Shellac on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Shellac () is a
Shellac () is a
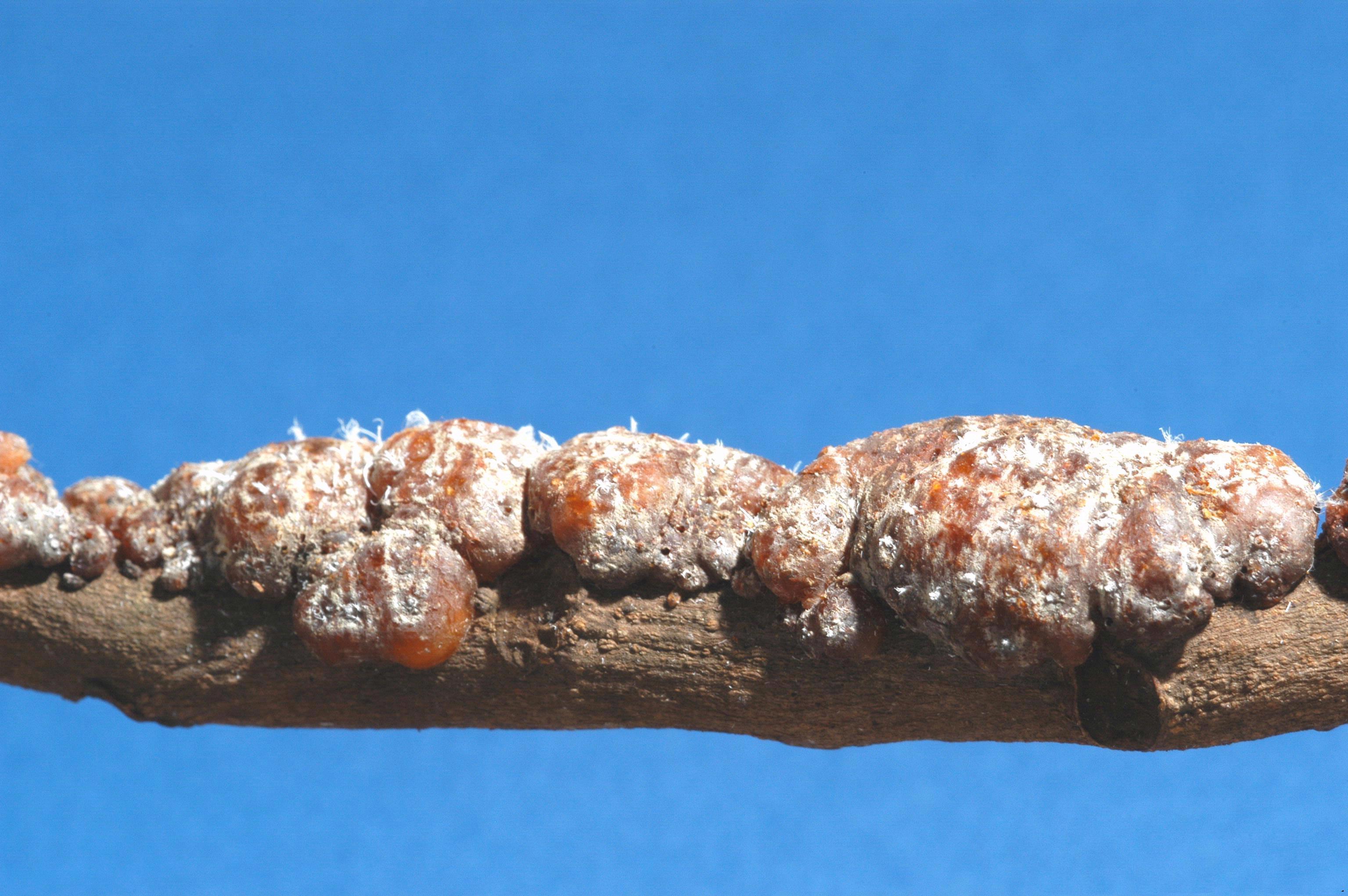

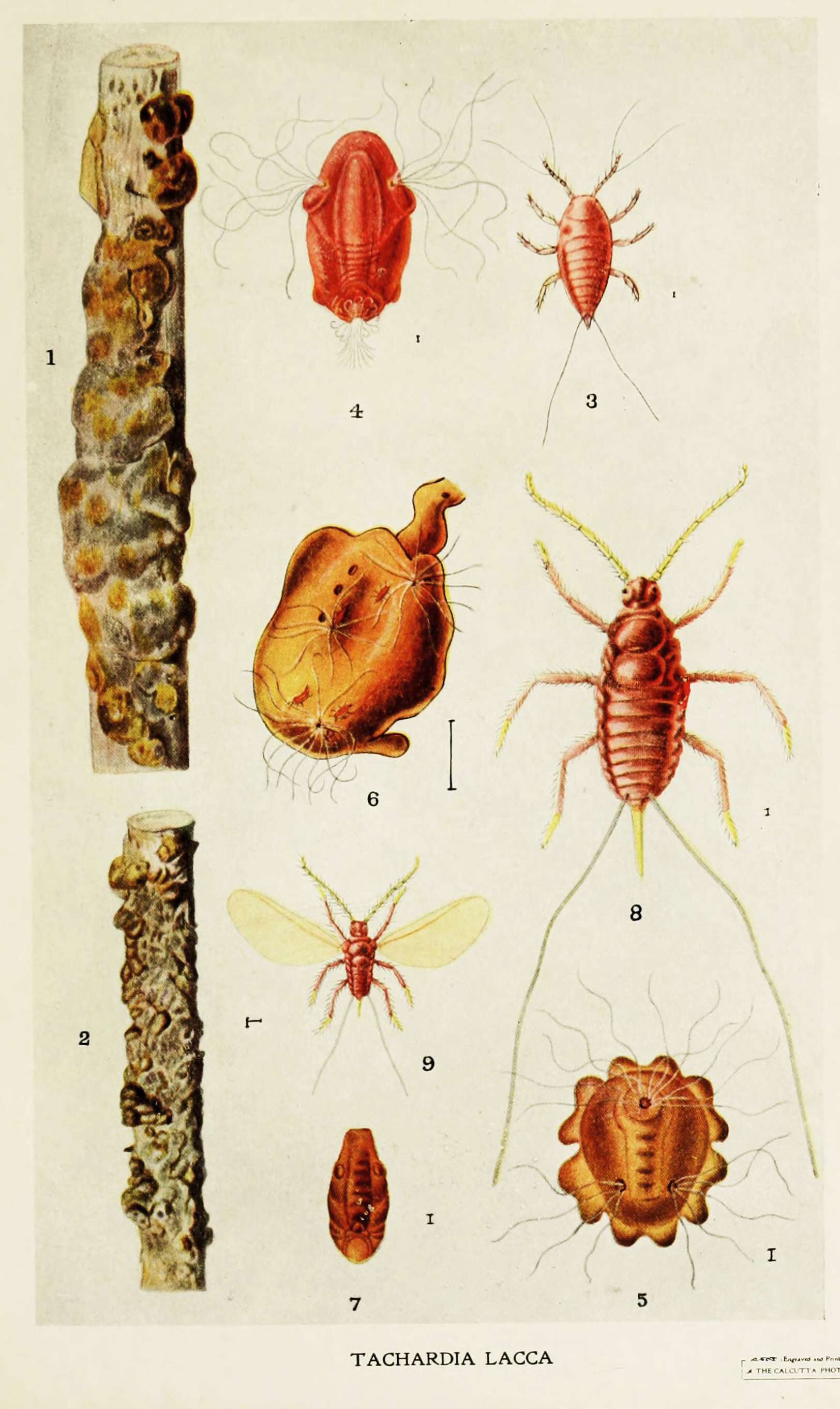 Shellac is scraped from the
Shellac is scraped from the
 Shellac is a natural
Shellac is a natural
/ref> According to the ancient Indian epic poem, the
WoodworkDetails.com: Shellac as a Woodworking Finish
/ref>
File:Schellak.jpg, Blonde shellac flakes
File:Shellac.JPG, Dewaxed Bona (L) and Waxy #1 Orange (R) shellac flakes. The latter—orange shellac—is the traditional shellac used for decades to finish wooden wall paneling, kitchen cabinets and tool handles.
File:Shellac flakes closeup.JPG, Closeup of Waxy #1 Orange (L) and Dewaxed Bona (R) shellac flakes. The former—orange shellac—is the traditional shellac used for centuries to finish wooden wall paneling and kitchen cabinets.
File:Shellac board.JPG, "Quick and dirty" example of a pine board coated with 1-5 coats of Dewaxed Dark shellac (a darker version of traditional orange shellac)
Shellac.net
US shellac vendor – properties and uses of dewaxed and non-dewaxed shellac
DIYinfo.org's Shellac Wiki
practical information on everything to do with shellac
A short introduction to the origin of shellac, the history of Japanning and French polishing, and how to conserve and repair these finishes sympathetically
By Smith & Rodger {{Authority control Wood finishing materials Food additives Insect products Polymers Resins Waxes Excipients Forestry in India Non-timber forest products E-number additives

 Shellac () is a
Shellac () is a resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on nat ...
secreted by the female lac bug
''Kerriidae'' is a family of scale insects, commonly known as lac insects or lac scales. Some members of the genera ''Metatachardia'', ''Tachardiella'', ''Austrotacharidia'', ''Afrotachardina'', ''Tachardina'', and ''Kerria'' are raised for comm ...
on trees in the forests of India and Thailand. It is processed and sold as dry flakes and dissolved in alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
to make liquid shellac, which is used as a brush-on colorant, food glaze and wood finish. Shellac functions as a tough natural primer
Primer may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth
* ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour
Literature
* Primer (textbook), a te ...
, sanding sealant
Sealant is a substance used to block the passage of fluids through openings in materials, a type of mechanical seal. In building construction ''sealant'' is sometimes synonymous with '' caulking'' and also serve the purposes of blocking dust, so ...
, tannin
Tannins (or tannoids) are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
The term ''tannin'' (from Anglo-Norman ''tanner'' ...
-blocker, odour
An odor (American English) or odour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds that are generally found in low concentrations that humans and animals can perceive via their sens ...
-blocker, stain
A stain is a discoloration that can be clearly distinguished from the surface, material, or medium it is found upon. They are caused by the chemical or physical interaction of two dissimilar materials. Accidental staining may make materials ap ...
, and high-gloss varnish
Varnish is a clear transparent hard protective coating or film. It is not a stain. It usually has a yellowish shade from the manufacturing process and materials used, but it may also be pigmented as desired, and is sold commercially in variou ...
. Shellac was once used in electrical applications as it possesses good insulation qualities and it seals out moisture. Phonograph
A phonograph, in its later forms also called a gramophone (as a trademark since 1887, as a generic name in the UK since 1910) or since the 1940s called a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogu ...
and 78 rpm gramophone record
A phonograph record (also known as a gramophone record, especially in British English), or simply a record, is an analog sound storage medium in the form of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove. The groove usually starts ne ...
s were made of it until they were replaced by vinyl long-playing record
The LP (from "long playing" or "long play") is an analog sound storage medium, a phonograph record format characterized by: a speed of rpm; a 12- or 10-inch (30- or 25-cm) diameter; use of the "microgroove" groove specification; and ...
s from 1948 onwards.
From the time it replaced oil and wax finishes in the 19th century, shellac was one of the dominant wood finishes in the western world until it was largely replaced by nitrocellulose lacquer in the 1920s and 1930s.
Etymology
''Shellac'' comes from ''shell'' and '' lac'', acalque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language ...
of French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, 'lac in thin pieces', later , 'gum lac'. Most European languages (except Romance ones and Greek) have borrowed the word for the substance from English or from the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
equivalent .
Production

 Shellac is scraped from the
Shellac is scraped from the bark
Bark may refer to:
* Bark (botany), an outer layer of a woody plant such as a tree or stick
* Bark (sound), a vocalization of some animals (which is commonly the dog)
Places
* Bark, Germany
* Bark, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland
Arts, e ...
of the trees where the female lac bug, '' Kerria lacca'' (order Hemiptera, family Kerriidae, also known as ''Laccifer lacca''), secretes it to form a tunnel-like tube as it traverses the branches of the tree. Though these tunnels are sometimes referred to as " cocoons", they are not cocoons in the entomological sense. This insect is in the same superfamily
SUPERFAMILY is a database and search platform of structural and functional annotation for all proteins and genomes. It classifies amino acid sequences into known structural domains, especially into SCOP superfamilies. Domains are functional, str ...
as the insect from which cochineal
The cochineal ( , ; ''Dactylopius coccus'') is a scale insect in the suborder Sternorrhyncha, from which the natural dye carmine is derived. A primarily sessile parasite native to tropical and subtropical South America through North America ...
is obtained. The insects suck the sap of the tree and excrete " sticklac" almost constantly. The least-coloured shellac is produced when the insects feed on the kusum tree (''Schleichera
''Schleichera'' is a monotypic genus of plants in the soapberry family, Sapindaceae. There is only one species, ''Schleichera oleosa'', a tree that occurs in the Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
Species
''Schleichera oleosa'', kusum ...
'').
The number of lac bugs required to produce of shellac has variously been estimated between and . The root word lakh
A lakh (; abbreviated L; sometimes written lac) is a unit in the Indian numbering system equal to one hundred thousand (100,000; scientific notation: 105). In the Indian 2,2,3 convention of digit grouping, it is written as 1,00,000. For e ...
is a unit in Indian numbering system
The Indian numbering system is used in all South Asian countries (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Afghanistan) to express large numbers. The terms ''lakh'' or 1,00,000 (one hundred thousand, written as ''100,00 ...
for and presumably refers to the huge numbers of insects that swarm on host trees, up to .
The raw shellac, which contains bark shavings and lac bugs removed during scraping, is placed in canvas tubes (much like long socks) and heated over a fire. This causes the shellac to liquefy, and it seeps out of the canvas, leaving the bark and bugs behind. The thick, sticky shellac is then dried into a flat sheet and broken into flakes, or dried into "buttons" (pucks/cakes), then bagged and sold. The end-user then crushes it into a fine powder and mixes it with ethyl alcohol before use, to dissolve the flakes and make liquid shellac.
Liquid shellac has a limited shelf life (about 1 year), so is sold in dry form for dissolution before use. Liquid shellac sold in hardware stores is often marked with the production (mixing) date, so the consumer can know whether the shellac inside is still good. Some manufacturers (e.g., Zinsser) have ceased labeling shellac with the production date, but the production date may be discernible from the production lot code. Alternatively, old shellac may be tested to see if it is still usable: a few drops on glass should dry to a hard surface in roughly 15 minutes. Shellac that remains tacky for a long time is no longer usable. Storage life depends on peak temperature, so refrigeration extends shelf life.
The thickness (concentration) of shellac is measured by the unit "pound cut", referring to the amount (in pounds) of shellac flakes dissolved in a gallon of denatured alcohol. For example: a 1-lb. cut of shellac is the strength obtained by dissolving one pound of shellac flakes in a gallon of alcohol (equivalent to ). Most pre-mixed commercial preparations come at a 3-lb. cut. Multiple thin layers of shellac produce a significantly better end result than a few thick layers. Thick layers of shellac do not adhere to the substrate or to each other well, and thus can peel off with relative ease; in addition, thick shellac will obscure fine details in carved designs in wood and other substrates.
Shellac naturally dries to a high-gloss sheen. For applications where a flatter (less shiny) sheen is desired, products containing amorphous silica, such as "Shellac Flat", may be added to the dissolved shellac.
Shellac naturally contains a small amount of wax (3%–5% by volume), which comes from the lac bug. In some preparations, this wax is removed (the resulting product being called "dewaxed shellac"). This is done for applications where the shellac will be coated with something else (such as paint or varnish), so the topcoat will adhere. Waxy (non-dewaxed) shellac appears milky in liquid form, but dries clear.
Colours and availability
Shellac comes in many warm colours, ranging from a very light blonde ("platina") to a very dark brown ("garnet"), with many varieties of brown, yellow, orange and red in between. The colour is influenced by the sap of the tree the lac bug is living on and by the time of harvest. Historically, the most commonly sold shellac is called "orange shellac", and was used extensively as a combination stain and protectant for wood panelling andcabinetry
A cabinet is a case or cupboard with shelves and/or drawers for storing or displaying items. Some cabinets are stand alone while others are built in to a wall or are attached to it like a medicine cabinet. Cabinets are typically made of wood (s ...
in the 20th century.
Shellac was once very common anywhere paints or varnishes were sold (such as hardware stores). However, cheaper and more abrasion- and chemical-resistant finishes, such as polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from ...
, have almost completely replaced it in decorative residential wood finishing such as hardwood floors, wooden wainscoting
Panelling (or paneling in the U.S.) is a millwork wall covering constructed from rigid or semi-rigid components. These are traditionally interlocking wood, but could be plastic or other materials.
Panelling was developed in antiquity to make ro ...
plank panelling, and kitchen cabinets. These alternative products, however, must be applied over a stain if the user wants the wood to be coloured; clear or blonde shellac may be applied over a stain without affecting the colour of the finished piece, as a protective topcoat. "Wax over shellac" (an application of buffed-on paste wax over several coats of shellac) is often regarded as a beautiful, if fragile, finish for hardwood floors. Luthier
A luthier ( ; AmE also ) is a craftsperson who builds or repairs string instruments that have a neck and a sound box. The word "luthier" is originally French and comes from the French word for lute. The term was originally used for makers of ...
s still use shellac to '' French polish'' fine acoustic stringed instruments, but it has been replaced by synthetic plastic lacquers and varnishes in many workshops, especially high-volume production environments.
Shellac dissolved in alcohol, typically more dilute than French-Polish, is now commonly sold as "sanding sealer" by several companies. It is used to seal wooden surfaces, often as preparation for a final more durable finish; it reduces the amount of final coating required by reducing its absorption into the wood.
Properties
 Shellac is a natural
Shellac is a natural bioadhesive Bioadhesives are natural polymeric materials that act as adhesives. The term is sometimes used more loosely to describe a glue formed synthetically from biological monomers such as sugars, or to mean a synthetic material designed to adhere to biolo ...
polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
and is chemically similar to synthetic polymers. It can thus can be considered a natural form of plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adapta ...
.
With a melting point of , it can be classed as a thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate ...
; used to bind wood flour, the mixture can be moulded with heat and pressure.
Shellac scratches more easily than most lacquers and varnishes, and application is more labour-intensive, which is why it has been replaced by plastic in most areas. Shellac is much softer than Urushi lacquer, for instance, which is far superior with regard to both chemical and mechanical resistance. But damaged shellac can easily be touched up with another coat of shellac (unlike polyurethane, which chemically cures to a solid) because the new coat merges with and bonds to the existing coat(s).
Shellac is soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubi ...
in alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
solutions of ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
, sodium borate, sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate, , (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions ...
, and sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and al ...
, and also in various organic solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
s. When dissolved in alcohol (typically denatured ethanol) for application, shellac yields a coating of good durability and hardness.
Upon mild hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
shellac gives a complex mix of aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane ...
and alicyclic hydroxy acids
α-Hydroxy acids, or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), are a class of chemical compounds that consist of a carboxylic acid with a hydroxyl group substituent on the adjacent (alpha) carbon. Prominent examples are glycolic acid, lactic acid, mandelic acid ...
and their polymers that varies in exact composition depending upon the source of the shellac and the season of collection. The major component of the aliphatic component is aleuritic acid, whereas the main alicyclic component is shellolic acid.Merck Index, 9th Ed. page 8224.
Shellac is UV-resistant, and does not darken as it ages (though the wood under it may do so, as in the case of pine).
History
The earliest written evidence of shellac goes back years, but shellac is known to have been used earlier.Naturalhandyman.com : DEFEND, PRESERVE, AND PROTECT WITH SHELLAC : The story of shellac/ref> According to the ancient Indian epic poem, the
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
, an entire palace was built out of dried shellac.
Shellac was in rare use as a dyestuff for as long as there was a trade with the East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around ...
. Merrifield cites 1220 for the introduction of shellac as an artist's pigment in Spain.
The use of overall paint or varnish decoration on large pieces of furniture was first popularised in Venice (then later throughout Italy). There are a number of 13th-century references to painted or varnished cassone, often dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment ...
cassone that were made deliberately impressive as part of dynastic marriages. The definition of varnish is not always clear, but it seems to have been a spirit varnish based on gum benjamin or mastic, both traded around the Mediterranean. At some time, shellac began to be used as well. An article from the ''Journal of the American Institute of Conservation'' describes using infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functi ...
to identify shellac coating on a 16th-century cassone. This is also the period in history where "varnisher" was identified as a distinct trade, separate from both carpenter and artist.
Another use for shellac is sealing wax
Sealing wax is a wax material of a seal which, after melting, hardens quickly (to paper, parchment, ribbons and wire, and other material) forming a bond that is difficult to separate without noticeable tampering. Wax is used to verify something ...
. Woods's ''The Nature and Treatment of Wax and Shellac Seals'' discusses the various formulations, and the period when shellac started to be added to the previous beeswax recipes.
The "period of widespread introduction" would seem to be around 1550 to 1650, when the substance moved from being a rarity on highly decorated pieces to being described in the standard texts of the day.
Uses
Historical
In the early- and mid-twentieth century, orange shellac was used as a one-product finish (combination stain and varnish-like topcoat) on decorative wood panelling used on walls and ceilings in homes, particularly in the US. In theAmerican South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
, use of knotty pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
plank panelling
Panelling (or paneling in the U.S.) is a millwork wall covering constructed from rigid or semi-rigid components. These are traditionally interlocking wood, but could be plastic or other materials.
Panelling was developed in antiquity to make r ...
covered with orange shellac was once as common in new construction as drywall
Drywall (also called plasterboard, dry lining, wallboard, sheet rock, gypsum board, buster board, custard board, and gypsum panel) is a panel made of calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum), with or without additives, typically extruded between thic ...
is today. It was also often used on kitchen cabinets and hardwood floors, prior to the advent of polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from ...
.
Until the advent of vinyl, most gramophone records
A phonograph record (also known as a gramophone record, especially in British English), or simply a record, is an analog sound storage medium in the form of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove. The groove usually starts near ...
were pressed from shellac compounds. From 1921 to 1928, tons of shellac were used to create 260 million records for Europe. In the 1930s, it was estimated that half of all shellac was used for gramophone records
A phonograph record (also known as a gramophone record, especially in British English), or simply a record, is an analog sound storage medium in the form of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove. The groove usually starts near ...
. Use of shellac for records was common until the 1950s and continued into the 1970s in some non-Western countries.
Until recent advances in technology, shellac ( French polish) was the only glue used in the making of ballet
Ballet () is a type of performance dance that originated during the Italian Renaissance in the fifteenth century and later developed into a concert dance form in France and Russia. It has since become a widespread and highly technical form ...
dancers' pointe shoes, to stiffen the box (toe area) to support the dancer en pointe. Many manufacturers of pointe shoes still use the traditional techniques, and many dancers use shellac to revive a softening pair of shoes.
Shellac was historically used as a protective coating on paintings.
Sheets of Braille
Braille (Pronounced: ) is a tactile writing system used by people who are visually impaired, including people who are blind, deafblind or who have low vision. It can be read either on embossed paper or by using refreshable braille displ ...
were coated with shellac to help protect them from wear
Wear is the damaging, gradual removal or deformation of material at solid surfaces. Causes of wear can be mechanical (e.g., erosion) or chemical (e.g., corrosion). The study of wear and related processes is referred to as tribology.
Wear in ...
due to being read by hand.
Shellac was used from the mid-nineteenth century to produce small moulded goods such as picture frame
A picture frame is a protective and decorative edging for a picture, such as a painting or photograph. It makes displaying the work safer and easier and both sets the picture apart from its surroundings and aesthetically integrates it with them. ...
s, boxes, toilet articles, jewelry
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry ( U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a w ...
, inkwells and even dentures. Advances in plastics
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptabi ...
have rendered shellac obsolete as a moulding compound.
Shellac (both orange and white varieties) was used both in the field and laboratory to glue and stabilise dinosaur bones until about the mid-1960s. While effective at the time, the long-term negative effects of shellac (being organic in nature) on dinosaur bones and other fossils is debated, and shellac is very rarely used by professional conservators and fossil preparators today.
Shellac was used for fixing inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a c ...
, motor, generator and transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
windings. It was applied directly to single-layer windings in an alcohol solution. For multi-layer windings, the whole coil was submerged in shellac solution, then drained and placed in a warm place to allow the alcohol to evaporate. The shellac locked the wire turns in place, provided extra insulation, prevented movement and vibration and reduced buzz and hum. In motors and generators it also helps transfer force generated by magnetic attraction and repulsion from the windings to the rotor or armature. In more recent times, shellac has been replaced in these applications by synthetic resins such as polyester resin. Some applications use shellac mixed with other natural or synthetic resins, such as pine resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on natu ...
or phenol-formaldehyde resin, of which Bakelite
Polyoxybenzylmethylenglycolanhydride, better known as Bakelite ( ), is a thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin, formed from a condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. The first plastic made from synthetic components, it was developed ...
is the best known, for electrical use. Mixed with other resins, barium sulfate
Barium sulfate (or sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba SO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium and ...
, calcium carbonate, zinc sulfide
Zinc sulfide (or zinc sulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of ZnS. This is the main form of zinc found in nature, where it mainly occurs as the mineral sphalerite. Although this mineral is usually black because of various ...
, aluminium oxide and/or cuprous carbonate (malachite
Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, with the formula Cu2CO3(OH)2. This opaque, green-banded mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often forms botryoidal, fibrous, or stalagmitic masses, in fracture ...
), shellac forms a component of heat-cured capping cement used to fasten the caps or bases to the bulbs of electric lamps.
Current
It is the central element of the traditional " French polish" method of finishing furniture, finestring instrument
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner.
Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the s ...
s, and piano
The piano is a stringed keyboard instrument in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather). It is played using a keyboa ...
s.
Shellac, edible, is used as a glazing agent
A glazing agent is a natural or synthetic substance that provides a waxy, homogeneous, coating to prevent water loss from a surface and provide other protection.
Natural
Natural glazing agents keep moisture inside plants and insects. Scientists ...
on pills (see excipient
An excipient is a substance formulated alongside the active ingredient of a medication, included for the purpose of long-term stabilization, bulking up solid formulations that contain potent active ingredients in small amounts (thus often referred ...
) and sweets, in the form of pharmaceutical glaze Resinous glaze is an alcohol-based solution of various types of food-grade shellac. The shellac is derived from the raw material sticklac, which is a resin scraped from the branches of trees left from when the small insect, ''Kerria lacca'' (also k ...
(or, "confectioner's glaze"). Because of its acidic properties (resisting stomach acids), shellac-coated pills may be used for a timed enteric or colonic release. Shellac is used as a 'wax' coating on citrus fruit to prolong its shelf/storage life. It is also used to replace the natural wax of the apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancest ...
, which is removed during the cleaning process. When used for this purpose, it has the food additive
Food additives are substances added to food to preserve Taste, flavor or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. Some additives have been used for centuries as part of an effort to preserve food, for example vinegar (pickling), sal ...
E number
E numbers ("E" stands for "Europe") are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly ...
E904.
Shellac is an odour and stain blocker and so is often used as the base of "''all-purpose''" primers. Although its durability against abrasives and many common solvents is not very good, shellac provides an excellent barrier against water vapour penetration. Shellac-based primers are an effective sealant to control odours associated with fire damage.
Shellac has traditionally been used as a dye for cotton and, especially, silk cloth in Thailand, particularly in the north-eastern region.Suanmuang Tulaphan, Phunsap, ''Silk Dyeing With Natural Dyestuffs in Northeastern Thailand'', 1999, p. 26-30 (in Thai) It yields a range of warm colours from pale yellow through to dark orange-reds and dark ochre.Punyaprasop, Daranee (Ed.)Colour ''And Pattern On Native Cloth'', 2001, p. 253, 256 (in Thai) Naturally dyed silk cloth, including that using shellac, is widely available in the rural northeast, especially in Ban Khwao District, Chaiyaphum province
Chaiyaphum ( th, ชัยภูมิ, ) is one of Thailand's seventy-six provinces (''changwat''), located in central northeastern Thailand , also called Isan. Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise) Khon Kaen, Nakhon Ratchasima, Lopb ...
. The Thai name for the insect and the substance is "khrang" (Thai: ครั่ง).
Wood finish
Wood finishing is one of the most traditional and still popular uses of shellac mixed with solvents or alcohol. This dissolved shellac liquid, applied to a piece of wood, is an evaporative finish: the alcohol of the shellac mixture evaporates, leaving behind a protective film. Shellac as wood finish is natural and non-toxic in its pure form. A finish made of shellac is UV-resistant. For water-resistance and durability, it does not keep up with synthetic finishing products. Because it is compatible with most other finishes, shellac is also used as a barrier or primer coat onwood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
to prevent the bleeding of resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on nat ...
or pigments into the final finish, or to prevent wood stain from blotching.ShellacWoodworkDetails.com: Shellac as a Woodworking Finish
/ref>
Other
Shellac is used: * in the tying of artificial flies for trout and salmon, where the shellac was used to seal all trimmed materials at the head of the fly. * in combination with wax for preserving and imparting a shine tocitrus fruits
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is nativ ...
, such as lemon
The lemon (''Citrus limon'') is a species of small evergreen trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, primarily Northeast India (Assam), Northern Myanmar or China.
The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culin ...
s.
* in dental technology
A dental technologist (dental laboratory technician) is a member of the dental team who, upon prescription from a dental clinician, constructs custom-made restorative and dental appliances.
There are four major disciplines within dental technol ...
, where it is occasionally used in the production of custom impression trays and (partial) denture production.
* as a binder in India ink.
* for bicycles
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.
Bi ...
, as a protective and decorative coating for bicycle handlebar tape, and as a hard-drying adhesive for tubular tyres, particularly for track racing
Track racing is a form of motorcycle racing where teams or individuals race opponents around an unpaved oval track. There are differing variants, with each variant racing on a different surface type.
The most common variant is Speedway which ha ...
.
* for re-attaching ink sacs when restoring vintage fountain pen
A fountain pen is a writing instrument which uses a metal nib (pen), nib to apply a Fountain pen ink, water-based ink to paper. It is distinguished from earlier dip pens by using an internal reservoir to hold ink, eliminating the need to repeat ...
s, the orange variety preferably.
* Shellac coating applied with either a standard or modified Huon-Stuehrer nozzle, can be economically micro-sprayed onto various smooth candies, such as chocolate coated peanuts. Irregularities on the surface of the product being sprayed may result in the formation of unsightly aggregates ("lac-aggs") which precludes the use of this technique on foods such as walnuts or raisins.
* for fixing pads to the key-cups of woodwind
Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the greater category of wind instruments. Common examples include flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two main types of woodwind instruments: flutes and re ...
instruments.
* for Luthier
A luthier ( ; AmE also ) is a craftsperson who builds or repairs string instruments that have a neck and a sound box. The word "luthier" is originally French and comes from the French word for lute. The term was originally used for makers of ...
applications, to bind wood fibres down and prevent tear out on the soft spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfam ...
soundboards.
* to stiffen and impart water-resistance to felt hats, for wood finishing and as a constituent of ''gossamer'' (or ''goss'' for short), a cheesecloth fabric coated in shellac and ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
solution used in the shell of traditional silk top and riding hats.
* for mounting insects, in the form of a gel adhesive mixture composed of 75% ethyl alcohol.
* as a binder in the fabrication of abrasive wheels, imparting flexibility and smoothness not found in vitrified (ceramic bond) wheels. 'Elastic' bonded wheels typically contain plaster of paris
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
, yielding a stronger bond when mixed with shellac; the mixture of dry plaster powder, abrasive (e.g. corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the pr ...
/ aluminium oxide Al2O3), and shellac are heated and the mixture pressed in a mould.
* in fireworks
Fireworks are a class of low explosive pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays (also called a fireworks show or pyrotechnics), combining a large number of devices ...
pyrotechnic compositions as a low-temperature fuel, where it allows the creation of pure 'greens' and 'blues'- colours difficult to achieve with other fuel mixes.
* In Jewellery
Jewellery ( UK) or jewelry ( U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a w ...
; shellac is often applied to the top of a 'shellac stick' in order to hold small, complex, objects. By melting the shellac, the jeweller can press the object (such as a stone setting mount) into it. The shellac, once cool, can firmly hold the object - allowing it to be manipulated with tools.
* in watchmaking, due to its low melting temperature (about ), shellac is used in most mechanical movements to adjust and adhere pallet stones to the pallet fork
The pallet fork is a component of the lever escapement of a mechanical watch. The pallet fork and the lever form one component that sits between the escape wheel and the balance wheel. Its purpose is to lock the escape wheel, and release it one t ...
and secure the roller jewel to the roller table of the balance wheel. Also for securing small parts to a 'wax chuck' ( faceplate ) in a watchmakers' lathe.
* in the early twentieth century, it was used to protect some military rifle
A rifle is a long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting, with a barrel that has a helical pattern of grooves ( rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with ...
stocks.
* in Jelly Belly jelly beans, in combination with beeswax
Beeswax (''cera alba'') is a natural wax produced by honey bees of the genus ''Apis''. The wax is formed into scales by eight wax-producing glands in the abdominal segments of worker bees, which discard it in or at the hive. The hive work ...
to give them their final buff and polish.
* in modern traditional archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In ...
, shellac is one of the hot-melt glue/resin products used to attach arrowhead
An arrowhead or point is the usually sharpened and hardened tip of an arrow, which contributes a majority of the projectile mass and is responsible for impacting and penetrating a target, as well as to fulfill some special purposes such as sign ...
s to wooden or bamboo arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers ...
shafts.
* Sanding sealer, is a solution of shellac dissolved in alcohol widely sold to seal sanded surfaces, typically wooden surfaces before a final coat of a more durable finish. Similar to French Polish but more dilute.
* as a topcoat in nail polish
Nail polish (also known as nail varnish or nail enamel) is a lacquer that can be applied to the human fingernail or toenails to decorate and protect the nail plates. The formula has been revised repeatedly to enhance its decorative properties ...
(although not all nail polish
Nail polish (also known as nail varnish or nail enamel) is a lacquer that can be applied to the human fingernail or toenails to decorate and protect the nail plates. The formula has been revised repeatedly to enhance its decorative properties ...
sold as "shellac" contains shellac, and some nail polish
Nail polish (also known as nail varnish or nail enamel) is a lacquer that can be applied to the human fingernail or toenails to decorate and protect the nail plates. The formula has been revised repeatedly to enhance its decorative properties ...
not labelled in this way does)
* in sculpture, to seal plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
and in conjunction with wax or oil-soaps, to act as a barrier during mold-making processes
* as a dilute solution in the sealing of harpsichord
A harpsichord ( it, clavicembalo; french: clavecin; german: Cembalo; es, clavecín; pt, cravo; nl, klavecimbel; pl, klawesyn) is a musical instrument played by means of a keyboard. This activates a row of levers that turn a trigger mechanism ...
soundboards, protecting them from dust and buffering humidity changes while maintaining a bare-wood appearance.
Gallery
See also
* shellac, Wiktionary entry *polymers
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
References
External links
Shellac.net
US shellac vendor – properties and uses of dewaxed and non-dewaxed shellac
DIYinfo.org's Shellac Wiki
practical information on everything to do with shellac
A short introduction to the origin of shellac, the history of Japanning and French polishing, and how to conserve and repair these finishes sympathetically
By Smith & Rodger {{Authority control Wood finishing materials Food additives Insect products Polymers Resins Waxes Excipients Forestry in India Non-timber forest products E-number additives