Strebe 1995 Projection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
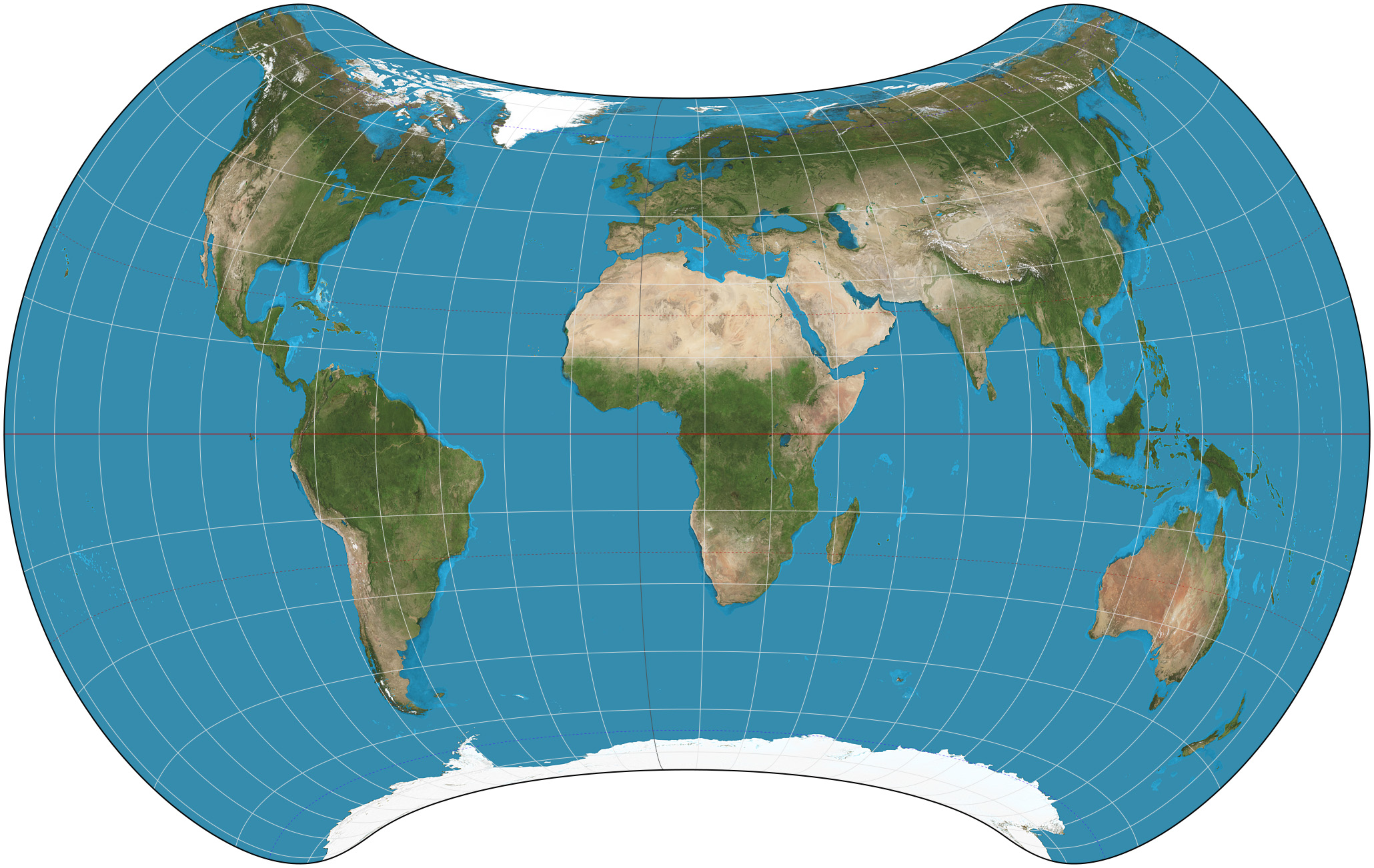 The Strebe 1995 projection, Strebe projection, Strebe lenticular equal-area projection, or Strebe equal-area polyconic projection is an equal-area
The Strebe 1995 projection, Strebe projection, Strebe lenticular equal-area projection, or Strebe equal-area polyconic projection is an equal-area
New York Times book review for Carl Zimmer's ''Science ink'', showing the Strebe projection as a large tattoo.
First published formulation of the Strebe projection.
{{Map projections Equal-area projections
 The Strebe 1995 projection, Strebe projection, Strebe lenticular equal-area projection, or Strebe equal-area polyconic projection is an equal-area
The Strebe 1995 projection, Strebe projection, Strebe lenticular equal-area projection, or Strebe equal-area polyconic projection is an equal-area map projection
In cartography, a map projection is any of a broad set of Transformation (function) , transformations employed to represent the curved two-dimensional Surface (mathematics), surface of a globe on a Plane (mathematics), plane. In a map projection, ...
presented by Daniel "daan" Strebe in 1994. Strebe designed the projection to keep all areas proportionally correct in size; to push as much of the inevitable distortion as feasible away from the continental masses and into the Pacific Ocean; to keep a familiar equatorial orientation; and to do all this without slicing up the map.
Description
Strebe first presented the projection at a joint meeting of the Canadian Cartographic Association and the North American Cartographic Information Society (NACIS) in August 1994. Its final formulation was completed in 1995. The projection has been available in the map projection software Geocart since Geocart 1.2, released in October 1994. The projection is arrived at by a series of steps, each of which preserves areas. Because each step preserves areas, the entire process preserves areas. The steps use a technique invented by Strebe called "substitute deprojection" or "Strebe's transformation". First, theEckert IV projection
The Eckert IV projection is an equal-area pseudocylindrical map projection. The length of the polar lines is half that of the equator, and lines of longitude are semiellipses, or portions of ellipses. It was first described by Max Eckert in 190 ...
is computed. Then, pretending that the Eckert projection is actually a shrunken portion of the Mollweide projection
400px, Mollweide projection of the world
400px, The Mollweide projection with Tissot's indicatrix of deformation
The Mollweide projection is an equal-area, pseudocylindrical map projection generally used for maps of the world or celestial sp ...
, the Eckert is "deprojected" back onto the sphere using the inverse transformation of the Mollweide projection. This yields a full-sphere-to-partial-sphere map. Then this mapped sphere is projected back to the plane using the Hammer projection
The Hammer projection is an equal-area map projection described by Ernst Hammer in 1892. Using the same 2:1 elliptical outer shape as the Mollweide projection, Hammer intended to reduce distortion in the regions of the outer meridians, where it ...
. While the projections named here are the ones that define the Strebe 1995 projection, the substitute deprojection principle is not constrained to particular projections.
The projection as described can be formulated as follows:
:
where is solved iteratively:
:
In these formulae, represents longitude and represents latitude.
Strebe's preferred arrangement is to set , as shown, and 11°E as the central meridian to avoid dividing eastern Siberia's Chukchi Peninsula
The Chukchi Peninsula (also Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula; , ''Chukotskiy poluostrov'', short form , ''Chukotka''), at about 66° N 172° W, is the easternmost peninsula of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village ...
. However, ''s'' can be modified to change the appearance without destroying the equal-area property.
See also
*List of map projections
This is a summary of map projections that have articles of their own on Wikipedia or that are otherwise WP:NOTABLE, notable. Because there is no limit to the number of possible map projections,
there can be no comprehensive list.
Table of proj ...
References
External links
New York Times book review for Carl Zimmer's ''Science ink'', showing the Strebe projection as a large tattoo.
First published formulation of the Strebe projection.
{{Map projections Equal-area projections