Shock (circulatory) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Shock is the state of insufficient
 Signs typically occur after exposure to an allergen and may include:
** Skin changes, such as hives, itching, flushing, and swelling.
** Wheezing and
Signs typically occur after exposure to an allergen and may include:
** Skin changes, such as hives, itching, flushing, and swelling.
** Wheezing and
 Vasopressors may be used if blood pressure does not improve with fluids. Common vasopressors used in shock include:
Vasopressors may be used if blood pressure does not improve with fluids. Common vasopressors used in shock include:
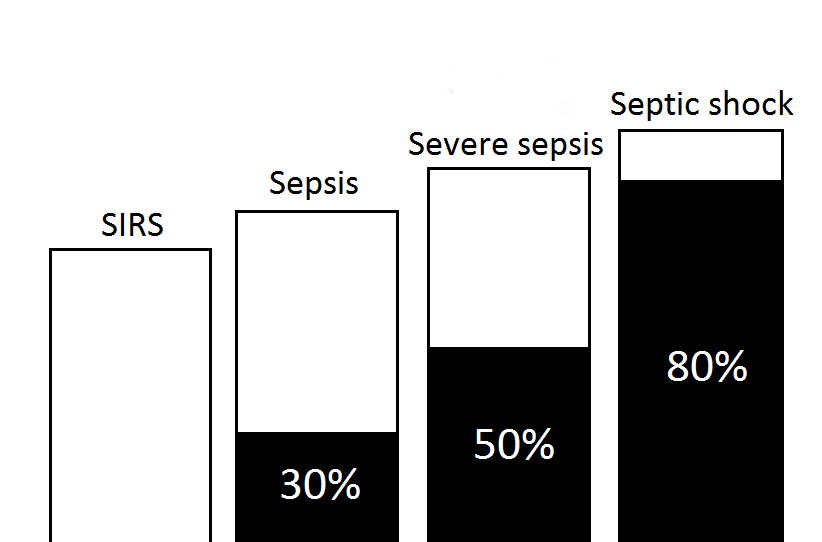 The prognosis of shock depends on the underlying cause and the nature and extent of concurrent problems. Low volume, anaphylactic, and neurogenic shock are readily treatable and respond well to medical therapy. Septic shock, especially septic shock where treatment is delayed or the antimicrobial drugs are ineffective, however has a mortality rate between 30% and 80%; cardiogenic shock has a mortality rate of up to 70% to 90%, though quick treatment with vasopressors and inotropic drugs, cardiac surgery, and the use of assistive devices can lower the mortality.
The prognosis of shock depends on the underlying cause and the nature and extent of concurrent problems. Low volume, anaphylactic, and neurogenic shock are readily treatable and respond well to medical therapy. Septic shock, especially septic shock where treatment is delayed or the antimicrobial drugs are ineffective, however has a mortality rate between 30% and 80%; cardiogenic shock has a mortality rate of up to 70% to 90%, though quick treatment with vasopressors and inotropic drugs, cardiac surgery, and the use of assistive devices can lower the mortality.
/ref> Other competing theories around the turn of the century included one penned by Malcom in 1907, in which the assertion was that prolonged vasoconstriction led to the pathophysiological signs and symptoms of shock. In the following World War I, research concerning shock resulted in experiments by Walter B. Cannon of Harvard and William M. Bayliss of London in 1919 that showed that an increase in permeability of the capillaries in response to trauma or toxins was responsible for many clinical manifestations of shock. In 1972 Hinshaw and Cox suggested the classification system for shock which is still used today.
blood flow
Hemodynamics American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or haemodynamics are the Fluid dynamics, dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostasis, homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydrau ...
to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart ...
. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, tachycardia, hyperventilation
Hyperventilation is irregular breathing that occurs when the rate or tidal volume of breathing eliminates more carbon dioxide than the body can produce. This leads to hypocapnia, a reduced concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blo ...
, sweating, anxiety, and increased thirst. This may be followed by confusion, unconsciousness
Unconsciousness is a state in which a living individual exhibits a complete, or near-complete, inability to maintain an awareness of self and environment or to respond to any human or environmental stimulus. Unconsciousness may occur as the r ...
, or cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest CA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the ...
, as complications worsen.
