Sodasa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sodasa (
Sodasa (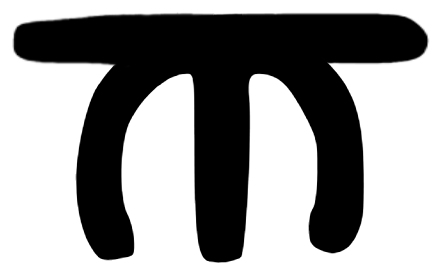

 , , also
, , also 

 , ) was an
, ) was an


 ) and (
) and (

 ), which are derived from the
), which are derived from the
/ref>Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empi ...
) or Mahakshatrapa (Great
Plate XIV
/ref> File:Vasu_doorjamb_inscription.jpg, The
File:Satrap Saudasa inscription.jpg, Another inscription of Sodasa in Mathura. This inscription records the gifts of a 









 "Of the Lord and Great Satrap Śudāsa") from the beginning of the second line.
File:Indian_mountain_temple_architecture_inscription_Mathura_site.jpg,
"Of the Lord and Great Satrap Śudāsa") from the beginning of the second line.
File:Indian_mountain_temple_architecture_inscription_Mathura_site.jpg,
 Sodasa's coins have been found in
Sodasa's coins have been found in
p.196
/ref> Three types of legends are known, with one coin type of Sodasa bearing the legend "son of Rajuvula": * "Satrap Sodasa, son of the Great Satrap" (''Mahakhatapasa putasa khatapasa śodasasa'' followed by a
p.136
/ref> * "Great Satrap Sodasa" (''Mahakhatapasa śodasasa'')
File:Sodasa.jpg, Coin of Sodasa. Reverse: ''"Mahakshatrapa putasa Khatapasa Sodasasa"'' ("Satrap Sodasa, son of the Great Satrap")
File:Sodasa.JPG, Coin of Sodasa, satrap of Mathura, AE.
Obv: Lakshmi standing between two symbols on the obverse and inscription around "Mahakhatapasa putasa Khatapasa Sodasasa ".
Rev: Standing Abhiseka Lakshmi anointed by two elephants.
Dates of Kanishka and the Indo-Scythians
{{authority control Northern Satraps 1st-century monarchs in Asia 1st-century Iranian people
 Sodasa (
Sodasa (Kharosthi
Kharosthi script (), also known as the Gandhari script (), was an ancient script originally developed in the Gandhara Region of modern-day Pakistan, between the 5th and 3rd century BCE. used primarily by the people of Gandhara alongside vari ...
: , ; Middle Brahmi script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as ...
: 



Indo-Scythian
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranian peoples, Iranic Scythians, Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwe ...
Northern Satrap and ruler of Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
during the later part of the 1st century BCE or the early part of 1st century CE. He was the son of Rajuvula, the Great Satrap of the region from Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the Pothohar region of Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the ...
to Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
. He is mentioned in the Mathura lion capital.
Name
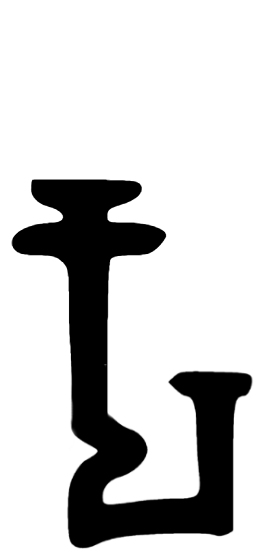
Sodasa's name is recorded in Kharosthi as () and in Brahmi as (



Saka
The Saka, Old Chinese, old , Pinyin, mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit (Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples, Eastern Iranian peoples who lived in the Eurasian ...
name , meaning "who kept the good acts in memory".
Rule
Sodasa reigned during the 1st century CE, and also took the title of Great Satrap at one point, probably in the area of Mathura as well, but possibly under the suzerainty of theIndo-Parthian
The Indo-Parthian kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the Indian ...
king Gondophares
Gondophares I ( Greek: Γονδοφαρης ''Gondopharēs'', Υνδοφερρης ''Hyndopherrēs''; Kharosthi: 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪𐨿𐨣 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨂𐨵𐨪 ', ') was the founder of the Indo-Parthian K ...
. At the same time the Indo-Scythian Bhadayasa ruled in the eastern Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
. There were numerous cultural and political exchanges between the Indo-Scythians of the northwest and those of Mathura.
Sodasa may have been a contemporary of the Western Kshatrapa
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi: , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India (extending from Saurashtra in the south and Malwa in the east, covering moder ...
Nahapana
Nahapana (Ancient Greek: ; Kharosthi: , ; Brahmi script, Brahmi: , ;), was a member of Western Satraps, Kshaharata dynasty in northwestern India, who ruled during the 1st or 2nd century CE. According to one of his coins, he was the son of B ...
and the Indo-Parthian
The Indo-Parthian kingdom was a Parthian kingdom founded by Gondophares, and active from 19 CE to c. 226 CE. At their zenith, they ruled an area covering parts of eastern Iran, various parts of Afghanistan and the northwest regions of the Indian ...
Gondophares
Gondophares I ( Greek: Γονδοφαρης ''Gondopharēs'', Υνδοφερρης ''Hyndopherrēs''; Kharosthi: 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨥𐨪𐨿𐨣 ', '; 𐨒𐨂𐨡𐨂𐨵𐨪 ', ') was the founder of the Indo-Parthian K ...
. The Indo-Parthians may have destabilized Indo-Scythian rule in northern India, but there are no traces of Indo-Parthian presence in Mathura. Sodasa may have been displaced in Mathura by the Kushan ''Kushan'' or Kushana may refer to:
* Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan ...
ruler Vima Kadphises, who erected a throne in his name in Mathura, but nothing is known of these interactions.
At Mathura, Sodasa is the last of the Indo-Scythians to have left coins. Later, under Kanishka
Kanishka I, also known as Kanishka the Great, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (–150 CE) the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadp ...
, son of Vima Kadphises, the Great Satrap Kharapallana and the Satrap Vanaspara are said to have ruled in Mathura with Kanishka as suzerain, pointing to continued Indo-Scythian rule under Kushan suzerainty as least until the time of Kanishka.
Inscriptions
Numerous inscriptions from Mathura mentioning Sodasa's rule are known. The Mirzapur village inscription (in the vicinity of Mathura) refers to the erection of a water tank by Mulavasu and his consort Kausiki during the reign of Sodasa, assuming the title of "Svami (Lord) Mahakshatrapa (Great Satrap)".Buddhist art of Mathurā , Ramesh Chandra Sharma, Agam, 1984 Page 26 The Mathura lion capital mentions the reign of his father and predecessor Rajuvula as Mahaksatrapa while Sodasa is referred to as Ksatrapa. Sodasa probably also dedicated the Mora Well Inscription, where he presents himself as the son of Rajuvula. A large stone slab, the Kankali Tila tablet of Sodasa, discovered in Kankali in the area of Mathura, bears a three-line epigraph mentioning that in the year 42 or 72 of "Lord Mahaksatrapa Sodasa," a monument for worship was set up by a certain Amohini. A recent date for Sodasa's reign was given as 15 CE, meaning that the regnal date of the inscription would start from theVikrama era
Vikram Samvat (ISO: ''Vikrama Saṁvata''; abbreviated VS), also known as the Vikrami calendar is a Hindu calendar historically used in the Indian subcontinent and still also used in several Indian states and Nepal. It is a lunisolar calendar, ...
( Bikrami calendar (starting in 57 BCE)+72=15 CE). This would put the long reign of his father Rajuvula in the last quarter of the 1st century BCE, which is probable.Indian Studies, Volume 7, Ramakrishna Maitra, 1966 p.67
Another inscription of Sodasa in Mathura records the gifts of a Brahman
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' (; IAST: ''Brahman'') connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality of the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part XII In the ...
named Gajavara of the Segrava-gotra during the time of Saudasa the Great Satrap of the lord (paramount, whose name is lost) of tanks called Kshayawada, as well as a western tank, a well, a garden, and a pillar.Report For The Year 1871-72 Volume III, Alexander Cunningham/ref>
Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empi ...
).">
File:MathuraLionCapital.JPG, The Mathura lion capital mentions Sodasa as "Satrap", while his father Rajuvula was "Great Satrap".
File:Inscription of Sodasha Reign - Circa 1st Century BCE - Mirzapur - ACCN 79-29 - Government Museum - Mathura 2013-02-24 6105.JPG, Mirzapur stele inscription of Sodasa's Reign, Mirzapur area of Mathura. Mathura Museum
__NOTOC__
Government Museum, Mathura, commonly referred to as Mathura museum, is an archaeological museum in Mathura city of Uttar Pradesh state in India. The museum was founded by then collector of the Mathura district, Sir F. S. Growse in 1 ...
. The inscription refers to the erection of a water tank by Mulavasu and his consort Kausiki, during the reign of Sodasa, assuming the title of "Svami (Lord) Mahakshatrapa (Great Satrap)":
File:Amohini_relief,_Mathura,_circa_15_CE.jpg, The Kankali Tila tablet of Sodasa with an inscription mentioning the year 42 or 72 during the reign of Sodasa as Makakshatrapa (Great Satrap).The Jain stûpa and other antiquities of Mathurâ by Smith, Vincent ArthuPlate XIV
/ref> File:Vasu_doorjamb_inscription.jpg, The
Vasu Doorjamb Inscription
__NOTOC__
The Vasu Doorjamb Inscription is an early 1st-century CE Sanskrit inscription in Brahmi script dedicated to the deity Vāsudeva, related to the Vaishnavism tradition of Hinduism. It is also one of the several dedicatory inscriptions fro ...
.
Brahman
In Hinduism, ''Brahman'' (; IAST: ''Brahman'') connotes the highest universal principle, the ultimate reality of the universe.P. T. Raju (2006), ''Idealistic Thought of India'', Routledge, , page 426 and Conclusion chapter part XII In the ...
named Gajavara of the Segrava-gotra during the time of Saudasa the Great Satrap of the lord (paramount, whose name is lost) of tanks called Kshayawada, besides a western tank, a well, a garden, and a pillar.
File:Kankali Tila inscription of Sodasa.jpg, Kankali Tila
''Kankali Tila'' (also Kankali mound or Jaini mound) is a mound located at Mathura in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The name of the mound is derived from a modern temple of Hindu goddess Kankali. The famous Jain stupa was excavated here ...
inscription of Sodasa (from the Kankali Tila tablet of Sodasa). This inscription mentions the rule of ''Svamisa Mahakṣatrapasa Śodasa'' (





Mountain Temple inscription
__NOTOC__
The Mountain Temple inscription was found near Mathura, India. It is on a broken slab, and now housed at the Indian Museum, Kolkata.
Heinrich Lüders and Klaus Ludwig Janert
(1961), Mathurā inscriptions, Göttingen : Vandenhoeck & Rup ...
mentioning Sodasa and his father Rajuvula
File:1st_century_CE_Mora_Well_Inscription_Sanskrit_Mathura.jpg, Mora Well Inscription in the name of Rajuvula and his son Sodasa.
Coinage
 Sodasa's coins have been found in
Sodasa's coins have been found in Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
only, suggesting that he only ruled over the Mathura region. They do not follow traditional Indo-Scythian
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranian peoples, Iranic Scythians, Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwe ...
coinage patterns, but rather the designs of local rulers of Mathura, and are only made of lead and copper alloy. The legends only use the Indian Brahmi script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as ...
, whether Saodasa's father Rajuvula had used coins derived from the Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic-era Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" loosely describes a number of var ...
, with legends in Greek and Kharoshthi
Kharosthi script (), also known as the Gandhari script (), was an ancient script originally developed in the Gandhara Region of modern-day Pakistan, between the 5th and 3rd century BCE. used primarily by the people of Gandhara alongside vari ...
. This suggests that Sodasa had significantly integrated into the local Indian culture.
Sodasa's coins usually show on the obverse a standing female and tree-like symbol, with the legend ''"Mahakatapasa putasa Khatapasa Sodasa"'', i.e., "Satrap Sodasa, son of the Great Satrap". On the reverse appears a Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, , ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of wealth, fortune, prosperity, beauty, fertility, sovereignty, and abundance. She along with Parvat ...
with elephants pouring water over her.Catalogue Of The Coins In The Indian Museum Calcutta. Vol.1 by Smith, Vincent Ap.196
/ref> Three types of legends are known, with one coin type of Sodasa bearing the legend "son of Rajuvula": * "Satrap Sodasa, son of the Great Satrap" (''Mahakhatapasa putasa khatapasa śodasasa'' followed by a
svastika
The swastika (卐 or 卍, ) is a symbol used in various Eurasian religions and cultures, as well as a few African and American cultures. In the Western world, it is widely recognized as a symbol of the German Nazi Party who appropriated i ...
)
* "Satrap Sodasa, son of Rajuvula" (Svastika followed by ''Rajuvula putasa khatapasa śodasasa'')The Dynastic art of the Kushans, Rosenfield, University of California Press, 196p.136
/ref> * "Great Satrap Sodasa" (''Mahakhatapasa śodasasa'')
Obv: Lakshmi standing between two symbols on the obverse and inscription around "Mahakhatapasa putasa Khatapasa Sodasasa ".
Rev: Standing Abhiseka Lakshmi anointed by two elephants.
Sculptural styles
The abundance of dedicatory inscriptions in the name of Sodasa (eight of them are known, often on sculptural works), and the fact that Sodasa is known through his coinage as well as through his relations with other Indo-Scythian rulers whose dates are known, means that Sodasa functions as a historic marker to ascertain the sculptural styles at Mathura during his rule, in the first half of the 1st century CE. The next historical marker corresponds to the reign ofKanishka
Kanishka I, also known as Kanishka the Great, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (–150 CE) the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadp ...
under the Kushans, whose reign began circa 127 CE.
The Kankali Tila tablet of Sodasa is one of those sculptural works directly inscribed in the name of Sodasa. Another one is the Katra torana fragment. The sculptural styles at Mathura during the reign of Sodasa are quite distinctive, and significantly different from the style of the previous period circa 50 BCE, or the styles of the later period of the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
in the 2nd century CE. Stylistically similar works can then be dated to the same period of the reign of Sodasa.
Early representation of the Buddha
The "Isapur Buddha" fromMathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
, probably the earliest known representation of the Buddha (possibly together with Buddha statues
Much Buddhist art uses depictions of the historical Buddha, Gautama Buddha, which are known as () in Sanskrit and Pali. These may be statues or other images such as paintings. The main figure in an image may be someone else who has obtained B ...
found in Barikot in Swat
A SWAT (''Special Weapons and Tactics'') team is a generic term for a police tactical unit within the United States, though the term has also been used by other nations.
SWAT units are generally trained, equipped, and deployed to res ...
), on a railing post, is dated to circa 15 CE under the reign of Sodasa. Another depiction of the Buddha from the same period appears in the Bimaran casket.
Paleography
The inscriptions in the name of Sodasa are also an important marker for thepaleography
Palaeography (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, UK) or paleography (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, US) (ultimately from , , 'old', and , , 'to write') is the study and academic disciplin ...
of the Brahmi script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as ...
, the shape of the Brahmi letters having evolved in time, and also having varied depending on the regions.
References
External links
Dates of Kanishka and the Indo-Scythians
{{authority control Northern Satraps 1st-century monarchs in Asia 1st-century Iranian people