Sterling (
symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
:
£;
currency code: GBP) is the
currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific envi ...
of the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main
unit
Unit may refer to:
General measurement
* Unit of measurement, a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law
**International System of Units (SI), modern form of the metric system
**English units, histo ...
of sterling,
and the word ''
pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency generally,
often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling.
Sterling is the world's oldest currency in continuous use since its inception.
In 2022, it was the fourth-most-traded currency in the
foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, ...
, after the
United States dollar
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and International use of the U.S. dollar, several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introdu ...
, the
euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
, and the
Japanese yen
The is the official currency of Japan. It is the third-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar and the euro. It is also widely used as a third reserve currency after the US dollar and the euro.
Th ...
. Together with those three currencies and the
renminbi
The renminbi ( ; currency symbol, symbol: Yen and yuan sign, ¥; ISO 4217, ISO code: CNY; abbreviation: RMB), also known as the Chinese yuan, is the official currency of the China, People's Republic of China. The renminbi is issued by the Peop ...
, it forms the
basket of currencies
A currency basket is a portfolio of selected currencies with different weightings. A currency basket is commonly used by investors to minimize the risk of currency fluctuations and also governments when setting the market value of a country's ...
that
calculate the value of
IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of la ...
special drawing rights
Special drawing rights (SDRs, code ) are supplementary foreign exchange reserve assets defined and maintained by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). SDRs are units of account for the IMF, and not a currency ''per se''. They represent a claim ...
. As of late 2022, sterling is also the fourth most-held
reserve currency
A reserve currency is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international transactions, internat ...
in
global reserves.
The
Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
is the
central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
for sterling, issuing its own banknotes and regulating issuance of banknotes by private banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland. Sterling banknotes issued by other jurisdictions are not regulated by the Bank of England; their governments
guarantee convertibility at par. Historically, sterling was also used to varying degrees by the colonies and territories of the
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
.
Names
Etymology

The basic unit of currency in medieval England was the
silver penny
A penny is a coin (: pennies) or a unit of currency (: pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. At present, it is t ...
or sterling, weighing about of a
tower pound. 240 of these coins made a "pound of sterlings". This term (shortened to "pound sterling" in later usage) continued to be used in accounting even after the sterling had ceased to circulate. The earliest known instances of the term occur in
Orderic Vitalis
Orderic Vitalis (; 16 February 1075 – ) was an English chronicler and Benedictine monk who wrote one of the great contemporary chronicles of 11th- and 12th-century Normandy and Anglo-Norman England.Hollister ''Henry I'' p. 6 Working out of ...
's 12th-century ''Historia Ecclesiastica'', which makes mention of ''librae sterilensium''.
The origin of the word ''sterling'' itself is unclear. It first appears in the 11th and 12th centuries, suggesting that it was coined to describe the new, heavier penny introduced by the
Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; ; ) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and locals of West Francia. The Norse settlements in West Franc ...
. According to the ''
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
'', the most plausible theory is that it represents
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
*, meaning "coin with a star" (a pair of stars having appeared on certain Norman pennies).
[ The numismatist ]Philip Grierson
Philip Grierson, (15 November 1910 – 15 January 2006) was a British historian and numismatist. He was Professor of Numismatics at Cambridge University and a fellow of Gonville and Caius College for over seventy years. During his long and e ...
rejects this, however, noting that the starred penny was only minted between 1077 and 1080 and formed a tiny fraction of the total coinage issued by the Normans. Grierson suggests instead that the first element is *, meaning "stout" or "strong". In support of this theory, he notes that the Roman solidus
Solidus (Latin for "solid") may refer to:
* Solidus (coin)
The ''solidus'' (Latin 'solid'; : ''solidi'') or ''nomisma'' () was a highly pure gold coin issued in the Later Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire. It was introduced in the early ...
had a name with a very similar meaning and was also introduced to replace a lighter coin.Hanseatic
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the ...
merchants, is untenable on historical and phonological grounds.[
]
Symbol
The currency sign
A currency symbol or currency sign is a graphic symbol used to denote a currency unit. Usually it is defined by a monetary authority, such as the national central bank for the currency concerned.
A symbol may be positioned in various ways, acc ...
for the pound unit of sterling is , which (depending on typeface) may be drawn with one or two bars:[ ("£1 1st Series Treasury Issue" to "£5 Series B")] Historically, a simple capital (in the historic black-letter typeface, ) placed before the numerals, or an italic ''l.'' after them, was used in newspapers, books and letters. The Royal Mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's official maker of British coins. It is currently located in Llantrisant, Wales, where it moved in 1968.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly ow ...
was still using this style of notation as late as 1939. Use of the letter for pound derives from medieval Latin documents: "L" was the abbreviation for , the Roman pound
The units of measurement of ancient Rome were generally consistent and well documented.
Length
The basic unit of Roman linear measurement was the ''pes'' (plural: ''pedes'') or Roman foot. Investigation of its relation to the English foot goes ...
(weight), which in time became an English unit of weight defined as the tower pound. A "pound sterling" was literally a tower pound (weight) of sterling silver
Sterling silver is an alloy composed mass fraction (chemistry), by weight of 92.5% silver and 7.5% other metals, usually copper. The sterling silver silver standards, standard has a minimum millesimal fineness of 925.
''Fineness, Fine silver'' ...
.duodecimal
The duodecimal system, also known as base twelve or dozenal, is a positional numeral system using twelve as its base. In duodecimal, the number twelve is denoted "10", meaning 1 twelve and 0 units; in the decimal system, this number is i ...
) currency system, the term £sd
file:Guildhall Museum Collection- Drusilla Dunford Money Table Sampler 3304.JPG, A Sampler (needlework), sampler in the Rochester Guildhall, Guildhall Museum of Rochester, Medway, Rochester illustrates the conversion between pence and shillings ...
(or Lsd) for pounds, shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currency, currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 1 ...
s and pence
A penny is a coin (: pennies) or a unit of currency (: pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. At present, it is t ...
referred to the Roman , ''solidus
Solidus (Latin for "solid") may refer to:
* Solidus (coin)
The ''solidus'' (Latin 'solid'; : ''solidi'') or ''nomisma'' () was a highly pure gold coin issued in the Later Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire. It was introduced in the early ...
'', and ''denarius
The ''denarius'' (; : ''dēnāriī'', ) was the standard Ancient Rome, Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the ''antoninianus''. It cont ...
''.ISO 4217
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individ ...
code "GBP" (e.g., GBP 12,000) may also be seen should disambiguation become necessary.
Currency code
The ISO 4217
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individ ...
currency code for sterling is "GBP", formed from the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2
ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 codes are two-letter country codes defined in ISO 3166-1, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), to represent countries, dependent territories, and special ...
code for the United Kingdom ("GB") and the first letter of "pound".
In historical sources and some specialist banking uses, the abbreviation stg (in various styles) has been used to indicate sterling.London Stock Exchange
The London Stock Exchange (LSE) is a stock exchange based in London, England. the total market value of all companies trading on the LSE stood at US$3.42 trillion. Its current premises are situated in Paternoster Square close to St Paul's Cath ...
are quoted in penny sterling, using the unofficial code "GBX".
Cable
The exchange rate of sterling against the US dollar
The United States dollar (symbol: $; currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it int ...
is referred to as "cable" in the wholesale foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, ...
s. The origins of this term are attributed to the fact that from the mid-19th century, the sterling/dollar exchange rate was transmitted via transatlantic cable.
Slang terms
Historically almost every British coin had a widely recognised nickname, such as "tanner" for the sixpence and "bob" for the shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currency, currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 1 ...
.quid pro quo
''Quid pro quo'' (Latin: "something for something") is a Latin phrase used in English to mean an exchange of goods or services, in which one transfer is contingent upon the other; "a favor for a favor". Phrases with similar meanings include: " ...
'', literally, "what for what", or, figuratively, "An equal exchange or substitution". The term "nicker" (also both singular and plural) may also refer to the pound.
Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories
The currency of all the Crown Dependencies
The Crown Dependencies are three dependent territory, offshore island territories in the British Islands that are self-governing possessions of the The Crown, British Crown: the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Jersey, Bailiwick of Jersey, both lo ...
(Guernsey
Guernsey ( ; Guernésiais: ''Guernési''; ) is the second-largest island in the Channel Islands, located west of the Cotentin Peninsula, Normandy. It is the largest island in the Bailiwick of Guernsey, which includes five other inhabited isl ...
, Jersey
Jersey ( ; ), officially the Bailiwick of Jersey, is an autonomous and self-governing island territory of the British Islands. Although as a British Crown Dependency it is not a sovereign state, it has its own distinguishing civil and gov ...
, Isle of Man
The Isle of Man ( , also ), or Mann ( ), is a self-governing British Crown Dependency in the Irish Sea, between Great Britain and Ireland. As head of state, Charles III holds the title Lord of Mann and is represented by a Lieutenant Govern ...
) and a third of British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs) or alternatively referred to as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs) are the fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom that, ...
(British Antarctic Territory
The British Antarctic Territory (BAT) is a sector of Antarctica claimed by the United Kingdom as one of its 14 British Overseas Territories, of which it is by far the largest by area. It comprises the region south of 60°S latitude and betwee ...
; Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; ), commonly referred to as The Falklands, is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and from Cape Dub ...
and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI) is a British Overseas Territory in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands known as the ...
; Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
; and Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory located in the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and consisting of the island of Saint Helena, Ascension Island, and the archipelago of Tri ...
) is either sterling or pegged to sterling at par.
The other British Overseas Territories have a local currency that is pegged to the U.S. dollar
The United States dollar (symbol: $; currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it int ...
or the New Zealand dollar
The New Zealand dollar (; currency sign, sign: $; ISO 4217, code: NZD) is the official currency and legal tender of New Zealand, the Cook Islands, Niue, the Ross Dependency, Tokelau, and a British territory, the Pitcairn Islands. Within New Zeal ...
. The Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia (), officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA), is a British Overseas Territory made of two non-contiguous areas on the island of Cyprus. The areas, which include British military bases and instal ...
(in Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
) use the euro.
Subdivisions and other units
Decimal coinage
Since decimalisation
Decimalisation or decimalization (see American and British English spelling differences, spelling differences) is the conversion of a system of currency or of weights and measures to units related by Power of 10, powers of 10.
Most countries have ...
on Decimal Day
Decimal Day () in the United Kingdom and in Republic of Ireland, Ireland was Monday 15 February 1971, the day on which each country decimalised its respective £sd currency of pound sterling, pounds, Shilling (British coin), shillings, and pe ...
in 1971, the pound has been divided into 100 pence (denoted on coinage, until 1981, as "new pence"). The symbol for the penny is "p"; hence an amount such as 50p (£0.50) properly pronounced "fifty pence" is often pronounced "fifty pee" /fɪfti piː/. The old sign ''d'' was not reused for the ''new penny'' in order to avoid confusion between the two units. A decimal halfpenny (p, worth 1.2 old pennies) was issued until 1984 but was withdrawn due to inflation.
Pre-decimal
Before decimalisation in 1971, the pound was divided into 20 shillings
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 12 pence ...
, and each shilling into 12 pence
A penny is a coin (: pennies) or a unit of currency (: pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. At present, it is t ...