Shock is divided into four main types based on the underlying cause: hypovolemic, cardiogenic, obstructive, and distributive shock. Hypovolemic shock, also known as low volume shock, may be from bleeding, diarrhea, or vomiting. Cardiogenic shock may be due to a heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
or cardiac contusion. Obstructive shock may be due to cardiac tamponade or a tension pneumothorax. Distributive shock may be due to sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
, anaphylaxis, injury to the upper spinal cord, or certain overdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended. Retrieved on September 20, 2014.
s.
The diagnosis is generally based on a combination of symptoms, physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
, and laboratory tests. A decreased pulse pressure ( systolic blood pressure minus diastolic blood pressure) or a fast heart rate raises concerns.
Shock is a medical emergency and requires urgent medical care. If shock is suspected, emergency help should be called immediately. While waiting for medical care, the individual should be, if safe, laid down (except in cases of suspected head or back injuries). The legs should be raised if possible, and the person should be kept warm. If the person is unresponsive, breathing should be monitored and CPR may need to be performed.
Signs and symptoms
The presentation of shock is variable, with some people having only minimal symptoms such as confusion and weakness. While the general signs for all types of shock are low blood pressure, decreased urine output, and confusion, these may not always be present. While a fast heart rate is common, in those on β-blockers, those who are athletic, and in 30% of cases of those with shock due to intra abdominal bleeding, heart rate may be normal or slow. Specific subtypes of shock may have additional symptoms. Dry mucous membrane, reduced skin turgor, prolonged capillary refill time, weak peripheral pulses, and cold extremities can be early signs of shock.Low volume
Hypovolemic shock is the most common type of shock and is caused by insufficient circulatingvolume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch) ...
. The most common cause of hypovolemic shock is hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
(internal or external); however, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
and diarrhea are more common causes in children. Other causes include burns, as well as excess urine loss due to diabetic ketoacidosis and diabetes insipidus.
Signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock include:
* A rapid, weak, thready pulse due to decreased blood flow combined with tachycardia
* Cool skin due to vasoconstriction and stimulation of vasoconstriction
* Rapid and shallow breathing due to sympathetic nervous system stimulation and acidosis
* Hypothermia due to decreased perfusion and evaporation of sweat
* Thirst and dry mouth, due to fluid depletion
* Cold and mottled skin ( livedo reticularis), especially extremities, due to insufficient perfusion of the skin
The severity of hemorrhagic shock can be graded on a 1–4 scale on the physical signs. The shock index (heart rate divided by systolic blood pressure) is a stronger predictor of the impact of blood loss than heart rate and blood pressure alone. This relationship has not been well established in pregnancy-related bleeding.
Cardiogenic
Cardiogenic shock is caused by the failure of the heart to pump effectively. This can be due to damage to the heart muscle, most often from a largemyocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
. Other causes of cardiogenic shock include dysrhythmias, cardiomyopathy/ myocarditis, congestive heart failure (CHF), myocardial contusion, or valvular heart disease problems.
Symptoms of cardiogenic shock include:
* Distended jugular veins due to increased jugular venous pressure
* Weak or absent pulse
* Abnormal heart rhythms, often a fast heart rate
* Pulsus paradoxus in case of tamponade
* Reduced blood pressure
* Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
, due to pulmonary congestion
Obstructive
Obstructive shock is a form of shock associated with physical obstruction of the great vessels of the systemic or pulmonary circulation. Several conditions can result in this form of shock. * Cardiac tamponade, in which fluid in the pericardium prevents inflow of blood into the heart ( venous return). * Constrictive pericarditis, in which the pericardium shrinks and hardens, is similar in presentation. * Tension pneumothorax; Through increased intrathoracic pressure, venous return is impeded. * Pulmonary embolism is thromboembolism of thelung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s, hindering oxygenation and return of blood to the heart.
* Aortic stenosis hinders circulation by obstructing the cardiac output.
* Hypertrophic sub-aortic stenosis is overly thick ventricular muscle that dynamically occludes the ventricular outflow tract.
* Abdominal compartment syndrome defined as an increase in intra-abdominal pressure to > 20 mmHg with organ dysfunction. Increased intra-abdominal pressure can result from sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
and severe abdominal trauma. This increased pressure reduces venous return, thereby reducing lung-heart function, resulting in signs and symptoms of shock.
