Seasonal Tropical Forest on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Seasonal tropical forest, also known as moist deciduous, semi-evergreen seasonal, tropical mixed or monsoon forests, typically contain a range of tree species: only some of which drop some or all of their leaves during the dry season. This
Seasonal tropical forest, also known as moist deciduous, semi-evergreen seasonal, tropical mixed or monsoon forests, typically contain a range of tree species: only some of which drop some or all of their leaves during the dry season. This

 Seasonal (mixed) tropical forests can be found in many parts of the tropical zone, with examples found in:
* In the Asia-Pacific region: seasonal forests predominate across large areas of the Eastern Java, Wallacea,
Seasonal (mixed) tropical forests can be found in many parts of the tropical zone, with examples found in:
* In the Asia-Pacific region: seasonal forests predominate across large areas of the Eastern Java, Wallacea,  * In the
* In the

 ** the Upper Guinean forests (West Africa)
* Asia represented by
** the Upper Guinean forests (West Africa)
* Asia represented by
 Seasonal tropical forest, also known as moist deciduous, semi-evergreen seasonal, tropical mixed or monsoon forests, typically contain a range of tree species: only some of which drop some or all of their leaves during the dry season. This
Seasonal tropical forest, also known as moist deciduous, semi-evergreen seasonal, tropical mixed or monsoon forests, typically contain a range of tree species: only some of which drop some or all of their leaves during the dry season. This tropical forest
Tropical forests (a.k.a. jungle) are forested landscapes in tropical regions: ''i.e.'' land areas approximately bounded by the tropic of Cancer and Capricorn, but possibly affected by other factors such as prevailing winds.
Some tropical fore ...
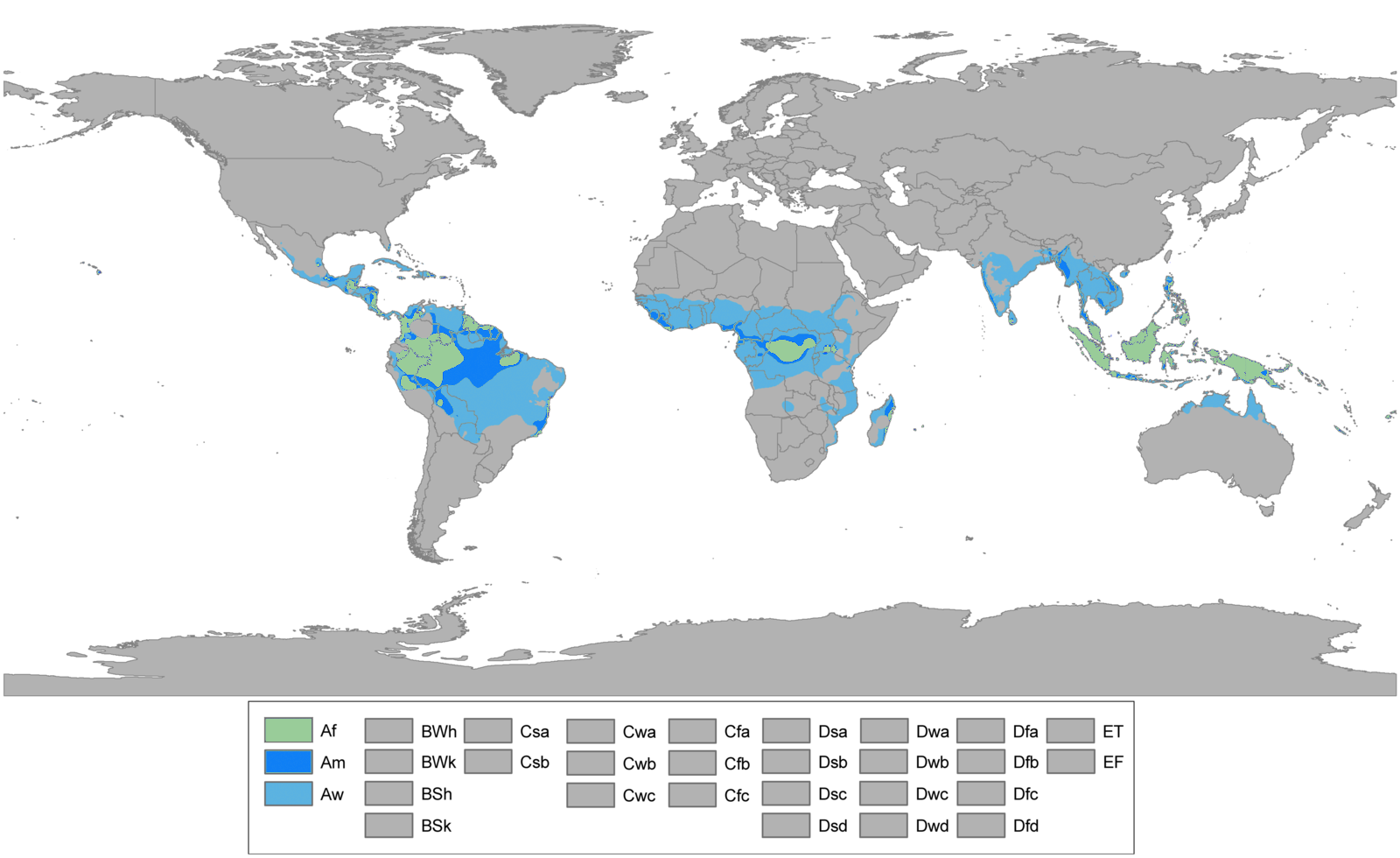
is classified under the Walter system as (i) tropical climate with high overall rainfall (typically in the 1000–2500 mm range; 39–98 inches) and (ii) having a very distinct wet season with (an often cooler “winter”) dry season. These forests represent a range of habitats influenced by monsoon (Am) or tropical wet savannah (Aw) climates (as in the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
). Drier forests in the Aw climate zone are typically deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, ...
and placed in the Tropical dry forest biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
: with further transitional zones ( ecotones) of savannah woodland then tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The biome is dominated by grass and/or shrubs located in semi-arid to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and t ...
.
Distribution

Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
and Indochina
** Eastern Java Monsoon forests
** Wallacea Forest
** Brahmaputra Valley semi-evergreen forests
** Mondulkiri Province, Cambodia
** Cat Tien National Park
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of ...
, Vietnam
** Khao Yai National Park and Huai Kha Khaeng Wildlife Sanctuary, Thailand
** Northern Australia: Cape York Peninsula (Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
), Arnhem Land (Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory shares its borders with Western Aust ...
), The Kimberly (Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
)
 * In the
* In the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
** Atlantic forests of Brazil
** Central and eastern Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
: with Barro Colorado Island
Barro Colorado Island is located in the man-made Gatun Lake in the middle of the Panama Canal. The island was formed when the waters of the Chagres River were dammed to form the lake in 1913. When the waters rose, they covered a significant par ...
especially well studied
* In Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
** Coastal West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
: Guinean seasonal forest: from south-western Gambia to eastern Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
Climate
The climate of seasonal forests is typically controlled by a system called the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), located near the equator and created by the convergence of the trade winds from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The position of these bands vary seasonally, moving north in the northern summer and south in the northern winter, and ultimately controlling the wet and dry seasons in the tropics. These regions appear to have experienced strong warming, at a mean rate of 0.26 degrees Celsius per decade, which coincides with a global rise in temperature resulting from theanthropocentric
Anthropocentrism (; ) is the belief that human beings are the central or most important entity in the universe. The term can be used interchangeably with humanocentrism, and some refer to the concept as human supremacy or human exceptionalism. ...
inputs of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Studies have also found that precipitation has declined and tropical Asia has experienced an increase in dry season intensity whereas Amazonian has no significant pattern change in precipitation or dry season. Additionally, El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events drive the inter-annual climatic variability in temperature and precipitation and result in drought and increased intensity of the dry season. As anthropogenic warming increases the intensity and frequency of ENSO will increase, rendering tropical rainforest regions susceptible to stress and increased mortality of trees and other plants.
Structure
As withtropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equa ...
s there are different canopy layers, but these may be less pronounced in mixed forests, which are often characterised by numerous lianas
A liana is a long- stemmed, woody vine that is rooted in the soil at ground level and uses trees, as well as other means of vertical support, to climb up to the canopy in search of direct sunlight. The word ''liana'' does not refer to a t ...
due to their growth advantage during the dry season.Ya-Jun Chen, Kun-Fang Cao, Stefan A. Schnitzer, Ze-Xin Fan, Jiao-Lin Zhang, Frans Bongers (2015) Water-use advantage of lianas over trees in seasonal tropical forests. ''New Phytologist'', 205 128–136 The colloquial term jungle, derived from the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
word for "forest", has no specific ecological meaning but originally referred to this type of primary and especially secondary forest in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. Determining which strands of mixed forest are primary and secondary can also be problematic, since the species mixture is influenced by factors such as soil depth and climate, as well as human interference.
Characteristic biology
The fauna and flora of seasonal tropical mixed forest are usually distinctive. Examples of thebiodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
and habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
type are often well described for National Parks in:
* Africa represented by:
** the northern part of Korup National Park
Korup National Park is in the Southwest Province of Cameroon and extends over 1,260 km2 of mostly undisturbed primary forest. It is reputedly one of Africa’s oldest and richest tropical forests in terms of floral and faunal diversity. It is ...
in Cameroon (central region)
 ** the Upper Guinean forests (West Africa)
* Asia represented by
** the Upper Guinean forests (West Africa)
* Asia represented by Cat Tien National Park
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of ...
and Huai Kha Khaeng in the ( Indochina region)
* Pacific region
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
: including the Queensland forest reserves
* Central American wildlife is well represented in:
** Costa Rica ''e.g.'' Corcovado National Park
** the Soberanía National Park in Panama.
* South American flora listed and represented in Rio Doce State Park
References
See also
*International Tropical Timber Organization
The International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO) is an intergovernmental organization that promotes conservation of tropical forest resources and their sustainable management, use and trade.
Organization
The organization was established unde ...
(ITTO)
* List of tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregions
This is a list of tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregions, arranged by biogeographic realm.
Afrotropical realm
Australasian realm
Indomalayan realm
Neotropical realm
Oceanian realm
Palearctic realm
{{Paleartic tropical ...
* Trees of the world
* Tropical dry forest
* Tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equa ...
* Tropical vegetation
Tropical vegetation is any vegetation in tropical latitudes. Plant life that occurs in climates that are warm year-round is in general more biologically diverse that in other latitudes. Some tropical areas may receive abundant rain the whole ye ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Seasonal Tropical Forests
Terrestrial biomes
Moist broadleaf forests
Ecoregions
Forests