Sustainable Development Goal 11 (SDG 11 or Global Goal 11), titled "
sustainable cities and communities", is one of
17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the
United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; , AGNU or AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as its main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ. Currently in its Seventy-ninth session of th ...
in 2015. The official mission of SDG 11 is to "Make cities inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable".
[Shaurya And Ansh United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development]
A/RES/71/313
The 17 SDGs take into account that action in one area will affect outcomes in other areas as well, and that
development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development (music), the process by which thematic material is reshaped
* Photographic development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
* Development hell, when a proje ...
must balance
social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives fro ...
, economic and
environmental sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): env ...
.
SDG 11 has 10 targets to be achieved, and this is being measured with 15 indicators. The seven ''outcome targets'' include safe and affordable housing, affordable and
sustainable transport
Sustainable transport is transportation sustainability, sustainable in terms of their social and Environmental issue, environmental impacts. Components for evaluating sustainability include the particular vehicles used; the source of energy; and ...
systems, inclusive and sustainable urbanization, protection of the world's
cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
and
natural heritage
Natural heritage refers to the sum total of the elements of biodiversity, includes flora and fauna, ecosystems and geological structures. It forms part of our natural resources.
Definition
Definitions:
* Natural heritage refers to natural feat ...
, reduction of the adverse effects of
natural disaster
A natural disaster is the very harmful impact on a society or community brought by natural phenomenon or Hazard#Natural hazard, hazard. Some examples of natural hazards include avalanches, droughts, earthquakes, floods, heat waves, landslides ...
s, reduction of the
environmental impacts of cities and to provide access to safe and inclusive green and public spaces. The three ''means of implementation targets
[ Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License]'' include strong national and regional development planning, implementing policies for inclusion,
resource efficiency Resource efficiency is the maximising of the supply of money, materials, staff, and other assets that can be drawn on by a person or organization in order to function effectively, with minimum wasted (natural) resource expenses. It means using the ...
, and
disaster risk reduction Disaster risk reduction aims to make disasters less likely to happen. The approach, also called DRR or disaster risk management, also aims to make disasters less damaging when they do occur. DRR aims to make communities stronger and better prepared ...
in supporting the
least developed countries
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed b ...
in sustainable and resilient building.
3.9 billion people—half of the world's population—currently live in cities globally. It is projected that 5 billion people will live in cities by 2030. Cities across the world occupy just 3 percent of the Earth's land, yet account for 60–80 percent of
energy consumption
Energy consumption is the amount of energy used.
Biology
In the body, energy consumption is part of energy homeostasis. It derived from food energy. Energy consumption in the body is a product of the basal metabolic rate and the physical acti ...
and 75 percent of
carbon emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
. There are serious challenges for the viability and safety of cities to meet increased future demands.
Background
SDG 11 addresses slums, human settlement management and planning, climate change mitigation and adaptation, and urban economies. Prior to the adoption of the 2030 Agenda,
Millennium Development Goal 7, target 4, called for efforts to achieve a "significant improvement in the lives of at least 100 million slum dwellers" by 2020.
There has been a rapid growth of
mega-cities, especially in the developing world: "In 1990, there were ten mega-cities with 10 million inhabitants or more, and in 2014, there were 28 mega-cities, home to a total of 453 million people".
With regards to slums, data shows that "828 million people live in slums today and most them are found in Eastern and South-Eastern Asia".
SDG 11 represents "a shift in international development cooperation from a focus on poverty as a rural phenomenon to recognizing that cities, especially in the global south, are facing major challenges with extreme poverty, environmental degradation and risks due to climate change and natural disasters".
Targets, indicators and progress
The UN has defined 10 targets and 15 indicators for SDG 11.
Targets specify the goals, and indicators represent the metrics by which the world aims to track whether these targets are achieved. Six of them are to be achieved by the year 2030 and one by the year 2020 and three have no target years. Each of the targets also has one or two indicators which will be used to measure progress.