Many of the signs of obstructive shock are similar to cardiogenic shock, although treatments differ. Symptoms of obstructive shock include:
* Abnormal heart rhythms, often a fast heart rate.
* Reduced blood pressure.
* Cool, clammy, mottled skin, often due to low blood pressure and vasoconstriction.
* Decreased urine output.
Distributive
Distributive shock is low blood pressure due to a dilation of blood vessels within the body. This can be caused by systemic infection ( septic shock), a severe allergic reaction ( anaphylaxis), or spinal cord injury ( neurogenic shock). * Septic shock is the most common cause of distributive shock. It is caused by an overwhelming systemic infection resulting in vasodilation leading to hypotension. Septic shock can be caused by Gram negative bacteria such as (among others) ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'', Proteus species, '' Klebsiella pneumoniae'' (which have an endotoxin on their surface that produces adverse biochemical, immunological and occasionally neurological effects which are harmful to the body), other Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
The Gram stain is ...
cocci, such as pneumococci and streptococci, and certain fungi as well as Gram-positive bacterial toxins. Septic shock also includes some elements of cardiogenic shock. In 1992, the ACCP/ SCCM Consensus Conference Committee defined septic shock: " ... sepsis-induced hypotension (systolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg or a reduction of 40 mmHg from baseline) despite adequate fluid resuscitation along with the presence of perfusion abnormalities that may include, but are not limited to: lactic acidosis, oliguria, or an acute alteration in mental status. Patients who are receiving inotropic or vasopressor agents may have a normalized blood pressure at the time that perfusion abnormalities are identified. The pathophysiology behind septic shock is as follows: 1) Systemic leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells 2) Reduced contractility of the heart 3) Activation of the coagulation pathways, resulting in disseminated intravascular coagulation 4). Increased levels of neutrophils
** The main manifestations of septic shock are due to the massive release of histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
which causes intense dilation of the blood vessels. People with septic shock will also likely be positive for SIRS criteria. The most generally accepted treatment for these patients is early recognition of symptoms, and early administration of broad spectrum and organism specific antibiotics.
** Signs of septic shock include:
*** Abnormal heart rhythms, often a fast heart rate
*** Reduced blood pressure
*** Decreased urine output
*** Altered mental status
* Anaphylactic shock is caused by a severe anaphylactic reaction to an allergen, antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
, drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
, or foreign protein causing the release of histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
which causes widespread vasodilation, leading to hypotension and increased capillary permeability. shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
.
** Abdominal pain, diarrhea, and vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
.
** Lightheadedness, confusion, headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
s, loss of consciousness.
* High spinal injuries may cause neurogenic shock, which is commonly classified as a subset of distributive shock. The classic symptoms include a slow heart rate due to loss of cardiac sympathetic tone and warm skin due to dilation of the peripheral blood vessels. (This term can be confused with spinal shock which is a recoverable loss of function of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
after injury and does not refer to the hemodynamic instability.)
Endocrine
Although not officially classified as a subcategory of shock, many endocrinological disturbances in their severe form can result in shock. * Hypothyroidism (can be considered a form of cardiogenic shock) in people who are critically ill patients reduces cardiac output and can lead tohypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is ...
and respiratory insufficiency.
* Thyrotoxicosis ( cardiogenic shock) may induce a reversible cardiomyopathy.
* Acute adrenal insufficiency ( distributive shock) is frequently the result of discontinuing corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
treatment without tapering the dosage. However, surgery and intercurrent disease in patients on corticosteroid therapy without adjusting the dosage to accommodate for increased requirements may also result in this condition.
* Relative adrenal insufficiency ( distributive shock) in critically ill patients where present hormone levels are insufficient to meet the higher demands.
Cause
Shock is a common end point of many medical conditions. Shock triggered by a seriousallergic reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
is known as anaphylactic shock, shock triggered by severe dehydration or blood loss is known as hypovolemic shock, shock caused by sepsis is known as septic shock, etc. Shock itself is a life-threatening condition as a result of compromised body circulation. It can be divided into four main types based on the underlying cause: hypovolemic, distributive, cardiogenic, and obstructive. A few additional classifications are occasionally used, such as endocrinologic shock.
