Stapes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''stapes'' or stirrup is a
 The ''stapes'' is the third bone of the three
The ''stapes'' is the third bone of the three
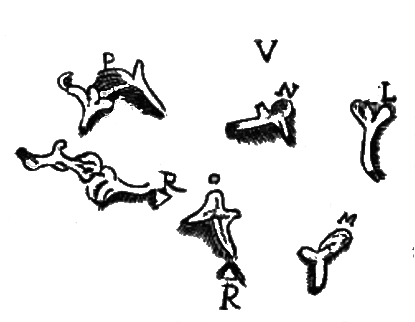 The ''stapes'' is commonly described as having been discovered by the professor Giovanni Filippo Ingrassia in 1546 at the
The ''stapes'' is commonly described as having been discovered by the professor Giovanni Filippo Ingrassia in 1546 at the
bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
in the middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes), which transfer the vibrations ...
of humans and other tetrapods which is involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
. This bone is connected to the oval window by its annular ligament, which allows the footplate (or base) to transmit sound energy through the oval window into the inner ear. The ''stapes'' is the smallest and lightest bone in the human body
The human body is the entire structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently Organ (biology), organs and then Organ system, org ...
, and is so-called because of its resemblance to a stirrup ().
Structure
 The ''stapes'' is the third bone of the three
The ''stapes'' is the third bone of the three ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three irregular bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, and are among the smallest bones in the human body. Although the term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone" (from Latin ''ossi ...
in the middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes), which transfer the vibrations ...
and the smallest in the human body. It measures roughly , greater along the head-base span. It rests on the oval window, to which it is connected by an annular ligament and articulates with the ''incus
The ''incus'' (: incudes) or anvil in the ear is one of three small bones (ossicles) in the middle ear. The incus receives vibrations from the malleus, to which it is connected laterally, and transmits these to the stapes medially. The incus i ...
'', or anvil through the incudostapedial joint
The incudostapedial joint is a small, synovial ball-and-socket joint between the ''incus'' (anvil) and the '' stapes'' (stirrup). The joint's function is to transfer vibrations between the two ossicles. The incudostapedial joint lies between the ...
. They are connected by anterior and posterior limbs ().
Development
The ''stapes'' develops from the secondpharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are transient structures seen in the Animal embryonic development, embryonic development of humans and other vertebrates, that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, t ...
during the sixth to eighth week of embryological life. The central cavity of the ''stapes'', the ''obturator foramen'', is due to the presence embryologically of the stapedial artery, which usually regresses in humans during normal development.
Animals
The ''stapes'' is one of three ossicles in mammals. In non-mammaliantetrapods
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four- limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all extant and extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the lat ...
, the bone homologous to the ''stapes'' is usually called the columella; however, in reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s, either term may be used. In fish, the homologous bone is called the hyomandibular, and is part of the gill arch supporting either the spiracle or the jaw, depending on the species. The equivalent term in amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s is the '.
Variation
The ''stapes'' appears to be relatively constant in size in different ethnic groups. In 0.01–0.02% of people, the stapedial artery does not regress, and persists in the central foramen. In this case, a pulsatile sound may be heard in the affected ear, or there may be no symptoms at all. Rarely, the ''stapes'' may be completely absent.Function
Situated between the incus and the inner ear, the ''stapes'' transmits sound vibrations from the incus to the oval window, a membrane-covered opening to the inner ear. The ''stapes'' is also stabilized by the stapedius muscle, which is innervated by thefacial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of ta ...
.
Clinical relevance
Otosclerosis is a congenital or spontaneous-onset disease characterized by abnormal bone remodeling in the inner ear. Often this causes the ''stapes'' to adhere to the oval window, which impedes its ability to conduct sound, and is a cause ofconductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss (CHL) is a type of hearing impairment that occurs when sound waves are unable to efficiently travel through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear structures such as the ossicles. This blockage or dysfun ...
. Clinical otosclerosis is found in about 1% of people, although it is more common in forms that do not cause noticeable hearing loss. Otosclerosis is more likely in young age groups, and females. Two common treatments are stapedectomy, the surgical removal of the ''stapes'' and replacement with an artificial prosthesis, and stapedotomy, the creation of a small hole in the base of the ''stapes'' followed by the insertion of an artificial prosthesis into that hole. Surgery may be complicated by a persistent stapedial artery, fibrosis-related damage to the base of the bone, or obliterative otosclerosis, resulting in obliteration of the base.
History
 The ''stapes'' is commonly described as having been discovered by the professor Giovanni Filippo Ingrassia in 1546 at the
The ''stapes'' is commonly described as having been discovered by the professor Giovanni Filippo Ingrassia in 1546 at the University of Naples
The University of Naples Federico II (; , ) is a public university, public research university in Naples, Campania, Italy. Established in 1224 and named after its founder, Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II, it is the oldest public, s ...
, although this remains the nature of some controversy, as Ingrassia's description was published posthumously in his 1603 anatomical commentary '. Spanish anatomist Pedro Jimeno is first to have been credited with a published description, in (1549). The bone is so-named because of its resemblance to a stirrup (), an example of a late Latin
Late Latin is the scholarly name for the form of Literary Latin of late antiquity.Roberts (1996), p. 537. English dictionary definitions of Late Latin date this period from the 3rd to 6th centuries CE, and continuing into the 7th century in ...
word, probably created in mediaeval times from "to stand" (), as stirrups did not exist in the early Latin-speaking world.
References
External links
* {{Good article Auditory system Skeletal system Ossicles Otorhinolaryngology Otology Human head and neck