rangeland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Rangelands are grasslands, shrublands,
Rangelands are grasslands, shrublands,
/ref>
/ref> or as areas where more water is lost by
 Of the land within the
Of the land within the "Arizona Rethinking Open Range Laws"
article by Marc Lacey in ''
File:Palouse from Steptoe Butte.jpg, Palouse Hills of Washington
File:Sedona pano.jpg, Sonoran Desert
File:Konza.jpg, Konza Prairie
File:Buffalo USDA94c4147.jpg, Buffalo grazing on rangeland in Crook County, Wyoming.
File:Triodia hummock grassland.jpg, Triodia Hummock Grasslands
File:Savannah near Kuruman.JPG, Savannah in southern Africa
File:Carrizo Caliente Peak.JPG, Caliente Peak, California
File:Flora of the Swan Lake NSA.jpg, Lake Swan, Nevada
''Rangelands'' 1979-2003 archive
- freely available volumes published b
The Society For Range ManagementSociety for Range ManagementBureau of Land ManagementUSDA Forest ServiceUniversity of Idaho - Rangeland Ecology and Management
* * * {{Authority control Grasslands Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands
 Rangelands are grasslands, shrublands,
Rangelands are grasslands, shrublands, woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
s, wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (Anoxic waters, anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in t ...
s, and deserts that are grazed by domestic livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to ani ...
or wild animals. Types of rangelands include tallgrass and shortgrass prairie
The shortgrass prairie is an ecosystem located in the Great Plains of North America. The two most dominant grasses in the shortgrass prairie are blue grama (''Bouteloua gracilis'') and buffalograss ('' Bouteloua dactyloides''), the two less do ...
s, desert grasslands and shrublands, woodlands, savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground ...
s, chaparrals, steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
s, and tundras. Rangelands do not include forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
s lacking grazable understory vegetation, barren desert, farmland
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous with bo ...
, or land covered by solid rock, concrete and/or glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such a ...
s.
Rangelands are distinguished from pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or sw ...
lands because they grow primarily native vegetation
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often popularised as "with no human intervention") during history. The term is eq ...
, rather than plants established by humans. Rangelands are also managed principally with practices such as managed livestock grazing and prescribed fire rather than more intensive agricultural practices of seeding, irrigation, and the use of fertilizers.
Grazing is an important use of rangelands but the term ''rangeland'' is not synonymous with ''grazingland''. Livestock grazing can be used to manage rangelands by harvesting forage to produce livestock, changing plant composition, or reducing fuel loads.
Fire is also an important regulator of range vegetation, whether set by humans or resulting from lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an average ...
. Fires tend to reduce the abundance of woody plants and promote herbaceous plants including grasses, forbs, and grass-like plants. The suppression or reduction of periodic wildfires from desert shrublands, savannas, or woodlands frequently invites the dominance of trees and shrubs to the near exclusion of grasses and forbs.
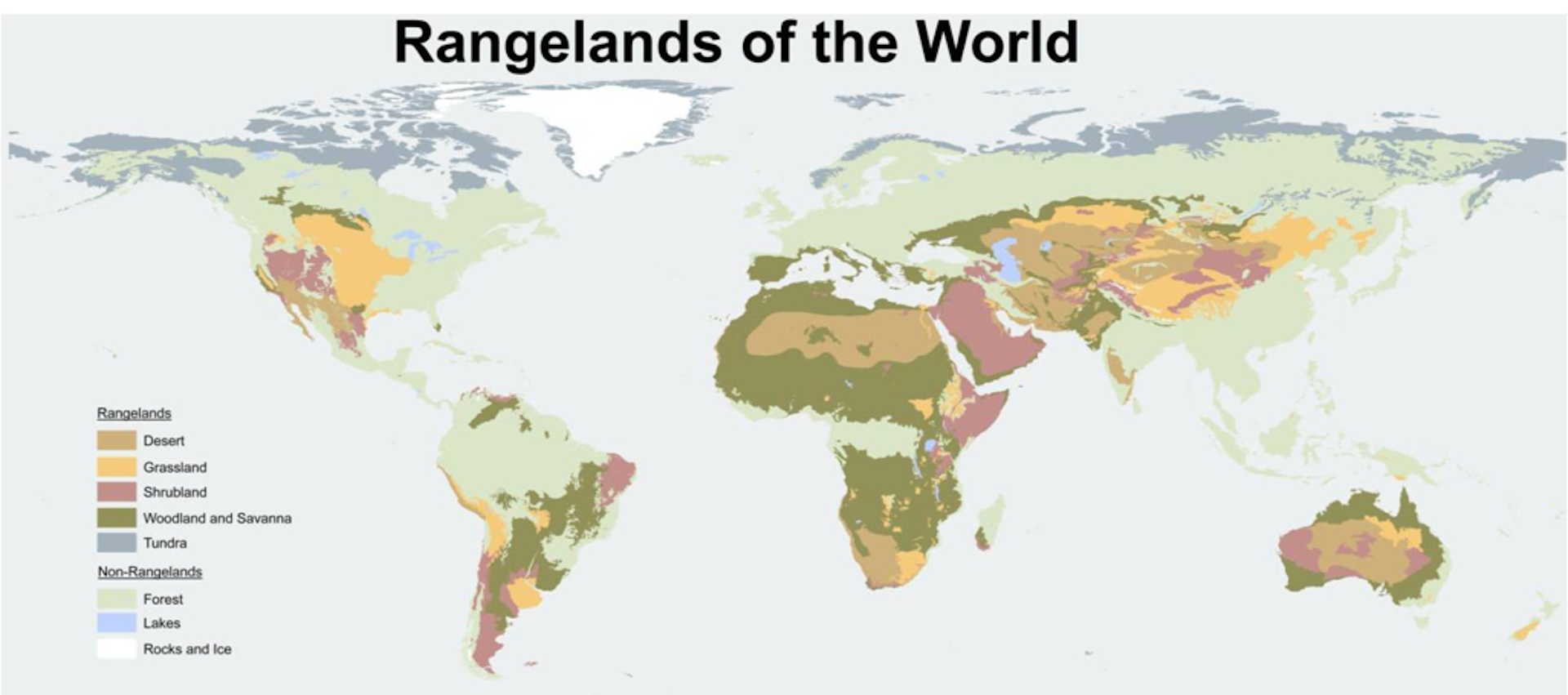
Types of rangeland
TheUnited States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it ...
defines rangeland as "lands on which the native vegetation (climax or natural potential plant community) is predominantly grasses, grass-like plants, forbs, or shrubs suitable for grazing or browsing use." The EPA classifies natural grassland and savannas as rangeland, and in some cases includes wetlands, deserts, tundra, and "certain forb and shrub communities." The primary difference between rangeland and pasture is management; rangelands tend to have natural vegetation along with a few introduced plant species, but all managed by grazing, while pastures have forage that is adapted for livestock and managed, by seeding, mowing, fertilization and irrigation.
Prairie
Prairies are considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublandsbiome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type
Vegetation classification is the process of classifying and mapping the vegetation over an area of the earth's surface. Vegetation classification is often performed by state based agencies as part of land use, resource and environmental managemen ...
. Temperate grassland regions include the Pampas of Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
, and the steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
s of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
.
Grasslands
Grasslands are areas where thevegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic charac ...
is dominated by grasses ( Poaceae) and other herbaceous (non-woody) plants. However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) families can also be found. Grasslands occur naturally on all continents except Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
. In temperate latitudes, such as northwest Europe and the Great Plains and California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
, native grasslands are dominated by perennial bunch grass species, whereas in warmer climates annual species form a greater component of the vegetation.NASA Earth Observatory webpage/ref>
Steppe
Steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
, in physical geography, refers to a biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
region characterized by grassland plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes. The prairie (especially the shortgrass and mixed prairie
Mixed is the past tense of ''mix''.
Mixed may refer to:
* Mixed (United Kingdom ethnicity category), an ethnicity category that has been used by the United Kingdom's Office for National Statistics since the 1991 Census
* Mixed (album), ''Mixed'' ...
) is an example of a steppe, though it is not usually called such. It may be semi- desert, or covered with grass or shrubs or both, depending on the season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and ...
and latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
. The term is also used to denote the climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
encountered in regions too dry to support a forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
, but not dry enough to be a desert.
Pampas
Pampas are the fertileSouth America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
n lowlands that include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, La Pampa
La Pampa () is a sparsely populated province of Argentina, located in the Pampas in the center of the country. Neighboring provinces are from the north clockwise San Luis, Córdoba, Buenos Aires, Río Negro, Neuquén and Mendoza.
History
...
, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos and Córdoba, most of Uruguay, and the State of Rio Grande do Sul, in the southernmost end of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
covering more than . These vast plains are only interrupted by the low Ventana and Tandil hills near Bahía Blanca and Tandil (Argentina), with a height of and respectively. The climate is mild, with precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
of to , more or less evenly distributed through the year, making the soils appropriate for agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
. This area is also one of the distinct physiography provinces of the larger Paraná-Paraguay Plain division. These plains contain unique wildlife because of the different terrains around it. Some of this wildlife includes the rhea, the badger, and the prairie chicken.
Shrubland
Shrubland is a plant community characterized byvegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic charac ...
dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophyte
A storage organ is a part of a plant specifically modified for storage of energy
(generally in the form of carbohydrates) or water. Storage organs often grow underground, where they are better protected from attack by herbivores. Plants that have ...
s. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity. It may be the mature vegetation type in a particular region and remain stable over time, or a transitional community that occurs temporarily as the result of a disturbance, such as fire. A stable state may be maintained by regular natural disturbance such as fire or browsing. Shrubland may be unsuitable for human habitation because of the danger of fire. The term "shrubland" was first coined in 1903.
Woodland
Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
is a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade. Woodlands may support an understory of shrubs and herbaceous plants including grasses. Woodland may form a transition to shrubland under drier conditions or during early stages of primary or secondary succession. Higher densities and areas of trees, with largely closed canopy, provide extensive and nearly continuous shade are referred to as forest.
Savanna
Savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground ...
is a grassland ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
characterized by the trees being sufficiently small or widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of C4 grasses.
Desert
Desert is a landscape orregion
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
, defined as areas with an average annual precipitation of less than per year,What is a desert?/ref> or as areas where more water is lost by
evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transp ...
than falls as precipitation. In the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
system, deserts are classed as ''BWh'' (hot desert) or ''BWk'' (temperate desert). In the Thornthwaite climate classification system, deserts would be classified as arid megathermal climates.
Tundra
Tundra is abiome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sami word ''tūndâr'' "uplands," "treeless mountain tract." There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine tundra, and Antarctic tundra In tundra, the vegetation
Vegetation is an assemblage of plant species and the ground cover they provide. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic charac ...
is composed of dwarf shrubs, sedges and grasses, mosses, and lichens. Scattered trees grow in some tundra. The ecotone
An ecotone is a transition area between two biological communities, where two communities meet and integrate. It may be narrow or wide, and it may be local (the zone between a field and forest) or regional (the transition between forest and gras ...
(or ecological boundary region) between the tundra and the forest is known as the tree line or timberline.
North America
Canada
Rangeland is a prominent feature of ruralCanada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
. A provincial jurisdiction, administration and policy regarding range use varies across the country. As in many other Commonwealth countries, public tenures on crown land for the purpose of range activities are common in geographically compatible areas. Reconciling the economic needs of ranchers and the need for environmental conservation is one of the primary themes in modern range discourse.
In western Canada, both grassland and forested range are significant. In British Columbia, 70 percent of grassland range is privately owned and 60 percent of the total annual livestock forage requirement is provided by grazing on Crown rangeland (34 million hectares), 80 percent of which is forested range. Grassland range predominates in much of the prairie provinces’ ranching area; however, forested range is particularly important in the boreal region.
Certain rangelands are preserved as provincially-protected areas similar to parks, others are managed as community resources. For example, in Alberta since 2003 there has been legislation allowing the creation of "Heritage Rangelands" within the parks system. As of 2012 there were 2 heritage rangelands and 6 proposed future heritage rangelands run by Alberta Parks
Alberta Parks is an agency of the Government of Alberta which is responsible for managing Alberta's provincial parks and protected areas.
History
Alberta's system of provincial parks began with the striking of a committee on parks by then Premier ...
. There are also 32 provincial grazing reserves located throughout Alberta administered as public lands by Alberta Sustainable Resource Development. The federal government has administered several "Community Pastures" in Western Canada that were reclaimed lands suffering erosion during the 1930s. In 2012, it was announced that this federal involvement would be phased out over a six-year period.
United States
 Of the land within the
Of the land within the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
borders, 36% is considered rangeland. The western side of the United States is 53% rangeland. Around 399 million acres (1,610,000 km2) of rangeland are privately owned. The Bureau of Land Management manages about 167 million acres (676,000 km2) of publicly owned rangeland, with the United States Forest Service
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture that administers the nation's 154 United States National Forest, national forests and 20 United States Nationa ...
managing approximately 95 million acres (380,000 km2) more. Ranchers may lease portions of this public rangeland and pay a fee based on the number and type of livestock and the period for which they are on the land.
Historically much of the land in the western United States was used for grazing and much of some states still is. In many of those states, such as Arizona, an open-range law applies which requires a land owner to fence cattle out rather than in; thus cattle are theoretically allowed to roam free. In modern times open-range laws can conflict with urban development as occasional stray cows, bulls, or even herds wander into subdivisions or onto highways.article by Marc Lacey in ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' October 11, 2010. Retrieved October 13, 2010.North American rangelands - grasslands
*Tall Grass Prairie *Mixed Grass Prairie *Short Grass Prairie *Pacific Bunchgrass *Annual GrasslandsNorth American rangelands - shrublands
*Sagebrush Steppe *Salt Desert Shrublands *Desert ShrublandsElsewhere
The different types of rangeland together form about 70% (excluding Antarctica) of the Earth's surface.
Australia
Australia’s rangelands extend from tropical savannas in the north dominated by summer rainfall, though large areas of desert in central Australia to the southern rangelands dominated by winter rainfall. They cover approximately 80 per cent of the Australian continent and equate broadly with the ‘ Outback’. However, rangelands also occur in higher rainfall areas where limitations other than rainfall restrict use to management of the natural landscape. The rangelands are where values and societal benefits are based primarily on natural resources. They are areas which have not been intensively developed for agriculture but extensive livestock production is a major land use, accounting for 55 per cent of the rangelands. Conservation reserves utilise around 11 per cent of the rangelands and the rangelands have areas of significant biodiversity and natural attractions on a world scale. Although mining and petroleum extraction uses a very small percentage of the rangelands, it economically contributes most to Australia’s Gross Domestic Product compared with other rangeland industries (cattle, sheep and goat production, tourism, harvesting of native products). Indigenous land tenures of various types cover around 59 per cent of the rangelands and overlap with grazing and conservation uses. Although rangelands cover 80 per cent of Australia’s land mass, at the 2016 Census, they were home to just over two per cent of the population (394,000 people), with 28 per cent of rangeland residents identifying as being Indigenous.South America
Rangelands in South America are located in regions with climate ranging from arid to sub-humid. Annual precipitation in these areas ranges from approximately 150 to 1500 mm (6–60 inches). Within South America, rangelands cover about 33% of the total land area. South American rangelands include; grasslands, shrublands, savannas, and hot and cold deserts. Rangelands in South America exclude hyperarid deserts. Examples of the South American rangelands include the; Patagonian Steppe, the Monte, the Pampas, the "Lianos" or "Cerrado," the "Chaco" and the "Caatinga." The change in the intensity and location of tropical thunderstorms and other weather patterns is the driving force in the climates of southern South America.Africa
InKenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, rangelands make up for 85% of the land surface area, and are largely inhabited by nomadic pastoralists who are largely dependent on livestock. This movement often brings along an incursion of different diseases with the common one being the rinderpest virus in the Kenyan wildlife population from the Somali ecosystem.
Asia
In the past, rangelands in western China supported a pastoral economy and large wildlife populations. Now the rangelands have shrunk due to population growth, economic, government, and social factors. Rangeland types in China include; Semi-desert, Dry Alpine Grasslands, Alpine Dwarf Shrub, Wetland types.Uses of rangeland
Rangelands produce a wide variety of goods and services desired by society, including livestock forage (Grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to roam around and consume wild vegetations in order to convert the otherwise indigestible (by human gut) cellulose within grass and ot ...
), wildlife habitat, water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, mineral resources
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. O ...
, wood products
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
, wildland recreation, open space and natural beauty. The geographic extent and many important resources of rangelands make their proper use and management vitally important to people everywhere.
Gallery
See also
* Applied ecology * Coastal plain * Coastal prairie * Experimental range * Field *Forage
Forage is a plant material (mainly plant leaves and stems) eaten by grazing livestock. Historically, the term ''forage'' has meant only plants eaten by the animals directly as pasture, crop residue, or immature cereal crops, but it is also use ...
* Grassland
* Grass valley
*Holistic management
Holistic Management (from ''holos'', a Greek word meaning ''all'', ''whole'', ''entire'', ''total'') in agriculture is an approach to managing resources that was originally developed by Allan Savory. Holistic Management is a registered trade ...
*Meadow
A meadow ( ) is an open habitat, or field, vegetated by grasses, herbs, and other non- woody plants. Trees or shrubs may sparsely populate meadows, as long as these areas maintain an open character. Meadows may be naturally occurring or arti ...
*Pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or sw ...
* Potrero
*Plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
* Prairie
* Range condition scoring
*Savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground ...
*Steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
* Veld
References
External links
''Rangelands'' 1979-2003 archive
- freely available volumes published b
The Society For Range Management
* * * {{Authority control Grasslands Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands