus leaving their genetic trace around the world. With greater implications outside shoveling itself, the human variation in shoveling also supports the idea that populations are dynamic.
Applications
In the mid 20th century, shovel-shaped incisors were considered to be a trait useful for racial categorization, since the occurrence of shovel-shape incisors varies between many populations. A 1964 text said that manyanthropologist
An anthropologist is a scientist engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropologists study aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms, values ...
s at the time used the trait of shovel-shaped incisors as a diagnostic for race.
The presence of shovel-shaped incisors, among many dental characteristics, is used in forensic dentistry
Forensic dentistry or forensic odontology involves the handling, Inspection, examination, and evaluation of dentistry, dental evidence in a criminal justice system, criminal justice context. Forensic dentistry is used in both criminal and civil ...
to identify an individual's ancestry
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder, or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from ...
, since this trait occurs predominantly in Asian and Native American populations.
See also
* Sinodonty and Sundadonty *Mongoloid
Mongoloid () is an obsolete racial grouping of various peoples indigenous to large parts of Asia, the Americas, and some regions in Europe and Oceania. The term is derived from a now-disproven theory of biological race. In the past, other terms ...
References
{{oral pathology Types of teeth