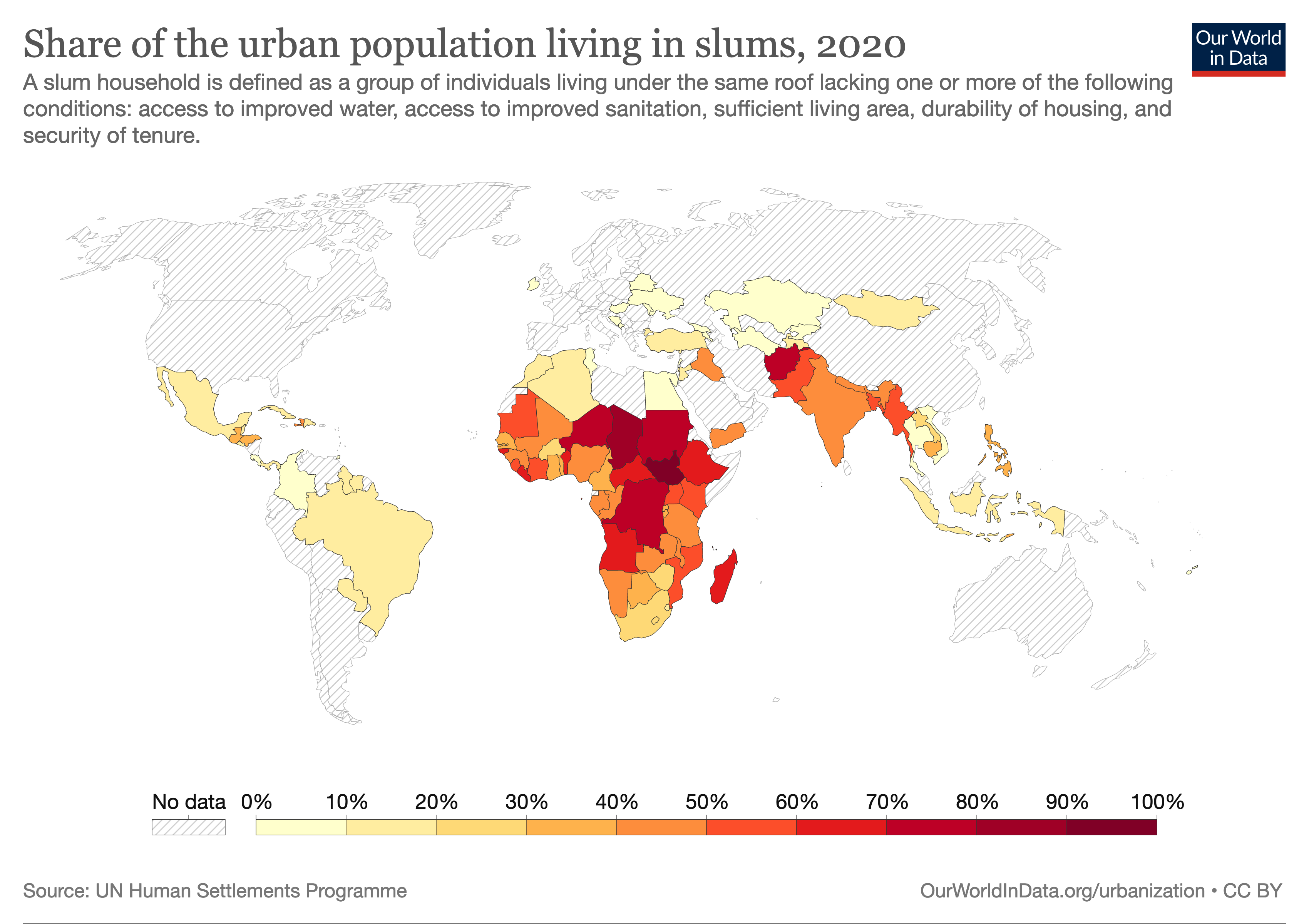
Target 11.1: Safe and affordable housing
The full title of Target 11.1 is "By 2030, ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services and upgrade slums".
This target has one Indicator: Indicator 11.1.1 is the "Proportion of the
urban population
An urban area is a human settlement with a high population density and an infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas originate through urbanization, and researchers categorize them as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbani ...
living in slum households".
People who live in slums have no access to
improved water, access to
improved sanitation, sufficient living area, and durable housing.
