Sex-determination system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A sex-determination system is a
A sex-determination system is a

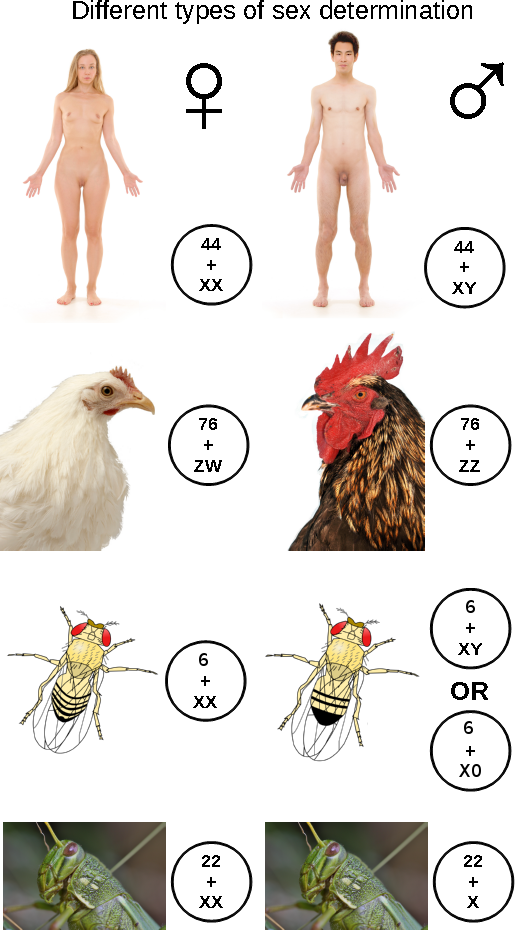
 The XX/XY sex-determination system is the most familiar, as it is found in humans. The XX/XY system is found in most other
The XX/XY sex-determination system is the most familiar, as it is found in humans. The XX/XY system is found in most other


 Sex determination systems may have evolved from
Sex determination systems may have evolved from
 A sex-determination system is a
A sex-determination system is a biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fu ...
. Most organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fu ...
s that create their offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by a single organism or, in the case of sexual reproduction, two organisms. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny in a more general way. This ca ...
using sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote th ...
have two sexes.
In some species there are hermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes.
Many taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrates) do not have ...
s. There are also some species that are only one sex due to parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen ...
, the act of a female reproducing without fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
.
In some species, sex determination is genetic: males and females have different allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chrom ...
s or even different gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s that specify their sexual morphology. In animals this is often accompanied by chromosomal
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy. The sexual differentiation is generally triggered by a main gene (a "sex locus"), with a multitude of other genes following in a domino effect.
In other cases, sex of a fetus is determined by environmental
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scal ...
variables (such as temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
). The details of some sex-determination systems are not yet fully understood. Hopes for future fetal biological system analysis include complete-reproduction-system initialized signals that can be measured during pregnancies to more accurately determine whether a determined sex of a fetus is male, or female. Such analysis of biological systems could also signal whether the fetus is hermaphrodite, which includes total or partial of both male and female reproduction organs.
Some species such as various plants and fish do not have a fixed sex, and instead go through life cycles and change sex based on genetic cues during corresponding life stages of their type. This could be due to environmental factors such as seasons and temperature. In some gonochoric species, a few individuals may have sex characteristics of both sexes, a condition called intersex
Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical b ...
.
While diversity in sex determination systems is common throughout the diversity of biology, the systems beyond XY/XX/XO in mammals are often characterized as less common or abnormal, because of the social influence of centering certain human cultural norms when researching sex determination. As such, general biology courses often focus on the simplified genetics of this one system, harmfully excluding people and other organisms from what most people learn in their biology courses.
Discovery
Sex determination was discovered in the mealworm by the American geneticistNettie Stevens
Nettie Maria Stevens (July 7, 1861 – May 4, 1912) was an American geneticist who discovered sex chromosomes. In 1905, soon after the rediscovery of Mendel's paper on genetics in 1900, she observed that male mealworms produced two kinds of sp ...
in 1903.
Chromosomal systems
XX/XY sex chromosomes
mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
s, as well as some insects. In this system, most females have two of the same kind of sex chromosome (XX), while most males have two distinct sex chromosomes (XY). The X and Y sex chromosomes are different in shape and size from each other, unlike the rest of the chromosomes (autosome
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
s), and are sometimes called allosome
A sex chromosome (also referred to as an allosome, heterotypical chromosome, gonosome, heterochromosome, or idiochromosome) is a chromosome that differs from an ordinary autosome in form, size, and behavior. The human sex chromosomes, a typical ...
s. In some species, such as humans, organisms remain sex indifferent for a time after they're created; in others, however, such as fruit flies, sexual differentiation occurs as soon as the egg is fertilized.
Y-centered sex determination
Some species (including humans) have a gene SRY on the Y chromosome that determinesmale
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization.
A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to ...
ness. Members of SRY-reliant species can have uncommon XY chromosomal combinations such as XXY and still live.
Human sex is determined by the presence or absence of a Y chromosome with a functional SRY gene. Once the SRY gene is activated, cells create testosterone and anti-müllerian hormone which typically ensures the development of a single, male reproductive system. In typical XX embryos, cells secrete estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
, which drives the body toward the female pathway.
In Y-centered sex determination, the SRY gene is the main gene in determining male characteristics, but multiple genes are required to develop testes. In XY mice, lack of the gene DAX1 on the X chromosome results in sterility, but in humans it causes adrenal hypoplasia congenita. However, when an extra DAX1 gene is placed on the X chromosome, the result is a female, despite the existence of SRY. Even when there are normal sex chromosomes in XX females, duplication or expression of SOX9 causes testes to develop. Gradual sex reversal in developed mice can also occur when the gene FOXL2
Forkhead box protein L2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FOXL2'' gene.
Function
FOXL2 (OMIM 605597) is a transcription factor belonging to the forkhead box (FOX) superfamily, characterized by the forkhead box/winged-helix DNA-b ...
is removed from females. Even though the gene DMRT1
Doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 1, also known as DMRT1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DMRT1'' gene.
Function
DMRT1 is a dose sensitive transcription factor protein that regulates Sertoli cells and germ cell ...
is used by birds as their sex locus, species who have XY chromosomes also rely upon DMRT1, contained on chromosome 9, for sexual differentiation at some point in their formation.
X-centered sex determination
Some species, such as fruit flies, use the presence of two X chromosomes to determinefemale
Female ( symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Fema ...
ness. Species that use the number of Xs to determine sex are nonviable with an extra X chromosome.
Other variants of XX/XY sex determination
Some fish have variants of the XY sex-determination system, as well as the regular system. For example, while having an XY format, '' Xiphophorus nezahualcoyotl'' and ''X. milleri'' also have a second Y chromosome, known as Y', that creates XY' females and YY' males. At least one monotreme, theplatypus
The platypus (''Ornithorhynchus anatinus''), sometimes referred to as the duck-billed platypus, is a semiaquatic, egg-laying mammal endemic to eastern Australia, including Tasmania. The platypus is the sole living representative or mono ...
, presents a particular sex determination scheme that in some ways resembles that of the ZW sex chromosomes of birds and lacks the SRY gene. The platypus
The platypus (''Ornithorhynchus anatinus''), sometimes referred to as the duck-billed platypus, is a semiaquatic, egg-laying mammal endemic to eastern Australia, including Tasmania. The platypus is the sole living representative or mono ...
has ten sex chromosomes; males have an XYXYXYXYXY pattern while females have ten X chromosomes. Although it is an XY system, the platypus' sex chromosomes share no homologues with eutherian sex chromosomes. Instead, homologues with eutherian sex chromosomes lie on the platypus chromosome 6, which means that the eutherian sex chromosomes were autosomes at the time that the monotremes diverged from the therian mammals (marsupials and eutherian mammals). However, homologues to the avian DMRT1
Doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 1, also known as DMRT1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DMRT1'' gene.
Function
DMRT1 is a dose sensitive transcription factor protein that regulates Sertoli cells and germ cell ...
gene on platypus sex chromosomes X3 and X5 suggest that it is possible the sex-determining gene for the platypus is the same one that is involved in bird sex-determination. More research must be conducted in order to determine the exact sex determining gene of the platypus.
XX/X0 sex chromosomes
In this variant of the XY system, females have two copies of the sex chromosome (XX) but males have only one (X0). The ''0'' denotes the absence of a second sex chromosome. Generally in this method, the sex is determined by amount of genes expressed across the two chromosomes. This system is observed in a number of insects, including the grasshoppers and crickets of order Orthoptera and in cockroaches (orderBlattodea
Blattodea is an order of insects that contains cockroaches and termites. Formerly, termites were considered a separate order, Isoptera, but genetic and molecular evidence suggests they evolved from within the cockroach lineage, cladistically mak ...
). A small number of mammals also lack a Y chromosome. These include the Amami spiny rat ('' Tokudaia osimensis'') and the Tokunoshima spiny rat ('' Tokudaia tokunoshimensis'') and ''Sorex araneus'', a shrew
Shrews (family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to differ ...
species. Transcaucasian mole voles ('' Ellobius lutescens'') also have a form of XO determination, in which both sexes lack a second sex chromosome. The mechanism of sex determination is not yet understood.
The nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant- parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a bro ...
''C. elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (r ...
'' is male with one sex chromosome (X0); with a pair of chromosomes (XX) it is a hermaphrodite.
Its main sex gene is XOL, which encodes XOL-1 and also controls the expression of the genes TRA-2 and HER-1. These genes reduce male gene activation and increase it, respectively.
ZW/ZZ sex chromosomes
The ZW sex-determination system is found in birds, some reptiles, and some insects and other organisms. The ZW sex-determination system is reversed compared to the XY system: females have two different kinds ofchromosomes
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
(ZW), and males have two of the same kind of chromosomes (ZZ). In the chicken, this was found to be dependent on the expression of DMRT1. In birds, the genes FET1 and ASW are found on the W chromosome for females, similar to how the Y chromosome contains SRY. However, not all species depend upon the W for their sex. For example, there are moths and butterflies that are ZW, but some have been found female with ZO, as well as female with ZZW. Also, while mammals deactivate one of their extra X chromosomes when female, it appears that in the case of Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) is an order of insects that includes butterflies and moths (both are called lepidopterans). About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 families and 46 superfamilies, 10 percent of the total described speci ...
, the males produce double the normal amount of enzymes, due to having two Z's. Because the use of ZW sex determination is varied, it is still unknown how exactly most species determine their sex. However, reportedly, the silkworm ''Bombyx mori'' uses a single female-specific piRNA as the primary determiner of sex. Despite the similarities between the ZW and XY systems, these sex chromosomes evolved separately. In the case of the chicken, their Z chromosome is more similar to humans' autosome 9. The chicken's Z chromosome also seems to be related to the X chromosome of the platypus. When a ZW species, such as the Komodo dragon
The Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis''), also known as the Komodo monitor, is a member of the monitor lizard family Varanidae that is endemic to the Indonesian islands of Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang. It is the largest extant ...
, reproduces parthenogenetically
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development ...
, usually only males are produced. This is due to the fact that the haploid eggs double their chromosomes, resulting in ZZ or WW. The ZZ become males, but the WW are not viable and are not brought to term.
In both XY and ZW sex determination systems, the sex chromosome carrying the critical factors is often significantly smaller, carrying little more than the genes necessary for triggering the development of a given sex.
ZZ/Z0 sex chromosomes
The ZZ/Z0 sex-determination system is found in some moths. In these insects there is one sex chromosome, Z. Males have two Z chromosomes, whereas females have one Z. Males are ZZ, while females are Z0.UV sex chromosomes
In some Bryophyte and somealgae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular micr ...
species, the gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternating multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the ...
stage of the life cycle, rather than being hermaphrodite, occurs as separate male or female individuals that produce male and female gametes respectively. When meiosis occurs in the sporophyte generation of the life cycle, the sex chromosomes known as U and V assort in spores that carry either the U chromosome and give rise to female gametophytes, or the V chromosome and give rise to male gametophytes.

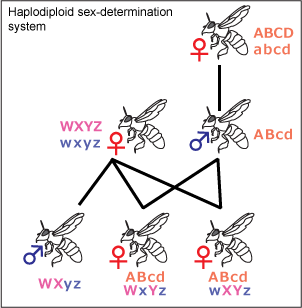
Haplodiploidy
Haplodiploidy is found in insects belonging to Hymenoptera, such as ants andbee
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfami ...
s. Sex determination is controlled by the zygosity of a complementary sex determiner (''csd'') locus. Unfertilized eggs develop into haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respective ...
individuals which have a single, hemizygous copy of the ''csd'' locus and are therefore males. Fertilized eggs develop into diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectiv ...
individuals which, due to high variability in the ''csd'' locus, are generally heterozygous females. In rare instances diploid individuals may be homozygous, these develop into sterile males.
The gene acting as a ''csd'' locus has been identified in the honeybee and several candidate genes have been proposed as a ''csd'' locus for other Hymenopterans.
Most females in the Hymenoptera order can decide the sex of their offspring by holding received sperm in their spermatheca and either releasing it into their oviduct or not. This allows them to create more workers, depending on the status of the colony.
Other chromosomal systems
Other uncommon systems include those of the green swordtail (a polyfactorial system with the sex-determining genes on several chromosomes) the Chironomus midges; the juvenile hermaphroditism of zebrafish, with an unknown trigger; and the platyfish, which has W, X, and Y chromosomes. This allows WY, WX, or XX females and YY or XY males.Mating type
Mating types are the microorganism equivalent to sexes in multicellular lifeforms and are thought to be the ancestor to distinct sexes. They also occur in macro-organisms such as fungi.
