Renewable energy in Brazil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 As of 2018, renewable energy accounted for 79% of the domestically produced electricity used in Brazil.
Brazil relies on
As of 2018, renewable energy accounted for 79% of the domestically produced electricity used in Brazil.
Brazil relies on
/ref> In the electric energy matrix, the difference between Brazil and the world is even greater: while the world only had 25% of renewable electric energy in 2019, Brazil had 83%. The Brazilian electric matrix is composed of: hydraulic energy, 64.9%; biomass, 8.4%; wind energy, 8.6%; solar energy, 1%; natural gas, 9.3%; oil products, 2%; nuclear, 2.5%; coal and derivatives, 3.3%.
 The
The
 In July 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed wind power. In 2021 Brazil was the 7th country in the world in terms of installed wind power (21 GW),RENEWABLE CAPACITY STATISTICS 2021
In July 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed wind power. In 2021 Brazil was the 7th country in the world in terms of installed wind power (21 GW),RENEWABLE CAPACITY STATISTICS 2021
/ref> and the 4th largest producer of wind energy in the world (72 TWh), behind only China, USA and Germany. the total installed wind power capacity in Brazil was 18.9 GW, with 16.4 GW in the Northeast Region and 2.0 GW in the
ImageSize = width:500 height:300
PlotArea = width:450 height:250 left:50 bottom:40
AlignBars = late
DateFormat = x.y
Period = from:0 till:25000
TimeAxis = orientation:vertical
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:1000 start:0
BarData=
bar:1 text:"2005"
bar:2 text:"2006"
bar:3 text:"2007"
bar:4 text:"2008"
bar:5 text:"2009"
bar:6 text:"2010"
bar:7 text:"2011"
bar:8 text:"2012"
bar:9 text:"2013"
bar:10 text:"2014"
bar:11 text:"2015"
bar:12 text:"2016"
bar:13 text:"2017"
bar:14 text:"2018"
bar:15 text:"2019"
bar:16 text:"2020"
bar:17 text:"2021"
bar:18 text:"jul22"
Colors =
id:lightgrey value:gray(0.7)
id:darkgrey value:gray(0.1)
id:barra value:rgb(0.3,0.6,0.3)
TextData =
pos:(60,300) textcolor:black fontsize:S
