The smallest organisms found on Earth can be determined according to various aspects of
organism
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
size, including
volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). Th ...
,
mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different element ...
,
height
Height is measure of vertical distance, either vertical extent (how "tall" something or someone is) or vertical position (how "high" a point is).
For example, "The height of that building is 50 m" or "The height of an airplane in-flight is ab ...
,
length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the Inte ...
, or
genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
size.
Given the incomplete nature of
scientific knowledge
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for ...
, it is possible that the smallest organism is undiscovered. Furthermore, there is some debate over the definition of
life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimu ...
, and what entities qualify as organisms; consequently the smallest known organism (microorganism) is debatable.
Microorganisms
Obligate endosymbiotic bacteria
The genome of ''
Nasuia deltocephalinicola
''Nasuia deltocephalinicola'' was reported in 2013 to have the smallest genome of all bacteria, with 112,091 nucleotides. For comparison, the human genome has 3.2 billion nucleotides. The second smallest genome, from bacteria '' Tremblaya princep ...
'', a
symbiont
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or paras ...
of the European pest leafhopper, ''
Macrosteles quadripunctulatus'', consists of a
circular chromosome
A circular chromosome is a chromosome in bacteria, archaea, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, in the form of a molecule of circular DNA, unlike the linear chromosome of most eukaryotes.
Most prokaryote chromosomes contain a circular DNA molecul ...
of 112,031 base pairs.
The genome of ''
Nanoarchaeum equitans
''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum. Strains o ...
'' is 490,885 nucleotides long.
''Pelagibacter ubique''

''
Pelagibacter ubique
"''Candidatus'' Pelagibacter", with the single species "''Ca.'' P. communis", was isolated in 2002 and given a specific name, although it has not yet been described as required by the bacteriological code. It is an abundant member of the SAR11 c ...
'' is one of the smallest known free-living bacteria, with a length of and an average cell diameter of . They also have the smallest free-living bacterium genome: 1.3 Mbp, 1354 protein genes, 35 RNA genes. They are one of the most common and smallest organisms in the ocean, with their total weight exceeding that of all fish in the sea.
''Mycoplasma genitalium''
''
Mycoplasma genitalium
''Mycoplasma genitalium'' (''MG'', commonly known as Mgen) is a sexually transmitted, small and pathogenic bacterium that lives on the mucous epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tracts in humans. Medical reports published in 2007 and 2 ...
'', a
parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
bacterium
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were a ...
which lives in the
primate
Primates are a diverse order (biology), order of mammals. They are divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include the Tarsiiformes, tarsiers and ...
bladder, waste disposal organs, genital, and respiratory tracts, is thought to be the smallest known organism capable of independent
growth
Growth may refer to:
Biology
* Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth
* Bacterial growth
* Cell growth
* Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth
* Human development (biology)
* Plant growth
* Secondary grow ...
and
reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – " offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual o ...
. With a size of approximately 200 to 300
nm, ''M. genitalium'' is an
ultramicrobacterium
Ultramicrobacteria are bacteria that are smaller than 0.1 μm3 under all growth conditions. This term was coined in 1981, describing cocci in seawater that were less than 0.3 μm in diameter. Ultramicrobacteria have also been recovered from soil a ...
, smaller than other small bacteria, including
rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The term "ricke ...
and
chlamydia
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several w ...
. However, the vast majority of bacterial strains have not been studied, and the marine ultramicrobacterium ''Sphingomonas'' sp. strain RB2256 is reported to have passed through a
ultrafilter
In the mathematical field of order theory, an ultrafilter on a given partially ordered set (or "poset") P is a certain subset of P, namely a maximal filter on P; that is, a proper filter on P that cannot be enlarged to a bigger proper filter o ...
. A complicating factor is nutrient-downsized bacteria, bacteria that become much smaller due to a lack of available
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excr ...
s.
''Nanoarchaeum''
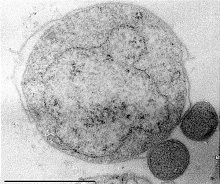
''
Nanoarchaeum equitans
''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' is a species of marine archaea that was discovered in 2002 in a hydrothermal vent off the coast of Iceland on the Kolbeinsey Ridge by Karl Stetter. It has been proposed as the first species in a new phylum. Strains o ...
'' is a species of
microbe
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
in diameter. It was discovered in 2002 in a
hydrothermal vent off the coast of
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
by
Karl Stetter
Karl Otto Stetter (born 16 July 1941) is a German microbiologist and authority on astrobiology. He is an expert on microbial life at high temperatures.
Career
Stetter was born in Munich and studied biology at the Technical University of Munic ...
. A
thermophile
A thermophile is an organism—a type of extremophile—that thrives at relatively high temperatures, between . Many thermophiles are archaea, though they can be bacteria or fungi. Thermophilic eubacteria are suggested to have been among the earl ...
that grows in near-boiling temperatures, ''Nanoarchaeum'' appears to be an obligatory
symbiont
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or paras ...
on the
archaeon
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebact ...
''
Ignicoccus
''Ignicoccus'' is a genus of hyperthermophillic Archaea living in marine hydrothermal vents. They were discovered in samples taken at the Kolbeinsey Ridge north of Iceland, as well as at the East Pacific Rise (at 9 degrees N, 104 degrees W) ...
''; it must be in contact with the host organism to survive.
Guinness World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a reference book published annually, listing world ...
recognizes ''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' as the smallest living organism.
Eukaryotes (Eukaryota)
Prasinophyte
The prasinophytes are a group of unicellular green algae. Prasinophytes mainly include marine planktonic species, as well as some freshwater representatives.Sym, S. D. and Pienaar, R. N. 1993. The class Prasinophyceae. In Round, F. E. and Chapman ...
alga
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from u ...
e of the genus ''
Ostreococcus
''Ostreococcus'' is a genus of unicellular coccoid or spherically shaped green algae belonging to the class Mamiellophyceae. It includes prominent members of the global picoplankton community, which plays a central role in the oceanic carbon cyc ...
'' are the smallest free-living
eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
. The single cell of an ''Ostreococcus'' measures across.
Viruses
Some
biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual cell, a multicellular organism, or a community of interacting populations. They usually speciali ...
s consider
virus
A virus is a wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and ...
es to be non-living because they lack a
cellular
Cellular may refer to:
*Cellular automaton, a model in discrete mathematics
*Cell biology, the evaluation of cells work and more
*Cellular (film), ''Cellular'' (film), a 2004 movie
*Cellular frequencies, assigned to networks operating in cellular ...
structure and cannot
metabolize
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
by themselves, requiring a host cell to replicate and synthesize new products. Some hold that, because viruses do have
genetic material
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main clas ...
and can employ the metabolism of their host, they can be considered organisms. Also, an emerging concept that is gaining traction among some virologists is that of the
virocell
The smallest organisms found on Earth can be determined according to various aspects of organism size, including volume, mass, height, length, or genome size.
Given the incomplete nature of scientific knowledge, it is possible that the smalle ...
, in which the actual
phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological prop ...
of a virus is the infected cell, and the virus particle (or ''virion'') is merely a reproductive or dispersal stage, much like pollen or a spore.
The smallest viruses in terms of genome size are single-stranded DNA (
ssDNA) viruses. Perhaps the most famous is the
bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bact ...
Phi-X174
The phi X 174 (or ΦX174) bacteriophage is a single-stranded DNA ( ssDNA) virus that infects ''Escherichia coli'', and the first DNA-based genome to be sequenced. This work was completed by Fred Sanger and his team in 1977. In 1962, Walter Fi ...
with a genome size of 5,386
nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecul ...
s. However, some ssDNA viruses can be even smaller. For example,
Porcine circovirus
Porcine circovirus (PCV) is a group of four single-stranded DNA viruses that are non-enveloped with an unsegmented circular genome. They are members of the genus '' Circovirus'' that can infect pigs. The viral capsid is icosahedral and approxi ...
type 1 has a genome of 1,759 nucleotides and a
capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
diameter of . As a whole, the viral family
geminiviridae
''Geminiviridae'' is a family of plant viruses that encode their genetic information on a circular genome of single-stranded (ss) DNA. There are 520 species in this family, assigned to 14 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: br ...
is about in length. However, the two capsids making up the virus are fused; divided, the capsids would be in length. Other environmentally characterized ssDNA viruses such as CRESS DNA viruses, among others, can have genomes that are considerably less than 2,000 nucleotides.
The smallest
RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA ( ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruse ...
in terms of
genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
size is phage BZ13 strain T72 at 3,393 nucleotides length. Viruses using both DNA and RNA in their replication (
retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
es) range in size from 7,040 to 12,195 nucleotides. The smallest double-stranded
DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and ...
es are the
hepadnaviruses
''Hepadnaviridae'' is a family of viruses. Humans, apes, and birds serve as natural hosts. There are currently 18 species in this family, divided among 5 genera. Its best-known member is hepatitis B virus. Diseases associated with this family ...
such as
hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. F ...
, at 3.2 kb and ;
parvovirus
Parvoviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family ''Parvoviridae''. They have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes that typically contain two genes encoding for a replication initiator protein, called NS1, and the p ...
es have smaller capsids, at , but larger genomes, at 5 kb. It is important to consider other self-replicating genetic elements, such as
satelliviruses,
viroid
Viroids are small single-stranded, circular RNAs that are infectious pathogens. Unlike viruses, they have no protein coating. All known viroids are inhabitants of angiosperms (flowering plants), and most cause diseases, whose respective econo ...
s and
ribozymes
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demons ...
.
Animals (Animalia)
Several species of
Myxozoa
Myxozoa (etymology: Greek: μύξα ''myxa'' "slime" or "mucus" + thematic vowel o + ζῷον ''zoon'' "animal") is a subphylum of aquatic cnidarian animals – all obligate parasites. It contains the smallest animals ever known to have lived. O ...
(obligately parasitic
cnidarian
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in Fresh water, freshwater and Marine habitats, marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocyt ...
s) never grow larger than . One of the smallest species (''Myxobolus shekel'') is no more than when fully grown, making it the smallest known animal.
Molluscs (Molluska)
Bivalvia
The shell of the nut clam ''
Condylonucula maya
''Condylonucula maya'' is a tiny species of saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusk or micromollusk in the family Nuculidae, the nut clams. This species grows to a length of about and is believed to be the smallest living bivalve. '' grows long.
Gastropods (Gastropoda)
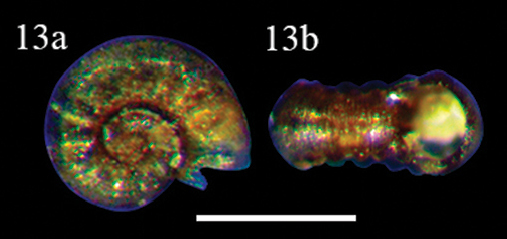
The smallest water
snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class G ...
(of all snails) is ''
Ammonicera minortalis
''Ammonicera'' is a genus of minute sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs or micromollusks in the family Omalogyridae.Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S. (2012). ''Ammonicera'' Vayssière, 1893. Accessed through: World Register of Marine * At http://www.marin ...
