Smelt-whiting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Sillaginidae, commonly known as the smelt-whitings, whitings, sillaginids, sand borers and sand-smelts, are a


 *Family SILLAGINIDAE
**Genus '' Sillaginodes'' T.N. Gill, 1861
*** ''
*Family SILLAGINIDAE
**Genus '' Sillaginodes'' T.N. Gill, 1861
*** ''
ImageSize = width:1000px height:auto barincrement:15px
PlotArea = left:10px bottom:50px top:10px right:10px
Period = from:-65.5 till:10
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:5 start:-65.5
ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:-65.5
TimeAxis = orientation:hor
AlignBars = justify
Colors =
#legends
id:CAR value:claret
id:ANK value:rgb(0.4,0.3,0.196)
id:HER value:teal
id:HAD value:green
id:OMN value:blue
id:black value:black
id:white value:white
id:cenozoic value:rgb(0.54,0.54,0.258)
id:paleogene value:rgb(0.99,0.6,0.32)
id:paleocene value:rgb(0.99,0.65,0.37)
id:eocene value:rgb(0.99,0.71,0.42)
id:oligocene value:rgb(0.99,0.75,0.48)
id:neogene value:rgb(0.999999,0.9,0.1)
id:miocene value:rgb(0.999999,0.999999,0)
id:pliocene value:rgb(0.97,0.98,0.68)
id:quaternary value:rgb(0.98,0.98,0.5)
id:pleistocene value:rgb(0.999999,0.95,0.68)
id:holocene value:rgb(0.999,0.95,0.88)
BarData=
bar:eratop
bar:space
bar:periodtop
bar:space
bar:NAM1
bar:NAM2
bar:space
bar:period
bar:space
bar:era
PlotData=
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:M mark:(line,black) width:25
shift:(7,-4)
bar:periodtop
from: -65.5 till: -55.8 color:paleocene text:
 The Sillaginidae are distributed throughout the Indo-Pacific region, ranging from the west coast of Africa to Japan and
The Sillaginidae are distributed throughout the Indo-Pacific region, ranging from the west coast of Africa to Japan and
 The sillaginids are some of the most important commercial fishes in the Indo-Pacific region, with a few species making up the bulk of whiting catches. Their high numbers, coupled with their highly regarded
The sillaginids are some of the most important commercial fishes in the Indo-Pacific region, with a few species making up the bulk of whiting catches. Their high numbers, coupled with their highly regarded
 A small number of sillaginids have large enough populations to allow an entire fishery to be based around them, with King George whiting, northern whiting, Japanese whiting, sand whiting, and school whiting the major species. There have been no reliable estimates of catches for the entire family, as catch
A small number of sillaginids have large enough populations to allow an entire fishery to be based around them, with King George whiting, northern whiting, Japanese whiting, sand whiting, and school whiting the major species. There have been no reliable estimates of catches for the entire family, as catch
Colour photographs of many Sillaginid species
{{Authority control Acanthuriformes families Fish of the Pacific Ocean Commercial fish Marine fish families
family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
of benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "the depths". ...
coastal
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
marine fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
historically classified in the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
Perciformes
Perciformes (), also called the Acanthopteri, is an order or superorder of ray-finned fish in the clade Percomorpha. ''Perciformes'' means " perch-like". Among the well-known members of this group are perches and darters ( Percidae), and als ...
, although the 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World
''Fishes of the World'' is a standard reference for the systematics of fishes. It was first written in 1976 by the American ichthyologist Joseph S. Nelson (1937–2011). Now in its fifth edition (2016), the work is a comprehensive overview of t ...
'' places the family in the Spariformes
Spariformes is an order of ray-finned fishes consisting of six families within the series Percomorpha.
Taxonomy
Spariformes was first used as a taxonomic term in 1860 by the Dutch physician, herpetologist and ichthyologist Pieter Bleeker. Trad ...
. The smelt-whitings inhabit a wide region covering much of the Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the ...
, from the west coast of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
east to Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and south to Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
. The family comprises only five genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
and 35 species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, of which a number are dubious, with the last major revision of the family in 1992 unable to confirm the validity of a number of species. They are elongated, slightly compressed fish, often light brown to silver in colour, with a variety of markings and patterns on their upper bodies. The Sillaginidae are not related to a number of fishes commonly called ' whiting' in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
, including the fish originally called whiting, ''Merlangius merlangus
''Merlangius merlangus'', commonly known as whiting or merling, is an important food fish in the eastern North Atlantic Ocean and the northern Mediterranean, western Baltic, and Black Sea. In Anglophonic countries outside the whiting's natural ...
''.
The smelt-whitings are mostly inshore
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
fishes that inhabit sandy, silty, and muddy substrates on both low- and high-energy environments ranging from protected tidal flat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal ...
s and estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
to surf zone
The surf zone or breaker zone is the nearshore part of a body of open water between the line at which the waves break and the shore. As ocean surface waves approach a shore, they interact with the bottom, wave shoaling, get taller and steeper, an ...
s. A few species predominantly live offshore on deep sand shoal
In oceanography, geomorphology, and Earth science, geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank (geography), bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material, and rises from the bed of a body ...
s and reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral, or similar relatively stable material lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic component, abiotic (non-living) processes such as deposition (geol ...
s, although the larvae and juvenile phases of most species return to inshore grounds, where they spend the first few years of their lives. Smelt-whitings are benthic carnivores
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly mu ...
that prey
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not ki ...
predominantly on polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine Annelid, annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called c ...
s, a variety of crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, and to a lesser extent echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as ...
s and fish, feeding by detecting vibrations emitted by their prey.
