radial nerve on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the
 The radial nerve originates as a terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It goes through the arm, first in the posterior compartment of the arm, and later in the
The radial nerve originates as a terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It goes through the arm, first in the posterior compartment of the arm, and later in the
 Cutaneous innervation by the radial nerve is provided by the following nerve branches:
* Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm (originates in axilla)
* Inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm (originates in arm)
* Posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm (originates in arm)
The superficial branch of the radial nerve provides sensory innervation to much of the back of the hand, including the web of skin between the thumb and index finger.
Cutaneous innervation by the radial nerve is provided by the following nerve branches:
* Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm (originates in axilla)
* Inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm (originates in arm)
* Posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm (originates in arm)
The superficial branch of the radial nerve provides sensory innervation to much of the back of the hand, including the web of skin between the thumb and index finger.

 Within the distal forearm:
* Common mechanism of injury: Wartenberg's syndrome, (not to be confused with Wartenberg's sign), due to nerve entrapment beneath the tendinous insertion of
Within the distal forearm:
* Common mechanism of injury: Wartenberg's syndrome, (not to be confused with Wartenberg's sign), due to nerve entrapment beneath the tendinous insertion of
File:Gray413_color.png, Cross-section through the middle of upper arm.
File:Gray417_color.PNG, Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
File:Gray525.png, The brachial artery.
File:Gray811and813.PNG, Cutaneous nerves of right upper extremity.
File:Gray815.png, Superficial palmar nerves.
File:Nerves_of_the_left_upper_extremity.gif, Nerves of the left upper extremity.
File:Gray817.png, Deep palmar nerves.
File:Gray1235 (English).svg, Front of right upper extremity, showing surface markings for bones, arteries, and nerves.
File:Gray1236.png, Back of right upper extremity, showing surface markings for bones and nerves.
File:Brachial plexus 1.jpg, Radial nerve at newborn
File:Radial nerve 3.JPG, Radial nerve
File:Radial nerve 2.JPG, Radial nerve
File:Slide14yyy.JPG, Radial nerve
File:Slide10PPP.JPG, Radial nerve
File:Muscles of upper limb.(cross section - human cadaver).jpg, Muscles of upper limb.Cross section.
triceps brachii muscle
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of 3 parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. It is the muscle principally respon ...
of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.
It originates from the brachial plexus, carrying fibers from the ventral roots of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 & T1.
The radial nerve and its branches provide motor innervation to the dorsal arm muscles (the triceps brachii and the anconeus) and the extrinsic extensors of the wrists and hands; it also provides cutaneous sensory innervation Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve.
Dermatomes are similar; however, a dermatome only specifies the area served by a spinal nerve. In some cases, the dermatome is less specific (whe ...
to most of the back of the hand, except for the back of the little finger and adjacent half of the ring finger (which are innervated by the ulnar nerve).
The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve, and a superficial branch, which goes on to innervate the dorsum (back) of the hand.
This nerve was historically referred to as the musculospiral nerve.
Structure
 The radial nerve originates as a terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It goes through the arm, first in the posterior compartment of the arm, and later in the
The radial nerve originates as a terminal branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. It goes through the arm, first in the posterior compartment of the arm, and later in the anterior compartment of the arm
The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb (the arm) of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these se ...
, and continues in the posterior compartment of the forearm.
Arm
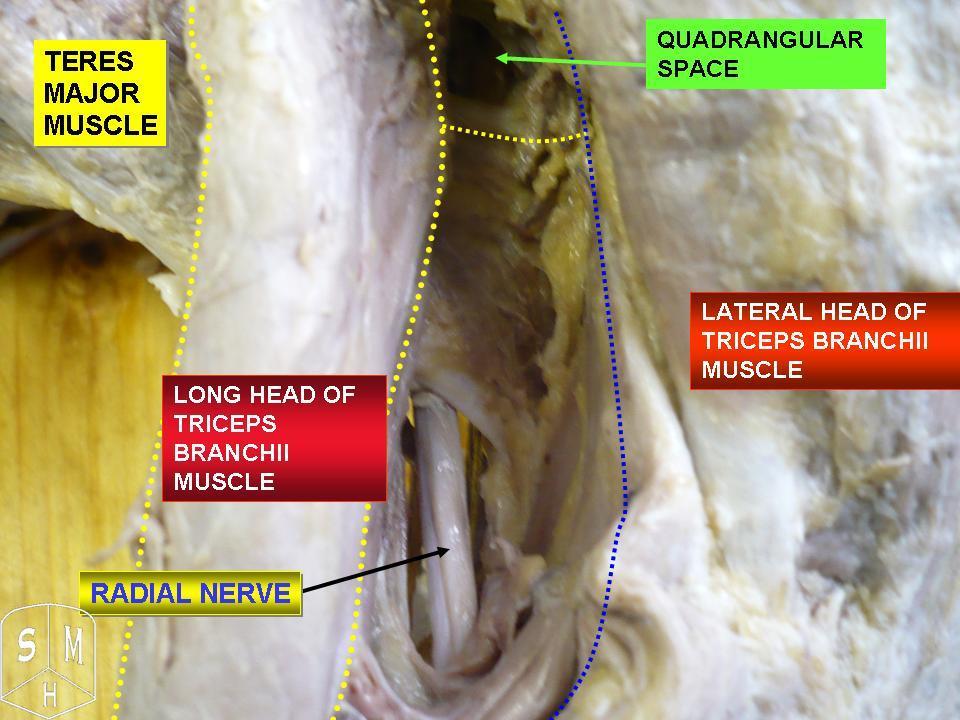
The radial nerve originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus with root values of C5 to C8 and T1. From the brachial plexus, it travels behind the third part of the axillary artery (part of the axillary artery distal to the pectoralis minor). In the arm, it runs behind the brachial artery and then enters thelower triangular space
The triangular interval (also known as the lateral triangular space, lower triangular space, and triceps hiatus) is a space found in the axilla. It is one of the three intermuscular spaces found in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: q ...
to reach the radial sulcus
The radial groove (also known as the musculospiral groove, radial sulcus, or spiral groove) is a broad but shallow oblique depression for the radial nerve and deep brachial artery. It is located on the center of the lateral border of the humerus b ...
of back of the humerus. It travel downwards together with profunda brachii artery
The deep artery of arm (also known as arteria profunda brachii and the deep brachial artery) is a large vessel which arises from the lateral and posterior part of the brachial artery, just below the lower border of the teres major.
Structure
It ...
, between the lateral and medial heads of triceps brachii until it reaches the lateral side the arm at 5 cm below the deltoid tuberosity
In human anatomy, the deltoid tuberosity is a rough, triangular area on the anterolateral (front-side) surface of the middle of the humerus. It is a site of attachment of deltoid muscle.
Structure
Variation
The deltoid tuberosity has been re ...
where it pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to reach the anterior compartment of the arm
The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb (the arm) of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these se ...
. Then, it descends down to cross the lateral epicondyle of the humerus where the nerve terminates by branching itself into superficial and deep branch which continues into cubital fossa
The cubital fossa, chelidon, or elbow pit, is the triangular area on the anterior side of the upper limb between the arm and forearm of a human or other hominid animals. It lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin ) when in standard anatomical position ...
and then into the forearm.
Radial nerve gives out muscular branches to supply the long head, medial head, and lateral head of triceps brachii muscles before and during its course in the radial sulcus. After it emerges out from the radial sulcus, it supplies the brachialis
The brachialis (brachialis anticus), also known as the Teichmann muscle, is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies deeper than the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa (elbow ...
, brachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way ...
and extensor carpi radialis longus
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each ...
.
Above the radial sulcus, the radial nerve gives off posterior cutaneous nerve of the arm
The posterior cutaneous nerve of arm (internal cutaneous branch of musculospiral, posterior brachial cutaneous nerve) is a branch of the radial nerve that provides sensory innervation for much of the skin on the back of the arm. It arises in the ...
which supplies the skin at the back of the arm. In the radial sulcus, it gives off lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm and posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm
The posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm is a nerve found in humans and other animals. It is also known as the dorsal antebrachial cutaneous nerve, the external cutaneous branch of the musculospiral nerve, and the posterior antebrachial cutaneous ...
. The radial nerve also gives articular branches to supply the elbow joint.
Forearm and hand
In the forearm, it is divided into a superficial branch (primarily sensory) and a deep branch (primarily motor). * The superficial branch of the radial nerve is widely separated from theradial artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
Structure
The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of the f ...
in the upper one third of the forearm, closely related to radial artery in the middle third of the forearm, and in the lower third, it descends in the forearm under the tendon of brachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way ...
. It crosses brachioradialis to enter posterior of forearm near the back of the wrist and supply dorsum of hand. It gives sensory supply to dorsal aspect of hand, dorsal aspect of thumb, index finger, middle finger and lateral side of ring finger except the nail beds, which are supplied by proper digital branches of median nerve.
* The deep branch of the radial nerve
The radial nerve divides into a superficial (sensory) and deep (motor) branch at the cubital fossa. The deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the S ...
(also known as posterior interosseous nerve by some authors)) pierces the supinator muscle, winds around the radius under the cover of supinator to reach posterior of forearm where it again pierces supinator and after which it is known as the posterior interosseous nerve. It pierces the posterior extensor muscles and comes to lie between superficial and deep muscles of the back of the forearm. At the lower border of extensor pollicis brevis, it passes deep to the extensor pollicis longus
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together ...
and then run on the posterior interosseous membrane. It continues to move along with posterior interosseous artery(a deep branch of common interosseous artery which is a branch of ulnar artery), and ends as a pseudoganglion below extensor retinaculum by supplying the wrist and intercarpal joints.
Variation
It is commonly believed that the radial nerve also provided motor innervation to the long head of the triceps. However, a study conducted in 2004 found out that axillary nerve innervates the long head of triceps in 20 cadavers without any supply from radial nerve.Function
The following are branches of the radial nerve (including the superficial branch of the radial nerve and the deep branch of the radial nerve/posterior interosseous nerve).Cutaneous
Motor

Muscular branches of the radial nerve
The muscular branches of the radial nerve supply the Triceps brachii, Anconæus, Brachioradialis, and Extensor carpi radialis longus, and are grouped as medial, posterior, and lateral.
Medial
The medial muscular branches supply the medial head o ...
:
* Triceps brachii
* Anconeus
*Brachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way ...
*Extensor carpi radialis longus
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each ...
Deep branch of the radial nerve
The radial nerve divides into a superficial (sensory) and deep (motor) branch at the cubital fossa. The deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the S ...
:
* Extensor carpi radialis brevis
* Supinator
Posterior interosseous nerve (a continuation of the deep branch after the supinator):
* Extensor digitorum
* Extensor digiti minimi
* Extensor carpi ulnaris
* Abductor pollicis longus
* Extensor pollicis brevis
*Extensor pollicis longus
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together ...
*Extensor indicis
In human anatomy, the extensor indicis roprius'' is a narrow, elongated skeletal muscle in the deep layer of the dorsal forearm, placed medial to, and parallel with, the extensor pollicis longus. Its tendon goes to the index finger, which it exte ...
The radial nerve (and its deep branch) provides motor innervation to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the arm and forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in ...
, which are mostly extensors
In anatomy, extension is a movement of a joint that increases the angle between two bones or body surfaces at a joint. Extension usually results in straightening of the bones or body surfaces involved. For example, extension is produced by extendin ...
.
Clinical significance
Injury
Injury to the radial nerve at different levels causes different syndromes with varying motor and sensory deficits. At the axilla * Common mechanisms of injury: Saturday night palsy, crutch palsy,lesions
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classifi ...
* Motor deficit:
** Loss of extension
Extension, extend or extended may refer to:
Mathematics
Logic or set theory
* Axiom of extensionality
* Extensible cardinal
* Extension (model theory)
* Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values that satisfy the predicate
* Ext ...
of forearm, weakness of supination, and loss of extension of hand and fingers.
** Presence of wrist drop
Wrist drop is a medical condition in which the wrist and the fingers cannot extend at the metacarpophalangeal joints. The wrist remains partially flexed due to an opposing action of flexor muscles of the forearm. As a result, the extensor muscles ...
, due to inability to extend the hand and fingers.
* Sensory deficit: Loss of sensation in lateral arm, posterior forearm, the radial half of dorsum of hand, and dorsal aspect of radial digits, excluding their nail beds.
At mid-arm
* Common mechanism of injury: Mid-shaft humeral fracture
* Motor deficit:
** Weakness of supination, and loss of extension of hand and fingers.
** Presence of wrist drop
Wrist drop is a medical condition in which the wrist and the fingers cannot extend at the metacarpophalangeal joints. The wrist remains partially flexed due to an opposing action of flexor muscles of the forearm. As a result, the extensor muscles ...
, due to inability to extend the hand and fingers.
* Sensory deficit: Loss of sensation in posterior forearm, the radial half of dorsum of hand, and dorsal aspect of radial digits, excluding their nail beds.
Just below the elbow
* Common mechanism of injury: Neck of radius fracture, elbow dislocation or fracture, tight cast, rheumatoid nodules, injections due to tennis elbow, injuring the deep branch of the radial nerve that pierces the radial head, causing posterior interosseous nerve syndrome
* Motor deficit:
** Weakness in extension of hand and loss of extension of fingers.
** Presence of finger drop, and partial wrist drop, since the extensor carpi radialis longus
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each ...
and brachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way ...
muscles are working.
* Sensory deficit: None, as sensation is supplied by the superficial radial nerve Within the distal forearm:
* Common mechanism of injury: Wartenberg's syndrome, (not to be confused with Wartenberg's sign), due to nerve entrapment beneath the tendinous insertion of
Within the distal forearm:
* Common mechanism of injury: Wartenberg's syndrome, (not to be confused with Wartenberg's sign), due to nerve entrapment beneath the tendinous insertion of brachioradialis
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way ...
, tight jewellery, and watch bands.
* Motor deficit: None
* Sensory deficit: Numbness and tingling in radial half of dorsum of hand, and dorsal aspect of radial digits, excluding their nail beds.
* In Wartenberg's syndrome, there is significant radial wrist pain, and close resemblance to symptoms in de Quervain's tenosynovitis. Finkelstein's test
Finkelstein's test is a test used to diagnose de Quervain's tenosynovitis in people who have wrist pain.
Classical descriptions of the Finkelstein's test are when the examiner grasps the thumb and ulnar deviates the hand sharply. If sharp pai ...
may be positive.
History
Additional images
See also
*Muscular branches of the radial nerve
The muscular branches of the radial nerve supply the Triceps brachii, Anconæus, Brachioradialis, and Extensor carpi radialis longus, and are grouped as medial, posterior, and lateral.
Medial
The medial muscular branches supply the medial head o ...
* Posterior brachial cutaneous nerve
* Dorsal antibrachial cutaneous nerve
* Superficial branch of the radial nerve
* Deep branch of the radial nerve
The radial nerve divides into a superficial (sensory) and deep (motor) branch at the cubital fossa. The deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the S ...
* Radial neuropathy
* Radial tunnel syndrome
References
External links
* * - "Axilla, dissection, anterior view" {{Authority control Nerves of the upper limb