Sunburn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as
"Do sunscreens prevent skin cancer"
Press release No. 132, 5 June 2000
"Solar and ultraviolet radiation"
IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Volume 55, November 1997 which in extreme cases can be life-threatening. Sunburn is an inflammatory response in the tissue triggered by direct DNA damage by UV radiation. When the cells'
 Typically, there is initial redness, followed by varying degrees of pain, the severity of which correlates with the duration and intensity of sun exposure.
Other symptoms can include blistering, swelling ( edema), itching ( pruritus), peeling skin, rash,
Typically, there is initial redness, followed by varying degrees of pain, the severity of which correlates with the duration and intensity of sun exposure.
Other symptoms can include blistering, swelling ( edema), itching ( pruritus), peeling skin, rash,
, Skin Cancer Foundation Of greatest concern is that the melanoma risk increases dose-dependently proportional to the number of a person's lifetime cumulative episodes of sunburn. An estimated 1/3 of melanomas in the United States and Australia could be prevented with regular sunscreen use.
Fact-Sheets.com. 2004. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
 Because of variations in the intensity of UV radiation passing through the atmosphere, the risk of sunburn increases with proximity to the tropic latitudes, located between 23.5° north and south latitude. All else being equal (e.g., cloud cover,
Because of variations in the intensity of UV radiation passing through the atmosphere, the risk of sunburn increases with proximity to the tropic latitudes, located between 23.5° north and south latitude. All else being equal (e.g., cloud cover,
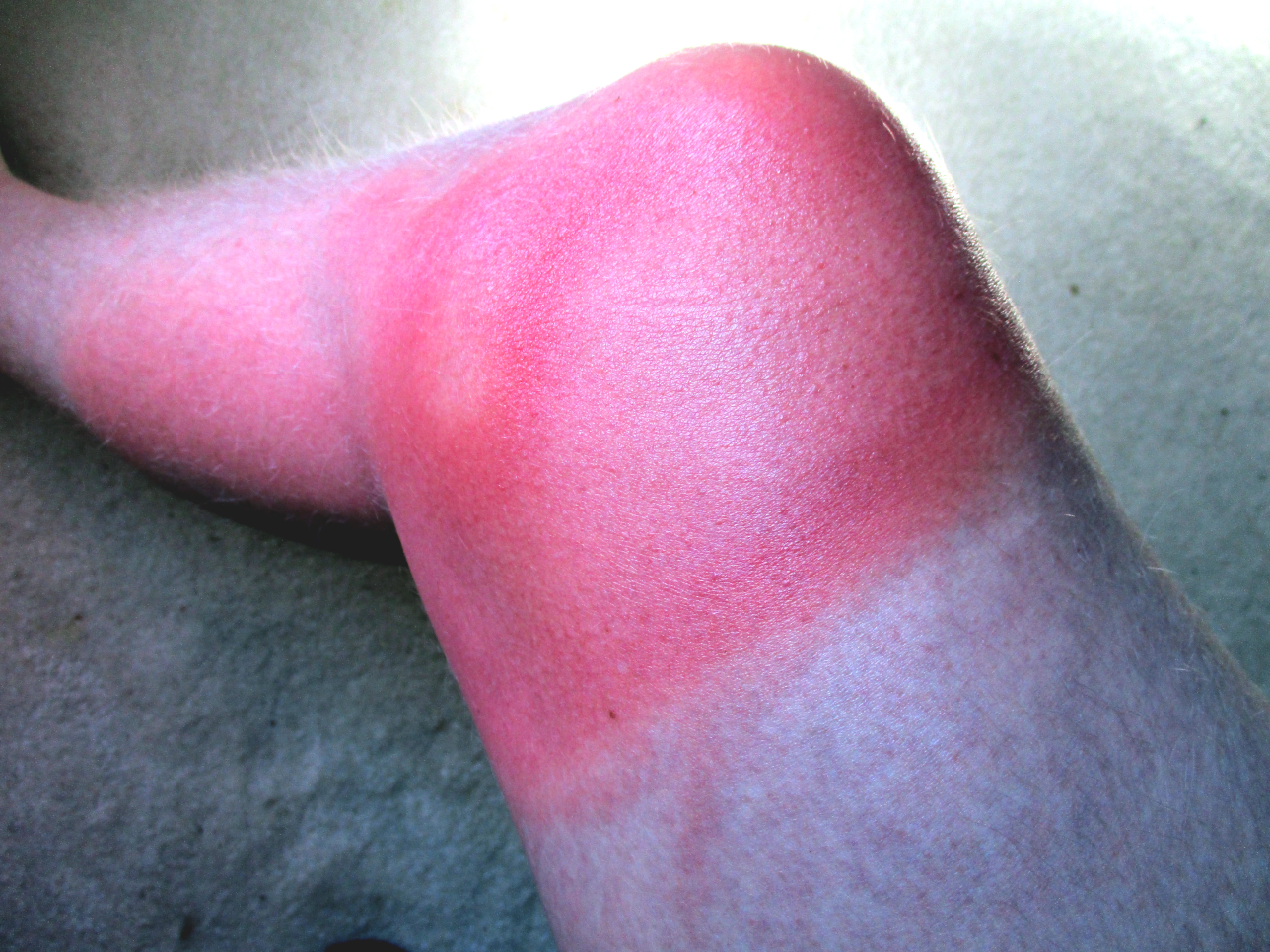
 The most effective way to prevent sunburn is to reduce the amount of UV radiation reaching the skin. The World Health Organization, American Academy of Dermatology, and Skin Cancer Foundation recommend the following measures to prevent excessive UV exposure and skin cancer:
* Limiting sun exposure between the hours of 10 am and 4 pm, when UV rays are the strongest
* Seeking shade when UV rays are most intense
* Wearing sun-protective clothing, including a wide-brim hat, sunglasses, and tightly woven, loose-fitting clothing
* Using sunscreen
* Avoiding tanning beds and artificial UV exposure
The most effective way to prevent sunburn is to reduce the amount of UV radiation reaching the skin. The World Health Organization, American Academy of Dermatology, and Skin Cancer Foundation recommend the following measures to prevent excessive UV exposure and skin cancer:
* Limiting sun exposure between the hours of 10 am and 4 pm, when UV rays are the strongest
* Seeking shade when UV rays are most intense
* Wearing sun-protective clothing, including a wide-brim hat, sunglasses, and tightly woven, loose-fitting clothing
* Using sunscreen
* Avoiding tanning beds and artificial UV exposure
New study reveals surprising cause of sunburn: It’s not DNA
{{Authority control Burns Sun tanning Hazards of outdoor recreation
skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
(UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and other animals include red or reddish skin that is hot to the touch or pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
ful, general fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
, and mild dizziness. Other symptoms include blistering, peeling skin, swelling, itching, and nausea. Excessive UV radiation is the leading cause of (primarily) non-malignant skin tumors,World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, International Agency for Research on Cance"Do sunscreens prevent skin cancer"
Press release No. 132, 5 June 2000
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
, International Agency for Research on Cance"Solar and ultraviolet radiation"
IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Volume 55, November 1997 which in extreme cases can be life-threatening. Sunburn is an inflammatory response in the tissue triggered by direct DNA damage by UV radiation. When the cells'
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
is overly damaged by UV radiation, type I cell-death is triggered and the tissue is replaced.
Sun protective measures like sunscreen and sun protective clothing are widely accepted to prevent sunburn and some types of skin cancer. Special populations, including children, are especially susceptible to sunburn and protective measures should be used to prevent damage.
Signs and symptoms
 Typically, there is initial redness, followed by varying degrees of pain, the severity of which correlates with the duration and intensity of sun exposure.
Other symptoms can include blistering, swelling ( edema), itching ( pruritus), peeling skin, rash,
Typically, there is initial redness, followed by varying degrees of pain, the severity of which correlates with the duration and intensity of sun exposure.
Other symptoms can include blistering, swelling ( edema), itching ( pruritus), peeling skin, rash, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, chills, and fainting ( syncope). Also, heat is produced from capillaries close to the skin surface, therefore the affected area feels warm to touch. Sunburns may be classified as superficial or partial-thickness burns. Blistering is a sign of second-degree sunburn.
