
Systems engineering is an
interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, economi ...
field of
engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
and
engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage
complex system
A complex system is a system composed of many components that may interact with one another. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communication sy ...
s over their
life cycles. At its core, systems engineering utilizes
systems thinking
Systems thinking is a way of making sense of the complexity of the world by looking at it in terms of wholes and relationships rather than by splitting it down into its parts.Anderson, Virginia, & Johnson, Lauren (1997). ''Systems Thinking Ba ...
principles to organize this
body of knowledge
A body of knowledge (BOK or BoK) is the complete set of concepts, terms and activities that make up a professional domain, as defined by the relevant learned society or professional association.Oliver, G.R. (2012). ''Foundations of the Assumed Bus ...
. The individual outcome of such efforts, an engineered system, can be defined as a combination of components that work in
synergy
Synergy is an interaction or cooperation giving rise to a whole that is greater than the simple sum of its parts (i.e., a non-linear addition of force, energy, or effect). The term ''synergy'' comes from the Attic Greek word συνεργία ' f ...
to collectively perform a useful
function.
Issues such as
requirements engineering
Requirements engineering (RE) is the process of defining, documenting, and maintaining requirements in the engineering design process. It is a common role in systems engineering and software engineering.
The first use of the term ''requiremen ...
,
reliability,
logistics
Logistics is the part of supply chain management that deals with the efficient forward and reverse flow of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the Consumption (economics), point of consumption according to the ...
, coordination of different teams, testing and evaluation, maintainability, and many other
disciplines, aka
"ilities", necessary for successful
system design
The basic study of system design is the understanding of component parts and their subsequent interaction with one another.
Systems design has appeared in a variety of fields, including sustainability, computer/software architecture, and sociolog ...
, development,
implementation
Implementation is the realization of an application, execution of a plan, idea, scientific modelling, model, design, specification, Standardization, standard, algorithm, policy, or the Management, administration or management of a process or Goal ...
, and ultimate decommission become more difficult when dealing with large or complex
project
A project is a type of assignment, typically involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a specific objective.
An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of events: a "set of interrelated tasks to be ...
s. Systems engineering deals with work processes, optimization methods, and
risk management
Risk management is the identification, evaluation, and prioritization of risks, followed by the minimization, monitoring, and control of the impact or probability of those risks occurring. Risks can come from various sources (i.e, Threat (sec ...
tools in such projects. It overlaps technical and human-centered disciplines such as
industrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
,
production systems engineering,
process systems engineering
Process engineering is a field of study focused on the development and optimization of industrial processes. It consists of the understanding and application of the fundamental principles and laws of nature to allow humans to transform raw ma ...
,
mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines and mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and engineering mathematics, mathematics principl ...
,
manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering.
Manufac ...
,
production engineering,
control engineering
Control engineering, also known as control systems engineering and, in some European countries, automation engineering, is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with d ...
,
software engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principl ...
,
electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
,
cybernetics
Cybernetics is the transdisciplinary study of circular causal processes such as feedback and recursion, where the effects of a system's actions (its outputs) return as inputs to that system, influencing subsequent action. It is concerned with ...
,
aerospace engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is s ...
,
organizational studies
Organization studies (also called organization science or organizational studies) is the academic field interested in a ''collective activity, and how it relates to organization, organizing, and management''. It is "the examination of how individ ...
,
civil engineering
Civil engineering is a regulation and licensure in engineering, professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads ...
and
project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
. Systems engineering ensures that all likely aspects of a project or system are considered and integrated into a whole.
The systems engineering process is a discovery process that is quite unlike a
manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
process. A manufacturing process is focused on repetitive activities that achieve high-quality outputs with minimum cost and time. The systems engineering process must begin by discovering the real problems that need to be resolved and identifying the most probable or highest-impact failures that can occur. Systems engineering involves finding solutions to these problems.
History
The term ''systems engineering'' can be traced back to
Bell Telephone Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
in the 1940s. The need to identify and manipulate the properties of a system as a whole, which in complex engineering projects may greatly differ from the sum of the parts' properties, motivated various industries, especially those developing systems for the U.S. military, to apply the discipline.
When it was no longer possible to rely on design evolution to improve upon a system and the existing tools were not sufficient to meet growing demands, new methods began to be developed that addressed the complexity directly. The continuing evolution of systems engineering comprises the development and identification of new methods and modeling techniques. These methods aid in a better comprehension of the design and developmental control of engineering systems as they grow more complex. Popular tools that are often used in the systems engineering context were developed during these times, including
Universal Systems Language (USL),
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly ...
(UML),
Quality function deployment (QFD), and
Integration Definition (IDEF).
In 1990, a professional society for systems engineering, the ''National Council on Systems Engineering'' (NCOSE), was founded by representatives from a number of U.S. corporations and organizations. NCOSE was created to address the need for improvements in systems engineering practices and education. As a result of growing involvement from systems engineers outside of the U.S., the name of the organization was changed to the
International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) in 1995. Schools in several countries offer graduate programs in systems engineering, and
continuing education
Continuing education is the education undertaken after initial education for either personal or professional reasons. The term is used mainly in the United States and Canada.
