
The Radcliffe Line was the boundary demarcated between the
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
n and
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
i portions of the
Punjab Province and
Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia an ...
of
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
. It was named after
Cyril Radcliffe
Cyril John Radcliffe, 1st Viscount Radcliffe, (30 March 1899 – 1 April 1977) was a British lawyer and Law Lord best known for his role in the Partition of India. He served as the first chancellor of the University of Warwick from its foundatio ...
, who, as the joint chairman of the two boundary commissions for the two provinces, had the ultimate responsibility to equitably divide of territory with 88 million people.
The demarcation line was published on 17 August 1947 upon the
Partition of British India. Today, its western side of the line is part of the
India–Pakistan border
The Indo–Pak border or India-Pakistan border is the international boundary that separates India and Pakistan. At its northern end is the Line of Control, which separates Indian-administered Kashmir from Pakistani-administered Kashmir; and ...
while its eastern side serves as the
Bangladesh–India border
The Bangladesh–India border, known locally as the International Border (IB), is an international border running between Bangladesh and India that demarcates the eight divisions of Bangladesh and the Indian states.
Bangladesh and India sha ...
.
Background
Events leading up to the Radcliffe Boundary Commissions

On 18 July 1947, the
Indian Independence Act 1947
The Indian Independence Act 1947 947 CHAPTER 30 10 and 11 Geo 6is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that partitioned British India into the two new independent dominions of India and Pakistan. The Act received Royal Assent on 18 Ju ...
of the Parliament of the United Kingdom stipulated that British rule in India would come to an end just one month later, on 15 August 1947. The Act also stipulated the partition of the
Presidencies and provinces of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
into two new sovereign
dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
s: India and Pakistan.
Pakistan was intended as a Muslim homeland, while India remained
secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
. Muslim-majority British provinces in the northwest were to become the foundation of Pakistan. The provinces of
Baluchistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western Asia, Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian S ...
(91.8% Muslim before partition) and
Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
(72.7%) and
North-West Frontier Province
The North-West Frontier Province (NWFP; ps, شمال لویدیځ سرحدي ولایت, ) was a Chief Commissioner's Province of British India, established on 9 November 1901 from the north-western districts of the Punjab Province. Followi ...
became entirely Pakistani territory. However, two provinces did not have an overwhelming Muslim majority—
Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
in the northwest (55.7% Muslim) and
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
in the northeast (54.4% Muslim). After elaborate discussions, these two provinces ended up being partitioned between India and Pakistan.
The Punjab's population distribution was such that there was no line that could neatly divide the
Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
,
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, and
Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The ter ...
. Likewise, no line could appease both the
Muslim League Muslim League may refer to:
Political parties Subcontinent
; British India
*All-India Muslim League, Mohammed Ali Jinah, led the demand for the partition of India resulting in the creation of Pakistan.
**Punjab Muslim League, a branch of the organ ...
, headed by
Jinnah, and the
Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
led by
Jawaharlal Nehru
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru (; ; ; 14 November 1889 – 27 May 1964) was an Indian Anti-colonial nationalism, anti-colonial nationalist, secular humanist, social democrat—
*
*
*
* and author who was a central figure in India du ...
and
Vallabhbhai Patel
Vallabhbhai Jhaverbhai Patel (; ; 31 October 1875 – 15 December 1950), commonly known as Sardar, was an Indian lawyer, influential political leader, barrister and statesman who served as the first Deputy Prime Minister and Home Minister of I ...
. Moreover, any division based on religious communities was sure to entail "cutting through road and rail communications, irrigation schemes, electric power systems and even individual landholdings."
Prior ideas of partition
The idea of partitioning the provinces of Bengal and Punjab had been present since the beginning of the 20th century. Bengal had in fact been
partitioned by the then viceroy
Lord Curzon
George Nathaniel Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon of Kedleston, (11 January 1859 – 20 March 1925), styled Lord Curzon of Kedleston between 1898 and 1911 and then Earl Curzon of Kedleston between 1911 and 1921, was a British Conservative statesman ...
in 1905, along with its adjoining regions. The resulting 'Eastern Bengal and Assam' province, with its capital at
Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest ...
, had a Muslim majority and the 'West Bengal' province, with its capital at
Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, commer ...
, had a Hindu majority. However, this partition of Bengal was reversed in 1911 in an effort to mollify
Bengali nationalism
Bengalism or Bengali nationalism () was a form of nationalism that focused on Bengalis as a singular nation. The people of Bengali ethnicity speak Bengali language. Bengalis mostly live across Bangladesh and the Indian states of Tripura an ...
.
Proposals for partitioning Punjab had been made starting in 1908. Its proponents included the Hindu leader
Bhai Parmanand
Bhai Parmanand (4 November 1876 – 8 December 1947) was an Indian nationalist and a prominent leader of the Hindu Mahasabha.
Early life
Parmanand was born into a prominent family of the Punjab, Mohyal Brahmins. His father, Tara Chand Mohyal, c ...
, Congress leader
Lala Lajpat Rai
Lala Lajpat Rai (28 January 1865 - 17 November 1928) was an Indian author, freedom fighter, and politician. He played a vital role in the Indian Independence movement. He was popularly known as Punjab Kesari. He was one of the three members of ...
, industrialist
G. D. Birla
Ghanshyam Das Birla (10 April 1894 – 11 June 1983) was an Indian businessman and member of the Birla Family.
Birla family history
Ghanshyam Das Birla was born on 10 April 1894 at Pilani town in Jhunjhunu district, in the region known as Ra ...
, and various Sikh leaders. After the 1940
Lahore resolution of the Muslim League demanding Pakistan,
B. R. Ambedkar wrote a 400-page tract titled ''Thoughts on Pakistan.'' In the tract, he discussed the boundaries of Muslim and non-Muslim regions of Punjab and Bengal. His calculations showed a Muslim majority in 16 western districts of Punjab and non-Muslim majority in 13 eastern districts. In Bengal, he showed non-Muslim majority in 15 districts. He thought the Muslims could have no objection to redrawing provincial boundaries. If they did, "they
idnot understand the nature of their own demand".
After the breakdown of the 1945
Simla Conference
The Simla Conference of 1945 was a meeting between the Viceroy of India Lord Wavell and the major political leaders of British India at the Viceregal Lodge in Simla. When it was clear that British intended to leave India, they desperately ne ...
of viceroy
Lord Wavell
Field Marshal Archibald Percival Wavell, 1st Earl Wavell, (5 May 1883 – 24 May 1950) was a senior officer of the British Army. He served in the Second Boer War, the Bazar Valley Campaign and the First World War, during which he was wounded i ...
, the idea of Pakistan began to be contemplated seriously. Sir
Evan Jenkins, the private secretary of the viceroy (later the governor of Punjab), wrote a memorandum titled "Pakistan and the Punjab", where he discussed the issues surrounding the partition of Punjab.
K. M. Panikkar
Kavalam Madhava Panikkar (3 June 1895 – 10 December 1963), popularly known as Sardar K. M. Panikkar, was an Indian statesman and diplomat. He was also a professor, newspaper editor, historian and novelist. He was born in Travancore, then a ...
, then prime minister of the
Bikaner State, sent a memorandum to the viceroy titled "Next Step in India", wherein he recommended that the principle of 'Muslim homeland' be conceded but territorial adjustments made to the two provinces to meet the claims of the Hindus and Sikhs. Based on these discussions, the viceroy sent a note on the "Pakistan theory" to the
Secretary of State for India
His (or Her) Majesty's Principal Secretary of State for India, known for short as the India Secretary or the Indian Secretary, was the British Cabinet minister and the political head of the India Office responsible for the governance of th ...
. The viceroy informed the Secretary of State that Jinnah envisaged the ''full provinces'' of Bengal and Punjab going to Pakistan with only minor adjustments, whereas Congress was expecting ''almost half'' of these provinces to remain in India. This essentially framed the problem of partition.
The Secretary of State responded by directing Lord Wavell to send 'actual proposals for defining genuine Muslim areas'. The task fell on
V. P. Menon
Rao Bahadur Vappala Pangunni Menon, CSI, CIE (30 September 1893 – 31 December 1965) was an Indian civil servant who served as Secretary to the Government of India in the Ministry of the States, under Sardar Patel.
By appointment fr ...
, the Reforms Commissioner, and his colleague Sir
B. N. Rau
Sir Benegal Narsing Rau (26 February 1887 – 30 November 1953) was an Indian civil servant, jurist, diplomat and statesman known for his key role in drafting the Constitution of India. He was the Constitutional Advisor to Constituent Assembl ...
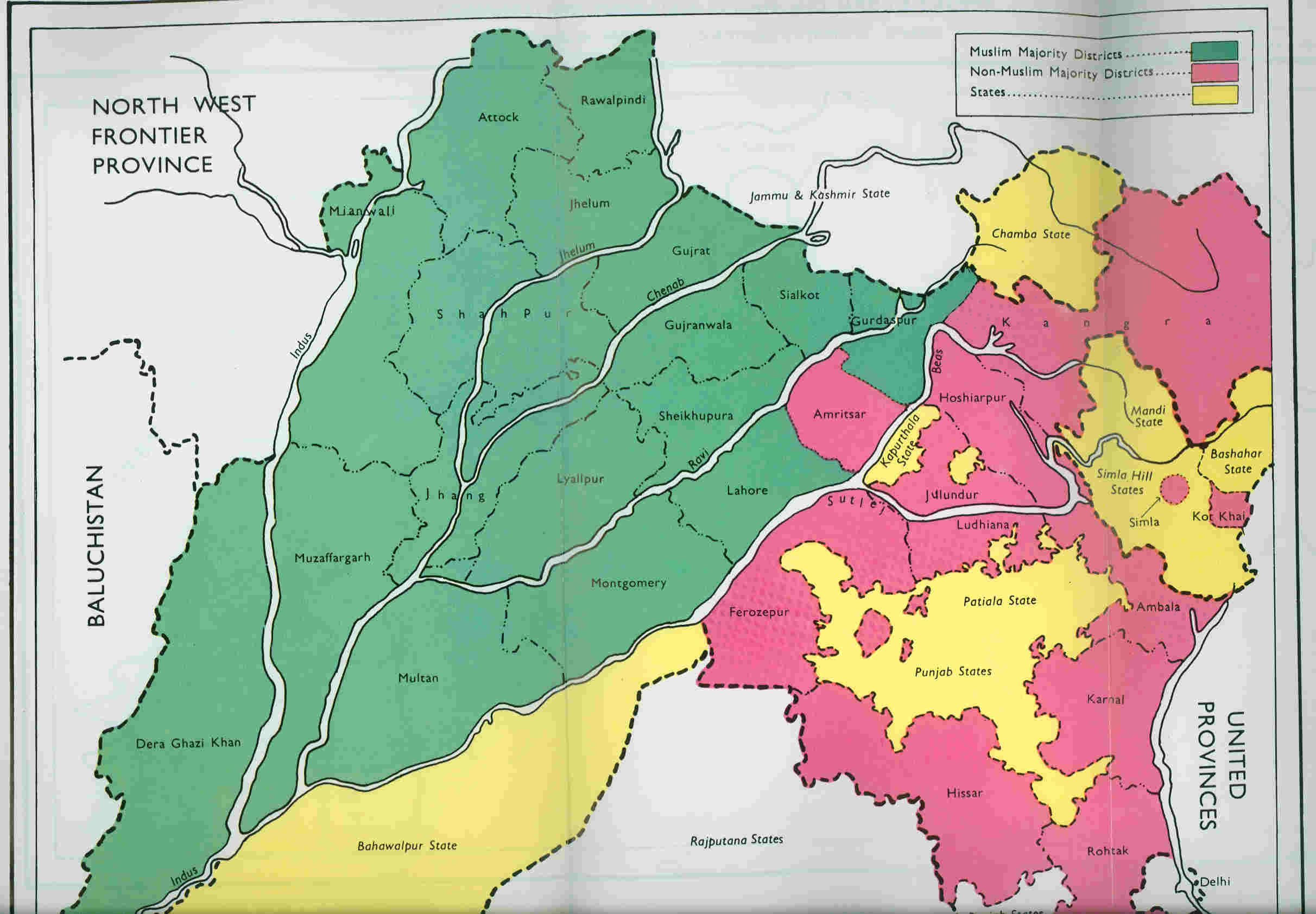
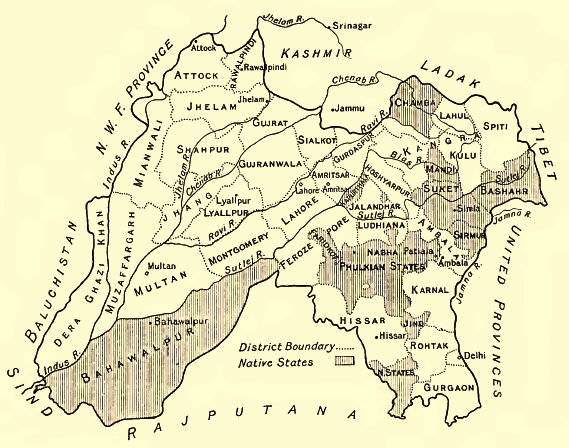
in the Reforms Office. They prepared a note called "Demarcation of Pakistan Areas", where they included the three western divisions of Punjab (
Rawalpindi, Multan and Lahore) in Pakistan, leaving two eastern divisions of Punjab in India (
Jullundur and Delhi). However, they noted that this allocation would leave 2.2 million Sikhs in the Pakistan area and about 1.5 million in India. Excluding the
Amritsar
Amritsar (), historically also known as Rāmdāspur and colloquially as ''Ambarsar'', is the second largest city in the Indian state of Punjab, after Ludhiana. It is a major cultural, transportation and economic centre, located in the Majha ...
and
Gurdaspur districts of the Lahore Division from Pakistan would put a majority of Sikhs in India. (Amritsar had a non-Muslim majority and Gurdaspur a marginal Muslim majority.) To compensate for the exclusion of the Gurdaspur district, they included the entire
Dinajpur district in the eastern zone of Pakistan, which similarly had a marginal Muslim majority. After receiving comments from John Thorne, member of the Executive Council in charge of Home affairs, Wavell forwarded the proposal to the Secretary of State. He justified the exclusion of the Amritsar district because of its sacredness to the Sikhs and that of Gurdaspur district because it had to go with Amritsar for 'geographical reasons'. The Secretary of State commended the proposal and forwarded it to the India and Burma Committee, saying, "I do not think that any better division than the one the Viceroy proposes is likely to be found".
Sikh concerns
The Sikh leader
Master Tara Singh could see that any division of Punjab would leave the Sikhs divided between Pakistan and Hindustan. He espoused the doctrine of self-reliance,
opposed the partition of India and called for independence on the grounds that no single religious community should control Punjab. Other Sikhs argued that just as Muslims feared Hindu domination the Sikhs also feared Muslim domination. Sikhs warned the British government that the morale of Sikh troops in the British Army would be affected if Pakistan was forced on them.
Giani Kartar Singh drafted a scheme of a separate Sikh state if India was to be divided.
During the Partition developments, Jinnah offered Sikhs to live in Pakistan with safeguards for their rights. Sikhs refused because they opposed the concept of Pakistan and also because they did not want to become a small minority within a Muslim majority.
Vir Singh Bhatti distributed pamphlets for the creation of a separate Sikh state "Khalistan". Master Tara Singh wanted the right for an independent Khalistan to federate with either Hindustan or Pakistan. However, the Sikh state being proposed was for an area where no religion was in absolute majority.
[The Sikhs of the Punjab, Volumes 2-3 , J S Grewal, page 176] Negotiations for the independent Sikh state had commenced at the end of World War II and the British initially agreed but the Sikhs withdrew this demand after pressure from Indian nationalists.
[Ethnic Group's of South Asia and the Pacific: An Encyclopedia, James Minahan, page 292] The proposals of the Cabinet Mission Plan had seriously jolted the Sikhs because while both the Congress and League could be satisfied the Sikhs saw nothing in it for themselves. as they would be subjected to a Muslim majority. Master Tara Singh protested this to Pethic-Lawrence on 5 May. By early September the Sikh leaders accepted both the long term and interim proposals despite their earlier rejection.
The Sikhs attached themselves to the Indian state with the promise of religious and cultural autonomy.
Final negotiations
In March 1946, the British government sent a
Cabinet Mission
A Cabinet Mission came to India in 1946 in order to discuss the transfer of power from the British government to the Indian political leadership, with the aim of preserving India's unity and granting its independence. Formed at the initiative of ...
to India to find a solution to resolve the conflicting demands of Congress and the Muslim League. Congress agreed to allow Pakistan to be formed with 'genuine Muslim areas'. The Sikh leaders asked for a Sikh state with
Ambala
Ambala () is a city and a municipal corporation in Ambala district in the state of Haryana, India, located on the border with the Indian state of Punjab and in proximity to both states capital Chandigarh. Politically, Ambala has two sub-ar ...
,
Jalandher,
Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second List of cities in Pakistan by population, most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th List of largest cities, most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is th ...
Divisions with some districts from the
Multan Division
Multan Division is an administrative division of Punjab Province, Pakistan. The reforms of 2000 abolished the third tier of government but the division system was restored again in 2008.
Districts
It consists of the following districts:
Histo ...
, which, however, did not meet the Cabinet delegates' agreement. In discussions with Jinnah, the Cabinet Mission offered either a 'smaller Pakistan' with all the Muslim-majority districts ''except Gurdaspur'' or a 'larger Pakistan' under the sovereignty of the Indian Union. The Cabinet Mission came close to success with its proposal for an Indian Union under a federal scheme, but it fell apart in the end because of Nehru's opposition to a heavily decentralised India.
In March 1947,
Lord Mountbatten
Louis Francis Albert Victor Nicholas Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma (25 June 1900 – 27 August 1979) was a British naval officer, colonial administrator and close relative of the British royal family. Mountbatten, who was of German ...
arrived in India as the next viceroy, with an explicit mandate to achieve the transfer of power before June 1948. Over ten days, Mountbatten obtained the agreement of Congress to the Pakistan demand except for the 13 eastern districts of Punjab (including Amritsar and Gurdaspur). However, Jinnah held out. Through a series of six meetings with Mountbatten, he continued to maintain that his demand was for six full provinces. He "bitterly complained" that the Viceroy was ruining his Pakistan by cutting Punjab and Bengal in half as this would mean a 'moth-eaten Pakistan'.
The Gurdaspur district remained a key contentious issue for the non-Muslims. Their members of the Punjab legislature made representations to Mountbatten's chief of staff
Lord Ismay as well as the Governor telling them that Gurdaspur was a "non-Muslim district". They contended that even if it had a marginal Muslim majority of 51%, which they believed to be erroneous, the Muslims paid only 35% of the land revenue in the district.
In April, the Governor of Punjab
Evan Jenkins wrote a note to Mountbatten proposing that Punjab be divided along Muslim and non-Muslim majority districts and proposed that a Boundary Commission be set up consisting of two Muslim and two non-Muslim members recommended by the Punjab Legislative Assembly. He also proposed that a British judge of the High Court be appointed as the chairman of the commission. Jinnah and the Muslim League continued to oppose the idea of partitioning the provinces, and the Sikhs were disturbed about the possibility of getting only 12 districts (without Gurdaspur). In this context, the Partition Plan of 3 June was announced with a notional partition showing 17 districts of Punjab in Pakistan and 12 districts in India, along with the establishment of a Boundary Commission to decide the final boundary. In Sialkoti's view, this was done mainly to placate the Sikhs.
Process and key people
A crude border had already been drawn up by
Lord Wavell
Field Marshal Archibald Percival Wavell, 1st Earl Wavell, (5 May 1883 – 24 May 1950) was a senior officer of the British Army. He served in the Second Boer War, the Bazar Valley Campaign and the First World War, during which he was wounded i ...
, the
Viceroy of India
The Governor-General of India (1773–1950, from 1858 to 1947 the Viceroy and Governor-General of India, commonly shortened to Viceroy of India) was the representative of the monarch of the United Kingdom and after Indian independence in 19 ...
prior to his replacement as Viceroy, in February 1947, by
Lord Louis Mountbatten. In order to determine exactly which territories to assign to each country, in June 1947, Britain appointed
Sir Cyril Radcliffe
Cyril John Radcliffe, 1st Viscount Radcliffe, (30 March 1899 – 1 April 1977) was a British lawyer and Law Lord best known for his role in the Partition of India. He served as the first chancellor of the University of Warwick from its foundatio ...
to chair two boundary commissions—one for Bengal and one for Punjab.
The commission was instructed to "demarcate the boundaries of the two parts of the Punjab on the basis of ascertaining the contiguous majority areas of Muslims and non-Muslims. In doing so, it will also take into account other factors." Other factors were undefined, giving Radcliffe leeway, but included decisions regarding "natural boundaries, communications, watercourses and irrigation systems", as well as socio-political consideration. Each commission also had four representatives—two from the
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British E ...
and two from the
Muslim League Muslim League may refer to:
Political parties Subcontinent
; British India
*All-India Muslim League, Mohammed Ali Jinah, led the demand for the partition of India resulting in the creation of Pakistan.
**Punjab Muslim League, a branch of the organ ...
. Given the deadlock between the interests of the two sides and their rancorous relationship, the final decision was essentially Radcliffe's.
After arriving in India on 8 July 1947, Radcliffe was given just five weeks to decide on a border.
He soon met with his fellow college alumnus Mountbatten and travelled to
Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second List of cities in Pakistan by population, most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th List of largest cities, most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is th ...
and
Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, commer ...
to meet with commission members, chiefly Nehru from the Congress and Jinnah, president of the Muslim League. He objected to the short time frame, but all parties were insistent that the line be finished by 15 August British withdrawal from India. Mountbatten had accepted the post as Viceroy on the condition of an early deadline. The decision was completed just a couple of days before the withdrawal, but due to political considerations, not published until 17 August 1947, two days after the grant of independence to India and Pakistan.
[
]
Members of the commissions
Each boundary commission consisted of five people – a chairman ( Radcliffe), two members nominated by the Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British E ...
and two members nominated by the Muslim League Muslim League may refer to:
Political parties Subcontinent
; British India
*All-India Muslim League, Mohammed Ali Jinah, led the demand for the partition of India resulting in the creation of Pakistan.
**Punjab Muslim League, a branch of the organ ...
.
The Bengal Boundary Commission consisted of justices C. C. Biswas, B. K. Mukherji, Abu Saleh Mohamed Akram and S.A.Rahman.Mehr Chand Mahajan
Justice Mehr Chand Mahajan (1889–1967) was the third Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of India. Prior to that he was the Prime Minister of the state of Jammu and Kashmir during the reign of Maharaja Hari Singh and played a key role in the ...
, Teja Singh, Din Mohamed and Muhammad Munir.[
]
Problems in the process
Boundary-making procedures
 All lawyers by profession, Radcliffe and the other commissioners had all of the polish and none of the specialized knowledge needed for the task. They had no advisers to inform them of the well-established procedures and information needed to draw a boundary. Nor was there time to gather the survey and regional information. The absence of some experts and advisers, such as the United Nations, was deliberate, to avoid delay. Britain's new Labour government "deep in wartime debt, simply couldn’t afford to hold on to its increasingly unstable empire." "The absence of outside participants—for example, from the United Nations—also satisfied the British Government's urgent desire to save face by avoiding the appearance that it required outside help to govern—or stop governing—its own empire."
All lawyers by profession, Radcliffe and the other commissioners had all of the polish and none of the specialized knowledge needed for the task. They had no advisers to inform them of the well-established procedures and information needed to draw a boundary. Nor was there time to gather the survey and regional information. The absence of some experts and advisers, such as the United Nations, was deliberate, to avoid delay. Britain's new Labour government "deep in wartime debt, simply couldn’t afford to hold on to its increasingly unstable empire." "The absence of outside participants—for example, from the United Nations—also satisfied the British Government's urgent desire to save face by avoiding the appearance that it required outside help to govern—or stop governing—its own empire."
Political representation
The equal representation given to politicians from Indian National Congress and the Muslim League appeared to provide balance, but instead created deadlock. The relationships were so tendentious that the judges "could hardly bear to speak to each other", and the agendas so at odds that there seemed to be little point anyway. Even worse, "the wife and two children of the Sikh judge in Lahore had been murdered by Muslims in Rawalpindi a few weeks earlier."
In fact, minimizing the numbers of Hindus and Muslims on the wrong side of the line was not the only concern to balance. The Punjab Border Commission was to draw a border through the middle of an area home to the Sikh community. Lord Islay was rueful for the British not to give more consideration to the community who, in his words, had "provided many thousands of splendid recruits for the Indian Army" in its service for the crown in World War I. However, the Sikhs were militant in their opposition to any solution which would put their community in a Muslim ruled state. Moreover, many insisted on their own sovereign state, something no one else would agree to.
Last of all, were the communities without any representation. The Bengal Border Commission representatives were chiefly concerned with the question of who would get Calcutta. The Buddhist tribes in the Chittagong Hill Tracts
The Chittagong Hill Tracts ( bn, পার্বত্য চট্টগ্রাম, Parbotto Chottogram), often shortened to simply the Hill Tracts and abbreviated to CHT, are group of districts within the Chittagong Division in southeast ...
in Bengal had no official representation and were left totally without information to prepare for their situation until two days after the partition.
Perceiving the situation as intractable and urgent, Radcliffe went on to make all the difficult decisions himself. This was impossible from inception, but Radcliffe seems to have had no doubt in himself and raised no official complaint or proposal to change the circumstances.
Local knowledge
Before his appointment, Radcliffe had never visited India and knew no one there. To the British and the feuding politicians alike, this neutrality was looked upon as an asset; he was considered to be unbiased toward any of the parties, except of course Britain.
Haste and indifference
Radcliffe justified the casual division with the truism A truism is a claim that is so obvious or self-evident as to be hardly worth mentioning, except as a reminder or as a rhetorical or literary device, and is the opposite of falsism.
In philosophy, a sentence which asserts incomplete truth conditio ...
that no matter what he did, people would suffer. The thinking behind this justification may never be known since Radcliffe "destroyed all his papers before he left India". He departed on Independence Day itself, before even the boundary awards were distributed. By his own admission, Radcliffe was heavily influenced by his lack of fitness for the Indian climate and his eagerness to depart India.
The implementation was no less hasty than the process of drawing the border. On 16 August 1947 at 5:00 pm, the Indian and Pakistani representatives were given two hours to study copies, before the Radcliffe award was published on 17 August.
Secrecy
To avoid disputes and delays, the division was done in secret. The final Awards were ready on 9 and 12 August, but not published until two days after the partition.
According to Read and Fisher, there is some circumstantial evidence that Nehru and Patel were secretly informed of the Punjab Award's contents on 9 or 10 August, either through Mountbatten or Radcliffe's Indian assistant secretary. Regardless of how it transpired, the award was changed to put a salient portion of the non-Muslim majority Ferozepur district (constituting of the two Muslim-majority tehsils of Ferozepur and Zira) east of the Sutlej canal within India's domain instead of Pakistan's. There were two apparent reasons for the switch: the area housed an army arms depot, and contained the headwaters of a canal which irrigated the princely state of Bikaner, which would accede to India.
Implementation
After the partition, the fledgling governments of India and Pakistan were left with all responsibility to implement the border. After visiting Lahore in August, Viceroy Mountbatten hastily arranged a Punjab Boundary Force to keep the peace around Lahore, but 50,000 men was not enough to prevent thousands of killings, 77% of which were in the rural areas. Given the size of the territory, the force amounted to less than one soldier per square mile. This was not enough to protect the cities much less the caravans of the hundreds of thousands of refugees who were fleeing their homes in what would become Pakistan.
Both India and Pakistan were loath to violate the agreement by supporting the rebellions of villages drawn on the wrong side of the border, as this could prompt a loss of face on the international stage and require the British or the UN to intervene. Border conflicts led to three wars, in 1947
It was the first year of the Cold War, which would last until 1991, ending with the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Events
January
* January–February – Winter of 1946–47 in the United Kingdom: The worst snowfall in the country i ...
, 1965
Events January–February
* January 14 – The Prime Minister of Northern Ireland and the Taoiseach of the Republic of Ireland meet for the first time in 43 years.
* January 20
** Lyndon B. Johnson is sworn in for a full term ...
, and 1971 *
The year 1971 had three partial solar eclipses ( February 25, July 22 and August 20) and two total lunar eclipses ( February 10, and August 6).
The world population increased by 2.1% this year, the highest increase in history.
Events
J ...
, and the Kargil conflict of 1999.
Disputes along the Radcliffe Line
There were disputes regarding the Radcliffe Line's award of the Chittagong Hill Tracts
The Chittagong Hill Tracts ( bn, পার্বত্য চট্টগ্রাম, Parbotto Chottogram), often shortened to simply the Hill Tracts and abbreviated to CHT, are group of districts within the Chittagong Division in southeast ...
and the Gurdaspur district
Gurdaspur district is a district in the Majha region of the state of Punjab, India. Gurdaspur is the district headquarters. It internationally borders Narowal District of Pakistani Punjab, and the districts of Amritsar, Pathankot, Kapurthala ...
. Disputes also evolved around the districts of Malda, Khulna
Khulna ( bn, খুলনা, ) is the third-largest city in Bangladesh, after Dhaka and Chittagong. It is the administrative centre of Khulna District and Khulna Division. Khulna's economy is the third-largest in Bangladesh, contributing $53 ...
, and Murshidabad
Murshidabad fa, مرشد آباد (, or ) is a historical city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located on the eastern bank of the Bhagirathi River, a distributary of the Ganges. It forms part of the Murshidabad district.
Durin ...
in Bengal and the sub-division of Karimganj
Karimganj is a city in the Karimganj District of the Indian state of Assam. It is the administrative headquarters of the district.
Karimganj city is located at . The area of Karimganj city is 16.09 km2. It has an average elevation of 13 ...
of Assam.
In addition to Gurdaspur's Muslim majority tehsils, Radcliffe also gave the Muslim majority tehsils of Ajnala (Amritsar District), Zira, Ferozpur (in Ferozpur District), Nakodar and Jullander (in Jullander District) to India instead of Pakistan.
Punjab
Lahore
Lahore having Muslims in majority with about 64.5% percent but Hindus and Sikhs controlled approximately 80% of city's assets, Radcliffe had originally planned to give Lahore
Lahore ( ; pnb, ; ur, ) is the second List of cities in Pakistan by population, most populous city in Pakistan after Karachi and 26th List of largest cities, most populous city in the world, with a population of over 13 million. It is th ...
to India.Kuldip Nayar
Kuldip Nayar (14 August 1923 – 23 August 2018) was an Indian journalist, syndicated columnist, human rights activist, author and former High Commissioner of India to the United Kingdom noted for his long career as a left-wing political com ...
, he stated "I nearly gave you Lahore. ... But then I realised that Pakistan would not have any large city. I had already earmarked Calcutta for India."
Ferozpur District
Indian historians now accept that Mountbatten probably did influence the Ferozpur award in India's favour.
Gurdaspur District
The Gurdaspur district was administratively subdivided into four tehsils
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administ ...
: Shakargarh
Shakargarh ( ur, ), the capital of Shakargarh Tehsil, is a city in the north-eastern part of Narowal District in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It borders Jammu, India to the north and Sialkot to the west Its literacy rate is more than 85% wh ...
and Pathankot
Pathankot is a city and the district headquarters of the Pathankot district in Punjab, India. Pathankot is the 6th most populous city of Punjab, after Ludhiana, Amritsar, Jalandhar, Patiala and Bathinda. Its local government is a municipal co ...
tehsils to the north, and Gurdaspur and Batala tehsils to the south. Of the four, only the Shakargarh tehsil, which was separated from the rest of the district by the Ravi river
The Ravi River () is a transboundary river crossing northwestern India and eastern Pakistan. It is one of five rivers associated with the Punjab region.
Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two other rivers were ...
and was the biggest in size, was awarded to Pakistan. (It was subsequently merged into the Narowal district
Narowal District (Punjabi and ur, ), is a district in the province of Punjab of Pakistan. Narowal city is the capital of the district. During the British rule, Narowal was the town of Raya Khas tehsil of Sialkot District. Narowal District ...
of West Punjab
West Punjab ( pnb, ; ur, ) was a province in the Dominion of Pakistan from 1947 to 1955. The province covered an area of 159,344 km2 (61523 sq mi), including much of the current Punjab province and the Islamabad Capital Territory, but exclu ...
.) The Gurdaspur, Batala and Pathankot tehsils became part of India's East Punjab state. The division of the district was followed by a population transfer between the two nations, with Muslims leaving for Pakistan and Hindus and Sikhs arriving from there.
The entire district of Gurdaspur had a bare majority of 50.2% Muslims. (In the `notional' award attached to the Indian Independence Act, all of Gurdaspur district was marked as Pakistan with a 51.14% Muslim majority. In the 1901 census, the population of Gurdaspur district was 49% Muslim, 40% Hindu, and 10% Sikh.) The Pathankot tehsil was predominantly Hindu while the other three tehsils were Muslim majority. In the event, only Shakargarh was awarded to Pakistan.
Radcliffe explained that the reason for deviating from the notional award in the case of Gurdaspur was that the headwaters of the canals that irrigated the Amritsar district lay in the Gurdaspur district and it was important to keep them under one administration. Lord Wavell had stated in February 1946 that Gurdaspur had to go with the Amritsar district, and the latter could not be in Pakistan due to its Sikh religious shrines. In addition, the railway line from Amritsar to Pathankot passed through the Batala and Gurdaspur tehsils.
Pakistanis have alleged that the award of the three tehsils to India was a manipulation of the Award by Lord Mountbatten in an effort to provide a land route for India to Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
. However, Shereen Ilahi points out that the land route to Kashmir was entirely within the Pathankot tehsil, which had a Hindu majority. The award of the Batala and Gurdaspur tehsils to India did not affect Kashmir.
Pakistani view on the award of Gurdaspur to India
Pakistan maintains that the Radcliffe Award was altered by Mountbatten; Gurdaspur was handed over to India and thus was manipulated the accession of Kashmir to India. In support of this view, some scholars claim the award to India "had little to do with Sikh demands but had much more to do with providing India a road link to Jammu and Kashmir."
As per the 'notional' award that had already been put into effect for purposes of administration ad interim, all of Gurdaspur district, owing to its Muslim majority, was assigned to Pakistan.Muhammad Zafarullah Khan
Chaudhry Sir Muhammad Zafarullah Khan ( ur, ; 6 February 1893 – 1 September 1985) was a Pakistani jurist and diplomat who served as the first Foreign Minister of Pakistan. After serving as foreign minister he continued his internation ...
, who represented the Muslim League in July 1947 before the Radcliffe Boundary Commission, stated that the boundary commission was a farce. A secret deal between Mountbatten and Congress leaders had already been struck. Mehr Chand Mahajan
Justice Mehr Chand Mahajan (1889–1967) was the third Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of India. Prior to that he was the Prime Minister of the state of Jammu and Kashmir during the reign of Maharaja Hari Singh and played a key role in the ...
, one of the two non-Muslim members of the boundary commission, in his autobiography, has acknowledged that when he was selected for the boundary commission, he was not inclined to accept the invitation as he believed that the commission was just a farce and that decisions were actually to be taken by Mountbatten himself. It was only under British pressure that the charges against Mountbatten of last minute alterations in the Radcliffe Award were not officially brought forward by Pakistani Government in the UN Security Council while presenting its case on Kashmir.
Zafrullah Khan states that, in fact, adopting the tehsil as a unit would have given Pakistan the Ferozepur and Zira tehsils of the Ferozpur District, the Jullundur and Rahon tehsils of Jullundur district and the Dasuya tehsil of the Hoshiarpur district. The line so drawn would also give Pakistan the princely state of Kapurthala (which had a Muslim majority) and would enclose within Pakistan the whole of the Amritsar district of which only one tehsil, Ajnala, had a Muslim majority. It would also give Pakistan the Shakargarh, Batala and Gurdaspur tehsils of the Gurdaspur district. If the boundary went by Doabs, Pakistan could get not only the 16 districts which had already under the notional partition been put into West Punjab, including the Gurdaspur District, but also get the Kangra District in the mountains, which was about 93% Hindu and was located to the north and east of Gurdaspur. Or one could go by commissioners' divisions. Any of these units being adopted would have been more favourable to Pakistan than the present boundary line. The tehsil was the most favourable unit.
Assessments on the 'Controversial Award of Gurdaspur to India and the Kashmir Dispute'
Stanley Wolpert writes that Radcliffe in his initial maps awarded Gurdaspur district to Pakistan but one of Nehru's and Mountbatten's greatest concerns over the new Punjab border was to make sure that Gurdaspur would not go to Pakistan, since that would have deprived India of direct road access to Kashmir. As per "The Different Aspects of Islamic Culture", a part of UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
’s Histories flagship project, recently disclosed documents of the history of the partition reveal British complicity with the top Indian leadership to wrest Kashmir from Pakistan. Alastair Lamb, based on the study of recently declassified documents, has convincingly proven that Mountbatten, in league with Nehru, was instrumental in pressurizing Radcliffe to award the Muslim-majority district of Gurdaspur in East Punjab to India which could provide India with the only possible access to Kashmir. Andrew Roberts believes that Mountbatten cheated over India-Pak frontier and states that if gerrymandering took place in the case of Ferozepur, it is not too hard to believe that Mountbatten also pressurized Radcliffe to ensure that Gurdaspur wound up in India to give India road access to Kashmir.Perry Anderson
Francis Rory Peregrine "Perry" Anderson (born 11 September 1938) is a British intellectual, historian and essayist. His work ranges across historical sociology, intellectual history, and cultural analysis. What unites Anderson's work is a preoc ...
states that Mountbatten, who was officially supposed to neither exercise any influence on Radcliffe nor to have any knowledge of his findings, intervened behind the scenes – probably at Nehru's behest – to alter the award. He had little difficulty in getting Radcliffe to change his boundaries to allot the Muslim-majority district of Gurdaspur to India instead of Pakistan, thus giving India the only road access from Delhi to Kashmir.
However, some British works suggest that the 'Kashmir State was not in anybody's mind' when the Award was being drawn and that even the Pakistanis themselves had not realized the importance of Gurdaspur to Kashmir until the Indian forces actually entered Kashmir. Both Mountbatten and Radcliffe, of course, have strongly denied those charges. It is impossible to accurately quantify the personal responsibility for the tragedy of Kashmir as the Mountbatten papers relating to the issue at the India Office Library and records are closed to scholars for an indefinite period.
Bengal
Chittagong Hill Tracts
Chittagong Hill Tracts
The Chittagong Hill Tracts ( bn, পার্বত্য চট্টগ্রাম, Parbotto Chottogram), often shortened to simply the Hill Tracts and abbreviated to CHT, are group of districts within the Chittagong Division in southeast ...
had a majority non-Muslim population of 97% (most of them Buddhists
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
), but was given to Pakistan. The Chittagong Hill Tracts People's Association (CHTPA) petitioned the Bengal Boundary Commission that, since the CHTs were inhabited largely by non-Muslims, they should remain within India. The Chittagong Hill Tracts was an excluded area since 1900 and was not part of Bengal. It had no representative at the Bengal Legislative Assembly in Calcutta, since it was not part of Bengal. Since they had no official representation, there was no official discussion on the matter, and many on the Indian side assumed the CHT would be awarded to India. On 15 August 1947, Chakma and other indigenous Buddhists celebrated independence day by hoisting Indian flag in
On 15 August 1947, Chakma and other indigenous Buddhists celebrated independence day by hoisting Indian flag in Rangamati
Rangamati (Bengali: রাঙ্গামাটি;) is the administrative headquarter and town of Rangamati Hill District in the Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh. The town is located at 22°37'60N 92°12'0E and has an altitude of . The dist ...
, the capital of Chittagong Hill Tracts. When the boundaries of Pakistan and India were announced by radio on 17 August 1947, they were shocked to know that the Chittagong Hill Tracts had been awarded to Pakistan. The Baluch Regiment of the Pakistani Army entered Chittagong Hill Tracts a week later and lowered the Indian flag at gun point. The rationale of giving the Chittagong Hill Tracts to Pakistan was that they were inaccessible to India and to provide a substantial rural buffer to support Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in ...
(now in Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
), a major city and port; advocates for Pakistan forcefully argued to the Bengal Boundary Commission that the only approach was through Chittagong.
The indigenous people sent a delegation led by Sneha Kumar Chakma to Delhi to seek help from the Indian leadership. Sneha Kumar Chakma contacted Sardar Patel by phone. Sardar Patel was willing to help, but insisted Sneha Kumar Chakma seek assistance from Prime Minister Pandit Nehru. But Nehru refused to help fearing that military conflict for Chittagong Hill Tracts might draw the British back to India.
Malda District
Another disputed decision made by Radcliffe was the division of the Malda district
Malda district, also spelt Maldah or Maldaha (, , often ), is a district in West Bengal, India. It lies 347 km (215 miles) north of Kolkata, the capital of West Bengal. Mango, jute and silk are the most notable products of this district. ...
of Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
. The district overall had a slight Muslim majority, but was divided and most of it, including Malda town, went to India. The district remained under East Pakistan administration for 3–4 days after 15 August 1947. It was only when the award was made public that the Pakistani flag was replaced by the Indian flag in Malda.
Khulna and Murshidabad Districts
The Khulna District
Khulna District ( bn, খুলনা জেলা , ''Khulna Jela'' also ''Khulna Zila'') is a district of Bangladesh. It is located in the Khulna Division. It is bordered on the north by the Jessore District and the Narail District, on the so ...
with a marginal Hindu majority of 51% was given to East Pakistan in lieu of the Murshidabad district with a 70% Muslim majority, which went to India. However, the Pakistani flag remained hoisted in Murshidabad for three days until it was replaced by the Indian flag on the afternoon of 17 August 1947.
Karimganj
Sylhet
Sylhet ( bn, সিলেট) is a metropolitan city in northeastern Bangladesh. It is the administrative seat of the Sylhet Division. Located on the north bank of the Surma River at the eastern tip of Bengal, Sylhet has a subtropical climate ...
district of Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
joined Pakistan in accordance with a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
. However, the Karimganj
Karimganj is a city in the Karimganj District of the Indian state of Assam. It is the administrative headquarters of the district.
Karimganj city is located at . The area of Karimganj city is 16.09 km2. It has an average elevation of 13 ...
sub-division with a Muslim majority was severed from Sylhet and given to India which became a district in 1983. As of the 2001 Indian Census, Karimganj district now has a Muslim majority of 52.3%.
Legacy
The Partition of India is one of the central events in the collective memory in India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. As a crucial determiner in the outcomes of the partition, the Radcliffe Line and award process has been referred to in many films, books, and other artistic depictions of the partition of India
The partition of India and the associated bloody riots inspired many creative minds in India and Pakistan to create literary/cinematic depictions of this event. While some creations depicted the massacres during the refugee migration, others co ...
. Apart from the larger story of the partition, the specific commemoration of the award itself or the recounting of the story of the process and the people involved in it has been comparatively rare.
Legacy and historiography
As a part of a series on borders, the explanatory news site Vox featured an episode looking at "the ways that the Radcliffe line changed Punjab, and its everlasting effects" including disrupting "a centuries-old Sikh pilgrimage" and separating "Punjabi people of all faiths from each other."
Artistic depictions of the Radcliffe Line
One notable depiction is '' Drawing the Line'', written by British playwright Howard Brenton. On his motivation to write '' Drawing the Line'', playwright Howard Brenton
Howard John Brenton FRSL (born 13 December 1942) is an English playwright and screenwriter. While little-known in the United States, he is celebrated in his home country and often ranked alongside contemporaries such as Edward Bond, Caryl Chu ...
said he first became interested in the story of the Radcliffe Line while vacationing in India and hearing stories from people whose families had fled across the new line.Ram Madhvani
Ram Madhvani is an Indian film director and producer known for his award-winning works in Hindi cinema, in the OTT space and in advertising. He is a-partner, director, and producer at Equinox Films, Ram Madhvani Films, and Equinox Virtual in par ...
created a nine-minute short film where he explored the plausible scenario of Radcliffe regretting the line he drew. The film was inspired by WH Auden's poem on the Partition.
Visual artists, Zarina Hashmi, Salima Hashmi
Salima Hashmi ( ur, ; born 1942) is a Pakistani painter artist, former college professor, anti-nuclear weapons activist and former caretaker minister in Sethi caretaker ministry. She has served for four years as a professor and the dean of Na ...
, Nalini Malini
Nalini ( Devanagari: नलिनी) is a female gender Indian given name, which means "lotus", "goddess Gayatri","mother of Vedas", "sweet nectar", "Amrit", Feminine "lily" in Sanskrit.''Baby Names''"Nalini" Retrieved on 9 January 2016. The nam ...
, Reena Saini Kallat, and Pritika Chowdhry
See also
* India–Pakistan border
The Indo–Pak border or India-Pakistan border is the international boundary that separates India and Pakistan. At its northern end is the Line of Control, which separates Indian-administered Kashmir from Pakistani-administered Kashmir; and ...
* Curzon line
The Curzon Line was a proposed demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and the Soviet Union, two new states emerging after World War I. It was first proposed by The 1st Earl Curzon of Kedleston, the British Foreign Secretary, ...
* Indo-Bangladesh enclaves
* McMahon Line
The McMahon Line is the boundary between Tibet and British India as agreed in the maps and notes exchanged by the respective plenipotentiaries on 24–25 March 1914 at Delhi, as part of the 1914 Simla Convention.
The line delimited the r ...
* Durand Line
The Durand Line ( ps, د ډیورنډ کرښه; ur, ), forms the Pakistan–Afghanistan border, a international land border between Pakistan and Afghanistan in South Asia. The western end runs to the border with Iran and the eastern end to th ...
* Sykes-Picot Agreement
* Rajkahini
''Rajkahini'' (English: ''Tale of Kings'', can also be called ''Tale of the Raj'') is an Indian Bengali-language historical drama film directed by Srijit Mukherji. The shooting of the film completed in June 2015 and the film released on 16 Oct ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
**
*
* Mansergh, Nicholas, ed. ''The Transfer of Power, 1942-7''. (12 volumes)
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
* India: Volume XI: The Mountbatten Viceroyalty-Announcement and Reception of 3 June Plan, 31 May-7 July 1947. Reviewed by Wood, J.R. "Dividing the Jewel: Mountbatten and the Transfer of Power to India and Pakistan". ''Pacific Affairs'', Vol. 58, No. 4 (Winter, 1985–1986), pp. 653–662
JSTOR
* Berg, E., and van Houtum, H
Routing borders between territories, discourses, and practices (p.128)
* Chester, Lucy P.
Borders and Conflict in South Asia: The Radcliffe Boundary Commission and the Partition of Punjab.
Manchester UP, 2009.
* Collins, L., and Lapierre, D. (1975) Freedom at Midnight
''Freedom at Midnight'' (1975) is a non-fiction book by Larry Collins and Dominique Lapierre about the events around the Indian independence movement and partition. It details the last year of the British Raj, from 1947 to 1948, beginning with ...
.
* Collins, L., and Lapierre, D
Mountbatten and the Partition of India
Delhi: Vikas Publishing House, 1983.
* Heward, E. The Great and the Good: A Life of Lord Radcliffe. Chichester: Barry Rose Publishers, 1994.
*
* Moon, P
The Transfer of Power, 1942-7: Constitutional Relations Between Britain and India: Volume X: The Mountbatten Viceroyalty-Formulation of a Plan
22 March-30 May 1947
Review "Dividing the Jewel" at JSTOR
* Moon, Blake, D., and Ashton, S.
The Transfer of Power, 1942-7: Constitutional Relations Between Britain and India: Volume XI: The Mountbatten Viceroyalty Announcement and Reception of the 3rd June Plan 31 May- 7 July 1947
Review "Dividing the Jewel" at JSTOR
* Smitha, F
MacroHistory website, 2001.
* Tunzelmann, A. ''Indian Summer''. Henry Holt.
* Wolpert, S. (1989). ''A New History of India'', 3rd ed. New York: Oxford University Press.
* Chopra, R. M., "The Punjab And Bengal", Punjabee Bradree, Calcutta, 1999.
Documentary Film and TV
* Johnny Harris and Christina Thornell (26 June 2019).
How a border transformed a subcontinent: This line divided India and Pakistan
'. Vox Media. Retrieved 26 July 2019. A brief history of how the region was split in two.
External links
{{Pakistan Movement
Bangladesh–India border
Geography of India
India–Pakistan border
Pakistan Movement
Partition of India
Eponymous border lines
 On 18 July 1947, the
On 18 July 1947, the  After the breakdown of the 1945
After the breakdown of the 1945  In March 1946, the British government sent a
In March 1946, the British government sent a  All lawyers by profession, Radcliffe and the other commissioners had all of the polish and none of the specialized knowledge needed for the task. They had no advisers to inform them of the well-established procedures and information needed to draw a boundary. Nor was there time to gather the survey and regional information. The absence of some experts and advisers, such as the United Nations, was deliberate, to avoid delay. Britain's new Labour government "deep in wartime debt, simply couldn’t afford to hold on to its increasingly unstable empire." "The absence of outside participants—for example, from the United Nations—also satisfied the British Government's urgent desire to save face by avoiding the appearance that it required outside help to govern—or stop governing—its own empire."
All lawyers by profession, Radcliffe and the other commissioners had all of the polish and none of the specialized knowledge needed for the task. They had no advisers to inform them of the well-established procedures and information needed to draw a boundary. Nor was there time to gather the survey and regional information. The absence of some experts and advisers, such as the United Nations, was deliberate, to avoid delay. Britain's new Labour government "deep in wartime debt, simply couldn’t afford to hold on to its increasingly unstable empire." "The absence of outside participants—for example, from the United Nations—also satisfied the British Government's urgent desire to save face by avoiding the appearance that it required outside help to govern—or stop governing—its own empire."
 On 15 August 1947, Chakma and other indigenous Buddhists celebrated independence day by hoisting Indian flag in
On 15 August 1947, Chakma and other indigenous Buddhists celebrated independence day by hoisting Indian flag in