Variations
Minor sunburns typically cause nothing more than slight redness and tenderness to the affected areas. In more serious cases, blistering can occur. Extreme sunburns can be painful to the point of debilitation and may require hospital care.Duration
Sunburn can occur in less than 15 minutes in response to sun exposure. However, the first signs of damage may not appear for a few hours. Sunburn can occur in seconds when exposed to non-shielded welding arcs or other sources of intense ultraviolet light. After sun exposure, the skin may turn red in as little as 30 minutes, but sunburn usually takes 2 to 6 hours. Sunburn symptoms are typically at their worst 24 to 36 hours after sun exposure and usually begin to improve after 3 to 5 days. After a few days, the skin may start to flake and peel, with full healing typically occurring within 7 days. For severe sunburns, some peeling and itching may continue for several weeks.Skin cancer
Ultraviolet radiation causes sunburns and increases the risk of three types of skin cancer:melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
, basal-cell carcinoma and squamous-cell carcinoma."Facts About Sunburn and Skin Cancer", Skin Cancer Foundation Of greatest concern is that the melanoma risk increases dose-dependently proportional to the number of a person's lifetime cumulative episodes of sunburn. An estimated 1/3 of melanomas in the United States and Australia could be prevented with regular sunscreen use.
Causes
Sunburn is caused by UV radiation from the Sun but may also result from artificial sources, such as tanning lamps,welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ...
arcs, or ultraviolet germicidal irradiation.
UVB damages mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
This triggers a fast pathway that leads to inflamination of the skin and sunburn. mRNA damage initially triggers a response in ribosomes though a protein known as ZAK-alpha in a ribotoxic stress response. This response acts as a cell surveillance system. Following this detection of RNA damage leads to inflammatory signaling and recruitment of immune cells. This, not DNA damage (which is slower to detect) results in UVB skin inflammation and acute sunburn.
DNA is damaged by UVB light. This damage is mainly the formation of a thymine dimer. The body recognizes such UVB damage on mRNA, which then triggers several defense mechanisms, including DNA repair to revert the damage, apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
and peeling to remove irreparably damaged skin cells, and increased melanin production to prevent future damage.
Melanin readily absorbs UV wavelength light, acting as a photoprotectant. By preventing UV photons from disrupting chemical bonds, melanin inhibits both the direct alteration of DNA, as well as the generation of free radicals, to prevent them from indirectly damaging DNA. However, human melanocyte
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural-crest, neural crest-derived cell (biology), cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis (skin), epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea),
the inner ear,
vagina ...
s contain over 2,000 genomic sites that are highly sensitive to UV, and such sites can be up to 170-fold more sensitive to UV induction of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers than the average site These sensitive sites often occur at biologically significant locations near gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s.
Sunburn causes an inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
process that includes the production of prostanoids and bradykinin. These chemical compounds increase sensitivity to heat by reducing the threshold of heat receptor ( TRPV1) activation from to . The pain may be caused by the overproduction of a protein called CXCL5, which activates nerve fibers.
Skin type determines the ease of sunburn. People with lighter skin tones and limited capacity to develop a tan after UV radiation exposure have a greater risk of sunburn. Fitzpatrick's Skin phototypes classification describes the normal variations of skin responses to UV radiation. Persons with type I skin have the greatest capacity to sunburn, and type VI have the least capacity to burn. However, all skin types can develop sunburn.
Fitzpatrick's skin phototypes:
* Type 0: Albino
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and reddish pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albinos.
Varied use and interpretation of ...
.
* Type I: Pale white skin, burns easily, does not tan.
* Type II: White skin, burns easily, tans with difficulty.
* Type III: White skin, may burn, but eventually tans easily.
* Type IV: Light brown/olive skin, hardly burns, tans easily.
* Type V: Brown skin, usually does not burn, tans easily.
* Type VI: Black skin, very unlikely to burn, becomes darker with UV radiation exposure.
Age also affects how skin reacts to the sun. Children younger than six and adults older than sixty are more sensitive to sunlight.
Certain genetic conditions, for example, xeroderma pigmentosum, increase a person's susceptibility to sunburn and subsequent skin cancers. These conditions involve defects in DNA repair mechanisms which decrease the ability to repair DNA damaged by UV radiation.
Medications
The risk of sunburn can be increased by pharmaceutical products that sensitize users to UV radiation. Certainantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s, oral contraceptives, antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s, acne medications, and tranquillizers have this effect."Avoiding Sun-Related Skin Damage"Fact-Sheets.com. 2004. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
UV intensity
The UV Index indicates the risk of sunburn at a given time and location. Contributing factors include: # The time of day. In most locations, the sun's rays are strongest between approximately 10 am and 4 pmdaylight saving time
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time, daylight time (Daylight saving time in the United States, United States and Daylight saving time in Canada, Canada), or summer time (British Summer Time, United Kingdom, ...
.
# Cloud cover. Clouds partially block UV, but even on an overcast day, a significant percentage of the sun's damaging UV radiation can pass through clouds.
# Proximity to reflective surfaces, such as water, sand, concrete, snow, and ice. All of these reflect the sun's rays and can cause sunburns.
# The season of the year. The Sun's position in late spring and early summer can cause a more-severe sunburn.
# Altitude. At a higher altitude, it is easier to become burnt, because there is less of the Earth's atmosphere to block the sunlight. UV exposure increases about 4% for every 1000 ft (305 m) gain in elevation.
# Proximity to the equator (latitude). Between the polar and tropical regions, the closer to the equator, the more direct sunlight passes through the atmosphere over a year. For example, the southern United States gets fifty percent more sunlight than the northern United States.
 Because of variations in the intensity of UV radiation passing through the atmosphere, the risk of sunburn increases with proximity to the tropic latitudes, located between 23.5° north and south latitude. All else being equal (e.g., cloud cover,
Because of variations in the intensity of UV radiation passing through the atmosphere, the risk of sunburn increases with proximity to the tropic latitudes, located between 23.5° north and south latitude. All else being equal (e.g., cloud cover, ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the a ...
, terrain
Terrain (), alternatively relief or topographical relief, is the dimension and shape of a given surface of land. In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientati ...
, etc.), each location within the tropic or polar regions receives approximately the same amount of UV radiation over a year. In the temperate zones between 23.5° and 66.5°, UV radiation varies substantially by latitude and season. The higher the latitude, the lower the intensity of the UV rays. Sun intensity in the northern hemisphere is greatest during May, June and Julyand in the southern hemisphere, November, December and January. On a minute-by-minute basis, the amount of UV radiation depends on the Sun's angle. Ultraviolet radiation is easily determined by the height ratio
In mathematics, a ratio () shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
of any object to the size of its shadow. Height is measured parallel to the Earth's gravitational field and the projected shadow is measured on a flat, level surface. For objects wider than skulls or poles, the height and length are best measured relative to the same occluding edge. The most significant risk is at solar noon when shadows are at their minimum, and the Sun's radiation passes most directly through the atmosphere. Regardless of one's latitude (assuming no other variables), equal shadow lengths mean equal amounts of UV radiation.
The skin and eyes are most sensitive to damage by UV at 265–275 nm wavelength, which is in the lower UVC band that is rarely encountered except from artificial sources like welding arcs. Longer wavelengths of UV radiation cause most sunburn because those wavelengths are more prevalent in ground-level sunlight.
Ozone depletion
In recent decades, the incidence and severity of sunburn have increased worldwide, partly because of chemical damage to the atmosphere's ozone layer. Between the 1970s and the 2000s, average stratospheric ozone decreased by approximately 4%, contributing an approximate 4% increase to the average UV intensity at the Earth's surface. Ozone depletion and the seasonal "ozone hole" have led to much larger changes in some locations, especially in the southern hemisphere.Tanning
Suntans, which naturally develop in some individuals as a protective mechanism against the sun, are viewed by most in the Western world as desirable. Tanning has led to an increased exposure to UV radiation from both the natural sun and tanning lamps. Suntans can provide a modest sun protection factor (SPF) of 3, meaning that tanned skin would tolerate up to three times the UV exposure as pale skin. Sunburns associated with indoor tanning can be severe. The World Health Organization, American Academy of Dermatology, and the Skin Cancer Foundation have recommended avoiding artificial UV sources such as tanning beds. Suntans are not recommended as a form of sun protection.Diagnosis

Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis of sunburn includes other skin pathology induced by UV radiation, including photoallergic reactions, phototoxic reactions to topical or systemic medications, and other dermatologic disorders that are aggravated by exposure to sunlight. Considerations for diagnosis include duration and intensity of UV exposure, topical or systemic medication use, history of dermatologic disease, and nutritional status. * Phototoxic reactions: Non-immunological response to sunlight interacting with certain drugs and chemicals in the skin which resembles an exaggerated sunburn. Common medications that may cause a phototoxic reaction include amiodarone, dacarbazine, fluoroquinolones, 5-fluorouracil, furosemide, nalidixic acid, phenothiazines, psoralens,retinoid
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are natural derivatives of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Synthetic retinoids are utilized in cosmetic formulations, clinical dermatology, and the treatment of some forms of cancer ...
s, sulfonamides, sulfonylurea
Sulfonylureas or sulphonylureas are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture. The functional group consists of a sulfonyl group (-S(=O)2) with its sulphur atom bonded to a nitrogen atom of a ureylene group (N,N-dehydrourea ...
s, tetracyclines, thiazides, and vinblastine.
* Photoallergic reactions: Uncommon immunological response to sunlight interacting with certain drugs and chemicals in the skin. When in an excited state by UVR, these drugs and chemicals form free radicals that react to form functional antigens and induce a Type IV hypersensitivity reaction. These drugs include 6- methylcoumarin, aminobenzoic acid and esters, chlorpromazine
Chlorpromazine (CPZ), marketed under the brand names Thorazine and Largactil among others, is an antipsychotic medication. It is primarily used to treat psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. Other uses include the treatment of bipolar d ...
, promethazine, diclofenac, sulfonamides, and sulfonylureas. Unlike phototoxic reactions which resemble exaggerated sunburns, photoallergic reactions can cause intense itching and can lead to thickening of the skin.
* Phytophotodermatitis: UV radiation induces skin inflammation after contact with certain plants (including limes, celery, and meadow grass). Causes pain, redness, and blistering of the skin in the distribution of plant exposure.
* Polymorphic light eruption: Recurrent abnormal reactions to UVR present in various ways, including pink-to-red bumps, blisters, plaques and urticaria.
* Solar urticaria: A rare allergic reaction to the sun that occurs within minutes of exposure and fades within hours.
* Other skin diseases exacerbated by sunlight: Several dermatologic conditions can increase in severity with exposure to UVR. These include systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), dermatomyositis, acne, atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditi ...
, and rosacea.
Additionally, since sunburn is a type of radiation burn, it can initially hide a severe exposure to radioactivity
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
. Excess radiation exposure may result in acute radiation syndrome or other radiation-induced illnesses, especially in sunny conditions. For instance, the difference between the erythema caused by sunburn and other radiation burns is not immediately obvious. Symptoms common to heat illness and the prodromic stage of acute radiation syndrome like nausea, vomiting, fever, weakness/fatigue, dizziness or seizure can add to further diagnostic confusion.
Prevention
UV intensity
The strength of sunlight is published in many locations as a UV Index. Sunlight is generally strongest when the Sun is close to the highest point in the sky. Due to time zones and daylight saving time, this is not necessarily at 12 pm, but often one to two hours later. Seeking shade using umbrellas and canopies can reduce UV exposure, but does not block all UV rays. The WHO recommends following the shadow rule: "Watch your shadow – Short shadow, seek shade!"Sunscreen
Commercial preparations that block UV light are known assunscreens
Sunscreen, also known as sunblock, sun lotion or sun cream, is a photoprotection, photoprotective topical product for the Human skin, skin that helps protect against sunburn and prevent skin cancer. Sunscreens come as lotions, sprays, gels, fo ...
or sunblocks. They have a sun protection factor (SPF) rating based on the sunblock's ability to suppress sunburn: The higher the SPF rating, the lower the amount of direct DNA damage. The stated protection factors are correct only if 2 mg of sunscreen is applied per square cm of exposed skin translates into about 28 mL (1 oz) to cover the whole body of an adult male. The recommended dose is much more than many people use in practice. Sunscreens function as chemicals such as oxybenzone
Oxybenzone or benzophenone-3 or BP-3 (trade names Milestab 9, Eusolex 4360, Escalol 567, KAHSCREEN BZ-3) is an organic compound belonging to the class of aromatic ketones known as benzophenones. It takes the form of pale-yellow crystals that are ...
and dioxybenzone (organic sunscreens) or opaque materials such as zinc oxide
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the Chemical formula, formula . It is a white powder which is insoluble in water. ZnO is used as an additive in numerous materials and products including cosmetics, Zinc metabolism, food supplements, rubbe ...
or titanium oxide (inorganic sunscreens) that mainly absorb UV radiation. Chemical and mineral sunscreens vary in the wavelengths of UV radiation blocked. Broad-spectrum sunscreens contain filters that protect against UVA radiation as well as UVB. Although UVA radiation does not primarily cause sunburn, it contributes to skin aging and increases skin cancer risk.
Sunscreen is effective and thus recommended for preventing melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer; it develops from the melanin-producing cells known as melanocytes. It typically occurs in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In very rare case ...
and squamous cell carcinoma. There is little evidence that it is effective in preventing basal cell carcinoma. Typical use of sunscreen does not usually result in vitamin D deficiency, but extensive usage may.
Recommendations
Research has shown that the best sunscreen protection is achieved by application 15 to 30 minutes before exposure, followed by one reapplication 15 to 30 minutes after exposure begins. Further reapplication is necessary after activities such as swimming, sweating, and rubbing. Recommendations are product dependent varying from 80 minutes in water to hours based on the indications and protection shown on the label. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends the following criteria in selecting a sunscreen: * Broad spectrum: protects against both UVA and UVB rays * SPF 30 or higher * Water resistant: sunscreens are classified as water resistant based on time, either 40 minutes, 80 minutes, or not water resistantEyes
The eyes are also sensitive to sun exposure at about the same UV wavelengths as skin; snow blindness is sunburn of the cornea. Wrap-around sunglasses or the use by spectacle-wearers of glasses that block UV light reduce harmful radiation. UV light has been implicated in the development of age-related macular degeneration, pterygium andcataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or ...
s. Concentrated clusters of melanin, commonly known as freckles, are often found within the iris.
The tender skin of the eyelids can also become sunburned and can be especially irritating.
Lips
The lips can become chapped (cheilitis) by sun exposure. Sunscreen on the lips does not have a pleasant taste and might be removed by saliva. Some lip balms (ChapSticks) have SPF ratings and contain sunscreens.Feet
The skin of the feet is often tender and protected, so sudden prolonged exposure to UV radiation can be particularly painful and damaging to the top of the foot. Protective measures include sunscreen, socks, or swimwear that covers the foot.Diet
Dietary factors influence susceptibility to sunburn, recovery from sunburn, and risk of secondary complications. Several dietary antioxidants, including essential vitamins, are effective in protecting against sunburn and skin damage associated with ultraviolet radiation, in both human and animal studies. Supplementation withVitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
and Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a group of eight compounds related in molecular structure that includes four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. The tocopherols function as fat-soluble antioxidants which may help protect cell membranes from reactive oxygen speci ...
was shown in one study to reduce the amount of sunburn after a controlled amount of UV exposure.
A review of scientific literature through 2007 found that beta carotene (Vitamin A) supplementation had a protective effect against sunburn. The effects of beta carotene were only evident in the long-term, with studies of supplementation for periods less than ten weeks in duration failing to show any effects. There is also evidence that common foods may have some protective ability against sunburn if taken for a period before exposure.
Protecting children
Babies and children are particularly susceptible to UV damage which increases their risk of both melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers later in life. Children should not sunburn at any age, and protective measures can reduce their future risk of skin cancer. * Infants 0–6 months: Children under 6mo generally have skin too sensitive for sunscreen and protective measures should focus on avoiding excessive UV exposure by using window mesh covers, wide-brim hats, loose clothing that covers the skin, and reducing UV exposure between the hours of 10am and 4pm. * Infants 6–12 months: Sunscreen can safely be used on infants this age. It is recommended to apply a broad-spectrum, water-resistant SPF 30+ sunscreen to exposed areas and avoid excessive UV exposure by using wide-brim hats and protective clothing. * Toddlers and Preschool-aged children: Apply a broad-spectrum, water-resistant SPF 30+ sunscreen to exposed areas, use wide-brim hats and sunglasses, avoid peak UV intensity hours of 10 am - 4 pm and seek shade. Sun-protective clothing with an SPF rating can also provide additional protection.Artificial UV exposure
The WHO recommends that artificial UV exposure, including tanning beds, should be avoided as no safe dose has been established. Special protective clothing (for example, welding helmets/shields) should be worn when exposed to any artificial source of occupational UV. Such sources can produce UVC, an extremely carcinogenic wavelength of UV, which ordinarily is not present in normal sunlight, having been filtered out by the atmosphere.Treatment
The primary measure of treatment is avoiding further exposure to the sun. The best treatment for most sunburns is time; most sunburns heal completely within a few weeks. TheAmerican Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) is a non-profit professional organization of dermatologists in the United States and Canada, based in Rosemont, Illinois, near Chicago. It was founded in 1938 and has more than ''21,000'' members. The Acad ...
recommends the following for the treatment of sunburn:
* For pain relief, take cool baths or showers frequently.
* Use soothing moisturizers that contain aloe vera
''Aloe vera'' () is a succulent plant species of the genus ''Aloe''. It is widely distributed, and is considered an invasive species in many world regions.
An evergreen perennial plant, perennial, it originates from the Arabian Peninsula, but ...
or soy.
* Anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
or aspirin can help with pain.
* Keep hydrated and drink extra water.
* Do not pop blisters
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, Serum (blood), serum, Plasma (blood), plasma, blood, or pus) within the Epidermis, upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure o ...
on a sunburn; let them heal on their own instead.
* Protect sunburned skin (see: Sun protective clothing and Sunscreen) with loose clothing when going outside to prevent further damage while not irritating the sunburn.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
or naproxen), and aspirin may decrease redness and pain. Local anesthetics such as benzocaine
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is a local anesthetic, belonging to the amino ester drug class, commonly used as a topical painkiller or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter ...
, however, are contraindicated. Schwellnus et al. state that topical steroids (such as hydrocortisone cream) do not help with sunburns, although the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) is a non-profit professional organization of dermatologists in the United States and Canada, based in Rosemont, Illinois, near Chicago. It was founded in 1938 and has more than ''21,000'' members. The Acad ...
says they can be used on especially sore areas. While lidocaine cream (a local anesthetic) is often used as a sunburn treatment, there is little evidence for the effectiveness of such use.
A home treatment that may help the discomfort is using cool and wet cloths on the sunburned areas. Applying soothing lotions that contain aloe vera
''Aloe vera'' () is a succulent plant species of the genus ''Aloe''. It is widely distributed, and is considered an invasive species in many world regions.
An evergreen perennial plant, perennial, it originates from the Arabian Peninsula, but ...
to sunburned areas was supported by multiple studies. However, others have found aloe vera to have no effect. Note that aloe vera cannot protect people from new or further sunburn. Another home treatment is using a moisturizer
A moisturizer, or emollient, is a Cosmetics, cosmetic preparation used for protecting, moisturizing, and lubricating the Human skin, skin. These functions are normally performed by Sebaceous gland, sebum produced by healthy skin. The word "emollie ...
that contains soy. Furthermore, sunburn draws fluid to the skin's surface and away from the rest of the body. Drinking extra water is recommended to help prevent dehydration.
See also
* Sun tanning * Freckles * Skin cancer * Snow blindness * Chapped lipsReferences
External links
New study reveals surprising cause of sunburn: It’s not DNA
{{Authority control Burns Sun tanning Hazards of outdoor recreation