Recognized forms of post-secondary learning activities within the d ...
options are also available for practicing engineers.
Concept
Systems engineering signifies only an approach and, more recently, a discipline in engineering. The aim of education in systems engineering is to formalize various approaches simply and in doing so, identify new methods and research opportunities similar to that which occurs in other fields of engineering. As an approach, systems engineering is holistic and interdisciplinary in flavor.
Origins and traditional scope
The traditional scope of engineering embraces the conception, design, development, production, and operation of physical systems. Systems engineering, as originally conceived, falls within this scope. "Systems engineering", in this sense of the term, refers to the building of engineering concepts.
Evolution to a broader scope
The use of the term "systems engineer" has evolved over time to embrace a wider, more holistic concept of "systems" and of engineering processes. This evolution of the definition has been a subject of ongoing controversy, and the term continues to apply to both the narrower and a broader scope.
Traditional systems engineering was seen as a branch of engineering in the classical sense, that is, as applied only to physical systems, such as spacecraft and aircraft. More recently, systems engineering has evolved to take on a broader meaning especially when humans were seen as an essential component of a system.
Peter Checkland
Peter Checkland (born 18 December 1930, in Birmingham, UK) is a British management scientist and emeritus professor of systems at Lancaster University. He is the developer of soft systems methodology (SSM): a methodology based on a way of system ...
, for example, captures the broader meaning of systems engineering by stating that 'engineering' "can be read in its general sense; you can engineer a meeting or a political agreement."
Consistent with the broader scope of systems engineering, the
Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK) has defined three types of systems engineering:
* Product Systems Engineering (PSE) is the traditional systems engineering focused on the design of physical systems consisting of hardware and software.
* Enterprise Systems Engineering (ESE) pertains to the view of enterprises, that is, organizations or combinations of organizations, as systems.
* Service Systems Engineering (SSE) has to do with the engineering of service systems. Checkland defines a service system as a system which is conceived as serving another system.
Most civil infrastructure systems are service systems.
Holistic view
Systems engineering focuses on analyzing and
eliciting customer needs and required functionality early in the
development cycle, documenting requirements, then proceeding with design synthesis and system validation while considering the complete problem, the
system lifecycle. This includes fully understanding all of the
stakeholders involved. Oliver et al. claim that the systems engineering process can be decomposed into:
* A ''Systems Engineering Technical Process''
* A ''Systems Engineering Management Process''
Within Oliver's model, the goal of the Management Process is to organize the technical effort in the lifecycle, while the Technical Process includes ''assessing available information'', ''defining effectiveness measures'', to ''create a behavior model'', ''create a structure model'', ''perform trade-off analysis'', and ''create sequential build & test plan''.
Depending on their application, although there are several models that are used in the industry, all of them aim to identify the relation between the various stages mentioned above and incorporate feedback. Examples of such models include the
Waterfall model
The waterfall model is a breakdown of developmental activities into linear sequential phases, meaning that each phase is passed down onto each other, where each phase depends on the deliverables of the previous one and corresponds to a speciali ...
and the
VEE model (also called the V model).
Interdisciplinary field
System development often requires contribution from diverse technical disciplines. By providing a systems (
holistic) view of the development effort, systems engineering helps mold all the technical contributors into a unified team effort, forming a structured development process that proceeds from concept to production to operation and, in some cases, to termination and disposal. In an acquisition, the holistic integrative discipline combines contributions and balances tradeoffs among cost, schedule, and performance while maintaining an acceptable level of risk covering the entire life cycle of the item.
This perspective is often replicated in educational programs, in that systems engineering courses are taught by faculty from other engineering departments, which helps create an interdisciplinary environment.