'' in North America, originally described from Cuba. It measures .
The smallest land snail is ''
Acmella nana
''Acmella nana'' is a species of land snail discovered from Borneo, Malaysia, in 2015. It was described by Jaap J. Vermeulen of the JK Art and Science in Leiden, Thor-Seng Liew of the Institute for Tropical Biology and Conservation at the Univers ...
''. Discovered in
Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the List of islands by area, third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java Isl ...
, and described in November 2015, it measures . The previous record was that of ''
Angustopila dominikae
''Angustopila dominikae'' is a species of light grey, round, land snails, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc in the family Hypselostomatidae. ''Angustopila dominikae'' have been found in southern China, and are considered to be one of ...
'' from China, which was reported in September 2015. This snail measures .
Cephalopods (Cephalopoda)
''
Maximites
''Maximites'' is a genus of Late Carboniferous ammonoids. Adult specimens were the smallest known ammonoids, only at about in diameter of shells. Fossils are found in various Late Carboniferous marine strata in North America. ''Maximites'' is ...
'' was the smallest known
ammonoid
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefi ...
. Adult specimens reached only in shell diameter.
Arthropods (Arthropoda)
Arachnids (Arachnida)
* There is a debate about which
spider
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species d ...
is smallest. According to Guinness World Records, "Two contenders are from the
Symphytognathidae
Symphytognathidae is a family of spiders with 90 described species in eight genera. They occur in the tropics of Central and South America and the Australian region (with Oceania). Exceptions include ''Anapistula benoiti'', ''Anapistula caecula' ...
genus ''
Patu
A patu is a club or pounder used by the Māori. The word ''patu'' in the Māori language means to strike, hit, beat, kill or subdue.
Weapons
These types of short-handled clubs were mainly used as a striking weapon. The blow administered wit ...
'': males of ''
Patu digua
''Patu digua'' is a very small species of spider. The male holotype and female paratype
In zoology and botany, a paratype is a specimen of an organism that helps define what the scientific name of a species and other taxon actually represen ...
'' described in Colombia had a body length of , while the Samoan moss spider (
''P. marplesi'') could be as small as long."
Other possible smallest spider species are the Frade cave spider known as ''Anapistula ataecina,'' and the dwarf orb weaver (''Anapistula caecula''), the females of which are and respectively.
Males of both species are potentially smaller than the females, but no ''Anapistula ataecina or Anapistula caecula'' have been measured yet.
* ''
Cochlodispus minimus
''Cochlodispus minimus'' is a species of mite from the family Microdispidae, formally described by Sándor Mahunka in 1976. One adult individual was measured with a body length of 79 μm (0.079 mm), making it the smallest known mite species. It ...
'' is the smallest mite. An adult individual measured with a body length of . However, PBS claims "The tiniest mite on record is 82 microns long" but does not name a species.
Non-hexapod crustaceans (Crustacea)
The smallest
crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...
is the
tantulocarid
Tantulocarida is a highly specialised group of parasitic crustaceans that consists of about 33 species, treated as a class in superclass Multicrustacea. They are typically ectoparasites that infest copepods, isopods, tanaids, amphipods and os ...
''
Stygotantulus stocki'', at a length of .
Insects (Insecta)
* Adult males of the parasitic
wasp
A wasp is any insect of the narrow-waisted suborder Apocrita of the order Hymenoptera which is neither a bee nor an ant; this excludes the broad-waisted sawflies (Symphyta), which look somewhat like wasps, but are in a separate suborder. Th ...
''
Dicopomorpha echmepterygis
''Dicopomorpha echmepterygis'' is the smallest known insect and a species of parasitoid wasp in the family Mymaridae, which exhibits strong sexual dimorphism. The males are blind, apterous, and their body length is only 40% that of females. With ...
'' can be as small as long, smaller than some species of protozoa (single-cell creatures); females are 40% larger. ''
Megaphragma caribea
''Megaphragma caribea'' is a species of wasp. It has been found acting as an egg parasitoid of ''Heliothrips haemorrhoidalis
''Heliothrips haemorrhoidalis'' is a species of thrips in the family Thripidae. It is most commonly known as the green ...
'' from
Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands— Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the ...
, measuring long, is another contender for smallest known insect in the world.
*
Beetle
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describ ...
s of the tribe
Nanosellini are all less than long; the smallest confirmed specimen is of ''
Scydosella musawasensis
''Scydosella'' is a genus of beetles that consists of only one species ''Scydosella musawasensis''. The species is regarded as the smallest free-living insect, as well as the smallest beetle. They are among featherwing beetle, named because of ...
'' at long; a few other nanosellines are reportedly smaller, in historical literature, but none of these records have been confirmed using accurate modern tools. These are among the tiniest non-parasitic insects.

* The
western pygmy blue
The western pygmy blue (''Brephidium exilis'' or ''Brephidium exile'') is one of the smallest butterflies in the world and the smallest in North America. It has reached Hawaii, as well as the Persian Gulf, including eastern Saudi Arabia, Bahrain ...
(''Brephidium exilis'') is one of the smallest
butterflies
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises t ...
in the world, with a wingspan of about .
Echinoderms (Echinodermata)
The smallest
sea cucumber
Sea cucumbers are echinoderms from the class Holothuroidea (). They are marine animals with a leathery skin and an elongated body containing a single, branched gonad. Sea cucumbers are found on the sea floor worldwide. The number of holothu ...
, and also the smallest
echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the s ...
, is ''Psammothuria ganapati'', a
synaptid that lives between sand grains on the coast of India. Its maximum length is .
Sea urchins
The smallest
sea urchin
Sea urchins () are spiny, globular echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species of sea urchin live on the seabed of every ocean and inhabit every depth zone from the intertidal seashore down to . The spherical, hard shells (tests) ...