Pathophysiology
Shock is a complex and continuous condition, and there is no sudden transition from one stage to the next. At a cellular level, shock is the process of oxygen demand becoming greater than oxygen supply. One of the key dangers of shock is that it progresses by a positive feedback loop. Poor blood supply leads to cellular damage, which results in an inflammatory response to increase blood flow to the affected area. Normally, this causes the blood supply level to match with tissue demand for nutrients. However, if there is enough increased demand in some areas, it can deprive other areas of sufficient supply, which then start demanding more. This then leads to an ever escalating cascade. As such, shock is a runaway condition of homeostatic failure, where the usual corrective mechanisms relating to oxygenation of the body no longer function in a stable way. When it occurs, immediate treatment is critical in order to return an individual's metabolism into a stable, self-correcting trajectory. Otherwise the condition can become increasingly difficult to correct, surprisingly quickly, and then progress to a fatal outcome. In the particular case of anaphylactic shock, progression to death might take just a few minutes.Initial
During the Initial stage (Stage 1), the state of hypoperfusion causes hypoxia. Due to the lack of oxygen, the cells perform lactic acid fermentation. Since oxygen, the terminal electron acceptor in theelectron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
, is not abundant, this slows down entry of pyruvate into the Krebs cycle, resulting in its accumulation. The accumulating pyruvate is converted to lactate (lactic acid) by lactate dehydrogenase. The accumulating lactate causes lactic acidosis.
Compensatory
The Compensatory stage (Stage 2) is characterised by the body employing physiological mechanisms, including neural, hormonal, and bio-chemical mechanisms, in an attempt to reverse the condition. As a result of the acidosis, the person will begin to hyperventilate in order to rid the body of carbon dioxide (CO2) since it indirectly acts to acidify the blood; the body attempts to return to acid–base homeostasis by removing that acidifying agent. The baroreceptors in the arteries detect thehypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is ...
resulting from large amounts of blood being redirected to distant tissues, and cause the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
. Norepinephrine causes predominately vasoconstriction with a mild increase in heart rate, whereas epinephrine predominately causes an increase in heart rate with a small effect on the vascular Vascular can refer to:
* blood vessels, the vascular system in animals
* vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex transporting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue ...
tone; the combined effect results in an increase in blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
. The renin–angiotensin axis is activated, and arginine vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone) is released to conserve fluid by reducing its excretion via the renal system. These hormones cause the vasoconstriction of the kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s, gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
, and other organs to divert blood to the heart, lungs and brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
. The lack of blood to the renal system causes the characteristic low urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
production. However, the effects of the renin–angiotensin axis take time and are of little importance to the immediate homeostatic mediation of shock.
Progressive/decompensated
The Progressive stage (stage 3) results if the underlying cause of the shock is not successfully treated. During this stage, compensatory mechanisms begin to fail. Due to the decreased perfusion of the cells in the body,sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
ions build up within the intracellular space while potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
ions leak out. Due to lack of oxygen, cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cell ...
diminishes and anaerobic metabolism predominates. As anaerobic metabolism continues, the arteriolar smooth muscle and precapillary sphincters relax such that blood remains in the capillaries. Due to this, the hydrostatic pressure will increase and, combined with histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
release, will lead to leakage of fluid and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
into the surrounding tissues. As this fluid is lost, the blood concentration and viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
increase, causing sludging of the micro-circulation. The prolonged vasoconstriction will also cause the vital organs to be compromised due to reduced perfusion. If the bowel becomes sufficiently ischemic, bacteria may enter the blood stream, resulting in the increased complication of endotoxic shock.
Refractory
At Refractory stage (stage 4), the vital organs have failed and the shock can no longer be reversed. Brain damage and cell death are occurring, and death will occur imminently. One of the primary reasons that shock is irreversible at this point is that much of the cellular ATP (the basic energy source for cells) has been degraded into adenosine in the absence of oxygen as an electron receptor in the mitochondrial matrix. Adenosine easily perfuses out of cellular membranes into extracellular fluid, furthering capillary vasodilation, and then is transformed intouric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the Chemical formula, formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the meta ...
