data compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compressi ...
, Shannon–Fano coding, named after Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, computer scientist, cryptographer and inventor known as the "father of information theory" and the man who laid the foundations of th ...
and Robert Fano
Roberto Mario "Robert" Fano (11 November 1917 – 13 July 2016) was an Italian-American computer scientist and professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He became a student and working ...
, is one of two related techniques for constructing a prefix code
A prefix code is a type of code system distinguished by its possession of the prefix property, which requires that there is no whole Code word (communication), code word in the system that is a prefix (computer science), prefix (initial segment) of ...
based on a set of symbols and their probabilities (estimated or measured).
* Shannon's method chooses a prefix code where a source symbol is given the codeword length . One common way of choosing the codewords uses the binary expansion of the cumulative probabilities. This method was proposed in Shannon's "A Mathematical Theory of Communication
"A Mathematical Theory of Communication" is an article by mathematician Claude E. Shannon published in '' Bell System Technical Journal'' in 1948. It was renamed ''The Mathematical Theory of Communication'' in the 1949 book of the same name, a s ...
" (1948), his article introducing the field of information theory
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification (science), quantification, Data storage, storage, and telecommunications, communication of information. The field was established and formalized by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, ...
.
* Fano's method divides the source symbols into two sets ("0" and "1") with probabilities as close to 1/2 as possible. Then those sets are themselves divided in two, and so on, until each set contains only one symbol. The codeword for that symbol is the string of "0"s and "1"s that records which half of the divides it fell on. This method was proposed in a later (in print) technical report
A technical report (also scientific report) is a document that describes the process, progress, or results of technical or scientific research or the state of a technical or scientific research problem. It might also include recommendations and ...
by Fano (1949).
Shannon–Fano codes are suboptimal in the sense that they do not always achieve the lowest possible expected codeword length, as Huffman coding
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code is Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by ...
does. However, Shannon–Fano codes have an expected codeword length within 1 bit of optimal. Fano's method usually produces encoding with shorter expected lengths than Shannon's method. However, Shannon's method is easier to analyse theoretically.
Shannon–Fano coding should not be confused with Shannon–Fano–Elias coding (also known as Elias coding), the precursor to arithmetic coding
Arithmetic coding (AC) is a form of entropy encoding used in lossless data compression. Normally, a String (computer science), string of characters is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in the American Standard Code for In ...
.
Naming
Regarding the confusion in the two different codes being referred to by the same name, Krajči et al. write:Stanislav Krajči, Chin-Fu Liu, Ladislav Mikeš and Stefan M. Moser (2015), "Performance analysis of Fano coding", ''2015 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT)''.Around 1948, both Claude E. Shannon (1948) and Robert M. Fano (1949) independently proposed two different source coding algorithms for an efficient description of a discrete memoryless source. Unfortunately, in spite of being different, both schemes became known under the same name ''Shannon–Fano coding''. There are several reasons for this mixup. For one thing, in the discussion of his coding scheme, Shannon mentions Fano’s scheme and calls it “substantially the same” (Shannon, 1948, p. 17 eprint. For another, both Shannon’s and Fano’s coding schemes are similar in the sense that they both are efficient, but ''suboptimal'' prefix-free coding schemes with a similar performance.Shannon's (1948) method, using predefined word lengths, is called Shannon–Fano coding by Cover and Thomas, Goldie and Pinch, Jones and Jones, and Han and Kobayashi. It is called Shannon coding by Yeung. Fano's (1949) method, using binary division of probabilities, is called Shannon–Fano coding by Salomon and Gupta. It is called Fano coding by Krajči et al.
Shannon's code: predefined word lengths
Shannon's algorithm
Shannon's method starts by deciding on the lengths of all the codewords, then picks a prefix code with those word lengths. Given a source with probabilities the desired codeword lengths are . Here, is theceiling function
In mathematics, the floor function is the function that takes as input a real number , and gives as output the greatest integer less than or equal to , denoted or . Similarly, the ceiling function maps to the least integer greater than or eq ...
, meaning the smallest integer greater than or equal to .
Once the codeword lengths have been determined, we must choose the codewords themselves. One method is to pick codewords in order from most probable to least probable symbols, picking each codeword to be the lexicographically first word of the correct length that maintains the prefix-free property.
A second method makes use of cumulative probabilities. First, the probabilities are written in decreasing order . Then, the cumulative probabilities are defined as
:
so and so on.
The codeword for symbol is chosen to be the first binary digits in the binary expansion
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method for representing numbers that uses only two symbols for the natural numbers: typically "0" ( zero) and "1" ( one). A ''binary number'' may als ...
of .
Example
This example shows the construction of a Shannon–Fano code for a small alphabet. There 5 different source symbols. Suppose 39 total symbols have been observed with the following frequencies, from which we can estimate the symbol probabilities. : This source hasentropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the micros ...
bits.
For the Shannon–Fano code, we need to calculate the desired word lengths .
:
We can pick codewords in order, choosing the lexicographically first word of the correct length that maintains the prefix-free property. Clearly A gets the codeword 00. To maintain the prefix-free property, B's codeword may not start 00, so the lexicographically first available word of length 3 is 010. Continuing like this, we get the following code:
:
Alternatively, we can use the cumulative probability method.
:
Note that although the codewords under the two methods are different, the word lengths are the same. We have lengths of 2 bits for A, and 3 bits for B, C, D and E, giving an average length of
:
which is within one bit of the entropy.
Expected word length
For Shannon's method, the word lengths satisfy : Hence the expected word length satisfies : Here, is theentropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the micros ...
, and Shannon's source coding theorem says that any code must have an average length of at least . Hence we see that the Shannon–Fano code is always within one bit of the optimal expected word length.
Fano's code: binary splitting
Outline of Fano's code
In Fano's method, the symbols are arranged in order from most probable to least probable, and then divided into two sets whose total probabilities are as close as possible to being equal. All symbols then have the first digits of their codes assigned; symbols in the first set receive "0" and symbols in the second set receive "1". As long as any sets with more than one member remain, the same process is repeated on those sets, to determine successive digits of their codes. When a set has been reduced to one symbol this means the symbol's code is complete and will not form the prefix of any other symbol's code. The algorithm produces fairly efficient variable-length encodings; when the two smaller sets produced by a partitioning are in fact of equal probability, the one bit of information used to distinguish them is used most efficiently. Unfortunately, Shannon–Fano coding does not always produce optimal prefix codes; the set of probabilities is an example of one that will be assigned non-optimal codes by Shannon–Fano coding. Fano's version of Shannon–Fano coding is used in theIMPLODE compression method, which is part of the ZIP file format.
The Shannon–Fano tree
A Shannon–Fano tree is built according to a specification designed to define an effective code table. The actual algorithm is simple: # For a given list of symbols, develop a corresponding list ofprobabilities
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning Event (probability theory), events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probab ...
or frequency counts so that each symbol’s relative frequency of occurrence is known.
# Sort the lists of symbols according to frequency, with the most frequently occurring symbols at the left and the least common at the right.
# Divide the list into two parts, with the total frequency counts of the left part being as close to the total of the right as possible.
# The left part of the list is assigned the binary digit 0, and the right part is assigned the digit 1. This means that the codes for the symbols in the first part will all start with 0, and the codes in the second part will all start with 1.
# Recursively apply the steps 3 and 4 to each of the two halves, subdividing groups and adding bits to the codes until each symbol has become a corresponding code leaf on the tree.
Example
We continue with the previous example. : All symbols are sorted by frequency, from left to right (shown in Figure a). Putting the dividing line between symbols B and C results in a total of 22 in the left group and a total of 17 in the right group. This minimizes the difference in totals between the two groups. With this division, A and B will each have a code that starts with a 0 bit, and the C, D, and E codes will all start with a 1, as shown in Figure b. Subsequently, the left half of the tree gets a new division between A and B, which puts A on a leaf with code 00 and B on a leaf with code 01. After four division procedures, a tree of codes results. In the final tree, the three symbols with the highest frequencies have all been assigned 2-bit codes, and two symbols with lower counts have 3-bit codes as shown table below: : This results in lengths of 2 bits for A, B and C and per 3 bits for D and E, giving an average length of : We see that Fano's method, with an average length of 2.28, has outperformed Shannon's method, with an average length of 2.62.Expected word length
It is shown by Krajči et al that the expected length of Fano's method has expected length bounded above by , where is the probability of the least common symbol.Comparison with other coding methods
Neither Shannon–Fano algorithm is guaranteed to generate an optimal code. For this reason, Shannon–Fano codes are almost never used;Huffman coding
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code is Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by ...
is almost as computationally simple and produces prefix codes that always achieve the lowest possible expected code word length, under the constraints that each symbol is represented by a code formed of an integral number of bits. This is a constraint that is often unneeded, since the codes will be packed end-to-end in long sequences. If we consider groups of codes at a time, symbol-by-symbol Huffman coding is only optimal if the probabilities of the symbols are independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in Pennsylvania, United States
* Independentes (English: Independents), a Portuguese artist ...
and are some power of a half, i.e., . In most situations, arithmetic coding
Arithmetic coding (AC) is a form of entropy encoding used in lossless data compression. Normally, a String (computer science), string of characters is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in the American Standard Code for In ...
can produce greater overall compression than either Huffman or Shannon–Fano, since it can encode in fractional numbers of bits which more closely approximate the actual information content of the symbol. However, arithmetic coding has not superseded Huffman the way that Huffman supersedes Shannon–Fano, both because arithmetic coding is more computationally expensive and because it is covered by multiple patents.
Huffman coding
A few years later, David A. Huffman (1952) gave a different algorithm that always produces an optimal tree for any given symbol probabilities. While Fano's Shannon–Fano tree is created by dividing from the root to the leaves, the Huffman algorithm works in the opposite direction, merging from the leaves to the root. # Create a leaf node for each symbol and add it to apriority queue
In computer science, a priority queue is an abstract data type similar to a regular queue (abstract data type), queue or stack (abstract data type), stack abstract data type.
In a priority queue, each element has an associated ''priority'', which ...
, using its frequency of occurrence as the priority.
# While there is more than one node in the queue:
## Remove the two nodes of lowest probability or frequency from the queue
## Prepend 0 and 1 respectively to any code already assigned to these nodes
## Create a new internal node with these two nodes as children and with probability equal to the sum of the two nodes' probabilities.
## Add the new node to the queue.
# The remaining node is the root node and the tree is complete.
Example with Huffman coding
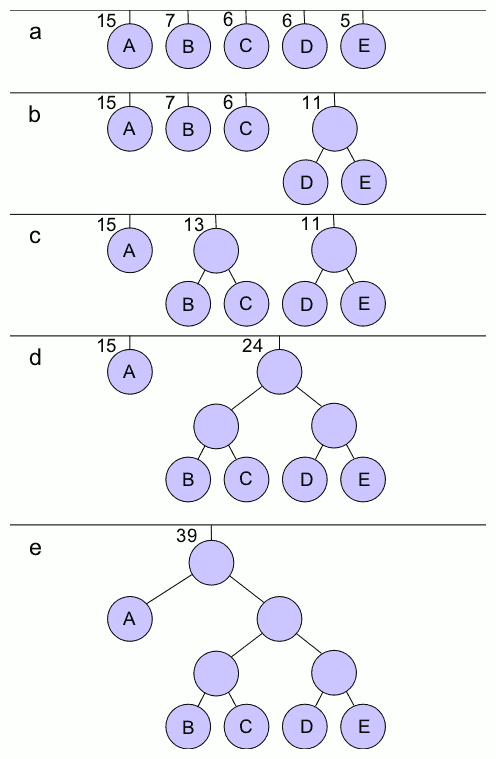 We use the same frequencies as for the Shannon–Fano example above, viz:
:
In this case D & E have the lowest frequencies and so are allocated 0 and 1 respectively and grouped together with a combined probability of 0.282. The lowest pair now are B and C so they're allocated 0 and 1 and grouped together with a combined probability of 0.333. This leaves BC and DE now with the lowest probabilities so 0 and 1 are prepended to their codes and they are combined. This then leaves just A and BCDE, which have 0 and 1 prepended respectively and are then combined. This leaves us with a single node and our algorithm is complete.
The code lengths for the different characters this time are 1 bit for A and 3 bits for all other characters.
:
This results in the lengths of 1 bit for A and per 3 bits for B, C, D and E, giving an average length of
:
We see that the Huffman code has outperformed both types of Shannon–Fano code, which had expected lengths of 2.62 and 2.28.
We use the same frequencies as for the Shannon–Fano example above, viz:
:
In this case D & E have the lowest frequencies and so are allocated 0 and 1 respectively and grouped together with a combined probability of 0.282. The lowest pair now are B and C so they're allocated 0 and 1 and grouped together with a combined probability of 0.333. This leaves BC and DE now with the lowest probabilities so 0 and 1 are prepended to their codes and they are combined. This then leaves just A and BCDE, which have 0 and 1 prepended respectively and are then combined. This leaves us with a single node and our algorithm is complete.
The code lengths for the different characters this time are 1 bit for A and 3 bits for all other characters.
:
This results in the lengths of 1 bit for A and per 3 bits for B, C, D and E, giving an average length of
:
We see that the Huffman code has outperformed both types of Shannon–Fano code, which had expected lengths of 2.62 and 2.28.
Notes
References
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Shannon-Fano coding Claude Shannon Entropy coding Data compression