Sarcoidosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the
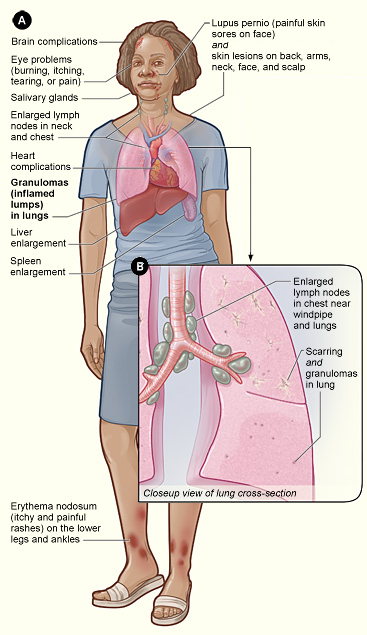 Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease that can affect any organ, although it can be
Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease that can affect any organ, although it can be
Image:Sarcoidosis_(1)_lymph_node_biopsy.jpg, Sarcoidosis in a lymph node
Image:Asteroid body intermed mag.jpg, Pulmonary sarcoidosis with
File:HilarAdenopathy.png, Hilar adenopathy especially on the person's left (AP CXR)
File:HilarAdenopathyLt.png, Hilar adenopathy especially on the person's left (lateral CXR)
File:HilarAdenopathyCCor.png, Hilar adenopathy especially on the person's left (coronal CT)
File:HilarAdenopathyCT.png, Hilar adenopathy especially on the person's left (transverse CT)
 The disease can remit spontaneously or become chronic, with exacerbations and remissions. In some cases, it can progress to pulmonary fibrosis and death. In benign cases, remission can occur in 24 to 36 months without treatment but regular follow ups are required. Some cases, however, may persist several decades. Two-thirds of people with the condition achieve a remission within 10 years of the diagnosis. When the heart is involved, the prognosis is generally less favourable, though corticosteroids appear effective in improving AV conduction. The prognosis tends to be less favourable in African Americans than in white Americans. In a Swedish population-based analysis, the majority of cases who did not have severe disease at diagnosis had comparable mortality to the general population. The risk for premature death was markedly (2.3-fold) increased compared to the general population for a smaller group of cases with severe disease at diagnosis. Serious infections, sometimes multiple during the course of disease, and heart failure might contribute to the higher risk of early death in some patients with sarcoidosis.
Some 1990s studies indicated that people with sarcoidosis appear to be at significantly increased risk for cancer, in particular
The disease can remit spontaneously or become chronic, with exacerbations and remissions. In some cases, it can progress to pulmonary fibrosis and death. In benign cases, remission can occur in 24 to 36 months without treatment but regular follow ups are required. Some cases, however, may persist several decades. Two-thirds of people with the condition achieve a remission within 10 years of the diagnosis. When the heart is involved, the prognosis is generally less favourable, though corticosteroids appear effective in improving AV conduction. The prognosis tends to be less favourable in African Americans than in white Americans. In a Swedish population-based analysis, the majority of cases who did not have severe disease at diagnosis had comparable mortality to the general population. The risk for premature death was markedly (2.3-fold) increased compared to the general population for a smaller group of cases with severe disease at diagnosis. Serious infections, sometimes multiple during the course of disease, and heart failure might contribute to the higher risk of early death in some patients with sarcoidosis.
Some 1990s studies indicated that people with sarcoidosis appear to be at significantly increased risk for cancer, in particular
Sarcoidosis UK Information Hub
* {{Authority control Ailments of unknown cause Lung disorders Abdominal pain Monocyte- and macrophage-related cutaneous conditions Autoimmune diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Steroid-responsive inflammatory conditions Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate
lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
, skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, or lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphoc ...
. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, heart, and brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
, though any organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
can be affected. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no symptoms or only mild symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing
A wheeze is a clinical symptom of a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower ...
, coughing, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, enlarged hilar lymph nodes, arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
, and a rash known as erythema nodosum.
The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs and symptoms, which may be supported by biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
. Findings that make it likely include large lymph nodes at the root of the lung
The root of the lung is a group of structures that emerge at the hilum of each lung, just above the middle of the mediastinal surface and behind the cardiac impression of the lung. It is nearer to the back (posterior border) than the front (a ...
on both sides, high blood calcium
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range for total calcium is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L def ...
with a normal parathyroid hormone level, or elevated levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (), or ACE, is a central component of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), which controls blood pressure by regulating the volume of fluids in the body. It converts the hormone angiotensin I to the active vasocon ...
in the blood. The diagnosis should be made only after excluding other possible causes of similar symptoms such as tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
.
Sarcoidosis may resolve without any treatment within a few years. However, some people may have long-term or severe disease. Some symptoms may be improved with the use of anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
. In cases where the condition causes significant health problems, steroids such as prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
are indicated. Medications such as methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
, chloroquine
Chloroquine is an antiparasitic medication that treats malaria. It works by increasing the levels of heme in the blood, a substance toxic to the malarial parasite. This kills the parasite and stops the infection from spreading. Certain types ...
, or azathioprine may occasionally be used in an effort to decrease the side effects of steroids. The risk of death is 1–7%. The chance of the disease returning in someone who has had it previously is less than 5%.
In 2015, pulmonary sarcoidosis and interstitial lung disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue) and space around the alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulm ...
affected 1.9 million people globally and they resulted in 122,000 deaths. It is most common in Scandinavians, but occurs in all parts of the world. In the United States, risk is greater among black people as opposed to white people. It usually begins between the ages of 20 and 50. It occurs more often in women than men. Sarcoidosis was first described in 1877 by the English doctor Jonathan Hutchinson
Sir Jonathan Hutchinson (23 July 1828 – 23 June 1913), was an English surgeon, ophthalmologist, dermatologist, venereologist, and pathologist, who notably advocated for circumcision. He founded Haslemere Educational Museum.
Life
Jonathan H ...
as a non-painful skin disease.
Signs and symptoms
 Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease that can affect any organ, although it can be
Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease that can affect any organ, although it can be asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
and is discovered by accident in about 5% of cases. Common symptoms, which tend to be vague, include fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
(unrelieved by sleep; occurs in up to 85% of cases), lack of energy, weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
, joint aches and pains (which occur in about 70% of cases), arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
(14–38% of cases), dry eyes, swelling of the knees, blurry vision, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
, a dry, hacking cough, or skin lesions. Less commonly, people may cough up blood. Sarcoidosis is also accompanied by psychological distress and symptoms of anxiety and depression, which are also associated with fatigue. The cutaneous symptoms vary, and range from rash
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
es and noduli (small bumps) to erythema nodosum, granuloma annulare, or lupus pernio. Sarcoidosis and cancer may mimic one another, making the distinction difficult.
The combination of erythema nodosum, bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, and joint pain
Arthralgia () literally means 'joint pain'. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutic ...
is called Löfgren syndrome, which has a relatively good prognosis. This form of the disease occurs significantly more often in Scandinavian patients than in those of non-Scandinavian origin.
