Shakashen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Goygol ( , ) (Yelenino in 1931–1938, Khanlar in 1938–2008) is a city, municipality and the capital of the
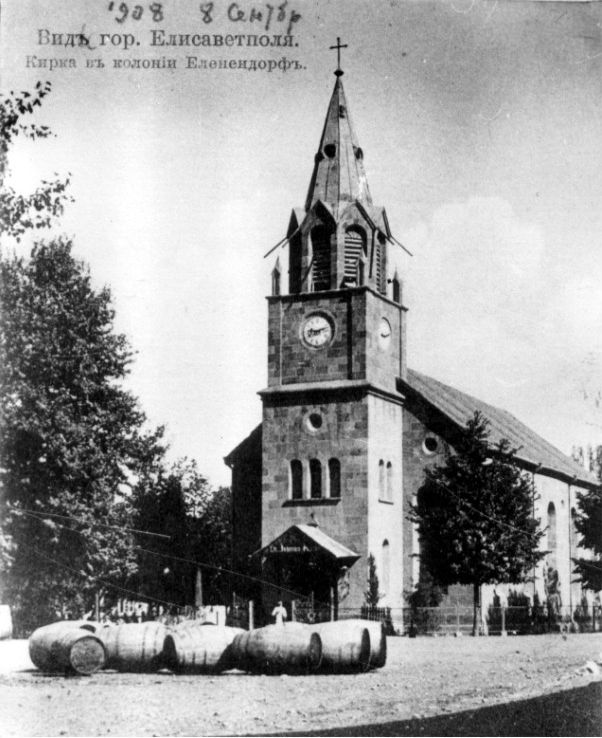 There has been a settlement at Goygol since at least the tenth century. An extensive cemetery was excavated in the 1990s, with many bronze weapons (swords, daggers, axes), some jewelry (rings, bracelets, necklaces), and clay black dishes with the geometric designs,Great Soviet Encyclopedia. Khanlar.
There has been a settlement at Goygol since at least the tenth century. An extensive cemetery was excavated in the 1990s, with many bronze weapons (swords, daggers, axes), some jewelry (rings, bracelets, necklaces), and clay black dishes with the geometric designs,Great Soviet Encyclopedia. Khanlar.
/ref> some of which are on display at the local museum. Under the Ganja Khanate a
"Helenendorf: Azerbaijan's First German Settlement" ''Azerbaijan International''
a magazine;
Satellite view of Khanlar City, Khanlar Raion, Azerbaijan from GoogleMap
{{DEFAULTSORT:Goygol (City) Populated places in Goygol District Populated places established in 1819
Goygol District
Goygol District () is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan, situated in the western part of the country within the Ganja-Dashkasan Economic Region. The district is bordered by districts of Goranboy, Kalbajar, Dashkasan, Shamkir, Samukh, and ...
in northwestern Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
. It is around south of Azerbaijan's third-largest city, Ganja
''Ganja'' (, ; ) is one of the oldest and most commonly used synonyms for cannabis flower, specifically marijuana or hashish. Its usage in English dates to before 1689.
Etymology
''Ganja'' is borrowed from Hindi (, IPA: �aːɲd͡ʒa� ...
. The city of Goygol has a population of 37,200 (est. 2010). The municipality includes the city of Goygol and the village of Qızılqaya.
Geography
Location
Goygol is situated in northwestern Azerbaijan south ofGanja
''Ganja'' (, ; ) is one of the oldest and most commonly used synonyms for cannabis flower, specifically marijuana or hashish. Its usage in English dates to before 1689.
Etymology
''Ganja'' is borrowed from Hindi (, IPA: �aːɲd͡ʒa� ...
city in the foothills of the Murovdag of the Lesser Caucasus Mountains. It is in the Kura River Basin, and the Gyandzha River () runs through the city. A spur to Ganja connects it to the Baku-Kazakh railway, and there is a highway into Ganja.
Climate
Goygol has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: Cfa). July is the hottest month with an average temperature of and January is the coldest with an average temperature of . The wettest month is May with an average of .
History
 There has been a settlement at Goygol since at least the tenth century. An extensive cemetery was excavated in the 1990s, with many bronze weapons (swords, daggers, axes), some jewelry (rings, bracelets, necklaces), and clay black dishes with the geometric designs,Great Soviet Encyclopedia. Khanlar.
There has been a settlement at Goygol since at least the tenth century. An extensive cemetery was excavated in the 1990s, with many bronze weapons (swords, daggers, axes), some jewelry (rings, bracelets, necklaces), and clay black dishes with the geometric designs,Great Soviet Encyclopedia. Khanlar./ref> some of which are on display at the local museum. Under the Ganja Khanate a
Tatar
Tatar may refer to:
Peoples
* Tatars, an umbrella term for different Turkic ethnic groups bearing the name "Tatar"
* Volga Tatars, a people from the Volga-Ural region of western Russia
* Crimean Tatars, a people from the Crimea peninsula by the B ...
town on the site was known as Hanahlar. Subsequently, in 1795 it was conquered by the Qajar dynasty
The Qajar family (; 1789–1925) was an Iranian royal family founded by Mohammad Khan (), a member of the Qoyunlu clan of the Turkoman-descended Qajar tribe. The dynasty's effective rule in Iran ended in 1925 when Iran's '' Majlis'', conven ...
. It was abandoned during the Russian occupation of the area which began in 1804 and was formalised by the Treaty of Gulistan
The Treaty of Gulistan (also spelled Golestan: ; ) was a peace treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and Qajar Iran on 24 October 1813 in the village of Gülüstan, Goranboy, Gulistan (now in Goranboy District, the Goranboy District of Azerb ...
(Gyulistan Peace Treaty) in 1813.
Helenendorf was founded on the site in 1819 by Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
from Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Province of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern, two other histo ...
, as ordered by Czar Alexander to help settle the region. The region was known as Narimanov under the czar. In 1930 the rayon
Rayon, also called viscose and commercialised in some countries as sabra silk or cactus silk, is a semi-synthetic fiber made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose fiber, cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has t ...
(district) was established with Helenendorf as its administrative centre
An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune, is located.
In countries with French as the administrative language, such as Belgi ...
.
Expropriation of the colonists property and collectivization
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member- ...
in Helenendorf began in 1926 with the show trial of three community leaders, Gottlob Hummel, Heinrich Vohrer and Fritz Reitenbach, on charges of counter-revolutionary and nationalist activities. They were convicted, their property confiscated and they were sent to a labor camp in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
. By 1935, over 600 German families in the area had been convicted of "espionage" and sent to labor camps.
In 1931 the town was renamed Yelenino, and in 1938 the town was renamed Khanlar, in honor of the Azerbaijani labor organizer Khanlar Safaraliyev, and the rayon also became Khanlar.
In October 1941, the remaining German population was deported
Deportation is the expulsion of a person or group of people by a state from its Sovereignty, sovereign territory. The actual definition changes depending on the place and context, and it also changes over time. A person who has been deported or ...
to Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Central Asia and Siberia on Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
's orders.
In 2008, Khanlar was renamed Goygol after the nearby lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
, and the rayon became Goygol District
Goygol District () is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan, situated in the western part of the country within the Ganja-Dashkasan Economic Region. The district is bordered by districts of Goranboy, Kalbajar, Dashkasan, Shamkir, Samukh, and ...
.
Helenendorf
Helenendorf (German Helenendorf) is a German settlement founded in 1819 by settlers fromSwabia
Swabia ; , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia, one of ...
in Transcaucasia (now the territory of Azerbaijan). Named in honor of the Grand Duchess Elena Pavlovna, the daughter of the Russian Emperor Paul I. In 1938, its name was changed to Khanlar and in 2008 to Goygol.
Establishment of the colony
On May 10, 1817, the Russian Emperor Alexander I signed a petition of 700 Swabian families for resettlement in Transcaucasia. The city of Ulm was appointed the assembly point, from which the settlers were sent on ships down the Danube to Izmail. After the quarantine, they were resettled for wintering in the already extant Black Sea German colonies Peterstal, Josefstal, Karlstal and other Swabian villages. The settlers arrived in Transcaucasus in August 1819, accompanied by Cossacks. Of the seven hundred families that left Ulm, only about four hundred reached their destination. Some of the settlers died on the way from illnesses, while others stayed in the Black Sea region. At the same time, about one hundred families from the Black Sea colonies joined the settlers. Six settlements in Georgia and two (Annenfeld and Elenendorf) inAzerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
were founded in the Transcaucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
.
The colonists arrived at the appointed place in the winter of 1818, so they were forced to winter in Elizavetpole. In the spring of 1819, during the Easter holidays, government officials determined the exact place of construction of Elenendorf – the former "Tatar settlement" Hanahlar, where "besides the half-buried canal and the pits in the ground, nothing reminded of the former inhabitants." The plots for the yards were distributed along two streets. The founders of the Helenendorf colony were 127 Swabian families (ca. 600 people), who came mainly from Reutlingen under the leadership of Gottlieb Koch, Duke Shiman, Jakov Krause and Johannes Wuhrer. Initially, the colonists had to live in dugouts. For several years they lived in very difficult and even dangerous conditions; after the first winter (1818–1819) only 118 families survived. During the Russian-Persian War of 1826–1828, the Swabians twice had to flee to Elizavetpol and Tiflis
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი, ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), ( ka, ტფილისი, tr ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city of Georgia ( ...
from the advancing Persians; both times Helenendorf was burned by the Persians. In 1829–1830, mortality due to diseases (including plague and cholera) was two times higher than the birth rate. Only in the 1930s did the colonists manage to gradually regain their lives.
In 1843, the population of Helendorf was 609 people, and in 1926 2,157 people (but by this time the natives of Elenendorf had founded two more colonies – Georgsfeld 36 inhabitantsand Traubenfeld 93 inhabitants. They also moved to other subsidiary colonies, formed at the beginning of the 20th century. In October 1941, during the forced eviction of German colonists from Transcaucasia, the number of Germans living in Elenendorf and subject to eviction was 2,675 people.
Economic activities
By 1875, the colonists had fully paid the government credit (2000 rubles per family), which they received in 1818 for the relocation and arrangement of the farm. By this time, the colonists' main occupation was the cultivation of grapes and the production of spirits – various varieties of vintage and table wine, cognac, and champagne. The products produced in Elenendorf were sold by the local firms Brothers Hummel, Brothers Forehrer and Concordia not only in Russia – in particular inMoscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
and St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg, formerly known as Petrograd and later Leningrad, is the second-largest city in Russia after Moscow. It is situated on the River Neva, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea. The city had a population of 5,601, ...
, but also in Europe. Crafts were also developed. By 1908, the colony numbered eight workshops for the production of horse carts (also supplied to the Russian army), six for barrels, nine forges, nine carpentry and six carpentry workshops, four sewing masters, four painters and four stoves, three locksmith workshops, and one shoe master.
Social development
The Schwabs who settled in the Russian Empire wereLutherans
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation in 15 ...
but belonged to the Pietistic
Pietism (), also known as Pietistic Lutheranism, is a movement within Lutheranism that combines its emphasis on biblical doctrine with an emphasis on individual piety and living a holy Christian life.
Although the movement is aligned with Luth ...
movement, which, in fact, was one of the reasons for their resettlement to the Caucasus. In 1832 a pastor arrived from Hannover to the colony, and before that, from the time of the founding of Elenendorf, divine services, the sacraments, and rituals were conducted by a local teacher. In 1857 the stone church of St. John was built and consecrated in the village. In the 1930s, two newspapers were published in the German language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switze ...
, and .
Due to the fact that there was also a teacher among the arrivals, the children of the colonists had the opportunity to study reading, writing, and arithmetic, and later geography and history. In 1823 the first school was built, in which children were educated in two classes. As the population grew, the school expanded, and the number of subjects offered expanded. From the 1890s, it became compulsory to study the Russian language. In 1907, at the Elendendorf school, a boarding school was opened to accommodate children from other Swabian settlements of the Transcaucasus who studied there. In the 1920s, teachers from Germany were invited to work at the school. So, for example, Alois Melichar (Alois Melichar), future conductor of the Berlin Philharmonic
The Berlin Philharmonic () is a German orchestra based in Berlin. It is one of the most popular, acclaimed and well-respected orchestras in the world.
Throughout the 20th century, the orchestra was led by conductors Wilhelm Furtwängler (1922� ...
, conducted music lessons at Elendendorf school.
The cultural life in Helenendorf began with the formation in 1893 of the German Society (), originally a male club with a library, a reading room, and a bowling alley. Later on, the amateur wind and string orchestras and theater studio were organized, which held concerts and performances in the society's hall, where up to 400 spectators could be accommodated at various festive events, including in the public garden of Helendorf. In 1930, a music school was opened with pianoforte and stringed instrument classes. Various festivals, which gathered musical groups from all the Transcaucasian colonies, were often held in Helenendorf (by the 1930s there were 21 colonies).
Traces of the German settlement can be seen in the school buildings and the parish church built in 1854.
Demographics
In the 1920 census there were 2,259 people registered. The city today is overwhelmingly populated byAzeris
Azerbaijanis (; , ), Azeris (, ), or Azerbaijani Turks (, ) are a Turkic ethnic group living mainly in the Azerbaijan region of northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are predominantly Shia Muslims. They comprise the largest ...
. Starting in 1915, the town became home to a small Assyrian community, originally from Turkey and Iran. The last resident of Goygol of German descent died in 2007. The Assyrian population consisted of three families as of 2016.
Economy
A large wine machinery plant which aids in the processing of grapes is located in Goygol, as was a state-owned cattle-breeding farm as of 1990.Culture
There are a number of historical monuments in Goygol including the Goygol Wine Factory's champagne and wine shop, Goygol Printing House, District Music School, and Koroglu Hotel dating to the 19th century, as well as the former buildings of the District Prosecutor's Office and District Police Department, which were built in the 19th century. The History-Ethnography Museum of Goygol is located in the building of the Lutheran church built in 1856 and has operated as a museum since 1982. The State Flag Square was inaugurated in 2014 with theFlag of Azerbaijan
The national flag of Azerbaijan (), often referred to as the tricolour flag (), is a horizontal tricolour that features three equally sized bars of bright blue, red, and green; a white crescent; and a centred eight-pointed star. The flag has ...
flying at a height of . There is also a Museum of Azerbaijan State Symbols in the square.
See also
*Caucasus Germans
Caucasus Germans () are part of the German minority in Russia and the Soviet Union. They migrated to the Caucasus largely in the first half of the 19th century and settled in the North Caucasus, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Armenia and the region of Kars ...
Notes
References
* * Ulrich Mohl: ''Schwäbischer Pioniergeist im Kaukasus - Die russlanddeutsche Kolonie Helenendorf''. In: ''Schwäbische Heimat''. Heft 2002/3, ISSN 0342-7595 * Edgar Reitenbach: ''Deutsche im Kaukasus - Zusammengefasste, überarbeitete Neuauflage der Trilogie "Vom Kaukasus nach Kasachstan"'', 2017. * Karl Stumpp: ''Die Auswanderung aus Deutschland nach Rußland in den Jahren 1763 bis 1862''. Landsmannschaft der Deutschen aus Rußland, 2004.External links
"Helenendorf: Azerbaijan's First German Settlement" ''Azerbaijan International''
a magazine;
Satellite view of Khanlar City, Khanlar Raion, Azerbaijan from GoogleMap
{{DEFAULTSORT:Goygol (City) Populated places in Goygol District Populated places established in 1819