Stettin Lagoon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

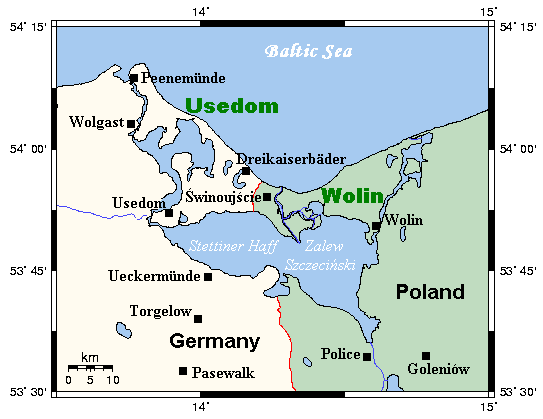
 Szczecin Lagoon (, ), also known as Oder Lagoon (), and Pomeranian Lagoon (), is a
Szczecin Lagoon (, ), also known as Oder Lagoon (), and Pomeranian Lagoon (), is a
 In the 10th century, the emerging Polish state strove for the area, but likely did not succeed with establishing control.
Following Poland's fragmentation, it formed part of the
In the 10th century, the emerging Polish state strove for the area, but likely did not succeed with establishing control.
Following Poland's fragmentation, it formed part of the

 Szczecin Lagoon (, ), also known as Oder Lagoon (), and Pomeranian Lagoon (), is a
Szczecin Lagoon (, ), also known as Oder Lagoon (), and Pomeranian Lagoon (), is a lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') an ...
in the Oder
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through wes ...
estuary, shared by Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
. It is separated from the Pomeranian Bay of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
by the islands of Usedom
Usedom ( , ) is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
It lies north of the Szczecin Lagoon estuary of the ...
and Wolin
Wolin (; ) is a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the island of Usedom (Uznam) by the Strait of Świna, and from mainla ...
. The lagoon is subdivided into the ''Kleines Haff'' (, "small lagoon") in the West and the ''Wielki Zalew'' (, "great lagoon") in the East. An ambiguous historical German name was ''Frisches Haff'', which later exclusively referred to the Vistula Lagoon
The Vistula Lagoon is a brackish water lagoon on the Baltic Sea roughly 56 miles (90 km) long, 6 to 15 miles (10 to 19 km) wide, and up to 17 feet (5 m) deep, separated from the Gdańsk Bay by the Vistula Spit.
Geography
The lag ...
.
Geography
From the South, the lagoon is fed by several arms of theOder
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through wes ...
river and smaller rivers like Ziese
Ziese is a river of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It forms a Bifurcation (river), pseudobifurcation: its water west of Kemnitz, Rappenhagen flows into the Bay of Greifswald, Dänische Wiek near Greifswald, and its water east of Rappenhagen f ...
, Peene
The Peene (; ) is a river in Germany.
Geography
The Westpeene, with the Ostpeene as its longer tributary, and the Kleine Peene/Teterower Peene (with a ''Peene '' without specification (or ''Nordpeene'') as its smaller and shorter affluent) f ...
, Zarow
The Zarow is a lowland river in Western Pomerania in the east of the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in Germany.
Description
The lower course of the river, also known topographically as Zarow, is formed from two ditches, the Landgraben and t ...
, Uecker
The Uecker () or Ucker () is a river in the northeastern German states of Brandenburg, where it is known as the ''Ucker'', and of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. It flows northward from Uckermark to the Szczecin Lagoon.
Path
Its source lies in the U ...
, and Ina. In the North, the lagoon is connected to the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
's Bay of Pomerania
The Bay of Pomerania ( ; ; ) is a basin in the southwestern Baltic Sea, off the Pomeranian shores of Poland and Germany. It stretches between the northernmost tip of the island of Rügen called ''Gellort'' northwest of Cape Arkona in the wes ...
with the three straits Peenestrom
The Peenestrom is a strait in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany, which separates the mainland from the island of Usedom. It is long and is the westernmost connection between the Szczecin Lagoon and the Baltic Sea (together with the Świna and D ...
, Świna
The Świna (; Pomeranian: ''Swina'') is a channel in northwest Poland, between from the German border. It connects the Szczecin Lagoon with the Baltic Sea separating the islands of Uznam (German: Usedom) and Wolin. It is a part of the Oder estu ...
and Dziwna
The Dziwna () is a channel of the Oder River in northwestern Poland, one of three straits connecting the Szczecin Lagoon with the Bay of Pomerania of the Baltic Sea. It separates the island of Wolin from the Polish mainland. The other two ch ...
, which divide the mainland and the islands of Usedom
Usedom ( , ) is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
It lies north of the Szczecin Lagoon estuary of the ...
and Wolin
Wolin (; ) is a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the island of Usedom (Uznam) by the Strait of Świna, and from mainla ...
.
The lagoon covers an area of 687 km2, its natural depth is an average 3.8 metres, and 8.5 metres at maximum.Ulrich Schiewer, ''Ecology of Baltic coastal waters'', Springer, 2008, p.115, The depth of shipping channels however can exceed 10.5 metres. Thus, the lagoon holds about 2.58 km3 of water. The annual average water temperature is 11 °C.Ulrich Schiewer, ''Ecology of Baltic coastal waters'', Springer, 2008, p.117,
The Oder river and its confluences are responsible for 94% of the water loads discharged into the lagoon, amounting to an average annual 17 km3 or 540 m3 per second.Ulrich Schiewer, ''Ecology of Baltic coastal waters'', Springer, 2008, p.116, All other confluences contribute a combined annual 1 km3. Since no reliable data for an inflow from the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
exist, the combined inflow is an estimated 18 km3 from a catchment area of 129,000 km2, residing in the lagoon for an average 55 days before being discharged into the Pomeranian Bay. The nutrients
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
thereby transported into the lagoon have made it hyper(eu)trophic to eutrophic
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the s ...
.Ulrich Schiewer, ''Ecology of Baltic coastal waters'', Springer, 2008, p.118, The straits Peenestrom
The Peenestrom is a strait in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany, which separates the mainland from the island of Usedom. It is long and is the westernmost connection between the Szczecin Lagoon and the Baltic Sea (together with the Świna and D ...
, Świna
The Świna (; Pomeranian: ''Swina'') is a channel in northwest Poland, between from the German border. It connects the Szczecin Lagoon with the Baltic Sea separating the islands of Uznam (German: Usedom) and Wolin. It is a part of the Oder estu ...
and Dziwna
The Dziwna () is a channel of the Oder River in northwestern Poland, one of three straits connecting the Szczecin Lagoon with the Bay of Pomerania of the Baltic Sea. It separates the island of Wolin from the Polish mainland. The other two ch ...
are responsible for 17%, 69%, and 14% of the discharge, respectively.Ulrich Schiewer, ''Ecology of Baltic coastal waters'', Springer, 2008, p.119,
The average salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
is between 0.5 and 2 grams of salt per kilogram of water (approximately equivalent to 0.5 and 2 parts per thousand
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe the small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction.
Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures ...
pt. Occasionally northerly winds reverse the direction of the Świna, admitting sea water from the Baltic Sea into the lagoon, raising the local salinity to 6 ppt.
Towns around the Lagoon
*Szczecin
Szczecin ( , , ; ; ; or ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Poland-Germany border, German border, it is a major port, seaport, the la ...
(Poland)
*Świnoujście
Świnoujście (; ; ; meaning " Świna ivermouth"; ) is a city in Western Pomerania and seaport on the Baltic Sea and Szczecin Lagoon, in the extreme north-west of Poland, mainly on the islands of Usedom and Wolin, and Karsibór island, once ...
(Poland)
*Police
The police are Law enforcement organization, a constituted body of Law enforcement officer, people empowered by a State (polity), state with the aim of Law enforcement, enforcing the law and protecting the Public order policing, public order ...
(Poland)
*Ueckermünde
Ueckermünde () is a seaport town in northeast Germany, located in the district of Vorpommern-Greifswald, Pomerania, Western Pomerania, near Germany's border with Poland's Police County.
Ueckermünde has a long and varied history, going back to ...
(Germany)
*Wolin
Wolin (; ) is a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the island of Usedom (Uznam) by the Strait of Świna, and from mainla ...
(Poland)
*Usedom
Usedom ( , ) is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
It lies north of the Szczecin Lagoon estuary of the ...
(Germany)
*Nowe Warpno
Nowe Warpno (; ) is a historic town in northwestern Poland, within Police County in West Pomeranian Voivodeship
West Pomeranian Voivodeship is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) in northwestern Poland. Its capital and largest cit ...
(Poland)
History
 In the 10th century, the emerging Polish state strove for the area, but likely did not succeed with establishing control.
Following Poland's fragmentation, it formed part of the
In the 10th century, the emerging Polish state strove for the area, but likely did not succeed with establishing control.
Following Poland's fragmentation, it formed part of the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (; ; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country existed in the Middle Ages between years 1121–11 ...
. In the 17th century, it passed to Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
. Later on, it gradually passed to the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
in the 18th and 19th century, and from 1871 was part of unified Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
. In 1880, the '' Kaiserfahrt'' ("Emperor's passage") channel on Usedom was opened, a water route with a depth of 10 metres connecting the lagoon with the Baltic Sea by bypassing the eastern part of the Swine, allowing large ships to enter the lagoon and the seaport of Stettin quicker and safer.
The canal, approximately 12 km long and 10 metres deep, was dug by the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
between 1874 and 1880, during the reign of the first Kaiser Wilhelm Kaiser Wilhelm is a common reference to two German emperors:
* Wilhelm I, German Emperor (1797–1888)
* Wilhelm II, German Emperor (1859–1941)
Kaiser Wilhelm may also refer to:
* Kaiser Wilhelm (baseball) (1874–1936), early 20th century baseba ...
(1797–1888) after whom it was named. Also, the work resulted in a new island named Kaseburg (Karsibór
Karsibór ( or ''Caseburg'') is an island in the Szczecin Lagoon, Poland, which was created by the cutting of the Piast Canal which separated it from the island of Usedom. The island was named after its largest village (now district of the town ...
) being cut off from Usedom.
After the defeat of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
in 1945, the eastern part of the lagoon became part of Poland, while the western part became part of East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
. The ''Kaiserfahrt'' was renamed ''Piast Canal
The Piast Canal (, ) is a ship canal that connects the Szczecin Lagoon in the estuary of the Oder river with the Baltic Sea via the Świna river. The eastern part of the Świna is bypassed by the canal, providing a more convenient south-north c ...
'', after the Polish Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule in Pol ...
, which first included the region to Poland in the 10th century.
The German–Polish border also divides the Nowe Warpno Lake near , Luckow.
Economy
The lagoon has served as an important fishing grounds for centuries, as a major transportation pathway since the 18th century, and as a tourist destination since the 20th century.Heringsdorf Airport
Heringsdorf Airport () is a regional airport located near Garz on the island of Usedom in Germany. It used to be an East German airbase and today features summer leisure routes from cities in Germany and Switzerland as well as general aviation.
...
on Usedom
Usedom ( , ) is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
It lies north of the Szczecin Lagoon estuary of the ...
island is located on the shores of the lagoon.
Nature
The southern shore of the lagoon belongs to the Am Stettiner Haff Nature Park, its northern shore and the island of Usedom to theUsedom Island Nature Park
The Usedom Island Nature Park () comprises the German part of the island of Usedom in the district of Vorpommern-Greifswald in the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. In addition to the island itself, the park covers the waterbody between th ...
. To the west is the Anklamer Stadtbruch Nature Reserve and, within it, the Anklamer Torfmoor
The Anklamer Torfmoor, also called the Anklamer Stadtbruch od ''Städtisches Torfmoor'', is an extensive area of bog on the western shore of the Stettin Lagoon. Much of the area is part of the Anklamer Stadtbruch Nature Reserve.
A storm surge on ...
, a protected wetland which is renaturalising after being used for peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of the most ...
extraction.
See also
*Curonian Lagoon
The Curonian Lagoon (or Bay, Gulf; Prussian: ''Kursjanmari'', , ) is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surface area is . The Neman River () supplies about 90% of its inflows; its watershed consists of ...
*Vistula Lagoon
The Vistula Lagoon is a brackish water lagoon on the Baltic Sea roughly 56 miles (90 km) long, 6 to 15 miles (10 to 19 km) wide, and up to 17 feet (5 m) deep, separated from the Gdańsk Bay by the Vistula Spit.
Geography
The lag ...
References
External links
* {{Authority control Lagoons of Germany Lagoons of Poland Baltic Sea Lagoons of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania Landforms of West Pomeranian Voivodeship Nature parks in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania Parks in West Pomeranian Voivodeship Natura 2000 in Germany Natura 2000 in Poland International lakes of Europe Germany–Poland border