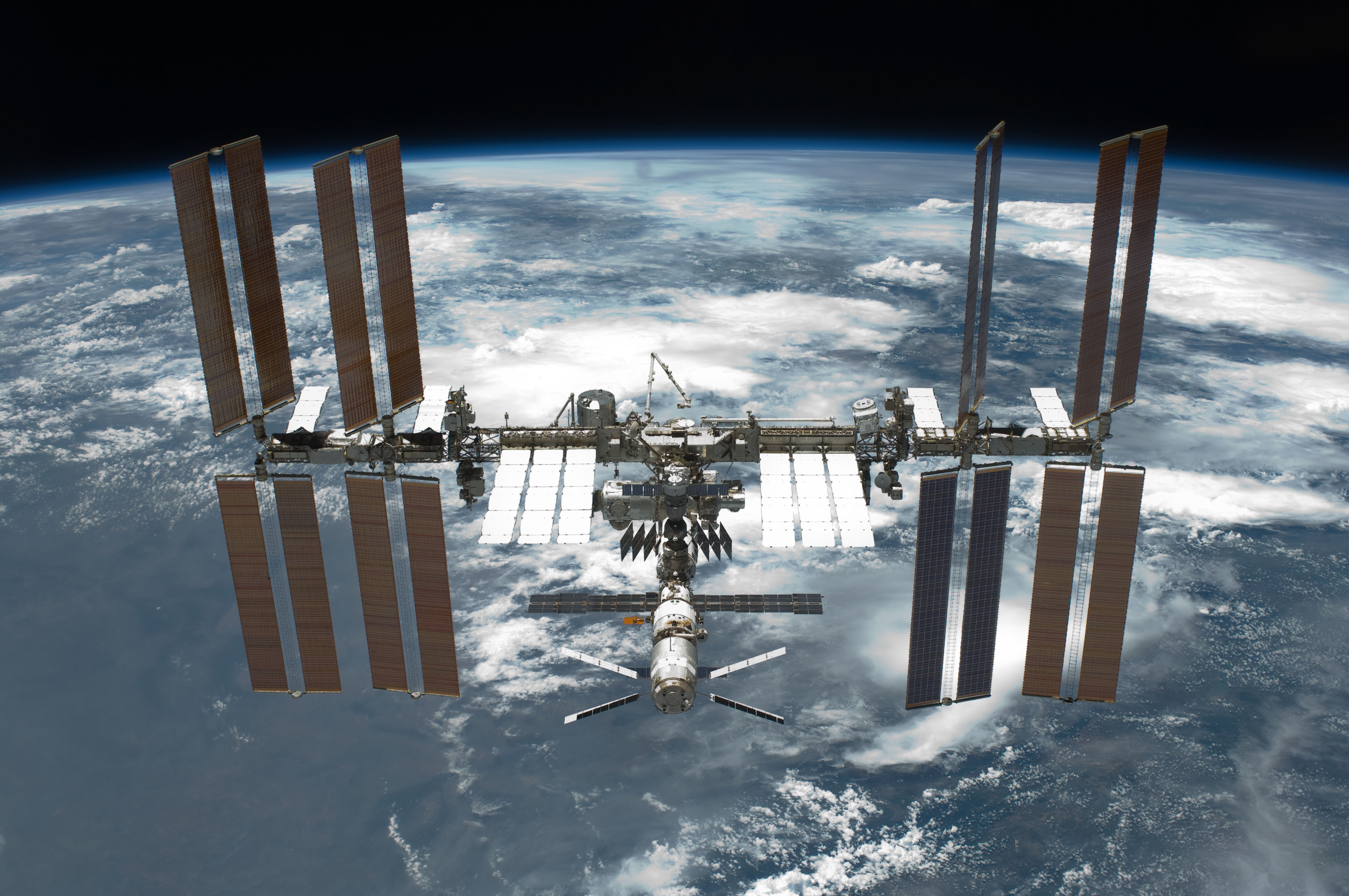
Managing complexity
The need for systems engineering arose with the increase in complexity of systems and projects, in turn exponentially increasing the possibility of component friction, and therefore the unreliability of the design. When speaking in this context, complexity incorporates not only engineering systems but also the logical human organization of data. At the same time, a system can become more complex due to an increase in size as well as with an increase in the amount of data, variables, or the number of fields that are involved in the design. The
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
is an example of such a system.

The development of smarter control
algorithms
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for per ...
,
microprocessor design, and
analysis of environmental systems also come within the purview of systems engineering. Systems engineering encourages the use of tools and methods to better comprehend and manage complexity in systems. Some examples of these tools can be seen here:
* ''
System architecture''
* ''
System model,
modeling, and
simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in ...
''
* ''
Mathematical optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
''
* ''
System dynamics''
* ''
Systems analysis
Systems analysis is "the process of studying a procedure or business to identify its goal and purposes and create systems and procedures that will efficiently achieve them". Another view sees systems analysis as a problem-solving technique that ...
''
* ''
Statistical analysis
Statistical inference is the process of using data analysis to infer properties of an underlying probability distribution.Upton, G., Cook, I. (2008) ''Oxford Dictionary of Statistics'', OUP. . Inferential statistical analysis infers properties of ...
''
* ''
Reliability engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability is defined as the probability that a product, system, or service will perform its intended functi ...
''
* ''
Decision making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be either ra ...
''
Taking an
interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, economi ...
approach to engineering systems is inherently complex since the
behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of Individual, individuals, organisms, systems or Artificial intelligence, artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or or ...
of and interaction among system components is not always immediately
well defined or understood. Defining and characterizing such
system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
s and subsystems and the interactions among them is one of the goals of systems engineering. In doing so, the gap that exists between informal requirements from users,
operators,
marketing
Marketing is the act of acquiring, satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of Business administration, business management and commerce.
Marketing is usually conducted by the seller, typically a retailer or ma ...
organizations, and
technical specifications
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
There are different types of technical or engineering specificati ...
is successfully bridged.
Scope
The principles of systems engineering – holism, emergent behavior, boundary, et al. – can be applied to any system, complex or otherwise, provided
systems thinking
Systems thinking is a way of making sense of the complexity of the world by looking at it in terms of wholes and relationships rather than by splitting it down into its parts.Anderson, Virginia, & Johnson, Lauren (1997). ''Systems Thinking Ba ...
is employed at all levels. Besides defense and aerospace, many information and technology-based companies,
software development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, wri ...
firms, and industries in the field of
electronics & communications require systems engineers as part of their team.