. Because cells can only produce adenosine at a rate of about 2% of the cell's total need per hour, even restoring oxygen is futile at this point because there is no adenosine to phosphorylate into ATP.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of shock is commonly based on a combination of symptoms,physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
, and laboratory tests. Many signs and symptoms are not sensitive or specific for shock, thus many clinical decision-making tools have been developed to identify shock at an early stage.
Shock is, hemodynamically speaking, inadequate blood flow or cardiac output, Unfortunately, the measurement of cardiac output requires an invasive catheter, such as a pulmonary artery catheter. Mixed venous oxygen saturation (SmvO2) is one of the methods of calculating cardiac output with a pulmonary artery catheter. Central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) as measured via a central line correlates well with SmvO2 and is easier to acquire.
Tissue oxygenation
is critically dependent on blood flow. When the oxygenation of tissues is compromised anaerobic metabolism will begin and lactic acid will be produced.
Management
Treatment of shock is based on the likely underlying cause. An open airway and sufficient breathing should be established. Any ongoing bleeding should be stopped, which may require surgery or embolization. Intravenous fluid, such as Ringer's lactate or packed red blood cells, is often given. Efforts to maintain a normal body temperature are also important. Vasopressors may be useful in certain cases. Shock is both common and has a high risk of death. In the United States about 1.2 million people present to the emergency room each year with shock and their risk of death is between 20 and 50%. The best evidence exists for the treatment of septic shock in adults. However, the pathophysiology of shock in children appears to be similar so treatment methodologies have been extrapolated to children. Management may include securing the airway via intubation if necessary to decrease the work of breathing and for guarding against respiratory arrest. Oxygen supplementation,intravenous fluids
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
, passive leg raising (not Trendelenburg position) should be started and blood transfusions added if blood loss is severe. In select cases, compression devices like non-pneumatic anti-shock garments (or the deprecated military anti-shock trousers) can be used to prevent further blood loss and concentrate fluid in the body's head and core. It is important to keep the person warm to avoid hypothermia as well as adequately manage pain and anxiety as these can increase oxygen consumption. Negative impact by shock is reversible if it's recognized and treated early in time.
Fluids
Aggressive intravenous fluids are recommended in most types of shock (e.g. 1–2 liter normal saline bolus over 10 minutes or 20 mL/kg in a child) which is usually instituted as the person is being further evaluated. Colloids and crystalloids appear to be equally effective with respect to outcomes., Balanced crystalloids and normal saline also appear to be equally effective in critically ill patients. If the person remains in shock after initial resuscitation, packed red blood cells should be administered to keep thehemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
greater than 100 g/L.
For those with hemorrhagic shock, the current evidence supports limiting the use of fluids for penetrating thorax and abdominal injuries allowing mild hypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is ...
to persist (known as permissive hypotension). Targets include a mean arterial pressure of 60 mmHg, a systolic blood pressure of 70–90 mmHg, or until the patient has adequate mentation and peripheral pulses. Hypertonic fluid may also be an option in this group.
Medications
 Vasopressors may be used if blood pressure does not improve with fluids. Common vasopressors used in shock include:
Vasopressors may be used if blood pressure does not improve with fluids. Common vasopressors used in shock include: norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
, phenylephrine, dopamine, and dobutamine.
There is no evidence of substantial benefit of one vasopressor over another; however, using dopamine leads to an increased risk of arrhythmia when compared with norepinephrine. Vasopressors have not been found to improve outcomes when used for hemorrhagic shock from trauma but may be of use in neurogenic shock. Activated protein C (Xigris), while once aggressively promoted for the management of septic shock, has been found not to improve survival and is associated with a number of complications. Activated protein C was withdrawn from the market in 2011, and clinical trials were discontinued. The use of sodium bicarbonate is controversial as it has not been shown to improve outcomes. If used at all it should only be considered if the blood pH is less than 7.0.
People with anaphylactic shock are commonly treated with epinephrine. Antihistamines, such as Benadryl
Benadryl is a brand of various antihistamine medications used to stop allergy, allergies, whose content varies in different countries, but which includes some combination of diphenhydramine, acrivastine, or cetirizine.
It is sold by Kenvue and ...