Definition
Mating types are the microorganism equivalent to ...
in microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in old ...
s is analogous to sex in multi-cellular organisms, and is sometimes described using those terms, though they are not necessarily correlated with physical body structures. Some species have more than two mating types. '' Tetrahymena,'' a type of ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a differen ...
, has seven mating types. '' Schizophyllum commune,'' a type of fungus, has 23,328.
Environmental systems

Temperature-dependent
Many other sex-determination systems exist. In some species of reptiles, includingalligator
An alligator is a large reptile in the Crocodilia order in the genus ''Alligator'' of the family Alligatoridae. The two extant species are the American alligator (''A. mississippiensis'') and the Chinese alligator (''A. sinensis''). Additional ...
s, some turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked t ...
s, and the tuatara, sex is determined by the temperature at which the egg is incubated during a temperature-sensitive period. There are no examples of temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) in birds. Megapodes
The megapodes, also known as incubator birds or mound-builders, are stocky, medium-large, chicken-like birds with small heads and large feet in the family Megapodiidae. Their name literally means "large foot" and is a reference to the heavy leg ...
had formerly been thought to exhibit this phenomenon, but were found to actually have different temperature-dependent embryo mortality rates for each sex. For some species with TSD, sex determination is achieved by exposure to hotter temperatures resulting in the offspring being one sex and cooler temperatures resulting in the other. This type of TSD is called ''Pattern I''. For others species using TSD, it is exposure to temperatures on both extremes that results in offspring of one sex, and exposure to moderate temperatures that results in offspring of the opposite sex, called ''Pattern II'' TSD. The specific temperatures required to produce each sex are known as the female-promoting temperature and the male-promoting temperature. When the temperature stays near the threshold during the temperature sensitive period, the sex ratio
The sex ratio (or gender ratio) is usually defined as the ratio of males to females in a population. As explained by Fisher's principle, for evolutionary reasons this is typically about 1:1 in species which reproduce sexually. Many species dev ...
is varied between the two sexes. Some species' temperature standards are based on when a particular enzyme is created. These species that rely upon temperature for their sex determination do not have the SRY gene, but have other genes such as DAX1, DMRT1
Doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 1, also known as DMRT1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DMRT1'' gene.
Function
DMRT1 is a dose sensitive transcription factor protein that regulates Sertoli cells and germ cell ...
, and SOX9 that are expressed or not expressed depending on the temperature. The sex of some species, such as the Nile tilapia, Australian skink lizard, and Australian dragon lizard, has an initial bias, set by chromosomes, but can later be changed by the temperature of incubation.
It is unknown how exactly temperature-dependent sex determination evolved. It could have evolved through certain sexes being more suited to certain areas that fit the temperature requirements. For example, a warmer area could be more suitable for nesting, so more females are produced to increase the amount that nest next season.
In amniotes, environmental sex determination preceded the genetically determined systems of birds and mammals; it is thought that a temperature-dependent amniote was the common ancestor of amniotes with sex chromosomes.
Other environmental systems
There are otherenvironmental sex determination
Environmental sex determination is the establishment of sex by a non-genetic cue, such as nutrient availability, experienced within a discrete period after fertilization. Environmental factors which often influence sex determination during develop ...
systems including location-dependent determination systems as seen in the marine worm ''Bonellia viridis
''Bonellia viridis'', the green spoonworm, is a marine worm (class Polychaeta , phylum Annelida) noted for displaying exceptional sexual dimorphism and for the biocidal properties of a pigment in its skin.Murina, G. (2008). Bonellia viridis R ...
'' – larvae become males if they make physical contact with a female, and females if they end up on the bare sea floor. This is triggered by the presence of a chemical produced by the females, bonellin. Some species, such as some snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class ...
s, practice sex change
Sex change is a natural or artificial process in which an individual's sex is changed.
Sex change may also refer to:
Biology and medicine
*Sex reassignment therapy
* Sex reassignment surgery
* Sequential hermaphroditism, a phenomenon whereby so ...
: adults start out male, then become female. In tropical clown fish
Clownfish or anemonefish are fishes from the subfamily Amphiprioninae in the family Pomacentridae. Thirty species of clownfish are recognized: one in the genus ''Premnas'', while the remaining are in the genus ''Amphiprion''. In the wild, the ...
, the dominant individual in a group becomes female while the other ones are male, and bluehead wrasses ('' Thalassoma bifasciatum'') are the reverse. Some species, however, have no sex-determination system. Hermaphrodite species include the common earthworm and certain species of snails. A few species of fish, reptiles, and insects reproduce by parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen ...
and are female altogether. There are some reptiles, such as the boa constrictor and Komodo dragon
The Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis''), also known as the Komodo monitor, is a member of the monitor lizard family Varanidae that is endemic to the Indonesian islands of Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang. It is the largest extant ...
that can reproduce both sexually and asexually, depending on whether a mate is available.
Evolution
 Sex determination systems may have evolved from
Sex determination systems may have evolved from mating type
Mating types are the microorganism equivalent to sexes in multicellular lifeforms and are thought to be the ancestor to distinct sexes. They also occur in macro-organisms such as fungi.
Definition
Mating types are the microorganism equivalent to ...
, which is a feature of microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in old ...
s.
Chromosomal sex determination may have evolved early in the history of eukaryotes. But in plants it has been suggested to have evolved recently.
The accepted hypothesis of XY and ZW sex chromosome evolution in amniotes is that they evolved at the same time, in two different branches.
No genes are shared between the avian ZW and mammal XY chromosomes and the chicken Z chromosome is similar to the human autosomal chromosome 9, rather than X or Y. This suggests not that the ZW and XY sex-determination systems share an origin but that the sex chromosomes are derived from autosomal chromosomes of the common ancestor of birds and mammals. In the platypus
The platypus (''Ornithorhynchus anatinus''), sometimes referred to as the duck-billed platypus, is a semiaquatic, egg-laying mammal endemic to eastern Australia, including Tasmania. The platypus is the sole living representative or mono ...
, a monotreme, the X1 chromosome shares homology with therian mammals, while the X5 chromosome contains an avian sex-determination gene, further suggesting an evolutionary link.
However, there is some evidence to suggest that there could have been transitions between ZW and XY, such as in '' Xiphophorus maculatus'', which have both ZW and XY systems in the same population, despite the fact that ZW and XY have different gene locations. A recent theoretical model raises the possibility of both transitions between the XY/XX and ZZ/ZW system and environmental sex determination The platypus' genes also back up the possible evolutionary link between XY and ZW, because they have the DMRT1
Doublesex and mab-3 related transcription factor 1, also known as DMRT1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''DMRT1'' gene.
Function
DMRT1 is a dose sensitive transcription factor protein that regulates Sertoli cells and germ cell ...
gene possessed by birds on their X chromosomes. Regardless, XY and ZW follow a similar route. All sex chromosomes started out as an original autosome of an original amniote that relied upon temperature to determine the sex of offspring. After the mammals separated, the reptile branch further split into Lepidosauria
The Lepidosauria (, from Greek meaning ''scaled lizards'') is a subclass or superorder of reptiles, containing the orders Squamata and Rhynchocephalia. Squamata includes snakes, lizards, and amphisbaenians. Squamata contains over 9,000 species, m ...
and Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizard ...
. These two groups both evolved the ZW system separately, as evidenced by the existence of different sex chromosomal locations. In mammals, one of the autosome pair, now Y, mutated its SOX3
Transcription factor SOX-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOX3'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) family of transcription factors involved in the regulation of embryonic brain development and i ...
gene into the SRY gene, causing that chromosome to designate sex. After this mutation, the SRY-containing chromosome inverted and was no longer completely homologous with its partner. The regions of the X and Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abs ...
s that are still homologous to one another are known as the pseudoautosomal region. Once it inverted, the Y chromosome became unable to remedy deleterious mutations, and thus degenerated. There is some concern that the Y chromosome will shrink further and stop functioning in ten million years: but the Y chromosome has been strictly conserved after its initial rapid gene loss.
There are some vertebrate species, such as the medaka
The Japanese rice fish (''Oryzias latipes''), also known as the medaka, is a member of genus ''Oryzias'' (ricefish), the only genus in the subfamily Oryziinae. This small (up to about ) native of East Asia is a denizen of rice paddies, marshes, ...
fish, that evolved sex chromosomes separately; their Y chromosome never inverted and can still swap genes with the X. These species' sex chromosomes are relatively primitive and unspecialized. Because the Y does not have male-specific genes and can interact with the X, XY and YY females can be formed as well as XX males. Non-inverted Y chromosomes with long histories are found in pythons and emus, each system being more than 120 million years old, suggesting that inversions are not necessarily an eventuality. XO sex determination can evolve from XY sex determination with about 2 million years.
See also
* Clarence Erwin McClung, who discovered the role of chromosomes in sex determination * Testis-determining factor * Maternal influence on sex determination * Sequential hermaphroditism * Sex determination and differentiation (human)References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Sex-Determination System Epigenetics