Respiratory tract
Localization to the lungs is by far the most common manifestation of sarcoidosis. At least 90% of those affected experience lung involvement. Overall, about 50% develop permanent pulmonary abnormalities, and 5 to 15% have progressive fibrosis of the lungparenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
. Sarcoidosis of the lung is primarily an interstitial lung disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue) and space around the alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulm ...
in which the inflammatory process involves the alveoli, small bronchi, and small blood vessels. In acute and subacute cases, physical examination usually reveals dry crackles
Crackles are the clicking, rattling, or crackling noises that may be made by one or both lungs of a human or animal with a respiratory disease during inhalation, and occasionally during exhalation. They are usually heard only with a stethosco ...
. At least 5% of cases include pulmonary arterial hypertension
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a syndrome in which the blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries and pulmonary arterioles (the blood vessels located proximal to the capillary bed, the site of oxygen exchange in the lungs) is elevated. T ...
. The upper respiratory tract (including the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
, pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
, and sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoi ...
) may be affected, which occurs in between 5 and 10% of cases.
The four stages of pulmonary involvement are based on radiological stage of the disease, which is helpful in prognosis:
* Stage I: bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy (BHL) alone
* Stage II: BHL with pulmonary infiltrates
* Stage III: pulmonary infiltrates without BHL
* Stage IV: fibrosis
Use of the Scadding scale only provides general information regarding the prognosis of the pulmonary disease over time. Caution is recommended, as it only shows a general relation with physiological markers of the disease and the variation is such that it has limited applicability in individual assessments, including treatment decisions.
Skin
Sarcoidosis involves the skin in between 9 and 37% of cases and is more common in black people than in Europeans. The skin is the second-most commonly affected organ after the lungs. The most common lesions are erythema nodosum, plaques, maculopapular eruptions, subcutaneous nodules, and lupus pernio. Treatment is not required, since the lesions usually resolve spontaneously in 2–4 weeks. Although it may be disfiguring, cutaneous sarcoidosis rarely causes major problems. Sarcoidosis of the scalp presents with diffuse or patchy hair loss.Heart
Histologically, sarcoidosis of the heart is an active granulomatous inflammation surrounded by reactive oedema. The distribution of affected areas is patchy with localised enlargement of heart muscles. This causes scarring and remodelling of the heart, which leads to dilatation of heart cavities and thinning of heart muscles. As the situation progresses, it leads toaneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward :wikt:bulge, bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also b ...
of heart chambers. When the distribution is diffuse, there would be dilatation of both ventricles of the heart, causing heart failure and arrhythmia. When the conduction system in the intraventricular septum is affected, it would lead to heart block, ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a cardiovascular disorder in which fast heart rate occurs in the ventricles of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple ...
and ventricular arrhythmia, causing sudden death. Nevertheless, the involvement of pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), ...
and heart valves are uncommon.
The frequency of cardiac involvement varies and is significantly influenced by race; in Japan, more than 25% of those with sarcoidosis have symptomatic cardiac involvement, whereas in the US and Europe, only about 5% of cases present with cardiac involvement. Autopsy studies in the US have revealed a frequency of cardiac involvement of about 20–30%, whereas autopsy studies in Japan have shown a frequency of 60%. The presentation of cardiac sarcoidosis can range from asymptomatic conduction abnormalities to fatal ventricular arrhythmia.
Conduction abnormalities are the most common cardiac manifestations of sarcoidosis in humans and can include complete heart block. Second to conduction abnormalities, in frequency, are ventricular arrhythmias, which occurs in about 23% of cases with cardiac involvement. Sudden cardiac death, either due to ventricular arrhythmias or complete heart block is a rare complication of cardiac sarcoidosis. Cardiac sarcoidosis can cause fibrosis, granuloma formation, or the accumulation of fluid in the interstitium of the heart, or a combination of the former two. Cardiac sarcoidosis may also cause congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically pr ...
when granulomas cause myocardial fibrosis and scarring. Congestive heart failure affects 25-75% of those with cardiac sarcoidosis. Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
and sarcoidosis-related arrhythmias are believed to be strong risk factors of heart failure in sarcoidosis. A small (20-40%) increased risk of acute myocardial infarction has also been described. Pulmonary arterial hypertension occurs by two mechanisms in cardiac sarcoidosis: reduced left heart function due to granulomas weakening the heart muscle or from impaired blood flow.
Eye
Eye involvement occurs in about 10–90% of cases. Manifestations in the eye includeuveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and ...
, uveoparotitis, and retinal inflammation, which may result in loss of visual acuity or blindness. The most common ophthalmologic manifestation of sarcoidosis is uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and ...
. The combination of anterior uveitis, parotitis
Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, in humans. The parotid gland is the salivary gland most commonly affected by inflammation.
Etymology
From Greek παρωτῖ ...
, VII cranial nerve paralysis and fever is called uveoparotid fever or Heerfordt syndrome (). Development of scleral nodule associated with sarcoidosis has been observed.
Nervous system
Any of the components of the nervous system can be involved. Sarcoidosis affecting the nervous system is known as neurosarcoidosis. Cranial nerves are most commonly affected, accounting for about 5–30% of neurosarcoidosis cases, and peripheral facial nerve palsy, often bilateral, is the most common neurological manifestation of sarcoidosis. It occurs suddenly and is usually transient. The central nervous system involvement is present in 10–25% of sarcoidosis cases. Other common manifestations of neurosarcoidosis include optic nerve dysfunction,papilledema
Papilledema or papilloedema is optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure due to any cause. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks. Unilateral presentation is extremely rare.
In ...
, palate dysfunction, neuroendocrine changes, hearing abnormalities, hypothalamic and pituitary abnormalities, chronic meningitis, and peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
. Myelopathy
Myelopathy describes any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord.
When due to trauma, myelopathy is known as (acute) spinal cord injury. When inflammatory, it is known as myelitis. Disease that is vascular in nature is known as vascular ...
, that is spinal cord involvement, occurs in about 16–43% of neurosarcoidosis cases and is often associated with the poorest prognosis of the neurosarcoidosis subtypes. Whereas facial nerve palsies and acute meningitis due to sarcoidosis tend to have the most favourable prognosis, another common finding in sarcoidosis with neurological involvement is autonomic or sensory small-fiber neuropathy. Neuroendocrine sarcoidosis accounts for about 5–10% of neurosarcoidosis cases and can lead to diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. The amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. Reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. ...
, changes in menstrual cycle and hypothalamic dysfunction. The latter can lead to changes in body temperature, mood, and prolactin (see the endocrine and exocrine section for details).
Endocrine and exocrine
Prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin and mammotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secr ...
is frequently increased in sarcoidosis, between 3 and 32% of cases have hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinaemia (also spelled hyperprolactinemia) is a condition characterized by abnormally high levels of prolactin in the blood. In women, normal prolactin levels average to about 13 ng/mL, while in men, they average 5 ng/mL. ...
this frequently leads to amenorrhea
Amenorrhea or amenorrhoea is the absence of a menstrual period in a female organism who has reached reproductive age. Physiological states of amenorrhoea are most commonly seen during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding). In humans, it is wher ...