text:MW
pos:(460,20) textcolor:black fontsize:S
text:Year
pos:(90,300) textcolor:black fontsize:L
text:Evolution of installed wind power
PlotData=
width:25 color:barra align:center
bar:1 color:barra from:0 till:27
bar:2 color:barra from:0 till:235
bar:3 color:barra from:0 till:246
bar:4 color:barra from:0 till:341
bar:5 color:barra from:0 till:601
bar:6 color:barra from:0 till:932
bar:7 color:barra from:0 till:1529
bar:8 color:barra from:0 till:1894
bar:9 color:barra from:0 till:2202
bar:10 color:barra from:0 till:4888
bar:11 color:barra from:0 till:7633
bar:12 color:barra from:0 till:10129
bar:13 color:barra from:0 till:12304
bar:14 color:barra from:0 till:14843
bar:15 color:barra from:0 till:15438
bar:16 color:barra from:0 till:17198
bar:17 color:barra from:0 till:21161
bar:18 color:barra from:0 till:22000
PlotData=
bar:1 at:27 fontsize:S text: 27 shift:(0,5)
bar:2 at:235 fontsize:S text: 235 shift:(0,5)
bar:3 at:246 fontsize:S text: 246 shift:(0,5)
bar:4 at:341 fontsize:S text: 341 shift:(0,5)
bar:5 at:601 fontsize:S text: 601 shift:(0,5)
bar:6 at:932 fontsize:S text: 932 shift:(0,5)
bar:7 at:1529 fontsize:S text: 1529 shift:(0,5)
bar:8 at:1894 fontsize:S text: 1894 shift:(0,5)
bar:9 at:2202 fontsize:S text: 2202 shift:(0,5)
bar:10 at:4888 fontsize:S text: 4888 shift:(0,5)
bar:11 at:7633 fontsize:S text: 7633 shift:(0,5)
bar:12 at:10129 fontsize:S text: 10129 shift:(0,5)
bar:13 at:12304 fontsize:S text: 12304 shift:(0,5)
bar:14 at:14843 fontsize:S text: 14843 shift:(0,5)
bar:15 at:15438 fontsize:S text: 15438 shift:(0,5)
bar:16 at:17198 fontsize:S text: 17198 shift:(0,5)
bar:17 at:21161 fontsize:S text: 21161 shift:(0,5)
bar:18 at:22000 fontsize:S text: 22000 shift:(0,5)
TextData=
fontsize:S pos:(20,20)
text:data by ABEE, IRENA, ONS and ANEEL - Graphic design by Wikipedia
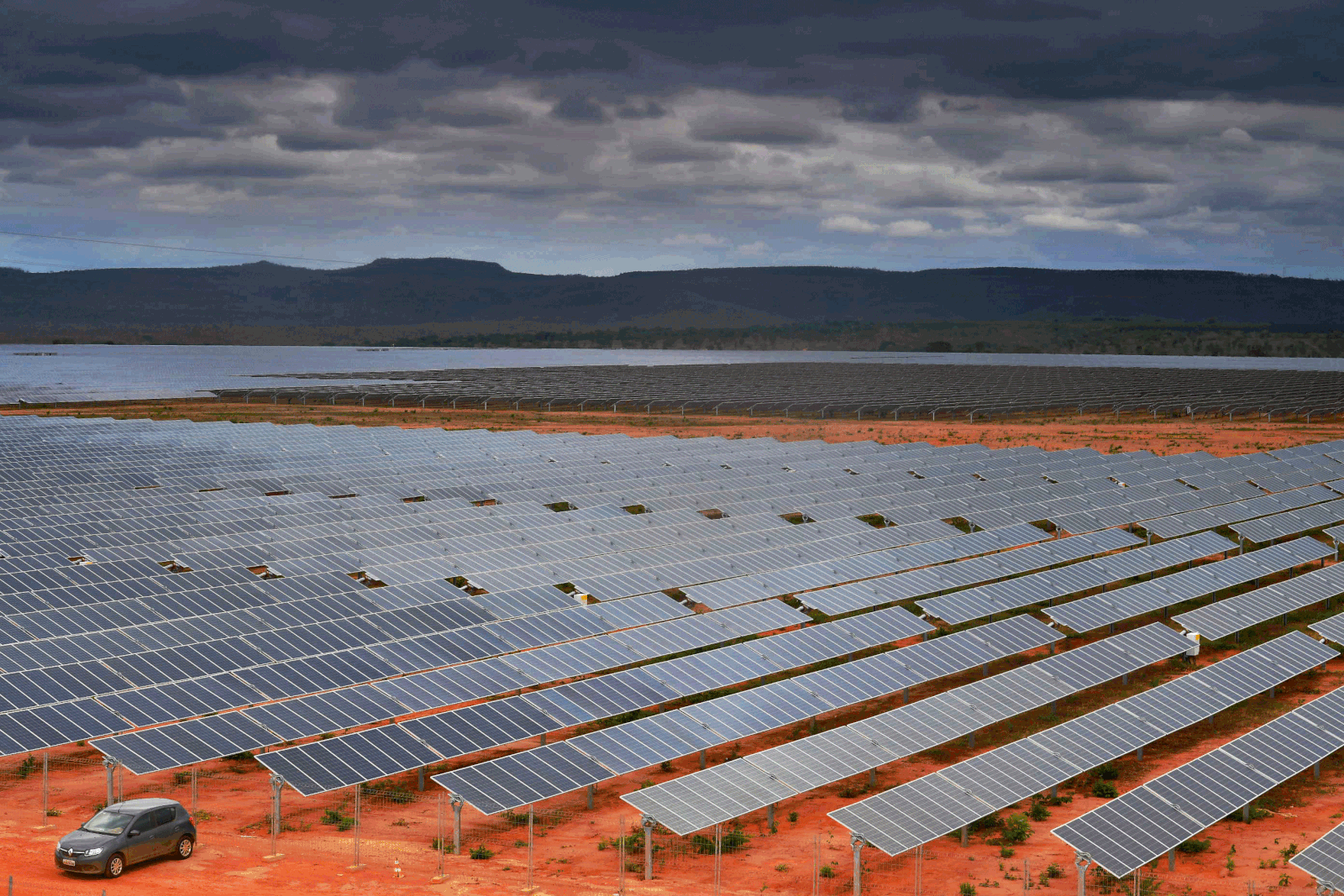 In October 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed solar power. In 2021, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (13 GW), and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).
according to ONS, total installed capacity of
In October 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed solar power. In 2021, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (13 GW), and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).
according to ONS, total installed capacity of
ImageSize = width:500 height:300
PlotArea = width:450 height:250 left:50 bottom:40
AlignBars = late
DateFormat = x.y
Period = from:0 till:25000
TimeAxis = orientation:vertical
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:1000 start:0
BarData=
bar:1 text:"2013"
bar:2 text:"2014"
bar:3 text:"2015"
bar:4 text:"2016"
bar:5 text:"2017"
bar:6 text:"2018"
bar:7 text:"2019"
bar:8 text:"2020"
bar:9 text:"2021"
bar:10 text:"oct22"
Colors =
id:lightgrey value:gray(0.7)
id:darkgrey value:gray(0.1)
id:barra value:rgb(0.3,0.6,0.3)
TextData =
pos:(60,300) textcolor:black fontsize:S
text:MW
pos:(460,20) textcolor:black fontsize:S
text:Year
pos:(90,300) textcolor:black fontsize:L
text:Evolution of installed solar power
PlotData=
width:25 color:barra align:center
bar:1 color:barra from:0 till:8
bar:2 color:barra from:0 till:20
bar:3 color:barra from:0 till:41
bar:4 color:barra from:0 till:108
bar:5 color:barra from:0 till:1296
bar:6 color:barra from:0 till:2470
bar:7 color:barra from:0 till:4615
bar:8 color:barra from:0 till:7881
bar:9 color:barra from:0 till:13055
bar:10 color:barra from:0 till:21000
PlotData=
bar:1 at:8 fontsize:S text: 8 shift:(0,5)
bar:2 at:20 fontsize:S text: 20 shift:(0,5)
bar:3 at:41 fontsize:S text: 41 shift:(0,5)
bar:4 at:108 fontsize:S text: 108 shift:(0,5)
bar:5 at:1296 fontsize:S text: 1296 shift:(0,5)
bar:6 at:2470 fontsize:S text: 2470 shift:(0,5)
bar:7 at:4615 fontsize:S text: 4615 shift:(0,5)
bar:8 at:7881 fontsize:S text: 7881 shift:(0,5)
bar:9 at:13055 fontsize:S text: 13055 shift:(0,5)
bar:10 at:21000 fontsize:S text: 21000 shift:(0,5)
TextData=
fontsize:S pos:(20,20)
text:data by IRENA et ANEEL - Graphic design by Wikipedia
 In 2020, Brazil was the 2nd largest country in the world in the production of energy through
In 2020, Brazil was the 2nd largest country in the world in the production of energy through
 As of 2018, renewable energy accounted for 79% of the domestically produced electricity used in Brazil.
Brazil relies on
As of 2018, renewable energy accounted for 79% of the domestically produced electricity used in Brazil.
Brazil relies on hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
for 65% of its electricity, and the Brazilian government plans to expand the share of wind energy
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically, w ...
(currently 11%), solar energy
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating), and solar architecture. It is an essen ...
(currently 2.5%) and biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bio ...
as alternatives. Wind energy has the greatest potential in Brazil during the dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The ...
, so it is considered a hedge
A hedge or hedgerow is a line of closely spaced shrubs and sometimes trees, planted and trained to form a barrier or to mark the boundary of an area, such as between neighbouring properties. Hedges that are used to separate a road from adjoi ...
against low rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
and the geographical spread of existing hydroelectric resources.
Brazil held its first wind-only energy auction in 2009, in a move to diversify its energy portfolio. Foreign companies scrambled to take part.
The bidding lead to the construction of 2 gigawatts
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wat ...
(GW) of wind production with an investment of about $6 billion over the following two years.
Brazil's technical potential for wind energy is 143 GW due to the country's blustery kilometres coastline
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in ...
where most projects are based.
The Brazilian Wind Energy Association and the government have set a goal of achieving 20 GW of wind energy capacity by 2020 from the current 5 GW (2014). The industry hopes the auction will help kick-start the wind-energy sector, which already accounts for 70% of the total in all of Latin America.
According to Brazil's Energy Master-plan 2016-2026 (PDE2016-2026), Brazil is expected to install 18,5GW of additional wind power generation, 84% in the North-East and 14% in the South.
Brazil started focusing on developing alternative sources of energy, mainly sugarcane ethanol, after the oil shocks in the 1970s.
Brazil's large sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
farms helped the development.
In 1985, 91% of cars produced that year ran on sugarcane ethanol.
The success of flexible-fuel vehicle
A flexible-fuel vehicle (FFV) or dual-fuel vehicle ( colloquially called a flex-fuel vehicle) is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethan ...
s, introduced in 2003, together with the mandatory E25 blend throughout the country, have allowed ethanol fuel consumption in the country to achieve a 50% market share of the gasoline-powered fleet by February 2008.
Total energy matrix and Electric energy matrix
The main characteristic of the Brazilian energy matrix is that it is much more renewable than that of the world. While in 2019 the world matrix was only 14% made up of renewable energy, Brazil's was at 45%. Petroleum and oil products made up 34.3% of the matrix; sugar cane derivatives, 18%; hydraulic energy, 12.4%; natural gas, 12.2%; firewood and charcoal, 8.8%; varied renewable energies, 7%; mineral coal, 5.3%; nuclear, 1.4%, and other non-renewable energies, 0.6%.Matriz Energética e Elétrica/ref> In the electric energy matrix, the difference between Brazil and the world is even greater: while the world only had 25% of renewable electric energy in 2019, Brazil had 83%. The Brazilian electric matrix is composed of: hydraulic energy, 64.9%; biomass, 8.4%; wind energy, 8.6%; solar energy, 1%; natural gas, 9.3%; oil products, 2%; nuclear, 2.5%; coal and derivatives, 3.3%.
Electricity
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectric power plant
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
s produced almost 80% of the electrical energy consumed in Brazil (now 60%).
Brazil has the third highest potential for hydroelectricity, following Russia and China. At the end of 2021 Brazil was the 2nd country in the world in terms of installed hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
(109.4 GW).
Itaipu power plant
 The
The Itaipu Dam
The Itaipu Dam ( pt, Barragem de Itaipu , es, Represa de Itaipú ) is a hydroelectric dam on the Paraná River located on the border between Brazil and Paraguay. The construction of the dam was first contested by Argentina, but the negotiations ...
is the world's second largest hydroelectric power station by installed capacity.
Built on the Paraná River
The Paraná River ( es, Río Paraná, links=no , pt, Rio Paraná, gn, Ysyry Parana) is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some ."Parana River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Br ...
dividing Brazil and Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to t ...
, the dam provides over 75% of Paraguay's electric power needs, and meets more than 20% of Brazil's total electricity demand.
The river runs along the border of the two countries, and during the initial diplomatic talks for the dam construction both countries were suffering from droughts.
The original goal was therefore to provide better management and utilization of water resources for the irrigation of crops.
Argentina was also later incorporated in some of the governmental planning and agreements because it is directly affected, being downstream, by the regulation of the water on the river.
If the dam were to completely open the water flow, areas as far south as Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
could potentially flood.
Construction of the dam started in 1975, and the first generator was opened in 1983.
It is estimated that 10,000 locals were displaced by the construction of the dam, and around 40,000 people were hired to help with the construction of the project.
Many environmental concerns were overlooked when constructing the dam, due to the trade-off considering the production of such a large amount of energy without carbon emissions, and no immediate harmful byproducts, such as with nuclear energy.
Wind power
/ref> and the 4th largest producer of wind energy in the world (72 TWh), behind only China, USA and Germany. the total installed wind power capacity in Brazil was 18.9 GW, with 16.4 GW in the Northeast Region and 2.0 GW in the
South Region Southern Region or South Region may refer to:
* Southern Nigeria
* Southern Region (Boy Scouts of America)
* Southern Region, Bauchi, Nigeria
* South Region, Brazil, an official grouping of states for economic and statistical purposes
* Southern ...
.
Wind is more intense from June to December, coinciding with the months of lower rainfall intensity.
This puts the wind as a potential complementary source of energy to hydroelectricity.
Brazil's first wind energy turbine was installed in Fernando de Noronha
Fernando de Noronha () is an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, part of the State of Pernambuco, Brazil, and located off the Brazilian coast. It consists of 21 islands and islets, extending over an area of . Only the eponymous main island is in ...
Archipelago in 1992.
Ten years later the government created the Program for Incentive of Alternative Electric Energy Sources (Proinfa) to encourage the use of other renewable sources, such as wind power, biomass, and small hydro.
Since the inception of Proinfa, Brazil's wind energy production has grown from 22 MW in 2003 to 602 MW in 2009, and to over 8,700 MW by 2015.
Developing these wind power sources in Brazil is helping the country to meet its strategic objectives of enhancing energy security
Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to (relatively) cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven d ...
, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and creating jobs.
The potential for this type of power generation in Brazil could reach up to 145,000 MW, according to the 2001 Brazilian Wind Power Potential Report by the Electric Energy Research Centre (Cepel).
While the 2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference
The 2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference, commonly known as the Copenhagen Summit, was held at the Bella Center in Copenhagen, Denmark, between 7 and 18 December. The conference included the 15th session of the Conference of the Part ...
(COP15) was taking place in Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan a ...
, Brazil's National Electric Energy Agency (ANEEL
Anil or Anıl may refer to:
People
* Anil (given name), an Indian given name (including a list of persons with the name)
* Anıl (given name), a Turkish given name (including a list of persons with the name)
* Anil (director), active in the Malaya ...
) held the country's first ever wind-only energy auction.
On December 14, 2009, around 1,800 megawatts (MW) were contracted with energy from 71 wind power plants scheduled to be delivered beginning July 1, 2012. The 716 MW Lagoa dos Ventos began operating in 2021.
Solar power
 In October 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed solar power. In 2021, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (13 GW), and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).
according to ONS, total installed capacity of
In October 2022 Brazil reached 22 GW of installed solar power. In 2021, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (13 GW), and the 11th largest producer of solar energy in the world (16.8 TWh).
according to ONS, total installed capacity of photovoltaic solar
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
was 15.18 GW, with 10 GW of distributed solar
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid-connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to ...
(where Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literall ...
stood out with 1.73 GW, São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaW ...
with 1.29 GW and Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, , ; "Great River of the South") is a state in the southern region of Brazil. It is the fifth-most-populous state and the ninth largest by area. Located in the southernmost part of the country, Rio Grande do Sul is border ...
with 1.17 GW of this total) and 5.18 GW in solar plant
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
s (where Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro) and the 5th-larges ...
, with 1,354 MW, Piauí
Piaui (, ) is one of the states of Brazil, located in the country's Northeast Region. The state has 1.6% of the Brazilian population and produces 0.7% of the Brazilian GDP.
Piaui has the shortest coastline of any coastal Brazilian state at 66& ...
, with 1,205 MW, Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literall ...
, with 730 MW, São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaW ...
, with 588 MW and Ceará
Ceará (, pronounced locally as or ) is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northeastern part of the country, on the Atlantic coast. It is the eighth-largest Brazilian State by population and the 17th by area. It is also one of the ...
, with 499 MW stood out)
Brazil has one of the highest solar incidence in the world.
The largest solar plants in Brazil consist of Ituverava and the Nova Olinda plants. The Ituverava solar plant produces 254 MW and the Nova Olinda plant produces 292 MW.
Ethanol fuel
Brazil'sethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
program started in 1975, when soaring oil prices put a chokehold on the economy.
Sugarcane was an obvious candidate, given Brazil's large amount of arable land
Arable land (from the la, arabilis, "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for th ...
and favourable climate.
Most cars on the road today in Brazil can run on blends of up to 25% ethanol, and motor vehicle manufacturers already produce vehicles designed to run on much higher ethanol blends.
Most car makers in Brazil sell flexible-fuel
A flexible-fuel vehicle (FFV) or dual-fuel vehicle (colloquially called a flex-fuel vehicle) is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethanol or ...
cars, trucks, and minivans that can use gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
and ethanol blends ranging from pure gasoline up to 100% ethanol (E100).
In 2009, 90% of cars produced that year ran on sugarcane ethanol.
Brazil is the second largest producer of ethanol in the world and is the largest exporter
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is an ...
of the fuel.
In 2008, Brazil produced 454,000 bbl/d of ethanol, up from 365,000 in 2007.
All gasoline in Brazil contains ethanol, with blending levels varying from 2025%.
Over half of all cars in the country are of the flex-fuel variety, meaning that they can run on 100% ethanol or an ethanol-gasoline mixture.
According to ANP, Brazil also produced about 20,000 bbl/d of biodiesel
Biodiesel is a form of diesel fuel derived from plants or animals and consisting of long-chain fatty acid esters. It is typically made by chemically reacting lipids such as animal fat ( tallow), soybean oil, or some other vegetable oi ...
in 2008, and the agency has enacted a 3% blending requirement for domestic diesel sales.
The importance of ethanol in Brazil's domestic transportation fuels market is expected to increase in the future.
According to Petrobras
Petróleo Brasileiro S.A., better known by the portmanteau Petrobras (), is a state-owned Brazilian multinational corporation in the petroleum industry headquartered in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The company's name translates to Brazilian Petrole ...
, ethanol accounts for more than 50% of current light vehicle fuel demand, and the company expects this to increase to over 80% by 2020.
Because ethanol production continues to grow faster than domestic demand, Brazil has sought to increase ethanol exports.
According to industry sources, Brazil's ethanol exports reached 86,000 bbl/d in 2008, with 13,000 bbl/d going to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. Brazil is the largest ethanol exporter in the world, holding over 90% of the global export market.
Biomass
biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bio ...
(energy production from solid biofuels and renewable waste), with 15,2 GW installed.
Biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bio ...
is a clean energy source used in Brazil. It reduces environmental pollution as it uses organic garbage, agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
remains, wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
shaving or vegetable oil. Refuse cane, with its high energetic value, has been used to produce electricity. More than 1 million people in the country work in the production of biomass, and this energy represents 27% of Brazil's energetic matrix.
The recent interest in converting biomass to electricity comes not only from its potential as a low-cost, indigenous supply of power, but for its potential environmental and developmental benefits. For example, biomass may be a globally important mitigation option to reduce the rate of CO2 buildup by sequestering carbon
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. Carbon dioxide () is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. These changes can be accelerated through changes in land ...
and by displacing fossil fuels. Renewably grown biomass contributes only a very small amount of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon ma ...
to the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A ...
. Locally, plantations can lessen soil erosion, provide a means to restore degraded lands, offset emissions and local impacts from fossil-fired power generation, and, perhaps, reduce demands on existing forests. In addition to the direct power and environmental benefits, biomass energy systems offer numerous other benefits, especially for developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
such as Brazil. Some of these benefits include the employment of underutilized labour and the production of co- and by-products, for example, fuelwood.
Nearly all of the experiences with biomass for power generation are based on the use of waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste pr ...
and residue fuels (primarily wood/wood wastes and agricultural residues). The production of electric power from plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
-grown wood is an emerging technology with considerable promise. However, actual commercial use of plantation-grown fuels for power generation is limited to a few isolated instances. Wood from plantations is not an inexpensive energy feedstock
A raw material, also known as a feedstock, unprocessed material, or primary commodity, is a basic material that is used to produce goods, finished goods, energy, or intermediate materials that are feedstock for future finished products. As feeds ...
, and as long as worldwide prices of coal, oil and gas are relatively low, the establishment of plantations dedicated to supplying electric power or other higher forms of energy will occur only where financial subsidies
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector (business, or individual) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Although commonly extended from the government, the ter ...
or incentives exist or where other sources of energy are not available.
Where biomass plantations are supplying energy on a commercial basis in Brazil, the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, it can be shown that a combination of government policies or high conventional energy prices have stimulated the use of short-rotation plantations for energy. Brazil used tax incentives beginning in the mid-1960s to initiate a reforestation program to provide for industrial wood energy and wood product needs. As a consequence of the Brazilian Forestry Code with its favourable tax incentives, the planted forest area in Brazil increased from 470,000hectares to 6.5 millionhectares by 1993. With the discontinuation of the tax incentives in 1988, plantation establishment in Brazil has slowed, although the commercial feasibility of using eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as ...
for energy and other products has been clearly demonstrated.
External funding
TheEuropean Investment Bank
The European Investment Bank (EIB) is the European Union's investment bank and is owned by the EU Member States. It is one of the largest supranational lenders in the world. The EIB finances and invests both through equity and debt solution ...
provided a €200 million loan starting 2021 to support renewable energy projects, specifically to establish a wind farm
A wind farm or wind park, also called a wind power station or wind power plant, is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electricity. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundred wind turb ...
and solar power plant. This will support a series of onshore wind farms divided into two clusters, in Paraiba, Piauí
Piaui (, ) is one of the states of Brazil, located in the country's Northeast Region. The state has 1.6% of the Brazilian population and produces 0.7% of the Brazilian GDP.
Piaui has the shortest coastline of any coastal Brazilian state at 66& ...
, and Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo, Minas Gerais, and Rio de Janeiro) and the 5th-larges ...
. A s olar photovoltaic plant will be built 10 km away from the Paraiba wind farm, with a total capacity of 574 MW (425 MW of wind power and 149 MW of solar power).
See also
*Solar power in Brazil
The total installed solar power in Brazil was estimated at about 21 GW at October 2022, generating approximately 2.48% of the country's electricity demand, up from 0.7% in 2018. In 2021, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of insta ...
* Energy policy of Brazil
Brazil is the 10th largest energy consumer in the world and the largest in South America. At the same time, it is an important oil and gas producer in the region and the world's second largest ethanol fuel producer. The government agencies re ...
* Nuclear power in Brazil
* Electricity sector in Brazil
Brazil has the largest electricity sector in Latin America.
Its capacity at the end of 2021 was 181,532 MW.https://antigo.aneel.gov.br/web/guest/sala-de-imprensa-exibicao-2/-/asset_publisher/zXQREz8EVlZ6/content/brasil-termina-2021-com-maior-ac ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Renewable Energy In Brazil