Spaying on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Neutering, from the

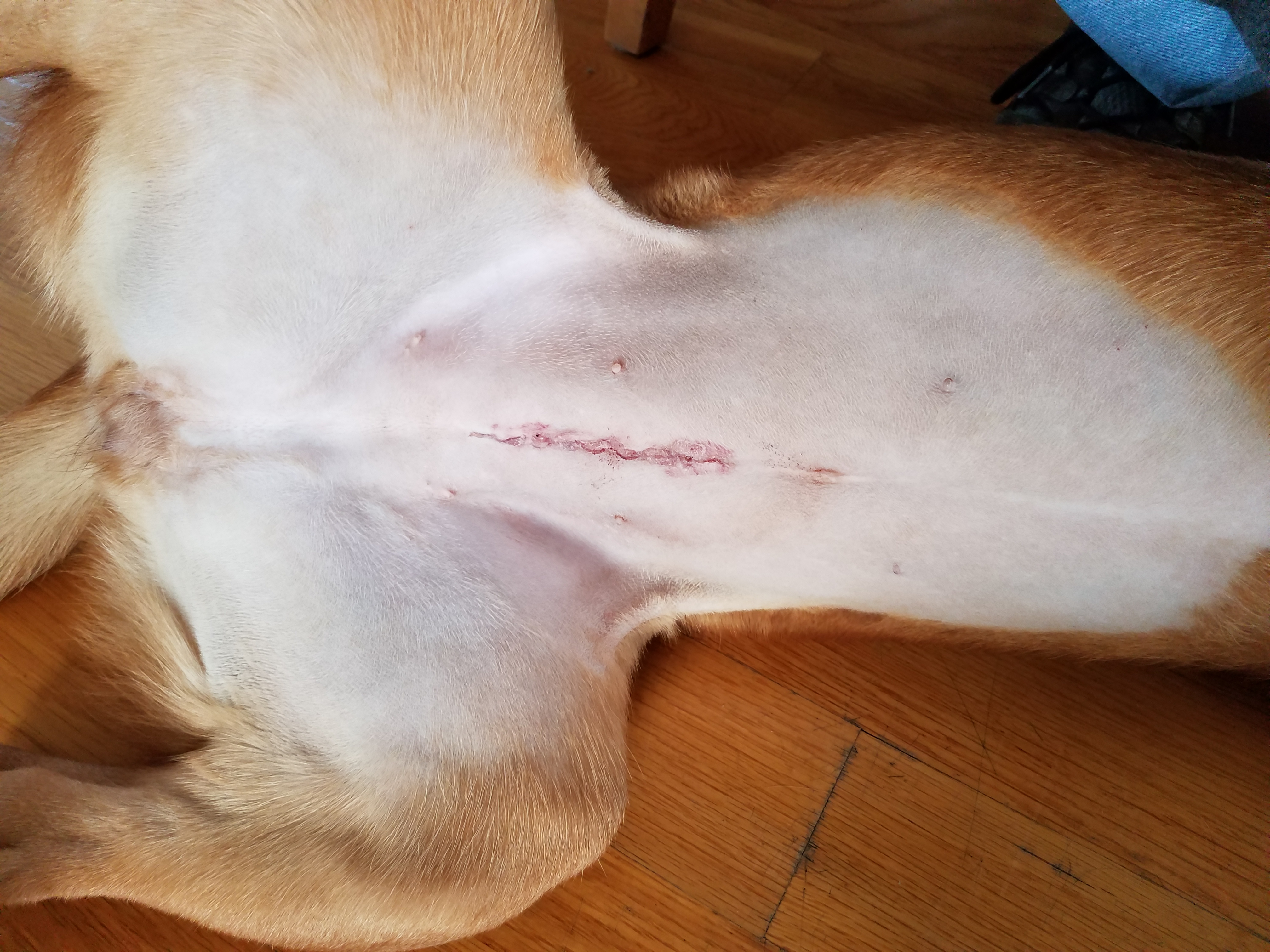 Spaying is the surgical removal of the ovaries and sometimes uterus in female animals. It is commonly performed as a method of birth control and behavior modification.
In non-human animals, the technical term is an ovo-
Spaying is the surgical removal of the ovaries and sometimes uterus in female animals. It is commonly performed as a method of birth control and behavior modification.
In non-human animals, the technical term is an ovo- The surgery can be performed using a traditional open approach or by laparoscopic "keyhole" surgery. Open surgery is more widely available, as laparoscopic surgical equipment costs are expensive. Traditional open surgery is usually performed through a ventral midline incision below the umbilicus. The incision size varies depending upon the surgeon and the size of the animal. The uterine horns are identified and the ovaries are found by following the horns to their ends.
There is a ligament that attaches the ovaries to the body wall, which may need to be broken down so the ovaries can be identified. The ovarian arteries are then ligated with resorbable suture material and then the arteries transected. The uterine body (which is very short in litter-bearing species) and related arteries are also tied off just in front of the
The surgery can be performed using a traditional open approach or by laparoscopic "keyhole" surgery. Open surgery is more widely available, as laparoscopic surgical equipment costs are expensive. Traditional open surgery is usually performed through a ventral midline incision below the umbilicus. The incision size varies depending upon the surgeon and the size of the animal. The uterine horns are identified and the ovaries are found by following the horns to their ends.
There is a ligament that attaches the ovaries to the body wall, which may need to be broken down so the ovaries can be identified. The ovarian arteries are then ligated with resorbable suture material and then the arteries transected. The uterine body (which is very short in litter-bearing species) and related arteries are also tied off just in front of the
 In male animals,
In male animals,
RE37,224
(as of 2006-06-06), CA paten
2137263
(issued 1999-06-15). Product commercially known as SpayVac, a single injection causes a treated female mammal to produce antibodies that bind to ZP3 on the surface of her ovum, blocking sperm from fertilizing it for periods from 22 months up to 7 years (depending on the animal). This will not prevent the animal from going into heat (ovulating) and other than birth control, none of the advantages or disadvantages mentioned below apply.
at CanadianVeterinarians.net A task force recommends that cats are spayed–neutered prior to 5 months of age. While the age-unrelated risks and benefits cited above also apply to early-age neutering, various studies have indicated that the procedure is safe and not associated with increased mortality or serious health and behavioral problems when compared to conventional age neutering. Anesthesia recovery in young animals is usually more rapid and there are fewer complications. One study found that in female dogs there is an increasing risk of urinary incontinence the earlier the procedure is carried out; the study recommended that female dogs be spayed no earlier than 3 to 4 months of age. A later study comparing female dogs spayed between 4 and 6 months and after 6 months showed no increased risk. One study showed the incidence of hip dysplasia increased to 6.7% for dogs neutered before 5.5 months compared to 4.7% for dogs neutered after 5.5 months, although the cases associated with early age neutering seems to be of a less severe form. There was no association between age of neutering and arthritis or long-bone fractures. Another study showed no correlation between age of neutering and musculoskeletal problems. A study of large breed dogs with cranial cruciate ligament rupture associated early-age neutering with the development of an excessive tibial plateau angle. Of particular note are two recent studies from Lynette Hart's lab at UC Davis. The first study from 2013, published in a well-known interdisciplinary peer-reviewed journal demonstrated "no cases of CCL (cruciate ligament tear) diagnosed in intact males or females, but in early-neutered males and females the occurrences were 5 percent and 8 percent, respectively. Almost 10 percent of early-neutered males were diagnosed with LSA (lymphosarcoma), 3 times more than intact males. The percentage of HSA (hemangiosarcoma) cases in late-neutered females (about 8 percent) was 4 times more than intact and early-neutered females. There were no cases of MCT (mast cell tumor) in intact females, but the occurrence was nearly 6 percent in late-neutered females". The second study from 2014 highlighted significant difference in closely related breeds (retrievers), suggesting that inter-breed variability is quite high and that sweeping legal measures and surgical mandates are not the best solutions to canine welfare and health. Specifically the study states: "In Labrador Retrievers, where about 5 percent of gonadally intact males and females had one or more joint disorders, neutering at 6 months doubled the incidence of one or more joint disorders in both sexes. In male and female Golden Retrievers, with the same 5 percent rate of joint disorders in intact dogs, neutering at 6 months increased the incidence of a joint disorder to 4–5 times that of intact dogs. The incidence of one or more cancers in female Labrador Retrievers increased slightly above the 3 percent level of intact females with neutering. In contrast, in female Golden Retrievers, with the same 3 percent rate of one or more cancers in intact females, neutering at all periods through 8 years of age increased the rate of at least one of the cancers by 3–4 times. In male Golden and Labrador Retrievers neutering had relatively minor effects in increasing the occurrence of cancers." In terms of behavior in dogs,
DVM Article on health effects of spay/neuter: Long-Term Health Risks and Benefits Associated with Spay / Neuter in Dogs
Determining the optimal age for gonadectomy of dogs and cats, AVMA (pdf)
Canine Spay Photos and Description
Castration Veterinary castration Dog health Surgical removal procedures Cat health Animal welfare
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
('of neither sex'), is the removal of a non-human animal's reproductive organ
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting ...
, either all of it or a considerably large part. The male-specific term is castration, while spaying is usually reserved for female animals. Colloquially, both terms are often referred to as fixing. In male horses, castrating is referred to as gelding
A gelding (Help:IPA/English, /ˈɡɛldɪŋ/) is a castration, castrated male horse or other equine, such as a pony, donkey or a mule. The term is also used with certain other animals and livestock, such as domesticated Camelidae, camels. By compa ...
. An animal that has not been neutered is sometimes referred to as entire or intact. Often the term ''neuter ng' is used to specifically mean castration, e.g. in phrases like "spay and neuter".
Neutering is the most common method for animal sterilization. Humane societies, animal shelter
An animal shelter or pound is a place where stray, lost, abandoned or surrendered animals – mostly dogs and cats – are housed. The word "pound" has its origins in the animal pounds of the agricultural communities, where stray livestock w ...
s, and rescue groups urge pet owners to have their pets neutered to prevent the births of unwanted litters, which contribute to the overpopulation of unwanted animals in the rescue system. Many countries require that all adopted cats and dogs be sterilized before going to their new homes.
Methods of sterilization
Females (spaying)
 Spaying is the surgical removal of the ovaries and sometimes uterus in female animals. It is commonly performed as a method of birth control and behavior modification.
In non-human animals, the technical term is an ovo-
Spaying is the surgical removal of the ovaries and sometimes uterus in female animals. It is commonly performed as a method of birth control and behavior modification.
In non-human animals, the technical term is an ovo-hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. Supracervical hysterectomy refers to removal of the uterus while the cervix is spared. These procedures may also involve removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy), fallopian tubes ( salpi ...
or ovariohysterectomy; while in humans, this is called a hystero-oophorectomy
Oophorectomy (; from Greek , , 'egg-bearing' and , , 'a cutting out of'), historically also called ''ovariotomy'', is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term is mostly used in reference ...
. One form of spaying is to remove only the ovaries (oophorectomy or ovariectomy), which is mainly done in cat
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the ...
s and young dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the gray wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it was selectively bred from a population of wolves during the Late Pleistocene by hunter-gatherers. ...
s as well as in laparoscopic procedures. Another, less commonly performed method is an "ovary-sparing spay" in which the uterus is removed but one (or both) ovaries are left. A complete ovariohysterectomy may involve removal of the ovaries, uterus, oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
s, and uterine horns
The uterine horns (cornua of uterus) are the points in the upper uterus where the fallopian tubes or oviducts exit to meet the ovaries. They are one of the points of attachment for the round ligament of uterus (the other being the mons pubis). T ...
.
 The surgery can be performed using a traditional open approach or by laparoscopic "keyhole" surgery. Open surgery is more widely available, as laparoscopic surgical equipment costs are expensive. Traditional open surgery is usually performed through a ventral midline incision below the umbilicus. The incision size varies depending upon the surgeon and the size of the animal. The uterine horns are identified and the ovaries are found by following the horns to their ends.
There is a ligament that attaches the ovaries to the body wall, which may need to be broken down so the ovaries can be identified. The ovarian arteries are then ligated with resorbable suture material and then the arteries transected. The uterine body (which is very short in litter-bearing species) and related arteries are also tied off just in front of the
The surgery can be performed using a traditional open approach or by laparoscopic "keyhole" surgery. Open surgery is more widely available, as laparoscopic surgical equipment costs are expensive. Traditional open surgery is usually performed through a ventral midline incision below the umbilicus. The incision size varies depending upon the surgeon and the size of the animal. The uterine horns are identified and the ovaries are found by following the horns to their ends.
There is a ligament that attaches the ovaries to the body wall, which may need to be broken down so the ovaries can be identified. The ovarian arteries are then ligated with resorbable suture material and then the arteries transected. The uterine body (which is very short in litter-bearing species) and related arteries are also tied off just in front of the cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time ...
(leaving the cervix as a natural barrier). The entire uterus and ovaries are then removed. The abdomen is checked for bleeding and then closed with a three-layer closure. The linea alba and then the subcutaneous layer are closed with resorbable suture material. The skin is then stapled, sutured, or glued closed. For suturing the feline linea alba, the most appropriate suture bite and stitch interval size was suggested to be 5 mm.
Laparoscopic surgery is performed using a camera and instruments placed through small incisions (ports) in the body wall. The patient is under anaesthesia and lying on the back. The incisions are between and the number varies according to the equipment and technique used. The surgeon watches on a screen during the operation. The first port is made just behind the umbilicus and the camera is inserted. The abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to create a space in which to operate. A second port is introduced a few centimeters in front of the navel and a long grasping instrument called a Babcock forceps is inserted. The surgeon finds the ovary with the instrument and uses it to suspend the ovary from a needle placed through the abdominal wall. This lifts the ovary and uterus safely away from other organs. The surgeon then removes the grasping instrument and replaces it with an instrument that cauterizes and cuts tissue. This instrument uses electricity to heat the blood vessels to seal them and to cut them. No sutures are placed inside. The ovary is separated from the uterus and round ligament. The cautery instrument is removed and replaced by the grasping instrument, which is used to pull the ovary out through the small abdominal incision (port). This is repeated on the other side and the small holes are closed with a few sutures. Another method uses ligatures and even the uterus is removed.
The benefits of laparoscopic surgery are less pain, faster recovery, and smaller wounds to heal. A study has shown that patients are 70% more active in the first three days post-surgery compared to open surgery. The reason open surgery is more painful is that larger incisions are required, and the ovary needs to be pulled out of the body, which stretches and tears tissue in the abdomen (it is not uncommon for patients to react under anaesthesia by breathing faster at this point).
Removing the ovaries in female dogs removes the production of progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ...
, which is a natural calming hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
and a serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
uplifter. Spaying may therefore escalate any observable aggressive behaviour, either to humans or other dogs.
The risk of infections, bleeding, ruptures, inflammation and reactions to the drugs given to the animal as part of the procedure are all possibilities that should be considered.
Males (castration)
 In male animals,
In male animals, castration
Castration is any action, surgery, surgical, chemical substance, chemical, or otherwise, by which a male loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical cas ...
involves the removal of the testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
(testicles), and is commonly practiced on both household pets (for birth control and behaviour modification) and on livestock (for birth control, as well as to improve commercial value). Often the term ''neuter ng' is used to specifically mean castration, e.g. in phrases like "spay and neuter".
Sterilization alternatives
Hormone-Sparing Surgery
Vasectomy
Vasectomy is an elective surgical procedure that results in male sterilization, often as a means of permanent contraception. During the procedure, the male vasa deferentia are cut and tied or sealed so as to prevent sperm from entering into ...
: In a more delicate procedure than castration, the vasa deferentia – ducts that run from the testes to the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
– are cut then tied or sealed, to prevent sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
from entering into the urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
. Failure rates are insignificantly small. Breeders routinely have this procedure carried out on male ferret
The ferret (''Mustela furo'') is a small, domesticated species belonging to the family Mustelidae. The ferret is most likely a domesticated form of the wild European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), as evidenced by the ferret's ability to inter ...
s and sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
to manipulate the estrus cycles of in-contact females. It is uncommon in other animal species. Because a vasectomy is usually a more expensive procedure, among pet-keepers it is more often performed on show animals, to cosmetically preserve their appearance (though depending upon the fancier organization, the procedure may invalidate the animal's candidacy for certain awards, or relegate it to a non- pedigree, generic "household pet" competition division, just as with full castration).
Tubal ligation
Tubal ligation (commonly known as having one's "tubes tied") is a surgical procedure for female sterilization in which the fallopian tubes are permanently blocked, clipped or removed. This prevents the fertilization of eggs by sperm and thus the ...
: Snipping and tying of oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
s as a sterilization measure can be performed on female cats, dogs, and other species; it is essentially the female equivalent of vasectomy, but a more invasive procedure. Risk of unwanted pregnancies is insignificantly small. Only a few veterinarians perform the procedure.
Like other forms of neutering, vasectomy and tubal ligation eliminate the ability to produce offspring. They differ from neutering in that they leave the animal's levels and patterns of sex hormone
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effects a ...
unchanged. Both sexes will retain their normal reproductive behavior, and other than birth control, none of the advantages and disadvantages listed below apply. This method is favored by some people who seek minimal infringement on the natural state of companion animals to achieve the desired reduction of unwanted births of cats and dogs.
=Injectable
= * Male dogs – Two intratesticular injectable formulations are known to sterilize male dogs. Zeuterin was approved by the United StatesFood and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) for permanent sterilization of male dogs ages three months and older by causing necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
of the testicle. It is not currently available commercially. Calcium chloride dissolved in a variety of diluents have also been studied, with the majority of research and most promising results using calcium chloride dissolved in ethyl alcohol. Calcium chloride formulations can be purchased for use in animals from compounding pharmacies, but the use of calcium chloride for sterilization of males is not approved by the FDA or any other international regulatory agency.
* Male cats – Calcium chloride formulations have also been studied in male cats.
* Male rats – Adjudin
Adjudin (AF-2364) is a drug which is under development as a potential non-hormonal male contraceptive drug, which acts by blocking the production of sperm in the testes, but without affecting testosterone production. It is an analogue of the che ...
( analogue of indazole-carboxylic acid), induces reversible germ cell loss from the seminiferous epithelium by disrupting cell adhesion function between nurse cells and immature sperm cells, preventing maturation.
* Male mice – injection of a solution of the JQ1 molecule to bind to a pocket of BRDT necessary for chromatin remodeling, which gives the proteins that regulate how genes act access to the genetic material
* Male sheep and pigs – Wireless Microvalve. A proposed non-chemical, reversible sterilization method using a piezoelectric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied stress (mechanics), mechanical s ...
polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
that will deform when exposed to a specific electric field broadcast from an emitter. The valve will then open or close, preventing the passage of sperm, but not seminal fluid
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is a bodily fluid that contains spermatozoa which is secreted by the male gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals. In humans and placental mammals, seminal fluid i ...
. Located in a section of the vas deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididyma ...
that occurs just after the epididymis
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; ...
, the implantation can be carried out by use of a hypodermic needle.
* Female mammals – Vaccine of antigens (derived from purified porcine zona pellucida) encapsulated in liposomes (cholesterol and lecithin) with an adjuvant, latest US patenRE37,224
(as of 2006-06-06), CA paten
2137263
(issued 1999-06-15). Product commercially known as SpayVac, a single injection causes a treated female mammal to produce antibodies that bind to ZP3 on the surface of her ovum, blocking sperm from fertilizing it for periods from 22 months up to 7 years (depending on the animal). This will not prevent the animal from going into heat (ovulating) and other than birth control, none of the advantages or disadvantages mentioned below apply.
Other
* Male mice – reversible regulation of the KATNAL1 gene in the Sertoli cell microtubule dynamics of the testes. * Female mammals – orally administered phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor ORG 9935 daily before and during ovulation, which blocks the resumption of meiosis resulting in ovulation of a non-fertilizable, immature oocyte without rupturing the follicle. "" is breeders' informal term for surgical techniques by which male livestock, such as bulls, retain their fulllibido
In psychology, libido (; ) is psychic drive or energy, usually conceived of as sexual in nature, but sometimes conceived of as including other forms of desire. The term ''libido'' was originally developed by Sigmund Freud, the pioneering origin ...
(and related effects like sex pheromones that would be lost through castration), but are rendered incapable of copulation. This is done to stimulate and identify estrous
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is a set of recurring physiological changes induced by reproductive hormones in females of mammalian subclass Theria. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous phases ...
females without the risk of transmitting venereal diseases or causing a pregnancy by a male other than the one intended for selective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant m ...
. Animals altered for this purpose are referred to as teasers (teaser bulls, etc.), or gomers. Several methods are used. Penile translocation surgically alters the penis to point far enough away from its normal direction that it cannot manage vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
l penetration. Penile fixation permanently attaches the penis to the abdomen so that it cannot be lowered for penetration. Penectomy is the partial or complete removal of the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
.
Early-age neutering
Early-age neutering, also known aspediatric spaying
Pediatric spaying (also known as “prepuberal” or “early” spaying) or neutering is defined as performing an ovariohysterectomy (spaying) or orchidectomy (castration or neutering) on a kitten or puppy between the ages of 6 and 14 weeks. Spa ...
or prepubertal gonadectomy, is the removal of the ovaries or testes before the onset of puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
. It is used mainly in animal sheltering and rescue where puppies and kittens can be neutered before being adopted out, eliminating non-compliance with sterilization agreement, which is typically above 40%. The American Veterinary Medical Association
The American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) is an American not-for-profit association founded in 1863 that represents more than 105,000 veterinarians.
The AVMA provides information resources, continuing education opportunities, publicat ...
, American Animal Hospital Association and the Canadian Veterinary Medical Association support the procedure for population control, provided that the veterinarian uses their best knowledge when making the decision about the age at neutering.Dog and Cat Spay/Castrationat CanadianVeterinarians.net A task force recommends that cats are spayed–neutered prior to 5 months of age. While the age-unrelated risks and benefits cited above also apply to early-age neutering, various studies have indicated that the procedure is safe and not associated with increased mortality or serious health and behavioral problems when compared to conventional age neutering. Anesthesia recovery in young animals is usually more rapid and there are fewer complications. One study found that in female dogs there is an increasing risk of urinary incontinence the earlier the procedure is carried out; the study recommended that female dogs be spayed no earlier than 3 to 4 months of age. A later study comparing female dogs spayed between 4 and 6 months and after 6 months showed no increased risk. One study showed the incidence of hip dysplasia increased to 6.7% for dogs neutered before 5.5 months compared to 4.7% for dogs neutered after 5.5 months, although the cases associated with early age neutering seems to be of a less severe form. There was no association between age of neutering and arthritis or long-bone fractures. Another study showed no correlation between age of neutering and musculoskeletal problems. A study of large breed dogs with cranial cruciate ligament rupture associated early-age neutering with the development of an excessive tibial plateau angle. Of particular note are two recent studies from Lynette Hart's lab at UC Davis. The first study from 2013, published in a well-known interdisciplinary peer-reviewed journal demonstrated "no cases of CCL (cruciate ligament tear) diagnosed in intact males or females, but in early-neutered males and females the occurrences were 5 percent and 8 percent, respectively. Almost 10 percent of early-neutered males were diagnosed with LSA (lymphosarcoma), 3 times more than intact males. The percentage of HSA (hemangiosarcoma) cases in late-neutered females (about 8 percent) was 4 times more than intact and early-neutered females. There were no cases of MCT (mast cell tumor) in intact females, but the occurrence was nearly 6 percent in late-neutered females". The second study from 2014 highlighted significant difference in closely related breeds (retrievers), suggesting that inter-breed variability is quite high and that sweeping legal measures and surgical mandates are not the best solutions to canine welfare and health. Specifically the study states: "In Labrador Retrievers, where about 5 percent of gonadally intact males and females had one or more joint disorders, neutering at 6 months doubled the incidence of one or more joint disorders in both sexes. In male and female Golden Retrievers, with the same 5 percent rate of joint disorders in intact dogs, neutering at 6 months increased the incidence of a joint disorder to 4–5 times that of intact dogs. The incidence of one or more cancers in female Labrador Retrievers increased slightly above the 3 percent level of intact females with neutering. In contrast, in female Golden Retrievers, with the same 3 percent rate of one or more cancers in intact females, neutering at all periods through 8 years of age increased the rate of at least one of the cancers by 3–4 times. In male Golden and Labrador Retrievers neutering had relatively minor effects in increasing the occurrence of cancers." In terms of behavior in dogs,
separation anxiety
Separation anxiety disorder (SAD) is an anxiety disorder in which an individual experiences excessive anxiety regarding separation from home and/or from people to whom the individual has a strong emotional attachment (e.g., a parent, caregive ...
, aggression, escape behavior and inappropriate elimination are reduced with neutering while noise phobia and sexual behavior has been shown to potentially increase. In males with aggression issues, earlier neutering may increase barking. In cats, asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, gingivitis, and hyperactivity
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple ...
were decreased, while shyness
Shyness (also called diffidence) is the feeling of apprehension, lack of comfort, or awkwardness especially when a person is around other people. This commonly occurs in new situations or with unfamiliar people; a shy person may simply opt ...
was increased. In male cats, occurrence of abscesses, aggression toward veterinarians, sexual behaviors, and urine spraying
In ethology, territory is the sociographical area that an animal consistently defends against conspecific competition (or, occasionally, against animals of other species) using agonistic behaviors or (less commonly) real physical aggression. ...
was decreased, while hiding was increased.
Health and behavioral effects
Advantages
Besides being a birth control method, and being convenient to many owners, castrating/spaying has the following health benefits: *Sexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
behaviors such as mounting and urine spraying
In ethology, territory is the sociographical area that an animal consistently defends against conspecific competition (or, occasionally, against animals of other species) using agonistic behaviors or (less commonly) real physical aggression. ...
are reduced due to the decrease in hormone levels brought about by neutering. In species other than dogs, certain forms of male aggression
Aggression is behavior aimed at opposing or attacking something or someone. Though often done with the intent to cause harm, some might channel it into creative and practical outlets. It may occur either reactively or without provocation. In h ...
are also reduced. Sexual behavior in cats seems to make them especially undesirable to pet owners.
* Early spaying significantly reduces the risk of development of mammary tumours in female dogs. The incidence of mammary tumours in un-spayed female dogs is 71% (of which approximately 50% will be malignant and 50% will be benign), but if a dog is spayed before its first heat cycle, the risk of developing a mammary tumour is reduced to 0.35%—a 99.5% reduction. The positive effects of spaying on reduction of later mammary tumours decreases with each heat the dog has (backing up the contention that the greatest benefit to reduce future mammary tumour development is to spay before the first heat), and there is no added benefit to spaying to reduce recurrence of a mammary tumour once it has been diagnosed.
* Neutering increases life expectancy in cats: one study found castrated male cats live twice as long as intact males, while spayed female cats live 39% longer than intact females. Non-neutered cats in the U.S. are three times more likely to require treatment for an animal bite. Having a cat neutered confers health benefits, because castrated males cannot develop testicular cancer, spayed females cannot develop uterine, cervical or ovarian cancer, and both have a reduced risk of mammary cancer.
* Without the ability to reproduce, a female necessarily has zero risk of pregnancy complications, such as spotting and false pregnancy
False pregnancy (or pseudocyesis, ) is the appearance of clinical or subclinical signs and symptoms associated with pregnancy although the individual is not physically carrying a fetus. The mistaken impression that one is pregnant includes sign ...
, the latter of which can occur in more than 50% of unspayed female dogs.
* Pyometra
Pyometra or pyometritis is a uterine infection. Though it is most commonly known as a disease of the unaltered female dog, it is also a notable human disease. It is also seen in female cattle, horses, goats, sheep, swine, cats, rabbits, hamsters, ...
, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different ...
, and testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system. Symptoms may include a lump in the testicle or swelling or pain in the scrotum. Treatment may result in infertility.
Risk factors include an c ...
are prevented, as the susceptible organs are removed, though stump pyometra may still occur in spayed females.
* Pyometra (or a pus filled womb) ('Pyo' = pus; 'metra' = uterus or womb) is a life-threatening condition that requires emergency veterinary treatment. The risk of a non-spayed female dog developing pyometra by age 10 is 25% across all breeds, but can be as high as 54% in some breeds. The treatment of choice for a closed-pyometra (where the cervix is closed and the pus cannot drain) is admission to hospital, commencement on intravenous fluids and appropriate antibiotics and, once stable enough for the anaesthetic and surgery, emergency removal of the infected pus-filled uterus. Medical management can be attempted if the animal's condition allows (for example in the case of an 'open' pyometra where the pus drains per-vaginum from the uterus via the open cervix) or dictates (where the animal is too old or otherwise unwell to withstand surgery), if the owner wishes to keep the dog entire to breed or if the owner is unable to afford the veterinary fees associated with surgery. Emergency removal of the infected uterus carries a much higher degree of risk of death than a routine 'spay' operation. The risk of death from in dogs undergoing surgical treatment for pyometra is up to 17%. Thus the risk of death in entire female dogs from a pyometra, even if given correct veterinary attention can be up to 9% by 10 years of age (17% of 54%). This risk is reduced to virtually zero if spayed.
Disadvantages
* As with any surgical procedure, immediate complications of neutering include the usualanesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into t ...
and surgical
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery ...
complications, such as bleeding, infection, and death. These risks are relatively low in routine neutering; however, they may be increased for some animals due to other pre-existing health factors. In one study the risk of anesthetic-related death (not limited to neutering procedures) was estimated at 0.05% for healthy dogs and 0.11% for healthy cats. The risks for sick animals were 1.33% for dogs and 1.40% for cats.
* Spaying and castrating cats and dogs may increase the risk of obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
if nutritional intake is not reduced to reflect the lower metabolic requirements of neutered animals. In cats, a decrease in sex hormone levels seems to be associated with an increase in food intake. In dogs, the effects of neutering as a risk factor for obesity vary among breeds.
* Neutered dogs of both sexes are at a twofold excess risk to develop osteosarcoma
An osteosarcoma (OS) or osteogenic sarcoma (OGS) is a cancerous tumor in a bone. Specifically, it is an aggressive malignant neoplasm that arises from primitive transformed cells of mesenchyme, mesenchymal origin (and thus a sarcoma) and that exhi ...
(bone cancer) as compared to intact dogs. The risk of osteosarcoma increases with increasing breed size and especially height.
* Studies of cardiac tumors in dogs showed that there was a 5 times greater risk of hemangiosarcoma (cancer of blood vessel lining), one of the three most common cancers in dogs, in spayed females than intact females and a 2.4 times greater risk of hemangiosarcoma in castrated dogs as compared to intact males.
* Spaying and castrating is associated with an increase in urinary tract cancers in dogs, however the risk is still less than 1%.
* Neutered dogs of both sexes have a 27% to 38% increased risk of adverse reactions to vaccinations. However, the incidence of adverse reactions for neutered and intact dogs combined is only 0.32%.
* Neutered dogs have been known to develop hormone-responsive alopecia
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring ...
(hair loss).
* A 2004 study found that neutered dogs had a higher incidence of cranial cruciate ligament (CCL) rupture, a form of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury.
* A study of golden retrievers found that castrated males were 3 times more likely than intact males to be diagnosed with lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph node ...
and 2 times more likely to have hip dysplasia.
* Castration and spaying can increase the risk of geriatric cognitive impairment.
* About 2% of castrated male dogs eventually develop prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ...
, compared to less than 0.6% of intact males. The evidence is most conclusive for Bouviers.
* In a study of 29 intact male dogs and 47 castrated males aged 11–14, the neutered males were significantly more likely to progress from one geriatric cognitive impairment condition (out of the four conditions – disorientation in the house or outdoors, changes in social interactions with human family members, loss of house training, and changes in the sleep-wake cycle) to two or more conditions. Testosterone in intact males is thought to slow the progression of cognitive impairment, at least in dogs that already have mild impairment.
* As compared to intact males, castrated cats are at an increased risk for certain problems associated with feline lower urinary tract disease
Feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD) is a generic category term to describe any disorder affecting the bladder or urethra of cats.
It encompasses around 10 different diseases of the lower urinary tract, all of which can present with very si ...
. They are much more likely to suffer from feline cystitis which can escalate into a life-threatening urethral blockage.
* Neutering has been associated with an increased likelihood of urethral sphincter incontinence in male dogs.
* There is evidence that spaying can increase the risk of urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a significant effect on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women ...
in dogs, especially when done before the age of three months. Up until 12 months of age, the risk decreases as the age at spaying increases.
* Spayed female dogs are at an increased risk of hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, co ...
.
Current research
Various studies of the effects neutering has overall on male and female dog aggression have been unable to arrive at a consensus. A possible reason for this according to two studies is changes to other factors have more of an effect than neutering. One study reported results of aggression towards familiar and strange people and other dogs reduced between 10 and 60 percent of cases, while other studies reported increases in possessive aggression and aggression towards familiar and strange people, and more studies reported there was no significant difference in aggression risk between neutered and non-neutered males. For females with existing aggression, many studies reported increases in aggressive behavior and some found increased separation anxiety behavior. A report from the American Kennel Club Canine Health Foundation reported significantly more behavioral problems in castrated dogs. The most commonly observed behavioral problem in spayed females was fearful behavior and the most common problem in males was aggression. Early age gonadectomy is associated with an increased incidence of noise phobias and .Terminology for neutered animals
A specialized vocabulary is used inanimal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, animal fiber, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, management, production, nutrition, selective breeding, and the raising ...
and animal fancy
Animal fancy is a hobby involving the appreciation, promotion, or breeding of pet or domestic animals.
Fancy may include ownership, showing, animal sports and other competitions, and breeding. Hobbyists may simply collect specimens of the anima ...
for neutered (castrated) animals:
Religious views
Islam
There are differing views inIslam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
with regard to neutering animals, with some Islamic associations stating that when done to maintain the health and welfare of both the animals and the community, neutering is allowed on the basis of being in the interest of 'maslaha
''Maslaha'' or ''maslahah'' (, ) is a concept in Sharia (Islamic divine law) regarded as a basis of law.I. Doi, Abdul Rahman. (1995). "Mașlahah". In John L. Esposito. ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Modern Islamic World''. Oxford: Oxford Univer ...
' (general good) or "choosing the lesser of two evils".
Judaism
Orthodox Judaism
Orthodox Judaism is a collective term for the traditionalist branches of contemporary Judaism. Theologically, it is chiefly defined by regarding the Torah, both Torah, Written and Oral Torah, Oral, as literally revelation, revealed by God in Ju ...
forbids the castration of both humans and non-human animals by Jews, except in lifesaving situations. In 2007, the Sephardic
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
Chief Rabbi
Chief Rabbi () is a title given in several countries to the recognized religious leader of that country's Jewish community, or to a rabbinic leader appointed by the local secular authorities. Since 1911, through a capitulation by Ben-Zion Meir ...
of Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
Rabbi Shlomo Amar issued a ruling stating that it is permissible to have companion animals neutered on the basis of the Jewish mandate to prevent cruelty to animals.
See also
* Animal population control *Animal shelter
An animal shelter or pound is a place where stray, lost, abandoned or surrendered animals – mostly dogs and cats – are housed. The word "pound" has its origins in the animal pounds of the agricultural communities, where stray livestock w ...
* Cruelty to animals
Cruelty to animals, also called animal abuse, animal neglect or animal cruelty, is the infliction of suffering or Injury, harm by humans upon animals, either by omission (neglect) or by commission. More narrowly, it can be the causing of harm ...
* Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. Supracervical hysterectomy refers to removal of the uterus while the cervix is spared. These procedures may also involve removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy), fallopian tubes ( salpi ...
* Oophorectomy
Oophorectomy (; from Greek , , 'egg-bearing' and , , 'a cutting out of'), historically also called ''ovariotomy'', is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term is mostly used in reference ...
* Overpopulation in companion animals
In some countries, there is an Overpopulation (biology), overpopulation of pets such as domestic cat, cats, domestic dog, dogs, and exotic animals. In the United States, six to eight million animals are brought to Animal shelter, shelters each yea ...
* Wildlife contraceptive
* World Spay Day
References
External links
{{wiktionary, spayingDVM Article on health effects of spay/neuter: Long-Term Health Risks and Benefits Associated with Spay / Neuter in Dogs
Determining the optimal age for gonadectomy of dogs and cats, AVMA (pdf)
Canine Spay Photos and Description
Castration Veterinary castration Dog health Surgical removal procedures Cat health Animal welfare