, making 240 pence to the pound. The symbol for the shilling was "''s''." not from the first letter of "shilling", but from the Latin ''solidus
Solidus (Latin for "solid") may refer to:
* Solidus (coin)
The ''solidus'' (Latin 'solid'; : ''solidi'') or ''nomisma'' () was a highly pure gold coin issued in the Later Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire. It was introduced in the early ...
''. The symbol for the penny was "''d''.", from the French ''denier'', from the Latin ''denarius
The ''denarius'' (; : ''dēnāriī'', ) was the standard Ancient Rome, Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the ''antoninianus''. It cont ...
'' (the solidus and denarius were Roman coins). A mixed sum of shillings and pence, such as 3 shillings and 6 pence, was written as "3/6" or "3''s''. 6''d''." and spoken as "three and six" or "three and sixpence" except for "1/1", "2/1" etc., which were spoken as "one and a penny", "two and a penny", etc. 5 shillings, for example, was written as "5''s''." or, more commonly, "5/–" (five shillings, no pence).
Various coin denominations had, and in some cases continue to have, special names, such as florin
The Florentine florin was a gold coin (in Italian ''Fiorino d'oro'') struck from 1252 to 1533 with no significant change in its design or metal content standard during that time.
It had 54 grains () of nominally pure or 'fine' gold with a pu ...
(2/–), crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, parti ...
(5/–), farthing (''d''), sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title that can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to ...
(£1) and guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
(21s, 21/–, £1–1–0 or £1.05 in decimal notation).
By the 1950s, coins of Kings George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and ...
, George IV and William IV had disappeared from circulation, but coins (at least the penny) bearing the head of every British monarch from Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
onwards could be found in circulation. Silver coins were replaced by those in cupro-nickel
Cupronickel or copper–nickel (CuNi) is an alloy of copper with nickel, usually along with small quantities of other metals added for strength, such as iron and manganese. The copper content typically varies from 60 to 90 percent. ( Monel is a ...
in 1947, and by the 1960s the silver coins were rarely seen. Silver/cupro-nickel sixpences, shillings (from any period after 1816) and florin
The Florentine florin was a gold coin (in Italian ''Fiorino d'oro'') struck from 1252 to 1533 with no significant change in its design or metal content standard during that time.
It had 54 grains () of nominally pure or 'fine' gold with a pu ...
s (2 shillings) remained legal tender after decimalisation (as 2½p, 5p and 10p respectively) until 1980, 1990 and 1993 respectively, but are now officially demonetised.
History (600–1945)
 The pound sterling emerged after the adoption of the Carolingian monetary system in England . Here is a summary of changes to its value in terms of silver or gold until 1816.
The pound sterling emerged after the adoption of the Carolingian monetary system in England . Here is a summary of changes to its value in terms of silver or gold until 1816.
Anglo-Saxon
 The pound was a unit of account in
The pound was a unit of account in Anglo-Saxon England
Anglo-Saxon England or early medieval England covers the period from the end of Roman Empire, Roman imperial rule in Roman Britain, Britain in the 5th century until the Norman Conquest in 1066. Compared to modern England, the territory of the ...
. By the ninth century it was equal to 240 silver pence
A penny is a coin (: pennies) or a unit of currency (: pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. At present, it is t ...
.
The accounting system of dividing one pound into twenty shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currency, currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 1 ...
s, a shilling into twelve pence, and a penny into four farthings was adopted from the livre carolingienne
The livre (abbreviation: Pound sign, £ or Livre tournois, ₶., French language, French for (pound)) was the currency of Kingdom of France and its predecessor states of Francia and West Francia from 781 to 1794. Several different livres exist ...
system introduced by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
to the Frankish Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lomba ...
. The penny was abbreviated to "d", from ''denarius
The ''denarius'' (; : ''dēnāriī'', ) was the standard Ancient Rome, Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the ''antoninianus''. It cont ...
'', the Roman equivalent of the penny; the shilling to "s" from solidus
Solidus (Latin for "solid") may refer to:
* Solidus (coin)
The ''solidus'' (Latin 'solid'; : ''solidi'') or ''nomisma'' () was a highly pure gold coin issued in the Later Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire. It was introduced in the early ...
(written with a long s
The long s, , also known as the medial ''s'' or initial ''s'', is an Archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter , found mostly in works from the late 8th to early 19th centuries. It replaced one or both of the letters ''s'' in a double-''s ...
, , later evolving into a simple slash
Slash may refer to:
* Slash (punctuation), the "/" character
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Slash (Marvel Comics)
* Slash (''Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles'')
Music
* Harry Slash & The Slashtones, an American rock band
* Nash th ...
, ); and the pound to "L" (subsequently £) from ''Libra
Libra generally refers to:
* Libra (constellation), a constellation
* Libra (astrology), an astrological sign based on the star constellation
Libra may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Libra'' (novel), a 1988 novel by Don DeLillo
Musi ...
'' or ''Livre
Livre may refer to:
Currency
* French livre, one of a number of obsolete units of currency of France
* Livre tournois, one particular obsolete unit of currency of France
* Livre parisis, another particular obsolete unit of currency of France
* Fre ...
''.
The origins of sterling lie in the reign of King Offa of Mercia (757–796), who introduced a "sterling" coin made by physically dividing a Tower pound (5,400 grains, 349.9 grams) of silver into 240 parts. In practice, the weights of the coins were not consistent, 240 of them seldom added up to a full pound; there were no shilling or pound coins and these units were used only as an accounting convenience.
Halfpennies and farthings worth and penny respectively were also minted, but small change was more commonly produced by cutting up a whole penny.
Medieval, 1158
 The early pennies were struck from fine silver (as pure as was available). In 1158, a new coinage was introduced by King
The early pennies were struck from fine silver (as pure as was available). In 1158, a new coinage was introduced by King Henry II
Henry II may refer to:
Kings
* Saint Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor (972–1024), crowned King of Germany in 1002, of Italy in 1004 and Emperor in 1014
*Henry II of England (1133–89), reigned from 1154
*Henry II of Jerusalem and Cyprus (1271–1 ...
(known as the '' Tealby penny''), with a Tower Pound (5,400 grains, 349.9 g) of 92.5% silver minted into 240 pennies, each penny containing 20.82 grains (1.349 g) of fine silver.sterling silver
Sterling silver is an alloy composed mass fraction (chemistry), by weight of 92.5% silver and 7.5% other metals, usually copper. The sterling silver silver standards, standard has a minimum millesimal fineness of 925.
''Fineness, Fine silver'' ...
, the alloy is harder than the 99.9% fine silver
The fineness of a precious metal object (coin, bar, jewelry, etc.) represents the weight of ''fine metal'' therein, in proportion to the total weight which includes alloying base metals and any impurities. Alloy metals are added to increase hardn ...
that was traditionally used, and sterling silver coins did not wear down as rapidly as fine silver ones.
The introduction of the larger French ''gros tournois
Gros may refer to:
People
*Gros (surname)
* Gross (surname), the German variant of Gros
* Le Gros, the Norman variant of Gros
Other uses
* Gros (coinage), a type of 13th-century silver coinage of France
* Gros (grape), another name for Elbling, ...
'' coins in 1266, and their subsequent popularity, led to additional denominations in the form of groats
Groats (or in some cases, "berries") are the hulled kernels of various cereal grains, such as oats, wheat, rye, and barley. Groats are whole grains that include the cereal germ and fiber-rich bran portion of the grain, as well as the endos ...
worth four pence and half groats worth two pence.gold penny
The gold penny was a medieval English coin with a value of twenty pence (i.e. pound sterling), minted in 1257 during the reign of Henry III. The coin was short-lived as it quickly became undervalued, which led to its almost complete disappeara ...
weighing twice the silver penny and valued at 20 silver pence was also issued in 1257 but was not successful.
The English penny remained nearly unchanged from 800 and was a prominent exception in the progressive debasements of coinage which occurred in the rest of Europe. The Tower Pound, originally divided into 240 pence, devalued to 243 pence by 1279.
Edward III, 1351
 During the reign of
During the reign of King Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after t ...
, the introduction of gold coins received from Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
as payment for English wool provided substantial economic and trade opportunities but also unsettled the currency for the next 200 years.
Henry IV, 1412
The exigencies of the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a conflict between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France and a civil war in France during the Late Middle Ages. It emerged from feudal disputes over the Duchy ...
during the reign of King Henry IV resulted in further debasements toward the end of his reign, with the English penny reduced to 15 grains sterling silver (0.899 g fine silver) and the half-noble reduced to 54 grains (3.481 g fine gold).stuiver
The stuiver was a coin used in the Netherlands, worth of a guilder (16 ''penning'' or 8 '' duit'', later 5 cents). It was also minted on the Lower Rhine region and the Dutch colonies. The word can still refer to the 5 euro cent coin, which ...
(shilling) of 1.63 g fine silver was valued close to 2 pence sterling at 1.8 g.[ which gives the fine silver content of a Stuiver as 3.4 × 0.479 or almost 1.63 g.] This approximate pairing of English half-nobles and half-groats to Continental ''livres'' and ''sols'' persisted up to the 1560s.
Great slump, 1464
The Great Bullion Famine
The Great Bullion Famine was a shortage of precious metals that struck Europe in the 15th century, with the worst years of the famine lasting from 1457 to 1464. During the Middle Ages, gold and silver coins saw widespread use as currency in Europ ...
and the Great Slump of the mid-15th century resulted in another reduction in the English penny to 12 grains sterling silver (0.719 g fine silver) and the introduction of a new half-angel gold coin of 40 grains (2.578 g), worth th pound or 40 pence.Burgundian Netherlands
The Burgundian Netherlands were those parts of the Low Countries ruled by the Dukes of Burgundy during the Burgundian Age between 1384 and 1482. Within their Burgundian State, which itself belonged partly to the Holy Roman Empire and partly t ...
made the English groat (4-pence) mutually exchangeable with the Burgundian ''double patard'' (or 2-''stuiver'') minted under Charles the Bold
Charles Martin (10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), called the Bold, was the last duke of Burgundy from the House of Valois-Burgundy, ruling from 1467 to 1477. He was the only surviving legitimate son of Philip the Good and his third wife, ...
.Troy Ounce
Troy weight is a system of units of mass that originated in the Kingdom of England in the 15th century and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The troy weight units are the grain, the pennyweight (24 grains), the troy ounce (20 p ...
(480 grains, 31.1035 g) of sterling silver. It was approximately on a par with France's livre parisis
The (; ), also known as the Paris or Parisian livre, was a medieval French coin and unit of account originally notionally equivalent to a French pound of silver. It was the chief currency of the Capetian dynasty before being generally replac ...
of one French ounce (30.594 g), and in 1524 it would also be the model for a standardised German currency in the form of the Guldengroschen
The ''Guldengroschen'' or ''Guldiner'' was a large silver coin originally minted in Tirol in 1486, but which was introduced into the Duchy of Saxony in 1500.
The name "''Guldengroschen''" came from the fact that it has an equivalent denominat ...
, which also weighed 1 German ounce of silver or .
Tudor, 1551
 The last significant depreciation in sterling's
The last significant depreciation in sterling's silver standard
The silver standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed weight of silver. Silver was far more widespread than gold as the monetary standard worldwide, from the Sumerians 3000 BC until 1873. Following t ...
occurred amidst the 16th century influx of precious metals from the Americas arriving through the Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands were the parts of the Low Countries that were ruled by sovereigns of the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. This rule began in 1482 and ended for the Northern Netherlands in 1581 and for the Southern Netherlands in 1797. ...
. Enforcement of monetary standards amongst its constituent provinces was loose, spending under King Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
was extravagant, and England loosened the importation of cheaper continental coins for exchange into full-valued English coins.the Great Debasement
The Great Debasement (1544–1551) was a currency debasement policy introduced in 1544 England under the order of Henry VIII which saw the amount of precious metal in gold and silver coins reduced and in some cases replaced entirely with cheaper ba ...
which resulted in a significant rd reduction in the bullion content of each pound sterling in 1551.Crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, parti ...
.
Prior to 1551, English coin denominations closely matched with corresponding sol (2''d'') and livre (40''d'') denominations in the Continent, namely:
* Silver; see farthing (''d''), halfpenny (''d''), penny
A penny is a coin (: pennies) or a unit of currency (: pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. At present, it is ...
(1''d''), half-groat (2''d''), and groat (4''d'')
* Gold; see ''1351'': noble (20''d''), noble (40''d'') and noble or angel
An angel is a spiritual (without a physical body), heavenly, or supernatural being, usually humanoid with bird-like wings, often depicted as a messenger or intermediary between God (the transcendent) and humanity (the profane) in variou ...
(80''d'').
After 1551 new denominations were introduced,shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currency, currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 1 ...
or testoon (1s or 1/–).
* In silver or gold: the crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, parti ...
(5/- (5s) or 60''d''), replacing the angel of 40''d''; and the half crown (2/6''d'' or 30''d''), replacing the angel of 20''d''
* And in gold: the new half sovereign
The half sovereign is a British gold coin face value, denominated at one-half of a pound sterling. First issued in its present form in 1817, it has been struck by the Royal Mint in most years since 1980 as a collector's and bullion coin, bulli ...
(10/–) and sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title that can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to ...
(£1 or 20/–)
1601 to 1816
 The silver basis of sterling remained essentially unchanged until the 1816 introduction of the Gold Standard, save for the increase in the number of pennies in a troy ounce from 60 to 62 (hence, 0.464 g fine silver in a penny). Its gold basis remained unsettled, however, until the gold guinea was fixed at 21 shillings in 1717.
The
The silver basis of sterling remained essentially unchanged until the 1816 introduction of the Gold Standard, save for the increase in the number of pennies in a troy ounce from 60 to 62 (hence, 0.464 g fine silver in a penny). Its gold basis remained unsettled, however, until the gold guinea was fixed at 21 shillings in 1717.
The guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
was introduced in 1663 with guineas minted out of 12 troy ounces of 22-karat gold (hence, 7.6885 g fine gold) and initially worth £1 or 20 shillings. While its price in shillings was not legally fixed at first, its persistent trade value above 21 shillings reflected the poor state of clipped underweight silver coins tolerated for payment. Milled shillings of full weight were hoarded and exported to the Continent
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous mainland of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by so ...
, while clipped, hand-hammered shillings stayed in circulation (as Gresham's law
In economics, Gresham's law is a monetary principle stating that "bad money drives out good". For example, if there are two forms of commodity money in circulation, which are accepted by law as having similar face value, the more valuable commo ...
describes).
In the 17th century, English merchants tended to pay for imports in silver but were generally paid for exports in gold. This effect was notably driven by trade with the Far East, as the Chinese insisted on payments for their exports being settled in silver. From the mid-17th century, around of silver were received by China, principally from European powers, in exchange for Chinese tea and other goods. In order to be able to purchase Chinese exports in this period, England initially had to export to other European nations and request payment in silver, until the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
was able to foster the indirect sale of opium to the Chinese.
Domestic demand for silver bullion in Britain further reduced silver coinage in circulation, as the improving fortunes of the merchant class led to increased demand for tableware. Silversmiths had always regarded coinage as a source of raw material, already verified for fineness by the government. As a result, sterling silver coins were being melted and fashioned into "sterling silverware" at an accelerating rate. An Act of the Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the Great Council of England, great council of Lords Spi ...
in 1697 tried to stem this tide by raising the minimum acceptable fineness on wrought plate from sterling's 92.5% to a new Britannia silver
Britannia silver is an alloy of silver containing 11 ozt 10 dwt (i.e. 11½ troy oz.) silver in the pound troy, equivalent to , or 95.833% by weight (mass) silver, the rest usually being copper.
This standard was introduced in England by Act o ...
standard of 95.83%. Silverware made purely from melted coins would be found wanting when the silversmith took his wares to the assay office Assay offices are institutions set up to assay (test the purity of) precious metals. This is often done to protect consumers from buying fake items. Upon successful completion of an assay (i.e. if the metallurgical content is found be equal or bette ...
, thus discouraging the melting of coins.
During the time of Sir Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment that followed. His book (''Mathe ...
, Master of the Mint
Mint or The Mint may refer to:
Plants
* Lamiaceae, the mint family
** ''Mentha'', the genus of plants commonly known as "mint"
Coins and collectibles
* Mint (facility), a facility for manufacturing coins
* Mint condition, a state of like-new ...
, the gold guinea was fixed at 21 shillings (£1/1/-) in 1717. But without addressing the problem of underweight silver coins, and with the high resulting gold-silver ratio of 15.2, it gave sterling a firmer footing in gold guineas rather than silver shillings, resulting in a de facto gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
. Silver and copper tokens issued by private entities partly relieved the problem of small change until the Great Recoinage of 1816.
Establishment of modern currency
The Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
was founded in 1694, followed by the Bank of Scotland
The Bank of Scotland plc (Scottish Gaelic: ''Banca na h-Alba'') is a commercial bank, commercial and clearing (finance), clearing bank based in Edinburgh, Scotland, and is part of the Lloyds Banking Group. The bank was established by the Par ...
a year later.}banknote
A banknote or bank notealso called a bill (North American English) or simply a noteis a type of paper money that is made and distributed ("issued") by a bank of issue, payable to the bearer on demand. Banknotes were originally issued by commerc ...
s from "the late 1600s".
Currency of Great Britain (1707) and the United Kingdom (1801)
In the 17th century Scots currency was pegged to sterling at a value of £12 Scots = £1 sterling.
In 1707, the kingdoms of England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
merged into the Kingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
. In accordance with the Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new political state of Great Britain. The treaty, effective since 1707, brought the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Ki ...
, the currency of Great Britain was sterling, with the pound Scots
The pound ( Modern and Middle Scots: ''Pund'') was the currency of Scotland prior to the 1707 Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England, which created the Kingdom of Great Britain. It was introduced by David I ...
soon being replaced by sterling at the pegged value.
In 1801, Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland (; , ) was a dependent territory of Kingdom of England, England and then of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1542 to the end of 1800. It was ruled by the monarchs of England and then List of British monarchs ...
were united to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the union of the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into one sovereign state, established by the Acts of Union 1800, Acts of Union in 1801. It continued in this form until ...
. However, the Irish pound
The pound ( Irish: ) was the currency of Ireland until 2002. Its ISO 4217 code was IEP, and the symbol was £ (or £Ir for distinction.) The Irish pound was replaced by the euro on 1 January 1999. Euro currency did not begin circulation unti ...
was not replaced by sterling until January 1826. The conversion rate had long been £13 Irish to £12 sterling. In 1928, six years after the Anglo-Irish Treaty
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty (), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain an ...
restored Irish autonomy within the British Empire, the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-ye ...
established a new Irish pound, initially pegged at par to sterling.
Use in the Empire
Sterling circulated in much of the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
. In some areas it was used alongside local currencies. For example, the gold sovereign was legal tender in Canada despite the use of the Canadian dollar
The Canadian dollar (currency symbol, symbol: $; ISO 4217, code: CAD; ) is the currency of Canada. It is abbreviated with the dollar sign $. There is no standard disambiguating form, but the abbreviations Can$, CA$ and C$ are frequently used f ...
. Several colonies and dominions adopted the pound as their own currency. These included Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
, British West Africa
British West Africa was the collective name for British settlements in West Africa during the colonial period, either in the general geographical sense or the formal colonial administrative entity. British West Africa as a colonial entity was ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
, British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
, the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-ye ...
, Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
and Southern Rhodesia
Southern Rhodesia was a self-governing British Crown colony in Southern Africa, established in 1923 and consisting of British South Africa Company (BSAC) territories lying south of the Zambezi River. The region was informally known as South ...
. Some of these retained parity with sterling throughout their existence (e.g. the South African pound), while others deviated from parity after the end of the gold standard (e.g. the Australian pound). These currencies and others tied to sterling constituted the core of the sterling area
The sterling area (or sterling bloc, legally scheduled territories) was a group of countries that either adopted or pegged their currencies to the pound sterling.
The area began to appear informally during the early 1930s, after sterling had l ...
.
The original English colonies on mainland North America were not party to the sterling area because the above-mentioned silver shortage in England coincided with these colonies' formative years. As a result of equitable trade (and rather less equitable piracy), the Spanish milled dollar became the most common coin within the English colonies.
Gold standard
 During the
During the American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
and the Napoleonic wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
, Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
notes were legal tender
Legal tender is a form of money that Standard of deferred payment, courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment in court for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything ...
, and their value floated relative to gold. The Bank also issued silver tokens to alleviate the shortage of silver coins. In 1816, the gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
was adopted officially, with silver coins minted at a rate of 66 shillings to a troy pound (weight) of sterling silver, thus rendering them as "token" issues (i.e. not containing their value in precious metal). In 1817, the sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title that can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to ...
was introduced, valued at 20/–. Struck in 22‑carat gold, it contained 113 grains or of fine gold and replaced the guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
as the standard British gold coin without changing the gold standard.
By the 19th century, sterling notes were widely accepted outside Britain. The American journalist Nellie Bly
Elizabeth Cochrane Seaman (born Elizabeth Jane Cochran; May 5, 1864 – January 27, 1922), better known by her pen name Nellie Bly, was an American journalist who was widely known for her record-breaking circumnavigation, trip around the world ...
carried Bank of England notes on her 1889–1890 trip around the world in 72 days.United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, Can$
The Canadian dollar (currency symbol, symbol: $; ISO 4217, code: CAD; ) is the currency of Canada. It is abbreviated with the dollar sign $. There is no standard disambiguating form, but the abbreviations Can$, CA$ and C$ are frequently used f ...
4.87 in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, ƒ12.11 in Dutch territories, F 25.22 in French territories
Overseas France (, also ) consists of 13 French territories outside Europe, mostly the remnants of the French colonial empire that remained a part of the French state under various statuses after decolonisation. Most are part of the European ...
(or equivalent currencies of the Latin Monetary Union
The Monetary Convention of 23 December 1865 was a unified system of coinage that provided a degree of monetary integration among several European countries, initially Belgium, France, Italy and Switzerland, at a time when the circulation of bank ...
), 20 ℳ 43 ₰ in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Rbls 9.46 in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
or K 24.02 in Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
. After the International Monetary Conference of 1867 in Paris, the possibility of the UK joining the Latin Monetary Union
The Monetary Convention of 23 December 1865 was a unified system of coinage that provided a degree of monetary integration among several European countries, initially Belgium, France, Italy and Switzerland, at a time when the circulation of bank ...
was discussed, and a Royal Commission
A royal commission is a major ad-hoc formal public inquiry into a defined issue in some monarchies. They have been held in the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Norway, Malaysia, Mauritius and Saudi Arabia. In republics an equi ...
on International Coinage examined the issues, resulting in a decision against joining it.
First world war: suspension of the gold standard
The gold standard was suspended at the outbreak of First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
in 1914, with Bank of England and Treasury notes becoming legal tender. Before that war, the United Kingdom had one of the world's strongest economies
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with ...
, holding 40% of the world's overseas investments. But after the end of the war, the country was highly indebted: Britain owed £850 million (about £ today) with interest costing the country some 40% of all government spending. The British government under Prime Minister David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. A Liberal Party (United Kingdom), Liberal Party politician from Wales, he was known for leadi ...
and Chancellor of the Exchequer Austen Chamberlain
Sir Joseph Austen Chamberlain (16 October 1863 – 16 March 1937) was a British statesman, son of Joseph Chamberlain and older half-brother of Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain. He served as a Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of ...
tried to make up for the deficit with a deflationary policy, but this only led to the Depression of 1920–21
Depression may refer to:
Mental health
* Depression (mood), a state of low mood and aversion to activity
* Mood disorders characterized by depression are commonly referred to as simply ''depression'', including:
** Major depressive disorder, al ...
.
By 1917, production of gold sovereigns had almost halted (the remaining production was for collector's sets and other very specific occasions), and by 1920, the silver coinage was debased from its original .925 fine to just .500 fine. That was due to a drastic increase in silver prices from an average 27/6''d''. �1.375per troy pound
Troy weight is a system of Physical unit, units of mass that originated in the Kingdom of England in the 15th century and is primarily used in the precious metals industry. The troy weight units are the Grain (unit), grain, the pennyweight (24 ...
in the period between 1894 and 1913, to 89/6''d''. �4.475in August 1920.
Interwar period: gold standard reinstated
To try to resume stability, a version of the gold standard was reintroduced in 1925, under which the currency was fixed to gold at its pre-war peg, but one could only exchange currency for gold bullion, not for coins. On 21 September 1931, this was abandoned during the Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
, and sterling suffered an initial devaluation of some 25%.
Since the suspension of the gold standard in 1931, sterling has been a fiat currency
Fiat money is a type of government-issued currency that is not backed by a precious metal, such as gold or silver, nor by any other tangible asset or commodity. Fiat currency is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tender, ...
, with its value determined by its continued acceptance in the national and international economy.
World War II
In 1940, an agreement with the US pegged sterling to the US dollar
The United States dollar (symbol: $; currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it int ...
at a rate of £1 = US$4.03. (Only the year before, it had been US$4.86.) This rate was maintained through the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and became part of the Bretton Woods system
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial relations among 44 countries, including the United States, Canada, Western European countries, and Australia, after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement until the ...
which governed post-war exchange rates.
History (1946–present)
Bretton Woods
Under continuing economic pressure, and despite months of denials that it would do so, on 19 September 1949 the government devalued the pound by 30.5% to US$2.80.currency markets
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, it i ...
, exchange controls
Foreign exchange controls are various forms of controls imposed by a government on the purchase/sale of foreign currencies by residents, on the purchase/sale of local currency by nonresidents, or the transfers of any currency across national bo ...
were tightened by the Wilson government. Among the measures, tourists were banned from taking more than £50 out of the country in travellers' cheques and remittances, plus £15 in cash; this restriction was not lifted until 1979. Sterling was devalued by 14.3% to £1 = US$2.40 on 18 November 1967.
Decimalisation
Until decimalisation, amounts in sterling were expressed in pounds, shillings, and pence, with various widely understood notations. The same amount could be stated as 32''s''. 6''d''., 32/6, £1. 12''s''. 6''d''., or £1/12/6. It was customary to specify some prices (for example professional fees and auction prices for works of art) in guineas (abbr: gn. or gns.), although guinea coins were no longer in use.
Formal parliamentary proposals to decimalise sterling were first made in 1824 when Sir John Wrottesley, MP for Staffordshire
Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation ''Staffs''.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England. It borders Cheshire to the north-west, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, ...
, asked in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
whether consideration had been given to decimalising the currency. Wrottesley raised the issue in the House of Commons again in 1833, and it was again raised by John Bowring
Sir John Bowring , or Phrayā Siam Mānukūlakicca Siammitra Mahāyaśa (17 October 1792 – 23 November 1872) was a British political economist, traveller, writer, literary translator, polyglot and the fourth Governor of Hong Kong. He was ...
, MP for Kilmarnock Burghs, in 1847 whose efforts led to the introduction in 1848 of what was in effect the first decimal coin in the United Kingdom, the florin, valued at one-tenth of a pound. However, full decimalisation was resisted, although the florin coin, re-designated as ''ten new pence'', survived the transfer to a full decimal system in 1971, with examples surviving in British coinage until 1993.
John Benjamin Smith
John Benjamin Smith (7 February 1794 – 15 September 1879) was an English Liberal Party politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1847 to 1874.
Life
Smith was the son of Benjamin Smith, a merchant of Manchester. He was himself a merchan ...
, MP for Stirling Burghs, raised the issue of full decimalisation again in Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
in 1853, resulting in the Chancellor of the Exchequer, William Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British politican, starting as Conservative MP for Newark and later becoming the leader of the Liberal Party.
In a career lasting over 60 years, he was Prime Minister ...
, announcing soon afterwards that "the great question of a decimal coinage" was "now under serious consideration". A full proposal for the decimalisation of sterling was then tabled in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
in June 1855, by William Brown, MP for Lancashire Southern, with the suggestion that the pound sterling be divided into one thousand parts, each called a "mil", or alternatively a farthing, as the pound was then equivalent to 960 farthings which could easily be rounded up to one thousand farthings in the new system. This did not result in the conversion of sterling into a decimal system, but it was agreed to establish a Royal Commission
A royal commission is a major ad-hoc formal public inquiry into a defined issue in some monarchies. They have been held in the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Norway, Malaysia, Mauritius and Saudi Arabia. In republics an equi ...
to look into the issue. However, largely due to the hostility to decimalisation of two of the appointed commissioners, Lord Overstone (a banker) and John Hubbard (Governor of the Bank of England
The governor of the Bank of England is the most senior position in the Bank of England. It is nominally a civil service post, but the appointment tends to be from within the bank, with the incumbent choosing and mentoring a successor. The governor ...
), decimalisation in Britain was effectively quashed for over a hundred years.
However, sterling was decimalised in various British colonial territories before the United Kingdom (and in several cases in line with William Brown's proposal that the pound be divided into 1,000 parts, called mils). These included Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
from 1863 to 1866; Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
from 1955 until 1960 (and continued on the island as the division of the Cypriot pound
The pound, or lira (, plural , and , , from the Latin language, Latin via the Italian language, Italian ; Currency symbol, sign: £, sometimes £C for distinction), was the currency of Cyprus, including the Sovereign Base Areas in Akrotiri and D ...
until 1983); and the Palestine Mandate
The Mandate for Palestine was a League of Nations mandate for British administration of the territories of Palestine and Transjordanwhich had been part of the Ottoman Empire for four centuriesfollowing the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in Wo ...
from 1926 until 1948.
Later, in 1966, the UK Government decided to include in the Queen's Speech
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or their representative, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a session is opened. The address sets fo ...
a plan to convert sterling into a decimal currency. As a result of this, on 15 February 1971, the UK decimalised sterling, replacing the shilling and the penny with a single subdivision, the ''new penny'', which was worth 2.4''d''. For example, a price tag of £1/12/6. became . The word "new" was omitted from coins minted after 1981.
Free-floating pound
 With the breakdown of the
With the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial relations among 44 countries, including the United States, Canada, Western European countries, and Australia, after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement until the ...
, sterling floated from August 1971 onwards. At first, it appreciated a little, rising to almost in March 1972 from , the upper bound of the band in which it had been fixed. The sterling area
The sterling area (or sterling bloc, legally scheduled territories) was a group of countries that either adopted or pegged their currencies to the pound sterling.
The area began to appear informally during the early 1930s, after sterling had l ...
effectively ended at this time, when the majority of its members also chose to float freely against sterling and the dollar.
1976 sterling crisis

James Callaghan
Leonard James Callaghan, Baron Callaghan of Cardiff ( ; 27 March 191226 March 2005) was a British statesman and Labour Party (UK), Labour Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1976 to 1979 and Leader of the L ...
became Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
in 1976. He was immediately told the economy was facing huge problems, according to documents released in 2006 by the National Archives
National archives are the archives of a country. The concept evolved in various nations at the dawn of modernity based on the impact of nationalism upon bureaucratic processes of paperwork retention.
Conceptual development
From the Middle Ages i ...
. The effects of the failed Barber Boom and the 1973 oil crisis
In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against countries that had supported Israel at any point during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, which began after Eg ...
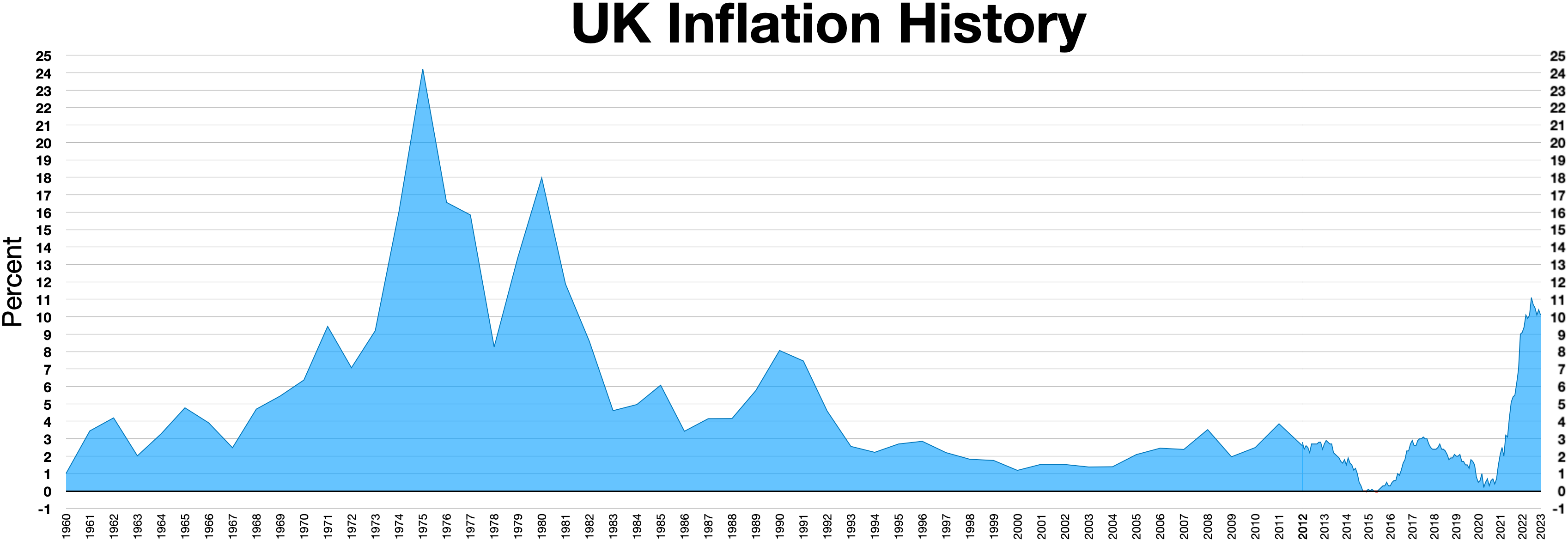
were still being felt, with inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
rising to nearly 27% in 1975. Financial markets were beginning to believe the pound was overvalued, and in April that year ''The Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' (''WSJ''), also referred to simply as the ''Journal,'' is an American newspaper based in New York City. The newspaper provides extensive coverage of news, especially business and finance. It operates on a subscriptio ...
'' advised the sale of sterling investments in the face of high taxes, in a story that ended with "goodbye, Great Britain. It was nice knowing you". At the time the UK Government
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. was running a budget deficit, and the Labour government's strategy emphasised high public spending.[ Callaghan was told there were three possible outcomes: a disastrous free fall in sterling, an internationally unacceptable siege economy, or a deal with key allies to prop up the pound while painful economic reforms were put in place. The ]US Government
The Federal Government of the United States of America (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States.
The U.S. federal government is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, execut ...
feared the crisis could endanger NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
and the European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organisation created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisbo ...
(EEC), and in light of this, the US Treasury
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States. It is one of 15 current U.S. government departments.
The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and ...
set out to force domestic policy changes. In November 1976, the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
(IMF) announced the conditions for a loan, including deep cuts in public expenditure
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichkei ...
.
1979–1989
The Conservative Party was elected to office in 1979
Events
January
* January 1
** United Nations Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim heralds the start of the ''International Year of the Child''. Many musicians donate to the ''Music for UNICEF Concert'' fund, among them ABBA, who write the song ...
, on a programme of fiscal austerity. Initially, sterling rocketed, moving above £1 to US$2.40, as interest rates rose in response to the monetarist
Monetarism is a school of thought in monetary economics that emphasizes the role of policy-makers in controlling the amount of money in circulation. It gained prominence in the 1970s, but was mostly abandoned as a direct guidance to monetary ...
policy of targeting money supply
In macroeconomics, money supply (or money stock) refers to the total volume of money held by the public at a particular point in time. There are several ways to define "money", but standard measures usually include currency in circulation (i ...
. The high exchange rate was widely blamed for the deep recession of 1981. Sterling fell sharply after 1980; at its lowest, £1 stood at just US$1.03 in March 1985, before rising to US$1.70 in December 1989.
Following the Deutsche Mark
In 1988, the Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and the head of HM Treasury, His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, t ...
, Nigel Lawson
Nigel Lawson, Baron Lawson of Blaby, (11 March 1932 – 3 April 2023) was a British politician and journalist. A member of the Conservative Party, he served as Member of Parliament for Blaby in Leicestershire from 1974 to 1992, and served ...
, decided that sterling should "shadow" the Deutsche Mark
The Deutsche Mark (; "German mark (currency), mark"), abbreviated "DM" or "D-Mark" (), was the official currency of West Germany from 1948 until 1990 and later of unified Germany from 1990 until the adoption of the euro in 2002. In English, it ...
(DM), with the unintended result of a rapid rise in inflation as the economy boomed due to low interest rates.
Following German reunification
German reunification () was the process of re-establishing Germany as a single sovereign state, which began on 9 November 1989 and culminated on 3 October 1990 with the dissolution of the East Germany, German Democratic Republic and the int ...
in 1990, the reverse held true, as high German borrowing costs to fund Eastern reconstruction, exacerbated by the political decision to convert the Ostmark to the D–Mark on a 1:1 basis, meant that interest rates in other countries shadowing the D–Mark, especially the UK, were far too high relative to domestic circumstances, leading to a housing decline and recession.
Following the European Currency Unit
On 8 October 1990 the Conservative government (Third Thatcher ministry
Margaret Thatcher was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 4 May 1979 to 28 November 1990, during which time she led a Conservative majority government. She was the first woman to hold that office. During her premiership, Thatcher moved t ...
) decided to join the European Exchange Rate Mechanism
The European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM II) is a system introduced by the European Economic Community on 1 January 1999 alongside the introduction of a single currency, the euro (replacing ERM 1 and the euro's predecessor, the ECU) as ...
(ERM), with £1 set at DM 2.95. However, the country was forced to withdraw from the system on "Black Wednesday
Black Wednesday, or the 1992 sterling crisis, was a financial crisis that occurred on 16 September 1992 when the UK Government was forced to withdraw sterling from the (first) European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERMI), following a failed at ...
" (16 September 1992) as Britain's economic performance made the exchange rate unsustainable. The event was also triggered by comments by Bundesbank president Helmut Schlesinger
Helmut Schlesinger (4 September 1924 – 23 December 2024) was a German economist and President of the Bundesbank from 1991 to 1993. Having worked for the institution and its precursor from 1952, he pursued monetary stability.
Biography Early l ...
who suggested the pound would eventually have to be devalued.
"Black Wednesday" saw interest rates jump from 10% to 15% in an unsuccessful attempt to stop the pound from falling below the ERM limits. The exchange rate fell to DM 2.20. Those who had argued for a lower GBP/DM exchange rate were vindicated since the cheaper pound encouraged exports and contributed to the economic prosperity of the 1990s.
Following inflation targets
In 1997, the newly elected Labour government handed over day-to-day control of interest rates to the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
(a policy that had originally been advocated by the Liberal Democrats). The Bank is now responsible for setting its base rate of interest so as to keep inflation (as measured by the Consumer Price Index
A consumer price index (CPI) is a statistical estimate of the level of prices of goods and services bought for consumption purposes by households. It is calculated as the weighted average price of a market basket of Goods, consumer goods and ...
(CPI)) very close to 2% per annum. Should CPI inflation be more than one percentage point above or below the target, the Governor of the Bank of England is required to write an open letter to the Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and the head of HM Treasury, His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, t ...
explaining the reasons for this and the measures which will be taken to bring this measure of inflation back in line with the 2% target. On 17 April 2007, annual CPI inflation was reported at 3.1% (inflation of the Retail Prices Index was 4.8%). Accordingly, and for the first time, the Governor had to write publicly to the UK Government explaining why inflation was more than one percentage point higher than its target.
Euro
In 2007, Gordon Brown
James Gordon Brown (born 20 February 1951) is a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Labour Party (UK), Leader of the Labour Party from 2007 to 2010. Previously, he was Chancellor of the Ex ...
, then Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and the head of HM Treasury, His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, t ...
, ruled out membership in the eurozone for the foreseeable future, saying that the decision not to join had been right for Britain and for Europe.
On 1 January 2008, with the Republic of Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the third lar ...
switching its currency from the Cypriot pound
The pound, or lira (, plural , and , , from the Latin language, Latin via the Italian language, Italian ; Currency symbol, sign: £, sometimes £C for distinction), was the currency of Cyprus, including the Sovereign Base Areas in Akrotiri and D ...
to the euro, the British sovereign bases on Cyprus (Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia (), officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA), is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory made of two non-contiguous areas on the island of Geography of Cyprus, Cyprus. The area ...
) followed suit, making the Sovereign Base Areas
Akrotiri and Dhekelia (), officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA), is a British Overseas Territory made of two non-contiguous areas on the island of Cyprus. The areas, which include British military bases and instal ...
the only territory under British sovereignty to officially use the euro.
The government of former Prime Minister Tony Blair
Sir Anthony Charles Lynton Blair (born 6 May 1953) is a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1997 to 2007 and Leader of the Labour Party (UK), Leader of the Labour Party from 1994 to 2007. He was Leader ...
had pledged to hold a public referendum to decide on the adoption of the Euro should "five economic tests
The five economic tests were the criteria defined by the UK treasury under Gordon Brown that were to be used to assess the UK's readiness to join the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union (EMU), and so adopt the euro as its official c ...
" be met, to increase the likelihood that any adoption of the euro would be in the national interest. In addition to these internal (national) criteria, the UK would have to meet the European Union's economic convergence criteria
The euro convergence criteria (also known as the Maastricht criteria) are the criteria European Union member states are required to meet to enter the third stage of the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union, Economic and Monetary Un ...
(Maastricht criteria) before being allowed to adopt the euro. The Conservative and Liberal Democrat coalition government (2010–2015) ruled out joining the euro for that parliamentary term.
The idea of replacing sterling with the euro was always controversial with the British public, partly because of sterling's identity as a symbol of British sovereignty and because it would, according to some critics, have led to suboptimal interest rates, harming the British economy. In December 2008, the results of a BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
poll of 1,000 people suggested that 71% would vote no to the euro, 23% would vote yes, while 6% said they were unsure. Sterling did not join the Second European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM II) after the euro was created. Denmark and the UK had opt-outs from entry to the euro. Theoretically, every EU nation but Denmark must eventually sign up.
As a member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, the United Kingdom could have adopted the euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
as its currency. However, the subject was always politically controversial, and the UK negotiated an opt-out on this issue. Following the UK's withdrawal from the EU, on 31 January 2020, the Bank of England ended its membership of the European System of Central Banks
The European System of Central Banks (ESCB) is an institution that comprises the European Central Bank (ECB) and the national central banks (NCBs) of all 27 member states of the European Union (EU). Its objective is to ensure price stability ...
, and shares in the European Central Bank
The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's Big Four (banking)#International ...
were reallocated to other EU banks.
Recent exchange rates

 Sterling and the euro fluctuate in value against one another, although there may be correlation between movements in their respective exchange rates with other currencies such as the US dollar. Inflation concerns in the UK led the Bank of England to raise interest rates in late 2006 and 2007. This caused sterling to appreciate against other major currencies and, with the US dollar depreciating at the same time, sterling hit a 15-year high against the US dollar on 18 April 2007, with £1 reaching US$2 the day before, for the first time since 1992. Sterling and many other currencies continued to appreciate against the dollar; sterling hit a 26-year high of £1 to US$2.1161 on 7 November 2007 as the dollar fell worldwide. From mid-2003 to mid-2007, the pound/euro rate remained within a narrow range (€1.45 ± 5%).
Following the
Sterling and the euro fluctuate in value against one another, although there may be correlation between movements in their respective exchange rates with other currencies such as the US dollar. Inflation concerns in the UK led the Bank of England to raise interest rates in late 2006 and 2007. This caused sterling to appreciate against other major currencies and, with the US dollar depreciating at the same time, sterling hit a 15-year high against the US dollar on 18 April 2007, with £1 reaching US$2 the day before, for the first time since 1992. Sterling and many other currencies continued to appreciate against the dollar; sterling hit a 26-year high of £1 to US$2.1161 on 7 November 2007 as the dollar fell worldwide. From mid-2003 to mid-2007, the pound/euro rate remained within a narrow range (€1.45 ± 5%).
Following the 2008 financial crisis
The 2008 financial crisis, also known as the global financial crisis (GFC), was a major worldwide financial crisis centered in the United States. The causes of the 2008 crisis included excessive speculation on housing values by both homeowners ...
, sterling depreciated sharply, declining to £1 to US$1.38 on 23 January 2009 and falling below £1 to €1.25 against the euro in April 2008. There was a further decline during the remainder of 2008, most dramatically on 29 December when its euro rate hit an all-time low at €1.0219, while its US dollar rate depreciated. Sterling appreciated in early 2009, reaching a peak against the euro of £1 to €1.17 in mid-July. In the following months sterling remained broadly steady against the euro, with £1 valued on 27 May 2011 at €1.15 and US$1.65.
On 5 March 2009, the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
announced that it would pump £75 billion of new capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
into the British economy
The United Kingdom has a highly developed social market economy. From 2017 to 2025 it has been the sixth-largest national economy in the world measured by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), tenth-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP), ...
, through a process known as quantitative easing
Quantitative easing (QE) is a monetary policy action where a central bank purchases predetermined amounts of government bonds or other financial assets in order to stimulate economic activity. Quantitative easing is a novel form of monetary polic ...
(QE). This was the first time in the United Kingdom's history that this measure had been used, although the Bank's Governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
Mervyn King suggested it was not an experiment.asset
In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything (tangible or intangible) that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can b ...
s such as government bond
A government bond or sovereign bond is a form of Bond (finance), bond issued by a government to support government spending, public spending. It generally includes a commitment to pay periodic interest, called Coupon (finance), coupon payments' ...
s, secured commercial paper
Commercial paper, in the global financial market, is an Unsecured debt, unsecured promissory note with a fixed Maturity (finance), maturity of usually less than 270 days. In layperson terms, it is like an "IOU" but can be bought and sold becaus ...
, or corporate bond
A corporate bond is a bond issued by a corporation in order to raise financing for a variety of reasons such as to ongoing operations, mergers & acquisitions, or to expand business. It is a longer-term debt instrument indicating that a corpo ...
s.Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and the head of HM Treasury, His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, t ...
Alistair Darling
Alistair Maclean Darling, Baron Darling of Roulanish, (28 November 1953 – 30 November 2023) was a British politician who served as Chancellor of the Exchequer under prime minister Gordon Brown from 2007 to 2010. A member of the Labour Party ...
had given permission for up to £150 billion to be created if necessary.
Annual inflation rate
 The Bank of England had stated in 2009 that the decision had been taken to prevent the rate of
The Bank of England had stated in 2009 that the decision had been taken to prevent the rate of inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
falling below the 2% target rate.interest rates
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
had already been cut to their lowest level ever (0.5%) and it was unlikely that they would be cut further.Consumer Price Index
A consumer price index (CPI) is a statistical estimate of the level of prices of goods and services bought for consumption purposes by households. It is calculated as the weighted average price of a market basket of Goods, consumer goods and ...
) in September 2011, then decreased to around 2.5% the following year. After a number of years when inflation remained near or below the Bank's 2% target, 2021 saw a significant and sustained increase on all indices: , RPI had reached 7.1%, CPI 5.1% and CPIH 4.6%.
Coins
Pre-decimal coins
The silver penny (plural: ''pence''; abbreviation: ''d'') was the principal and often the only coin in circulation from the 8th century until the 13th century. Although some fractions of the penny were struck (see farthing and halfpenny), it was more common to find pennies cut into halves and quarters to provide smaller change. Very few gold coins were struck, with the gold penny
The gold penny was a medieval English coin with a value of twenty pence (i.e. pound sterling), minted in 1257 during the reign of Henry III. The coin was short-lived as it quickly became undervalued, which led to its almost complete disappeara ...
(equal in value to 20 silver pennies) a rare example. However, in 1279, the '' groat'', worth 4''d'', was introduced, with the half groat following in 1344. 1344 also saw the establishment of a gold coinage with the introduction (after the failed gold florin) of the ''noble
A noble is a member of the nobility.
Noble may also refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Noble Glacier, King George Island
* Noble Nunatak, Marie Byrd Land
* Noble Peak, Wiencke Island
* Noble Rocks, Graham Land
Australia
* Noble Island, Gr ...
'' worth six shillings and eight pence (6/8''d'') (i.e. 3 nobles to the pound), together with the half and quarter noble. Reforms in 1464 saw a reduction in value of the coinage in both silver and gold, with the noble renamed the ''ryal'' and worth 10/– (i.e. 2 to the pound) and the ''angel
An angel is a spiritual (without a physical body), heavenly, or supernatural being, usually humanoid with bird-like wings, often depicted as a messenger or intermediary between God (the transcendent) and humanity (the profane) in variou ...
'' introduced at the noble's old value of 6/8''d''.
The reign of Henry VII saw the introduction of two important coins: the shilling
The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currency, currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 1 ...
(abbr.: ''s''; known as the ''testoon'', equivalent to twelve pence) in 1487 and the pound (known as the ''sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title that can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to ...
'', abbr.: ''£'' before numerals or "''l''." (lower-case L) after them, equivalent to twenty shillings) in 1489. In 1526, several new denominations of gold coins were added, including the ''crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, parti ...
'' and '' half crown'', worth five shillings (''5/–'') and two shillings and six pence (''2/6'', ''two and six'') respectively. Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
's reign (1509–1547) saw a high level of debasement
A debasement of coinage is the practice of lowering the intrinsic value of coins, especially when used in connection with commodity money, such as gold or silver coins, while continuing to circulate it at face value. A coin is said to be debased ...
which continued into the reign of Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. The only surviving son of Henry VIII by his thi ...
(1547–1553). This debasement was halted in 1552, and new silver coinage was introduced, including coins for 1''d'', 2''d'', 3d, 4''d'' and 6''d'', 1/–, 2/6''d'' and 5/–. In the reign of Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
(1558–1603), silver ''d'' and ''d'' coins were added, but these denominations did not last. Gold coins included the half-crown, crown, angel, half-sovereign (10/–) and sovereign (£1). Elizabeth's reign also saw the introduction of the horse-drawn screw press to produce the first "milled" coins.
Following the succession of the Scottish King James VI
James may refer to:
People
* James (given name)
* James (surname)
* James (musician), aka Faruq Mahfuz Anam James, (born 1964), Bollywood musician
* James, brother of Jesus
* King James (disambiguation), various kings named James
* Prince Ja ...
to the English throne, a new gold coinage was introduced, including the ''spur ryal
The Spur Ryal was an extremely rare English gold coin issued in the reign of King James I. The coin is a development of the earlier Rose Noble, or Ryal which was worth ten shillings when issued by Kings Edward IV and Henry VII, and fifteen sh ...
'' (15/–), the '' unite'' (20/–) and the ''rose ryal'' (30/–). The ''laurel
Laurel may refer to:
Plants
* Lauraceae, the laurel family
* Laurel (plant), including a list of trees and plants known as laurel
People
* Laurel (given name), people with the given name
* Laurel (surname), people with the surname
* Laurel (mus ...
'', worth 20/–, followed in 1619. The first base metal coins were also introduced: tin
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
farthings. Copper halfpenny coins followed in the reign of Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
. During the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
, a number of siege coinages were produced, often in unusual denominations.
Following the restoration of the monarchy in 1660, the coinage was reformed, with the ending of production of hammered coins in 1662. The ''guinea
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the southeast, and Sier ...
'' was introduced in 1663, soon followed by the , 2 and 5 guinea coins. The silver coinage consisted of denominations of 1''d'', 2''d'', 3''d'', 4''d'' and 6''d'', 1/–, 2/6''d'' and 5/–. Due to the widespread export of silver in the 18th century, the production of silver coins gradually came to a halt, with the half crown and crown not issued after the 1750s, and the 6''d'' and 1/– stopping production in the 1780s. In response, copper 1''d'' and 2''d'' coins and a gold guinea (7/–) were introduced in 1797. The copper penny was the only one of these coins to survive long.
To alleviate the shortage of silver coins, between 1797 and 1804, the Bank of England counterstamped Spanish dollar
The Spanish dollar, also known as the piece of eight (, , , or ), is a silver coin of approximately diameter worth eight Spanish reales. It was minted in the Spanish Empire following a monetary reform in 1497 with content fine silver. It w ...
s (8 reales) and other Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
and Spanish colonial
The Spanish Colonial Revival architecture (), often known simply as Spanish Revival, is a term used to encompass a number of revivalist architectural styles based in both Spanish colonial architecture and Spanish architecture in general. These ...
coins for circulation. A small counterstamp of the King's head was used. Until 1800, these circulated at a rate of 4/9''d'' for 8 reales. After 1800, a rate of 5/– for 8 reales was used. The Bank then issued silver tokens for 5/– (struck over Spanish dollars) in 1804, followed by tokens for 1/6''d'' and 3/– between 1811 and 1816.
In 1816, a new silver coinage was introduced in denominations of 6''d'', 1/–, 2/6''d'' (half-crown) and 5/– (crown). The crown was only issued intermittently until 1900. It was followed by a new gold coinage in 1817 consisting of 10/– and £1 coins, known as the half sovereign and sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title that can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to ...
. The silver 4''d'' coin was reintroduced in 1836, followed by the 3''d'' in 1838, with the 4''d'' coin issued only for colonial use after 1855. In 1848, the 2/– ''florin
The Florentine florin was a gold coin (in Italian ''Fiorino d'oro'') struck from 1252 to 1533 with no significant change in its design or metal content standard during that time.
It had 54 grains () of nominally pure or 'fine' gold with a pu ...
'' was introduced, followed by the short-lived double florin in 1887. In 1860, copper was replaced by bronze in the farthing (quarter penny, ''d''), halfpenny and penny.
During the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, production of the sovereign and half-sovereign
The half sovereign is a British gold coin denominated at one-half of a pound sterling. First issued in its present form in 1817, it has been struck by the Royal Mint in most years since 1980 as a collector's and bullion piece.
The half sove ...
was suspended, and although the gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
was later restored, the coins saw little circulation thereafter. In 1920, the silver standard, maintained at .925 since 1552, was reduced to .500. In 1937, a nickel-brass 3''d'' coin was introduced; the last silver 3''d'' coins were issued seven years later. In 1947, the remaining silver coins were replaced with cupro-nickel
Cupronickel or copper–nickel (CuNi) is an alloy of copper with nickel, usually along with small quantities of other metals added for strength, such as iron and manganese. The copper content typically varies from 60 to 90 percent. ( Monel is a ...
, with the exception of Maundy coinage which was then restored to .925. Inflation caused the farthing to cease production in 1956 and be demonetised in 1960. In the run-up to decimalisation, the halfpenny and half-crown were demonetised in 1969.
Decimal coins
British coinage timeline:
* 1968: The first decimal coins were introduced. These were cupro-nickel
Cupronickel or copper–nickel (CuNi) is an alloy of copper with nickel, usually along with small quantities of other metals added for strength, such as iron and manganese. The copper content typically varies from 60 to 90 percent. ( Monel is a ...
5p and 10p coins which were the same size as, equivalent in value to, and circulated alongside, the one shilling coin and the florin (two shilling coin) respectively.
* 1969: The curved equilateral heptagon
In geometry, a heptagon or septagon is a seven-sided polygon or 7-gon.
The heptagon is sometimes referred to as the septagon, using ''Wikt:septa-, septa-'' (an elision of ''Wikt:septua-, septua-''), a Latin-derived numerical prefix, rather than ...
al cupro-nickel 50p coin replaced the ten shilling note (10/–).
* 1970: The half crown (2/6''d'', 12.5p) was demonetised.
* 1971: The decimal coinage was completed when decimalisation came into effect in 1971 with the introduction of the bronze half new penny (p), new penny (1p), and two new pence (2p) coins and the withdrawal of the (old) penny (1''d'') and (old) threepence (3''d'') coins.
* 1980: Withdrawal of the sixpence (6''d'') coin, which had continued in circulation at a value of p.
* 1982: The word "new" was dropped from the coinage and a 20p coin was introduced.
* 1983: A (round, brass) £1 coin
The British one pound (£1) coin is a denomination of sterling coinage. Its obverse has featured the profile of Charles III since 2024 and bears the Latin engraving CHARLES III D G REX () F D (), which means 'Charles III, by the grace of God, ...
was introduced.
* 1983: The p coin was last produced.
* 1984: The p coin was withdrawn from circulation.
* 1990: The crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, parti ...
, historically valued at five shillings (25p), was re-tariffed for future issues as a commemorative coin at £5.
* 1990: A new, smaller 5p coin was introduced, replacing the original size that had been the same as the shilling coins of the same value that it had in turn replaced. These first generation 5p coins and any remaining old shilling coins were withdrawn from circulation in 1991.
* 1992: A new, smaller 10p coin was introduced, replacing the original size that had been the same as the florin or two shilling coins of the same value that it had in turn replaced. These first generation 10p coins and any remaining old florin coins were withdrawn from circulation over the following two years.
* 1992: 1p and 2p coins began to be minted in copper-plated steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
(the original bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
coins continued in circulation).
* 1997: A new 50p coin was introduced, replacing the original size that had been in use since 1969, and the first generation 50p coins were withdrawn from circulation.
* 1998: The bi-metallic £2 coin
The pound sign () is the symbol for the pound unit of sterling – the currency of the United Kingdom and its associated Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories and previously of Great Britain and of the Kingdom of England. The sa ...
was introduced.
* 2007: By now the value of copper in the pre-1992 1p and 2p coins (which are 97% copper) exceeded those coins' face value to such an extent that melting down the coins by entrepreneur
Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value in ways that generally entail beyond the minimal amount of risk (assumed by a traditional business), and potentially involving values besides simply economic ones.
An entreprene ...
s was becoming worthwhile (with a premium of up to 11%, with smelting costs reducing this to around 4%)—although this is illegal, and the market value
Market value or OMV (open market valuation) is the price at which an asset would trade in a competitive auction setting. Market value is often used interchangeably with ''open market value'', ''fair value'' or '' fair market value'', although t ...
of copper has subsequently fallen dramatically from these earlier peaks.
* In April 2008, an extensive redesign of the coinage was unveiled. The 1p, 2p, 5p, 10p, 20p, and 50p coins feature parts of the Royal Shield on their reverse; and the reverse of the pound coin showed the whole shield. The coins were issued gradually into circulation, starting in mid-2008. They have the same sizes, shapes and weights as those with the old designs which, apart from the round pound coin which was withdrawn in 2017, continue to circulate.
* 2012: The 5p and 10p coins were changed from cupro-nickel to nickel-plated steel.
* 2017: A more secure twelve-sided bi-metallic £1 coin was introduced to reduce forgery. The old round £1 coin ceased to be legal tender on 15 October 2017.
Banknotes
The first sterling notes were issued by the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
shortly after its foundation in 1694. Denominations were initially handwritten on the notes at the time of issue. From 1745, the notes were printed in denominations between £20 and £1,000, with any odd shillings added by hand. £10 notes were added in 1759, followed by £5 in 1793 and £1 and £2 in 1797. The lowest two denominations were withdrawn after the end of the Napoleonic wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
. In 1855, the notes were converted to being entirely printed, with denominations of £5, £10, £20, £50, £100, £200, £300, £500 and £1,000 issued.
The Bank of Scotland
The Bank of Scotland plc (Scottish Gaelic: ''Banca na h-Alba'') is a commercial bank, commercial and clearing (finance), clearing bank based in Edinburgh, Scotland, and is part of the Lloyds Banking Group. The bank was established by the Par ...
began issuing notes in 1695. Although the pound Scots
The pound ( Modern and Middle Scots: ''Pund'') was the currency of Scotland prior to the 1707 Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England, which created the Kingdom of Great Britain. It was introduced by David I ...
was still the currency of Scotland, these notes were denominated in sterling in values up to £100. From 1727, the Royal Bank of Scotland
The Royal Bank of Scotland Public Limited Company () is a major retail banking, retail and commercial bank in Scotland. It is one of the retail banking subsidiaries of NatWest Group, together with NatWest and Ulster Bank. The Royal Bank of Sco ...
also issued notes. Both banks issued some notes denominated in guineas as well as pounds. In the 19th century, regulations limited the smallest note issued by Scottish banks to be the £1 denomination, a note not permitted in England.
With the extension of sterling to Ireland in 1825, the Bank of Ireland
Bank of Ireland Group plc () is a commercial bank operation in Ireland and one of the traditional Big Four Irish banks. Historically the premier banking organisation in Ireland, the bank occupies a unique position in Irish banking history. At ...
began issuing sterling notes, later followed by other Irish banks. These notes included the unusual denominations of 30/– and £3. The highest denomination issued by the Irish banks was £100.
In 1826, banks at least from London were given permission to issue their own paper money. From 1844, new banks were excluded from issuing notes in England and Wales but not in Scotland and Ireland. Consequently, the number of private banknotes dwindled in England and Wales but proliferated in Scotland and Ireland. The last English private banknotes were issued in 1921.
In 1914, the Treasury
A treasury is either
*A government department related to finance and taxation, a finance ministry; in a business context, corporate treasury.
*A place or location where treasure, such as currency or precious items are kept. These can be ...
introduced notes for 10/– and £1 to replace gold coins. These circulated until 1928 when they were replaced by Bank of England notes. Irish independence reduced the number of Irish banks issuing sterling notes to five operating in Northern Ireland. The Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
had a drastic effect on the note production of the Bank of England. Fearful of mass forgery by the Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
s (see Operation Bernhard
Operation Bernhard was an exercise by Nazi Germany to forge British Banknotes of the pound sterling, bank notes. The initial plan was to drop the notes over Britain to bring about a economic collapse, collapse of the Economy of the United Kingdom ...
), all notes for £10 and above ceased production, leaving the bank to issue only 10/–, £1 and £5 notes. Scottish and Northern Irish issues were unaffected, with issues in denominations of £1, £5, £10, £20, £50 and £100.
Due to repeated devaluations and spiralling inflation the Bank of England reintroduced £10 notes in 1964. In 1969, the 10/– note was replaced by the 50p coin, again due to inflation. £20 Bank of England notes were reintroduced in 1970, followed by £50 in 1981. A £1 coin was introduced in 1983, and Bank of England £1 notes were withdrawn in 1988. Scottish and Northern Irish banks followed, with only the Royal Bank of Scotland continuing to issue this denomination.
UK notes include raised print (e.g. on the words "Bank of England"); watermarks; embedded metallic thread; holograms; and fluorescent ink visible only under UV lamps. Three printing techniques are involved: offset litho
Offset printing is a common printing technique in which the inked image is transferred (or "offset") from a plate to a rubber blanket and then to the printing surface. When used in combination with the lithographic process, which is based on ...
, intaglio and letterpress
Letterpress printing is a technique of relief printing for producing many copies by repeated direct impression of an inked, raised surface against individual sheets of paper or a continuous roll of paper. A worker composes and locks movable t ...
; and the notes incorporate a total of 85 specialized inks.
The Bank of England produces notes named "giant
In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: ''wiktionary:gigas, gigas'', cognate wiktionary:giga-, giga-) are beings of humanoid appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''gia ...
" and "titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
". A giant is a one million pound note, and a titan is a one hundred million pound bank note. Giants and titans are used only within the banking system
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
.
Polymer banknotes
The Northern Bank £5 note, issued by Northern Ireland's Northern Bank
Northern Bank Limited, trading as Danske Bank, is a retail bank in Northern Ireland. Northern Banking Company Limited was formed from a private bank, with the Deed of Partnership being signed on 1 August 1824. It is one of the oldest banks in ...
(now Danske Bank
Danske Bank A/S (, ) is a Danish multinational banking and financial services corporation. Headquartered in Copenhagen, it is the largest bank in Denmark and a major retail bank in the northern European region with over 5 million retail custome ...
) in 2000, was the only polymer banknote
Polymer banknotes are banknotes made from a synthetic polymer such as biaxially oriented polypropylene (BOPP). Such notes incorporate many security features not available in paper banknotes, including the use of metameric inks. Polymer banknote ...
in circulation until 2016. The Bank of England introduced £5 polymer banknotes in September 2016, and the paper £5 notes were withdrawn on 5 May 2017. A polymer £10 banknote was introduced on 14 September 2017, and the paper note was withdrawn on 1 March 2018. A polymer £20 banknote was introduced on 20 February 2020, followed by a polymer £50 in 2021.
Monetary policy
As the central bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the mo ...
of the United Kingdom which has been delegated authority by the government, the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
sets the monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
for the British pound by controlling the amount of money in circulation. It has a monopoly on the issuance of banknotes in England and Wales and regulates the amount of banknotes issued by seven authorized banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland. HM Treasury
His Majesty's Treasury (HM Treasury or HMT), and informally referred to as the Treasury, is the Government of the United Kingdom’s economic and finance ministry. The Treasury is responsible for public spending, financial services policy, Tax ...
has reserve powers to give orders to the committee "if they are required in the public interest and by extreme economic circumstances" but such orders must be endorsed by Parliament within 28 days.
Unlike banknotes which have separate issuers in Scotland and Northern Ireland, all British coins are issued by the Royal Mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's official maker of British coins. It is currently located in Llantrisant, Wales, where it moved in 1968.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly ow ...
, an independent enterprise (wholly owned by the Treasury
A treasury is either
*A government department related to finance and taxation, a finance ministry; in a business context, corporate treasury.
*A place or location where treasure, such as currency or precious items are kept. These can be ...
) which also mints coins for other countries.
Legal tender and national issues

Legal tender
Legal tender is a form of money that Standard of deferred payment, courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment in court for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything ...
in the United Kingdom is defined such that "a debtor cannot successfully be sued for non-payment if he pays into court in legal tender." Parties can alternatively settle a debt by other means with mutual consent. Strictly speaking, it is necessary for the debtor to offer the exact amount due as there is no obligation for the other party to provide change.Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the Kingdom of England, English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one ...
notes are legal tender for any amount in England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. Th ...
, but not in Scotland or Northern Ireland.[ (Bank of England 10/– and £1 notes were legal tender, as were Scottish banknotes, during ]World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
under the Currency (Defence) Act 1939, which was repealed on 1 January 1946.) Channel Islands
The Channel Islands are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They are divided into two Crown Dependencies: the Jersey, Bailiwick of Jersey, which is the largest of the islands; and the Bailiwick of Guernsey, ...
and Manx banknotes are legal tender only in their respective jurisdictions.
Bank of England, Scottish, Northern Irish, Channel Islands, Isle of Man, Gibraltar, and Falkland banknotes may be offered anywhere in the UK, although there is no obligation to accept them as a means of payment, and acceptance varies. For example, merchants in England generally accept Scottish and Northern Irish notes, but some unfamiliar with them may reject them. However, Scottish and Northern Irish notes both tend to be accepted in Scotland and Northern Ireland, respectively. Merchants in England generally do not accept Jersey, Guernsey, Manx, Gibraltarian, and Falkland notes but Manx notes are generally accepted in Northern Ireland. Bank of England notes are generally accepted in the Falklands and Gibraltar, but for example, Scottish and Northern Irish notes are not. Since all of the notes are denominated in sterling, banks will exchange them for locally issued notes at face value, though some in the UK have had trouble exchanging Falkland Islands notes.legal tender
Legal tender is a form of money that Standard of deferred payment, courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment in court for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything ...
, as are the bullion coin
A bullion coin (also known as a specie) is a coin struck from highly refined precious metal (bullion) and kept as a store of value or an investment rather than used in day-to-day commerce, or collectable, with numismatic value beyond that of its ...
s issued by the Mint.
Pegged currencies
In Britain's Crown Dependencies
The Crown Dependencies are three dependent territory, offshore island territories in the British Islands that are self-governing possessions of the The Crown, British Crown: the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Jersey, Bailiwick of Jersey, both lo ...
, the Manx pound
The pound (abbreviation: IMP; sign: £), or Manx pound (; in order to distinguish it from other similar-named currencies), is the currency of the Isle of Man, at parity with sterling. The Manx pound is divided into 100 pence. Notes and coins ...
, Jersey pound
The pound (, Jèrriais: ''Louis d'Jèrri''; abbreviation: JEP; sign: £) is the currency of Jersey. Jersey is in currency union with the United Kingdom, and the Jersey pound is not a separate currency but is an issue of banknotes and coins by t ...
, and Guernsey pound
The pound is the currency of Guernsey. Since 1921, Guernsey has been in currency union with the United Kingdom and the Guernsey pound is not a separate currency but is a local issue of sterling banknotes and coins, in a similar way to the banknot ...
are unregulated by the Bank of England and are issued independently. However, they are maintained at a fixed exchange rate
A fixed exchange rate, often called a pegged exchange rate, is a type of exchange rate regime in which a currency's value is fixed or pegged by a monetary authority against the value of another currency, a currency basket, basket of other currenc ...
by their respective governments, and Bank of England notes have been made legal tender on the islands, forming a sort of one-way de facto currency union
A currency union (also known as monetary union) is an intergovernmental agreement that involves two or more states sharing the same currency. These states may not necessarily have any further integration (such as an economic and monetary union ...
. Internationally they are considered local issues of sterling so do not have ISO 4217
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individ ...
codes. "GBP" is usually used to represent all of them; informal abbreviations resembling ISO codes are used where the distinction is important.
British Overseas Territories
The British Overseas Territories (BOTs) or alternatively referred to as the United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs) are the fourteen dependent territory, territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom that, ...
are responsible for the monetary policy of their own currencies (where they exist), and have their own ISO 4217 codes. The Falkland Islands pound
The pound is the currency of the Falkland Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the South Atlantic Ocean. The symbol is the pound sign, £. The ISO 4217 currency code is ''FKP''.
The Falkland Islands pound has always been Fixed exchange rate, ...
, Gibraltar pound
The pound ( sign: £; ISO code: GIP) is the currency of Gibraltar. It is pegged to – and exchangeable with – British pound sterling at par value. Coins and banknotes of the Gibraltar pound are issued by the Government of Gibraltar.
His ...
, and Saint Helena pound
The Saint Helena pound is the currency of the Atlantic islands of Saint Helena and Ascension, which are constituent parts of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. It is fixed at parity with sterling, ...
are set at a fixed 1:1 exchange rate with the British pound by local governments.
Value
In 2006, the House of Commons Library
The House of Commons Library is the library and information resource of the lower house of the British Parliament. It was established in 1818, although its original 1828 construction was destroyed during the burning of Parliament in 1834.
Th ...
published a research paper which included an index of prices for each year between 1750 and 2005, where 1974 was indexed at 100.
Regarding the period 1750–1914 the document states: "Although there was considerable year on year fluctuation in price levels prior to 1914 (reflecting the quality of the harvest, wars, etc.) there was not the long-term steady increase in prices associated with the period since 1945". It goes on to say that "Since 1945 prices have risen in every year with an aggregate rise of over 27 times".
The value of the index in 1751 was 5.1, increasing to a peak of 16.3 in 1813 before declining very soon after the end of the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
to around 10.0 and remaining in the range 8.5–10.0 at the end of the 19th century. The index was 9.8 in 1914 and peaked at 25.3 in 1920, before declining to 15.8 in 1933 and 1934—prices were only about three times as high as they had been 180 years earlier.
Inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
has had a dramatic effect during and after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
: the index was 20.2 in 1940, 33.0 in 1950, 49.1 in 1960, 73.1 in 1970, 263.7 in 1980, 497.5 in 1990, 671.8 in 2000 and 757.3 in 2005. The smallest coin in 1971 was the p, worth about 6.4p in 2015 prices.
The following table shows the equivalent amount of goods and services that, in a particular year, could be purchased with £1.
Exchange rate
Sterling is freely bought and sold on the foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, ...
s around the world, and its value relative to other currencies therefore fluctuates.
Reserve
Sterling is used as a reserve currency
A reserve currency is a foreign currency that is held in significant quantities by central banks or other monetary authorities as part of their foreign exchange reserves. The reserve currency can be used in international transactions, internat ...
around the world. , it is ranked fourth in value held as reserves.
See also
* Commonwealth banknote-issuing institutions
Commonwealth banknote-issuing institutions also British Empire Paper Currency Issuers comprises a list of public, private, state-owned banks and other government bodies and Currency Boards who issued legal tender: banknotes.
Africa
Biafra
*Bank ...
* List of British currencies
A variety of currencies are tender in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and crown dependencies. This list covers all of those currently in circulation.
References
See also
* Sterling area
* Bank of England
* Currencies of the ...
* List of currencies in Europe
There are 27 currency, currencies currently used in the List of countries in Europe#Recognised states, 50 countries of Europe. All ''de facto'' present currencies in Europe, and an incomplete list of the preceding currency, are listed here.
In E ...
* List of the largest trading partners of United Kingdom
This is a list of the largest trading partners of the United Kingdom as of October 2024.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Trading partners of United Kingdom
Foreign trade of the United Kingdom
Economy-related lists of superlatives
United Kingdom
...
* Pound (currency)
Pound is a name of various units of currency. It is used in some countries today and previously was used in many others. The English word "pound" derives from the Latin language, Latin expression , "a pound by weight", in which means 'scale' or ' ...
other currencies with a "pound" unit of account.
Footnotes
References
Further reading
* ''World Currency Monitor Annual, 1976–1989: Pound Sterling: The Value of the British Pound Sterling in Foreign Terms''. Bank of America/Meckler Mecklermedia (1990). . .
*
* Fernand Braudel
Fernand Paul Achille Braudel (; 24 August 1902 – 27 November 1985) was a French historian. His scholarship focused on three main projects: ''The Mediterranean'' (1923–49, then 1949–66), ''Civilization and Capitalism'' (1955–79), and the un ...
, 1984. ''The Perspective of the World'', Vol III of ''Civilisation and Capitalism'', (in French 1979).
* John Brennan (1983). ''The political pound: British investment overseas and exchange controls past—and future?''. Henderson Administration. .
* Barry Eichengreen (Editor), Michael D. Bordo (Editor) (1993). ''A Retrospective on the Bretton Woods System: Lessons for International Monetary Reform (National Bureau of Economic Research Project Report)''. Published by University of Chicago Press
The University of Chicago Press is the university press of the University of Chicago, a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. It is the largest and one of the oldest university presses in the United States. It pu ...
,
* Milton Friedman, Anna Jacobson Schwartz (1971). ''Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960''. Princeton University Press
Princeton University Press is an independent publisher with close connections to Princeton University. Its mission is to disseminate scholarship within academia and society at large.
The press was founded by Whitney Darrow, with the financial ...
. .
* John Kevin Green. ''The international role of the pound sterling: Its benefits and costs to the United Kingdom''.
*
* Mary Poovey (2002). ''The Financial System in Nineteenth-Century Britain''. The Victorian Archives Series. Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
. .
*
*
* Lewis D. Solomon (1996). ''Rethinking Our Centralised Monetary System: The Case for a System of Local Currencies''. Praeger Publishers .
* Philip Stephens (1995). ''Politics and the Pound: The Conservatives' Struggle with Sterling''. .
* Horst Ungerer, Jouko J. Hauvonen (1990)
''The European Monetary System: Developments and Perspectives''
Occasional Paper No. 73. International Monetary Fund. . .
* J. K Whitaker and Maxwell W. Hudgins, Jr. (April 1977). "The Floating Pound Sterling of the Nineteen-Thirties: An Econometric Study". ''Southern Economic Journal''. Vol. 43, No. 4, pp. 1478-1485. . .
External links
* of the Royal Mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's official maker of British coins. It is currently located in Llantrisant, Wales, where it moved in 1968.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly ow ...
Pound Sterling
– BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
(Foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange market (forex, FX, or currency market) is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. By trading volume, ...
news)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pound Sterling
Currencies of the United Kingdom
Currencies of dependent territories of the United Kingdom
Currencies of the British Empire
Circulating currencies
Currencies of England
Currencies of Europe
Currencies of North America
Currencies of the Caribbean
Currencies of Oceania
Currencies of Scotland
Currencies of South America
Currencies of Zimbabwe
Currencies with multiple banknote issuers
Currencies of Africa
Currencies of Asia
Pound (currency)
 The basic unit of currency in medieval England was the
The basic unit of currency in medieval England was the  The pound sterling emerged after the adoption of the Carolingian monetary system in England . Here is a summary of changes to its value in terms of silver or gold until 1816.
The pound sterling emerged after the adoption of the Carolingian monetary system in England . Here is a summary of changes to its value in terms of silver or gold until 1816.
 The pound was a unit of account in
The pound was a unit of account in  The early pennies were struck from fine silver (as pure as was available). In 1158, a new coinage was introduced by King
The early pennies were struck from fine silver (as pure as was available). In 1158, a new coinage was introduced by King  During the reign of
During the reign of  The last significant depreciation in sterling's
The last significant depreciation in sterling's  The silver basis of sterling remained essentially unchanged until the 1816 introduction of the Gold Standard, save for the increase in the number of pennies in a troy ounce from 60 to 62 (hence, 0.464 g fine silver in a penny). Its gold basis remained unsettled, however, until the gold guinea was fixed at 21 shillings in 1717.
The
The silver basis of sterling remained essentially unchanged until the 1816 introduction of the Gold Standard, save for the increase in the number of pennies in a troy ounce from 60 to 62 (hence, 0.464 g fine silver in a penny). Its gold basis remained unsettled, however, until the gold guinea was fixed at 21 shillings in 1717.
The  During the
During the  With the breakdown of the
With the breakdown of the 

 The Bank of England had stated in 2009 that the decision had been taken to prevent the rate of
The Bank of England had stated in 2009 that the decision had been taken to prevent the rate of