Sorting (sediment) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Sorting describes the distribution of
Sorting describes the distribution of
 Sorting describes the distribution of
Sorting describes the distribution of grain size
Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. This is different from the crystallite size, which ...
of sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
s, either in unconsolidated deposits or in sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or de ...
s. The degree of sorting is determined by the range of grain sizes in a sediment deposit and is the result of various transport processes (rivers
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it ru ...
, debris flow
Debris flows are geological phenomena in which water-laden masses of soil and fragmented Rock (geology), rock flow down mountainsides, funnel into stream channels, entrain objects in their paths, and form thick, muddy deposits on valley floors. ...
, wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heatin ...
, glaciers
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
, etc.). This should not be confused with crystallite
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains.
Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel Wikt:longulite ...
size, which refers to the individual size of a crystal in a solid. Crystallite is the building block of a grain.
Sorting parameters
The terms describing sorting in sediments – very poorly sorted, poorly sorted, moderately sorted, well sorted, very well sorted – have technical definitions and semi-quantitatively describe the amount of variance seen in particle sizes.''Very poorly sorted'' indicates that the sediment sizes are mixed (largevariance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion ...
); whereas ''well sorted'' indicates that the sediment sizes are similar (low variance). In the field, sedimentologists use graphical charts to accurately describe the sorting of a sediment using one of these terms. Tucker, M.E., 1996, ''Sedimentary rocks in the field'', John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 153 p.
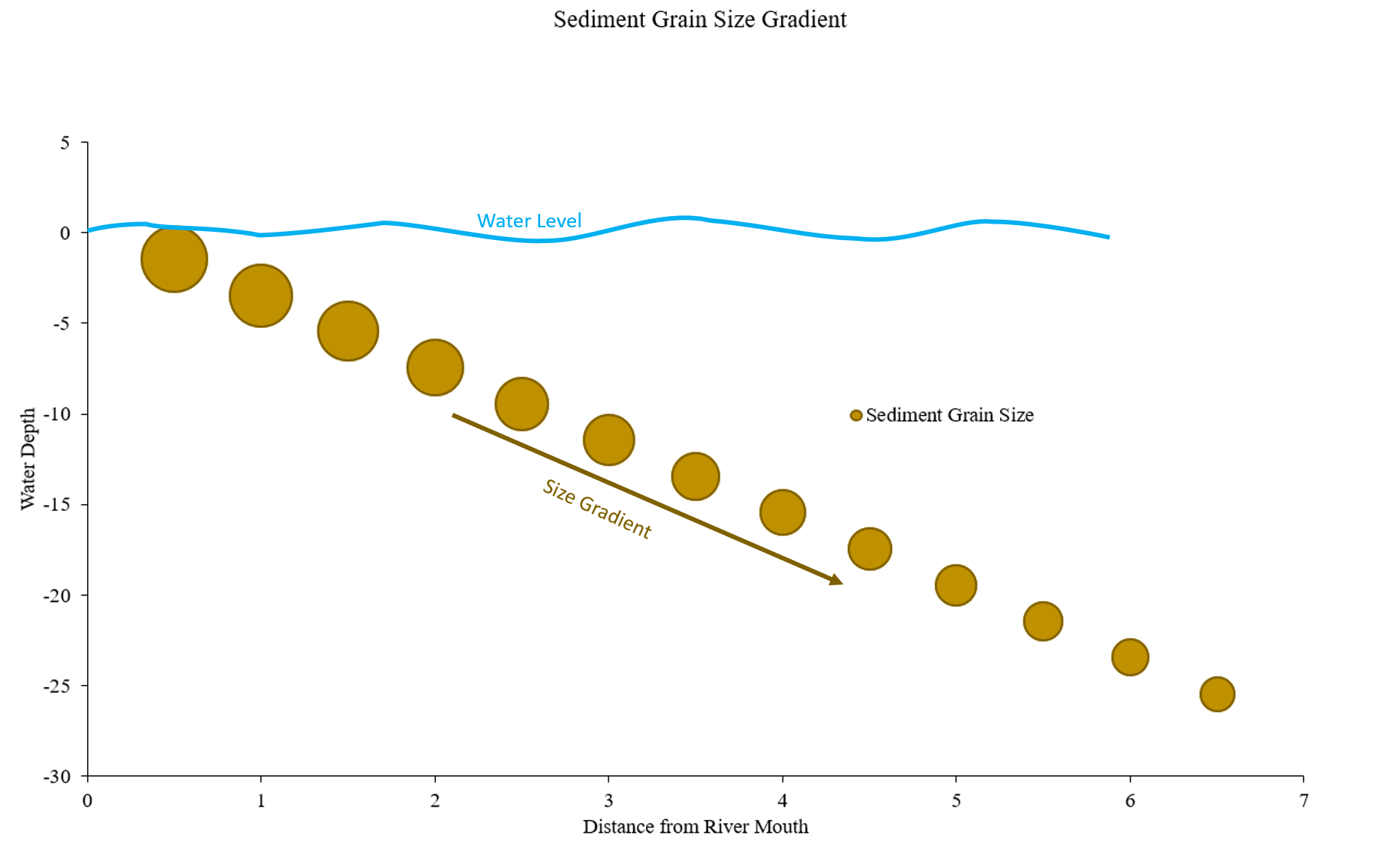
Tangential sorting is the result of sediment being deposited in same direction as flow. Normal tangential sorting results in a gradient of sediment sizes deposited from largest to finest as they travel downstream. When sediments are deposited from smallest to largest as they travel downstream, this is referred to as reverse sorting.
Rocks derived from well sorted sediments are commonly both porous and permeable, while poorly sorted rocks have low porosity and low permeability, particularly when fine grained. Processes involved in sorting
Sediment sorting is influenced by: grain sizes of sediment, processes involved in graintransport
Transport (in British English) or transportation (in American English) is the intentional Motion, movement of humans, animals, and cargo, goods from one location to another. Mode of transport, Modes of transport include aviation, air, land tr ...
, deposition, and post-deposition processes such as winnowing. As a result, studying the degree of sorting in deposits of sediment can give insight into the energy, rate, and/or duration of deposition, as well as the transport process responsible for laying down the sediment.
Aeolian processes
In reference to windblown sediment, a wide range of conditions such as distance and height of transport and varying wind patterns at the sediment source can affect grain size, rate of transport and distribution of sediment. Windblown sediment travels one of three ways--rolling, saltation or suspension in the air. Loess that is reworked by fluvial processes tends to have more poorly sorted sediment as compared to sediment sorted by only Aeolian processes because loess particles become mixed with preexisting sediment of varying grain sizes within bodies of water.See also
* Graded bedding *Rounding
Rounding or rounding off is the process of adjusting a number to an approximate, more convenient value, often with a shorter or simpler representation. For example, replacing $ with $, the fraction 312/937 with 1/3, or the expression √2 with ...
* Porosity
* Soil texture
* Deposition
* Fluvial processes
* Aeolian transport
*Grain size
Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. This is different from the crystallite size, which ...
References
Sedimentary rocks {{Petrology-stub