, ''Echinocyamus scaber'', has a
test
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film), ...
across.
Starfish
''
Patiriella parvivipara'' is the smallest
starfish, at across.
Fish (Pisces)
* One of the smallest
vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, wi ...
and the smallest fish based on the minimum size at maturity is ''
Paedocypris progenetica
''Paedocypris progenetica'' is a species of tiny cyprinid fish endemic to the Indonesian islands of Sumatra and Bintan where it is found in peat swamps and blackwater streams. It was discovered by Singaporean ichthyologist Heok Hui
Tan. He ha ...
'' from
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, with mature females measuring as little as in
standard length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies. These data are used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fisheries biology.
Overall length
* Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish ...
.
This fish, a member of the
carp family, has a translucent body and a head unprotected by a skeleton.
* One of the smallest fish based on the minimum size at maturity is ''
Schindleria brevipinguis
''Schindleria brevipinguis'' is a species of marine fish in family Gobiidae of Perciformes. Known as the stout infantfish, it is native to Australia's Great Barrier Reef and to Osprey Reef in the Coral Sea.
Anatomy
''S. brevipinguis'' is among ...
'' from Australia, their females reach and males . Males of ''S. brevipinguis'' have an average
standard length
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies. These data are used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fisheries biology.
Overall length
* Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish ...
of ; a gravid female was .
This fish, a member of the
goby family, differs from similar members of the group in having its first
anal fin
Fins are distinctive anatomical features composed of bony spines or rays protruding from the body of a fish. They are covered with skin and joined together either in a webbed fashion, as seen in most bony fish, or similar to a flipper, as s ...
ray further forward, under
dorsal fin
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates within various taxa of the animal kingdom. Many species of animals possessing dorsal fins are not particularly closely related to each other, though through c ...
4.
* Male individuals of the
anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence ...
species ''
Photocorynus spiniceps
''Photocorynus spiniceps'' is a species of anglerfish in the family Linophrynidae. It is in the monotypic genus ''Photocorynus''.
The known mature male individuals are 6.2–7.3 millimeters (0.25-0.3 inches), smaller than any other ma ...
'' have been documented to be at maturity, and thus claimed to be a smaller species. However, these survive only by
sexual parasitism
Fish reproductive organs include testes and ovaries. In most species, gonads are paired organs of similar size, which can be partially or totally fused. There may also be a range of secondary organs that increase reproductive fitness. The geni ...
and the female individuals reach the significantly larger size of .
Amphibians (Amphibia)
Frogs and toads (Anura)
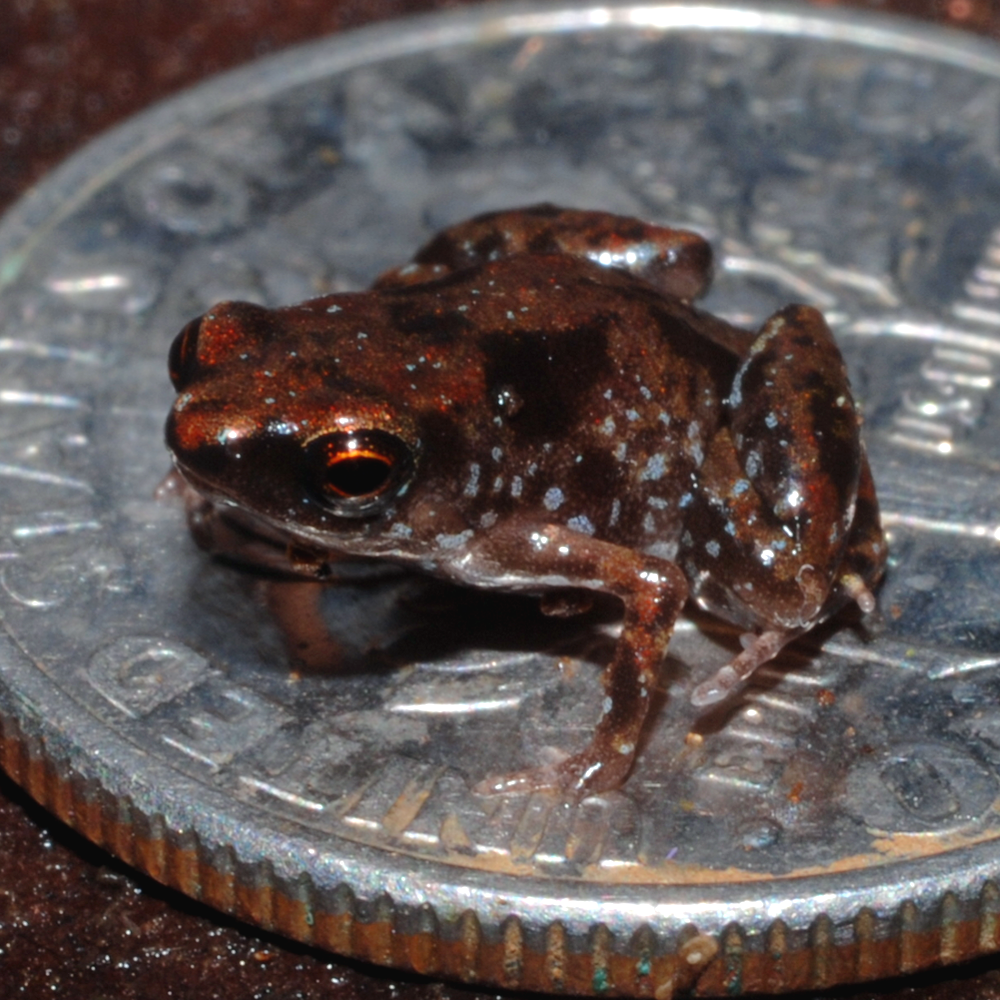


The smallest
vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s (and smallest amphibians) known are ''
Paedophryne amauensis
''Paedophryne amauensis'' is a species of microhylid frog endemic to eastern Papua New Guinea. At in snout-to-vent length, it is considered the world's smallest known vertebrate. (See also Ecological guild.)