There are currently (in 2022) about 1 billion people living in urban slums.
Target 11.2: Affordable and sustainable transport systems

The full text of Target 11.2 is "By 2030, provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all, improving road safety, notably by expanding public transport, with special attention to the needs of those in vulnerable situations, women, children, persons with disabilities and older persons".
This target has one Indicator: Indicator 11.2.1 is the "Proportion of population that has convenient access to public transport, by sex, age and
Persons With Disabilities".
Improving transport systems to refine the use of accessibility is key because due to physical or mental disabilities, impaired sight or hearing, carrying heavy bags or traveling with small children, as this causes an average of 25% of the population to experience a degree of reduced mobility.
A sustainable transportation system considers different socioeconomic groups' travel concerns to achieve the validity of accessibility metrics. Transportation and transportation planning should be coordinated with land use planning. Employment and residential areas are relatively concentrated, and urban and suburban settings should be planned and reconstructed in concert.
Target 11.3: Inclusive and sustainable urbanization
The full-text Target 11.3 is "By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory, integrated and sustainable human settlement planning and management in all countries".
The target has two indicators:
* Indicator 11.3.1: "Ratio of land consumption rate to the population growth rate"
* Indicator 11.3.2: "Proportion of cities with a direct participation structure of civil society in
urban planning
Urban planning (also called city planning in some contexts) is the process of developing and designing land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportatio ...
and management that operate regularly and democratically"
Indicator 11.3.2 may be challenging to calculate. There is currently no data available for this indicator.

Target 11.4: Protect the world's cultural and natural heritage
The full text of Target 11.4 is "Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world's
cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
and
natural heritage
Natural heritage refers to the sum total of the elements of biodiversity, includes flora and fauna, ecosystems and geological structures. It forms part of our natural resources.
Definition
Definitions:
* Natural heritage refers to natural feat ...
."
It has one indicator: Indicator 11.4.1 is the "Total per capita expenditure on the preservation, protection and conservation of all cultural and natural heritage, by the source of funding (public, private), type of heritage (cultural, natural) and level of government (national, regional, and local/municipal)".
This indicator is difficult to calculate. There are currently no data available for this indicator.
Due to civil wars, more than half of the In Danger WHSs are located in war zones in Afghanistan, Congo, Iraq, Libya, Mali, Palestine, Syria, and Yemen. The modern era sees never-ending civil wars in several developing countries, acts of vandalism at cultural sites committed by terrorists and warlords, threats to destroy Iranian cultural heritage sites by US President Donald Trump, a change of identity of a WHS (Hagia Sophia) by the Turkish government, deforestation, rapid climate change, out-of-control urbanization, and tourism mismanagement by governments which leads to
overtourism
Overtourism is congestion or overcrowding from an excess of tourists, resulting in conflicts with locals. The World Tourism Organization defines overtourism as "the impact of tourism on a destination, or parts thereof, that excessively influ ...
and hyper-exploitation of tourism resources. Because these problems exist, this target has become more prominent than ever.
Target 11.5: Reduce the adverse effects of natural disasters



The full text of Target 11.5 is "By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected and substantially decrease the direct economic losses relative to global gross domestic product caused by
disaster
A disaster is an event that causes serious harm to people, buildings, economies, or the environment, and the affected community cannot handle it alone. '' Natural disasters'' like avalanches, floods, earthquakes, and wildfires are caused by na ...
s, including water-related disasters, with a focus on protecting the poor and people in vulnerable situations".
Indicators are:
* Indicator 11.5.1: "Number of deaths, missing persons and directly affected persons attributed to disasters per 100,000 population. Indicators measured here report mortality rates internally displaced persons, missing persons and total numbers affected by natural disasters"
* Indicator 11.5.2: "Direct economic loss in relation to global GDP, damage to critical infrastructure and the number of disruptions to basic services, attributed to disasters."
Target 11.6: Reduce the environmental impacts of cities

The full text of Target 11.6 is "By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management."
The target has two indicators:
* Indicator 11.6.1: Proportion of municipal solid waste collected and managed in controlled facilities out of total municipal waste generated, by cities
* Indicator 11.6.2: "Annual mean levels of fine particulate matter (e.g.
PM2.5 and PM
10) in cities (population weighted)"
Target 11.7: Provide access to safe and inclusive green and public spaces
The full text of Target 11.7 is: "By 2030, provide universal access to safe, inclusive and accessible, green and public spaces, in particular for women and children, older persons and
Persons With Disabilities"
The two indicators include:
* The Indicator 11.7.1: "Average share of the built-up area of cities that is open space for public use for all, by sex, age and persons with disabilities"
* The Indicator 11.7.2: "Proportion of person victim of physical or
sexual harassment
Sexual harassment is a type of harassment based on the sex or gender of a victim. It can involve offensive sexist or sexual behavior, verbal or physical actions, up to bribery, coercion, and assault. Harassment may be explicit or implicit, wit ...
, by sex, age, disability status and place of occurrence, in the previous 12 months"
Target 11.a: Strong national and regional development planning
The full text of Target 11.a is "Support positive economic, social and environmental links between urban,
peri-urban and rural areas by strengthening national and regional development planning".
It has one indicator: Indicator 11.a.1 is the "Number of countries that have national urban policies or regional development plans that (a) respond to population dynamics; (b) ensure balanced territorial development, and (c) increase local fiscal space."
This indicator is "one of the key metrics to benchmark and monitor urbanization".
[UN-Habitat (2018)]
SDG Indicator 11.a.1 Training Module: National Urban Policy
United Nations Human Settlement Programme (UN-Habitat), Nairobi. However, there is currently no data available for this indicator.
The New Urban Agenda was adopted by world leaders in 2016 and provides a series of standards for sustainable urban development.
Target 11.b: Implement policies for inclusion, resource efficiency and disaster risk reduction
The full text of Target 11.b is "By 2020, substantially increase the number of cities and human settlements adopting and implementing integrated policies and plans towards inclusion,
resource efficiency Resource efficiency is the maximising of the supply of money, materials, staff, and other assets that can be drawn on by a person or organization in order to function effectively, with minimum wasted (natural) resource expenses. It means using the ...
, mitigation and
adaptation to climate change, resilience to disasters, and develop and implement, in line with the Sendai Framework for
Disaster risk reduction Disaster risk reduction aims to make disasters less likely to happen. The approach, also called DRR or disaster risk management, also aims to make disasters less damaging when they do occur. DRR aims to make communities stronger and better prepared ...
2015–2030, holistic disaster risk management at all levels."
Unlike most
SDGs
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
which have the target year of 2030, this indicator is set to be achieved by 2020.
The two indicators include:
* Indicator 11.b.1: "Number of countries that adopt and implement national disaster risk reduction strategies in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015–2030"
* Indicator 11.b.2: "Proportion of local governments that adopt and implement local disaster risk reduction strategies in line with national disaster risk reduction strategies"
A number of challenges in implementing the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction have been identified, including inconsistent, unstructured, disorganized data collection and reporting, the lack of incentives for proactive report disaster loss, and the lack of governmental mandate on disaster loss reporting.
Target 11.c: Support least developed countries in sustainable and resilient building
The full text of Target 11.c is formulated as "Support
least developed countries
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed b ...
, including through financial and
technical assistance, in building sustainable and resilient buildings using local materials".
This target has one Indicator: Indicator 11.c.1 is the "Proportion of financial support to the least developed countries that is allocated to the
construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
and
retrofitting
Retrofitting is the addition of new technology or features to older systems. Retrofits can happen for a number of reasons, for example with big capital expenditures like naval vessels, military equipment or manufacturing plants, businesses or go ...
of sustainable, resilient and resource-efficient buildings using local materials".
It was suggested in 2020 to delete Indicator 11.c.1.
Custodian agencies
The custodian agencies are responsible for data gathering and reporting on the indicators:
* For the indicators of Targets 11.1, 11.2 and 11.3 and also for Indicator 11.a.1 and Indicator 11.c.1:
United Nations Human Settlements Programme
The United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat) is the United Nations programme for human settlements and sustainable urban development. It was established in 1977 as an outcome of the first United Nations Conference on Human Settle ...
(UN-HABITAT)
* For Indicator 11.4.1:
United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization-Institute for Statistics (UNESCO-UIS)
* For the two indicators under Target 11.5 and for Indicator 11.b.2:
United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* United (2003 film), ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* United (2011 film) ...
(UNISDR)
* For Indicator 11.6.1:
United Nations Human Settlements Programme
The United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat) is the United Nations programme for human settlements and sustainable urban development. It was established in 1977 as an outcome of the first United Nations Conference on Human Settle ...
(UN-HABITAT),
Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA) and UNSD
* For Indicator 11.6.2: World Health Organization
Monitoring
High-level progress reports are prepared by
United Nations Secretary General annually, evaluating the progress towards all the Sustainable Development Goals. The most recent report was published in 2021. The previous report was from April 2020.
[United Nations Economic and Social Council. (28 April 2020)]
Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals Report of the Secretary-General
/ref>
In 2018, High-level Political Forum (HLPF) took stock of progress on the Sustainable Development Goals
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
and discussed progress, successes, challenges and lessons learned on the road to a fairer, more peaceful and prosperous world and a healthy planet by 2030.COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
. Due to the direct and indirect impacts of the pandemic, this Goal is increasingly less likely to be achieved in a timely manner.UN member states
The United Nations comprise sovereign states and the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
The Charter of the United Nations defines the rules for admission of ...
are committed to following up their progress towards implementing the 2030 Agenda and its goals and targets. Almost all the UN member states have presented their national progress towards the SDGs through Voluntary National Review (VNR).
Challenges
Impacts of COVID-19 pandemic
Cities in many countries were epicentres of COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
.epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
s through aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or Human impact on the environment, human causes. The term ''aerosol'' co ...
s, droplets and fomite
A fomite () or fomes () is any inanimate object that, when contaminated with or exposed to infectious agents (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses or fungi), can transfer disease to a new host.
Transfer of pathogens by fomites
A fomite is any ...
s.[United Nations. (2021). The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2021. https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2021/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2021.pdf.] The success of SDG 11 post-pandemic requires concerted action on the part of Governments at all levels, civil society and development partners.Smart city
A smart city is an urban area that uses digital technology to collect data and operate services. Data is collected from citizens, devices, buildings, or cameras. Applications include traffic and transportation systems, power plants, utilities ...
technologies and solutions have contributed to resilience in cities by facilitating gathering and exchange of information in real time, decreasing risk, and enhancing planning, absorption and adaptation abilities.
Links with other SDGs
SDG 11 interlinks with many of the other SDGs. First, the impact on health ( SDG 3, Target 3.9) of city dwellers, as well as improve cities resilience to natural and climate change-induced disasters. It is related to SDG 6 (target 6.1, 6.2 and 6.5), SDG 12 (target 12.4), SDG 14 (target 14.3) Lastly, reducing the impact of communicable diseases and maternal and children mortality which can be found under SDG 3 (targets 3.2 and 3.3).
Furthermore, SDG 11 interlinks with SDG 13 on climate action
Climate action (or climate change action) refers to a range of activities, mechanisms, policy instruments, and so forth that aim at reducing the severity of human-induced climate change and its impacts. "More climate action" is a central demand o ...
: The world's cities account for 60–80 per cent of energy consumption
Energy consumption is the amount of energy used.
Biology
In the body, energy consumption is part of energy homeostasis. It derived from food energy. Energy consumption in the body is a product of the basal metabolic rate and the physical acti ...
and 75 per cent of carbon emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
(this is because 4.2 billion people, or 55 percent of the world's population, lived in cities in 2018).
Organizations
UN system
* United for Smart Sustainable Cities Initiative (U4SSC) which has been pilot to monitor urban-environment related Sustainable Development Goals
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – wh ...
(SDGs) projectsInter-American Development Bank
The Inter-American Development Bank (IDB or IADB) is an international development finance institution headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States of America. It serves as one of the leading sources of development financing for the countri ...
(IDB)
* UN Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO)
* UN Economic Commission for Africa (ECA)
* United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* United (2003 film), ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* United (2011 film) ...
(UNISDR)
*United Nations Human Settlements Programme
The United Nations Human Settlements Programme (UN-Habitat) is the United Nations programme for human settlements and sustainable urban development. It was established in 1977 as an outcome of the first United Nations Conference on Human Settle ...
.
Major NGOs
The following NGOs and other organizations are helping to achieve SDG 11:
* C40 cities is a network of the world's megacities committed to addressing climate change,climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.green economy
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without environmental degradation, degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological econ ...
and smart infrastructure.Rockefeller Foundation
The Rockefeller Foundation is an American private foundation and philanthropic medical research and arts funding organization based at 420 Fifth Avenue, New York City. The foundation was created by Standard Oil magnate John D. Rockefeller (" ...
helps cities around the world to become more resilient to physical, social, and economic shocks and stresses and it supports the adoption and incorporation of a view of resilience that includes not just the shocks, earthquakes, fires, floods, but also the stresses that weaken the fabric of a city on a day to day or cyclical basis.
Examples at country level
Canada
The Canadian federal government has allotted $10 billion CAD over 3 years to the Canadian Infrastructure Bank to begin investing in green projects across the country focusing on areas such as transit, renewable energy, and building retrofits.
See also
* Climate change and cities
* List of most-polluted cities by particulate matter concentration
*
References
External links
UN Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform – SDG 11
"Global Goals" Campaign – SDG 11
SDG-Track.org – SDG 11
UN SDG 11 in the US
{{Cities
Sustainable Development Goals
Urban economics
2015 establishments in New York City
Projects established in 2015

 The full text of Target 11.2 is "By 2030, provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all, improving road safety, notably by expanding public transport, with special attention to the needs of those in vulnerable situations, women, children, persons with disabilities and older persons".
This target has one Indicator: Indicator 11.2.1 is the "Proportion of population that has convenient access to public transport, by sex, age and Persons With Disabilities". Improving transport systems to refine the use of accessibility is key because due to physical or mental disabilities, impaired sight or hearing, carrying heavy bags or traveling with small children, as this causes an average of 25% of the population to experience a degree of reduced mobility.
A sustainable transportation system considers different socioeconomic groups' travel concerns to achieve the validity of accessibility metrics. Transportation and transportation planning should be coordinated with land use planning. Employment and residential areas are relatively concentrated, and urban and suburban settings should be planned and reconstructed in concert.
The full text of Target 11.2 is "By 2030, provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all, improving road safety, notably by expanding public transport, with special attention to the needs of those in vulnerable situations, women, children, persons with disabilities and older persons".
This target has one Indicator: Indicator 11.2.1 is the "Proportion of population that has convenient access to public transport, by sex, age and Persons With Disabilities". Improving transport systems to refine the use of accessibility is key because due to physical or mental disabilities, impaired sight or hearing, carrying heavy bags or traveling with small children, as this causes an average of 25% of the population to experience a degree of reduced mobility.
A sustainable transportation system considers different socioeconomic groups' travel concerns to achieve the validity of accessibility metrics. Transportation and transportation planning should be coordinated with land use planning. Employment and residential areas are relatively concentrated, and urban and suburban settings should be planned and reconstructed in concert.



 The full text of Target 11.5 is "By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected and substantially decrease the direct economic losses relative to global gross domestic product caused by
The full text of Target 11.5 is "By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected and substantially decrease the direct economic losses relative to global gross domestic product caused by  The full text of Target 11.6 is "By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management."
The target has two indicators:
* Indicator 11.6.1: Proportion of municipal solid waste collected and managed in controlled facilities out of total municipal waste generated, by cities
* Indicator 11.6.2: "Annual mean levels of fine particulate matter (e.g. PM2.5 and PM10) in cities (population weighted)"
The full text of Target 11.6 is "By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management."
The target has two indicators:
* Indicator 11.6.1: Proportion of municipal solid waste collected and managed in controlled facilities out of total municipal waste generated, by cities
* Indicator 11.6.2: "Annual mean levels of fine particulate matter (e.g. PM2.5 and PM10) in cities (population weighted)"