subcarriers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A subcarrier is a
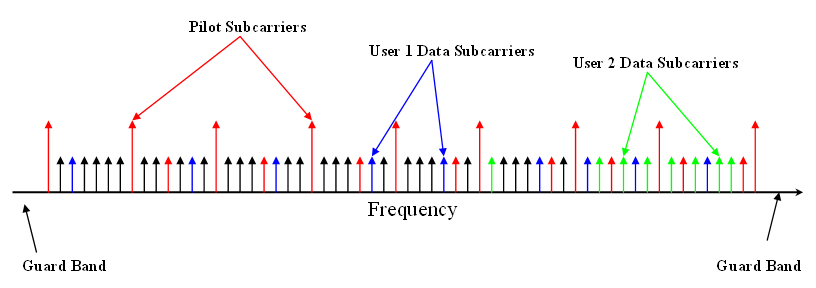 The RDS/
The RDS/
FM Receiver with subcarrier decoding circuit
United States Patent 4476581
United States Patent 3974520 {{Audio broadcasting Broadcast engineering
sideband
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, that are the result of the modulation process. The sidebands carry the information transmitted by the radio signal. The sidebands c ...
of a radio frequency carrier wave, which is modulated to send additional information. Examples include the provision of colour in a black and white television system or the provision of stereo in a monophonic radio broadcast. There is no physical difference between a carrier and a subcarrier; the "sub" implies that it has been derived from a carrier, which has been amplitude modulated by a steady signal and has a constant frequency relation to it.
FM stereo
Stereo broadcasting is made possible by using a subcarrier onFM radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting that uses frequency modulation (FM) of the radio broadcast carrier wave. Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to transmit high fidelity, high-f ...
stations, which takes the left channel and "subtracts" the right channel from it — essentially by hooking up the right-channel wires backward (reversing polarity) and then joining left and reversed-right. The result is modulated with suppressed carrier AM, more correctly called sum and difference modulation or SDM, at 38 kHz in the FM signal, which is joined at 2% modulation with the mono left+right audio (which range
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
s 50 Hz ~ 15 kHz). A 19 kHz pilot tone
In telecommunications, a pilot signal is a signal, usually a single frequency, transmitted over a communications system for supervisory, control, equalization, continuity, synchronization, or reference purposes.
Uses in different communication ...
is also added at a 9% modulation to trigger radios to decode the stereo subcarrier, making FM stereo fully compatible with mono.
Once the receiver demodulate
Demodulation is the process of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (or computer program in a software-defined radio) that is used to recover the information content from ...
s the L+R and L−R signals, it adds the two signals ( +R+ −R= 2L) to get the left channel and subtracts ( +R− −R= 2R) to get the right channel. Rather than having a local oscillator
In electronics, the term local oscillator (LO) refers to an electronic oscillator when used in conjunction with a Frequency mixer, mixer to change the frequency of a signal. This frequency conversion process, also called Heterodyne, heterodyning ...
, the 19 kHz pilot tone provides an in-phase reference signal used to reconstruct the missing carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave, carrier signal, or just carrier, is a periodic waveform (usually sinusoidal) that conveys information through a process called ''modulation''. One or more of the wave's properties, such as amplitude or freq ...
from the 38 kHz signal.
For AM broadcasting
AM broadcasting is radio broadcasting using amplitude modulation (AM) transmissions. It was the first method developed for making audio radio transmissions, and is still used worldwide, primarily for medium wave (also known as "AM band") transm ...
, different analog (AM stereo
AM stereo is a term given to a series of mutually incompatible techniques for radio broadcasting stereo audio in the AM band in a manner that is compatible with standard AM receivers. There are two main classes of systems: independent sideban ...
) and digital (HD Radio
HD Radio (HDR) is a trademark for in-band on-channel (IBOC) digital radio broadcast technology. HD radio generally simulcast, simulcasts an existing analog radio station in digital format with less noise and with additional text information. HD R ...
) methods are used to produce stereophonic audio. Modulated subcarriers of the type used in FM broadcasting are impractical for AM broadcast due to the relatively narrow signal bandwidth allocated for a given AM signal. On standard AM broadcast radios, the entire 9 kHz to 10 kHz allocated bandwidth of the AM signal may be used for audio.
Television
Likewise, analog TV signals are transmitted with theblack and white
Black-and-white (B&W or B/W) images combine black and white to produce a range of achromatic brightnesses of grey. It is also known as greyscale in technical settings.
Media
The history of various visual media began with black and white, ...
luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls wit ...
part as the main signal, and the color chrominance
Chrominance (''chroma'' or ''C'' for short) is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture (see YUV color model), separately from the accompanying Luma (video), luma signal (or Y' for short). Chrominance is usu ...
as the subcarriers. A black and white TV simply ignores the extra information, as it has no decoder for it. To reduce the bandwidth of the color subcarriers, they are filtered to remove higher frequencies. This is made possible by the fact that the human eye
The human eye is a sensory organ in the visual system that reacts to light, visible light allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm, and Balance (ability), keeping balance.
The eye can be considered as a living ...
sees much more detail in contrast than in color. In addition, only blue and red are transmitted, with green being determined by subtracting the other two from the luminance and taking the remainder
In mathematics, the remainder is the amount "left over" after performing some computation. In arithmetic, the remainder is the integer "left over" after dividing one integer by another to produce an integer quotient ( integer division). In a ...
. (See: YIQ
YIQ is the color space used by the analog NTSC color TV system. ''I'' stands for ''in-phase'', while ''Q'' stands for ''quadrature'', referring to the components used in quadrature amplitude modulation. Other TV systems used different color spa ...
, YCbCr
YCbCr, Y′CbCr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in digital video and digital photography, photography systems. Like YPbPr, YPBPR, it is based on RGB primaries; the two ...
, YPbPr
YPbPr or Y'P'bP'r, also written as , is a color space used in video electronics, in particular in reference to component video cables. Like YCBCR, it is based on gamma corrected RGB primaries; the two are numerically equivalent but YPBPR is de ...
) Various broadcast television systems use different subcarrier frequencies, in addition to differences in encoding
In communications and Data processing, information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter (alphabet), letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes data compression, shortened or ...
.
For the audio part, MTS uses subcarriers on the video that can also carry three audio channels, including one for stereo (same left-minus-right method as for FM), another for second audio program
Second audio program (SAP), also known as secondary audio programming, is an auxiliary audio channel for analog television that can be broadcast or transmitted both over-the-air and by cable television. Used mostly for audio description or ot ...
s (such as descriptive video service for the vision-impaired, and bilingual programs), and yet a third hidden one for the studio to communicate with reporters or technicians in the field (or for a technician
A technician is a worker in a field of technology who is proficient in the relevant skill and technique, with a relatively practical understanding of the theoretical principles.
Specialisation
The term technician covers many different special ...
or broadcast engineer at a remote transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of sig ...
site to talk back to the studio), or any other use a TV station
A television station is a set of equipment managed by a business, organisation or other entity such as an amateur television (ATV) operator, that transmits video content and audio content via radio waves directly from a transmitter on the earth's ...
might see fit. (See also NICAM
Near Instantaneous Companded Audio Multiplex (NICAM) is an early form of lossy compression for digital audio. It was originally developed in the early 1970s for point-to-point links within broadcasting networks.Croll, M.G., Osborne, D.W. and Spi ...
, A2 Stereo.)
In RF-transmitted composite video
Composite video, also known as CVBS (composite video baseband signal or color, video, blanking and sync), is an analog video format that combines image information—such as brightness (luminance), color (chrominance), and synchronization, int ...
, subcarriers remain in the baseband signal after main carrier demodulation
Demodulation is the process of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit (or computer program in a software-defined radio) that is used to recover the information content fro ...
to be separated in the receiver. The mono audio component of the transmitted signal is in a separate carrier and not integral to the video component. In wired video connections, composite video
Composite video, also known as CVBS (composite video baseband signal or color, video, blanking and sync), is an analog video format that combines image information—such as brightness (luminance), color (chrominance), and synchronization, int ...
retains the integrated subcarrier signal structure found in the transmitted baseband signal, while S-Video
S-Video (also known as separate video, Y/C, and erroneously Super-Video) is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video, typically at 525 lines or 625 lines. It encodes video luma and chrominance on two separate chann ...
places the chrominance and luminance signals on separate wires to eliminate subcarrier crosstalk and enhance the signal bandwidth and strength (picture sharpness and brightness).