, galactorrhea
Galactorrhea ( also spelled galactorrhoea) ( galacto- + -rrhea) or lactorrhea ( lacto- + -rrhea) is the spontaneous flow of milk from the breast, unassociated with childbirth or nursing.
Galactorrhea is reported to occur in 5–32% of females. ...
, or nonpuerperal mastitis in women. It also frequently causes an increase in 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D, the active metabolite of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
, which is usually hydroxylated within the kidney, but in sarcoidosis patients, hydroxylation of vitamin D can occur outside the kidneys, namely inside the immune cells found in the granulomas the condition produces. 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D is the main cause for hypercalcemia in sarcoidosis and is overproduced by sarcoid granulomata. Gamma-interferon produced by activated lymphocytes and macrophages plays a major role in the synthesis of 1 alpha, 25(OH)2D3. Hypercalciuria (excessive secretion of calcium in one's urine) and hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia, also spelled hypercalcaemia, is a high calcium (Ca2+) level in the blood serum. The normal range for total calcium is 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L), with levels greater than 2.6 mmol/L def ...
(an excessively high amount of calcium in the blood) are seen in <10% of individuals and likely results from the increased 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D production.
Thyroid dysfunction is seen in 4.2–4.6% of cases.
Parotid enlargement occurs in about 5–10% of cases. Bilateral involvement is the rule. The gland is usually not tender, but firm and smooth. Dry mouth
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is a subjective complaint of dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.
This symptom is very common and is o ...
can occur; other exocrine glands are affected only rarely. The eyes, their glands, or the parotid glands are affected in 20–50% of cases.
Gastrointestinal and genitourinary
Symptomatic gastrointestinal (GI) involvement occurs in less than 1% of cases (if one excludes the liver), and most commonly the stomach is affected, although the small or large intestine may also be affected in a small portion of cases. Studies at autopsy have revealed GI involvement in less than 10% of people. These cases would likely mimicCrohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
, which is a more commonly intestine-affecting granulomatous disease. About 1–3% of people have evidence of pancreatic involvement at autopsy. Symptomatic kidney involvement occurs in just 0.7% of cases, although evidence of kidney involvement at autopsy has been reported in up to 22% of people and occurs exclusively in cases of chronic disease. Symptomatic kidney involvement is usually nephrocalcinosis, although granulomatous interstitial nephritis that presents with reduced creatinine
Creatinine (; ) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass).
Biological relevance
Serum creatinine (a blood measurement) is an impor ...
clearance and little proteinuria
Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein, less than 150 mg/day; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become fo ...
is a close second. Less commonly, the epididymis
The epididymis (; : epididymides or ) is an elongated tubular genital organ attached to the posterior side of each one of the two male reproductive glands, the testicles. It is a single, narrow, tightly coiled tube in adult humans, in length; ...
, testicles
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
, prostate
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemica ...
, ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
, fallopian tubes
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (: salpinx), are paired tubular sex organs in the human female body that stretch from the ovaries to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive sy ...
, uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
, or the vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, lab ...
may be affected, the latter may cause vulva itchiness. Testicular involvement has been reported in about 5% of people at autopsy. In males, sarcoidosis may lead to infertility.
Around 70% of people have granulomas in their livers, although only in about 20–30% of cases, liver function test anomalies reflecting this fact are seen. About 5–15% of patients exhibit hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is enlargement of the liver. It is a non-specific sign (medicine), medical sign, having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, hepatic tumours, and metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly presents as an abdomin ...
. Only 5–30% of cases of liver involvement are symptomatic. Usually, these changes reflect a cholestatic pattern and include raised levels of alkaline phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryo ...
(which is the most common liver function test anomaly seen in those with sarcoidosis), while bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (adopted from German, originally bili—bile—plus ruber—red—from Latin) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normcomponent of the straw-yellow color in urine. Another breakdown product, stercobilin, causes the brown ...
and aminotransferases are only mildly elevated. Jaundice is rare.
Blood
Abnormal blood tests are frequent, accounting for over 50% of cases, but are not diagnostic.Lymphopenia
Lymphocytopenia is the condition of having an abnormally low level of lymphocytes in the blood. Lymphocytes are a white blood cell with important functions in the immune system. It is also called lymphopenia. The opposite is lymphocytosis, which r ...
is the most common blood anomaly in sarcoidosis. Anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
occurs in about 20% of people with sarcoidosis. Leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes). It places individuals at increased risk of infection as white blood cells are the body's primary defense against infections.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include:
* s ...
is less common and occurs in even fewer cases but is rarely severe. Thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coag ...
and hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels (intravascular hemolysis) or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonl ...
are fairly rare. In the absence of splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulat ...
, leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes). It places individuals at increased risk of infection as white blood cells are the body's primary defense against infections.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms may include:
* s ...
may reflect bone marrow involvement, but the most common mechanism is a redistribution of blood T cells to sites of disease. Other nonspecific findings include monocytosis, occurring in the majority of sarcoidosis cases, increased hepatic enzymes or alkaline phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryo ...
. People with sarcoidosis often have immunologic anomalies like allergies to test antigens such as '' Candida'' or purified protein derivative. Polyclonal hypergammaglobulinemia is also a fairly common immunologic anomaly seen in sarcoidosis.
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In c ...
(swollen glands) is common in sarcoidosis and occurs in 15% of cases. Intrathoracic nodes are enlarged in 75 to 90% of all people; usually this involves the hilar nodes, but the paratracheal nodes are commonly involved. Peripheral lymphadenopathy is very common, particularly involving the cervical (the most common head and neck manifestation of the disease), axillary, epitrochlear, and inguinal nodes. Approximately 75% of cases show microscopic involvement of the spleen, although only in about 5–10% of cases does splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulat ...
appear.
Bone, joints, and muscles
Sarcoidosis can be involved with the joints, bones, and muscles. This causes a wide variety of musculoskeletal complaints that act through different mechanisms. About 5–15% of cases affect the bones, joints, or muscles. Arthritic syndromes can be categorized as acute or chronic. Sarcoidosis patients with acute arthritis often also have bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy and erythema nodosum. These three associated syndromes often occur together in Löfgren syndrome. The arthritis symptoms of Löfgren syndrome occur most frequently in the ankles, followed by the knees, wrists, elbows, and metacarpophalangeal joints. Usually, true arthritis is not present, but instead, periarthritis appears as a swelling in the soft tissue around the joints that can be seen by ultrasonographic methods. These joint symptoms tend to precede or occur at the same time as erythema nodosum develops. Even when erythema nodosum is absent, it is believed that the combination of hilar lymphadenopathy and ankle periarthritis can be considered as a variant of Löfgren syndrome. Enthesitis also occurs in about one-third of patients with acute sarcoid arthritis, mainly affecting the Achilles tendon and heels. Soft-tissue swelling of the ankles can be prominent, and biopsy of this soft tissue reveals no granulomas, but does show panniculitis similar to erythema nodosum. Chronic sarcoid arthritis usually occurs in the setting of more diffuse organ involvement. The ankles, knees, wrists, elbows, and hands may all be affected in the chronic form and often this presents itself in a polyarticular pattern. Dactylitis similar to that seen inpsoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that may occur in some people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic features of psoriatic arthritis include dactylitis (sausage-like swelling of the fingers ...
