Subject Side Parameter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The subject-side parameter, also called the specifier–head parameter, is a proposed
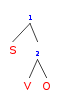 In this sentence, the subject
In this sentence, the subject
 Above, the subject ''na'' comes at the beginning of the sentence, the
Above, the subject ''na'' comes at the beginning of the sentence, the

 One of the explanations for such
One of the explanations for such
 Desmond C. Derbyshire suggested that this
Desmond C. Derbyshire suggested that this
parameter
A parameter (), generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system (meaning an event, project, object, situation, etc.). That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when ...
within generative linguistics
Generative grammar, or generativism , is a linguistic theory that regards linguistics as the study of a hypothesised innate grammatical structure. It is a biological or biologistic modification of earlier structuralist theories of linguistics ...
which states that the position of the subject may precede or follow the head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may no ...
. In the world's languages, Specifier-first order (i.e., subject-initial order) is more common than Specifier-final order (i.e., subject-final order). For example, in the World Atlas of Linguistic Structures (WALS), 76% of the languages in their sample Specifier-first (either SOV or SVO). In this respect, the subject-side parameter contrasts with the head-directionality parameter
In linguistics, head directionality is a proposed parameter that classifies languages according to whether they are head-initial (the head of a phrase precedes its complements) or head-final (the head follows its complements). The head is t ...
. The latter, which classifies languages according to whether the head precedes or follows its complement, shows a roughly 50-50 split: in languages that have a fixed word order, about half have a Head-Complement order, and half have a Complement-Head order.
History
First developed in the late 1960s and later introduced in his ''Lectures on Government and Binding
''Lectures on Government and Binding: The Pisa Lectures'' (''LGB'') is a book by the linguist Noam Chomsky, published in 1981. It is based on the lectures Chomsky gave at the GLOW conference and workshop held at the Scuola Normale Superiore in Pi ...
'' (1981), Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is ...
presented his work on principles and parameters
Principles and parameters is a framework within generative linguistics in which the syntax of a natural language is described in accordance with general ''principles'' (i.e. abstract rules or grammars) and specific ''parameters'' (i.e. markers, ...
. Originally, it was not understood if word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
was distinct from head order, but this was later proven by Flynn and Espinal using the case of Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of v ...
and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national id ...
showing the need for a subject side parameter.
Statistics
The following are 6 possibleword order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
s that we can find across human languages. WALS
WALS (102.1 FM) is an American radio station broadcasting a country music format. Licensed to Oglesby, Illinois, United States, the station serves the LaSalle-Peru area. Branded as WALLS 102, the station is currently owned by Laco Radio and fe ...
, the World Atlas of Language Structures, presents a statistical estimation on languages with their own word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
s.
The WALS database indicates that languages with the order subject-object-verb (SOV) and subject-verb-object (SVO) are overwhelmingly the most numerous. WALS
WALS (102.1 FM) is an American radio station broadcasting a country music format. Licensed to Oglesby, Illinois, United States, the station serves the LaSalle-Peru area. Branded as WALLS 102, the station is currently owned by Laco Radio and fe ...
cites there are 189 languages that have no dominant word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
. However, taking this data into account as it is the most complete source of language structure data, X-bar Theory
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase-structure grammar and a theory of syntactic category formation that was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ...
states that underlying structure Deep structure and surface structure (also D-structure and S-structure although those abbreviated forms are sometimes used with distinct meanings) are concepts used in linguistics, specifically in the study of syntax in the Chomskyan tradition of t ...
will differ from surface structure, especially in languages that have seemingly non-dominant structures. Additionally, WALS
WALS (102.1 FM) is an American radio station broadcasting a country music format. Licensed to Oglesby, Illinois, United States, the station serves the LaSalle-Peru area. Branded as WALLS 102, the station is currently owned by Laco Radio and fe ...
data appears to lack any data on Amerindian languages
Over a thousand indigenous languages are spoken by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. These languages cannot all be demonstrated to be related to each other and are classified into a hundred or so language families (including a large numbe ...
or signed languages.
Theories in word ordering
Subject-initial order
SVO
UsingWALS
WALS (102.1 FM) is an American radio station broadcasting a country music format. Licensed to Oglesby, Illinois, United States, the station serves the LaSalle-Peru area. Branded as WALLS 102, the station is currently owned by Laco Radio and fe ...
data, subject-verb-object languages, such as English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national id ...
, French and Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
, are the second most populous languages in the world at 35.44% of the world's languages. SVO word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
is thought to be derived from SOV word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
to avoid the possible ambiguity caused by the topicalization
Topicalization is a mechanism of syntax that establishes an expression as the sentence or clause topic by having it appear at the front of the sentence or clause (as opposed to in a canonical position further to the right). This involves a phrasa ...
of the objects. For example, the topicalization
Topicalization is a mechanism of syntax that establishes an expression as the sentence or clause topic by having it appear at the front of the sentence or clause (as opposed to in a canonical position further to the right). This involves a phrasa ...
in SVO word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
would result in OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
, which leaves the same sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
as in P NP VP
P, or p, is the sixteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''pee'' (pronounced ), plural ''pees''.
History
Th ...
One example of SVO language is an Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intelligi ...
example:
 In this sentence, the subject
In this sentence, the subject noun phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently o ...
''je'' comes at the beginning of the sentence, the verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descr ...
''croi'' comes the next and then the object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ai ...
noun phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently o ...
''qu'elle...'' follows to form SVO word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
. If we were to topicalize the object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ai ...
, then we would have two noun phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently o ...
s before the verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descr ...
, which will cause the ambiguity on which of the two noun phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently o ...
s is the subject and which is the object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ai ...
.
SOV
Subject-object-verb is another commonsentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
found in many languages. SOV has been thought to be the most "unmarked" word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
and assumed to be the base of the other word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
s according to X-bar Theory
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase-structure grammar and a theory of syntactic category formation that was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ...
. Similarly, in two well-known studies done by Li and Thompson (1975), it is suggested that SOV word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
codes definite
In linguistics, definiteness is a semantic feature of noun phrases, distinguishing between referents or senses that are identifiable in a given context (definite noun phrases) and those which are not (indefinite noun phrases). The prototypical ...
object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ai ...
. Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
and Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
are some languages that use SOV word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
. In Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
, the subject comes at the beginning of the sentence, followed by the object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ai ...
and then the verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descr ...
. For example:
 Above, the subject ''na'' comes at the beginning of the sentence, the
Above, the subject ''na'' comes at the beginning of the sentence, the object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ai ...
''Yenghi'' follows and then the verb ''po-ass-e'' comes at the end. This forms SOV word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
.
Subject-medial order
VSO
Verb-subject-object structure is thought to be derived from the SVO structure. Examples of VSO languages areWelsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
. The rarity of this word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
may be occur as a result of this language occurring when V-fronting moves the verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descr ...
out of the verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''qu ...
in the SVO structure and places it before the subject This modification disrupts the underlying X-bar structure and thus makes VSO rarer due to the complexity of grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraint ...
. Thus, there is no X-bar Theory
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase-structure grammar and a theory of syntactic category formation that was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ...
tree form for this. The subject position in VSO languages is not properly governed, in that it can sway between VSO and SVO.
Alternately, there is evidence that many languages with a VSO word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
can take on SVO as an alternate word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
. There is evidence of the underlying structure Deep structure and surface structure (also D-structure and S-structure although those abbreviated forms are sometimes used with distinct meanings) are concepts used in linguistics, specifically in the study of syntax in the Chomskyan tradition of t ...
in VSO languages being SVO. For example, in Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
, there is a SVO structure occurring after auxiliaries
Auxiliaries are support personnel that assist the military or police but are organised differently from regular forces. Auxiliary may be military volunteers undertaking support functions or performing certain duties such as garrison troops, ...
but otherwise the sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
is VSO.
Below are two synonymous examples from Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
. Example 5 shows a sentence with VSO structure and example 6 shows a sentence with SVO structure:

OSV
Object-subject-verb is the rarestsentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
compared with the above sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
s. No languages are identified as having a basic OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
structure, however it thought that some Amazonian languages
Amazonian languages is the term used to refer to the indigenous languages of "Greater Amazonia." This area is significantly larger than the Amazon and extends from the Atlantic coast all the way to the Andes, while its southern border is usuall ...
do. There are some languages that are identified as having some OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
s. Some of these languages are American Sign Language
American Sign Language (ASL) is a natural language that serves as the predominant sign language of Deaf communities in the United States of America and most of Anglophone Canada. ASL is a complete and organized visual language that is express ...
(ASL), English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national id ...
and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
. However, ASL
American Sign Language (ASL) is a natural language that serves as the predominant sign language of Deaf communities in the United States of America and most of Anglophone Canada. ASL is a complete and organized visual language that is express ...
, like many others, does not consistently utilize an OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
structure. Sometimes if the verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descr ...
is relating to aspect, it can adopt an SOV structure. Here is an example of the order in which someone would sign:
One possibility that can explain the rarity of these languages, is that, in general, objects do not occur in initial position often. Subjects occur more often in initial position. This is why SVO and SOV are more common than both OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
and OVS.
The word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
of OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
does not fit with the current X-bar Theory
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase-structure grammar and a theory of syntactic category formation that was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ...
and therefore we can not draw a tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
. There is some undetermined movement that occurs or the tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
structure may be altered so that the subject may be the sister of the verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descr ...
.
Subject-final order
VOS
Verb-object-subject is an uncommonsentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
. Languages being classified to this structure are Malagasy and Ch'ol.
In these languages, it is mainly divided into two parts: subject and predicate
Predicate or predication may refer to:
* Predicate (grammar), in linguistics
* Predication (philosophy)
* several closely related uses in mathematics and formal logic:
**Predicate (mathematical logic)
**Propositional function
**Finitary relation, ...
. In Malagasy, the position in a sentence is related to the degree of topicalization
Topicalization is a mechanism of syntax that establishes an expression as the sentence or clause topic by having it appear at the front of the sentence or clause (as opposed to in a canonical position further to the right). This involves a phrasa ...
. The normal word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
is that subject is preceded by predicate
Predicate or predication may refer to:
* Predicate (grammar), in linguistics
* Predication (philosophy)
* several closely related uses in mathematics and formal logic:
**Predicate (mathematical logic)
**Propositional function
**Finitary relation, ...
. The following example is in Malagasy.
 One of the explanations for such
One of the explanations for such word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
is that there is a movement occurred in the sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
. Specifically, the movement is phrasal fronting as proposed by Jessica Coon in her paper focusing on Ch'ol, but it is very likely to be used to explain other languages having VOS word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
. This proposal is a result of moving the verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''qu ...
to a higher position in a syntactic tree form. The verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''qu ...
is assumed to move to the specifier position of tense phrase. The reasons why there is a verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''qu ...
movement based on two main factors: agreement Agreement may refer to:
Agreements between people and organizations
* Gentlemen's agreement, not enforceable by law
* Trade agreement, between countries
* Consensus, a decision-making process
* Contract, enforceable in a court of law
** Meeting of ...
features on tense phrase and restriction on head movement
Syntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of ''discontinuous constituents'' or ''displacement''. Some constituen ...
. The whole verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''qu ...
movement acts as the last resort because the language disallow only the head to move. It must take the whole phrase
In syntax and grammar, a phrase is a group of words or singular word acting as a grammatical unit. For instance, the English expression "the very happy squirrel" is a noun phrase which contains the adjective phrase "very happy". Phrases can con ...
to move instead.
In addition, Diana Massam also proposed that the Extended Projection Principle The extended projection principle (EPP) is a linguistic hypothesis about subjects. It was proposed by Noam Chomsky as an addendum to the projection principle. The basic idea of the EPP is that clauses must contain a noun phrase or determiner phr ...
can be taken in account for the verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''qu ...
movement, given the predicate
Predicate or predication may refer to:
* Predicate (grammar), in linguistics
* Predication (philosophy)
* several closely related uses in mathematics and formal logic:
**Predicate (mathematical logic)
**Propositional function
**Finitary relation, ...
feature
Feature may refer to:
Computing
* Feature (CAD), could be a hole, pocket, or notch
* Feature (computer vision), could be an edge, corner or blob
* Feature (software design) is an intentional distinguishing characteristic of a software item ...
on the tense phrase.
OVS
Object-verb-subject is a minoritysentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
. There are some South American languages such as Hixkaryana
Hixkaryana is one of the Cariban languages, spoken by just over 500 people on the Nhamundá River, a tributary of the Amazon River in Brazil. It is one of around a dozen languages that are described as having object–verb–subject word order ...
and Urarina
The Urarina are an indigenous people of the Peruvian Amazon Basin ( Loreto) who inhabit the valleys of the Chambira, Urituyacu, and Corrientes Rivers. According to both archaeological and historical sources, they have resided in the Chambira B ...
that have this uncommon structure. The following example is from Hixkaryana
Hixkaryana is one of the Cariban languages, spoken by just over 500 people on the Nhamundá River, a tributary of the Amazon River in Brazil. It is one of around a dozen languages that are described as having object–verb–subject word order ...
:
 Desmond C. Derbyshire suggested that this
Desmond C. Derbyshire suggested that this word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
in Hixkaryana
Hixkaryana is one of the Cariban languages, spoken by just over 500 people on the Nhamundá River, a tributary of the Amazon River in Brazil. It is one of around a dozen languages that are described as having object–verb–subject word order ...
is based on its native-speakers' intuitions and statistical evidence
Scientific evidence is evidence that serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis, although scientists also use evidence in other ways, such as when applying theories to practical problems. "Discussions about empirical ev ...
. These two pieces of evidence show that the object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ai ...
is followed by a verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual descr ...
and the subject occurs in final position. On the other hand, Laura Kalin proposed there are three factors to make movement occur in the sentence structure
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constitue ...
: focus
Focus, or its plural form foci may refer to:
Arts
* Focus or Focus Festival, former name of the Adelaide Fringe arts festival in South Australia Film
*''Focus'', a 1962 TV film starring James Whitmore
* ''Focus'' (2001 film), a 2001 film based ...
, contrastive topic
Topic, topics, TOPIC, topical, or topicality may refer to:
Topic / Topics
* Topić, a Slavic surname
* ''Topics'' (Aristotle), a work by Aristotle
* Topic (chocolate bar), a brand of confectionery bar
* Topic (DJ), German musician
* Topic ...
and wh-questions
A question is an utterance which serves as a request for information. Questions are sometimes distinguished from interrogatives, which are the grammatical forms typically used to express them. Rhetorical questions, for instance, are interrogative ...
. This is the driving force to make the verb phrase
In linguistics, a verb phrase (VP) is a syntactic unit composed of a verb and its arguments except the subject of an independent clause or coordinate clause. Thus, in the sentence ''A fat man quickly put the money into the box'', the words ''qu ...
move to initial position.
Why are some word orders more common?
Though there are logically 6 possibleword order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
s — namely SVO, SOV, VOS, OVS, VSO and OSV OSV may be:
* OSV-96, a Russian anti-materiel rifle
* Object–subject–verb word order
* Offshore vessel
* Old Sturbridge Village
* Open-source voting
* ''Our Sunday Visitor
Our Sunday Visitor (OSV) is a Catholic publishing company in Hunti ...
— some orders are more common than others. There are research and studies been done in order to account for such phenomenon; a few of the possible reasons are as follows:
In Matthew Hall, Victor Ferreira and Rachel Mayberry’s paper, they argue that because there are three constraints — being efficient, keeping subjects before objects, avoiding SOV for reversible events — that the SVO word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
can allow its users, it becomes more popular than others. Moreover, they clam that when gestural consistency and a passive interlocutor were both present, the SVO word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
will appear significantly. Meanwhile, according to Luke Maurits, Amy Perfors and Daniel Navarro, the reason for object-initial languages to be less common than other word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
s could be explained by the effects of Uniform Information Density (UID). They suggest that “object-first word orders lead to the least uniform information density in all three of heirestimated event distributions”(Maurits et al., 2010, p. 7), and was therefore least common. On the other hand, a stimulation study on word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
bias also demonstrates that local syntax is one of the triggers of bias towards SOV/ SVO word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
s; furthermore, the global syntax is also constrained by language encoded semantic structures.
Principle of Semantic Interpretation
Keenan (1978) postulates a Principle of Semantic Interpretation, which aims to explain why subject–predicate order is more common than predicate–subject order among the languages of the world. : ''Principle of Semantic Interpretation: The meaning of the predicate phrase often depends on the reference of the subject.'' Whereas a noun has a relatively fixed meaning (usually referring to a specific object in space), the meaning of a verb or adjective is sometimes disambiguated by the noun upon which it is predicated. One example of this phenomenon is the verb ''run''. This verb has a different meaning in each of the following sentences, determined by the respective subject: : ''The children are running.'' : ''The fish are running.'' : ''The buses are running today.'' : ''This watch is running.'' : ''The colors are running.'' : ''The water is running.'' : ''The stockings are running.'' : ''My nose is running.'' In a language with predicate–subject order, a listener must wait for the subject in order to correctly disambiguate the intended meaning of the predicate. Thus, Keenan proposes that subject–predicate order is intuitively preferable to predicate–subject order. Keenan also suggests that this principle has anontological
In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophical study of being, as well as related concepts such as existence, becoming, and reality.
Ontology addresses questions like how entities are grouped into categories and which of these entities exi ...
basis rather than a purely semantic one: objects can exist independently of properties that are ascribed to them, but properties cannot exist independently of objects that exemplify them.
Changes over time
In some languages, there is evidence that the dominantword order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
has changed over time. For example, the dominant word order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
in Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin (; ) is a group of Chinese (Sinitic) dialects that are natively spoken across most of northern and southwestern China. The group includes the Beijing dialect, the basis of the phonology of Standard Chinese, the official language ...
and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
shifted from SOV to SVO. In Modern Chinese
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standar ...
, one factor for this shift is the productivity of compound verbs. This increase in compound verbs lead to an increase in post-positions such as ''le'', ''bei'' and ''ba'', which are used as aspect markers.
Li. C, Thompson. S. An Explanation of Word Order Change SVO→SOV Charles N. Springer Article, Vol. 12, No. 2 (Nov., 1974), pp. 201-214 https://www.jstor.org/stable/25000832
See also
*Extended Projection Principle The extended projection principle (EPP) is a linguistic hypothesis about subjects. It was proposed by Noam Chomsky as an addendum to the projection principle. The basic idea of the EPP is that clauses must contain a noun phrase or determiner phr ...
* Principles and parameters
Principles and parameters is a framework within generative linguistics in which the syntax of a natural language is described in accordance with general ''principles'' (i.e. abstract rules or grammars) and specific ''parameters'' (i.e. markers, ...
* Word Order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. C ...
* X-bar theory
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase-structure grammar and a theory of syntactic category formation that was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ...
* Head-directionality parameter
In linguistics, head directionality is a proposed parameter that classifies languages according to whether they are head-initial (the head of a phrase precedes its complements) or head-final (the head follows its complements). The head is t ...
* Head (linguistics)
In linguistics, the head or nucleus of a phrase is the word that determines the syntactic category of that phrase. For example, the head of the noun phrase ''boiling hot water'' is the noun ''water''. Analogously, the head of a compound is the ...
* Generative linguistics
Generative grammar, or generativism , is a linguistic theory that regards linguistics as the study of a hypothesised innate grammatical structure. It is a biological or biologistic modification of earlier structuralist theories of linguistics ...
* Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is ...
* Transformational grammar
In linguistics, transformational grammar (TG) or transformational-generative grammar (TGG) is part of the theory of generative grammar, especially of natural languages. It considers grammar to be a system of rules that generate exactly those combin ...
Further reading
* *References
{{Reflist, 30em Generative linguistics Generative syntax Syntax