Siberian Route on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
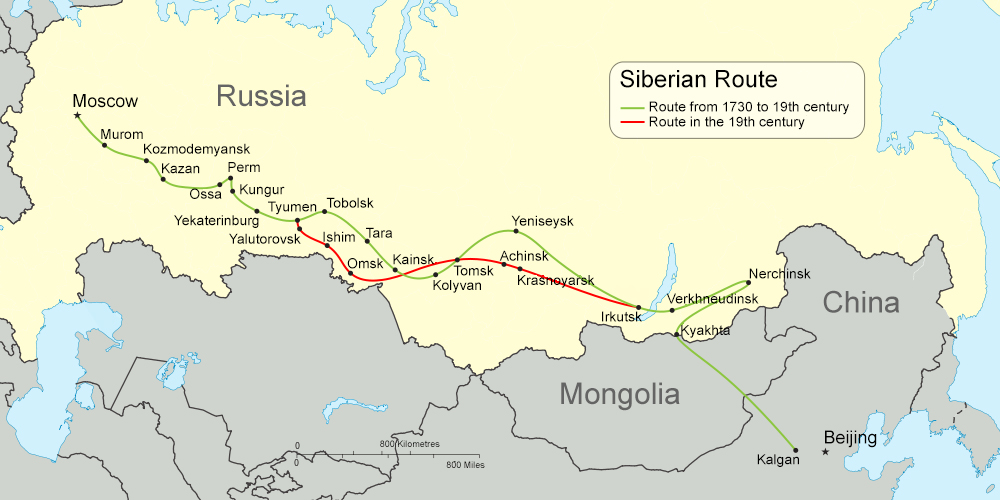 The Siberian Route (russian: Сибирский тракт; ''Sibirsky trakt''), also known as the Moscow Highway (, Московский тракт) and Great Highway (, Большой тракт), was a historic route that connected
The Siberian Route (russian: Сибирский тракт; ''Sibirsky trakt''), also known as the Moscow Highway (, Московский тракт) and Great Highway (, Большой тракт), was a historic route that connected

 The Siberian Route (russian: Сибирский тракт; ''Sibirsky trakt''), also known as the Moscow Highway (, Московский тракт) and Great Highway (, Большой тракт), was a historic route that connected
The Siberian Route (russian: Сибирский тракт; ''Sibirsky trakt''), also known as the Moscow Highway (, Московский тракт) and Great Highway (, Большой тракт), was a historic route that connected European Russia
European Russia (russian: Европейская Россия, russian: европейская часть России, label=none) is the western and most populated part of Russia. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the cou ...
to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
and China.
History
The construction of the road was decreed by the Tsar and was not finished until the mid-19th century. Previously, Siberian transport had been mostly by river viaSiberian River Routes
Siberian River Routes were the main ways of communication in Russian Siberia before the 1730s, when roads began to be built. The rivers were also of primary importance in the process of Russian conquest and exploration of vast Siberian territorie ...
. The first Russian settlers arrived in Siberia by the Cherdyn river route which was superseded by the Babinov overland route in the late 1590s. The town of Verkhoturye in the Urals was the most eastern point of the Babinov Road.
The much longer Siberian route started in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
as the Vladimir Highway and passed through Murom
Murom ( rus, Муром, p=ˈmurəm; Old Norse: ''Moramar'') is a historical city in Vladimir Oblast, Russia, which sprawls along the left bank of the Oka River. Population:
History
In the 9th century AD, the city marked the easternmost settle ...
, Kozmodemyansk Kozmodemyansk (russian: Козьмодемьянск) is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia.
;Urban localities
* Kozmodemyansk, Mari El Republic, a town in the Mari El Republic;
;Rural localities
* Kozmodemyansk, Sovetsky Distri ...
, Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering ...
, Perm, Kungur
Kungur (russian: Кунгу́р) is a town in the southeast of Perm Krai, Russia, located in the Ural Mountains at the confluence of the rivers Iren and Shakva with the Sylva (Kama's basin). Population: 64,800 (1959); 36,000 (1939).
Histo ...
, Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg ( ; rus, Екатеринбург, p=jɪkətʲɪrʲɪnˈburk), alternatively romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( rus, Свердло́вск, , svʲɪrˈdlofsk, 1924–1991), is a city and the administrat ...
, Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura River. Fueled by the Russian oil and gas i ...
, Tobolsk
Tobolsk (russian: Тобо́льск) is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh rivers. Founded in 1590, Tobolsk is the second-oldest Russian settlement east of the Ural Mountains in Asian Russia, ...
, Tara, Kainsk
Kuybyshev (russian: Ку́йбышев) is a town in Novosibirsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Om River (Irtysh's tributary), west of Novosibirsk, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: 40,000 (1970).
History
It was founded a ...
, Tomsk
Tomsk ( rus, Томск, p=tomsk, sty, Түң-тора) is a city and the administrative center of Tomsk Oblast in Russia, located on the Tom River. Population:
Founded in 1604, Tomsk is one of the oldest cities in Siberia. The city is a not ...
