Root certificate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
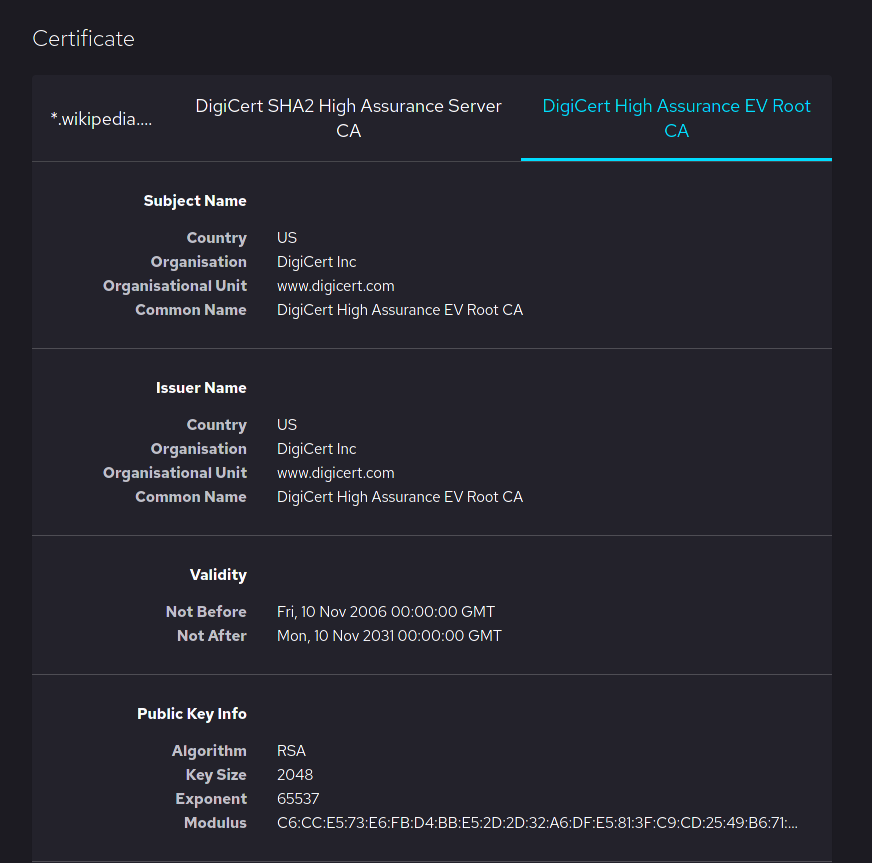 In 2009, an employee of the
In 2009, an employee of the
cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from grc, , translit=kryptós "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or '' -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adv ...
and computer security
Computer security, cybersecurity (cyber security), or information technology security (IT security) is the protection of computer systems and networks from attack by malicious actors that may result in unauthorized information disclosure, t ...
, a root certificate is a public key certificate
In cryptography, a public key certificate, also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate, is an electronic document used to prove the validity of a public key. The certificate includes information about the key, information about t ...
that identifies a root certificate authority
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. Thi ...
(CA). Root certificates are self-signed (and it is possible for a certificate to have multiple trust paths, say if the certificate was issued by a root that was cross-signed) and form the basis of an X.509
In cryptography, X.509 is an International Telecommunication Union (ITU) standard defining the format of public key certificates. X.509 certificates are used in many Internet protocols, including TLS/SSL, which is the basis for HTTPS, the secu ...
-based public key infrastructure
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. The purpose of a PKI is to facili ...
(PKI). Either it has matched Authority Key Identifier with Subject Key Identifier, in some cases there is no Authority Key identifier, then Issuer string should match with Subject string (). For instance, the PKIs supporting HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is enc ...
for secure web
Web most often refers to:
* Spider web, a silken structure created by the animal
* World Wide Web or the Web, an Internet-based hypertext system
Web, WEB, or the Web may also refer to:
Computing
* WEB, a literate programming system created by ...
browsing and electronic signature
An electronic signature, or e-signature, is data that is logically associated with other data and which is used by the signatory to sign the associated data. This type of signature has the same legal standing as a handwritten signature as long as ...
schemes depend on a set of root certificates.
A certificate authority
In cryptography, a certificate authority or certification authority (CA) is an entity that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. A digital certificate certifies the ownership of a public key by the named subject of the certificate. Thi ...
can issue multiple certificates in the form of a tree structure
A tree structure, tree diagram, or tree model is a way of representing the hierarchical nature of a structure in a graphical form. It is named a "tree structure" because the classic representation resembles a tree, although the chart is genera ...
. A root certificate is the top-most certificate of the tree, the private key which is used to "sign" other certificates. All certificates signed by the root certificate, with the "CA" field set to true, inherit the trustworthiness of the root certificate—a signature by a root certificate is somewhat analogous to "notarizing" identity in the physical world. Such a certificate is called an intermediate certificate or subordinate CA certificate. Certificates further down the tree also depend on the trustworthiness of the intermediates.
The root certificate is usually made trustworthy by some mechanism other than a certificate, such as by secure physical distribution. For example, some of the best-known root certificates are distributed in operating systems by their manufacturers. Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washi ...
distributes root certificates belonging to members of the Microsoft Root Certificate Program to Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for se ...
desktops and Windows Phone 8. Apple distributes root certificates belonging to members of its own root program.
Incidents of root certificate misuse
DigiNotar hack of 2011
In 2011, theDutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
certificate authority DigiNotar suffered a security breach. This led to the issuing of various fraudulent certificates, which was among others abused to target Iranian Gmail users. The trust in DigiNotar certificates was retracted and the operational management of the company was taken over by the Dutch government
The politics of the Netherlands take place within the framework of a parliamentary representative democracy, a constitutional monarchy, and a decentralised unitary state.''Civil service systems in Western Europe'' edited by A. J. G. M. Bekk ...
.
China Internet Network Information Center (CNNIC) Issuance of Fake Certificates
 In 2009, an employee of the
In 2009, an employee of the China Internet Network Information Center The China Internet Network Information Center (), or CNNIC, is the administrative agency responsible for domain registry affairs of .cn under the Cyberspace Administration of China.
Founded on 3 June 1997, it is now a government department based in ...
(CNNIC) applied to Mozilla
Mozilla (stylized as moz://a) is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, spreads and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting exclusively free software and open standards, ...
to add CNNIC to Mozilla's root certificate list and was approved. Later, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washi ...
also added CNNIC to the root certificate list of Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for se ...
.
In 2015, many users chose not to trust the digital certificates issued by CNNIC because an intermediate CA issued by CNNIC was found to have issued fake certificates for Google domain names and raised concerns about CNNIC's abuse of certificate issuing power.
On April 2, 2015, Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
announced that it no longer recognized the electronic certificate issued by CNNIC. on April 4, following Google, Mozilla also announced that it no longer recognized the electronic certificate issued by CNNIC. in August 2016, the official website of CNNIC had abandoned the root certificate issued by itself and replaced it with the certificate issued by DigiCert
DigiCert, Inc. is an American digital security company headquartered in Lehi, Utah, with offices in Australia, Ireland, Japan, India, France, South Africa, Switzerland and United Kingdom. As a certificate authority (CA) and trusted third party, D ...
-issued certificate.
WoSign and StartCom: Issuing fake and backdating certificates
In 2016,WoSign
Qihoo 360 (; approximate pronunciation CHEE-hoo), full name 360 Security Technology Inc., is a Chinese internet security company that has developed the antivirus software programs 360 Safeguard and 360 Mobile Safe, the Web browser 360 Secure Brows ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
's largest CA certificate issuer owned by Qihoo 360
Qihoo 360 (; approximate pronunciation CHEE-hoo), full name 360 Security Technology Inc., is a Chinese internet security company that has developed the antivirus software programs 360 Safeguard and 360 Mobile Safe, the Web browser 360 Secure Br ...
and its Israeli
Israeli may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel
* Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel
* Modern Hebrew, a language
* ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008
* Guni Israeli (b ...
subsidiary StartCom
StartCom was a certificate authority founded in Eilat, Israel, and later based in Beijing, China, that had three main activities: StartCom Enterprise Linux (Linux distribution), StartSSL (certificate authority) and MediaHost (web hosting). Start ...
, were denied recognition of their certificates by Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
.
WoSign and StartCom revealed to have issued hundreds of certificates with the same serial number in just five days, as well as issuing backdating certificates. WoSign and StartCom even issued a fake GitHub
GitHub, Inc. () is an Internet hosting service for software development and version control using Git. It provides the distributed version control of Git plus access control, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, cont ...
certificate.
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washi ...
also said in 2017 that they would remove the relevant certificates offline, but in February 2021 users still reported that certificates from WoSign and StartCom were still effective in Windows 10
Windows 10 is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It is the direct successor to Windows 8.1, which was released nearly two years earlier. It was released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and later to retail on ...
and could only be removed manually.
See also
*Online Certificate Status Protocol
The Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) is an Internet protocol used for obtaining the revocation status of an X.509 digital certificate. It is described in RFC 6960 and is on the Internet standards track. It was created as an alternative ...
(OCSP)
* SHA-1
In cryptography, SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1) is a cryptographically broken but still widely used hash function which takes an input and produces a 160- bit (20- byte) hash value known as a message digest – typically rendered as 40 hexa ...
* Timestamp
A timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. Timestamps do not have to be based on some absolut ...
* Verisign
Verisign Inc. is an American company based in Reston, Virginia, United States that operates a diverse array of network infrastructure, including two of the Internet's thirteen root nameservers, the authoritative registry for the , , and gene ...
References