Private audio
Beforesatellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scient ...
, Muzak
Muzak is an American brand of background music played in retail stores and other public establishments owned by Mood Media.
The name ''Muzak'', a blend of music and the popular camera brand name Kodak, has been in use since 1934 and has been ...
and similar services were transmitted to department store
A department store is a retail establishment offering a wide range of consumer goods in different areas of the store under one roof, each area ("department") specializing in a product category. In modern major cities, the department store mad ...
s on FM subcarriers. The fidelity of the subcarrier audio was limited compared to the primary FM radio audio channel. The United States Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, internet, wi-fi, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains j ...
(FCC) also allowed betting parlors in New York state to get horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance activity, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its bas ...
results from the state gaming commission via the same technology.
Many non-commercial educational
A non-commercial educational station (NCE station) is a radio station or television station that does not accept on-air advertisements (television advertisement, TV ads or radio advertisement, radio ads), as defined in the United States by the Fed ...
FM stations in the US (especially public radio
Public broadcasting (or public service broadcasting) is radio, television, and other electronic media outlets whose primary mission is public service with a commitment to avoiding political and commercial influence. Public broadcasters receive ...
stations affiliated with NPR) broadcast a radio reading service for the blind, which reads articles in local newspapers and sometimes magazines. The vision-impaired can request a special radio, permanently tuned to receive audio on a particular subcarrier frequency (usually 67 kHz or 92 kHz), from a particular FM station.
Services like these and others on broadcast FM subcarriers are referred to as a Subsidiary Communications Authority
Subsidiary Communications Authorization (SCA) in the United States, and Subsidiary Communications Multiplex Operation (SCMO) in Canada, is a subcarrier on a radio station, allowing the station to broadcast additional services as part of its signa ...
(SCA) service by the FCC in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, and as Subsidiary Communications Multiplex Operations (SCMO) by the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC; ) is a public organization in Canada tasked with the mandate as a regulatory agency tribunal for various electronic communications, covering broadcasting and telecommunic ...
(CRTC) in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
.
Datacasting
 The RDS/
The RDS/RBDS
Radio Data System (RDS) is a communications protocol standard for embedding small amounts of digital information in conventional FM radio broadcasts. RDS standardizes several types of information transmitted, including time, station identificat ...
subcarrier (57 kHz) allows FM radios to display what station they are on, pick another frequency on the same network or with the same format, scroll brief messages like station slogans, news, weather, or traffic—even activate pagers or remote billboards. It can also broadcast EAS messages, and has a station " format" name ALERT to automatically trigger radios to tune in for emergency info, even if a CD is playing. While it never really caught on in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
an stations frequently rely on this system.The radio station Heart FM used this service to cause people's radio sets to switch over to adverts for commercial vehicles during the morning and evening rush hours An upgraded version is built into digital radio
Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services. This should not be confused with In ...
.
xRDS
The extensible resource descriptor sequence (XRDS) is an XML-based file format that provides a list of services.
Background
The XML format used by XRDS was originally developed in 2004 by the OASIS XRI ( extensible resource identifier) Techn ...
is a system with which broadcasters can multiply the speed of data transmission in the FM channel by using further normal RDS subcarriers, shifted into the higher frequencies of the FM multiplex. The extra RDS subcarriers are placed in the upper empty part of the multiplex spectrum and carry the extra data payload. xRDS has no fixed frequencies for the additional 57 kHz carriers.
Until 2012, MSN Direct
MSN Direct was an FM radio-based digital service which allowed ' SPOT' portable devices to receive information from MSN services. Devices that supported MSN Direct included wristwatches, desktop clocks, in-car GPS satellite navigation units, and ...
used subcarriers to transmit traffic, gas prices, movie times, weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmo ...
and other information to GPS navigation devices, wristwatch
A watch is a timepiece carried or worn by a person. It is designed to maintain a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is worn around the wrist, attached by a watch strap or another type of ...
es, and other devices. Many of the subcarriers were from stations owned by Clear Channel. The technology was known as DirectBand.
FMeXtra
FMeXtra is a deprecated in-band on-channel digital radio broadcasting technology created by Digital Radio Express. It was intended to allow a second all-digital signal to be simulcast with an existing analog FM radio station, offering a less noisy ...
on FM uses dozens of small COFDM
In telecommunications, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a type of digital transmission used in digital modulation for encoding digital (binary) data on multiple Carrier wave, carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popul ...
subcarriers to transmit digital radio in a fully in-band on-channel
In-band on-channel (IBOC) is a hybrid method of transmitting digital radio and analog radio broadcast signals simultaneously on the same frequency. The name refers to the new digital signals being broadcast in the same AM or FM band (in-band), ...
manner. Removing other analog subcarriers (such as stereo) increases either the audio quality or channels available, the latter making it possible to send non-audio metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
* Descriptive ...
along with it, such as album covers, song lyrics, artist info, concert data, and more.
Telemetry and foldback
Many stations use subcarriers for internal purposes, such as gettingtelemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', 'far off', an ...
back from a remote transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of sig ...
, often located in a difficult-to-access area at the top of a mountain. A station's engineer can carry a decoder around with them and know anything that is wrong, as long as the station is on the air and they are within range. This is the essence of a wireless
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information (''telecommunication'') between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided transm ...
transmitter/studio link.
On wireless studio/transmitter link
A studio transmitter link (STL) sends a radio station's or television station's audio and video from the broadcast studio or origination facility to a radio transmitter, television transmitter or uplink facility in another location. This is accom ...
s (STLs), not only are the broadcast station's subcarriers transmitted, but other remote control
A remote control, also known colloquially as a remote or clicker, is an consumer electronics, electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operat ...
commands as well.
Interruptible foldback, such as for remote broadcasting, is also possible over subcarriers, though its role is limited.
MCPC satellites
Analogsatellite television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location.ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems ...
and terrestrial analog microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switc ...
communications rely on subcarriers transmitted with the video carrier on a satellite transponder
In telecommunications, a transponder is a device that, upon receiving a signal, emits a different signal in response. The term is a blend of ''transmitter'' and ''responder''.
In air navigation or radio frequency identification, a flight trans ...
or microwave channel for the audio channels of a video feed. There are usually at frequencies of 5.8, 6.2, or 6.8 MHz (the video carrier usually resides below 5 MHz on a satellite transponder or microwave relay). Extra subcarriers are sometimes transmitted at around 7 or 8 MHz for extra audio (such as radio stations) or low-to-medium-speed data. This is referred to as multiple channel per carrier (MCPC).
This is now mostly superseded by digital TV
Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative adv ...
(usually DVB-S
Digital Video Broadcasting – Satellite (DVB-S) is the original DVB standard for satellite television and dates from 1995, in its first release, while development lasted from 1993 to 1997. The first commercial applications were by Canal+ in ...
, DVB-S2
Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation (DVB-S2) is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the Digital Video Broadcasting Proj ...
or another MPEG-2
MPEG-2 (a.k.a. H.222/H.262 as was defined by the ITU) is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods ...
-based system), where audio and video data are packaged together (multiplex
Multiplex may refer to:
Science and technology
* Multiplex communication, combining many signals into one transmission circuit or channel
** Multiplex (television), a group of digital television or radio channels that are combined for broadcast
* ...
ed) in a single MPEG transport stream
MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS, MTS) or simply transport stream (TS) is a standard digital container format for transmission and storage of audio, video, and Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) data. It is used in broadcast syst ...
.
See also
*Subsidiary Communications Authority
Subsidiary Communications Authorization (SCA) in the United States, and Subsidiary Communications Multiplex Operation (SCMO) in Canada, is a subcarrier on a radio station, allowing the station to broadcast additional services as part of its signa ...
(SCA)
*xRDS
The extensible resource descriptor sequence (XRDS) is an XML-based file format that provides a list of services.
Background
The XML format used by XRDS was originally developed in 2004 by the OASIS XRI ( extensible resource identifier) Techn ...
References
External links
FM Receiver with subcarrier decoding circuit
United States Patent 4476581
United States Patent 3974520 {{Audio broadcasting Broadcast engineering