The species was listed in the '' ...
'' frogs from Papua New Guinea, which range in length from , and average .
Other very small frogs include ''
Brachycephalus didactylus
The Brazilian gold frog (''Brachycephalus didactylus''), also known as Izecksohn's toad or flea-frog, is a very small species of frogs in the family Brachycephalidae. It is endemic to southeastern Brazil and is known from the central part of the ...
'' from Brazil (reported as ), several species of ''
Eleutherodactylus
''Eleutherodactylus'' is a genus of frogs in the family Eleutherodactylidae.Hedges, S. B., W. E. Duellman, and M. P. Heinicke . 2008. New World direct-developing frogs (Anura: Terrarana): molecular phylogeny, classification, biogeography, and c ...
'' such as ''
E. iberia'' (around ) and ''
E. limbatus'' () and ''
Eleutherodactylus orientalis
''Eleutherodactylus orientalis'', the Oriental robber frog or Baracoa dwarf frog, is a species of frog in the family Eleutherodactylidae. It is endemic to the vicinity of El Yunque, Baracoa, in easternmost Cuba. Although locally common, it requi ...
'' () from Cuba, Gardiner's Frog ''
Sechellophryne gardineri
Gardiner's Seychelles frog (''Sechellophryne gardineri'') is a small frog of the family Sooglossidae and endemic to the Seychelles. It is named after John Stanley Gardiner, English zoologist and oceanographer.
Description
Gardiner's frog is on ...
'' from the Seychelles (up to ), several species of ''
Stumpffia
''Stumpffia'' is a genus of microhylid frogs that are endemic to Madagascar. They are mostly brown frogs that typically live among leaf litter. ''S. contumelia'' has a snout–vent length of about , making it one of the world's smallest frogs ...
'' such as ''
S. tridactyla'' () and ''
S. pygmaea'' (males ; females: ) and ''
Wakea madinika
''Wakea madinika'' is a species of frogs in the Mantellidae, mantellid subfamily Mantellinae. It is the only species in the monotypic genus ''Wakea''. It is Endemism, endemic to Madagascar.
Discovery
''Wakea madinika'' reaches males snout-Cloa ...
'' (males: ; females: ) from Madagascar. ''
Paedophryne swiftorum
''Paedophryne swiftorum'' is a species of frog from Papua New Guinea discovered in 2008 and formally described in January 2012. It lives among leaf litter on the tropical rainforest floor and was named after the Swift family who had provided ...
'' (body length ) is not included in the smallest vertebrates known with other nine species of frogs. The two species ''
Microhyla borneensis
''Microhyla borneensis'' ( junior synonym ''Microhyla nepenthicola''), also known as the Matang narrow-mouthed frog, is a species of microhylid frog found in the Matang Range in Sarawak, Borneo. It was once the smallest known frog from the Old ...
'' (males: ; females: ) and ''
Arthroleptella rugosa
''Arthroleptella rugosa'' is a species of frog in the family Pyxicephalidae. It is endemic to South Africa and only known from the Klein Swartberg Mountain, an inselberg near Caledon, Western Cape. The specific name ''rugosa'' is Latin for ''w ...
'' (males: ; females: ) were once the smallest known frogs from the
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by th ...
. In general these extremely small frogs occur in tropical forest and montane environments. There is relatively little data on size variation among individuals, growth from metamorphosis to adulthood or size variation among populations in these species. Additional studies and the discovery of further minute frog species are likely to change the rank order of this list.
Salamanders, newts and allies (Urodela)
The average snout-to-
vent
Vent or vents may refer to:
Science and technology Biology
*Vent, the cloaca region of an animal
*Vent DNA polymerase, a thermostable DNA polymerase
Geology
* Hydrothermal vent, a fissure in a planet's surface from which geothermally heated wate ...
length (
SVL) of several specimens of the salamander ''
Thorius arboreus
''Thorius arboreus'', commonly known as the arboreal minute salamander, is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is endemic to Sierra de Juarez, Oaxaca, Mexico. The specific name ''arboreus'', derives from the Latin word ''arbo ...
'' was .
Sauropsids (Sauropsida)
Lizards and snakes (Squamata)

* The
dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') is the smallest known
reptile species and smallest lizard, with a snout-vent length of . ''S. ariasae'' was first described in 2001 by the biologists
Blair Hedges
Stephen Hedges
Stephen Blair Hedges (known as S. Blair Hedges) is Laura H. Carnell Professor of Science and director of the Center for Biodiversity at Temple University where he researches the tree of life and leads conservation efforts in Haiti ...
and Richard Thomas. This dwarf gecko lives in
Jaragua National Park
Jaragua National Park ( es, Parque Nacional Jaragua) is a national park of the Dominican Republic. Jaragua National Park is located in the Pedernales Province in the extreme southwest of the Dominican Republic. Jaragua National Park has a total ar ...
in the
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
and on
Beata Island
Beata Island ( es, Isla Beata) is a small island on the Caribbean Sea, located southwest from Cape Beata. Some southwest of it lies the smaller Alto Velo Island. It is politically part of the Dominican Republic, and is roughly triangle-shaped an ...