, that is associated with pain, swelling, overlying skin erythema, and underlying bony changes may also occur. Development of Jaccoud arthropathy (a nonerosive deformity) is very rarely seen.
Bone involvement in sarcoidosis has been reported in 1–13% of cases. The most frequent sites of involvement are the hands and feet, whereas the spine is less commonly affected. Half of the patients with bony lesions experience pain and stiffness, whereas the other half remain asymptomatic.
Periostitis is rarely seen in sarcoidosis and has been found to present itself at the femoral bone.
Cause
The exact cause of sarcoidosis is not known. The current working hypothesis is, in genetically susceptible individuals, sarcoidosis is caused through alteration to the immune response after exposure to an environmental, occupational, or infectious agent. Some cases may be caused by treatment withtumor necrosis factor
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors o ...
(TNF) inhibitors like etanercept
Etanercept, sold under the brand name Enbrel among others, is a biologic medical product that is used to treat autoimmune diseases by interfering with tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a soluble inflammatory cytokine, by acting as a TNF inhibitor. ...
.
Genetics
The heritability of sarcoidosis varies according toethnicity
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they Collective consciousness, collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, ...
. About 20% of African American
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from an ...
s with sarcoidosis have a family member with the condition, whereas the same figure for European Americans
European Americans are Americans of European ancestry. This term includes both people who descend from the first European settlers in the area of the present-day United States and people who descend from more recent European arrivals. Since th ...
is about 5%. Additionally, in African Americans, who seem to experience more severe and chronic disease, siblings and parents of sarcoidosis cases have about a 2.5-fold increased risk for developing the disease. In Swedish individuals heritability was found to be 39%. In this group, if a first-degree family member was affected, a person has a four-fold greater risk of being affected.
Investigations of genetic susceptibility yielded many candidate genes, but only few were confirmed by further investigations and no reliable genetic markers are known. Currently, the most interesting candidate gene is '' BTNL2''; several ''HLA-DR
HLA-DR is an MHC class II cell surface receptor encoded by the human leukocyte antigen complex on chromosome 6 region 6p21.31. The complex of HLA-DR (Human Leukocyte Antigen – DR isotype) and peptide, generally between 9 and 30 amino acids in l ...
'' risk alleles are also being investigated. In persistent sarcoidosis, the HLA haplotype '' HLA-B7- DR15'' is either cooperating in disease or another gene between these two loci is associated. In nonpersistent disease, a strong genetic association exists with '' HLA DR3-DQ2''. Cardiac sarcoid has been connected to tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFA) variants.
Infectious agents
Several infectious agents appear to be significantly associated with sarcoidosis, but none of the known associations is specific enough to suggest a direct causative role. The major implicated infectious agents include:mycobacteria
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis ('' M. tuberculosis'') a ...
, fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, borrelia
''Borrelia'' is a genus of bacteria of the spirochete phylum. Several species cause Lyme disease, also called Lyme borreliosis, a zoonotic, vector-borne disease transmitted by ticks. Other species of ''Borrelia'' cause relapsing fever, and are ...
, and rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The genus was n ...
. A meta-analysis investigating the role of mycobacteria in sarcoidosis found it was present in 26.4% of cases, but they also detected a possible publication bias
In published academic research, publication bias occurs when the outcome of an experiment or research study biases the decision to publish or otherwise distribute it. Publishing only results that show a Statistical significance, significant find ...
, so the results need further confirmation. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis.
First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' ha ...
'' catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting ...
-peroxidase
Peroxidases or peroxide reductases ( EC numberbr>1.11.1.x are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides, and should not be confused with other ...
has been identified as a possible antigen catalyst of sarcoidosis. The disease has also been reported by transmission via organ transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ (anatomy), organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or org ...
s. A large epidemiological study found little evidence that infectious diseases spanning years before sarcoidosis diagnosis could confer measurable risks for sarcoidosis diagnosis in the future.
Autoimmune
Association ofautoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
disorders has been frequently observed. The exact mechanism of this relation is not known, but some evidence supports the hypothesis that this is a consequence of Th1 lymphokine prevalence. Tests of delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity have been used to measure progression.
Pathophysiology
Granulomatous inflammation is characterized primarily by the accumulation ofmacrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s and activated T-lymphocytes, with increased production of key inflammatory mediators, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF), interferon gamma
Interferon gamma (IFNG or IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. ...
, interleukin 2
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is an interleukin, which is a type of cytokine signaling molecule forming part of the immune system. It is a 15.5–16 Dalton (unit), kDa protein that regulates the activities of white blood cells (leukocytes, often ...
(IL-2), IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IL-18, IL-23 and transforming growth factor beta
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other ...
(TGF-β), indicative of a T helper cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
-mediated immune response.
Sarcoidosis has paradoxical effects on inflammatory processes; it is characterized by increased macrophage and CD4 helper T-cell activation, resulting in accelerated inflammation, but immune response to antigen challenges such as tuberculin is suppressed. This paradoxic state of simultaneous hyper- and hypoactivity is suggestive of a state of anergy. The anergy may also be responsible for the increased risk of infections and cancer. The regulatory T-lymphocytes in the periphery of sarcoid granulomas appear to suppress IL-2 secretion, which is hypothesized to cause the state of anergy by preventing antigen-specific memory responses.
While TNF is widely believed to play an important role in the formation of granulomas (this is further supported by the finding that in animal models of mycobacterial granuloma formation inhibition of either TNF or IFN-γ production inhibits granuloma formation), sarcoidosis can and does still develop in those being treated with TNF antagonists like etanercept
Etanercept, sold under the brand name Enbrel among others, is a biologic medical product that is used to treat autoimmune diseases by interfering with tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a soluble inflammatory cytokine, by acting as a TNF inhibitor. ...
.
B cells also likely play a role in the pathophysiology of sarcoidosis. Serum levels of soluble human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans that encode cell-surface proteins responsible for regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histo ...
(HLA) class I antigens and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) are higher in people with sarcoidosis. Likewise the ratio of CD4/CD8 T cells in bronchoalveolar lavage is usually higher in people with pulmonary sarcoidosis (usually >3.5), although it can be normal or even abnormally low in some cases. Serum ACE levels have been found to usually correlate with total granuloma load.
Cases of sarcoidosis have also been reported as part of the immune reconstitution syndrome of HIV, that is, when people receive treatment for HIV, their immune system rebounds and the result is that it starts to attack the antigens of opportunistic infections caught prior to said rebound and the resulting immune response starts to damage healthy tissue.
Histopathology
Sarcoidosis is characterized by the formation of non-necrotizing ("non-caseating")granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such sub ...
s in various organs and tissues. Giant cell
A giant cell (also known as a multinucleated giant cell, or multinucleate giant cell) is a mass formed by the union of several distinct cells (usually histiocytes), often forming a granuloma.
Although there is typically a focus on the patholog ...
s, specifically Langhans giant cell
Langhans giant cells (LGC) are giant cells found in granulomatous conditions.
They are formed by the fusion of epithelioid cells (macrophages), and contain nuclei arranged in a horseshoe-shaped pattern in the cell periphery.
Although tradit ...
s, are often seen in sarcoidosis. Schaumann bodies seen in sarcoidosis are calcium and protein inclusions inside of giant cells as part of a granuloma. Asteroid bodies can be seen in sarcoidosis. Hamazaki–Wesenberg bodies can be seen in lymph nodes and more rarely in lung biopsies with sarcoidosis and are inclusion bodies of lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
s with protein, glycoprotein and iron.
granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such sub ...
s with Langhans giant cell
Langhans giant cells (LGC) are giant cells found in granulomatous conditions.
They are formed by the fusion of epithelioid cells (macrophages), and contain nuclei arranged in a horseshoe-shaped pattern in the cell periphery.
Although tradit ...
s and asteroid bodies
Image:Sarcoidosis - Schaumann body 2.jpg, Schaumann body in sarcoidosis
Image:Sarcoidosis - Asteroid body (6152059052).jpg, Asteroid body in sarcoidosis
Image:Sarcoidosis - Hamazaki-Wesenberg (H-W) bodies- Lymph node (6134890353).jpg, Hamazaki–Wesenberg bodies in sarcoidosis in lymph node
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of sarcoidosis is a matter of exclusion, as there is no specific test for the condition other than the Kveim-Siltzbach test. To exclude sarcoidosis in a case presenting with pulmonary symptoms might involve achest radiograph
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.
L ...
, CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
of chest, PET scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in Metabolism, metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including bloo ...
, CT-guided biopsy, mediastinoscopy, open lung biopsy, bronchoscopy with biopsy, endobronchial ultrasound, and endoscopic ultrasound with fine-needle aspiration of mediastinal lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphoc ...
(EBUS FNA). Tissue from biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
of lymph nodes is subjected to both flow cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure the physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles.
In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the ...
to rule out cancer and special stains ( acid fast bacilli stain and Gömöri methenamine silver stain) to rule out microorganisms
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in ...
and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
.
Serum markers of sarcoidosis, include: serum amyloid A, soluble interleukin-2 receptor
The interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R) is a heterotrimeric protein expressed on the surface of certain immune cells, such as lymphocytes, that binds and responds to a cytokine called IL-2.
Composition
IL-2 binds to the IL-2 receptor, which has ...
, lysozyme
Lysozyme (, muramidase, ''N''-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase; systematic name peptidoglycan ''N''-acetylmuramoylhydrolase) is an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. It is a glycoside hydrolase ...
, angiotensin converting enzyme, and the glycoprotein KL-6. Angiotensin-converting enzyme blood levels are used in the monitoring of sarcoidosis. A bronchoalveolar lavage can show an elevated (of at least 3.5) CD4/CD8 T cell ratio, which is indicative (but not proof) of pulmonary sarcoidosis. In at least one study the induced sputum ratio of CD4/CD8 and level of TNF was correlated to those in the lavage fluid. A sarcoidosis-like lung disease called granulomatous–lymphocytic interstitial lung disease can be seen in patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) and therefore serum antibody levels should be measured to exclude CVID.
Differential diagnosis includes metastatic disease, lymphoma, septic emboli, rheumatoid nodules, granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis (WG), after Nazi German physician Friedrich Wegener, is a rare, long-term, systemic disorder that involves the formation of granulomas and vasculitis, inflammatio ...
, varicella infection, tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, and atypical infections, such as ''Mycobacterium avium
''Mycobacterium avium ''complex is a group of mycobacteria comprising ''Mycobacterium intracellulare'' and ''Mycobacterium avium'' that are commonly grouped because they infect humans together; this group, in turn, is part of the group of nontu ...
'' complex, cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (CMV) (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betaherp ...
, and cryptococcus. Sarcoidosis is confused most commonly with neoplastic diseases, such as lymphoma, or with disorders characterized also by a mononuclear cell granulomatous inflammatory process, such as the mycobacterial and fungal disorders.
Chest radiograph changes are divided into four stages:
# bihilar lymphadenopathy
# bihilar lymphadenopathy and reticulonodular infiltrates
# bilateral pulmonary infiltrates
# fibrocystic sarcoidosis typically with upward hilar retraction, cystic and bullous changes
Although people with stage 1 radiographs tend to have the acute or subacute, reversible form of the disease, those with stages 2 and 3 often have the chronic, progressive disease; these patterns do not represent consecutive "stages" of sarcoidosis. Thus, except for epidemiologic purposes, this categorization is mostly of historic interest.
In sarcoidosis presenting in the Caucasian population, hilar adenopathy and erythema nodosum are the most common initial symptoms. In this population, a biopsy of the gastrocnemius muscle is a useful tool in correctly diagnosing the person. The presence of a noncaseating epithelioid granuloma in a gastrocnemius specimen is definitive evidence of sarcoidosis, as other tuberculoid and fungal diseases extremely rarely present histologically in this muscle.
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) is one modality for diagnosing cardiac sarcoidosis. It has 78% specificity in diagnosing cardiac sarcoidosis. Its T2-weighted imaging can detect acute inflammation. Meanwhile, late gadolinium contrast (LGE) can detect fibrosis or scar. Lesions at the subpericardium and midwall enhancement of basal septum or inferolateral wall is strongly suggestive of sarcoidosis. MRI can also follow up on the treatment efficacy of corticosteroids and prognosis
Prognosis ( Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing"; : prognoses) is a medical term for predicting the likelihood or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) ...
of cardiac sarcoidosis.
PET scan is able to quantify disease activity which cannot be performed by CMR.
Classification
Sarcoidosis may be divided into the following types: * Annular sarcoidosis * Erythrodermic sarcoidosis * Ichthyosiform sarcoidosis * Hypopigmented sarcoidosis * Löfgren syndrome * Lupus pernio * Morpheaform sarcoidosis * Mucosal sarcoidosis * Neurosarcoidosis * Papular sarcoid * Scar sarcoid * Subcutaneous sarcoidosis * Systemic sarcoidosis * Ulcerative sarcoidosisTreatment
Treatments for sarcoidosis vary greatly depending on the patient. At least half of patients require no systemic therapy. Most people (>75%) only require symptomatic treatment withnonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
s (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
or aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is ...
. For those presenting with lung symptoms, unless the respiratory impairment is devastating, active pulmonary sarcoidosis is observed usually without therapy for two to three months; if the inflammation does not subside spontaneously, therapy is instituted.
Major categories of drug interventions include glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s, antimetabolites, biologic agents especially monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor antibodies. Investigational treatments include specific antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
combinations and mesenchymal stem cells
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), also known as mesenchymal stromal cells or medicinal signaling cells, are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts (bone cells), chondrocytes (cartilage ...
. If drug intervention is indicated, a step-wise approach is often used to explore alternatives in order of increasing side effects and to monitor potentially toxic effects.
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s, most commonly prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
or prednisolone
Prednisolone is a corticosteroid, a steroid hormone used to treat certain types of allergies, inflammation, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders, and cancers, Electrolyte imbalance, electrolyte imbalances and skin conditions. Some of ...
, have been the standard treatment for many years. In some people, this treatment can slow or reverse the course of the disease, but other people do not respond to steroid therapy. The use of corticosteroids in mild disease is controversial because in many cases the disease remits spontaneously.
Antimetabolites
Antimetabolites, also categorized as steroid-sparing agents, such as azathioprine,methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
, mycophenolic acid
Mycophenolic acid is an immunosuppressant medication used to prevent rejection following organ transplantation and to treat autoimmune conditions such as Crohn's disease and lupus. Specifically it is used following kidney, heart, and live ...
, and leflunomide
Leflunomide, sold under the brand name Arava among others, is an immunosuppressive disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), used in active moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. It is a pyrimidine synthesis inhib ...
are often used as alternatives to corticosteroids. Of these, methotrexate is most widely used and studied. Methotrexate is considered a first-line treatment in neurosarcoidosis, often in conjunction with corticosteroids. Long-term treatment with methotrexate is associated with liver damage in about 10% of people and hence may be a significant concern in people with liver involvement and requires regular liver function test monitoring. Methotrexate can also lead to pulmonary toxicity (lung damage), although this is fairly uncommon and more commonly it can confound the leukopenia caused by sarcoidosis. Due to these safety concerns it is often recommended that methotrexate is combined with folic acid in order to prevent toxicity. Azathioprine treatment can also lead to liver damage. However, the risk of infection appears to be about 40% lower in those treated with methotrexate instead of azathioprine. Leflunomide is being used as a replacement for methotrexate, possibly due to its purportedly lower rate of pulmonary toxicity. Mycophenolic acid has been used successfully in uveal sarcoidosis, neurosarcoidosis (especially CNS sarcoidosis; minimally effective in sarcoidosis myopathy), and pulmonary sarcoidosis.
Immunosuppressants
As the granulomas are caused by collections of immune system cells, particularlyT cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s, there has been some success using immunosuppressants (like cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
, cladribine, chlorambucil, and cyclosporine
Ciclosporin, also spelled cyclosporine and cyclosporin, is a calcineurin inhibitor, used as an immunosuppressant medication. It is taken orally or intravenously for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease, nephrotic syndrome, ecz ...
), immunomodulatory ( pentoxifylline and thalidomide
Thalidomide, sold under the brand names Contergan and Thalomid among others, is an oral administered medication used to treat a number of cancers (e.g., multiple myeloma), graft-versus-host disease, and many skin disorders (e.g., complication ...
), and anti-tumor necrosis factor
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors o ...
treatment (such as infliximab
Infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody, sold under the brand name Remicade among others, is a medication used to treat a number of autoimmune diseases. This includes Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing ...
, etanercept
Etanercept, sold under the brand name Enbrel among others, is a biologic medical product that is used to treat autoimmune diseases by interfering with tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a soluble inflammatory cytokine, by acting as a TNF inhibitor. ...
, golimumab, and adalimumab
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira and others, is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug and monoclonal antibody used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn' ...
).
In a clinical trial cyclosporine added to prednisone treatment failed to demonstrate any significant benefit over prednisone alone in people with pulmonary sarcoidosis, although there was evidence of increased toxicity from the addition of cyclosporine to the steroid treatment including infections, malignancies (cancers), hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
, and kidney dysfunction. Likewise chlorambucil and cyclophosphamide are seldom used in the treatment of sarcoidosis due to their high degree of toxicity, especially their potential for causing malignancies. Infliximab
Infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody, sold under the brand name Remicade among others, is a medication used to treat a number of autoimmune diseases. This includes Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing ...
has been used successfully to treat pulmonary sarcoidosis in clinical trials in a number of cases. Etanercept
Etanercept, sold under the brand name Enbrel among others, is a biologic medical product that is used to treat autoimmune diseases by interfering with tumor necrosis factor (TNF), a soluble inflammatory cytokine, by acting as a TNF inhibitor. ...
, on the other hand, has failed to demonstrate any significant efficacy in people with uveal sarcoidosis in a couple of clinical trials. Likewise golimumab has failed to show any benefit in those with pulmonary sarcoidosis. One clinical trial of adalimumab
Adalimumab, sold under the brand name Humira and others, is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug and monoclonal antibody used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn' ...
found treatment response in about half of subjects, which is similar to that seen with infliximab, but as adalimumab has better tolerability profile it may be preferred over infliximab.
Specific organ treatments
Ursodeoxycholic acid has been used successfully as a treatment for cases with liver involvement.Thalidomide
Thalidomide, sold under the brand names Contergan and Thalomid among others, is an oral administered medication used to treat a number of cancers (e.g., multiple myeloma), graft-versus-host disease, and many skin disorders (e.g., complication ...
has also been tried successfully as a treatment for treatment-resistant lupus pernio in a clinical trial, which may stem from its anti-TNF activity, although it failed to exhibit any efficacy in a pulmonary sarcoidosis clinical trial. Cutaneous disease may be successfully managed with antimalarials (such as chloroquine
Chloroquine is an antiparasitic medication that treats malaria. It works by increasing the levels of heme in the blood, a substance toxic to the malarial parasite. This kills the parasite and stops the infection from spreading. Certain types ...
and hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, an ...
) and the tetracycline antibiotic, minocycline. Antimalarials have also demonstrated efficacy in treating sarcoidosis-induced hypercalcemia and neurosarcoidosis. Long-term use of antimalarials is limited, however, by their potential to cause irreversible blindness and hence the need for regular ophthalmologic screening. This toxicity is usually less of a problem with hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, an ...
than with chloroquine
Chloroquine is an antiparasitic medication that treats malaria. It works by increasing the levels of heme in the blood, a substance toxic to the malarial parasite. This kills the parasite and stops the infection from spreading. Certain types ...
, although hydroxychloroquine can disturb the glucose homeostasis.
Recently selective phosphodiesterase 4 At least four types of the enzyme phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) are known:
* PDE4A
* PDE4B
* PDE4C
* PDE4D
See also
* 3',5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase
* Phosphodiesterase (PDE)
* PDE4 inhibitor
A phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, commonly ref ...
(PDE4) inhibitors like apremilast (a thalidomide derivative), roflumilast, and the less subtype-selective PDE4 inhibitor
A phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, commonly referred to as a PDE4 inhibitor, is a drug used to block the degradative action of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). It is a member of the larger family of PDE inhibit ...
, pentoxifylline, have been tried as a treatment for sarcoidosis, with successful results being obtained with apremilast in cutaneous sarcoidosis in a small open-label study. Pentoxifylline has been used successfully to treat acute disease although its use is greatly limited by its gastrointestinal toxicity (mostly nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea). Case reports have supported the efficacy of rituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in children and ad ...
, an anti-CD20
B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 or CD20 is B lymphocyte cell-surface molecule.
It is a 33-37 kDa non-glycosylated protein. CD20 is expressed on the surface of B-cells from the pre-B phase, the expression is lost in terminally differentiated plasm ...
monoclonal antibody and a clinical trial investigating atorvastatin
Atorvastatin, sold under the brand name Lipitor among others, is a statin medication used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and to treat abnormal lipid levels. For the prevention of cardiovascular disease, statins are a ...
as a treatment for sarcoidosis is under-way. ACE inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of hypertension, high blood pressure and heart failure. This class of medicine works by causing relaxation of blood vessels as ...
have been reported to cause remission in cutaneous sarcoidosis and improvement in pulmonary sarcoidosis, including improvement in pulmonary function, remodeling of lung parenchyma and prevention of pulmonary fibrosis in separate case series'. Nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
patches have been found to possess anti-inflammatory effects in sarcoidosis patients, although whether they had disease-modifying effects requires further investigation. Antimycobacterial treatment (drugs that kill off mycobacteria, the causative agents behind tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
and leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a Chronic condition, long-term infection by the bacteria ''Mycobacterium leprae'' or ''Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the Peripheral nervous system, nerves, respir ...
) has also proven itself effective in treating chronic cutaneous (that is, it affects the skin) sarcoidosis in one clinical trial. Quercetin
Quercetin is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains; capers, red onions, and kale are common foods containing appreciable amounts of it. It has a bitter flavor ...
has also been tried as a treatment for pulmonary sarcoidosis with some early success in one small trial.
Because of its uncommon nature, the treatment of male reproductive tract sarcoidosis is controversial. Since the differential diagnosis includes testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system. Symptoms may include a lump in the testicle or swelling or pain in the scrotum. Treatment may result in infertility.
Risk factors include an c ...
, some recommend orchiectomy
Orchiectomy (also named orchidectomy) is a surgery, surgical procedure in which one or both testicles are removed. The surgery can be performed for various reasons:
*treatment for testicular cancer
*as part of gender-affirming surgery for trans ...
, even if evidence of sarcoidosis in other organs is present. In the newer approach, testicular, epididymal biopsy and resection of the largest lesion has been proposed.
Symptoms
People with sarcoidosis may have a range of symptoms that do not correspond with objective physical evidence of disease but that still decreasequality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
.
Physical therapy, rehabilitation, and counseling can help avoid deconditioning, and improve social participation, psychological well-being, and activity levels. Key aspects are avoiding exercise intolerance and muscle weakness.
Low or moderate-intensity physical training has been shown to improve fatigue, psychological health, and physical functioning in people sarcoidosis without adverse effects. Inspiratory muscle training has also decreased severe fatigue perception in subjects with early stages of sarcoidosis, as well as improving functional and maximal exercise capacity and respiratory muscle strength. The duration, frequency, and physical intensity of exercise needs to accommodate impairments such as joint pain, muscle pain, and fatigue.
Neurostimulants such as methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
and modafinil
Modafinil, sold under the brand name Provigil among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and wakefulness-promoting agent, eugeroic (wakefulness promoter) medication used primarily to treat narcolepsy, a sleep disorder characteri ...
have shown some effectiveness as an adjunct for treatment of sarcoidosis fatigue.
Treatments for symptomatic neuropathic pain in sarcoidosis patients is similar to that for other causes, and include antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
s, anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs, antiseizure drugs, or anti-seizure medications (ASM)) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also used in the treatme ...
s and prolonged-release opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
s, however, only 30 to 60% of patients experience limited pain relief.
Prognosis
 The disease can remit spontaneously or become chronic, with exacerbations and remissions. In some cases, it can progress to pulmonary fibrosis and death. In benign cases, remission can occur in 24 to 36 months without treatment but regular follow ups are required. Some cases, however, may persist several decades. Two-thirds of people with the condition achieve a remission within 10 years of the diagnosis. When the heart is involved, the prognosis is generally less favourable, though corticosteroids appear effective in improving AV conduction. The prognosis tends to be less favourable in African Americans than in white Americans. In a Swedish population-based analysis, the majority of cases who did not have severe disease at diagnosis had comparable mortality to the general population. The risk for premature death was markedly (2.3-fold) increased compared to the general population for a smaller group of cases with severe disease at diagnosis. Serious infections, sometimes multiple during the course of disease, and heart failure might contribute to the higher risk of early death in some patients with sarcoidosis.
Some 1990s studies indicated that people with sarcoidosis appear to be at significantly increased risk for cancer, in particular
The disease can remit spontaneously or become chronic, with exacerbations and remissions. In some cases, it can progress to pulmonary fibrosis and death. In benign cases, remission can occur in 24 to 36 months without treatment but regular follow ups are required. Some cases, however, may persist several decades. Two-thirds of people with the condition achieve a remission within 10 years of the diagnosis. When the heart is involved, the prognosis is generally less favourable, though corticosteroids appear effective in improving AV conduction. The prognosis tends to be less favourable in African Americans than in white Americans. In a Swedish population-based analysis, the majority of cases who did not have severe disease at diagnosis had comparable mortality to the general population. The risk for premature death was markedly (2.3-fold) increased compared to the general population for a smaller group of cases with severe disease at diagnosis. Serious infections, sometimes multiple during the course of disease, and heart failure might contribute to the higher risk of early death in some patients with sarcoidosis.
Some 1990s studies indicated that people with sarcoidosis appear to be at significantly increased risk for cancer, in particular lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged ...
, lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph node ...
s, and cancer in other organs known to be affected in sarcoidosis. In sarcoidosis-lymphoma syndrome, sarcoidosis is followed by the development of a lymphoproliferative disorder such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredn ...
. This may be attributed to the underlying immunological abnormalities that occur during the sarcoidosis disease process. Sarcoidosis can also follow cancer or occur concurrently with cancer. There have been reports of hairy cell leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia is an uncommon hematological malignancy characterized by an accumulation of abnormal B lymphocytes. The incidence of hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is 0.28-0.30 cases per 100,000 people in Europe and the United States and the pre ...
, acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with haematopoiesis, normal blood cell production. Sympt ...
, and acute myeloblastic leukemia associated with sarcoidosis. Sometimes, sarcoidosis, even untreated, can be complicated by opportunistic infections although these are rare.
Epidemiology
Sarcoidosis most commonly affects young adults of both sexes, although studies have reported more cases in females. Incidence is highest for individuals younger than 40 and peaks in the age-group from 20 to 29 years; a second peak is observed for women over 50. Sarcoidosis occurs throughout the world in all races with an average incidence of 16.5 per 100,000 in men and 19 per 100,000 in women. The disease is most common in Northern European countries and the highest annual incidence of 60 per 100,000 is found in Sweden and Iceland. In the United Kingdom the prevalence is 16 in 100,000. In the United States, sarcoidosis is more common in people ofAfrican descent
Black is a racial classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid- to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin and often additional phenotypical ...
than Caucasians, with annual incidence reported as 35.5 and 10.9 per 100,000, respectively. Sarcoidosis is less commonly reported in South America, Spain, India, Canada, and the Philippines. There may be a higher susceptibility to sarcoidosis in those with celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
. An association between the two disorders has been suggested.
There also has been a seasonal clustering observed in sarcoidosis-affected individuals. In Greece about 70% of diagnoses occur between March and May every year, in Spain about 50% of diagnoses occur between April and June, and in Japan it is mostly diagnosed during June and July.
The differing incidence across the world may be at least partially attributable to the lack of screening programs in certain regions of the world, and the overshadowing presence of other granulomatous diseases, such as tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, that may interfere with the diagnosis of sarcoidosis where they are prevalent. There may also be differences in the severity of the disease between people of different ethnicities. Several studies suggest the presentation in people of African origin may be more severe and disseminated than for Caucasians, who are more likely to have asymptomatic disease. Manifestation appears to be slightly different according to race and sex. Erythema nodosum is far more common in men than in women and in Caucasians than in other races. In Japanese people, ophthalmologic and cardiac involvement are more common than in other races.
It is more common in certain occupations, namely firefighters, educators, military personnel, those who work in industries where pesticides are used, law enforcement, and healthcare personnel. In the year after the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
, the rate of sarcoidosis incidence went up four-fold (to 86 cases per 100,000).
History
It was first described in 1877 by Dr.Jonathan Hutchinson
Sir Jonathan Hutchinson (23 July 1828 – 23 June 1913), was an English surgeon, ophthalmologist, dermatologist, venereologist, and pathologist, who notably advocated for circumcision. He founded Haslemere Educational Museum.
Life
Jonathan H ...
, a dermatologist
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medi ...
as a condition causing red, raised rashes on the face, arms, and hands. In 1889 the term lupus pernio was coined by Dr. Ernest Besnier, another dermatologist. Later in 1892 lupus pernio's histology
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at large ...
was defined. In 1902 bone involvement was first described by a group of three doctors. Between 1909 and 1910 uveitis in sarcoidosis was first described, and later in 1915 it was emphasised, by Dr. Jörgen Nielsen Schaumann, that it was a systemic condition. This same year lung involvement was also described. In 1937 uveoparotid fever was first described and likewise in 1941 Löfgren syndrome was first described. In 1958 the first international conference on sarcoidosis was called in London, likewise the first USA sarcoidosis conference occurred in Washington, D.C., in the year 1961. It has also been called Besnier– Boeck disease or Besnier– Boeck– Schaumann disease.
Etymology
The word "sarcoidosis" comes from Greek �άρκο-''sarco-'' meaning "flesh", the suffix ''-(e)ido'' (from the Greek εἶδος -eidos sually omitting the initial e in English as the diphthong epsilon-iota in Classic Greek stands for a long "i" = English ee meaning "type", " resembles" or "like", and ''-sis'', a common suffix in Greek meaning "condition". Thus the whole word means "a condition that resembles crude flesh". The first cases of sarcoïdosis, which were recognised as a new pathological entity, in Scandinavia, at the end of the 19th century exhibited skin nodules resembling cutaneous sarcomas, hence the name initially given.Society and culture
The World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) is an organisation of physicians involved in the diagnosis and treatment of sarcoidosis and related conditions. WASOG publishes the journal ''Sarcoidosis, Vasculitis and Diffuse Lung Diseases''. Additionally, the Foundation for Sarcoidosis Research (FSR) is devoted to supporting research into sarcoidosis and its possible treatments. There have been concerns that World Trade Center rescue workers are at a heightened risk for sarcoidosis. Comedian and actor Bernie Mac had sarcoidosis. In 2005, he mentioned that the disease was in remission. His death on August 9, 2008, was caused by complications frompneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
, though Mac's agent states the sarcoidosis was not related to his fatal pneumonia.
Karen "Duff" Duffy, MTV
MTV (an initialism of Music Television) is an American cable television television channel, channel and the flagship property of the MTV Entertainment Group sub-division of the Paramount Media Networks division of Paramount Global. Launched on ...
personality and actress, was diagnosed with neurosarcoidosis in 1995.
American football player Reggie White died in 2004, with pulmonary and cardiac sarcoidosis being contributing factors to his fatal heart arrhythmia.
Singer Sean Levert died in 2008 of sarcoidosis complications.
Manning Marable, a professor of public policy at Columbia University, died of pneumonia in 2011, less than a year after undergoing a double lung transplant following a diagnosis of sarcoidosis. In 2012, he was posthumously awarded a Pulitzer Prize in history for his biography " Malcolm X: A Life of Reinvention."
Joseph Rago, Pulitzer Prize-winning writer known for his work at ''The Wall Street Journal'', died of sarcoidosis complications in 2017.
Several historical figures are suspected of having sarcoidosis. In a 2014 letter to the British medical journal ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
'', it was suggested that the French Revolution leader Maximilien Robespierre
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre (; ; 6 May 1758 – 28 July 1794) was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognised as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre ferv ...
may have had sarcoidosis, causing him impairment during his time as head of the Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (French: ''La Terreur'', literally "The Terror") was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the French First Republic, First Republic, a series of massacres and Capital punishment in France, nu ...
. The symptoms associated with Ludwig van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire ...
's 1827 death have been described as possibly consistent with sarcoidosis. Author Robert Louis Stevenson
Robert Louis Stevenson (born Robert Lewis Balfour Stevenson; 13 November 1850 – 3 December 1894) was a Scottish novelist, essayist, poet and travel writer. He is best known for works such as ''Treasure Island'', ''Strange Case of Dr Jekyll ...
(1850–1894) had a history of chronic coughs and chest complaints, and sarcoidosis has been suggested as a diagnosis.
Pregnancy
Sarcoidosis generally does not prevent successful pregnancy and delivery; the increase in estrogen levels during pregnancy may even have a slightly beneficial immunomodulatory effect. In most cases, the course of the disease is unaffected by pregnancy, with improvement in a few cases and worsening of symptoms in very few cases, although a number of the immunosuppressants (such asmethotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
, cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
) used in corticosteroid-refractory sarcoidosis are known teratogens
Teratology is the study of abnormalities of physiological development in organisms during their life span. It is a sub-discipline in medical genetics which focuses on the classification of congenital abnormalities in Dysmorphic feature, dysmor ...
. Increased risks associated with sarcoidosis ranging from 30 to 70% have been reported for preeclampsia/eclampsia, cesarian or preterm delivery as well as (non-cardiac) birth defects in first singleton pregnancies. In absolute numbers, birth defects and other complications such as maternal death, cardiac arrest, placental abruption or venous thromboembolism are extremely rare in sarcoidosis pregnancies.
References
External links
Sarcoidosis UK Information Hub
* {{Authority control Ailments of unknown cause Lung disorders Abdominal pain Monocyte- and macrophage-related cutaneous conditions Autoimmune diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Steroid-responsive inflammatory conditions Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate