Sustained Acoustic Medicine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Therapeutic ultrasound refers generally to the use of  In the above applications, the ultrasound passes through human tissue where it is the main source of the observed biological effect (the oscillation of abrasive dental tools at ultrasonic frequencies therefore do not belong to this class). The ultrasound within tissue consists of very high frequency sound waves, between 800,000 Hz and 20,000,000 Hz, which cannot be heard by humans.
Some of the advantages of ultrasound as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool include its safety profile, lack of radiation, portability, and low cost. Therapeutic ultrasound in medicine ranges from
In the above applications, the ultrasound passes through human tissue where it is the main source of the observed biological effect (the oscillation of abrasive dental tools at ultrasonic frequencies therefore do not belong to this class). The ultrasound within tissue consists of very high frequency sound waves, between 800,000 Hz and 20,000,000 Hz, which cannot be heard by humans.
Some of the advantages of ultrasound as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool include its safety profile, lack of radiation, portability, and low cost. Therapeutic ultrasound in medicine ranges from
 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
*
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
* 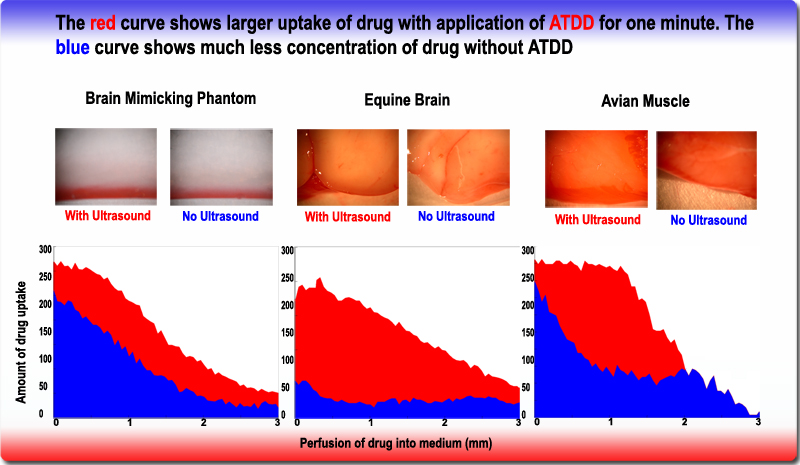 Drug Delivery
* Delivering chemotherapy to brain cancer cells and various drugs to other tissues is called
Drug Delivery
* Delivering chemotherapy to brain cancer cells and various drugs to other tissues is called  Vascular Surgery
* Ultrasound is essential to the procedures of ultrasound-guided
Vascular Surgery
* Ultrasound is essential to the procedures of ultrasound-guided
 Research Tools
*
Research Tools
*
ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
for the treatment of a medical condition or for therapeutic benefit. Physiotherapeutic ultrasound was introduced into clinical practice in the 1950s, with lithotripsy
Lithotripsy is a procedure involving the physical destruction of hardened masses like kidney stones, bezoars or gallstones, which may be done non-invasively. The term is derived from the Greek words meaning "breaking (or pulverizing) stones" ( lit ...
introduced in the 1980s. Other uses of ultrasound for therapeutic benefit are at various stages in transitioning from research to clinical use and include: high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), targeted ultrasound drug delivery, trans-dermal ultrasound drug delivery, ultrasound hemostasis
In biology, hemostasis or haemostasis is a process to prevent and stop bleeding, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel (the opposite of hemostasis is hemorrhage). It is the first stage of wound healing. Hemostasis involves three ...
, cancer therapy
Cancer treatments are a wide range of treatments available for the many different types of cancer, with each cancer type needing its own specific treatment. Treatments can include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targe ...
, and ultrasound assisted thrombolysis
Thrombolysis, also called fibrinolytic therapy, is the breakdown (lysis) of thrombus, blood clots formed in blood vessels, using medication. It is used in ST elevation myocardial infarction, stroke, and in cases of severe venous thromboembolism ( ...
Ultrasound used for therapeutic benefit often use focused ultrasound waves, however, unfocused ultrasound waves may also be used.
 In the above applications, the ultrasound passes through human tissue where it is the main source of the observed biological effect (the oscillation of abrasive dental tools at ultrasonic frequencies therefore do not belong to this class). The ultrasound within tissue consists of very high frequency sound waves, between 800,000 Hz and 20,000,000 Hz, which cannot be heard by humans.
Some of the advantages of ultrasound as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool include its safety profile, lack of radiation, portability, and low cost. Therapeutic ultrasound in medicine ranges from
In the above applications, the ultrasound passes through human tissue where it is the main source of the observed biological effect (the oscillation of abrasive dental tools at ultrasonic frequencies therefore do not belong to this class). The ultrasound within tissue consists of very high frequency sound waves, between 800,000 Hz and 20,000,000 Hz, which cannot be heard by humans.
Some of the advantages of ultrasound as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool include its safety profile, lack of radiation, portability, and low cost. Therapeutic ultrasound in medicine ranges from extracorporeal shockwave therapy
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a treatment using powerful acoustic pulses which is mostly used to treat kidney stones and in physical therapy and orthopedics.
Medical uses
The most common use of extracorporeal shockwave therapy ...
for the breaking of renal calculi
Kidney stone disease (known as nephrolithiasis, renal calculus disease, or urolithiasis) is a crystallopathy and occurs when there are too many minerals in the urine and not enough liquid or hydration. This imbalance causes tiny pieces of cry ...
to HIFU
High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), or MR-guided focused ultrasound surgery (MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation), is an incisionless therapeutic technique that uses non-ionizing ultrasonic waves to heat or ablate tissue. HIFU can be us ...
in which tumors are ablated. In the research field, use of ultrasound is being explored as a mechanism of enhancing drug delivery, sorting particles, and measuring properties of tissue. In physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
, there is some evidence that ultrasound is more effective than placebo treatment for treating patients with arthritis pain, a range of musculoskeletal injuries and for promoting tissue healing.
Medical uses
Relatively high-energy ultrasound can break up stony deposits, ablate tissue, accelerate the effect of drugs in a targeted area, assist in the measurement of the elastic properties of tissue, and sort cells or small particles for research. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
*
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
* Extracorporeal shockwave therapy
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a treatment using powerful acoustic pulses which is mostly used to treat kidney stones and in physical therapy and orthopedics.
Medical uses
The most common use of extracorporeal shockwave therapy ...
involves focused, high-energy ultrasound pulses that can be used to break solid masses into fragments. This is often utilized to break up calculi such as kidney stones and gallstones into pieces small enough to be passed from the body without undue difficulty, a procedure known as lithotripsy
Lithotripsy is a procedure involving the physical destruction of hardened masses like kidney stones, bezoars or gallstones, which may be done non-invasively. The term is derived from the Greek words meaning "breaking (or pulverizing) stones" ( lit ...
. The success of lithotripsy depends on the size and location of the stone, and the patient's age.
Oncology
* Ultrasound can ablate
Ablation ( – removal) is the removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosive processes, or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, including spacecraft material for ascent and ...
tumors or other tissue non-invasively. This is accomplished using a technique known as high intensity focused ultrasound
High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), or MR-guided focused ultrasound surgery (MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation), is an incisionless therapeutic technique that uses non-ionizing ultrasonic waves to heat or ablate tissue. HIFU can be u ...
(HIFU), also called ''focused ultrasound surgery''. This procedure uses generally lower frequencies than medical diagnostic ultrasound (250–2000 kHz), but significantly higher time-averaged intensities. The treatment is often guided by magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI); the combination is then referred to as ''magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound''. In the clinical setting, HIFU techniques are currently being investigated to treat liver, kidney, and prostatic tumors.
Ophthalmology
* Focused ultrasound sources may be used for cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or ...
treatment by phacoemulsification
Phacoemulsification is a cataract surgery method in which the internal lens of the eye which has developed a cataract is emulsified with the tip of an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye. Aspirated fluids are replaced with irrigation ...
in which the internal lens of the eye is broken down into small pieces that may then be aspirated. HIFU can also be used in ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a ...
to treat glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of ...
. This is accomplished by targeting the ultrasound beams to ablate the ciliary body
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary ...
.
 Drug Delivery
* Delivering chemotherapy to brain cancer cells and various drugs to other tissues is called
Drug Delivery
* Delivering chemotherapy to brain cancer cells and various drugs to other tissues is called acoustic targeted drug delivery
Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) is a noninvasive treatment, often used for tumor irradiation, that utilizes a sonosensitizer and the deep penetration of ultrasound to treat lesions of varying depths by reducing target cell number and preventing future t ...
. These procedures generally use high frequency ultrasound (1–10 MHz) and a range of intensities (0–20 W/cm2). The acoustic energy is focused on the tissue of interest to agitate the cellular matrix and make it more permeable for therapeutic drugs.
* Ultrasound has been used to trigger the release of anti-cancer drugs from delivery vectors including liposomes, polymeric microspheres and self-assembled polymeric.
* Phonophoresis
Sonophoresis also known as phonophoresis, is a method that utilizes ultrasound to enhance the delivery of topical medications through the stratum corneum, to the epidermis and dermis. Sonophoresis allows for the enhancement of the permeability of t ...
is a form of soft tissue treatment that involves the use of ultrasound combined with medication gels to enhance drug delivery to the desired area.
 Vascular Surgery
* Ultrasound is essential to the procedures of ultrasound-guided
Vascular Surgery
* Ultrasound is essential to the procedures of ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy (the word reflects the Greek ''skleros'', meaning ''hard'')
is a procedure used to treat blood vessel malformations ( vascular malformations) and also malformations of the lymphatic system. A medication is injected into the vessels ...
and endovenous laser treatment
Endovenous laser treatment (ELT) is a minimally invasive ultrasound-guided technique used for treating varicose veins using laser energy commonly performed by a phlebologist, interventional radiologist or vascular surgeon.
Methods
Endovenous las ...
for the non-surgical treatment of varicose veins. Ultrasound-guided sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy (the word reflects the Greek ''skleros'', meaning ''hard'')
is a procedure used to treat blood vessel malformations ( vascular malformations) and also malformations of the lymphatic system. A medication is injected into the vessels ...
techniques are also used to treat ovarian endometriomas, especially for patients who are pregnant.
Plastic Surgery
* Ultrasound-assisted lipectomy involves the use of ultrasound to aid in removal of subcutaneous fat
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and ...
during liposuction
Liposuction, or simply lipo, is a type of fat-removal procedure used in plastic surgery. Evidence does not support an effect on weight beyond a couple of months and does not appear to affect obesity-related problems. In the United States, lip ...
procedures. Highly focused ultrasound waves are used to emulsify fat cells and allow for easier removal with suction.
History
The first large scale application of ultrasound was around World War II. Sonar systems were being built and used to navigate submarines. It was realized that the high intensity ultrasound waves that they were using were heating and killing fish. This led to research in tissue heating and healing effects. Since the 1940s, ultrasound has been used by physical and occupational therapists for therapeutic effects.Physical therapy
Ultrasound is applied using a transducer or applicator that is in direct contact with the patient's skin. Gel is used on all surfaces of the head to reduce friction and assist transmission of the ultrasonic waves. Therapeutic ultrasound in physical therapy is alternatingcompression
Compression may refer to:
Physical science
*Compression (physics), size reduction due to forces
*Compression member, a structural element such as a column
*Compressibility, susceptibility to compression
* Gas compression
*Compression ratio, of a ...
and rarefaction
Rarefaction is the reduction of an item's density, the opposite of compression. Like compression, which can travel in waves (sound waves, for instance), rarefaction waves also exist in nature. A common rarefaction wave is the area of low relati ...
of sound waves with a frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
of 0.7 to 3.3 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base u ...
. Maximum energy absorption in soft tissue
Soft tissue connective tissue, connects and surrounds or supports internal organs and bones, and includes muscle, tendons, ligaments, Adipose tissue, fat, fibrous tissue, Lymphatic vessel, lymph and blood vessels, fasciae, and synovial membranes.� ...
occurs from 2 to 5 cm. Intensity decreases as the waves penetrate deeper. They are absorbed primarily by connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
: ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
s, tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue, dense fibrous connective tissue that connects skeletal muscle, muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tensi ...
s, and fascia
A fascia (; : fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; ) is a generic term for macroscopic membranous bodily structures. Fasciae are classified as superficial, visceral or deep, and further designated according to their anatomical location.
...
(and also by scar tissue
"Scar Tissue" is the first single from American rock band Red Hot Chili Peppers' seventh studio album, ''Californication'' (1999). Released on May 25, 1999, the song spent a then-record 16 consecutive weeks atop the US ''Billboard'' Hot Modern R ...
).
Ultrasound has been used to help physical therapists navigate transcutaneous modalities that aim to stimulate specific muscles beneath the skin; modalities such as dry needling
Dry needling, also known as trigger point dry needling and intramuscular stimulation, is a treatment technique used by various healthcare practitioners, including physical therapists, physicians, and chiropractors, among others. Acupuncturists us ...
and acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientif ...
. The use of ultrasound provides a way for physical therapists to better locate superficial musculature. Conditions for which ultrasound may be used for treatment include the following examples: ligament sprain
A sprain is a soft tissue injury of the ligaments within a joint, often caused by a sudden movement abruptly forcing the joint to exceed its functional range of motion. Ligaments are tough, inelastic fibers made of collagen that connect two or ...
s, muscle strains, tendonitis
Tendinopathy is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder ( rotator cuff tendinitis, biceps tendinitis), elbow ( tenn ...
, joint inflammation, plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis or plantar heel pain is a disorder of the plantar fascia, which is the connective tissue that supports the Arches of the foot, arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and Sole (foot), bottom of the foot that is usuall ...
, metatarsalgia
Metatarsalgia, literally 'metatarsal pain' and colloquially known as a stone bruise, is any painful foot condition affecting the metatarsal region of the foot. This is a common problem that can affect the joints and bones of the metatarsals.
Me ...
, facet irritation, impingement syndrome
Shoulder impingement syndrome is a syndrome involving tendonitis (inflammation of tendons) of the rotator cuff muscles as they pass through the subacromial space, the passage beneath the acromion. It is particularly associated with tendonitis of t ...
, bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae (synovial sacs) of synovial fluid in the body. They are lined with a synovial membrane that secretes a lubricating synovial fluid. There are more than 150 bursae in the human body. The bursae (bu ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
, and scar tissue adhesion. There is no evidence to support the use of ultrasound for the treatment of low back pain, and current clinical guidelines recommend that ultrasound is not used for this condition. In a critical review, it was demonstrated that therapeutic ultrasound was effective in improving pain, function, and cartilage repair in knee osteoarthritis. Another systematic review and meta-analysis of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on knee osteoarthritis demonstrated a significant effect on pain reduction and knee functional recovery. Ultrasound used for calcific tendonitis had a positive short term effect. For the long term, there was no significant difference with ultrasound use. This shows that for pain relief and short-term treatment ultrasound can be an effective treatment for Calcific Tendonitis A review with five small placebo‐controlled trials from 2011, did not support the use of ultrasound in the treatment of acute ankle sprains and the potential treatment effects of ultrasound appear to be generally small and of probably of limited clinical importance, especially in the context of the usually short‐term recovery period for these injuries. However, therapeutic ultrasound is reported to have beneficial effects in sports injuries pain relief, edema control, and range of joint motion, possibly by increasing pain thresholds, collagen extensibility, reducing edema, and therefore inflammation, muscle spasms, and joint stiffness. A meta-analysis found that ultrasound therapy is effective in reducing pain, increasing ROM, and reducing WOMAC functional scores in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
There are three potential therapeutic mechanisms of ultrasound in physical therapy. The first is the increase in blood flow in the treated area. The second is the decrease in pain from the reduction of swelling and edema. The third is the gentle massage of muscle tendons and ligaments in the treated area because no strain is added and existing scar tissue may be softened with ultrasound. These three benefits are achieved by two main effects of therapeutic ultrasound: thermal and non-thermal effects. Thermal effects are due to the absorption
Absorption may refer to:
Chemistry and biology
*Absorption (biology), digestion
**Absorption (small intestine)
*Absorption (chemistry), diffusion of particles of gas or liquid into liquid or solid materials
*Absorption (skin), a route by which su ...
of the sound waves and result in heating of biological tissue. Non-thermal effects are from cavitation
Cavitation in fluid mechanics and engineering normally is the phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapor pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When sub ...
, microstreaming and acoustic streaming.
Cavitation
Cavitation in fluid mechanics and engineering normally is the phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapor pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When sub ...
is the main non-thermal effect of therapeutic ultrasound. Cavitation results from the vibration of tissue causing microscopic bubbles to form. These microscopic bubbles may directly stimulate cell membranes and cause shockwaves within the tissue. This physical stimulation appears to enhance the cell-repair effects of the inflammatory response.
Knee osteoarthritis
According to recent research, therapeutic ultrasound has not shown any significant improvement for chronic low back pain, chronic neck pain, and hip pain in combination with other physiotherapeutic techniques. However, the most conclusive evidence to support therapeutic ultrasound use is seen with its use in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Knee osteoarthritis affects approximately 250 million people worldwide. While there is no known cure, therapeutic regimens are often used to intervene with the diseases chronic symptoms. In a systematic review of 15 studies, patients who received ultrasound treatments were compared to those who received a placebo treatment. The evidence demonstrated that therapeutic ultrasound significantly relieved pain, increases range of motion, and reduced WOMAC functional scores in patients with knee osteoarthritis when compared to the placebo group. In a separate meta-analysis, it reinforced the use of therapeutic ultrasound by deeming it as a safe non-pharmalogical treatment option that may provide additional pain relief as well as functional improvement when used secondarily to therapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis.Use of Ultrasound in Research
 Research Tools
*
Research Tools
* Acoustic tweezers
Acoustic tweezers (also known as acoustical tweezers) are a set of tools that use sound waves to manipulate the position and movement of very small objects. Strictly speaking, only a single-beam based configuration can be called acoustical tweeze ...
is an emerging tool for contactless separation, concentration and manipulation of microparticles and biological cells
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning ...
, using ultrasound in the low MHz range to form standing wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect t ...
s. This is based on the acoustic radiation force which causes particles to be attracted to either the or anti-nodes of the standing wave depending on the acoustic contrast factor
In acoustics, the acoustic contrast factor is a number that describes the relationship between the densities and the sound velocities of two media, or equivalently (because of the form of the expression), the relationship between the densities a ...
, which is a function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-orie ...
of the sound velocities and densities
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be use ...
of the particle and of the medium in which the particle is immersed.
*Application of focused ultrasound in conjunction with microbubbles has been shown to enable non-invasive delivery of epirubicin
Epirubicin is an anthracycline drug used for chemotherapy. It can be used in combination with other medications to treat breast cancer in patients who have had surgery to remove the tumor. It is marketed by Pfizer under the trade name Ellence in ...
across the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
in mouse models and non-invasive delivery of GABA in non human primates.
Biophysical Effects of Ultrasound
* Using ultrasound to generate cellular effects in soft tissue has fallen out of favor as research has shown a lack of efficacy and a lack of scientific basis for proposed biophysical effects.
*According to a 2017 meta-analysis and associated practice guideline, low intensity pulsed ultrasound
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) is a technology that can be used for therapeutic purposes. It exploits low intensity and pulsed mechanical waves in order to induce regenerative and anti-inflammatory effects on biological tissues, such as ...
should no longer been used for bone regeneration because high quality clinical studies failed to demonstrate a clinical benefit.
Enhancing Drug Delivery
* An additional effect of low-intensity ultrasound could be its potential to disrupt the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system ...
for drug delivery.
* Transcranial ultrasound is being tested for use in aiding tissue plasminogen activator
Tissue-type plasminogen activator, short name tPA, is a protein that facilitates the breakdown of blood clots. It acts as an enzyme to convert plasminogen into its active form plasmin, the major enzyme responsible for clot breakdown. It is a s ...
treatment in stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
patients in the procedure called ultrasound-enhanced systemic thrombolysis
Ultrasound enhanced systemic thrombolysis (UEST), also known as sonothrombolysis, is a method that uses ultrasound waves to mechanically break the thrombi, or clots, using the vibration carried via soundwaves. One major advantage of using ultraso ...
.
* Ultrasound has been shown to act synergistically with antibiotics in killing bacteria.
Musculoskeletal Research
* Long-duration therapeutic ultrasound called sustained acoustic medicine is a daily slow-release therapy that can be applied to increase local circulation and theoretically accelerates healing of musculoskeletal tissues after an injury. However, there is some evidence to suggest this may not be effective.
* Ultrasound has been shown to contribute to improvement of muscular strength of the forearm muscles and humerus muscles and an increase in range of motion in the elbow joint in flexion and outward rotation when accompanied with therapeutic exercise as well as a reduction in pain in men ages 30–40 with tendinitis
See also
* Home ultrasound * LILFUReferences
External links
* * * {{Authority control Medical ultrasonography Athletic training