(diphenhydramine
Diphenhydramine, sold under the brand name Benadryl among others, is an antihistamine and sedative. Although generally considered sedating, diphenhydramine can cause paradoxical central nervous system stimulation in some individuals, particula ...
) or ranitidine are also commonly administered. Albuterol, normal saline, and steroids are also commonly given.
Mechanical support
* Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) – a device inserted into the aorta that mechanically raises the blood pressure. Use of Intra-aortic balloon pumps is not recommended in cardiogenic shock. * Ventricular assist device (VAD) – A mechanical pump that helps pump blood throughout the body. Commonly used in short term cases of refractory primary cardiogenic shock. *Artificial heart
An artificial heart is a artificial organ, device that replaces the human heart, heart. Artificial hearts are typically used as a bridge to heart transplantation, but ongoing research aims to develop a device that could permanently replace the ...
(TAH)
* Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is a form of extracorporeal life support, providing prolonged cardiac and respiratory system, respiratory support to people whose human heart, heart and human lung, lungs are unable to provide an adequa ...
(ECMO) – an external device that completely replaces the work of the heart.
Treatment goals
The goal of treatment is to achieve a urine output of greater than 0.5 mL/kg/h, a central venous pressure of 8–12 mmHg and a mean arterial pressure of 65–95 mmHg. In trauma the goal is to stop the bleeding which in many cases requires surgical interventions. A good urine output indicates that the kidneys are getting enough blood flow.Epidemiology
Septic shock (a form of distributive shock) is the most common form of shock. Shock from blood loss occurs in about 1–2% of trauma cases. Overall, up to one-third of people admitted to theintensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine.
An inten ...
(ICU) are in circulatory shock. Of these, cardiogenic shock accounts for approximately 20%, hypovolemic about 20%, and septic shock about 60% of cases.
Prognosis
 The prognosis of shock depends on the underlying cause and the nature and extent of concurrent problems. Low volume, anaphylactic, and neurogenic shock are readily treatable and respond well to medical therapy. Septic shock, especially septic shock where treatment is delayed or the antimicrobial drugs are ineffective, however has a mortality rate between 30% and 80%; cardiogenic shock has a mortality rate of up to 70% to 90%, though quick treatment with vasopressors and inotropic drugs, cardiac surgery, and the use of assistive devices can lower the mortality.
The prognosis of shock depends on the underlying cause and the nature and extent of concurrent problems. Low volume, anaphylactic, and neurogenic shock are readily treatable and respond well to medical therapy. Septic shock, especially septic shock where treatment is delayed or the antimicrobial drugs are ineffective, however has a mortality rate between 30% and 80%; cardiogenic shock has a mortality rate of up to 70% to 90%, though quick treatment with vasopressors and inotropic drugs, cardiac surgery, and the use of assistive devices can lower the mortality.
History
There is no evidence of the word shock being used in its modern-day form prior to 1743. However, there is evidence thatHippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referr ...
used the word ''exemia'' to signify a state of being "drained of blood". Shock or "choc" was first described in a trauma victim in the English translation of Henri-François LeDran's 1740 text, Traité ou Reflexions Tire'es de la Pratique sur les Playes d'armes à feu (A treatise, or reflections, drawn from practice on gun-shot wounds.) In this text he describes "choc" as a reaction to the sudden impact of a missile. However, the first English writer to use the word shock in its modern-day connotation was James Latta, in 1795.
Prior to World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, there were several competing hypotheses behind the pathophysiology of shock. Of the various theories, the most well regarded was a theory penned by George W. Crile who suggested in his 1899 monograph, "''An Experimental Research into Surgical Shock"'', that shock was quintessentially defined as a state of circulatory collapse ( vasodilation) due to excessive nervous stimulation.Alt URL/ref> Other competing theories around the turn of the century included one penned by Malcom in 1907, in which the assertion was that prolonged vasoconstriction led to the pathophysiological signs and symptoms of shock. In the following World War I, research concerning shock resulted in experiments by Walter B. Cannon of Harvard and William M. Bayliss of London in 1919 that showed that an increase in permeability of the capillaries in response to trauma or toxins was responsible for many clinical manifestations of shock. In 1972 Hinshaw and Cox suggested the classification system for shock which is still used today.
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Shock (Circulatory) Intensive care medicine Medical emergencies Causes of death Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate