spermatogenesis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Spermatogenesis is the process by which
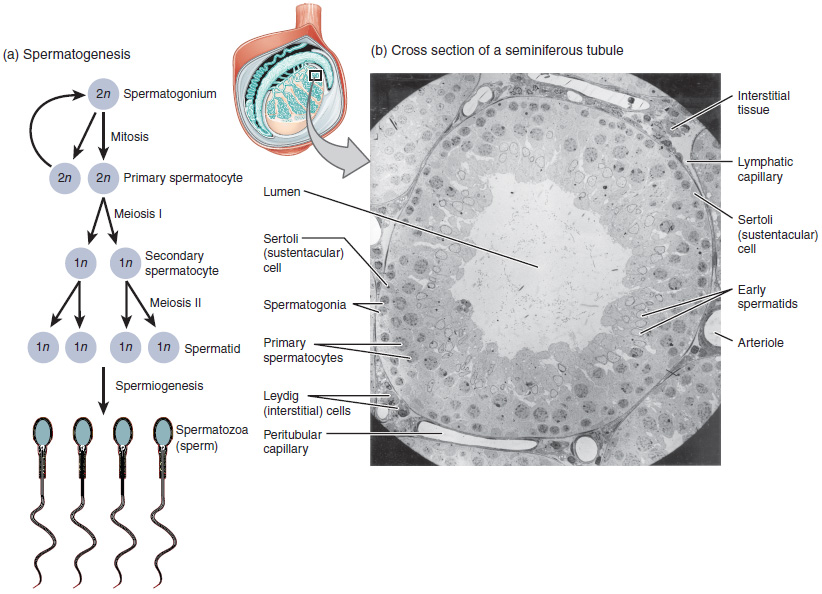
 Spermatocytogenesis is the male form of gametocytogenesis and results in the formation of
Spermatocytogenesis is the male form of gametocytogenesis and results in the formation of
 At all stages of differentiation, the spermatogenic cells are in close contact with Sertoli cells which are thought to provide structural and metabolic support to the developing sperm cells. A single Sertoli cell extends from the basement membrane to the lumen of the seminiferous tubule, although the cytoplasmic processes are difficult to distinguish at the light microscopic level.
Sertoli cells serve a number of functions during spermatogenesis, they support the developing gametes in the following ways:
* Maintain the environment necessary for development and maturation, via the blood-testis barrier
* Secrete substances initiating meiosis
* Secrete supporting testicular fluid
* Secrete androgen-binding protein (ABP), which concentrates
At all stages of differentiation, the spermatogenic cells are in close contact with Sertoli cells which are thought to provide structural and metabolic support to the developing sperm cells. A single Sertoli cell extends from the basement membrane to the lumen of the seminiferous tubule, although the cytoplasmic processes are difficult to distinguish at the light microscopic level.
Sertoli cells serve a number of functions during spermatogenesis, they support the developing gametes in the following ways:
* Maintain the environment necessary for development and maturation, via the blood-testis barrier
* Secrete substances initiating meiosis
* Secrete supporting testicular fluid
* Secrete androgen-binding protein (ABP), which concentrates
thefreedictionary.com > oligospermia
Citing: Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers, 2007 by Saunders; The American Heritage Medical Dictionary 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company; Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition 2009; McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine, 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies and is a common finding in
Spermatogenesis — male reproductive physiology
Spermatogenesis animation
{{Authority control Animal developmental biology Animal physiology Mammal male reproductive system Meiosis
haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; : spermatozoa; ) is a motile sperm cell (biology), cell produced by male animals relying on internal fertilization. A spermatozoon is a moving form of the ploidy, haploid cell (biology), cell that is ...
develop from germ cell
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they unde ...
s in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell ...
s located close to the basement membrane of the tubules. These cells are called spermatogonial stem cells. The mitotic division of these produces two types of cells. Type A cells replenish the stem cells, and type B cells differentiate into primary spermatocyte
Spermatocytes are a type of male gametocyte in animals. They derive from immature germ cells called spermatogonia. They are found in the testis, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and s ...
s. The primary spermatocyte divides meiotically (Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
I) into two secondary spermatocytes; each secondary spermatocyte divides into two equal haploid spermatids
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
Spermatids are con ...
by Meiosis II. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm) by the process of spermiogenesis. These develop into mature spermatozoa, also known as sperm cells. Thus, the primary spermatocyte gives rise to two cells, the secondary spermatocytes, and the two secondary spermatocytes by their subdivision produce four spermatozoa and four haploid cells.
Spermatozoa are the mature male gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s in many sexually reproducing organisms. Thus, spermatogenesis is the male version of gametogenesis, of which the female equivalent is oogenesis
Oogenesis () or ovogenesis is the differentiation of the ovum (egg cell) into a cell competent to further develop when fertilized. It is developed from the primary oocyte by maturation. Oogenesis is initiated before birth during embryonic devel ...
. In mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s it occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the male testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
in a stepwise fashion. Spermatogenesis is highly dependent upon optimal conditions for the process to occur correctly, and is essential for sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
. DNA methylation
DNA methylation is a biological process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. Methylation can change the activity of a DNA segment without changing the sequence. When located in a gene promoter (genetics), promoter, DNA methylati ...
and histone modification have been implicated in the regulation of this process. It starts during puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
and usually continues uninterrupted until death, although a slight decrease can be discerned in the quantity of produced sperm with increase in age (see Male infertility
Male infertility refers to a sexually mature male's inability to impregnate a fertile female. Male infertility can wholly or partially account for 40% of infertility among couples who are trying to have children. "A problem with the male is the s ...
).
Spermatogenesis starts in the bottom part of seminiferous tubes and, progressively, cells go deeper into tubes and moving along it until mature spermatozoa reaches the lumen, where mature spermatozoa are deposited. The division happens asynchronically; if the tube is cut transversally one could observe different maturation states. A group of cells with different maturation states that are being generated at the same time is called a spermatogenic wave.
Purpose
Spermatogenesis produces mature male gametes, commonly called ''sperm'' but more specifically known as ''spermatozoa'', which are able to fertilize the counterpart female gamete, theoocyte
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female ger ...
, during conception to produce a single-celled individual known as a zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
. This is the cornerstone of sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
and involves the two gametes both contributing half the normal set of chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s (haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
) to result in a chromosomally normal (diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
) zygote.
To preserve the number of chromosomes in the offspring – which differs between species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
– one of each gamete must have half the usual number of chromosomes present in other body cells. Otherwise, the offspring will have twice the normal number of chromosomes, and serious abnormalities may result. In humans, chromosomal abnormalities arising from incorrect spermatogenesis results in congenital defects and abnormal birth defects ( Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome (KS), also known as 47,XXY, is a chromosome anomaly where a male has an extra X chromosome. These complications commonly include infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles (if present). These symptoms are often n ...
) and in most cases, spontaneous abortion of the developing foetus.
Location in humans
Spermatogenesis takes place within several structures of themale reproductive system
The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvic cavity, pelvis.
The main male sex organs are the hu ...
. The initial stages occur within the testes and progress to the epididymis
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; ...
where the developing gametes mature and are stored until ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. ...
. The seminiferous tubules of the testes are the starting point for the process, where spermatogonial stem cells adjacent to the inner tubule wall divide in a centripetal direction—beginning at the walls and proceeding into the innermost part, or ''lumen''—to produce immature sperm. Maturation occurs in the epididymis. The location estes/Scrotumis specifically important as the process of spermatogenesis requires a lower temperature to produce viable sperm, specifically 1°-8 °C lower than normal body temperature of 37 °C (98.6 °F). Clinically, small fluctuations in temperature such as from an athletic support strap, causes no impairment in sperm viability or count.
Duration
For humans, the entire process of spermatogenesis is variously estimated as taking between 72 and 74 days (according to tritium-labelled biopsies) and approximately 120 days (according to DNA clock measurements). Including the transport on ductal system, it takes 3 months. Testes produce 200 to 300 million spermatozoa daily. However, only about half or 100 million of these become viable sperm.Stages
The entire process of spermatogenesis can be broken up into several distinct stages, each corresponding to a particular type of cell in humans. In the following table, ploidy, copy number and chromosome/chromatid counts are for one cell, generally prior to DNA synthesis and division (in G1 if applicable). The primary spermatocyte is arrested after DNA synthesis and prior to division.Spermatocytogenesis

spermatocyte
Spermatocytes are a type of male gametocyte in animals. They derive from immature germ cells called spermatogonia. They are found in the testis, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and s ...
s possessing half the normal complement of genetic material. In spermatocytogenesis, a diploid spermatogonium
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles.
There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in human ...
, which resides in the basal compartment of the seminiferous tubules, divides mitotically, producing two diploid intermediate cells called primary spermatocytes. Each primary spermatocyte then moves into the adluminal compartment of the seminiferous tubules and duplicates its DNA and subsequently undergoes ''meiosis I'' to produce two haploid secondary spermatocytes, which will later divide once more into haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
spermatids
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
Spermatids are con ...
. This division implicates sources of genetic variation, such as random inclusion of either parental chromosomes, and chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal crossover, or crossing over, is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes' sister chromatids, non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomes. It is one of the fina ...
that increases the genetic variability of the gamete. The DNA damage response (DDR) machinery plays an important role in spermatogenesis. The protein FMRP binds to meiotic chromosomes and regulates the dynamics of the DDR machinery during spermatogenesis. FMRP appears to be necessary for the repair of DNA damage.
During spermatocytogenesis, meiosis employs special DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is cons ...
processes that remove DNA damages and help maintain the integrity of the genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
that is passed on to progeny. These DNA repair processes include homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in Cell (biology), cellular organi ...
al repair and non-homologous end joining
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is a pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. It is called "non-homologous" because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homology directed repair ...
Each cell division from a spermatogonium to a spermatid is incomplete; the cells remain connected to one another by bridges of cytoplasm to allow synchronous development. Not all spermatogonia divide to produce spermatocytes; otherwise, the supply of spermatogonia would run out. Instead, spermatogonial stem cells divide mitotically to produce copies of themselves, ensuring a constant supply of spermatogonia to fuel spermatogenesis.
Spermatidogenesis
Spermatidogenesis is the creation of spermatids from secondary spermatocytes. Secondary spermatocytes produced earlier rapidly enter meiosis II and divide to produce haploid spermatids. The brevity of this stage means that secondary spermatocytes are rarely seen inhistological
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at large ...
studies.
Spermiogenesis
During spermiogenesis, the spermatids begin to form a tail by growing microtubules on one of the centrioles, which turns into basal body. These microtubules form an axoneme. Later the centriole is modified in the process of centrosome reduction. The anterior part of the tail (called midpiece) thickens because mitochondria are arranged around the axoneme to ensure energy supply. SpermatidDNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
also undergoes packaging, becoming highly condensed. The DNA is packaged firstly with specific nuclear basic proteins, which are subsequently replaced with protamines during spermatid elongation. The resultant tightly packed chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important r ...
is transcriptionally inactive. The Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins ...
surrounds the now condensed nucleus, becoming the acrosome.
Maturation then takes place under the influence of testosterone, which removes the remaining unnecessary cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
and organelles. The excess cytoplasm, known as ''residual bodies'', is phagocytosed by surrounding Sertoli cells in the testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
. The resulting spermatozoa are now mature but lack motility. The mature spermatozoa are released from the protective Sertoli cells into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule in a process called ''spermiation''.
The non-motile spermatozoa are transported to the epididymis
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; ...
in ''testicular fluid'' secreted by the Sertoli cells with the aid of peristaltic contraction. While in the epididymis the spermatozoa gain motility and become capable of fertilization. However, transport of the mature spermatozoa through the remainder of the male reproductive system
The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body, and within the pelvic cavity, pelvis.
The main male sex organs are the hu ...
is achieved via muscle contraction rather than the spermatozoon's recently acquired motility.
Role of Sertoli cells
testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
in close proximity to the developing gametes
** Testosterone is needed in very high quantities for maintenance of the reproductive tract, and ABP allows a much higher level of fertility
* Secrete hormones affecting pituitary gland control of spermatogenesis, particularly the polypeptide hormone, inhibin
* Phagocytose residual cytoplasm left over from spermiogenesis
* Secretion of anti-Müllerian hormone
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), also known as Müllerian-inhibiting hormone (MIH), is a glycoprotein hormone structurally related to Activin and inhibin, inhibin and activin from the transforming growth factor beta superfamily, whose key roles a ...
causes deterioration of the Müllerian duct
* Protect spermatids from the immune system of the male, via the blood-testis barrier
* Contribute to the spermatogonial stem cell
A spermatogonial stem cell (SSC), also known as a type A spermatogonium, is a spermatogonium that does not differentiate into a spermatocyte, a precursor of sperm cells. Instead, they continue dividing into other spermatogonia or remain dormant ...
niche
The intercellular adhesion molecule
In molecular biology, intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) are part of the immunoglobulin superfamily. They are important in inflammation, immune responses and in intracellular signalling event ...
s ICAM-1
ICAM-1 (Intercellular adhesion molecule, Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1) also known as CD54 (Cluster of Differentiation 54) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ICAM1'' gene. This gene encodes a cell surface glycoprotein which is ty ...
and soluble ICAM-1 have antagonistic effects on the tight junctions forming the blood-testis barrier. ICAM-2 molecules regulate spermatid adhesion on the apical side of the barrier (towards the lumen).
Influencing factors
The process of spermatogenesis is highly sensitive to fluctuations in the environment, particularlyhormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s and temperature. Testosterone is required in large local concentrations to maintain the process, which is achieved via the binding of testosterone by androgen binding protein present in the seminiferous tubules. Testosterone is produced by interstitial cells, also known as Leydig cells, which reside adjacent to the seminiferous tubules.
Seminiferous epithelium is sensitive to elevated temperature in humans and some other species, and will be adversely affected by temperatures as high as normal body temperature. In addition, spermatogonia do not achieve maturity at body temperature in most of mammals, as β-polimerase and spermatogenic recombinase need a specific optimal temperature. Consequently, the testes are located outside the body in a sac of skin called the scrotum
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin ...
. The optimal temperature is maintained at 2 °C (man
A man is an adult male human. Before adulthood, a male child or adolescent is referred to as a boy.
Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the f ...
) (8 °C mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
) below body temperature. This is achieved by regulation of blood flow and positioning towards and away from the heat of the body by the cremasteric muscle
The cremaster muscle is a paired structure made of thin layers of striated and smooth muscle that covers the testicles and the spermatic cords in human males. It consists of the lateral and medial parts. Cremaster is an involuntary muscle, respo ...
and the dartos smooth muscle in the scrotum.
One important mechanism is a thermal exchange between testicular arterial and venous blood streams. Specialized anatomic arrangements consist of two zones of coiling along the internal spermatic artery. This anatomic arrangement prolongs the time of contact and the thermal exchange between the testicular arterial and venous blood streams and may, in part, explain the temperature gradient between aortic and testicular arterial blood reported in dogs and rams. Moreover, reduction in pulse pressure, occurring in the proximal one third of the coiled length of the internal spermatic artery. Moreover, the activity of spermatogenic recombinase decreases, and this is supposed to be an important factor of testicles degeneration.
Dietary deficiencies (such as vitamins B, E and A), anabolic steroids, metals (cadmium and lead), x-ray exposure, dioxin, alcohol, and infectious diseases will also adversely affect the rate of spermatogenesis. In addition, the male germ line is susceptible to DNA damage caused by oxidative stress, and this damage likely has a significant impact on fertilization and pregnancy. According to the study by Omid Mehrpour et al exposure to pesticides also affects spermatogenesis.
Hormonal control
Hormonal control of spermatogenesis varies among species. In humans the mechanism is not completely understood; however it is known that initiation of spermatogenesis occurs at puberty due to the interaction of thehypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
, pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
and Leydig cells. If the pituitary gland is removed, spermatogenesis can still be initiated by follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
. In contrast to FSH, luteinizing hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH, also known as luteinising hormone, lutropin and sometimes lutrophin) is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (G ...
(LH) appears to have little role in spermatogenesis outside of inducing gonadal testosterone production.
FSH stimulates both the production of androgen binding protein (ABP) by Sertoli cells, and the formation of the blood-testis barrier. ABP is essential to concentrating testosterone in levels high enough to initiate and maintain spermatogenesis. Intratesticular testosterone levels are 20–100 or 50–200 times higher than the concentration found in blood, although there is variation over a 5- to 10-fold range amongst healthy men.. Testosterone production does not remain constant throughout the day, but follows a circadian rhythm. The maximum peak of testosterone occurs at 8 a.m., which explains why men frequently suffer from morning erections. In younger men, testosterone peaks are higher. FSH may initiate the sequestering of testosterone in the testes, but once developed only testosterone is required to maintain spermatogenesis. However, increasing the levels of FSH will increase the production of spermatozoa by preventing the apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
of ''type A spermatogonia''. The hormone inhibin acts to decrease the levels of FSH. Studies from rodent models suggest that gonadotropins (both LH and FSH) support the process of spermatogenesis by suppressing the proapoptotic signals and therefore promote spermatogenic cell survival.
The Sertoli cells themselves mediate parts of spermatogenesis through hormone production. They are capable of producing the hormones estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also called oestrogen, oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of female reproductive cycles such as estrous and menstrual cycles. Estradiol is responsible ...
and inhibin. The Leydig cells are also capable of producing estradiol in addition to their main product testosterone. Estrogen has been found to be essential for spermatogenesis in animals. However, a man with estrogen insensitivity syndrome (a defective ERα) was found produce sperm with a normal sperm count, albeit abnormally low sperm viability; whether he was sterile or not is unclear. Levels of estrogen that are too high can be detrimental to spermatogenesis due to suppression of gonadotropin secretion and by extension intratesticular testosterone production. The connection between spermatogenesis and prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin and mammotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secr ...
levels appears to be moderate, with optimal prolactin levels reflecting efficient sperm production.
Disorders
Disorders of spermatogenesis may cause oligospermia, which issemen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a bodily fluid that contains spermatozoon, spermatozoa which is secreted by the male gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphrodite, hermaphroditic animals. In humans and placen ...
with a low concentration of sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
Citing: Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers, 2007 by Saunders; The American Heritage Medical Dictionary 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company; Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition 2009; McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine, 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies
male infertility
Male infertility refers to a sexually mature male's inability to impregnate a fertile female. Male infertility can wholly or partially account for 40% of infertility among couples who are trying to have children. "A problem with the male is the s ...
.
See also
*Anisogamy
Different forms of anisogamy: A) anisogamy of motile cells, B) 283x283px
Anisogamy is a form of sexual reproduction">egg cell">oogamy (egg cell and sperm cell), C) anisogamy of non-motile cells (egg cell and spermatia).">283x283px
Anisogamy is ...
*Evolution of sexual reproduction
Sexually reproducing animals, plants, fungi and protists are thought to have evolved from a common ancestor that was a single-celled eukaryotic species.
Sexual reproduction is widespread in eukaryotes, though a few eukaryotic species have ...
* Folliculogenesis
* Germ cells
*Male infertility
Male infertility refers to a sexually mature male's inability to impregnate a fertile female. Male infertility can wholly or partially account for 40% of infertility among couples who are trying to have children. "A problem with the male is the s ...
*Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
* Oncofertility
*Oogenesis
Oogenesis () or ovogenesis is the differentiation of the ovum (egg cell) into a cell competent to further develop when fertilized. It is developed from the primary oocyte by maturation. Oogenesis is initiated before birth during embryonic devel ...
* Origin and function of meiosis
* Sertoli cells
*Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
* Semen analysis
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
Spermatogenesis — male reproductive physiology
Spermatogenesis animation
{{Authority control Animal developmental biology Animal physiology Mammal male reproductive system Meiosis