smooth muscle tissue on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of
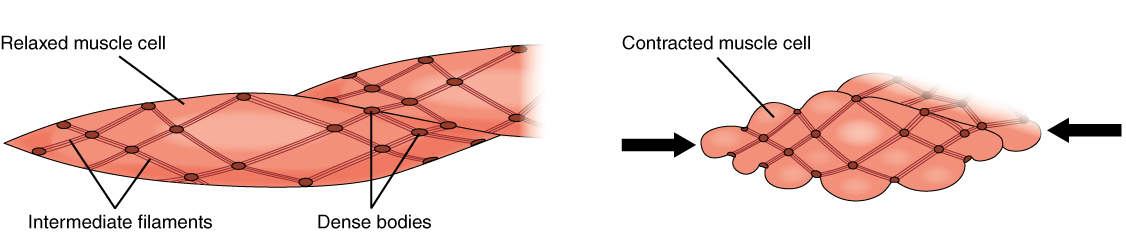 Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. Most smooth muscle is of the single-unit type, and is found in the walls of most internal organs (viscera); and lines blood vessels (except large elastic arteries), the urinary tract, and the
Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. Most smooth muscle is of the single-unit type, and is found in the walls of most internal organs (viscera); and lines blood vessels (except large elastic arteries), the urinary tract, and the
 A smooth-muscle cell is a spindle-shaped
A smooth-muscle cell is a spindle-shaped
in: ''The vascular smooth muscle cell: molecular and biological responses to the extracellular matrix''. Authors: Stephen M. Schwartz, Robert P. Mecham. Editors: Stephen M. Schwartz, Robert P. Mecham. Contributors: Stephen M. Schwartz, Robert P. Mecham. Publisher: Academic Press, 1995.
BBC
– baby born with smooth muscle condition has 8 organs transplanted
Stomach smooth muscle identified using antibody
* * "Smooth Muscle" *
Smooth muscle histology photomicrographs
(medlineplus.gov) {{Authority control Muscular system Muscle tissue
vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
muscle tissue
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to contract. ...
, the others being skeletal
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal fram ...
and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
. It is non- striated, so-called because it has no sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal striated muscle, Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular ...
s and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It can be divided into two subgroups, ''single-unit'' and ''multi-unit'' smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts
A contract is an agreement that specifies certain legally enforceable rights and obligations pertaining to two or more parties. A contract typically involves consent to transfer of goods, services, money, or promise to transfer any of thos ...
as a syncytium.
Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
, intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
, bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
and uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
. In the walls of blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s, and lymph vessels, (excluding blood and lymph capillaries) it is known as vascular smooth muscle
Vascular smooth muscle is the type of smooth muscle that makes up most of the walls of blood vessels.
Structure
Vascular smooth muscle refers to the particular type of smooth muscle found within, and composing the majority of the wall of blood v ...
. There is smooth muscle in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are al ...
systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscle
The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscleSchachar, Ronald A. (2012). "Anatomy and Physiology." (Chapter 4) . in the eye's middle layer, the uvea ( vascular layer). It controls accommodation for vie ...
s, iris dilator muscle
The iris dilator muscle (pupil dilator muscle, pupillary dilator, radial muscle of iris, radiating fibers), is a smooth muscle of the eye, running radially in the iris and therefore fit as a dilator. The pupillary dilator consists of a spokelik ...
, and iris sphincter muscle
The iris sphincter muscle (pupillary sphincter, pupillary constrictor, circular muscle of iris, circular fibers) is a muscle in the part of the eye called the iris. It encircles the pupil of the iris, appropriate to its function as a constricto ...
are types of smooth muscles. The iris dilator and sphincter muscles are contained in the iris and contract in order to dilate or constrict the pupils. The ciliary muscles change the shape of the lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
to focus on objects in accommodation. In the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili
The arrector pili muscles, also known as hair erector muscles, are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps (piloerection).
Structure ...
cause hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and ...
to stand erect in response to cold
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjectivity, subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute t ...
temperature and fear
Fear is an unpleasant emotion that arises in response to perception, perceived dangers or threats. Fear causes physiological and psychological changes. It may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the ...
.
Structure
Gross anatomy
 Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. Most smooth muscle is of the single-unit type, and is found in the walls of most internal organs (viscera); and lines blood vessels (except large elastic arteries), the urinary tract, and the
Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. Most smooth muscle is of the single-unit type, and is found in the walls of most internal organs (viscera); and lines blood vessels (except large elastic arteries), the urinary tract, and the digestive tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
. It is not found in the heart which has cardiac muscle.
In single-unit smooth muscle a single cell in a bundle is innervated by an autonomic nerve fiber (myogenic). An action potential can be propagated through neighbouring muscle cells due to the presence of many gap junctions between the cells. Due to this property, single-unit bundles form a syncytium that contracts in a coordinated fashion making the whole muscle contract or relax, such as the uterine muscles during childbirth.
Single-unit visceral smooth muscle is myogenic; it can contract regularly without input from a motor neuron (as opposed to multiunit smooth muscle, which is neurogenic - that is, its contraction must be initiated by an autonomic nervous system neuron). A few of the cells in a given single unit may behave as pacemaker cells, generating rhythmic action potentials due to their intrinsic electrical activity. Because of its myogenic nature, single-unit smooth muscle is usually active, even when it is not receiving any neural stimulation. Multiunit smooth muscle is found in the trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
, in the iris of the eye, and lining the large elastic arteries.
However, the terms single- and multi-unit smooth muscle represent an oversimplification. This is due to the fact that smooth muscles for the most part are controlled and influenced by a combination of different neural elements. In addition, it has been observed that most of the time there will be some cell-to-cell communication and activators/inhibitors produced locally. This leads to a somewhat coordinated response even in multiunit smooth muscle.
Smooth muscle differs from skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are a ...
and cardiac muscle in terms of structure, function, regulation of contraction, and excitation-contraction coupling. However, smooth muscle tissue tends to demonstrate greater elasticity and function within a larger length-tension curve than striated muscle. This ability to stretch and still maintain contractility is important in organs like the intestines and urinary bladder. Smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
is activated by a composite of smooth muscle cells (SMCs), interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs), and platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRα) that are electrically coupled and work together as an SIP functional syncytium.
Microanatomy
Smooth muscle cells
 A smooth-muscle cell is a spindle-shaped
A smooth-muscle cell is a spindle-shaped myocyte
A muscle cell, also known as a myocyte, is a mature contractile Cell (biology), cell in the muscle of an animal. In humans and other vertebrates there are three types: skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth, and Cardiac muscle, cardiac ...
with a wide middle and tapering ends, and a single nucleus. Like striated muscle, smooth muscle can tense and relax. In the relaxed state, each cell is 30–200 micrometers in length, some thousands of times shorter than a skeletal muscle cell. There are no myofibril
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as Skeletal muscle#Skeletal muscle cells, muscle fibers, and these cells contain ...
s present, but much of the cytoplasm is taken up by the proteins, myosin
Myosins () are a Protein family, family of motor proteins (though most often protein complexes) best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are adenosine triphosphate, ATP- ...
and actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
, which together have the capability to contract.p. 174in: ''The vascular smooth muscle cell: molecular and biological responses to the extracellular matrix''. Authors: Stephen M. Schwartz, Robert P. Mecham. Editors: Stephen M. Schwartz, Robert P. Mecham. Contributors: Stephen M. Schwartz, Robert P. Mecham. Publisher: Academic Press, 1995.
Myosin
Myosin is primarily class II in smooth muscle. * Myosin II contains two ''heavy chains'' (MHC) which constitute the head and tail domains. Each of these heavy chains contains the N-terminal head domain, while the C-terminal tails take on a coiled-coil morphology, holding the two heavy chains together (imagine two snakes wrapped around each other, such as in acaduceus
The caduceus (☤; ; , ) is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology and consequently by Hermes Trismegistus in Greco-Egyptian mythology. The same staff was borne by other heralds like Iris (mythology), Iris, the messenger of Hera. The s ...
). Thus, myosin II has two heads. In smooth muscle, there is a single gene ( MYH11) that codes for the heavy chains myosin II, but there are splice variants of this gene that result in four distinct isoforms. Also, smooth muscle may contain MHC that is not involved in contraction, and that can arise from multiple genes.
* Myosin II also contains 4 ''light chains'' (MLC), resulting in 2 per head, weighing 20 (MLC20) and 17 (MLC17) kDa. These bind the heavy chains in the "neck" region between the head and tail.
** The MLC20 is also known as the ''regulatory light chain'' and actively participates in muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in musc ...
. Two MLC20 isoforms are found in smooth muscle, and they are encoded by different genes, but only one isoform participates in contraction.
** The MLC17 is also known as the ''essential light chain''. Its exact function is unclear, but it is believed that it contributes to the structural stability of the myosin head along with MLC20. Two variants of MLC17 (MLC17a/b) exist as a result of alternative splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene ma ...
at the MLC17 gene.
Different combinations of heavy and light chains allow for up to hundreds of different types of myosin structures, but it is unlikely that more than a few such combinations are actually used or permitted within a specific smooth muscle bed. In the uterus, a shift in myosin expression has been hypothesized to avail for changes in the directions of uterine contractions that are seen during the menstrual cycle.
Actin
The thin filaments that are part of the contractile machinery are predominantly composed ofalpha-actin
Actin is a protein family, family of Globular protein, globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in myofibril, muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all Eukaryote, eukaryotic cel ...
and gamma-actin. Smooth muscle alpha-actin is the predominant isoform within smooth muscle. There is also a lot of actin (mainly beta-actin) that does not take part in contraction, but that polymerizes just below the plasma membrane in the presence of a contractile stimulant and may thereby assist in mechanical tension. Alpha-actin is also expressed as distinct genetic isoforms such as smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle specific isoforms of alpha-actin.
The ratio of actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
to myosin
Myosins () are a Protein family, family of motor proteins (though most often protein complexes) best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are adenosine triphosphate, ATP- ...
is between 2:1 and 10:1 in smooth muscle. Conversely, from a mass ratio standpoint (as opposed to a molar ratio), myosin is the dominant protein in striated skeletal muscle with the actin to myosin ratio falling in the 1:2 to 1:3 range. A typical value for healthy young adults is 1:2.2.
Other associated proteins
Smooth muscle does not contain the proteintroponin
Troponin, or the troponin complex, is a complex of three regulatory proteins (troponin C, troponin I, and troponin T) that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, but not smooth muscle. Measurements of cardiac-spe ...
; instead calmodulin (which takes on the regulatory role in smooth muscle), caldesmon and calponin are significant proteins expressed within smooth muscle.
* Tropomyosin is present in smooth muscle, spanning seven actin monomers and is laid out end to end over the entire length of the thin filaments. In striated muscle, tropomyosin serves to block actin–myosin interactions until calcium is present, but in smooth muscle, its function is unknown.
* Calponin molecules may exist in equal number as actin, and has been proposed to be a load-bearing protein.
* Caldesmon has been suggested to be involved in tethering actin, myosin and tropomyosin, and thereby enhance the ability of smooth muscle to maintain tension.
Also, all three of these proteins may have a role in inhibiting the ATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, ATP hydrolase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or ...
activity of the myosin complex that otherwise provides energy to fuel muscle contraction.
Dense bodies
The actin filaments are attached to dense bodies, which are analogous to the Z-discs in striated muscle sarcomeres. Dense bodies are rich in alpha-actinin (α-actinin), and also attach intermediate filaments (consisting largely ofvimentin
Vimentin is a structural protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VIM'' gene. Its name comes from the Latin ''vimentum'' which refers to an array of flexible rods.
Vimentin is a Intermediate filament#Type III, type III intermediate filamen ...
and desmin), and thereby appear to serve as anchors from which the thin filaments can exert force. Dense bodies also are associated with beta-actin, which is the type found in the cytoskeleton, suggesting that dense bodies may coordinate tensions from both the contractile machinery and the cytoskeleton. Dense bodies appear darker under an electron microscope, and so they are sometimes described as electron dense.
The intermediate filaments are connected to other intermediate filaments via dense bodies, which eventually are attached to adherens junctions (also called focal adhesions) in the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
of the smooth muscle cell, called the sarcolemma
The sarcolemma (''sarco'' (from ''sarx'') from Greek; flesh, and ''lemma'' from Greek; sheath), also called the myolemma, is the cell membrane surrounding a skeletal muscle fibre or a cardiomyocyte.
It consists of a lipid bilayer and a thin ...
. The adherens junctions consist of large number of proteins including alpha-actinin (α-actinin), vinculin and cytoskeletal actin. The adherens junctions are scattered around ''dense bands'' that are circumfering the smooth muscle cell in a rib-like pattern. The dense band (or dense plaques) areas alternate with regions of membrane containing numerous caveolae. When complexes of actin and myosin contract, force is transduced to the sarcolemma through intermediate filaments attaching to such dense bands.
Contraction
During contraction, there is a spatial reorganization of the contractile machinery to optimize force development. part of this reorganization consists of vimentin being phosphorylated at Ser56 by a p21 activated kinase, resulting in some disassembly of vimentin polymers. Also, the number of myosin filaments is dynamic between the relaxed and contracted state in some tissues as the ratio of actin to myosin changes, and the length and number of myosin filaments change. Isolated single smooth muscle cells have been observed contracting in a spiral corkscrew fashion, and isolated permeabilized smooth muscle cells adhered to glass (so contractile proteins allowed to internally contract) demonstrate zones of contractile protein interactions along the long axis as the cell contracts. Smooth muscle-containing tissue needs to be stretched often, so elasticity is an important attribute of smooth muscle. Smooth muscle cells may secrete a complex extracellular matrix containingcollagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
(predominantly types I and III), elastin
Elastin is a protein encoded by the ''ELN'' gene in humans and several other animals. Elastin is a key component in the extracellular matrix of gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly Elasticity (physics), elastic and present in connective ...
, glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
, and proteoglycans
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylation, glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalent bond, covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a ...
. Smooth muscle also has specific elastin and collagen receptors to interact with these proteins of the extracellular matrix. These fibers with their extracellular matrices contribute to the viscoelasticity
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist both shear flow and strain lin ...
of these tissues. For example, the great arteries are viscolelastic vessels that act like a Windkessel, propagating ventricular contraction and smoothing out the pulsatile flow, and the smooth muscle within the tunica media
The tunica media (Neo-Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the internal elastic lamina of the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside.
Artery
The ...
contributes to this property.
Caveolae
The sarcolemma also contains caveolae, which are microdomains oflipid raft
The cell membrane, plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids, cholesterol and protein Receptor (biochemistry), receptors organized in glycolipoprotein lipid microdomains termed lipid rafts. Their existence in cellular me ...
s specialized to cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the Biological process, process by which a Cell (biology), cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all Cell (biol ...
events and ion channels
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ...
. These invaginations in the sarcoplasm contain a host of receptors ( prostacyclin, endothelin, serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, ...
, muscarinic receptors, adrenergic receptors), second messenger generators ( adenylate cyclase, phospholipase C), G proteins (RhoA, G alpha), kinases ( rho kinase-ROCK, protein kinase C, protein Kinase A), ion channels (L type calcium channels, ATP sensitive potassium channels, calcium sensitive potassium channels) in close proximity. The caveolae are often close to sarcoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria, and have been proposed to organize signaling molecules in the membrane.
Excitation-contraction coupling
A smooth muscle is excited by external stimuli, which causes contraction. Each step is further detailed below.Inducing stimuli and factors
Smooth muscle may contract spontaneously (via ionic channel dynamics) or as in the gut special pacemakers cells interstitial cells of Cajal produce rhythmic contractions. Also, contraction, as well as relaxation, can be induced by a number of physiochemical agents (e.g., hormones, drugs, neurotransmitters – particularly from theautonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
).
Smooth muscle in various regions of the vascular tree, the airway and lungs, kidneys and vagina is different in their expression of ionic channels, hormone receptors, cell-signaling pathways, and other proteins that determine function.
External substances
For instance, blood vessels in skin, gastrointestinal system, kidney and brain respond tonorepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
and epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
(from sympathetic stimulation or the adrenal medulla) by producing vasoconstriction (this response is mediated through alpha-1 adrenergic receptors). However, blood vessels within skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle respond to these catecholamines producing vasodilation because they possess beta- adrenergic receptors. So there is a difference in the distribution of the various adrenergic receptors that explains the difference in why blood vessels from different areas respond to the same agent norepinephrine/epinephrine differently as well as differences due to varying amounts of these catecholamines that are released and sensitivities of various receptors to concentrations.
Generally, arterial smooth muscle responds to carbon dioxide by producing vasodilation, and responds to oxygen by producing vasoconstriction. Pulmonary blood vessels within the lung are unique as they vasodilate to high oxygen tension and vasoconstrict when it falls. Bronchiole, smooth muscle that line the airways of the lung, respond to high carbon dioxide producing vasodilation and vasoconstrict when carbon dioxide is low. These responses to carbon dioxide and oxygen by pulmonary blood vessels and bronchiole airway smooth muscle aid in matching perfusion and ventilation within the lungs. Further different smooth muscle tissues display extremes of abundant to little sarcoplasmic reticulum so excitation-contraction coupling varies with its dependence on intracellular or extracellular calcium.
Recent research indicates that sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) signaling is an important regulator of vascular smooth muscle
Vascular smooth muscle is the type of smooth muscle that makes up most of the walls of blood vessels.
Structure
Vascular smooth muscle refers to the particular type of smooth muscle found within, and composing the majority of the wall of blood v ...
contraction. When transmural pressure increases, sphingosine kinase 1 phosphorylates sphingosine to S1P, which binds to the S1P2 receptor in plasma membrane of cells. This leads to a transient increase in intracellular calcium, and activates Rac and Rhoa signaling pathways. Collectively, these serve to increase MLCK activity and decrease MLCP activity, promoting muscle contraction. This allows arterioles to increase resistance in response to increased blood pressure and thus maintain constant blood flow. The Rhoa and Rac portion of the signaling pathway provides a calcium-independent way to regulate resistance artery tone.
Spread of impulse
To maintain organ dimensions against force, cells are fastened to one another by adherens junctions. As a consequence, cells are mechanically coupled to one another such that contraction of one cell invokes some degree of contraction in an adjoining cell.Gap junctions
Gap junctions are Membrane channel, membrane channels between adjacent cells that allow the direct exchange of cytoplasmic substances, such small molecules, substrates, and metabolites.
Gap junctions were first described as ''close appositions' ...
couple adjacent cells chemically and electrically, facilitating the spread of chemicals (e.g., calcium) or action potentials between smooth muscle cells. Single unit smooth muscle displays numerous gap junctions and these tissues often organize into sheets or bundles which contract in bulk.
Contraction
Smooth muscle contraction is caused by the sliding ofmyosin
Myosins () are a Protein family, family of motor proteins (though most often protein complexes) best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are adenosine triphosphate, ATP- ...
and actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ...
filaments (a sliding filament mechanism) over each other. The energy for this to happen is provided by the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of ATP. Myosin functions as an ATPase utilizing ATP to produce a molecular conformational change of part of the myosin and produces movement. Movement of the filaments over each other happens when the globular heads protruding from myosin filaments attach and interact with actin filaments to form crossbridges. The myosin heads tilt and drag along the actin filament a small distance (10–12 nm). The heads then release the actin filament and then changes angle to relocate to another site on the actin filament a further distance (10–12 nm) away. They can then re-bind to the actin molecule and drag it along further. This process is called crossbridge cycling and is the same for all muscles (see muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in musc ...
). Unlike cardiac and skeletal muscle, smooth muscle does not contain the calcium-binding protein troponin. Contraction is initiated by a calcium-regulated phosphorylation of myosin, rather than a calcium-activated troponin system.
Crossbridge cycling causes contraction of myosin and actin complexes, in turn causing increased tension along the entire chains of tensile structures, ultimately resulting in contraction of the entire smooth muscle tissue.
Phasic or tonic
Smooth muscle may contract phasically with rapid contraction and relaxation, or tonically with slow and sustained contraction. The reproductive, digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts, skin, eye, and vasculature all contain this tonic muscle type. This type of smooth muscle can maintain force for prolonged time with only little energy utilization. There are differences in the myosin heavy and light chains that also correlate with these differences in contractile patterns and kinetics of contraction between tonic and phasic smooth muscle.Activation of myosin heads
Crossbridge cycling cannot occur until themyosin head
The myosin head is the part of the thick myofilament made up of myosin that acts in muscle contraction, by sliding over thin myofilaments of actin. Myosin is the major component of the thick filaments and most myosin molecules are composed of a ...
s have been activated to allow crossbridges to form. When the light chains are phosphorylated, they become active and will allow contraction to occur. The enzyme that phosphorylates the light chains is called myosin light-chain kinase (MLCK), also called MLC20 kinase. In order to control contraction, MLCK will work only when the muscle is stimulated to contract. Stimulation will increase the intracellular concentration of calcium ions. These bind to a molecule called calmodulin, and form a calcium-calmodulin complex. It is this complex that will bind to MLCK to activate it, allowing the chain of reactions for contraction to occur.
Activation consists of phosphorylation of a serine on position 19 (Ser19) on the MLC20 light chain, which causes a conformational change that increases the angle in the neck domain of the myosin heavy chain, which corresponds to the part of the cross-bridge cycle where the myosin head is unattached to the actin filament and relocates to another site on it. After attachment of the myosin head to the actin filament, this serine phosphorylation also activates the ATPase activity of the myosin head region to provide the energy to fuel the subsequent contraction. Phosphorylation of a threonine on position 18 (Thr18) on MLC20 is also possible and may further increase the ATPase activity of the myosin complex.
Sustained maintenance
Phosphorylation of the MLC20 myosin light chains correlates well with the shortening velocity of smooth muscle. During this period there is a rapid burst of energy utilization as measured by oxygen consumption. Within a few minutes of initiation the calcium level markedly decrease, MLC20 myosin light chains phosphorylation decreases, and energy utilization decreases and the muscle can relax. Still, smooth muscle has the ability of sustained maintenance of force in this situation as well. This sustained phase has been attributed to certain myosin crossbridges, termed latch-bridges, that are cycling very slowly, notably slowing the progression to the cycle stage whereby dephosphorylated myosin detaches from the actin, thereby maintaining the force at low energy costs. This phenomenon is of great value especially for tonically active smooth muscle. Isolated preparations of vascular and visceral smooth muscle contract with depolarizing high potassium balanced saline generating a certain amount of contractile force. The same preparation stimulated in normal balanced saline with an agonist such as endothelin or serotonin will generate more contractile force. This increase in force is termed calcium sensitization. The myosin light chain phosphatase is inhibited to increase the gain or sensitivity of myosin light chain kinase to calcium. There are a number of cell signalling pathways believed to regulate this decrease in myosin light chain phosphatase: a RhoA-Rock kinase pathway, a Protein kinase C-Protein kinase C potentiation inhibitor protein 17 (CPI-17) pathway, telokin, and a Zip kinase pathway. Further Rock kinase and Zip kinase have been implicated to directly phosphorylate the 20kd myosin light chains.Other contractile mechanisms
Other cell signaling pathways and protein kinases ( Protein kinase C, Rho kinase, Zip kinase, Focal adhesion kinases) have been implicated as well and actin polymerization dynamics plays a role in force maintenance. While myosin light chain phosphorylation correlates well with shortening velocity, other cell signaling pathways have been implicated in the development of force and maintenance of force. Notably the phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues on the focal adhesion adapter protein-paxillin by specific tyrosine kinases has been demonstrated to be essential to force development and maintenance. For example, cyclic nucleotides can relax arterial smooth muscle without reductions in crossbridge phosphorylation, a process termed force suppression. This process is mediated by the phosphorylation of the small heat shock protein, hsp20, and may prevent phosphorylated myosin heads from interacting with actin.Relaxation
The phosphorylation of the light chains by MLCK is countered by a myosin light-chain phosphatase, which dephosphorylates the MLC20 myosin light chains and thereby inhibits contraction. Other signaling pathways have also been implicated in the regulation actin and myosin dynamics. In general, the relaxation of smooth muscle is by cell-signaling pathways that increase the myosin phosphatase activity, decrease the intracellular calcium levels, hyperpolarize the smooth muscle, and/or regulate actin and myosin muscle can be mediated by the endothelium-derived relaxing factor-nitric oxide, endothelial derived hyperpolarizing factor (either an endogenous cannabinoid, cytochrome P450 metabolite, or hydrogen peroxide), or prostacyclin (PGI2).Nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes den ...
and PGI2 stimulate soluble guanylate cyclase and membrane bound adenylate cyclase, respectively. The cyclic nucleotides (cGMP and cAMP) produced by these cyclases activate Protein Kinase G and Protein Kinase A and phosphorylate a number of proteins. The phosphorylation events lead to a decrease in intracellular calcium (inhibit L type Calcium channels, inhibits IP3 receptor channels, stimulates sarcoplasmic reticulum Calcium pump ATPase), a decrease in the 20kd myosin light chain phosphorylation by altering calcium sensitization and increasing myosin light chain phosphatase activity, a stimulation of calcium sensitive potassium channels which hyperpolarize the cell, and the phosphorylation of amino acid residue serine 16 on the small heat shock protein (hsp20)by Protein Kinases A and G. The phosphorylation of hsp20 appears to alter actin and focal adhesion dynamics and actin-myosin interaction, and recent evidence indicates that hsp20 binding to 14-3-3 protein is involved in this process. An alternative hypothesis is that phosphorylated Hsp20 may also alter the affinity of phosphorylated myosin with actin and inhibit contractility by interfering with crossbridge formation. The endothelium derived hyperpolarizing factor stimulates calcium sensitive potassium channels and/or ATP sensitive potassium channels and stimulate potassium efflux which hyperpolarizes the cell and produces relaxation.
Invertebrate smooth muscle
In invertebrate smooth muscle, contraction is initiated with the binding of calcium directly to myosin and then rapidly cycling cross-bridges, generating force. Similar to the mechanism of vertebrate smooth muscle, there is a low calcium and low energy utilization catch phase. This sustained phase or catch phase has been attributed to a catch protein that has similarities to myosin light-chain kinase and the elastic protein-titin called twitchin. Clams and other bivalve mollusks use this catch phase of smooth muscle to keep their shell closed for prolonged periods with little energy usage.Specific effects
Although the structure and function is basically the same in smooth muscle cells in different organs, their specific effects or end-functions differ. The contractile function of vascular smooth muscle regulates the lumenal diameter of the small arteries-arterioles called resistance arteries, thereby contributing significantly to setting the level of blood pressure and blood flow to vascular beds. Smooth muscle contracts slowly and may maintain the contraction (tonically) for prolonged periods in blood vessels, bronchioles, and some sphincters. Activating arteriole smooth muscle can decrease the lumenal diameter 1/3 of resting so it drastically alters blood flow and resistance. Activation of aortic smooth muscle doesn't significantly alter the lumenal diameter but serves to increase the viscoelasticity of the vascular wall. In the digestive tract, smooth muscle contracts in a rhythmicperistaltic
Peristalsis ( , ) is a type of intestinal motility, characterized by symmetry in biology#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an wikt:anterograde, anterograde dir ...
fashion, rhythmically forcing foodstuffs through the digestive tract as the result of phasic contraction.
A non-contractile function is seen in specialized smooth muscle within the afferent arteriole of the juxtaglomerular apparatus, which secretes renin in response to osmotic and pressure changes, and also it is believed to secrete ATP in tubuloglomerular regulation of glomerular filtration rate. Renin in turn activates the renin–angiotensin system
The renin–angiotensin system (RAS), or renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid, and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance.
When renal blood flow is reduced, ...
to regulate blood pressure.
Growth and rearrangement
The mechanism in which external factors stimulate growth and rearrangement is not yet fully understood. A number of growth factors and neurohumoral agents influence smooth muscle growth and differentiation. The Notch receptor and cell-signaling pathway have been demonstrated to be essential to vasculogenesis and the formation of arteries and veins. The proliferation is implicated in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and is inhibited by nitric oxide. The embryological origin of smooth muscle is usually of mesodermal origin, after the creation ofmuscle cell
A muscle cell, also known as a myocyte, is a mature contractile Cell (biology), cell in the muscle of an animal. In humans and other vertebrates there are three types: skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth, and Cardiac muscle, cardiac ...
s in a process known as myogenesis
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscle, skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development.
Skeletal muscle#Skeletal muscle cells, Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor cell, precursor myoblasts in ...
. However, the smooth muscle within the Aorta and Pulmonary arteries (the Great Arteries of the heart) is derived from ectomesenchyme of neural crest
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural crest cells originate from this structure through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, ...
origin, although coronary artery smooth muscle is of mesodermal origin.
Related diseases
Multisystemic smooth muscle dysfunction syndrome is a genetic condition in which the body of a developing embryo does not create enough smooth muscle for the gastrointestinal system. This condition is fatal. Anti-smooth muscle antibodies (ASMA) can be a symptom of an auto-immune disorder, such ashepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver parenchyma, liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), Anorexia (symptom), poor appetite ...
, cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced ...
, or lupus.
Smooth muscle tumors are most commonly benign, and are then called leiomyomas. They can occur in any organ, but they usually occur in the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
, small bowel, and esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
. Malignant smooth muscle tumors are called leiomyosarcomas. Leiomyosarcomas are one of the more common types of soft-tissue sarcomas. Vascular smooth muscle tumors are very rare. They can be malignant or benign, and morbidity can be significant with either type. Intravascular leiomyomatosis is a benign neoplasm that extends through the veins; angioleiomyoma is a benign neoplasm of the extremities; vascular leiomyosarcomas is a malignant neoplasm that can be found in the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
, pulmonary arteries
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
and veins, and other peripheral vessels.
See Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by eleva ...
.
See also
* Atromentin has been shown to be a smooth musclestimulant
Stimulants (also known as central nervous system stimulants, or psychostimulants, or colloquially as uppers) are a class of drugs that increase alertness. They are used for various purposes, such as enhancing attention, motivation, cognition, ...
.
* Myogenic mechanism
* List of distinct cell types in the adult human body
References
External links
BBC
– baby born with smooth muscle condition has 8 organs transplanted
Stomach smooth muscle identified using antibody
* * "Smooth Muscle" *
Smooth muscle histology photomicrographs
(medlineplus.gov) {{Authority control Muscular system Muscle tissue