The family is highly important to fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a., fishing grounds). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farm ...
throughout the Indo-Pacific, with species such as the northern whiting
The northern whiting (''Sillago sihama''), also known as the silver whiting and sand smelt, is a marine fish, the most widespread and abundant member of the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The northern whiting was the first species of sillagi ...
, Japanese whiting
The Japanese whiting (''Sillago japonica''), also known as the Japanese sillago or Shiro-gisu, is a common species of coastal marine fish belonging to the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. As suggested by its name, the Japanese whiting was fi ...
, and King George whiting forming the basis of major fisheries throughout their range. Many species are also of major importance to small subsistence
A subsistence economy is an economy directed to basic subsistence (the provision of food, clothing and shelter) rather than to the market.
Definition
"Subsistence" is understood as supporting oneself and family at a minimum level. Basic subsiste ...
fisheries, while others are little more than occasional bycatch
Bycatch (or by-catch), in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juve ...
. Smelt-whitings are caught by a number of methods, including trawling
Trawling is an industrial method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch di ...
, seine net
Seine fishing (or seine-haul fishing; ) is a method of fishing that employs a surrounding net, called a seine, that hangs vertically in the water with its bottom edge held down by weights and its top edge buoyed by floats. Seine nets can be de ...
s, and cast nets. In Australia and Japan in particular, members of the family are often highly sought by recreational fishermen who also seek the fish for their prized flesh.
Taxonomy
The first species of sillaginid to bescientifically described
A species description is a formal scientific description of a newly encountered species, typically articulated through a scientific publication. Its purpose is to provide a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it diffe ...
was '' Sillago sihama'', by Peter Forsskål
Peter Forsskål, sometimes spelled Pehr Forsskål, Peter Forskaol, Petrus Forskål or Pehr Forsskåhl (11 January 1732 – 11 July 1763) was a Sweden, Swedish exploration, explorer, oriental studies, orientalist, natural history, naturalist, and ...
in 1775, who initially referred the species to a genus of hardyhead, ''Atherina
''Atherina'' is a genus of fish of silverside family Atherinidae, found in the temperate and tropic zones. Up to long, they are widespread in the Mediterranean, Black Sea and Sea of Azov; in lagoons such as Syvash in Ukraine; and estuaries. The ...
''. It was not until 1817 that the type
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* ...
genus ''Sillago'' was created by Georges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, baron Cuvier (23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier (; ), was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuv ...
based on his newly described species ''Sillago acuta'', which was later found to be a junior synonym
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently.
...
of ''S. sihama'' and subsequently discarded. Cuvier continued to describe species of sillaginid with the publishing of his ichthyological
Ichthyology is the branch of zoology devoted to the study of fish, including bony fish (Osteichthyes), cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes), and jawless fish (Agnatha). According to FishBase, 35,800 species of fish had been described as of March 2 ...
work '' Histoire Naturelle des Poissons'' with Achille Valenciennes
Achille Valenciennes (9 August 1794 – 13 April 1865) was a French zoology, zoologist.
Valenciennes was born in Paris, and studied under Georges Cuvier. His study of parasitic worms in humans made an important contribution to the study of parasi ...
in 1829, also erecting the genus '' Sillaginodes'' in this work. The species ''Cheilodipterus panijus'' was named in 1822 by Francis Buchanan-Hamilton and was subsequently reexamined by Theodore Gill
Theodore Nicholas Gill (March 21, 1837 – September 25, 1914) was an American ichthyologist, mammalogist, malacologist, and librarian.
Career
Born and educated in New York City under private tutors, Gill early showed interest in natural hist ...
in 1861, leading to the creation of the monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unisp ...
genus '' Sillaginopsis''. John Richardson was the first to propose that ''Sillago'', the only genus of sillaginid then recognised, be assigned to their own taxonomic family, "Sillaginidae" (used interchangeably with 'Sillaginoidae'), at a meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science
The British Science Association (BSA) is a Charitable organization, charity and learned society founded in 1831 to aid in the promotion and development of science. Until 2009 it was known as the British Association for the Advancement of Scienc ...
. There were, however, many differing opinions on the relationships of the "sillaginoids", leading to the naturalists of the day continually revising the position of the five genera, placing in them in a number of families. The first review of the sillaginid fishes was Gill's 1861 work "Synopsis of the sillaginoids", in which the name "Sillaginidae" was popularized and expanded on to include ''Sillaginodes'' and ''Sillaginopsis'', however the debate on the placement of the family remained controversial.
In the years after Gill's paper was published, over 30 'new' species of sillaginids were reported and scientifically described, many of which were synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are a ...
s of previously described species, with similarity between species, as well as minor geographical variation confounding taxonomist
In biology, taxonomy () is the science, scientific study of naming, defining (Circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxon, taxa (si ...
s. In 1985, Roland McKay of the Queensland Museum
The Queensland Museum Kurilpa is the state museum of Queensland, funded by the government, and dedicated to natural history, cultural heritage, science and human achievement. The museum currently operates from its headquarters and general museu ...
published a comprehensive review of the family to resolve these relationships, although a number of species are still listed as doubtful, with McKay unable to locate the holotypes. Along with the review of previously described species, McKay described an additional seven species, a number of which he described as subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
. After this 1985 paper, additional specimen
Specimen may refer to:
Science and technology
* Sample (material), a limited quantity of something which is intended to be similar to and represent a larger amount
* Biological specimen or biospecimen, an organic specimen held by a biorepository f ...
s came to light, proving that all the subspecies he had identified were individual species. In 1992, McKay published a synopsis of the Sillaginidae for the FAO
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition ...
, in which he elevated these subspecies to full species status.
The name "Sillaginidae" was derived from Cuvier's ''Sillago'', which itself takes its name from a locality in Australia, possibly Sillago reef off the coast of Queensland. The term "sillago" is derived from the Greek term ''syllego'', which means "to meet".
Classification
The following is a comprehensive list of the 35 knownextant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
species of sillaginids, with a number of the species still in doubt due to the loss of the holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
specimen. This classification follows ''Fishbase
FishBase is a global species database of fish species (specifically finfish). It is the largest and most extensively accessed online database on adult finfish on the web.
'', which itself is based on McKay's last revision of the family.




Sillaginodes punctatus
The King George whiting (''Sillaginodes punctatus''), also known as the spotted whiting or spotted sillago, is a coastal marine fish of the smelt-whitings family Sillaginidae. The King George whiting is endemic to Australia, inhabiting the sout ...
'' (Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, baron Cuvier (23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier (; ), was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuv ...
, 1829) (King George whiting)
**Genus '' Sillaginopodys'' Fowler, 1933
*** '' Sillaginopodys chondropus'' ( Bleeker, 1849) (Club-foot whiting)
**Genus '' Sillaginops'' Kaga, 2013
*** '' Sillaginops macrolepis'' (Bleeker, 1858) (Large-scale whiting)
**Genus '' Sillaginopsis''
*** ''Sillaginopsis panijus
The Gangetic whiting (''Sillaginopsis panijus''), also known as the Gangetic sillago or flathead sillago, is a species of inshore marine and estuarine fish of the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. It is the most distinctive Asian member of th ...
'' (Hamilton
Hamilton may refer to:
* Alexander Hamilton (1755/1757–1804), first U.S. Secretary of the Treasury and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States
* ''Hamilton'' (musical), a 2015 Broadway musical by Lin-Manuel Miranda
** ''Hamilton'' (al ...
, 1822) (Gangetic whiting)
**Genus ''Sillago
''Sillago'' is a genus of fish in the family (biology), family Sillaginidae and the only non-monotypic genus in the family. Distinguishing the species can be difficult, with many similar in appearance and colour, forcing the use of swim bladder ...
'' (Cuvier, 1816)
*** '' Sillago aeolus'' D. S. Jordan
David Starr Jordan (January 19, 1851 – September 19, 1931) was the founding president of Stanford University, serving from 1891 to 1913. He was an ichthyologist during his research career. Prior to serving as president of Stanford Universi ...
& Evermann, 1902 (Oriental sillago)
*** '' Sillago analis'' Whitley, 1943 (Golden-lined sillago)
*** '' Sillago arabica'' McKay
McKay, MacKay or Mackay is a Scottish and Irish surname. The last phoneme in the name is traditionally pronounced to rhyme with 'eye', but in some parts of the world this has come to rhyme with 'hey'. In Scotland, it corresponds to Clan Mackay. ...
& McCarthy, 1989 (Arabian sillago)
*** '' Sillago argentifasciata'' C. Martin & H. R. Montalban, 1935 (Silver-banded sillago)
*** '' Sillago asiatica'' McKay, 1982 (Asian sillago)
*** '' Sillago attenuata'' McKay, 1985 (Slender sillago)
*** '' Sillago bassensis'' G. Cuvier, 1829 (Western school sillago)
*** '' Sillago boutani'' Pellegrin, 1905 (Boutan's sillago)
*** ''Sillago burrus
The western trumpeter whiting (''Sillago burrus'') is a species of Marine (ocean), marine fish of the smelt whiting family Sillaginidae that is commonly found along the northern coast of Australia and in southern Indonesia and New Guinea. As its ...
'' Richardson, 1842 (Western trumpeter sillago)
*** '' Sillago caudicula'' Kaga, Imamura, Nakaya, 2010
*** ''Sillago ciliata
The sand whiting (''Sillago ciliata''), also known as the summer whiting, yellowfin whiting or blue-nose whiting, is a common species of coastal marine fish of the family Sillaginidae, the smelt-whitings. It is a slender, slightly compressed fish ...
'' G. Cuvier, 1829 (Sand sillago)
*** '' Sillago erythraea'' G. Cuvier, 1829
*** '' Sillago flindersi'' McKay, 1985 (Flinders' sillago)
*** '' Sillago indica'' McKay, Dutt Dutt () is an Indian family name. Its variation is Dutta.
Notable people with the name include:
Surname
* Amit Dutt, Indian scientist
* Anil Dutt, Indian cricketer
* Anjan Dutt, Indian film personality
* Aroti Dutt, Indian social worker
* Asho ...
& Sujatha, 1985 (Indian sillago)
*** '' Sillago ingenuua'' McKay, 1985 (Bay sillago)
*** '' Sillago intermedius'' Wongratana, 1977 (Intermediate sillago)
*** ''Sillago japonica
The Japanese whiting (''Sillago japonica''), also known as the Japanese sillago or Shiro-gisu, is a common species of coastal marine fish belonging to the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. As suggested by its name, the Japanese whiting was f ...
'' Temminck
Coenraad Jacob Temminck (; 31 March 1778 – 30 January 1858) was a Dutch patrician, zoologist and museum director.
Biography
Coenraad Jacob Temminck was born on 31 March 1778 in Amsterdam in the Dutch Republic. From his father, Jacob ...
& Schlegel, 1843 (Japanese sillago)
*** '' Sillago lutea'' McKay, 1985 (Mud sillago)
*** '' Sillago maculata'' Quoy & Gaimard
Joseph Paul Gaimard (31 January 1793 – 10 December 1858) was a French naval surgeon and naturalist.
Biography
Gaimard was born at Saint-Zacharie on January 31, 1793. He studied medicine at the naval medical school in Toulon, subsequent ...
, 1824 (Trumpeter sillago)
*** ''Sillago megacephalus
The large-headed whiting (''Sillago megacephalus'') is a dubious species of coastal marine fish in the smelt-whiting family that has only been recorded from one specimen captured off the coast of China in 1933. Although very similar to '' Sill ...
'' S. Y. Lin, 1933 (Large-headed sillago)
*** '' Sillago microps'' McKay, 1985 (Small-eyed sillago)
*** '' Sillago nierstraszi'' Hardenberg
Hardenberg (; or '' 'n Arnbarg'') is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Overijssel, Eastern Netherlands. The municipality of ...
, 1941 (Rough sillago)
*** '' Sillago nigrofasciata'' J. G. Xiao, Zheng-Sen Yu, Na Song & T. X. Gao, 2021
*** '' Sillago parvisquamis'' T. N. Gill] 1861 (Small-scale sillago)
*** '' Sillago robusta'' Stead, 1908 (Stout sillago)
*** '' Sillago schomburgkii'' W. K. H. Peters, 1864 (Yellowfin sillago)
*** '' Sillago sihama'' Forsskål, 1775 (Silver sillago)
*** '' Sillago sinica'' T. X. Gao, D. P. Ji, Y. S. Xiao, T. Q. Xue, Yanagimoto & Setoguma, 2011 (Chinese sillago)
*** '' Sillago soringa'' Dutt & Sujatha, 1982 (Soringa sillago)
*** '' Sillago suezensis'' Golani, R. Fricke & Tikochinski, 2013
*** '' Sillago vincenti'' McKay, 1980 (Vincent's sillago)
*** '' Sillago vittata'' McKay, 1985 (Banded sillago)
Evolution
A number of sillaginids have been identified from thefossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
, with the lower Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
marking the first appearance of the family. The family is thought to have evolved
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
in the Tethys Sea
The Tethys Ocean ( ; ), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean during much of the Mesozoic Era and early-mid Cenozoic Era. It was the predecessor to the modern Indian Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Eurasia ...
of central Australia, before colonizing southern Australia during the upper Eocene after a seaway broke through south of Tasmania. During the Oligocene, the family spread to the north and south, occupying a much more extensive range than their current Indo-Pacific distribution. Fossils suggest the sillaginids ranged as far north as Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, and as far south as New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, found in shallow water sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock formed by the cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedime ...
deposits along with other species of extant genera.
At least eight fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
sillaginid species have been found, all of which are believed to be of the genus ''Sillago'' based on the only remains found, otolith
An otolith (, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called otoconium, statolith, or statoconium, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule ...
s. Only one species of extant sillaginid, ''Sillago maculata'', has been found in the fossil record, and this was in very recent Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
s.
*''Sillago campbellensis'' (Schwarzhans, 1985) Australia, Miocene
*''Sillago hassovicus'' (Koken, 1891) Poland, Middle Miocene
*''Sillago maculata'' (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) New Zealand, Middle Pleistocene
*''Sillago mckayi'' (Schwarzhans, 1985) Australia, Oligocene
*''Sillago pliocaenica'' (Stinton, 1952) Australia, Pliocene
*''Sillago recta'' (Schwarzhans, 1980) New Zealand, Upper Miocene
*''Sillago schwarzhansi'' (Steurbaut, 1984) France, Lower Miocene
*''Sillago ventriosus'' (Steurbaut, 1984) France, Upper Oligocene
Timeline of genera
Paleocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), ...
from: -55.8 till: -33.9 color:eocene text:Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
from: -33.9 till: -23.03 color:oligocene text:Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
from: -23.03 till: -5.332 color:miocene text:Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
from: -5.332 till: -2.588 color:pliocene text: Plio.
from: -2.588 till: -0.0117 color:pleistocene text:Pleist.
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
from: -0.0117 till: 0 color:holocene text: H.
bar:eratop
from: -65.5 till: -23.03 color:paleogene text:Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the fir ...
from: -23.03 till: -2.588 color:neogene text:Neogene
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of th ...
from: -2.588 till: 0 color:quaternary text: Q.
PlotData=
align:left fontsize:M mark:(line,white) width:5 anchor:till align:left
color:oligocene bar:NAM1 from: -33.9 till: 0 text: Sillago
''Sillago'' is a genus of fish in the family (biology), family Sillaginidae and the only non-monotypic genus in the family. Distinguishing the species can be difficult, with many similar in appearance and colour, forcing the use of swim bladder ...
color:pliocene bar:NAM2 from: -5.332 till: 0 text: Sillaginoides
PlotData=
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:M mark:(line,black) width:25
bar:period
from: -65.5 till: -55.8 color:paleocene text:Paleocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), ...
from: -55.8 till: -33.9 color:eocene text:Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
from: -33.9 till: -23.03 color:oligocene text:Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
from: -23.03 till: -5.332 color:miocene text:Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
from: -5.332 till: -2.588 color:pliocene text: Plio.
from: -2.588 till: -0.0117 color:pleistocene text:Pleist.
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
from: -0.0117 till: 0 color:holocene text: H.
bar:era
from: -65.5 till: -23.03 color:paleogene text:Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the fir ...
from: -23.03 till: -2.588 color:neogene text:Neogene
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of th ...
from: -2.588 till: 0 color:quaternary text: Q.
Phylogeny
The relationships of the Sillaginidae are poorly known, with very similar morphological characteristics and a lack of genetic studies restricting the ability to performcladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
analyses on the family. Being the fossil sillaginids are based on the comparison of fossil otoliths, with no other type of remains found thus far, this also prevents the reconstruction of the evolution of the family through fossil species. While the position of the Sillaginidae in the order Perciformes was thought to be firmly established due to a number of synapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to ...
shared with other members of that order, no sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
has been established for the family. The 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' placed Sillaginidae in the order Spariformes but other workers have classified the family as ''incertae sedis
or is a term used for a taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty ...
'' within the series Eupercaria
Percomorpha () is an extremely large and diverse clade of ray-finned fish. With more than 17,000 known species (including tuna, seahorses, gobies, cichlids, flatfish, wrasse, perches, anglerfish, and pufferfish) known from both marine and fresh ...
. The current taxonomic
280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme of classes (a taxonomy) and the allocation ...
status of the family is thought to represent a basic picture of the group's phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or Taxon, taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, M ...
, with McKay further dividing the genus ''Sillago'' into three subgenera
In biology, a subgenus ( subgenera) is a taxonomic rank directly below genus.
In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, a subgeneric name can be used independently or included in a species name, in parentheses, placed between the ge ...
based on shared morphological characters of the swimbladder. The genera ''Sillaginodes'' and ''Sillaginopsis'' have the most plesiomorphic
In phylogenetics, a plesiomorphy ("near form") and symplesiomorphy are synonyms for an ancestral character shared by all members of a clade, which does not distinguish the clade from other clades.
Plesiomorphy, symplesiomorphy, apomorphy, an ...
characteristics; being monotypic, and distinct from ''Sillago''. ''Sillago'' is further divided into three subgenera based primarily on swim bladder morphology; ''Sillago'', ''Parasillago'' and ''Sillaginopodys'', which also represent evolutionary relationships. Whilst genetic studies have not been done on the family, they have been used to establish the relationship of what were thought to be various subspecies of school whiting, ''S. bassensis'' and ''S. flindersi''.Dixon, P.I., Crozier, R.H., Black, M. & Church, A. (1987): Stock identification and discrimination of commercially important whitings in Australian waters using genetic criteria (FIRTA 83/16). ''Centre for Marine Science, University of New South Wales. 69 p. Appendices 1-10.'' Furthermore, morphological data suggests a number of Australian species diverged very recently during the last glacial maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
, which caused land bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regression, in which sea le ...
s to isolate population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
s of fish. The two aforementioned species of school whiting, ''S. maculata'' and ''S. burrus'', and ''S. ciliata'' and ''S. analis'' are all thought to be products of such a process, although only the school whiting have anything other than similar morphology as evidence of this process.
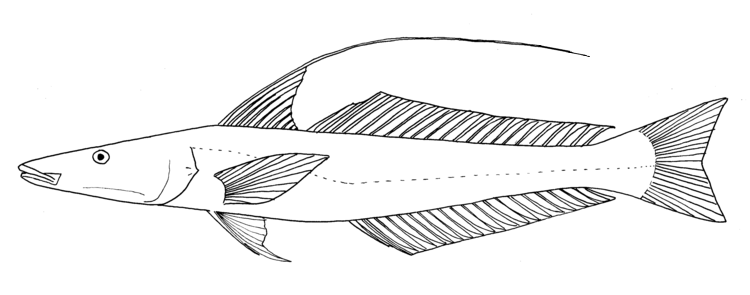
Morphology
The Sillaginidae are medium-sized fishes which grow to an average of around 20 cm and around 100 g, although the largest member of the family, the King George whiting is known to reach 72 cm and 4.8 kg inweight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is a quantity associated with the gravitational force exerted on the object by other objects in its environment, although there is some variation and debate as to the exact definition.
Some sta ...
. The body shape and fin placement of the family is quite similar to most of the members of the order Perciformes. Their bodies are elongate, slightly compressed, with a head that tapers toward a terminal mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also t ...
. The mouth has a band of brush-like teeth with canine teeth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. In the context of the upper jaw, they are also known as '' fangs''. They can appear more fl ...
present only in the upper jaw
The jaws are a pair of opposable articulated structures at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term ''jaws'' is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth ...
of ''Sillaginopsis''. The cranial sensory system of the family is well developed above and laterally, with the lower jaw having a pair of small pores behind which is a median pit containing a pore on each side. On each side of the elongate head the operculum has a short sharp spine. They have two true dorsal fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found ...
s; the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
one supported by 10 to 13 spines while the long rear one is held up by a single leading spine followed by 16 to 27 soft rays. The anal fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported o ...
is similar to the second dorsal fin, having two small slender spines followed by 14 to 26 soft rays. Their bodies are covered in ctenoid
A fish scale is a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish. The skin of most jawed fishes is covered with these protective scales, which can also provide effective camouflage through the use of reflection and colouration, as w ...
scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
, with the exception of the cheek
The cheeks () constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. ''Buccal'' means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of th ...
which may have cycloid or ctenoid scales. There is a wide variation in the amount of lateral line scales, ranging from 50 to 141. The swimbladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ in bony fish that functions to modulate buoyancy, and thus allowing the fish to stay at desired water depth without having to maintain lift via swimming, w ...
in the Sillaginidae is either absent, poorly developed, or highly complex with anterior and lateral extensions that project well into the caudal
Caudal may refer to:
Anatomy
* Caudal (anatomical term) (from Latin ''cauda''; tail), used to describe how close something is to the trailing end of an organism
* Caudal artery, the portion of the dorsal aorta of a vertebrate that passes into th ...
region. A unique duct
The word duct is derived from the Latin word for ''led/leading''. It may refer to:
* Duct (anatomy), various ducts in anatomy and physiology
** Tear duct, which carry tears to the eyes
* Duct (HVAC), for transfer of air between spaces in a struct ...
-like process is present from the ventral surface of the swimbladder to just before the urogenital opening
The urogenital opening is where bodily waste and reproductive fluids are expelled to the environment outside of the body cavity. In some organisms, including monotremes, birds and some fish, discharge from the urological, digestive, and reprod ...
in most species. The presence and morphology of each species' swim bladder is often their major diagnostic feature, with McKay's three proposed subgenera based on swimbladder morphology alone. The sillaginids have only a small range of body colour
Color (or colour in Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though color is not an inherent property of matter, color perception is related to an object's light absorp ...
ings and frequently the only colour characteristics to identify between species are the arrangements of spots and bars on their upper bodies. Most of the family are a pale brown – creamy white colour, while a few species are silver all over. The undersides of the fish are usually lighter than the upper side, and the fins range from yellow to transparent, often marked by bars and spots.
Distribution and habitat
 The Sillaginidae are distributed throughout the Indo-Pacific region, ranging from the west coast of Africa to Japan and
The Sillaginidae are distributed throughout the Indo-Pacific region, ranging from the west coast of Africa to Japan and Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
in the east, as well occupying as a number of small islands including New Caledonia
New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t ...
in the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
. While they have a fairly wide distribution, the highest species densities occur along the coasts of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Taiwan, South East Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, the Indonesian Archipelago and northern Australia
The unofficial geographic term Northern Australia includes those parts of Queensland and Western Australia north of latitude 26th parallel south, 26° and all of the Northern Territory. Those local government areas of Western Australia and Q ...
. One species of sillaginid, ''Sillago sihama'', has been declared an invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
to the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, passing through the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest ...
from the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
since 1977 as part of the Lessepsian migration
The Lessepsian migration (or Erythrean invasion) is the migration of marine species along the Suez Canal, usually from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea, and more rarely in the opposite direction. When the canal was completed in 1869, fish, ...
, becoming widespread.
Sillaginids are primarily inshore marine fishes inhabiting stretches of coastal waters, although a few species move offshore in their adult stages to deep sand banks or reefs to a maximum known depth of 180 m. All species primarily occupy sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is usually defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural ...
y, silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension (chemistry), suspension with water. Silt usually ...
y or mud
Mud (, or Middle Dutch) is loam, silt or clay mixed with water. Mud is usually formed after rainfall or near water sources. Ancient mud deposits hardened over geological time to form sedimentary rock such as shale or mudstone (generally cal ...
dy substrates, often using seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine (ocean), marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four Family (biology), families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and ...
or reef as cover. They commonly inhabit tidal flats, beach
A beach is a landform alongside a body of water which consists of loose particles. The particles composing a beach are typically made from Rock (geology), rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle beach, shingle, pebbles, etc., or biological s ...
zones, broken bottoms and large areas of uniform substrate. Although the family is marine, many species inhabit estuarine
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
environments, with some such as ''Sillaginopsis panijus
The Gangetic whiting (''Sillaginopsis panijus''), also known as the Gangetic sillago or flathead sillago, is a species of inshore marine and estuarine fish of the smelt-whiting family, Sillaginidae. It is the most distinctive Asian member of th ...
'' also found in the upper reaches of the estuary. Each species often occupies a specific niche
Niche may refer to:
Science
*Developmental niche, a concept for understanding the cultural context of child development and growth
*Ecological niche, a term describing the relational position of an organism's species
*Niche differentiation, in ec ...
to avoid competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indi ...
with co-occurring sillaginids, often inhabiting a specific substrate type, depth, or making use of surf zones and estuaries. The juveniles often show distinct changes in habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
preference as they mature, often moving to deeper waters. No members of the family are known to undergo migratory movements, and have been shown to be relatively weak swimmers, relying on currents to disperse juveniles.
Biology
Diet and feeding
The smelt-whitings are benthiccarnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they ar ...
s, with all of the species whose diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
s have been studied showing similar prey preferences. Smelt-whitings have well-developed chemosensory
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance (endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemorecept ...
systems compared to many other teleost fishes, with high taste bud
Taste buds are clusters of taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus, ...
densities on the outside tip of the snout. The turbulence and turbidity of the environment appear to determine how well developed the sensory systems are in an individual. Studies from the waters of Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
and Australia have shown that polychaetes
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class of generally marine annelid worms, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are m ...
, a variety of crustaceans, molluscs and to a lesser extent echinoderms and fish are the predominant prey items of the family. Commonly taken crustaceans include decapods
The Decapoda or decapods, from Ancient Greek δεκάς (''dekás''), meaning "ten", and πούς (''poús''), meaning "foot", is a large order (biology), order of crustaceans within the class Malacostraca, and includes crabs, lobsters, crayfis ...
, copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
s and isopod
Isopoda is an Order (biology), order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both Aquatic animal, aquatic species and Terrestrial animal, terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons ...
s, while the predominant molluscs taken are various species of bivalve
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed b ...
s, especially the unprotected siphon filters that protrude from the shells. In all species studied, some form of diet shift occurs as the fishes mature, often associated with a movement to deeper waters and thus to new potential prey. The juveniles often prey on planktonic
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in water (or air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they pro ...
prey, with small copepods, isopods and other small crustaceans often taken. Whilst many species have a change in niche to reduce intraspecific competition
Intraspecific competition is an interaction in population ecology, whereby members of the same species compete for limited resources. This leads to a reduction in fitness for both individuals, but the more fit individual survives and is able to ...
, there are often many species of sillaginid inhabiting a geographical area. Where this occurs, there is often definite diet differences between species, often associated with a niche specialization. The sillaginid's distinctive body shape and mouth placement is an adaptation to bottom feeding, which is the predominant method of feeding for all whiting species. All larger whiting feed by using their protrusile jaws and tube-like mouths to suck up various types of prey from in, on or above the ocean substrate, as well as using their nose as a 'plough
A plough or ( US) plow (both pronounced ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses but modern ploughs are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden ...
' to dig through the substrate.
There is a large body of evidence that shows whiting do not rely on visual
The visual system is the physiological basis of visual perception (the ability to detect and process light). The system detects, transduces and interprets information concerning light within the visible range to construct an image and buil ...
cues when feeding, instead using a system based on the vibrations emitted by their prey.
Predators
Smelt-whitings are a major link in thefood chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as ...
of most systems, and frequently fall prey to a variety of aquatic
Aquatic means relating to water; living in or near water or taking place in water; does not include groundwater, as "aquatic" implies an environment where plants and animals live.
Aquatic(s) may also refer to:
* Aquatic animal, either vertebrate ...
and aerial predator
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation ...
s. Their main aquatic predators are a wide variety of larger fish, including both teleost
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts (), is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes (class Actinopterygii), with 96% of all neontology, extant species of f ...
s and a variety of shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s and ray
Ray or RAY may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), the bony or horny spine on ray-finned fish
Science and mathematics
* Half-line (geometry) or ray, half of a line split at an ...
s. Marine mammal
Marine mammals are mammals that rely on marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as cetaceans, pinnipeds, sirenians, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their reliance on marine enviro ...
s including seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
and dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal in the cetacean clade Odontoceti (toothed whale). Dolphins belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontopori ...
s have been reported to have taken sillaginids as a main food source. Seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adaptation, adapted to life within the marine ecosystem, marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent ...
s are also another major predator of the family, with diving species such as Cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) ado ...
s taking older fish in deeper waters while juvenile fish in shallow water fall prey to wading bird
Birders in Canada and the United States refer to several families of long-legged wading birds in semi-aquatic ecosystems as waders. These include the families Phoenicopteridae (flamingos), Ciconiidae (storks), Threskiornithidae (ibises and s ...
s. Sillaginids are often called 'sandborers' due to their habit of burying themselves in the substrate to avoid predators, much in the same way as they forage, by ploughing their nose into the substrate. This defense is even used against human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
fishermen, who frequently wade barefoot to feel for buried fish. The Sillaginidae are also host to a variety of well studied internal and external parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
s, which are represented prominently by the groups Digenea
Digenea (Gr. ''Dis'' – double, ''Genos'' – race) is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms (known as ''flukes'') with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one or ...
, Monogenea
Monogeneans, members of the class Monogenea, are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they ...
and Myxosporea
Myxosporea is a class of microscopic animals, all of whom are parasites. They belong to the Myxozoa clade within Cnidaria. They have a complex life cycle that comprises vegetative forms in two hosts—one an aquatic invertebrate (generally an ann ...
, Copepoda
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthic (living on the sediments), several species have ...
and Nematoda
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitism, parasitic. Parasitic ...
.
Reproduction
The Sillaginidae are anoviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings kno ...
, non guarding family, whose species tend to show similar reproductive patterns to one another. Each species reaches sexual maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans, it is related to both puberty and adulthood. ''Puberty'' is the biological process of sexual maturation, while ''adulthood'', the condition of being socially recognized ...
at a slightly different age, with each sex often showing a disparity in time of maturation. Each species also spawns over a different season and the spawning season often differs within a species, usually as a function of latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
; a feature not unique to sillaginids. The proximity to shore of spawning is also different between species, as each species usually does not migrate
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
inshore to spawn, even if the juveniles require shallow water for protection, instead relying on currents. The fecundity of sillaginids is variable, with a normal range between 50 000 – 100 000. The eggs
An egg is an organic vessel in which an embryo begins to develop.
Egg, EGG or eggs may also refer to:
Biology
* Egg cell, the female reproductive cell (gamete) in oogamous organisms
Food
* Eggs as food
Places
* Egg, Austria
* Egg, Switzerland ...
are small (0.6 to 0.8 mm), spherical
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three ...
and pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the sur ...
, hatching around 20 days after fertilisation
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a zygote and initiate its development into a new individual organism or of ...
. The larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
e are quite similar, requiring a trained developmental biologist
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and di ...
to identify between species. The larvae and juveniles are at the mercy of the ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
s, being too weaker swimmers to actively seek out coastlines. Currents are thought to have been responsible for the distribution of mainland
Mainland is defined as "relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it egardless of status under territorial jurisdiction by an entity" The term is often politically, economically and/or demogr ...
species to offshore island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been ...
s as well as the current widespread distribution of ''Sillago sihama''. In all studied species, juveniles inhabit shallow waters in protected embayment
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a ''gulf'', ''sea'', ''sound'', or ''bight''. A ''cove'' is a small, ci ...
s, estuaries, tidal creek
A tidal creek or tidal channel is a narrow inlet or estuary that is affected by the ebb and flow of ocean tides. Thus, it has variable salinity and electrical conductivity over the tidal cycle, and flushes salts from inland soils. Tidal creeks a ...
s and lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') an ...
s as well as exposed surf zones, usually over tidal flats and seagrass beds. As the fish mature, they generally move to deeper waters, showing a change in diet.
Relationship to humans
 The sillaginids are some of the most important commercial fishes in the Indo-Pacific region, with a few species making up the bulk of whiting catches. Their high numbers, coupled with their highly regarded
The sillaginids are some of the most important commercial fishes in the Indo-Pacific region, with a few species making up the bulk of whiting catches. Their high numbers, coupled with their highly regarded flesh
Flesh is any aggregation of soft tissues of an organism. Various multicellular organisms have soft tissues that may be called "flesh". In mammals, including humans, ''flesh'' encompasses muscles, fats and other loose connective tissues, ...
are the reason for this, and their inshore nature also has made them popular targets for recreational fishermen in a number of countries. With overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
rife in some areas, sustainable aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
has allowed the commercial farming of a number of sillaginid species, as well as the use of farmed fish to restock depleted estuaries. At least one species, the Gangetic whiting, has occasionally been used in brackish water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuary ...
aquaria.
Commercial fisheries
 A small number of sillaginids have large enough populations to allow an entire fishery to be based around them, with King George whiting, northern whiting, Japanese whiting, sand whiting, and school whiting the major species. There have been no reliable estimates of catches for the entire family, as catch
A small number of sillaginids have large enough populations to allow an entire fishery to be based around them, with King George whiting, northern whiting, Japanese whiting, sand whiting, and school whiting the major species. There have been no reliable estimates of catches for the entire family, as catch statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
generally include only those species taken in large numbers, but there are some species which make up significant numbers of the bycatch. To add to this problem, many of the lesser known species are taken by subsistence fisheries and not reported. From estimates by the FAO
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition ...
, however, it is evident that the family is one of the most important in the Indo-Pacific region, having an estimated catch of 22 718 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s in 1990 alone. In this same report, it was shown that the greatest three utilizers of sillaginids were the Philippines, Western Australia and Thailand respectively. The records also suggested that the catch increased from 1983 when it was 17 570 t, up to the last estimate in 1990 of 22 718 t. No such estimates have been carried out since. Modern records for Australia show that this trend has reversed, with all catches from Australia totaling 4 372 t in 2006 compared with 1990's 6000 t haul. Statistics from other countries are unavailable for such comparison.
Sillaginids are taken by a variety of fishing methods, with inshore catches predominantly taken using beach seine nets and cast nets. Due to the alert nature of sillaginids, skill is required on creeping up quietly enough to be able to net fish with a cast net, with experienced fishers often paddling into the sun toward a school and drifting slowly upon it before casting the net. In deeper waters, commercial trawler
A fishing trawler is a commercial fishing vessel designed to operate fishing trawls. Trawling is a method of fishing that involves actively dragging or pulling a trawl through the water behind one or more trawlers. Trawls are fishing nets that ...
s and longliners take the most fish, with a number of sillaginids taken in prawn trawls as bycatch. The fish are normally marketed fresh locally under various names, with "Ashuos" commonly used in many countries for various sillaginids. At least one export fishery exists in Australia whereby ''S. flindersi'' is exported to Thailand where the fish are repackaged and sent to Japan frozen.
Recreational fisheries
In Australia and Japan, members of the family are highly sought after by anglers for their sporting and eating qualities, with anglers often taking more than commercial fishermen in some areas. The fishing techniques for all sillaginids are quite similar, with the shallow habitats often requiring light line and quiet movements. Whiting are also popular in part due to their accessibility, with tidal flats around beaches, estuaries andjetties
A jetty is a man-made structure that protrudes from land out into water. A jetty may serve as a breakwater, as a walkway, or both; or, in pairs, as a means of constricting a channel. The term derives from the French word ', "thrown", signif ...
common habitats from where many whiting species are caught without need for a boat. Tidal
Tidal is the adjectival form of tide.
Tidal may also refer to:
* ''Tidal'' (album), a 1996 album by Fiona Apple
* Tidal (king), a king involved in the Battle of the Vale of Siddim
* TidalCycles, a live coding environment for music
* Tidal (servic ...
movements also affect catches, as do lunar phases
A lunar phase or Moon phase is the apparent shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from the Earth. Because the Moon is Tidal locking, tidally locked with the Earth, the same Hemisphere (geometry), hemisphere is always facing the ...
, causing whiting to 'bite' when the tide is changing. Tackle used is kept light to avoid spooking the fish, and often requires only a simple setup, with a hook
A hook is a tool consisting of a length of material, typically metal, that contains a portion that is curved/bent back or has a deeply grooved indentation, which serves to grab, latch or in any way attach itself onto another object. The hook's d ...
and light sinker tied directly to the mainline usually effective. In deeper water fished from boats or where currents are strong, more complex rigs are used, often with hooks tied to dropper loops on the trace. in Australia, some specialist whiting fishermen who target the fish in the surf or on shallow banks use red bead
A bead is a small, decorative object that is formed in a variety of shapes and sizes of a material such as stone, bone, shell, glass, plastic, wood, or pearl and with a small hole for threading or stringing. Beads range in size from under 1 ...
s or tubing to attract the fish, claiming the method produces more fish. The bait used is normally anything from the surrounding environment which the whiting naturally prey on, with polychaetes, bivalves, crustaceans such as prawns and crabs, cephalopods and small fish effective for most species. As with most species, live bait is known to produce better catches. Lure fishing for whiting is not normally practiced, but saltwater flies have been used to good effect, as have small soft plastic lures and surface lures like poppers and stick baits imitating a fleeing fish or prawn. this type of fishing has experienced increasing popularity the last couple of years. In some areas, restrictions to the amount and size of fish are in place and enforced by fishery authorities.
Aquaculture
A number of sillaginid species have been the subject of brackish water aquaculture in Asia and India, with species including ''S. japonica'' commonly bred for consumption. In Australia, research has been undertaken in the breeding of sand whiting and King George whiting, and so far only sand whiting shows promise for commercial viability. King George whiting have been found to take too long to develop to be sustainable, but the use ofgrowth hormones
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in ...
is being investigated. In Australia, aquaculturally bred sand whiting have also been used to stock depleted estuaries.
References
External links
Colour photographs of many Sillaginid species
{{Authority control Acanthuriformes families Fish of the Pacific Ocean Commercial fish Marine fish families