, Yeniseysk
Yeniseysk ( rus, Енисейск, p=jɪnʲɪˈsʲejsk) is a town in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located on the Yenisei River. Population: 20,000 (1970).
History
Yeniseysk was founded in 1619 as a stockaded town—the first town on the Yenise ...
and Irkutsk. After crossing Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, I ...
the road split near Verkhneudinsk
Ulan-Ude (; bua, Улаан-Үдэ, , ; russian: Улан-Удэ, p=ʊˈlan ʊˈdɛ; mn, Улаан-Үд, , ) is the capital city of the Republic of Buryatia, Russia, located about southeast of Lake Baikal on the Uda River at its confluence wit ...
. One branch continued east to Nerchinsk
Nerchinsk ( rus, Не́рчинск; bua, Нэршүү, ''Nershüü''; mn, Нэрчүү, ''Nerchüü''; mnc, m=, v=Nibcu, a=Nibqu; zh, t=涅尔琴斯克(尼布楚), p=Niè'ěrqínsīkè (Níbùchǔ)) is a town and the administrative ce ...
while the other went south to the border post of Kyakhta
Kyakhta (russian: Кя́хта, ; bua, Хяагта, Khiaagta, ; mn, Хиагт, Hiagt, ) is a town and the administrative center of Kyakhtinsky District in the Republic of Buryatia, Russia, located on the Kyakhta River near the Mongolia–Rus ...
where it linked to camel caravans that crossed Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
to a Great Wall
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic grou ...
gate at Kalgan.
In the early 19th century, the route was moved to the south. From Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura River. Fueled by the Russian oil and gas i ...
the road proceeded through Yalutorovsk
Yalutorovsk (russian: Ялу́торовск) is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located on the Tobol River southeast of Tyumen. Population:
History
It was founded in 1659 as the settlement of Yalutorovsky () and was granted town status ...
, Ishim
Ishim may refer to:
*Ishim (river), a river in Kazakhstan and Russia
*Ishim, Tyumen Oblast, a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia
*Ishim (angel), a rank of angels in the Jewish angelic hierarchy
See also
*Ishimsky (disambiguation)
*Ishimbay
Ishimbay ...
, Omsk
Omsk (; rus, Омск, p=omsk) is the administrative center and largest city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia, and has a population of over 1.1 million. Omsk is the third largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk ...
, Tomsk
Tomsk ( rus, Томск, p=tomsk, sty, Түң-тора) is a city and the administrative center of Tomsk Oblast in Russia, located on the Tom River. Population:
Founded in 1604, Tomsk is one of the oldest cities in Siberia. The city is a not ...
, Achinsk
Achinsk (russian: А́чинск) is a city in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located on the right bank of the Chulym River near its intersection with the Trans-Siberian Railway, west of Krasnoyarsk. It has a population of 109,155 as of the 2010 C ...
and Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk ( ; rus, Красноя́рск, a=Ru-Красноярск2.ogg, p=krəsnɐˈjarsk) (in semantic translation - Red Ravine City) is the largest city and administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is situated along the Yen ...
before rejoining the older route at Irkutsk. It remained a vital artery connecting Siberia with Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
and Europe until the last decades of the 19th century, when it was superseded by the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the eas ...
and Amur Cart Road. The automobile equivalent is the Trans-Siberian Highway.

Etymology and legacy of name
The Siberian Route was also known as the Tea Road, owing to the great quantities of tea that were transported from China to Europe through Siberia. Charles Wenyon, who passed by the "Great Post Road" in 1893, subscribed to the popular belief that "the best tea produced in China goes to Russia". In 1915, China exported to Siberia 70,297 tons of tea, which accounted for 65% of the country's overall tea exports. The route is the namesake of the Russian Caravan blend of tea. It was imported primarily in the form of hefty hard-packed tea bricks which allowed each camel to carry large quantities in a more compact manner and could also pass for units of currency. From Kyakhta, tea was transported to the Irbit fair for further commercial transactions. Another popular Chinese import item was driedrhubarb
Rhubarb is the fleshy, edible stalks ( petioles) of species and hybrids (culinary rhubarb) of '' Rheum'' in the family Polygonaceae, which are cooked and used for food. The whole plant – a herbaceous perennial growing from short, thick r ...
root, which was sold west of St. Petersburg "for fifteen times what it cost in Kyakhta".
See also
*Tea in Russia
Tea is an important part of Russian culture. Due in part to Russia's cold northern climate, it is today considered the ''de facto'' national beverage, one of the most popular beverages in the country, and is closely associated with traditional Russ ...
* Kyakhta Russian-Chinese Pidgin
References
Further reading
* Avery, Martha. ''The Tea Road: China and Russia Meet Across the Steppe''. Mandarin Books, 2003. . * Alexander Michie, 'The Siberian Overland Route from Peking to Petersburg', 1864. -followed the route in 1863 {{Trade route 2 Roads in Russia Roads in Siberia History of Siberia Economic history of Russia Russian Empire 1689 establishments in Russia China–Russian Empire relations Historical roads