Roman people on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Roman people was the ethnicity and the body of Roman citizens
(; ) during the  The collapse of the
The collapse of the
 The term 'Roman' is today used interchangeably to describe a historical timespan, a
The term 'Roman' is today used interchangeably to describe a historical timespan, a
 Although Ancient Rome has been termed an 'evidently non-racist society', Romans carried considerable cultural stereotypes and prejudices against cultures and peoples that were not integrated into the Roman world, i.e. " barbarians". Though views differed through Roman history, the attitude towards peoples beyond the Roman frontier among most Roman writers in
Although Ancient Rome has been termed an 'evidently non-racist society', Romans carried considerable cultural stereotypes and prejudices against cultures and peoples that were not integrated into the Roman world, i.e. " barbarians". Though views differed through Roman history, the attitude towards peoples beyond the Roman frontier among most Roman writers in  A particularly disliked group of non-Romans within the empire were the Jews. The majority of the Roman populace detested Jews and Judaism, though views were more varied among the Roman elite. Although many, such as Tacitus, were also hostile to the Jews, others, such as Cicero, were merely unsympathetically indifferent. The Roman state was not wholly opposed to the Jews, since there was a sizeable Jewish population in Rome itself, as well as at least thirteen
A particularly disliked group of non-Romans within the empire were the Jews. The majority of the Roman populace detested Jews and Judaism, though views were more varied among the Roman elite. Although many, such as Tacitus, were also hostile to the Jews, others, such as Cicero, were merely unsympathetically indifferent. The Roman state was not wholly opposed to the Jews, since there was a sizeable Jewish population in Rome itself, as well as at least thirteen
 From the
From the  In most cases, it is not clear to what extent the majority of the new Roman citizens regarded themselves as being Roman, or to what extent they were regarded as such by others. For some provincials under Roman rule, the only experience with "Romans" prior to themselves being granted citizenship was through Rome's at times coercive tax-collection system or its army, aspects which were not assimilative in terms of forming an empire-spanning collective identity. Caracalla's grant marked a radical change in imperial policy towards the provincials. It is possible that decades, and in many cases centuries, of
In most cases, it is not clear to what extent the majority of the new Roman citizens regarded themselves as being Roman, or to what extent they were regarded as such by others. For some provincials under Roman rule, the only experience with "Romans" prior to themselves being granted citizenship was through Rome's at times coercive tax-collection system or its army, aspects which were not assimilative in terms of forming an empire-spanning collective identity. Caracalla's grant marked a radical change in imperial policy towards the provincials. It is possible that decades, and in many cases centuries, of
 The Roman army underwent considerable changes in the 4th century, experiencing what some have called 'barbarisation', traditionally understood as the result of recruitments of large amounts of barbarian soldiers. Though barbarian origins were seldom forgotten, the large scale and
The Roman army underwent considerable changes in the 4th century, experiencing what some have called 'barbarisation', traditionally understood as the result of recruitments of large amounts of barbarian soldiers. Though barbarian origins were seldom forgotten, the large scale and
 From the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century to the wars of Emperor
From the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century to the wars of Emperor
 The great turning point in the history of the latter-day Romans of the west was the wars of Justinian I (533–555), aimed at reconquering the lost provinces of the Western Roman Empire. During Justinian's early reign, eastern authors re-wrote 5th-century history to portray the west as "lost" to barbarian invasions, rather than attempting to further integrate the barbarian rulers into the Roman world. By the end of the Justinianic wars, imperial control had returned to northern Africa and Italy, but the wars being founded on the idea that anything outside of the eastern empire's direct control was no longer part of the Roman Empire meant that there could no longer be any doubt that the lands beyond the imperial frontier were no longer Roman and instead remained "lost to barbarians". As a result, Roman identity in the still barbarian-ruled regions (i.e. Gaul, Spain and Britain) declined dramatically. During the reconquest of Italy, the Roman Senate disappeared and most of its members moved to
The great turning point in the history of the latter-day Romans of the west was the wars of Justinian I (533–555), aimed at reconquering the lost provinces of the Western Roman Empire. During Justinian's early reign, eastern authors re-wrote 5th-century history to portray the west as "lost" to barbarian invasions, rather than attempting to further integrate the barbarian rulers into the Roman world. By the end of the Justinianic wars, imperial control had returned to northern Africa and Italy, but the wars being founded on the idea that anything outside of the eastern empire's direct control was no longer part of the Roman Empire meant that there could no longer be any doubt that the lands beyond the imperial frontier were no longer Roman and instead remained "lost to barbarians". As a result, Roman identity in the still barbarian-ruled regions (i.e. Gaul, Spain and Britain) declined dramatically. During the reconquest of Italy, the Roman Senate disappeared and most of its members moved to
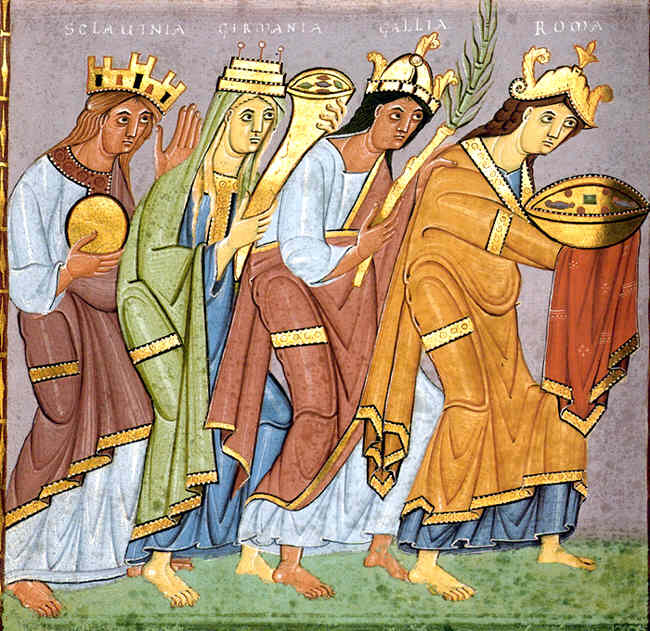 The population of the city of Rome continued to identify, and be identified, as Romans by westerners. Although Rome's history was not forgotten, the city's importance in the Middle Ages primarily stemmed from it being the seat of the
The population of the city of Rome continued to identify, and be identified, as Romans by westerners. Although Rome's history was not forgotten, the city's importance in the Middle Ages primarily stemmed from it being the seat of the
 Unlike the other kingdoms, the
Unlike the other kingdoms, the
 Eastern Mediterranean populations, which remained under Eastern Roman (or "
Eastern Mediterranean populations, which remained under Eastern Roman (or "
 As the Byzantine Empire lost its territories in
As the Byzantine Empire lost its territories in
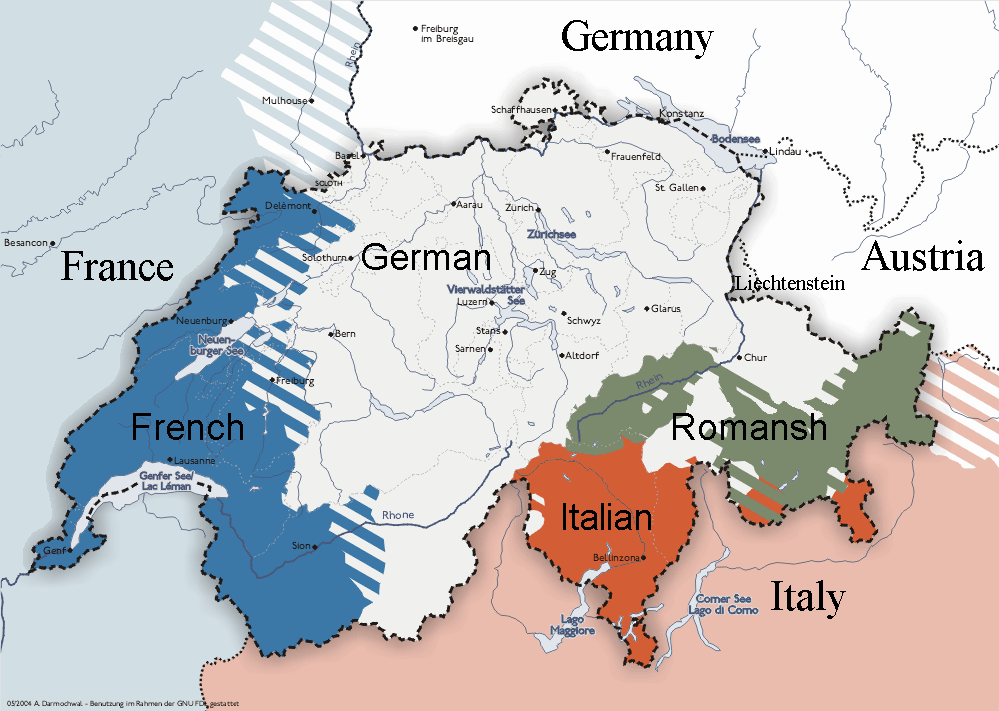 The vast majority of the Romance peoples that descended from the intermingling of Romans and Germanic peoples following the collapse of Roman political unity in the west diverged into groups that no longer identify as Romans. In the Alpine regions north of Italy however, Roman identity showed considerable tenacity. The Romansh people of Switzerland are descended from these populations, which in turn were descended from Romanised Rhaetians. Though most of the Romans of the region were assimilated by the
The vast majority of the Romance peoples that descended from the intermingling of Romans and Germanic peoples following the collapse of Roman political unity in the west diverged into groups that no longer identify as Romans. In the Alpine regions north of Italy however, Roman identity showed considerable tenacity. The Romansh people of Switzerland are descended from these populations, which in turn were descended from Romanised Rhaetians. Though most of the Romans of the region were assimilated by the
Roman Kingdom
The Roman Kingdom, also known as the Roman monarchy and the regal period of ancient Rome, was the earliest period of Ancient Rome, Roman history when the city and its territory were King of Rome, ruled by kings. According to tradition, the Roma ...
, the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
, and the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. This concept underwent considerable changes throughout the long history of the Roman civilisation, as its borders expanded and contracted. Originally only including the Latins of Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
itself, Roman citizenship was extended to the rest of the Italic peoples
The concept of Italic peoples is widely used in linguistics and historiography of ancient Italy. In a strict sense, commonly used in linguistics, it refers to the Osco-Umbrian languages, Osco-Umbrians and Latino-Faliscan languages, Latino-Falisca ...
by the 1st century BC and to nearly every subject of the Roman empire in late antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
. At their peak, the Romans ruled large parts of Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
, and North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
through conquests made during the Roman Republic and the subsequent Roman Empire. Although defined primarily as a citizenship, "Roman-ness" has also and variously been described as a cultural identity
Cultural identity is a part of a person's identity (social science), identity, or their self-conception and self-perception, and is related to nationality, ethnicity, religion, social class, generation, Locality (settlement), locality, gender, o ...
, a nationality
Nationality is the legal status of belonging to a particular nation, defined as a group of people organized in one country, under one legal jurisdiction, or as a group of people who are united on the basis of culture.
In international law, n ...
, or a multi-ethnicity
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they Collective consciousness, collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, ...
that eventually encompassed a vast regional diversity.
Citizenship grants, demographic growth, and settler and military colonies rapidly increased the number of Roman citizens. The increase achieved its peak with Emperor Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname Caracalla (; ), was Roman emperor from 198 to 217 AD, first serving as nominal co-emperor under his father and then r ...
's AD 212 Antonine Constitution, which extended citizenship rights to all free inhabitants of the empire. Roman identity provided a larger sense of common identity and became important when distinguishing from non-Romans, such as barbarian settlers and invaders. Roman culture was far from homogeneous; though there was a common cultural idiom, one of the strengths of the Roman Empire was also its ability to incorporate traditions from other cultures, notably but not exclusively Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
.
 The collapse of the
The collapse of the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
in the 5th century ended the political domination of the Roman Empire in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
, but Roman identity survived in the west as an important political resource. Through the failures of the surviving Eastern Roman Empire, also called the Byzantine Empire, of reconquering and keeping control of the west and suppression from the new Germanic kingdoms, Roman identity faded away in the west, more or less disappearing in the 8th and 9th centuries. In the Greek-speaking east, still under imperial control, Roman identity survived until the fall of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
in 1453 and beyond.
Whereas Roman identity faded away in most of the lands where it was once prominent, for some regions and peoples it proved considerably more tenacious. In Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, "Romans" (''Romani'' in Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and Italian) has continuously and uninterruptedly been the demonym
A demonym (; ) or 'gentilic' () is a word that identifies a group of people ( inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place ( hamlet, village, town, city, region, ...
of the citizens of Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
from the foundation of the city to the present-day. During the Eastern Roman Empire and for some time after its fall, Greeks identified as '' Romioi'', or related names. In Switzerland several names are Roman references: the Romands and the Romansh people. Several names derive from the Latin ''Romani'' (such as the Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
, Aromanians
The Aromanians () are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgari ...
and Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( or ) are a Romance languages, Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istria, Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. Howe ...
), or from the Germanic '' walhaz'' (a term originally referring to the Romans; adopted in the form '' Vlach'' as the self-designation of the Megleno-Romanians).
Romanness
Meaning of "Roman"
 The term 'Roman' is today used interchangeably to describe a historical timespan, a
The term 'Roman' is today used interchangeably to describe a historical timespan, a material culture
Material culture is culture manifested by the Artifact (archaeology), physical objects and architecture of a society. The term is primarily used in archaeology and anthropology, but is also of interest to sociology, geography and history. The fie ...
, a geographical location, and a personal identity. Though these concepts are related, they are not identical. Many modern historians tend to have a preferred idea of what being Roman meant, so-called '' Romanitas'', but this was a term rarely used in Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
itself. Like all identities, the identity of 'Roman' was flexible, dynamic and multi-layered, and never static or unchanging. Given that Rome was a geographically vast and chronologically long-lived state, there is no simple definition of what being Roman meant and definitions were inconsistent already in antiquity. Nevertheless, some elements remained common throughout much of Roman history.
Some ancient Romans considered aspects such as geography, language, and ethnicity as important markers of Romanness, whereas others saw Roman citizenship
Citizenship in ancient Rome () was a privileged political and legal status afforded to free individuals with respect to laws, property, and governance. Citizenship in ancient Rome was complex and based upon many different laws, traditions, and cu ...
and culture or behaviour as more important. At the height of the Roman Empire, Roman identity formed a collective geopolitical identity, extended to nearly all subjects of the Roman emperors and encompassing vast regional and ethnical diversity. Often, what individual believed and did was far more important to the concept of Roman identity than long bloodlines and shared descent. The key to 'Romanness' in the minds of some famous Roman orators, such as Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
, was keeping with Roman tradition and serving the Roman state. Cicero's view of Romanness were partly formed by his status as a "new man", the first of his family to serve in the Roman Senate, lacking prestigious lines of Roman descent himself. This is not to say that the importance of blood kinship was wholly dismissed. Orators such as Cicero frequently appealed to their noble contemporaries to live up to the 'greatness of their forefathers'. These appeals were typically only invoked towards illustrious noble families, with other important traditions emphasising Rome's collective descent.
Throughout its history, Rome proved to be uniquely capable of incorporating and integrating other peoples ( Romanisation). This sentiment originated from the city's foundation myths, including Rome being founded as something akin to a political sanctuary by Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
, as well as the rape of the Sabine women, which represented how different peoples had commingled since the very beginning of the city. Cicero and other Roman authors sneered at peoples such as the Athenians
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
, who prided themselves in their shared descent, and instead found pride in Rome's status as a "mongrel nation". Dionysius of Halicarnassus, a Greek historian who lived in Roman times, even embellished the multicultural origin of the Romans, writing that Romans had since the foundation of Rome welcomed innumerable immigrants not only from the rest of Italy, but from the entire world, whose cultures merged with theirs.
A handful of Roman authors, such as Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
and Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire. His most important surviving work is ''De vita Caesarum'', common ...
, expressed concerns in their writings concerning Roman "blood purity" as Roman citizens from outside of Roman Italy increased in number. Neither author, however, suggested that the naturalisation of new citizens should stop, only that manumission
Manumission, or enfranchisement, is the act of freeing slaves by their owners. Different approaches to manumission were developed, each specific to the time and place of a particular society. Historian Verene Shepherd states that the most wi ...
s (freeing slaves) and grants of citizenship should be less frequent. Their concerns of blood purity did not match modern ideas of race or ethnicity, and had little to do with features such as skin colour or physical appearance. Terms such as " Aethiop", which Romans used for black people
Black is a racial classification of people, usually a political and skin color-based category for specific populations with a mid- to dark brown complexion. Not all people considered "black" have dark skin and often additional phenotypical ...
, carried no social implications, and though phenotype-related stereotypes certainly existed in Ancient Rome, inherited physical characteristics were typically not relevant to social status; people who looked different from the typical Mediterranean populace, such as black people, were not excluded from any profession and there are no records of stigmas or biases against "mixed race
The term multiracial people refers to people who are mixed with two or more
races and the term multi-ethnic people refers to people who are of more than one ethnicities. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mul ...
" relationships. The main dividing social differences in Ancient Rome were not based on physical features, but rather on differences in class or rank. Romans practised slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
extensively, but slaves in Ancient Rome were part of various different ethnic groups, and were not enslaved because of their ethnic affiliation. According to the English historian Emma Dench
Emma Dench (born 1963) is an English ancient historian, classicist, and academic administrator. She has been McLean Professor of Ancient and Modern History at Harvard University since 2014, and Dean of its Graduate School of Arts and Science ...
, it was "notoriously difficult to detect slaves by their appearance" in Ancient Rome.
Non-Romans
 Although Ancient Rome has been termed an 'evidently non-racist society', Romans carried considerable cultural stereotypes and prejudices against cultures and peoples that were not integrated into the Roman world, i.e. " barbarians". Though views differed through Roman history, the attitude towards peoples beyond the Roman frontier among most Roman writers in
Although Ancient Rome has been termed an 'evidently non-racist society', Romans carried considerable cultural stereotypes and prejudices against cultures and peoples that were not integrated into the Roman world, i.e. " barbarians". Though views differed through Roman history, the attitude towards peoples beyond the Roman frontier among most Roman writers in late antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
can be summed up with "the only good barbarian is a dead barbarian". Throughout antiquity, the majority of Roman emperors included anti-barbarian imagery on their coinage, such as the emperor or Victoria (the personification and goddess of victory) being depicted as stepping on or dragging defeated barbarian enemies. Per the writings of Cicero, what made people barbarians was not their language or descent, but rather their customs and character, or lack thereof. Romans viewed themselves as superior over foreigners, but this stemmed not from perceived biological differences, but rather from what they perceived as a superior way of life. 'Barbarian' was as such a cultural, rather than biological, term. It was not impossible for a barbarian to become a Roman; the Roman state was itself seen as having the duty to conquer and transform, i.e. civilise, barbarian peoples. A particularly disliked group of non-Romans within the empire were the Jews. The majority of the Roman populace detested Jews and Judaism, though views were more varied among the Roman elite. Although many, such as Tacitus, were also hostile to the Jews, others, such as Cicero, were merely unsympathetically indifferent. The Roman state was not wholly opposed to the Jews, since there was a sizeable Jewish population in Rome itself, as well as at least thirteen
A particularly disliked group of non-Romans within the empire were the Jews. The majority of the Roman populace detested Jews and Judaism, though views were more varied among the Roman elite. Although many, such as Tacitus, were also hostile to the Jews, others, such as Cicero, were merely unsympathetically indifferent. The Roman state was not wholly opposed to the Jews, since there was a sizeable Jewish population in Rome itself, as well as at least thirteen synagogue
A synagogue, also called a shul or a temple, is a place of worship for Jews and Samaritans. It is a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels) where Jews attend religious services or special ceremonies such as wed ...
s in the city. Roman antisemitism
Antisemitism or Jew-hatred is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who harbours it is called an antisemite. Whether antisemitism is considered a form of racism depends on the school of thought. Antisemi ...
, which led to several wars, persecutions, and massacres in Judea
Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the pres ...
, was not rooted in racial prejudice, but rather in the perception that the Jews, uniquely among conquered peoples, refused to integrate into the Roman world. The Jews adhered to their own set of rules, restrictions and obligations, which were typically either disliked or misunderstood by the Romans, and they remained faithful to their own religion. The exclusivist religious practices of the Jews, and their opposition to abandoning their own customs in favour of those of Rome, even after being conquered and repeatedly suppressed, evoked the suspicion of the Romans.
Antiquity
Classical antiquity
Founding myths and Romans of the republic
Thefounding of Rome
The founding of Rome was a prehistoric event or process later greatly embellished by Roman historians and poets. Archaeological evidence indicates that Rome developed from the gradual union of several hillfort, hilltop villages during the Prehi ...
, and the history of the city and its people throughout its first few centuries, is steeped in myth and uncertainty. The traditional date for Rome's foundation, 753 BC, and the traditional date for the foundation of the Roman Republic, 509 BC, though commonly used even in modern historiography, are uncertain and mythical. The myths surrounding Rome's foundation combined, if not confused, several different stories, going from the origins of the Latin people under a king by the name Latinus, to Evander of Pallantium, who was said to have brought Greek culture to Italy, and a myth of Trojan origin through the heroic figure Aeneas. The actual mythical founder of the city itself, Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
, only appears many generations into the complex web of foundation myths. Interpretations of these myths varied among authors in Antiquity, but most agreed that their civilisation had been founded by a mixture of migrants and fugitives. These origin narratives would favour the later extensive integrations of foreigners into the Roman world.
The origins of the people that became the first Romans are clearer. As in neighbouring city-states, the early Romans were composed mainly of Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
-speaking Italic people, known as the Latins. The Latins were a people with a marked Mediterranean character, related to other neighbouring Italic peoples such as the Falisci
The Falisci were an Italic peoples, Italic tribe who lived in what is now northern Lazio, on the Etruscan side of the Tiber River. They spoke an Italic languages, Italic language, Faliscan language, Faliscan, closely related to Latin. Origina ...
. The early Romans were part of the Latin homeland, known as Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on whic ...
, and were Latins themselves. By the time of the 6th century, the inhabitants of Rome had conquered and destroyed all the other Latin settlements and communities such as Antemnae and Collatia and defeated the hegemony of the settlement of Alba Longa
Alba Longa (occasionally written Albalonga in Italian sources) was an ancient Latins (Italic tribe), Latin city in Central Italy in the vicinity of Lake Albano in the Alban Hills. The ancient Romans believed it to be the founder and head of the ...
, which had previously united the Latin people under its leadership, a position that now belonged to Rome.
From the middle of the 4th century onwards, Rome won a series of victories which saw them rise to rule all of Italy south of the Po river
The Po ( , ) is the longest river in Italy. It flows eastward across northern Italy, starting from the Cottian Alps. The river's length is , or if the Maira (river), Maira, a right bank tributary, is included. The headwaters of the Po are forme ...
by 270 BC. Following the conquest of Italy, the Romans waged war against the great powers of their time; Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
to the south and west and the various Hellenistic kingdoms to the east, and by the middle of the second century BC, all rivals had been defeated and Rome became recognised by other countries as the definite masters of the Mediterranean. By the late 3rd century BC, about a third of the people in Italy south of the Po river had been made Roman citizens, meaning that they were liable for military service, and the rest had been made into allies, frequently called on to join Roman wars. These allies were eventually made Roman citizens as well after refusal by the Roman government to make them so was met with the Social War, after which Roman citizenship was extended to all the people south of the Po river. In 49 BC, citizenship rights were also extended to the people of Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul (, also called ''Gallia Citerior'' or ''Gallia Togata'') was the name given, especially during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, to a region of land inhabited by Celts (Gauls), corresponding to what is now most of northern Italy.
Afte ...
by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
. The number of Romans would rapidly increase in later centuries through further extensions of citizenship. Typically, there were five different mechanisms for acquiring Roman citizenship: serving in the Roman army, holding office in cities with the Latin right, being granted it directly by the government, being part of a community that was granted citizenship as a "block grant" or, as a slave, being freed by a Roman citizen. Just as it could be gained, Roman status could also be lost, for instance through engaging practices considered corrupt or by being carried off into captivity in enemy raids (though one could again become a Roman upon returning from captivity).
Romans of the early empire
In the earlyRoman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, the population was composed of several groups of distinct legal standing, including the Roman citizens themselves (''cives romani''), the provincials (''provinciales''), foreigners (''peregrini'') and free non-citizens such as freedmen (freed slaves) and slaves. Roman citizens were subject to the Roman legal system while provincials were subject to whatever laws and legal systems had been in place in their area at the time it was annexed by the Romans. Over time, Roman citizenship was gradually extended more and more and there was a regular "siphoning" of people from less privileged legal groups to more privileged groups, increasing the total percentage of subjects recognised as Romans though the incorporation of the ''provinciales'' and ''peregrini''. The capability of the Roman Empire to integrate foreign peoples was one of the key elements that ensured its success. In antiquity, it was significantly easier as a foreigner to become a Roman than it was to become a member or citizen of any other contemporary state. This aspect of the Roman state was seen as important even by some of the emperors. For instance, Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
(41–54) pointed it out when questioned by the senate on admitting Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). Th ...
to join the senate:
Principate
The Principate was the form of imperial government of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the Dominate. The principate was ch ...
(27 BC – AD 284) onwards, barbarians settled and integrated into the Roman world. Such settlers would have been granted certain legal rights simply by being within Roman territory, becoming ''provinciales'' and thus being eligible to serve as ''auxilia
The (; ) were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen Roman legion, legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 27 BC. By the 2nd century, the contained the same number of infantry as the ...
'' (auxiliary soldiers), which in turn made them eligible to become full ''cives Romani''. Through this relatively rapid process, thousands of former barbarians could quickly become Romans. This tradition of straightforward integration eventually culminated in the Antonine Constitution, issued by Emperor Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname Caracalla (; ), was Roman emperor from 198 to 217 AD, first serving as nominal co-emperor under his father and then r ...
in 212, in which all free inhabitants of Empire were granted the citizenship. Caracalla's grant contributed to a vast increase in the number of people with the '' nomen'' (name indicating familial association) ''Aurelius''. By the time of the Antonine Constitution, many people throughout the provinces already considered themselves (and were considered by others) as Romans. Through the centuries of Roman expansion, large numbers of veterans and opportunists had settled in the provinces and colonies founded by Julius Caesar and Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
alone saw between 500,000 and a million people from Italy settled in Rome's provinces. In AD 14, four to seven percent of the free people in the provinces of the empire were already Roman citizens. In addition to colonists, many provincials had also become citizens through grants by emperors and through other methods.
Romanization
In linguistics, romanization is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Latin script, Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and tra ...
through Rome's cultural influence had already begun the evolution of a "national" Roman identity before 212 and that the grant only made the ongoing process legal, but the grant might also have served as the important prerequisite for a later nearly all-encompassing collective Roman identity. According to the British jurist Tony Honoré, the grant "gave many millions, perhaps a majority of the empire's inhabitants ..a new consciousness of being Roman". It is likely that local identities survived after Caracalla's grant and remained prominent throughout the empire, but that self-identification as Roman provided a larger sense of common identity and became important when dealing with and distinguishing oneself from non-Romans, such as barbarian settlers and invaders.
In many cases, ancient Romans associated the same things with their identity as historians do today: the rich ancient Latin literature, the impressive Roman architecture, the common marble statues, the variety of cult sites, the Roman infrastructure and legal tradition, as well as the almost corporate identity of the Roman army
The Roman army () served ancient Rome and the Roman people, enduring through the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (509–27 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC–AD 1453), including the Western Roman Empire (collapsed Fall of the W ...
were all cultural and symbolic ways to express Roman identity. Although there was a more or less unifying Roman identity, Roman culture in classical times was also far from homogeneous. There was a common cultural idiom, large portions of which was based in earlier Hellenistic culture, but Rome's strength also laid in its flexibility and its ability to incorporate traditions from other cultures. For instance, the religions of many conquered peoples were embraced through amalgamations of the gods of foreign pantheons with those of the Roman pantheon. In Egypt, Roman emperors were seen as the successors of the pharaohs (in modern historiography termed the Roman pharaohs) and were depicted as such in artwork and in temples. Many cults from the eastern Mediterranean and beyond spread to Western Europe over the course of Roman rule.
Late antiquity
Once the very core of ancient Romanness, the city of Rome gradually lost its exceptional status within the empire inlate antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
. By the end of the third century, the city's importance was almost entirely ideological, and several emperors and usurpers had begun reigning from other cities closer to the imperial frontier. Rome's loss of status was also reflected in the perceptions of the city by the Roman populace. In the writings of the 4th-century Greek-speaking Roman soldier and author Ammianus Marcellinus, Rome is described almost like a foreign city, with disparaging comments on its corruption and impurity. Few Romans in late antiquity embodied all aspects of traditional Romanness. Many of them would have come from remote or less prestigious provinces and practiced religions and cults unheard of in Rome itself. Many of them would also have spoken 'barbarian languages' or Greek instead of Latin. Few inscriptions from late antiquity explicitly identify individuals as 'Roman citizens' or 'Romans'. Before the Antonine Constitution, being a Roman had been a mark of distinction and often stressed, but after the 3rd century Roman status went without saying. This silence does not mean that Romanness no longer mattered in the late Roman Empire, but rather that it had become less distinctive than other more specific marks of identity (such as local identities) and only needed to be stressed or highlighted if a person had recently become a Roman, or if the Roman status of a person was in doubt. The prevalent view of the Romans themselves was that the ''populus Romanus'', or Roman people, were a "people by constitution", as opposed to the barbarian peoples who were ''gentes'', "peoples by descent" (i. e. ethnicities).
Given that Romanness had become near-universal within the empire, local identities became more and more prominent. In the late Roman Empire, one could identify as a Roman as a citizen of the empire, as a person originating from one of the major regions (Africa, Britannia, Gaul, Hispania etc.) or as originating from a specific province or city. Though the Romans themselves did not see them as equivalent concepts, there is no fundamental difference between such Roman sub-identities and the ''gens'' identities ascribed to barbarians. In some cases, Roman authors ascribed different qualities to citizens of different parts of the empire, such as Ammianus Marcellinus who wrote of the differences between 'Gauls' and 'Italians'. In the late Roman army, there were regiments named after Roman sub-identities, such as 'Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
' and ' Batavians', as well as regiments named after barbarian ''gentes'', such as the Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
or Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
.
 The Roman army underwent considerable changes in the 4th century, experiencing what some have called 'barbarisation', traditionally understood as the result of recruitments of large amounts of barbarian soldiers. Though barbarian origins were seldom forgotten, the large scale and
The Roman army underwent considerable changes in the 4th century, experiencing what some have called 'barbarisation', traditionally understood as the result of recruitments of large amounts of barbarian soldiers. Though barbarian origins were seldom forgotten, the large scale and meritocratic
Meritocracy (''merit'', from Latin , and ''-cracy'', from Ancient Greek 'strength, power') is the notion of a political system in which economic goods or political power are vested in individual people based on ability and talent, rather than ...
nature of the Roman army made it relatively easy for "barbarian" recruits to enter the army and rise through the ranks only through their skills and achievements. It is not clear to what extent there was actual non-Roman influence on the military; it is plausible that extensive numbers of barbarians were made part of the normal Roman military but it is equally plausible that there was also, or instead, a certain 'barbarian chic' in the army, comparable to the 19th-century French Zouaves (French military units in North Africa who adopted native clothing and cultural practices). The rise of non-Roman customs in the Roman military might not have resulted from increasing numbers of barbarian recruits, but rather from Roman military units along the imperial borders forming their own distinctive identities. In the late empire, the term "barbarian" was sometimes used in a general sense by Romans not in the military for Roman soldiers stationed alongside the imperial border, in reference to their perceived aggressive nature. No matter the reason, the Roman military increasingly came to embody 'barbarian' aspects that in previous times had been considered antithetical to the Roman ideal. Such aspects included emphasising strength and thirst for battle, as well as the assumption of "barbarian" strategies and customs, such as the ''barritus
''Barritus'' (''barrītūs)'' is a battle cry documented in writing since the 1st century among List of early Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes. The technique of ''Barritus'' later became popular among Germanic auxiliary troops in the Roman Army. ...
'' (a formerly Germanic battle cry), the '' Schilderhebung'' (raising an elected emperor up on a shield) as well as Germanic battle formations. The assumption of these customs might instead of barbarisation be attributable to the Roman army simply adopting customs it found useful, a common practice. Some barbarian soldiers recruited into the Roman army proudly embraced Roman identification and in some cases, the barbarian heritage of certain late Roman individuals was even completely ignored in the wider Roman world.
Religion had always been an important marker of Romanness. As Christianity gradually became the dominant religion in the Roman Empire through late antiquity, and eventually became the only legal faith, the Christianised Roman aristocracy had to redefine their Roman identity in Christian terms. The rise of Christianity did not go unnoticed or unchallenged by the conservative elements of the pagan Roman elite, who became aware that power was slipping from their hands. Many of them, pressured by the increasingly anti-pagan and militant Christians, turned to emphasising that they were the only 'true Romans' as they preserved the traditional Roman religion and literary culture. According to the Roman statesman and orator Quintus Aurelius Symmachus
Quintus Aurelius Symmachus Nickname, signo Eusebius (, ; c. 345 – 402) was a Roman statesman, orator, and intellectual. He held the offices of governor of proconsular Africa (province), Africa in 373, urban prefect of Rome in 384 and 385, and R ...
( 345–402), true Romans were those who followed the traditional Roman way of life, including its ancient religions, and it was adherence to those religions that in the end would protect the empire from its enemies, as in previous centuries. Per Symmachus and his supporters, Romanness had nothing to do with Christianity, but depended on Rome's pagan past and its status as the heart of a vast and polytheistic empire. The ideas of Symmachus were not popular among the Christians. Some church leaders, such as Ambrose, the Archbishop of Mediolanum, launched formal and vicious assaults on paganism and those members of the elite which defended it. Like Symmachus, Ambrose saw Rome as the greatest city of the Roman Empire, but not because of its pagan past but because of its Christian present. Throughout late antiquity, Romanness became increasingly defined by Christian faith, which would eventually become the standard. The status of Christianity was much increased through the adoption of the religion by the Roman emperors. Throughout late antiquity, the emperors and their courts were viewed as the Romans ''par excellence''.
As the Roman Empire lost, or ceded control of, territories to various barbarian rulers, the status of the Roman citizens in those provinces sometimes came into question. People born as Roman citizens in regions that then came under barbarian control could be subjected to the same prejudice as barbarians were. Over the course of the Roman Empire, men from nearly all of its provinces had come to rule as emperors. As such, Roman identity remained political, rather than ethnic, and open to people of various origins. This nature of Roman identity ensured that there was never a strong consolidation of a 'core identity' of Romans in Italy, but also likely contributed to the long-term endurance and success of the Roman state. The fall of the Western Roman Empire coincided with the first time the Romans actively excluded an influential foreign group within the empire, the barbarian and barbarian-descended generals of the 5th century, from Roman identity and access to the Roman imperial throne.
Later history
The Roman Empire's expansion facilitated the spread of Roman identity over a large stretch of territories that had never before had a common identity and never would again. The effects of Roman rule on the personal identities of the empire's subjects was considerable and the resulting Roman identity outlasted actual imperial control by several centuries.Western Europe
Early endurance of Roman identity
 From the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century to the wars of Emperor
From the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century to the wars of Emperor Justinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
in the 6th century, the predominant structure of societies in the west was a near-completely barbarian military but also a near-completely Roman civil administration and aristocracy. The new Barbarian rulers took steps to present themselves as legitimate rulers within the Roman framework, with the pretense of legitimacy being especially strong among the rulers of Italy. The early kings of Italy, first Odoacer and then Theoderic the Great, were legally and ostensibly viceroys of the eastern emperor and thus integrated into the Roman government. Like the western emperors before them, they continued to appoint western consuls, which were accepted in the east and by the other barbarian kings. The imperial court in the east extended various honours to powerful barbarian rulers in the west, which was interpreted by the barbarians as enhancing their legitimacy; something they used to justify territorial expansion. In the early 6th century, Clovis I
Clovis (; reconstructed Old Frankish, Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first List of Frankish kings, king of the Franks to unite all of the Franks under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a ...
of the Franks and Theoderic the Great of the Ostrogoths nearly went to war with each other, a conflict that could have resulted in the re-establishment of the western empire under either king. Concerned about such a prospect, the eastern court never again extended similar honours to western rulers, instead beginning to emphasise its own exclusive Roman legitimacy, which it would continue to do for the rest of its history.
Culturally and legally, Roman identity remained prominent in the west for centuries, still providing a sense of unity throughout the Mediterranean. Italy's Ostrogothic Kingdom preserved the Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Sena ...
, which often dominated politics in Rome, illustrating the survival of and continued respect for Roman institutions and identity. The barbarian kings continued to use Roman law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (), to the (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I.
Roman law also den ...
throughout the early Middle Ages, often issuing their own law collections. In 6th-century law collections issued by the Visigoths in Spain and the Franks in Gaul, it is clear that there were still large populations identifying as Romans in these regions given that the law collections distinguish between barbarians who live by their own laws and Romans who live by Roman law. Even after Italy was conquered by the Lombards
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written betwee ...
in the late 6th century, the continued administration and urbanisation of northern Italy attest to a continued survival of Roman institutions and values. It was still possible for non-citizens (such as barbarians) in the west to become Roman citizens well into the 7th and 8th centuries; several surviving Visigothic and Frankish documents explain the benefits of becoming a Roman citizen and there are records of rulers and nobles freeing slaves and making them into citizens. Despite this, Roman identity was in a steep decline by the 7th and 8th centuries.
Disappearances of Roman identity
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. Though the senate achieved a certain legacy in the west, the end of the institution removed a group that had always set the standard of what Romanness was supposed to mean. The war in Italy also divided the Roman elite there between those who enjoyed barbarian rule and those who supported the empire and later withdrew to imperial territory, meaning that Roman identity ceased to provide a sense of social and political cohesion.
The division of Western Europe into multiple different kingdoms accelerated the disappearance of Roman identity, as the previously unifying identity was replaced by local identities based on the region one was from. The fading connectivitiy also meant that while largely Roman law and culture continued on, the language became increasingly fragmented and split, Latin gradually developing into what would become the modern Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
. Where they had once been the majority of the population, the Romans of Gaul and Hispania gradually and quietly faded away as their descendants adopted other names and identities. In Sub-Roman Britain
Sub-Roman Britain, also called post-Roman Britain or Dark Age Britain, is the period of late antiquity in Great Britain between the end of Roman rule and the founding of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. The term was originally used to describe archae ...
, the people of the large urban centers clinged to Roman identity, but rural populations integrated and assimilated with Germanic colonisers (the Jutes
The Jutes ( ) were one of the Germanic people, Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the end of Roman rule in Britain, departure of the Roman Britain, Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic na ...
, Angles and Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
). Once the large cities declined, Roman identity faded away in Britain as well.
The adoption of local identities in Gaul and Hispania was made more attractive in that they were not binary opposed to the identity of the barbarian rulers in the same way that 'Roman' was; for instance, one could not be both Roman and Frankish, but it was possible to, for instance, be both Arvernian (i.e. from Auvergne) and Frankish. In Hispania, "Gothic" transitioned from simply an ethnic identity to being both an ethnic one (in the sense of descent from Goths) and a political one (in the sense of allegiance to the king). Gothic becoming more fluid and multi-dimensional as an identity facilitated a smooth transition from people identifying as Romans to people identifying as Goths. There were few differences between the Goths and the Romans of Hispania at this point; the Visigoths no longer practised Arian Christianity and Romans, just like the Goths, were from the 6th century onwards allowed to serve in the military. Though Roman identity was rapidly disappearing, the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic Spain or Kingdom of the Goths () was a Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic people ...
in the 6th and 7th centuries thus also produced several prominent latter-day Roman generals, such as Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
and Paulus.
The disappearance of the Romans is reflected in the barbarian law collections. In the Salic law
The Salic law ( or ; ), also called the was the ancient Frankish Civil law (legal system), civil law code compiled around AD 500 by Clovis I, Clovis, the first Frankish King. The name may refer to the Salii, or "Salian Franks", but this is deba ...
of Clovis I (from around 500), the Romans and the Franks are the two major parallel populations of the kingdom and both have well-defined legal statuses. A century later in the '' Lex Ripuaria'', the Romans are just one of many smaller semi-free populations, restricted in their legal capacity, with many of their former advantages now associated with Frankish identity. Such legal arrangements would have been unthinkable under the Roman Empire and under the early decades of barbarian rule. By Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
's imperial coronation in 800, Roman identity largely disappeared in Western Europe and fell to low social status. The situation was somewhat paradoxical: living Romans, in Rome and elsewhere, had a poor reputation, with records of anti-Roman attacks and the use of 'Roman' as an insult, but the name of Rome was also used a source of great and unfailing political power and prestige, employed by many aristocratic families (sometimes proudly proclaiming invented Roman origins) and rulers throughout history. Through suppressing Roman identity in the lands they ruled and discounting the remaining empire in the east as "Greek", the Frankish state hoped to avoid the possibility of the Roman people proclaiming a Roman emperor in the same way that the Franks proclaimed a Frankish king.
Reversion to Rome proper
 The population of the city of Rome continued to identify, and be identified, as Romans by westerners. Although Rome's history was not forgotten, the city's importance in the Middle Ages primarily stemmed from it being the seat of the
The population of the city of Rome continued to identify, and be identified, as Romans by westerners. Although Rome's history was not forgotten, the city's importance in the Middle Ages primarily stemmed from it being the seat of the pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
, a view shared by both westerners and the eastern empire. During the centuries following Justinian's reconquest, when the city was still under imperial control, the population was not specially administered and did not have any political participation in wider imperial affairs. When clashing with the emperors, the popes sometimes employed the fact that they had the backing of the ''populus Romanus'' ("people of Rome") as a legitimising factor, meaning that the city still endured some ideological importance in terms of Romanness. Western European authors and intellectuals increasingly associated Romanness only with the city itself. By the second half of the 8th century, westerners almost exclusively used the term to refer to the population of the city. When the temporal power of the papacy was established through the foundation of the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
in the 8th century, the popes used the fact that they were accompanied and supported by the ''populus Romanus'' as something that legitimised their sovereignty.
The Roman populace considered neither the eastern empire nor Charlemagne's new "Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
" to be properly Roman. Though the continuity from Rome to Constantinople was accepted in the west, surviving sources point to the easterners being seen as Greeks who had abandoned Rome and Roman identity. The Carolingian kings on the other hand were seen as having more to do with the Lombard kings of Italy than the ancient Roman emperors. The medieval Romans also often equated the Franks with the ancient Gauls, and viewed them as aggressive, insolent and vain. Despite this, the Holy Roman emperors were recognised by the citizens of Rome as true Roman emperors, albeit only because of their support and coronation by the popes.
The Franks and other westerners did not view the population of Rome favourably either. Foreign sources are generally hostile, ascribing traits such as unrest and deceit to the Romans and describing them as "as proud as they are helpless". Anti-Roman sentiment lasted throughout the Middle Ages. The Romans partly owed their bad reputation to sometimes trying to take an independent position towards the popes of the Holy Roman emperors. Given that these rulers were seen as having universal power, the Romans were considered intruders in affairs that exceeded their competence.
North Africa
 Unlike the other kingdoms, the
Unlike the other kingdoms, the Vandal Kingdom
The Vandal Kingdom () or Kingdom of the Vandals and Alans () was a confederation of Vandals and Alans, which was a barbarian kingdoms, barbarian kingdom established under Gaiseric, a Vandals, Vandalic warlord. It ruled parts of North Africa and th ...
in North Africa did not maintain a pretense of loyalty to the Roman Empire. Since the term 'Roman' was seen as implying political loyalty to the empire, it was regarded by the Vandal government as politically loaded and suspicious. As a consequence, the Roman population of the kingdom rarely self-identified as such, though important markers of Romanness, such as Roman naming customs, adherence to Nicene Christianity as well as the Latin-language literary tradition, survived throughout the kingdom's existence. Despite objections to 'Roman' as a term for the populace, the Vandals partly appealed to Roman legitimacy to legitimise themselves as rulers, given that the Vandal kings had marriage connections to the imperial Theodosian dynasty. However, the Vandal state more strongly worked to legitimise itself through appealing to the pre-Roman cultural elements of the region, particularly the Carthaginian Empire
Ancient Carthage ( ; , ) was an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic civilisation based in North Africa. Initially a settlement in present-day Tunisia, it later became a city-state, and then an empire. Founded by the Phoenicians ...
. Some symbols of the ancient state were revived and the city of Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
, capital of the kingdom, was heavily emphasised in poetry, on coinage and in the creation of a new "Carthaginian calendar". Coins minted by the Vandals were inscribed with ''Felix Karthago'' ("fortunate Carthage") and ''Carthagine Perpetua'' ("Carthage eternal").
The Vandalic promotion of independent African symbols had a profound effect on the formerly Roman populace of their kingdom. By the time the soldiers of the eastern empire landed in Africa during Justinian's Vandalic War
The Vandalic War (533–534) was a conflict fought in North Africa between the forces of the Byzantine Empire (also known as the Eastern Roman Empire) and the Germanic Vandal Kingdom. It was the first war of Emperor Justinian I's , wherein the ...
, the Romance people of North Africa had ceased to identify as Romans, instead preferring either Libyans (''Libicus'') or Punic people (''Punicus''). Contemporary eastern authors also described them as Libyans (Λίβυες). During the Vandal Kingdom's brief existence, the Vandal ruling class had culturally and ethnically merged with the Romano-Africans. By the time the kingdom fell, the only real cultural differences between the "Libyans" and "Vandals" were that Vandals adhered to Arian Christianity and were permitted to serve in the army. After North Africa was reincorporated into the empire, the eastern Roman government deported the Vandals from the region, which shortly thereafter led to disappearance of the Vandals as a distinct group. The only individuals recorded to have been deported were soldiers; given that the wives and children of the "Vandals" thus remained in North Africa, the name at this stage appears to mainly have denoted the soldier class.
Despite North Africa's reincorporation into the empire, the distinction between "Libyans" and "Romans" (i.e. the inhabitants of the eastern empire) was maintained by both groups. Per the writings of the 6th-century eastern historian Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea (; ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; ; – 565) was a prominent Late antiquity, late antique Byzantine Greeks, Greek scholar and historian from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Justinian I, Empe ...
, the Libyans were descended from Romans, ruled by the Romans, and served in the Roman army, but their Romanness had diverged too much from that of the populace of the empire as a result of the century of Vandal rule. Imperial policy reflected the view that the North Africans were no longer Romans. Whereas governors in the eastern provinces were often native to their respective provinces, the military and administrative staff in North Africa was almost entirely constituted by easterners. The imperial government distrusting the locals was hardly surprising given that imperial troops had been harassed by local (formerly Roman) peasants during the Vandalic War, supportive of the Vandal regime, and that there had been several rebels thereafter, such as Guntarith and Stotzas Stotzas (Greek language, Greek: Στότζας), also Stutias, Theophanes writes him Tzotzas (Τζότζας), was an Byzantine Empire, East Roman (Byzantine) soldier and leader of a military rebellion in the Praetorian prefecture of Africa in the 5 ...
, who sought to restore an independent kingdom. The distinction between the Romans and the Romance people of North Africa is also reflected in foreign sources, and the two populations appear to not yet have been reconciled by the time the African provinces fell during the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb
The conquest of the Maghreb by the Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphates commenced in 647 and concluded in 709, when the Byzantine Empire lost its last remaining strongholds to Caliph Al-Walid I. The North African campaigns were part of the century ...
and Roman rule was terminated.
Eastern Mediterranean
Survival of the Roman Empire in the east
 Eastern Mediterranean populations, which remained under Eastern Roman (or "
Eastern Mediterranean populations, which remained under Eastern Roman (or "Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
") control after the 5th century, retained "Roman" as their predominant identity; the majority of the population saw themselves as being Roman beyond any doubt and their emperor as ruling from the cultural and religious center of the Roman Empire: Constantinople, the New Rome. In the centuries when the Byzantine Empire was still a vast Mediterranean-spanning state, Roman identity was more strong in the imperial heartlands than on the peripheries, though it was also strongly embraced in the peripheral regions in times of uncertainty. As in earlier centuries, the Romans of the early Byzantine Empire were considered a people united by being subjects of the Roman state, rather than a people united through sharing ethnic descent (i.e. ''gens'' like those ascribed to different barbarian groups). The term extended to all Christian citizens of the empire, in a general sense referring to those who followed Chalcedonian Christianity
Chalcedonian Christianity is the branches of Christianity that accept and uphold theological resolutions of the Council of Chalcedon, the fourth ecumenical council, held in AD 451. Chalcedonian Christianity accepts the Christological Definiti ...
and were loyal to the emperor.
In Byzantine writings up until at least the 12th century, the idea of the Roman "homeland" consistently referred not to Greece or Italy, but to the entire old Roman world. Despite this, the Romans of Byzantium were also aware that their present empire was no longer as powerful as it once had been, and that centuries of warfare and strife had left the Roman Empire reduced in territory and somewhat humbled.
Given that the rulers of the Byzantine Empire were predominantly Hellenic, and the percentage of the population that was Hellenic became greater as the empire's borders were increasingly reduced, Western Europeans, from as early as the 6th century onwards, often referred to it as a Greek empire, inhabited by Greeks. To the early Byzantines themselves, up until the 11th century or so, terms such as "Hellenes" were seen as offensive, as it downplayed their Roman nature and furthermore associated them with the ancient Pagan Greeks rather than the more recent Christian Romans. The westerners were not unaware of Byzantium's Romanness; when not wishing to distance themselves from the eastern empire, the term ''Romani'' was frequently used for soldiers and subjects of the eastern emperors. From the 6th to 8th century, western authors also sometimes employed terms such as ''res publica'' or ''sancta res publica'' for the Byzantine Empire, still identifying it with the old Roman Republic. Such references ceased as Byzantine control of Italy and Rome itself crumbled and the Papacy began to use the term for their own, much more regional, domain and sphere of influence.
After the Muslim conquests
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and Italy, the Christians who lived in those regions ceased to be recognised by the Byzantine government as Romans, much in the same vein as had happened with the North Africans under Vandal rule. The decrease in the diversity of peoples recognised as being Roman meant that the term Roman increasingly came to be applied only to the now dominant Hellenic population of the remaining territories, rather than to all imperial citizens. As the Hellenic populace were united by following Orthodox Christianity, spoke the same Greek language, and believed that they shared a common ethnic origin, "Roman" (''Rhōmaîoi'' in Greek) thus gradually transformed into an ethnic identity. By the late 7th century, Greek, rather than Latin, had begun being referred to in the east as the ''rhomaisti'' (Roman way of speaking). In chronicles written in the 10th century, the ''Rhōmaîoi'' begin to appear as just one of the ethnicities in the empire (alongside, for instance, Armenians) and by the late 11th century, there are references in historical writings to people as being "''Rhōmaîos'' by birth", signalling the completion of the transformation of "Roman" into an ethnic description. At this point, "Roman" also began being used for Greek populations outside of the imperial borders, such as to the Greek-speaking Christians under Seljuk rule in Anatolia, who were referred to as ''Rhōmaîoi'' despite actively resisting attempts at re-integration by the Byzantine emperors. Only a handful of late sources retain the old view of a Roman being a citizen of the Roman world.
The capture of Constantinople by the non-Roman Latin crusaders of the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
in 1204 ended the unbroken Roman continuity from Rome to Constantinople. In order to legitimise themselve as Romans in the decades when they no longer controlled Constantinople, the Byzantine elite began to look to other markers of what Romans were. The elites of the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea (), also known as the Nicene Empire, was the largest of the three Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by Walter Abel Heurtley, W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C ...
, the Byzantine government-in-exile, chiefly looked to Greek cultural heritage and Orthodox Christianity, connecting the contemporary Romans to the ancient Greeks. This contributed to Romanness becoming even more increasingly associated with people who were ethno-culturally Hellenic. Under the Nicene emperors John III (1222–1254) and Theodore II (1254–1258), these ideas were taken further than ever before as they explicitly stated that the present ''Rhōmaîoi'' were ''Hellenes'', descendants of the Ancient Greeks. Though they saw themselves as Hellenic, the Nicene emperors also maintained that they were the only true Roman emperors. "Roman" and "Hellenic" were not viewed as opposing terms, but building blocks of the same double-identity. During the rule of the Palaiologos
The House of Palaiologos ( Palaiologoi; , ; female version Palaiologina; ), also found in English-language literature as Palaeologus or Palaeologue, was a Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek Nobility, noble family that rose to power and produced th ...
dynasty, from the recapture of Constantinople in 1261 to the fall of the empire in 1453, ''Hellene'' lost ground as a self-identity, with few known uses of the term, and ''Rhōmaîoi'' once again became the dominant term used for self-description.. Some Byzantine authors went as far as to return to using "Hellenic" and "Greek" solely as terms for the ancient pagan Greeks.
After the fall of Constantinople
''Rhōmaîoi'' survived the fall of the Byzantine Empire as the primary self-designation of the Christian Greek inhabitants of the new TurkishOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
. The popular historical memory of these Romans was not occupied with the glorious past of the Roman Empire of old or the Hellenism in the Byzantine Empire, but focused on legends of the fall and the loss of their Christian homeland and Constantinople. One such narrative was the myth that the last emperor, Constantine XI Palaiologos
Constantine XI Dragases Palaiologos or Dragaš Palaeologus (; 8 February 140429 May 1453) was the last reigning List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor from 23 January 1449 until his death in battle at the fall of Constantinople on 29 M ...
would one day return from the dead to reconquer the city, a myth that endured in Greek folklore up until the time of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
(1821–1829) and beyond.
In the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
, many Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks () were a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group in Anatolia. Originally from Central Asia, they migrated to Anatolia in the 13th century and founded the Ottoman Empire, in which they remained socio-politically dominant for the e ...
, especially those who lived in the cities and were not part of the military or administration, also self-identified as Romans (''Rūmī'', رومى), as inhabitants of former Byzantine territory. The term ''Rūmī'' had originally been used by Muslims for Christians in general, though later became restricted to just the Byzantines. After 1453, the term was not only sometimes a Turkish self-identification, but it was also used to refer to Ottoman Turks by other Islamic states and peoples. The identification of the Ottomans with the Romans was also made outside of the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
. 16th-century Portuguese sources refer to the Ottomans they battled in the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
as "rumes" and the Chinese Ming dynasty referred to the Ottomans as ''Lumi'' (魯迷), a transliteration of ''Rūmī'', and to Constantinople as ''Lumi cheng'' (魯迷城, "Lumi city"). As applied to Ottoman Turks, ''Rūmī'' began to fall out of use at the end of the 17th century, and instead the word increasingly became associated only with the Greek population of the empire, a meaning that it still bears in Turkey today.
As applied to the Greeks, the self-identity as Romans endured longer, and for a long time there was widespread hope that the Romans would be liberated and that their empire would be restored. By the time of the Greek War of Independence, the dominant self-identity of the Greeks was still ''Rhōmaîoi'' or ''Romioi''.
Modern identity
TheItalians
Italians (, ) are a European peoples, European ethnic group native to the Italian geographical region. Italians share a common Italian culture, culture, History of Italy, history, Cultural heritage, ancestry and Italian language, language. ...
of Rome continue to identify with the demonym 'Roman' to this day. Rome is the most populous city in Italy with the city proper being home to about 2.8 million citizens and the Rome metropolitan area to over four million people. Since the collapse of the western Roman empire, the Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
has continued the institution of the Pontifex Maximus and governments inspired by the ancient Roman Republic have been revived in the city four times. The earliest such government was the Commune of Rome in the 12th century, founded as opposition towards the temporal powers of the Pope, which was followed by the government of Cola di Rienzo, who used the titles of 'tribune' and 'senator', in the 14th century, a sister republic to revolutionary France in the 18th century, which restored the office of Roman consul, and finally as the short-lived Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
in 1849, with a government based on the triumvirate
A triumvirate () or a triarchy is a political institution ruled or dominated by three individuals, known as triumvirs (). The arrangement can be formal or informal. Though the three leaders in a triumvirate are notionally equal, the actual distr ...
s of ancient Rome.
Roman self-identification among Greeks only began losing ground with the Greek War of Independence, when multiple factors saw the name 'Hellene' rise to replace it. Among these factors were that names such as "Hellene", "Hellas" and "Greece" were already in use for the country and its people by the other nations in Europe, the absence of the old Byzantine government to reinforce Roman identity, and the term ''Romioi'' becoming associated with those Greeks still under Ottoman rule rather than those actively fighting for independence. Thus, in the eyes of the independence movement, a Hellene was a brave and rebellious freedom fighter while a Roman was an idle slave under the Ottomans. The new Hellenic national identity was heavily focused on the cultural heritage of ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
rather than medieval Byzantium, though adherence to Orthodox Christianity remained an important aspect of Greek identity. An identity re-oriented towards ancient Greece also worked in Greece's favour internationally. In Western Europe, the Greek War of Independence saw large-scale support owing to philhellenism, a sense of "civilisational debt" to the world of classical antiquity, rather than any actual interest in the modern country. Despite the modern Greeks bearing more resemblance to the medieval Byzantines than the Greeks of the ancient world, public interest in the revolt elsewhere in Europe hinged almost entirely on sentimental and intellectual attachments to a romanticised version of ancient Greece. Comparable uprisings against the Ottomans by other peoples in the Balkans, such as the First Serbian Uprising
The First Serbian Uprising (; sr-Cyrl, Први српски устанак; ) was an uprising of Serbs in Orašac (Aranđelovac), Orašac against the Ottoman Empire from 14 February 1804 to 7 October 1813. The uprising began as a local revolt ...
(1804–1814), had been almost entirely ignored in Western Europe.
Many Greeks, particularly those outside the then newly founded Greek state, continued to refer to themselves as ''Romioi'' well into the 20th century. What Greek identity ought to be remained unresolved for a long time. As late as the 1930s, more than a century of the war of independence, Greek artists and authors still debated the contribution of Greece to European culture, and whether it should derive from a romantic fascination with classical antiquity, a nationalist dream of a restored Byzantine Empire, the strong oriental influence from the centuries of Ottoman rule or if it should be something entirely new, or "Neohellenic", reminding Europe that there was not only an ancient Greece, but also a modern one. The modern Greek people
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Albania, Anatolia, parts of Italy and Egypt, and to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea. They also f ...
still sometimes use ''Romioi'' to refer to themselves, as well as the term "Romaic" ("Roman") to refer to their Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, or , ), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the language sometimes referred to ...
language.; ; . Roman identity also survives prominently in some of the Greek populations outside of Greece itself. For instance, Greeks in Ukraine, settled there as part of Catherine the Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
's Greek Plan in the 18th century, maintain Roman identity, designating themselves as ''Rumaioi''. The term ''Rum'' or ''Rumi'' also sees continued usage by Turks and Arabs as a religious term for followers of the Greek Orthodox Church, not only those of Greek ethnicity.
 The vast majority of the Romance peoples that descended from the intermingling of Romans and Germanic peoples following the collapse of Roman political unity in the west diverged into groups that no longer identify as Romans. In the Alpine regions north of Italy however, Roman identity showed considerable tenacity. The Romansh people of Switzerland are descended from these populations, which in turn were descended from Romanised Rhaetians. Though most of the Romans of the region were assimilated by the
The vast majority of the Romance peoples that descended from the intermingling of Romans and Germanic peoples following the collapse of Roman political unity in the west diverged into groups that no longer identify as Romans. In the Alpine regions north of Italy however, Roman identity showed considerable tenacity. The Romansh people of Switzerland are descended from these populations, which in turn were descended from Romanised Rhaetians. Though most of the Romans of the region were assimilated by the Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts ...
that settled there during the 5th and 6th centuries, the people who resisted assimilation became the Romansh people. In their own, Romansh language
Romansh ( ; sometimes also spelled Romansch and Rumantsch) is a Gallo-Romance languages, Gallo-Romance and/or Rhaeto-Romance languages, Rhaeto-Romance language spoken predominantly in the Switzerland, Swiss Cantons of Switzerland, canton of the ...
, they are called ''rumantsch'' or ''romontsch'', which derives from the Latin ''romanice'' ("Romance"). Roman identity also survives in the Romands, the French-speaking community of Switzerland, and their homeland, Romandy
Romandy ( or ; Arpitan: ''Romandia'')Before World War I, the term French Switzerland () waalso used ( or , , ) is the French-speaking historical and cultural region of Switzerland. In 2020, about 2 million people, or 22.8% of the Swiss pop ...
, which covers the western part of the country.
In some regions, the Germanic word for the Romans (also used for western neighbours in general), '' walhaz'', became an ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
, although it is in many cases only attested centuries after the end of Roman rule in said regions. The term ''walhaz'' is the origin of the modern term ' Welsh', i.e. the people of Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
, and of the historical exonym ' Vlach', which was used through the Middle Ages and the Modern Period for various Eastern Romance peoples. As endonyms, Roman identification was maintained by several Eastern Romance peoples. Prominently, the Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
call themselves ''români'' and their nation ''România''. How and when the Romanians came to adopt these names is not entirely clear, but one theory is the idea of Daco-Roman continuity, that the modern Romanians are descended from Daco-Roman
The term Daco-Roman describes the Romanization (cultural), Romanized culture of Dacia under the rule of the Roman Empire.
Etymology
The Daco-Roman mixing theory, as an origin for the Romanian people, was formulated by the earliest Romanian scho ...
s that came about as a result of Roman colonisation following the conquest of Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus ro ...
by Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
(98–117). The Aromanians
The Aromanians () are an Ethnic groups in Europe, ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian language, Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgari ...
, also of unclear origin, refer to themselves by various names, including ''arumani'', ''armani'', ''aromani'' and ''rumani'', all of which are etymologically derived from the Latin ''Rōmānī''. The Istro-Romanians
The Istro-Romanians ( or ) are a Romance languages, Romance ethnic group native to or associated with the Istria, Istrian Peninsula. Historically, they inhabited vast parts of it, as well as the western side of the island of Krk until 1875. Howe ...
sometimes identify as ''rumeri'' or similar terms, though these names have lost strength and Istro-Romanians often identify with their native villages instead. The Megleno-Romanians also identified as ''rumâni'' in the past, though this name was mostly replaced in favour of the term ''vlasi'' centuries ago. ''Vlasi'' is derived from "Vlach", in turn deriving from ''walhaz''.
See also
* List of ancient Italic peoples * Pan-Latinism *Romance-speaking world
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic branch of the Indo-European language family.
The f ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Ancient Rome topics Latins (Italic tribe) Romance peoples Ancient peoples of Europe