An analysis by the INCOSE Systems Engineering Center of Excellence (SECOE) indicates that optimal effort spent on systems engineering is about 15–20% of the total project effort.
At the same time, studies have shown that systems engineering essentially leads to a reduction in costs among other benefits.
However, no quantitative survey at a larger scale encompassing a wide variety of industries has been conducted until recently. Such studies are underway to determine the effectiveness and quantify the benefits of systems engineering.
Systems engineering encourages the use of
modeling and simulation
Modeling and simulation (M&S) is the use of models (e.g., physical, mathematical, behavioral, or logical representation of a system, entity, phenomenon, or process) as a basis for simulations to develop data utilized for managerial or technica ...
to validate assumptions or theories on systems and the interactions within them.
Use of methods that allow early detection of possible failures, in
safety engineering
Safety engineering is an engineering Branches of science, discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety. It is strongly related to industrial engineering/systems engineering, and the subset system safety en ...
, are integrated into the design process. At the same time, decisions made at the beginning of a project whose consequences are not clearly understood can have enormous implications later in the life of a system, and it is the task of the modern systems engineer to explore these issues and make critical decisions. No method guarantees today's decisions will still be valid when a system goes into service years or decades after first conceived. However, there are techniques that support the process of systems engineering. Examples include soft systems methodology,
Jay Wright Forrester's
System dynamics method, and the
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly ...
(UML)—all currently being explored, evaluated, and developed to support the engineering decision process.
Education
Education in systems engineering is often seen as an extension to the regular engineering courses, reflecting the industry attitude that engineering students need a foundational background in one of the traditional engineering disciplines (e.g.
aerospace engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is s ...
,
civil engineering
Civil engineering is a regulation and licensure in engineering, professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads ...
,
electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
,
mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines and mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and engineering mathematics, mathematics principl ...
,
manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering.
Manufac ...
,
industrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
,
chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of the operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials ...
)—plus practical, real-world experience to be effective as systems engineers. Undergraduate university programs explicitly in systems engineering are growing in number but remain uncommon, the degrees including such material are most often presented as a
BS in Industrial Engineering. Typically programs (either by themselves or in combination with interdisciplinary study) are offered beginning at the graduate level in both academic and professional tracks, resulting in the grant of either a
MS/
MEng or
Ph.D./
EngD degree.
INCOSE, in collaboration with the Systems Engineering Research Center at
Stevens Institute of Technology
Stevens Institute of Technology is a Private university, private research university in Hoboken, New Jersey. Founded in 1870, it is one of the oldest technological universities in the United States and was the first college in America solely de ...
maintains a regularly updated directory of worldwide academic programs at suitably accredited institutions.
As of 2017, it lists over 140 universities in North America offering more than 400 undergraduate and graduate programs in systems engineering. Widespread institutional acknowledgment of the field as a distinct subdiscipline is quite recent; the 2009 edition of the same publication reported the number of such schools and programs at only 80 and 165, respectively.
Education in systems engineering can be taken as ''systems-centric'' or ''domain-centric'':
* ''Systems-centric'' programs treat systems engineering as a separate discipline and most of the courses are taught focusing on systems engineering principles and practice.
* ''Domain-centric'' programs offer systems engineering as an option that can be exercised with another major field in engineering.
Both of these patterns strive to educate the systems engineer who is able to oversee interdisciplinary projects with the depth required of a core engineer.
Systems engineering topics
Systems engineering tools are
strategies, procedures, and
techniques that aid in performing systems engineering on a
project
A project is a type of assignment, typically involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a specific objective.
An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of events: a "set of interrelated tasks to be ...
or
product. The purpose of these tools varies from database management, graphical browsing, simulation, and reasoning, to document production, neutral import/export, and more.
System
There are many definitions of what a
system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
is in the field of systems engineering. Below are a few authoritative definitions:
*
ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organiz ...
/
EIA-632-1999: "An aggregation of end products and enabling products to achieve a given purpose."
*
DAU Systems Engineering Fundamentals: "an integrated composite of people, products, and processes that provide a capability to satisfy a stated need or objective."
*
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE ...
Std 1220-1998: "A set or arrangement of elements and processes that are related and whose behavior satisfies customer/operational needs and provides for life cycle sustainment of the products."
* INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: "homogeneous entity that exhibits predefined behavior in the real world and is composed of heterogeneous parts that do not individually exhibit that behavior and an integrated configuration of components and/or subsystems."
* INCOSE: "A system is a construct or collection of different elements that together produce results not obtainable by the elements alone. The elements, or parts, can include people, hardware, software, facilities, policies, and documents; that is, all things required to produce systems-level results. The results include system-level qualities, properties, characteristics, functions, behavior, and performance. The value added by the system as a whole, beyond that contributed independently by the parts, is primarily created by the relationship among the parts; that is, how they are interconnected."
*
ISO/IEC
ISO/IEC JTC 1, entitled "Information technology", is a joint technical committee (JTC) of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its purpose is to develop, maintain and ...
15288:2008: "A combination of interacting elements organized to achieve one or more stated purposes."
*
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
Systems Engineering Handbook: "(1) The combination of elements that function together to produce the capability to meet a need. The elements include all hardware, software, equipment, facilities, personnel, processes, and procedures needed for this purpose. (2) The end product (which performs operational functions) and enabling products (which provide life-cycle support services to the operational end products) that make up a system."
Systems engineering processes
Systems engineering processes encompass all creative, manual, and technical activities necessary to define the product and which need to be carried out to convert a system definition to a sufficiently detailed system design specification for product manufacture and deployment. Design and development of a system can be divided into four stages, each with different definitions:
* Task definition (informative definition)
* Conceptual stage (cardinal definition)
* Design stage (formative definition)
* Implementation stage (manufacturing definition)
Depending on their application, tools are used for various stages of the systems engineering process:

Using models
Model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , .
Models can be divided in ...
s play important and diverse roles in systems engineering. A model can be defined in several
ways, including:
* An abstraction of reality designed to answer specific questions about the real world
* An imitation, analog, or representation of a real-world process or structure; or
* A conceptual, mathematical, or physical tool to assist a decision-maker.
Together, these definitions are broad enough to encompass physical engineering models used in the verification of a system design, as well as schematic models like a
functional flow block diagram and mathematical (i.e. quantitative) models used in the trade study process. This section focuses on the last.
The main reason for using
mathematical model
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical m ...
s and
diagrams
A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a three- ...
in trade studies is to provide estimates of system effectiveness, performance or technical attributes, and cost from a set of known or estimable quantities. Typically, a collection of separate models is needed to provide all of these outcome variables. The heart of any mathematical model is a set of meaningful quantitative relationships among its inputs and outputs. These relationships can be as simple as adding up constituent quantities to obtain a total, or as complex as a set of
differential equations describing the trajectory of a spacecraft in a
gravitational field
In physics, a gravitational field or gravitational acceleration field is a vector field used to explain the influences that a body extends into the space around itself. A gravitational field is used to explain gravitational phenomena, such as ...
. Ideally, the relationships express causality, not just correlation.
Furthermore, key to successful systems engineering activities are also the methods with which these models are efficiently and effectively managed and used to simulate the systems. However, diverse domains often present recurring problems of modeling and simulation for systems engineering, and new advancements are aiming to cross-fertilize methods among distinct scientific and engineering communities, under the title of 'Modeling & Simulation-based Systems Engineering'.
Modeling formalisms and graphical representations
Initially, when the primary purpose of a systems engineer is to comprehend a complex problem, graphic representations of a system are used to communicate a system's
functional and data requirements. Common graphical representations include:
*
Functional flow block diagram (FFBD)
*
Model-based design
*
Data flow diagram
A data-flow diagram is a way of representing a flow of data through a process or a system (usually an information system). The DFD also provides information about the outputs and inputs of each entity and the process itself. A data-flow diagram ha ...
(DFD)
*
N2 chart
*
IDEF0 diagram
*
Use case diagram
*
Sequence diagram
*
Block diagram
A block diagram is a diagram of a system in which the principal parts or functions are represented by blocks connected by lines that show the relationships of the blocks.
*
Signal-flow graph
A signal-flow graph or signal-flowgraph (SFG), invented by Claude Shannon, but often called a Mason graph after Samuel Jefferson Mason who coined the term, is a specialized Flow graph (mathematics), flow graph, a directed graph in which nodes rep ...
*
USL function maps and type maps
*
Enterprise architecture frameworks
A graphical representation relates the various subsystems or parts of a system through functions, data, or interfaces. Any or each of the above methods is used in an industry based on its requirements. For instance, the N2 chart may be used where interfaces between systems are important. Part of the design phase is to create
structural
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
and
behavioral models of the system.
Once the requirements are understood, it is now the responsibility of a systems engineer to refine them and to determine, along with other engineers, the best technology for a job. At this point starting with a trade study, systems engineering encourages the use of weighted choices to determine the best option. A
decision matrix, or Pugh method, is one way (QFD is another) to make this choice while considering all criteria that are important. The trade study in turn informs the design, which again affects graphic representations of the system (without changing the requirements). In an SE process, this stage represents the iterative step that is carried out until a feasible solution is found. A decision matrix is often populated using techniques such as statistical analysis, reliability analysis, system dynamics (
feedback control), and optimization methods.
Other tools
Systems Modeling Language
Systems Modeling Language (SysML), a modeling language used for systems engineering applications, supports the specification, analysis, design, verification and validation of a broad range of complex systems.
Lifecycle Modeling Language
Lifecycle Modeling Language The Lifecycle Modeling Language (LML) is an open-standard modeling language designed for systems engineering. It supports the full lifecycle: conceptual, utilization, support and retirement stages. Along with the integration of all lifecycle discip ...