(''Isla Beata''), off the southern coast of the
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
. A few ''
Brookesia
''Brookesia'' is a genus of chameleons, endemic to Madagascar, that range from small to very small in size, and are known collectively as leaf chameleons (though this name also commonly is used for species in the genera ''Rieppeleon'' and ''Rha ...
'' chameleons from
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
are equally small, with a reported snout-vent length of for male dwarf chameleons (''
B. minima''), for male Mount d'Ambre leaf chameleons (''
B. tuberculata'') and for male ''
B. micra'', though females are larger. In 2021, a new species of ''
Brookesia
''Brookesia'' is a genus of chameleons, endemic to Madagascar, that range from small to very small in size, and are known collectively as leaf chameleons (though this name also commonly is used for species in the genera ''Rieppeleon'' and ''Rha ...
'', ''
B. nana'', was discovered, with a snout-vent length of , possibly making it the smallest known reptile.

* One of the smallest known
snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s is the recently discovered
Barbados threadsnake
The Barbados threadsnake (''Tetracheilostoma carlae'') is a species of threadsnake. It is the smallest known snake species. This member of the Leptotyphlopidae family is found on the Caribbean islands of Barbados and Anguilla.
Taxonomy and e ...
(''Leptotyphlops carlae''). Adults average about long, which is only about twice as long as the
hatchling
In oviparous biology, a hatchling is a newly hatched fish, amphibian, reptile, or bird. A group of mammals called monotremes lay eggs, and their young are hatchlings as well.
Fish
Fish hatchlings generally do not receive parental care, similar ...
s. The
Common blind snake
''Indotyphlops braminus'', commonly known as the brahminy blind snake and other names, is a non-venomous blind snake species found mostly in Africa and Asia, but has been introduced in many other parts of the world. They are completely fossorial ...
(''Indotyphlops braminus'') measures long, occasionally up to long.
Turtles and tortoises (Testudines)
The smallest
turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked ...
is the
speckled padloper tortoise
''Chersobius signatus'' is the world's smallest species of tortoise (family Testudinidae). The species is commonly known as the speckled tortoise and also known locally as the speckled padloper and internationally as the speckled Cape tortoise. ...
(''Homopus signatus'') from
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
. The males measure , while females measure up to almost .
Crocodiles and close relatives (Crocodylomorpha)
* The smallest extant
crocodilian
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
is the
Cuvier's dwarf caiman
Cuvier's dwarf caiman (''Paleosuchus palpebrosus'') is a small crocodilian in the alligator family from northern and central South America. It is found in Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Trin ...
(''Paleosuchus palpebrosus'') from northern and central South America. It reaches up to in length.
* Some extinct
crocodylomorph
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction.
During Mesozoic and early Cenozoic times, cro ...
s were even smaller. Fully grown ''
Bernissartia
''Bernissartia'' ('of Bernissart') is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodyliform that lived in the Early Cretaceous, around 130 million years ago.
At only in length, ''Bernissartia'' is one of the smallest crocodyliforms that ever lived. It ...
'' from the
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous ( chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pr ...
reached a bit more than in length.
* The
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous ( chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pr ...
terrestrial
notosuchia
Notosuchia is a suborder of primarily Gondwanan mesoeucrocodylian crocodylomorphs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous. Some phylogenies recover Sebecosuchia as a clade within Notosuchia, others as a sister group (see below); if Sebec ...
n ''
Malawisuchus
''Malawisuchus'' (meaning "Malawi crocodile") is an extinct genus of notosuchian mesoeucrocodylian from the Early Cretaceous Dinosaur Beds of Malawi. It was described in 1997 by Elizabeth Gomani as a member of the family Notosuchidae. The type ...
'' was no more than long. Other small notosuchians include ''
Anatosuchus
''Anatosuchus'' ("duck crocodile", the name from the Latin ''anas'' ("duck") and the Greek language, Greek ''souchos'' ("crocodile"), for the broad, duck-like snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian Crocodylomorpha, crocodylomorph discovered in ...
'' at and herbivorous ''
Simosuchus
''Simosuchus'' (meaning "pug-nosed crocodile" in Greek, referring to the animal's blunt snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorphs from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. It is named for its unusually short skull. Fully grown ind ...
'' at .
Pterosaurs (Pterosauria)
''
Nemicolopterus
''Nemicolopterus'' is a genus of tapejaromorph pterosaur, based on a very small specimen described as the smallest known "adult" pterosaur to date. It lived in the Jehol Biota 120 million years ago.
Discovery and naming
The generic name "N ...
'' was the smallest pterosaur, it reached about in wingspan.
Non-avian dinosaurs (Dinosauria)
Sizes of non-avian dinosaurs are commonly labelled with a level of uncertainty, as the available material often (or even usually) is incomplete. The smallest known extinct
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
is ''
Anchiornis
''Anchiornis'' is a genus of small, four-winged paravian dinosaurs, with only one known species, the type species ''Anchiornis huxleyi'', named for its similarity to modern birds. The Latin name ''Anchiornis'' derives from a Greek word meaning "n ...
'', a genus of feathered dinosaur that lived in what is now China during the Late
Jurassic Period
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
160 to 155 million years ago. Adult specimens range from long, and the weight has been estimated at up to . ''
Parvicursor
''Parvicursor'' (meaning "small runner") is a genus of tiny maniraptoran dinosaur with long slender legs for fast running. At only about from snout to end of tail, and in weight, it was initially seen as one of the smallest non-avian dinosaur ...
'' was initially seen as one of the smallest non-avian dinosaurs known from an adult specimen, at in length, and in weight. However, in 2022 its
holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of seve ...
was concluded to represent a juvenile individual. ''
Epidexipteryx
''Epidexipteryx'' is a genus of small paravian dinosaurs, known from one fossil specimen in the collection of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology in Beijing. ''Epidexipteryx'' represents the earliest known example of o ...
'' reached in length and in weight.
Birds (Aves)

* With a mass of approximately and a length of , the
bee hummingbird
The bee hummingbird, zunzuncito or Helena hummingbird (''Mellisuga helenae'') is a species of hummingbird, native to the island of Cuba in the Caribbean. It is the world's smallest bird.
Description
The bee hummingbird is the smallest living ...
(''Mellisuga helenae'') is the smallest known dinosaur as well as the smallest
bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
species, and the smallest
warm-blooded
Warm-blooded is an informal term referring to animal species which can maintain a body temperature higher than their environment. In particular, homeothermic species maintain a stable body temperature by regulating metabolic processes. The on ...
vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
. Called the ''zunzuncito'' in its native habitat on Cuba, it is lighter than a
Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
or
U.S. penny
The cent, the United States one-cent coin (symbol: ¢), often called the "penny", is a unit of currency equaling one one-hundredth of a United States dollar. It has been the lowest face-value physical unit of U.S. currency since the abolition o ...
. It is said that it is "more apt to be mistaken for a
bee
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfamil ...
than a bird". The bee hummingbird eats half its total
body mass
Human body weight is a person's mass or weight.
Strictly speaking, body weight is the measurement of weight without items located on the person. Practically though, body weight may be measured with clothes on, but without shoes or heavy accessor ...
and drinks eight times its total body mass each day. Its nest is across.
* The smallest
waterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which i ...
is
pygmy goose
The pygmy geese are a group of very small "perching ducks" in the genus ''Nettapus'' which breed in the Old World tropics. They are the smallest of all wildfowl. As the "perching ducks" are a paraphyletic group, they need to be placed elsewhere. ...
(''
Nettapus
The pygmy geese are a group of very small "perching ducks" in the genus ''Nettapus'' which breed in the Old World tropics. They are the smallest of all wildfowl. As the "perching ducks" are a paraphyletic group, they need to be placed elsewhere. ...
'').
African species reaches the average weight of about for males and for females and wingspans between and . The second smallest waterfowl is the extinct ''
Mioquerquedula
''Mioquerquedula'' is an extinct genus of ducks from the Middle Miocene containing two species, ''M. minutissima'' and ''M. velox''. It was one of the smallest anseriforms known. The genus was erected by Nikita Zelenkov and Evgenii Nikolaievich ...
'' from the
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ...
.
* The smallest
penguin
Penguins ( order Sphenisciformes , family Spheniscidae ) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is found north of the Equator. Highly adapt ...
species is the
little blue penguin
The little penguin (''Eudyptula minor'') is a species of penguin from New Zealand. They are commonly known as little blue penguins or blue penguins owing to their slate-blue plumage and are also known by their Māori name .
The Australian l ...
(''Eudyptula minor''), which stands around tall and weighs .
Non-mammalian synapsids (Synapsida)
The smallest
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Creta ...
mammaliaform
Mammaliaformes ("mammalian forms") is a clade that contains the crown group mammals and their closest extinct relatives; the group radiated from earlier probainognathian cynodonts. It is defined as the clade originating from the most recent ...
was ''
Hadrocodium
''Hadrocodium wui'' is an extinct mammaliaform that lived during the Sinemurian stage of the Early Jurassic approximately in the Lufeng Formation of the Lufeng Basin in what is now the Yunnan province in south-western China
(, paleocoordinates ) ...
'' with a skull of in length and a body mass of .
Mammals (Mammalia)
Marsupials (Marsupialia)
The smallest
marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
is the
long-tailed planigale
The long-tailed planigale (''Planigale ingrami''), also known as Ingram's planigale or the northern planigale, is the smallest of all marsupials, and one of the smallest of all mammals. It is rarely seen but is a quite common inhabitant of the b ...
from Australia. It has a body length of (including tail) and weigh on average. The
Pilbara ningaui
The Pilbara ningaui (''Ningaui timealeyi''), sometimes known as Ealey's ningaui, is a tiny species of marsupial carnivore found in Australia.
Taxonomy
The species was described by Mike Archer in 1975, distinguishing the new taxon from other ...
is considered to be of similar size and weight.
Shrews (Eulipotyphla)

The
Etruscan shrew
The Etruscan shrew (''Suncus etruscus''), also known as the Etruscan pygmy shrew or the white-toothed pygmy shrew, is the smallest known extant mammal by mass, weighing only about on average. (The bumblebee bat is regarded as the smallest mamm ...
(''Suncus etruscus''), is the smallest mammal by mass, weighing about on average. The smallest mammal that ever lived, the shrew-like ''
Batodonoides vanhouteni
''Batodonoides vanhouteni'' is an extinct shrew-like mammal, thought to be the smallest mammal that ever lived, as well as the smallest synapsid that ever lived. Based on the size of its molar teeth, it is estimated that ''Batodonoides vanhoute ...
'', weighed .
Bats (Chiroptera)
The
vulnerable
Vulnerable may refer to:
General
* Vulnerability
* Vulnerability (computing)
* Vulnerable adult
* Vulnerable species
Music
Albums
* ''Vulnerable'' (Marvin Gaye album), 1997
* ''Vulnerable'' (Tricky album), 2003
* ''Vulnerable'' (The Used album) ...
Kitti's hog-nosed bat
Kitti's hog-nosed bat (''Craseonycteris thonglongyai''), also known as the bumblebee bat, is a near-threatened species of bat and the only extant member of the family Craseonycteridae. It occurs in western Thailand and southeast Myanmar, where i ...
(''Craseonycteris thonglongyai''), also known as the bumblebee bat, from
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
and
Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
is the smallest
mammal, at in length and in weight.
Carnivorans (Carnivora)
The smallest member of the order
Carnivora
Carnivora is a monophyletic order of placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all cat-like and dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are formally referred to as carnivorans, ...
is the
least weasel
The least weasel (''Mustela nivalis''), little weasel, common weasel, or simply weasel is the smallest member of the genus '' Mustela,'' family Mustelidae and order Carnivora. It is native to Eurasia, North America and North Africa, and has b ...
(''Mustela nivalis''), with an average body length of . It weighs between with females being lighter.
Rodents (Rodentia)
The smallest known member of the
rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are roden ...
order is the
Baluchistan pygmy jerboa
The Baluchistan pygmy jerboa (''Salpingotulus michaelis'') or dwarf three-toed jerboa, is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is the only species in the genus ''Salpingotulus''. Adults average only in head and body length, with the ...
, with an average body length of .
Primates (Primates)
The smallest member of the
primate
Primates are a diverse order (biology), order of mammals. They are divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include the Tarsiiformes, tarsiers and ...
order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
is
Madame Berthe's mouse lemur
Madame Berthe's mouse lemur (''Microcebus berthae'') or Berthe's mouse lemur is the smallest of the mouse lemurs and the smallest primate in the world; the average body length is and seasonal weight is around . ''Microcebus berthae'' is one of ...
(''Microcebus berthae''), found in
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, with an average body length of .
Cetaceans (Cetacea)
The smallest
cetacean, which is also (as of 2006) the most endangered, is the
vaquita
The vaquita ( ; ''Phocoena sinus'') is a species of porpoise endemic to the northern end of the Gulf of California in Baja California, Mexico. Averaging (females) or (males) in length, it is the smallest of all living cetaceans. The species i ...
, a species of porpoise. Male vaquitas grow to an average of around ; the females are slightly longer, averaging about in length.
Plants (Plantae)
Gymnosperms (Gymnospermae)
''
Zamia pygmaea
''Zamia pygmaea'' is a species of plant in the family Zamiaceae found only in Cuba. It is the smallest living cycad. It is listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List based on its limited distribution, severely fragmented habitat ...
'' is a
cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male or f ...
found in Cuba, and the smallest known
gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, '' Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμν ...
. It grows to a height of .
Angiosperms (Angiospermae)

Duckweed
Lemnoideae is a subfamily of flowering aquatic plants, known as duckweeds, water lentils, or water lenses. They float on or just beneath the surface of still or slow-moving bodies of fresh water and wetlands. Also known as bayroot, they arose ...
s of the genus ''
Wolffia
''Wolffia'' is a genus of aquatic plants with a cosmopolitan distribution. They include the smallest flowering plants on Earth. Commonly called watermeal or duckweed, these aquatic plants resemble specks of cornmeal floating on the water. Indiv ...
'' are the smallest
angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of br ...
s. Fully grown, they measure and reach a mass of just 150
µg
In the metric system, a microgram or microgramme is a unit of mass equal to one millionth () of a gram. The unit symbol is μg according to the International System of Units (SI); the recommended symbol in the United States and United Kingdom wh ...
.
Dicotyledons
The smallest known
dicotyledon plant is the
Himalayan dwarf mistletoe
''Arceuthobium minutissimum'', known as the Indian dwarf mistletoe or Himalayan dwarf mistletoe, is a leafless parasitic plant of ''Pinus wallichiana''. It is considered the smallest known dicotyledonous plant.
Description
Individual shoots grow ...
(''Arceuthobium minutissimum''). Shoots grow up to in height.
Other
Nanobes
Nanobe
A nanobe () is a tiny filamental structure first found in some rocks and sediments. Some scientists hypothesize that nanobes are the smallest form of life, 1/10 the size of the smallest known bacteria.
No conclusive evidence exists that the ...
s are thought by some scientists to be the smallest known organisms,
about one tenth the size of the smallest known bacteria. Nanobes, tiny filamental structures first found in some
rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
s and
sediments
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand a ...
, were first described in 1996 by Philippa Uwins of the
University of Queensland
, mottoeng = By means of knowledge and hard work
, established =
, endowment = A$224.3 million
, budget = A$2.1 billion
, type = Public research university
, chancellor = Peter Varghese
, vice_chancellor = Deborah Terry
, city = ...
, but it is unclear what they are, and if they are alive.
See also
*
Largest organisms
The largest organisms now found on Earth can be determined according to various aspects of an organism's size, such as: mass, volume, area, length, height, or even genome size. Some organisms group together to form a superorganism (such as ants ...
*
Largest prehistoric organisms
The largest prehistoric animals include both vertebrate and invertebrate species. Many of them are described below, along with their typical range of size (for the general dates of extinction, see the link to each). Many species mentioned might ...
References
{{Reflist, colwidth=30em
External links
Featherwing beetleson the
UF /
IFAS IFAS may refer:
* Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences
* Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge, a sewage treatment process
* International French adjectival system, a grading system used in mountaineering
* Irish Federation of Astronomical ...
Featured Creatures Web site
Organism size
Biological records
es:Tamaño de los seres vivos
 ''
'' ''
'' The smallest water
The smallest water 
 The smallest
The smallest  * The dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') is the smallest known reptile species and smallest lizard, with a snout-vent length of . ''S. ariasae'' was first described in 2001 by the biologists
* The dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') is the smallest known reptile species and smallest lizard, with a snout-vent length of . ''S. ariasae'' was first described in 2001 by the biologists  * One of the smallest known
* One of the smallest known  The
The 