(LML), is an open-standard modeling language designed for systems engineering that supports the full lifecycle: conceptual, utilization, support, and retirement stages.
Related fields and sub-fields
Many related fields may be considered tightly coupled to systems engineering. The following areas have contributed to the development of systems engineering as a distinct entity:
Cognitive systems engineering
Cognitive systems engineering (CSE) is a specific approach to the description and analysis of
human-machine systems or
sociotechnical systems
Sociotechnical systems (STS) in organizational development is an approach to complex organizational work design that recognizes the interaction between people and technology in workplaces. The term also refers to coherent systems of human relati ...
. The three main themes of CSE are how humans cope with complexity, how work is accomplished by the use of
artifacts, and how human-machine systems and socio-technical systems can be described as joint cognitive systems. CSE has since its beginning become a recognized scientific discipline, sometimes also referred to as
cognitive engineering. The concept of a Joint Cognitive System (JCS) has in particular become widely used as a way of understanding how complex socio-technical systems can be described with varying degrees of resolution. The more than 20 years of experience with CSE has been described extensively.
Configuration management
Like systems engineering,
configuration management
Configuration management (CM) is a management process for establishing and maintaining consistency of a product's performance, functional, and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life. ...
as practiced in the
defense
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
and
aerospace industry
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astr ...
is a broad systems-level practice. The field parallels the taskings of systems engineering; where systems engineering deals with requirements development, allocation to development items and verification, configuration management deals with requirements capture, traceability to the development item, and audit of development item to ensure that it has achieved the desired functionality and outcomes that systems engineering and/or Test and Verification Engineering have obtained and proven through objective testing.
Control engineering
Control engineering
Control engineering, also known as control systems engineering and, in some European countries, automation engineering, is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with d ...
and its design and implementation of
control systems
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial co ...
, used extensively in nearly every industry, is a large sub-field of systems engineering. The cruise control on an automobile and the guidance system for a ballistic missile are two examples. Control systems theory is an active field of applied mathematics involving the investigation of solution spaces and the development of new methods for the analysis of the control process.
Industrial engineering
Industrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
is a branch of
engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
that concerns the development, improvement, implementation, and evaluation of integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information, equipment, energy, material, and process. Industrial engineering draws upon the principles and methods of engineering analysis and synthesis, as well as mathematical, physical, and social sciences together with the principles and methods of engineering analysis and design to specify, predict, and evaluate results obtained from such systems.
Production Systems Engineering
Production Systems Engineering (PSE) is an emerging branch of Engineering intended to uncover fundamental principles of production systems and utilize them for analysis, continuous improvement, and design.
Interface design
Interface design and its specification are concerned with assuring that the pieces of a system connect and inter-operate with other parts of the system and with external systems as necessary. Interface design also includes assuring that system interfaces are able to accept new features, including mechanical, electrical, and logical interfaces, including reserved wires, plug-space, command codes, and bits in communication protocols. This is known as
extensibility
Extensibility is a software engineering and systems design principle that provides for future growth. Extensibility is a measure of the ability to extend a system and the level of effort required to implement the extension. Extensions can be t ...
.
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) or Human-Machine Interface (HMI) is another aspect of interface design and is a critical aspect of modern systems engineering. Systems engineering principles are applied in the design of
communication protocols for
local area networks
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, campus, or building, and has its network equipment and interconnects locally managed. LANs facilitate the distribution of da ...
and
wide area networks.
Mechatronic engineering
Mechatronic engineering, like systems engineering, is a multidisciplinary field of engineering that uses dynamic systems modeling to express tangible constructs. In that regard, it is almost indistinguishable from Systems Engineering, but what sets it apart is the focus on smaller details rather than larger generalizations and relationships. As such, both fields are distinguished by the scope of their projects rather than the methodology of their practice.
Operations research
Operations research
Operations research () (U.S. Air Force Specialty Code: Operations Analysis), often shortened to the initialism OR, is a branch of applied mathematics that deals with the development and application of analytical methods to improve management and ...
supports systems engineering. Operations research, briefly, is concerned with the optimization of a process under multiple constraints.
Performance engineering
Performance engineering is the discipline of ensuring a system meets customer expectations for performance throughout its life. Performance is usually defined as the speed with which a certain operation is executed or the capability of executing a number of such operations in a unit of time. Performance may be degraded when operations queued to execute are throttled by limited
system capacity. For example, the performance of a
packet-switched network
In telecommunications, packet switching is a method of grouping data into short messages in fixed format, i.e. '' packets,'' that are transmitted over a digital network. Packets consist of a header and a payload. Data in the header is used b ...
is characterized by the end-to-end packet transit delay or the number of packets switched in an hour. The design of high-performance systems uses analytical or simulation modeling, whereas the delivery of high-performance implementation involves thorough performance testing. Performance engineering relies heavily on
statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
,
queueing theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operations research because th ...
, and
probability theory
Probability theory or probability calculus is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expre ...
for its tools and processes.
Program management and project management
Program management
Program management deals with overseeing a group or several projects that align with a company’s organizational strategy, goals, and mission. These Project, projects, are intended to improve an Organizational performance, organization's perfo ...
(or project management) has many similarities with systems engineering, but has broader-based origins than the engineering ones of systems engineering.
Project management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, crea ...
is also closely related to both program management and systems engineering. Both include
scheduling as engineering support tool in assessing interdisciplinary concerns under management process. In particular, the direct relationship of resources, performance features, and risk to the duration of a task or the
dependency links among tasks and impacts across the
system lifecycle are systems engineering concerns.
Proposal engineering
Proposal engineering is the application of scientific and mathematical principles to design, construct, and operate a cost-effective proposal development system. Basically, proposal engineering uses the "
systems engineering process" to create a cost-effective proposal and increase the odds of a successful proposal.
Reliability engineering
Reliability engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability is defined as the probability that a product, system, or service will perform its intended functi ...
is the discipline of ensuring a system meets customer expectations for reliability throughout its life (i.e. it does not fail more frequently than expected). Next to the prediction of failure, it is just as much about the prevention of failure. Reliability engineering applies to all aspects of the system. It is closely associated with
maintainability
Maintainability is the ease of maintaining or providing maintenance for a functioning product or service. Depending on the field, it can have slightly different meanings.
Usage in different fields Engineering
In engineering, maintainability ...
,
availability
In reliability engineering, the term availability has the following meanings:
* The degree to which a system, subsystem or equipment is in a specified operable and committable state at the start of a mission, when the mission is called for at ...
(
dependability or
RAMS
In engineering, reliability, availability, maintainability and safety (RAMS)integrated logistics support
Integrated logistics support (ILS) is a technology in the system engineering to lower a product life cycle cost and decrease demand for logistics by the maintenance (technical), maintenance system optimization to ease the product support. Althoug ...
. Reliability engineering is always a critical component of safety engineering, as in
failure mode and effects analysis
Failure is the social concept of not meeting a desirable or intended Goal, objective, and is usually viewed as the opposite of success. The criteria for failure depends on context, and may be relative to a particular observer or belief system ...
(FMEA) and
hazard fault tree analysis, and of
security engineering
Security engineering is the process of incorporating security controls into an information system so that the controls become an integral part of the system's operational capabilities. It is similar to other systems engineering activities in that ...
.
Risk management
Risk management
Risk management is the identification, evaluation, and prioritization of risks, followed by the minimization, monitoring, and control of the impact or probability of those risks occurring. Risks can come from various sources (i.e, Threat (sec ...
, the practice of assessing and dealing with
risk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environ ...
is one of the interdisciplinary parts of Systems Engineering. In development, acquisition, or operational activities, the inclusion of risk in tradeoffs with cost, schedule, and performance features, involves the iterative complex configuration management of traceability and evaluation to the scheduling and requirements management across domains and for the
system lifecycle that requires the interdisciplinary technical approach of systems engineering. Systems Engineering has Risk Management define, tailor, implement, and monitor a structured process for risk management which is integrated into the overall effort.
Safety engineering
The techniques of
safety engineering
Safety engineering is an engineering Branches of science, discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety. It is strongly related to industrial engineering/systems engineering, and the subset system safety en ...
may be applied by non-specialist engineers in designing complex systems to minimize the probability of safety-critical failures. The "System Safety Engineering" function helps to identify "safety hazards" in emerging designs and may assist with techniques to "mitigate" the effects of (potentially) hazardous conditions that cannot be designed out of systems.
Security engineering
Security engineering
Security engineering is the process of incorporating security controls into an information system so that the controls become an integral part of the system's operational capabilities. It is similar to other systems engineering activities in that ...
can be viewed as an
interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, economi ...
field that integrates the
community of practice
A community of practice (CoP) is a group of people who "share a concern or a passion for something they do and learn how to do it better as they interact regularly". The concept was first proposed by cognitive anthropologist Jean Lave and edu ...
for control systems design, reliability, safety, and systems engineering. It may involve such sub-specialties as
authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with iden ...
of system users, system targets, and others: people, objects, and processes.
Software engineering
From its beginnings,
software engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principl ...
has helped shape modern systems engineering practice. The techniques used in the handling of the complexities of large software-intensive systems have had a major effect on the shaping and reshaping of the tools, methods, and processes of Systems Engineering.
See also
*
Arcadia (engineering)
ARCADIA (Architecture Analysis & Design Integrated Approach) is a Systems engineering, system and Software engineering, software architecture engineering method based on architecture-centric and model-driven engineering activities.
History
In ...
*
Control engineering
Control engineering, also known as control systems engineering and, in some European countries, automation engineering, is an engineering discipline that deals with control systems, applying control theory to design equipment and systems with d ...
*
Design review (U.S. government)
*
Engineering management
*
Engineering information management
*
Enterprise systems engineering
*
Industrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
*
Interdisciplinarity
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, economi ...
*
Life-cycle engineering
*
List of production topics
*
List of requirements engineering tools
*
List of systems engineers
*
List of types of systems engineering
This list of types of systems engineering gives an overview of the types of systems engineering. The #References, reference section gives an overview of major publications in each field and the universities that offer these programs. Universities c ...
*
Management cybernetics
Management cybernetics is concerned with the application of cybernetics to management and organizations. "Management cybernetics" was first introduced by Stafford Beer in the late 1950s and introduces the various mechanisms of agency (philosophy) ...
*
Model-based systems engineering
*
Operations management
Operations management is concerned with designing and controlling the production (economics), production of good (economics), goods and service (economics), services, ensuring that businesses are efficiency, efficient in using resources to meet ...
*
Structured systems analysis and design method
Structured systems analysis and design method (SSADM) is a systems approach to the analysis and design of information systems. SSADM was produced for the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency, a UK government office concerned with the u ...
*
System of systems engineering (SoSE)
*
System accident
*
Systems architecture
A system architecture is the conceptual model that defines the structure, behavior, and view model, views of a system. An architecture description is a formal description and representation of a system, organized in a way that supports reasoning ...
*
Systems development life cycle
In systems engineering, information systems and software engineering, the systems development life cycle (SDLC), also referred to as the application development life cycle, is a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an informati ...
*
Systems thinking
Systems thinking is a way of making sense of the complexity of the world by looking at it in terms of wholes and relationships rather than by splitting it down into its parts.Anderson, Virginia, & Johnson, Lauren (1997). ''Systems Thinking Ba ...
(e.g.
theory of constraints
The theory of constraints (TOC) is a management paradigm that views any manageable system as being limited in achieving more of its goals by a very small number of constraints. There is always at least one constraint, and TOC uses a focusing p ...
,
value-stream mapping)
*
System information modelling
*
Tricotyledon theory of system design
References
Further reading
* Madhavan, Guru (2024). ''Wicked Problems: How to Engineer a Better World''. New York: W.W. Norton & Company.
* Blockley, D. Godfrey, P.
Doing it Differently: Systems for Rethinking Infrastructure, Second Edition', ICE Publications, London, 2017.
* Buede, D.M., Miller, W.D.
', John Wiley and Sons, 2016.
*
Chestnut, H., ''Systems Engineering Methods''. Wiley, 1967.
* Gianni, D. et al. (eds.), ''Modeling and Simulation-Based Systems Engineering Handbook'', CRC Press, 201
at CRC*
Goode, H.H., Robert E. Machol ''System Engineering: An Introduction to the Design of Large-scale Systems'', McGraw-Hill, 1957.
*
Hitchins, D. (1997
''World Class Systems Engineering''at hitchins.net.
* Lienig, J., Bruemmer, H.
''Fundamentals of Electronic Systems Design'' Springer, 2017 .
* Malakooti, B. (2013). Operations and Production Systems with Multiple Objectives. John Wiley & Sons.
* MITRE
The MITRE Systems Engineering Guidepdf
* NASA (2007)
Systems Engineering Handbook
', NASA/SP-2007-6105 Rev1, December 2007.
* NASA (2013)
NASA Systems Engineering Processes and Requirements
'' NPR 7123.1B, April 2013 NASA Procedural Requirements
* Oliver, D.W., et al. ''Engineering Complex Systems with Models and Objects. McGraw-Hill'', 1997.
* Parnell, G.S., Driscoll, P.J., Henderson, D.L. (eds.), ''Decision Making in Systems Engineering and Management'', 2nd. ed., Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2011. This is a textbook for undergraduate students of engineering.
* Ramo, S., St.Clair, R.K. ''The Systems Approach: Fresh Solutions to Complex Problems Through Combining Science and Practical Common Sense'', Anaheim, CA: KNI, Inc, 1998.
* Sage, A.P., ''Systems Engineering''. Wiley IEEE, 1992. .
* Sage, A.P., Olson, S.R., ''Modeling and Simulation in Systems Engineering'', 2001.
* SEBOK.org
Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)
* Shermon, D
''Systems Cost Engineering''
Gower Publishing, 2009
* Shishko, R., et al. (2005)
NASA Systems Engineering Handbook
'. NASA Center for AeroSpace Information, 2005.
* Stevens, R., et al. ''Systems Engineering: Coping with Complexity''. Prentice Hall, 1998.
* US Air Force
SMC Systems Engineering Primer & Handbook
2004
* US DoD Systems Management College (2001)
Systems Engineering Fundamentals
'' Defense Acquisition University Press, 2001
* US Do
Guide for Integrating Systems Engineering into DoD Acquisition Contracts
, 2006
* US Do
MIL-STD-499 System Engineering Management
External links
ICSEng homepage
INCOSE homepage
INCOSE UK homepage
PPI SE Goldmine homepage
Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge
Systems Engineering Tools
AcqNotes DoD Systems Engineering Overview
NDIA Systems Engineering Division
{{Authority control
Engineering disciplines
 Systems engineering is an
Systems engineering is an  The term ''systems engineering'' can be traced back to
The term ''systems engineering'' can be traced back to  The development of smarter control
The development of smarter control 